NOVEL CHARACTERIZATION OF bend.3 CELLS THAT EXPRESS LYMPHATIC VESSEL ENDOTHELIAL HYALURONAN RECEPTOR-1
|
|
|
- Dylan Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 73 Lymphology 47 (2014) NOVEL CHARACTERIZATION OF bend.3 CELLS THAT EXPRESS LYMPHATIC VESSEL ENDOTHELIAL HYALURONAN RECEPTOR-1 D. Yuen, R. Leu, J. Tse, S. Wang, L.L. Chen 2, L. Chen 1 1 Center for Eye Disease and Development (DY,RL,JT,LC), Program in Vision Science and School of Optometry, University of California, Berkeley, California, and 2 Department of Pathology (SW,LLC), Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, USA ABSTRACT Murine bend.3 endothelioma cell line has been widely used in vascular research and here we report the novel finding that bend.3 cells express lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor-1 (LYVE-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3). Moreover, these cells express progenitor cell markers of Sca-1 and CD133. Upon stimulation with tumor necrosis factoralpha (TNF-α), the bend.3 cells demonstrate enhanced formation of capillary-type tubes, which express LYVE-1. As the bend.3 cell line is derived from murine endothelioma, we further examined human tissues of endothelioma and identified lymphatic vessels in the tumor samples which express both LYVE-1 and podoplanin. Moreover, a significantly higher number of lymphatic vessels were detected in the endothelioma samples compared with normal control. Taken together, this study not only redefines bend.3 cells for vascular research, but also indicates a broader category of human diseases that are associated with lymphatics, such as endothelioma. Keywords: bend.3 cell, LYVE-1, lymphatics endothelioma The bend.3 endothelial cell line has been widely used for blood vascular research (1-4). These cells are originally generated from mouse endothelioma, a benign neoplasm of the endothelial tissue (5,6). To date, it has not been studied whether these cells express other recently identified endothelial cell molecules, such as lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor-1 (LYVE-1). LYVE-1 was identified in 1997 by searching EST databases for sequences homologous to the hyaluronan (HA) receptor CD44 and it is one of most employed endothelial markers for lymphatic identification and detection (7). In parallel to the blood circulatory, the lymphatic network is found in most tissues in the body and plays vital roles in many functions, including immune surveillance, body fluid regulation, and fat absorption (8,9). The lymphatic capillaries are distinguishable from blood capillaries for their large interendothelial gaps, discontinuous basement membrane, and lack of pericytes (10,11). Scores of disorders are associated with lymphatic dysfunction, such as cancer metastasis, inflammatory and immune diseases, hypertension, obesity, AIDS and lymphedema (8,9,12-16). Unfortunately, to date, there is still little effective treatment for most lymphatic disorders. It is therefore a field with an urgent demand for new experimental tools and therapeutic protocols. In this study, we provide the first evidence that the bend.3 cells express LYVE- 1, a widely used endothelial marker for lymphatic research. Additionally, these cells
2 74 express vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) (17), another molecule largely restricted to lymphatic endothelial expression, and progenitor cell markers of CD133 and Sca-1 (8,18,19). We also show that upon the stimulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), the bend.3 cells increase their ability in formation of capillary-type tubes, which express LYVE-1. Furthermore, we demonstrate that lymphatic vessels are present in human tumor tissues of endothelioma, and the number of lymphatic vessels in endothelioma tumor tissues is significantly increased compared to normal tissue controls. Taken together, this study not only defines new features of bend.3 cells, but also identifies a lymphatic component of the human disease of endothelioma, which warrants further investigation. MATERIALS AND METHODS Cell Culture The bend.3 cells (ATCC, VA, USA) were maintained in EGM-2-MV Medium (Lonza, Switzerland) containing 10% fetal bovine serum and supplemented with SingleQuot Kit (Lonza, Switzerland) according to the standard protocol recommended by the manufacturer. Antibodies The following primary and secondary antibodies and isotype controls were used: FITC-conjugated rat-anti-mouse CD31, rat IgG1, rabbit IgG, Rhodamine-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit secondary antibody, and FITC-conjugated goat-anti-rat secondary antibody were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). The purified rabbit-anti-mouse LYVE-1, rabbitanti-human LYVE-1, rabbit-anti-mouse CD133, and FITC-conjugated rat-anti-mouse Sca-1 antibodies were purchased from Abcam Inc. (Cambridge, MD, USA). The mouseanti-human CD31 and D2-40 antibodies were purchased from DAKO (Carpinteria, CA, USA) and the purified rat-anti-mouse VEGFR-3 antibody was a product of R&D Systems, Inc. (Minneapolis, MN, USA). FITC conjugated rat-anti-mouse isotype control and purified rat-anti-mouse CD16/CD32 Fc Block antibodies were purchased from BD Bioscience (San Jose, CA, USA). Flow Cytometric Assay The experiment was performed according to the standard protocol. Briefly, cells were cultured in until 80% confluent. Cells were then trypsinized, washed, and incubated with the Fc Block to block non-specific binding. After incubations with the primary and secondary antibodies, they were re-suspended in basal medium and filtered by 40 µm mesh (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA) before the analysis with the EPICS XL Flow Cytometer (Beckman-Coulter, Miami, FL, USA). The experiments were repeated at least three times. Immunocytofluorescent Microscopic Assay This assay was performed according to the standard protocol. Briefly, cells were seeded on slide chambers (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA) and incubated with 2% BSA with 0.5% Fc Block to block nonspecific bindings. After incubation with the first antibody, for direct staining, cells were mounted on the slides using the DAPI mounting medium (Vector Lab, Burlingame, CA, USA). For indirect staining, cells were further incubated with the secondary antibody before mounting. The slides were examined and photographed by a Zeiss Axioplan 2e microscope (Carl Zeiss Inc., Germany). The experiments were repeated at least three times. RNA Isolation and PCR RNA was isolated from the cells using RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (Qiagen Inc., Valencia,
3 75 TABLE 1 Details of the Primer Sequences Used in the Study CA, USA) according to the manufacturer s protocol. Superscript VILO cdna synthesis kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used to generate the first strand cdna. Taq DNApolymerase and deoxynucleotides were purchased from New England Biolab (Ipswich, MA, USA) and the primers were synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies Inc. (Coralville, IA, USA). The details of the primer sequences used in this study are summarized in Table 1 (18,20,21). All thermal cycles were carried out in a Mastercycler ep system (Eppendorf, Germany). The experiments were repeated at least three times. Three-Dimensional Culture and Tube Formation Assay Matrigel (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA) was prepared according to manufacturer s protocol. The cells, in either TNF-α (100 ng/ml; R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) or control medium treated, were gently added to the well and monitored continuously for 24 hours under an Zeiss Observer A1 (Carl Zeiss Inc., Germany) microscope. Tubes were fixed and stained as described above. Triplet experiments were repeated 6 times with similar results. Human Tissue Immunohistochemical Assay The experiment was performed according to the standard protocol. Briefly, 4 µm formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue sections from human tissues of pulmonary endothelioma and normal control tissues (n = 6) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) or using the primary and secondary antibodies after antigen retrieval. Signals were detected by the EnVision Plus system (DAKO, Carpinteria, CA, USA) according to manufacturer s protocol. For quantitative analysis, the total numbers of
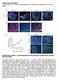
4 76 Fig. 1. bend.3 cells express CD31 and LYVE-1. (A) bend.3 cells formed an adherent monolayer in culture with elongated spindle shape. Scale bar, 100 µm. (B and C) bend.3 cells expressed CD31 (90%; B) and LYVE-1 (80%; C) as detected by flow cytometry. Gray, isotype control; black, CD31 (B) or LYVE-1 (C) staining. lymphatic vessels from three different regions were counted and the average numbers were calculated and compared accordingly. Student t test was used for the determination of significance levels between different groups using Prism software (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA). The differences were considered statistically significant when p < RESULTS bend.3 Cells Express LYVE-1, VEGFR-3, and CD31 As shown in Fig. 1A, bend.3 cells formed an adherent monolayer in culture with an elongated spindle shape. We first performed a flow cytometric assay and investigated the expression of CD31 (pan-endothelial cell marker) and LYVE-1 in these cells. Our results showed that the bend.3 cells expressed CD31, confirming their endothelial cell lineage (Fig. 1B). More interestingly, these cells also expressed LYVE-1 (Fig. 1C). To further confirm CD31 and LYVE-1 expression in bend.3 cells and to investigate whether these cells also express VEGFR-3, we next performed a series of immunocytofluorescent microscopic and RT-PCR assays for a detection at both protein and mrna levels. Our results from this set of experiments showed that in addition to CD31 and LYVE- 1, the bend.3 cells expressed VEGFR-3, and the results were consistent between the immunocytofluorescent microscopic (Fig. 2A-C) and RT-PCR (Fig. 2D) assays. bend.3 Cells Express Progenitor Cell Markers We next assessed the expression of CD133 and Sca-1, two progenitor cell markers (8,18,19), in bend.3 cells. As validated by a series of immunocytofluorescent microscopic and RT-PCR assays, both proteins and
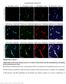
5 77 Fig. 2. bend.3 cells express other lymphatic endothelial cell markers. (A to C) Immunocytofluorescent micrographs demonstrating the protein expression profiles of CD31 (green; A), LYVE-1 (red; B), VEGFR-3 (green; C) but not Prox-1 (not shown) in bend.3 cells. No signals were detected in the isotype negative controls. Blue: DAPI nuclei staining. Scale bars, 100 µm. (D) mrna expression profiles of the lymphatic markers from reverse transcription followed by PCR further confirmed the results. mrnas of these molecules were detected on the bend.3 cells (Fig. 3). bend.3 Cells Increase Tube Formation upon TNF-α Stimulation To further examine whether the bend.3 cells are able to form capillary structures and how this is modulated by an inflammatory stimulation, we next employed a three Fig. 3. bend.3 cells express progenitor cell markers. (A and B) Representative immunocytofluorescent micrographs demonstrating the protein expression of Sca-1 (green; A) and CD133 (red; B) in bend.3 cells. No signals were detected in the isotype negative controls. Blue: DAPI nuclei staining. Scale bars, 100 µm. (C) mrna expression profiles of Sca-1 and CD133 from reverse transcription followed by PCR further confirmed the results. dimensional matrigel cell culture system to compare capillary tube formation of these cells between TNF-α treated and control conditions. The bend.3 cells demonstrated very limited ability in forming tubular structures under the control condition (Fig. 4A), as reported previously (22). However, after TNF-α stimulation, these cells assembled into well-organized capillary network (Fig. 4B), which expressed LYVE-1 (Fig. 4C).
6 78 Fig. 4. bend.3 cells up-regulate lymphatic tube formation after TNF-α stimulation. (A and B) Representative pictures of three-dimensional Matrigel cultures demonstrating the significant difference in tube formation between the normal (A) and inflamed condition (B). While bend.3 cells showed limited organization and tubular network capability under normal control condition, these cells were well-assembled into a tubular network 24 hours after TNF-α treatment. (C) Representative immunocytofluorescent micrograph confirming that the tubular network formed by the bend.3 cells expressed LYVE-1 (green). Scale bars, 100 µm. Fig. 5. Human endothelioma contains lymphatic vessels. Representative immunohistochemical micrographs showing (A) histology of endothelioma; (B) CD31 staining; (C) and (D) the presence of lymphatic tubular structures (indicated by arrowheads) that express LYVE-1 (C) and podoplanin (D). Scale bars, 100 µm. Fig. 6. Lymphatic vessels are significantly increased in human endothelioma. Representative immunohistochemical micrographs with D2-40 staining showing increased number of lymphatic vessels (indicated by arrowheads) within human endothelioma tissue (B) compared with normal control tissue (A). Scale bars, 200 µm. Quantitative analysis is presented in (C) (**p< 0.01).
7 79 Human Endothelioma Contains Lymphatic Vessels Since the bend.3 cell line was generated from mouse endothelioma, we assessed the possibility that human vascular disorder of endothelioma may contain a lymphatic component. As shown in Fig. 5, our results from a series of immunohistochemical assays showed that in addition to CD31, LYVE-1 was detected in human samples of endothelioma. This presence of lymphatic vessels was also confirmed by immunostaining with D2-40, an antibody specifically recognizing human lymphatic marker of podoplanin (23,24). Lymphatic Vessels Are Increased in Human Endothelioma As demonstrated in Fig. 6, our further analysis on human tissues of endothelioma showed that compared to normal tissue controls, the number of lymphatic vessels within endothelioma tumor samples was significantly increased. This finding indicates that human disease of endothelioma is associated with pathological lymphangiogenesis, which warrants further investigation as well. DISCUSSION In this study, we have shown that LYVE-1 is expressed in bend.3 cells, and that human endothelioma contains a lymphatic component. Since LYVE-1 has been widely used as a lymphatic endothelial marker, our finding on its expression in bend.3 cells may indicate a lymphatic trait of these cells. Allied to this notion is these cells expression of VEGFR-3, another widely used marker for lymphatic endothelial cells. However, since LYVE-1 and VEGFR-3 are occasionally found on non-lymphatic endothelial cells, such as macrophages and certain blood endothelial cells (25-27), it is yet to be determined whether these cells are blood, lymphatic, or mixed. Moreover, since molecular lymphatic research is still at its early stage, we currently do not have an adequate knowledge to fully categorize the endothelial cells. It is considered that blood and lymphatic endothelial cells share the same progenitor and the lymphatic endothelial cells are derived from a subset of cardinal vein cells during development (28). It is possible that there exist different populations of endothelial cells, and these populations express all or some of the endothelial markers that have been or yet to be identified. For example, we recently came across a new finding that the Schlemm s Canal of the eye expresses Prox-1 but not LYVE-1 or podoplanin (29). Moreover, though LYVE-1 has been widely used as a molecular marker for endothelial cells, its function still remains largely unknown. Since we have now identified its expression in the bend.3 cells, we may start to utilize these cells to investigate LYVE-1-related functions in endothelial cells. Since the bend.3 cell line has been extensively used in the past to study various molecular factors and pathways, a revisit of these preexisting data may provide some insightful information linking LYVE-1 to other factors or pathways as well. Furthermore, the bend.3 cells are originated from mouse endothelioma of the brain, one of few tissues in the body which are devoid of lymphatic vessels. Our data showing that these cells may carry some lymphatic-like features indicate that lymphatic abnormality may occur in the brain under certain pathological conditions, such as inflammation. Allied to this notion are cumulative data from us and other researchers showing that pathologic lymphangiogenesis occurs in the cornea, another alymphatic tissue under normal condition (13). Similar pathologic process may occur in the brain, which warrants further exploration. Also, our data show that an increased number of lymphatic vessels is present in human endothelioma. Though current treatment of this type of tumor is focused on blood vessels,
8 80 a future combination with antilymphatic therapy may offer more effective management of this disease, which warrants further investigation. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work is supported in part by research grants from National Institutes of Health, and the University of California at Berkeley (to LC). The authors thank Hector Nolla and Mei Zheng for technical assistance. REFERENCES 1. Hallmann, R, DL Savigni, EH Morgan, et al: Characterization of iron uptake from transferrin by murine endothelial cells. Endothelium 7 (2000), Koto, T, K Takubo, S Ishida, et al: Hypoxia disrupts the barrier function of neural blood vessels through changes in the expression of claudin-5 in endothelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 170 (2007), Perry BN, B Govindarajan, SS Bhandarkar, et al: Pharmacologic blockade of angiopoietin- 2 is efficacious against model hemangiomas in mice. J. Invest. Dermatol. 126 (2006), Sikorski, EE, R Hallmann, EL Berg, et al: The Peyer s patch high endothelial receptor for lymphocytes, the mucosal vascular addressin, is induced on a murine endothelial cell line by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-1. J. Immunol. 151 (1993), Montesano, R, MS Pepper, U Mohle-Steinlein, et al: Increased proteolytic activity is responsible for the aberrant morphogenetic behavior of endothelial cells expressing the middle T oncogene. Cell 62 (1990), Williams, RL, W Risau, HG Zerwes, et al: Endothelioma cells expressing the polyoma middle T oncogene induce hemangiomas by host cell recruitment. Cell 57 (1989), Banerji, S, J Ni, SX Wang, et al: LYVE-1, a new homologue of the CD44 glycoprotein, is a lymph-specific receptor for hyaluronan. J. Cell. Biol. 144 (1999), 144: Achen, MG, SA Stacker: Molecular control of lymphatic metastasis. Ann. NY Acad. Sci (2008), Brown, P: Lymphatic system: unlocking the drains. Nature 436 (2005), Schulte-Merker, S, A Sabine, TV Petrova: Lymphatic vascular morphogenesis in development, physiology, and disease. J. Cell. Biol. 193 (2011), 193: Pflicke, H, M Sixt: Preformed portals facilitate dendritic cell entry into afferent lymphatic vessels. J. Exp. Med. 206 (2009), Witte, MH, MJ Bernas, CP Martin, et al: Lymphangiogenesis and lymphangiodysplasia: From molecular to clinical lymphology. Microsc. Res. Tech. 55 (2001), 55: Chen, L: Ocular lymphatics: state-of-the-art review. Lymphology 42 (2009), Cueni, LN, M Detmar: The lymphatic system in health and disease. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 6 (2008), Tammela, T, K Alitalo: Lymphangiogenesis: Molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell 140 (2010), Alitalo, K: The lymphatic vasculature in disease. Nat Med 17 (2011), 17: Kaipainen, A, J Korhonen, T Mustonen, et al: Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 gene becomes restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92 (1995), Kotton, DN, RS Summer, X Sun, et al: Stem cell antigen-1 expression in the pulmonary vascular endothelium. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Molec. Physiol. 284 (2003), L Salven, P, S Mustjoki, R Alitalo, et al: VEGFR-3 and CD133 identify a population of CD34+ lymphatic/vascular endothelial precursor cells. Blood 101 (2003), Zhang, J, HY Zhi, F Ding, et al: Transglutaminase 3 expression in C57BL/6J mouse embryo epidermis and the correlation with its differentiation. Cell Res. 15 (2005), Morisada, T, Y Oike, Y Yamada, et al: Angiopoietin-1 promotes LYVE-1positive lymphatic vessel formation. Blood 105 (2005), Sheibani, N, PJ Newman, WA Frazier: Thrombospondin-1, a natural inhibitor of angiogenesis, regulates platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and endothelial cell morphogenesis. Molec. Biol. Cell 8 (1997), Weninger, W, TA Partanen, S Breiteneder- Geleff, et al: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 and podoplanin suggests a lymphatic endothelial cell origin of Kaposi s sarcoma tumor cells. Lab. Inves. 79 (1999), Frewer, NC, L Ye, PH Sun, et al: Potential implication of IL-24 in lymphangiogenesis of human breast cancer. Int. J. Molec. Med. 31 (2013),
9 Chen, L, C Cursiefen, S Barabino, et al: Novel expression and characterization of lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronate receptor 1 (LYVE-1) by conjunctival cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 46 (2005), Hamrah, P, L Chen, C Cursiefen, et al: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) on monocytic bone marrow-derived cells in the conjunctiva. Exp. Eye Res. 79 (2004), Bushway, ME, SA Gerber, BM Fenton, et al: Morphological and phenotypic analyses of the human placenta using whole mount immunofluorescence. Biol. Reprod Wigle, JT, N Harvey, M Detmar, et al: An essential role for Prox1 in the induction of the lymphatic endothelial cell phenotype. EMBO 21 (2002), Truong, TN, H Li, YK Hong, et al: Novel characterization and live imaging of Schlemm s canal expressing Prox-1. PloS one 9 (2014), e Lu Chen, MD, PhD 689 Minor Hall University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA Phone: Fax: chenlu@berkeley.edu.
Lymphatic research signifies a new field of discovery and. Spontaneous Lymphatic Vessel Formation and Regression in the Murine Cornea.
 Cornea Spontaneous Lymphatic Vessel Formation and Regression in the Murine Cornea Hui Zhang, 1 Xuemei Hu, 2 Julie Tse, 1 Firehiwott Tilahun, 1 Mengsheng Qiu, 2 and Lu Chen 1 PURPOSE. Lymphatic dysfunctions
Cornea Spontaneous Lymphatic Vessel Formation and Regression in the Murine Cornea Hui Zhang, 1 Xuemei Hu, 2 Julie Tse, 1 Firehiwott Tilahun, 1 Mengsheng Qiu, 2 and Lu Chen 1 PURPOSE. Lymphatic dysfunctions
MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Cornea Inhibits Inflammatory Lymphangiogenesis in Early and Middle Stages Don Yuen, 1 Bronek Pytowski, 2 and Lu Chen 1 PURPOSE. Lymphangiogenesis (LG) accompanies many corneal diseases after inflammatory,
Cornea Inhibits Inflammatory Lymphangiogenesis in Early and Middle Stages Don Yuen, 1 Bronek Pytowski, 2 and Lu Chen 1 PURPOSE. Lymphangiogenesis (LG) accompanies many corneal diseases after inflammatory,
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells
 CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease. Sunali Goyal MD
 Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal MD Mentor: Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Claes Dohlman Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea & Refractive Surgery Massachusetts
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal MD Mentor: Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Claes Dohlman Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea & Refractive Surgery Massachusetts
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Supplemental Information Garmy-Susini, et al., PI3Kα activates integrin α4β1 to establish a metastatic niche in lymph nodes
 Supplemental Information Garmy-Susini, et al., PI3Kα activates integrin α4β1 to establish a metastatic niche in lymph nodes Supplementary Figure 1: Lymphangiogenesis and metastasis in lymph nodes of tumorbearing
Supplemental Information Garmy-Susini, et al., PI3Kα activates integrin α4β1 to establish a metastatic niche in lymph nodes Supplementary Figure 1: Lymphangiogenesis and metastasis in lymph nodes of tumorbearing
Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice
 Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice Abdullah Alajati, Anna M. Laib, Holger Weber, Anja M. Boos, Arne Bartol, Kristian Ikenberg, Thomas Korff, Hanswalter Zentgraf, Cynthia Obodozie,
Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice Abdullah Alajati, Anna M. Laib, Holger Weber, Anja M. Boos, Arne Bartol, Kristian Ikenberg, Thomas Korff, Hanswalter Zentgraf, Cynthia Obodozie,
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Dellinger
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0052 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Dellinger CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX 75390 REPORT DATE: February 2013 TYPE OF REPORT: Annual
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0052 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Dellinger CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX 75390 REPORT DATE: February 2013 TYPE OF REPORT: Annual
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system
 Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system Françoise Bruyère, Laurence Melen-Lamalle, Silvia Blacher, Guy Roland, Marc Thiry, Lieve Moons, Francis Frankenne, Peter Carmeliet, Kari
Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system Françoise Bruyère, Laurence Melen-Lamalle, Silvia Blacher, Guy Roland, Marc Thiry, Lieve Moons, Francis Frankenne, Peter Carmeliet, Kari
LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE EMERGENCE OF MOLECULAR AND TRANSGENIC LYMPHOLOGY: WHAT DO WE (REALLY) KNOW SO FAR?
 1 Lymphology 39 (2006) 1-7 LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE EMERGENCE OF MOLECULAR AND TRANSGENIC LYMPHOLOGY: WHAT DO WE (REALLY) KNOW SO FAR? C. Suri Independent Biotechnology Consultant,* Tarrytown, New
1 Lymphology 39 (2006) 1-7 LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE EMERGENCE OF MOLECULAR AND TRANSGENIC LYMPHOLOGY: WHAT DO WE (REALLY) KNOW SO FAR? C. Suri Independent Biotechnology Consultant,* Tarrytown, New
Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts
 Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on
 Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target
 Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target Lecture Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Prof. Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences University of
Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target Lecture Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Prof. Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences University of
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary Materials for
 immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
HIV-infected subjects were recruited from an ongoing clinic-based cohort (SCOPE)
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Populations studied HIV-infected subjects were recruited from an ongoing clinic-based cohort (SCOPE) based at the University of California, San Francisco. From this cohort, we recruited
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Populations studied HIV-infected subjects were recruited from an ongoing clinic-based cohort (SCOPE) based at the University of California, San Francisco. From this cohort, we recruited
Lymphatic Network in Cancer and Some Chemical Observations
 Lymphatic Network in Cancer and Some Chemical Observations DORINA CORICOVAC 1, HORIA PLES 2, IULIA PINZARU 1, DANIELA IONESCU 1 * 1 Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy,
Lymphatic Network in Cancer and Some Chemical Observations DORINA CORICOVAC 1, HORIA PLES 2, IULIA PINZARU 1, DANIELA IONESCU 1 * 1 Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy,
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis
 Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Introduction Kit Components Cat. # # of vials Reagent Quantity Storage
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
VEGFR-3 in Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis
 VEGFR-3 in Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis Lotta Jussila Molecular/Cancer Biology Laboratory Haartman Institute and Helsinki University Central Hospital Biomedicum Helsinki University of Helsinki Finland
VEGFR-3 in Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis Lotta Jussila Molecular/Cancer Biology Laboratory Haartman Institute and Helsinki University Central Hospital Biomedicum Helsinki University of Helsinki Finland
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative. breast cancer patients
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and
 Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis
 The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Figure S1. A Non-lesional Lesional
 Figure S1 Non-lesional Lesional GEN1 Non-lesional GEN1 Lesional C Normal Negative control Figure S1. Dermal Populations of + cells are found in human skin. Immunohistochemistry for on fixed, frozen skin
Figure S1 Non-lesional Lesional GEN1 Non-lesional GEN1 Lesional C Normal Negative control Figure S1. Dermal Populations of + cells are found in human skin. Immunohistochemistry for on fixed, frozen skin
Precancerous Stem Cells Can Serve As Tumor Vasculogenic Progenitors
 Precancerous Stem Cells Can Serve As Tumor Vasculogenic Progenitors Rulong Shen, Yin Ye.,LiChen., Qingtao Yan, Sanford H. Barsky*, Jian-Xin Gao* Department of Pathology and Comprehensive Cancer Center,
Precancerous Stem Cells Can Serve As Tumor Vasculogenic Progenitors Rulong Shen, Yin Ye.,LiChen., Qingtao Yan, Sanford H. Barsky*, Jian-Xin Gao* Department of Pathology and Comprehensive Cancer Center,
CLARITY reveals dynamics of ovarian follicular architecture and vasculature in three-dimensions
 CLARITY reveals dynamics of ovarian follicular architecture and vasculature in three-dimensions Yi Feng, Peng Cui, Xiaowei Lu, Brian Hsueh, Fredrik Möller Billig, Livia Zarnescu Yanez, Raju Tomer, Derek
CLARITY reveals dynamics of ovarian follicular architecture and vasculature in three-dimensions Yi Feng, Peng Cui, Xiaowei Lu, Brian Hsueh, Fredrik Möller Billig, Livia Zarnescu Yanez, Raju Tomer, Derek
Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study
 Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study Antigen Species Clone Source Dilution Insulin Guinea pig - Dako, Carpinteria, 1:200 Glucagon Rabbit - Dako, Carpinteria,
Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study Antigen Species Clone Source Dilution Insulin Guinea pig - Dako, Carpinteria, 1:200 Glucagon Rabbit - Dako, Carpinteria,
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Anti-DC-SIGN/CD209 murine monoclonal antibodies
 Anti-DC-SIGN/CD209 murine monoclonal antibodies DC-SIGN (DC Specific, ICAM-3 Grabbing, Nonintegrin) / CD209 and L-SIGN (liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin CD299/ DC-SIGNR (DC-SIGN-related
Anti-DC-SIGN/CD209 murine monoclonal antibodies DC-SIGN (DC Specific, ICAM-3 Grabbing, Nonintegrin) / CD209 and L-SIGN (liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin CD299/ DC-SIGNR (DC-SIGN-related
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
Sipper BK Experimental Animal Co. (Shanghai, China) and bred in a specific. pathogen-free environment. The animal study protocol was approved by the
 Supplementary information, Data S1 Materials and Methods Mice, Ad vectors and reagents Female C57BL/6 mice, 8-10 weeks of age, were purchased from Joint Ventures Sipper BK Experimental Animal Co. (Shanghai,
Supplementary information, Data S1 Materials and Methods Mice, Ad vectors and reagents Female C57BL/6 mice, 8-10 weeks of age, were purchased from Joint Ventures Sipper BK Experimental Animal Co. (Shanghai,
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
Can lymphangiosarcoma be resurrected? A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of lymphatic differentiation in 49 angiosarcomas
 Histopathology 2010, 56, 364 371. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03484.x Can lymphangiosarcoma be resurrected? A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of lymphatic differentiation in 49 angiosarcomas
Histopathology 2010, 56, 364 371. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03484.x Can lymphangiosarcoma be resurrected? A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of lymphatic differentiation in 49 angiosarcomas
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3): /ISSN: /IJCEP
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3671-3676 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0046381 Original Article Comparison of immunofluorescence and immunohistochemical staining with anti-insulin antibodies on
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3671-3676 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0046381 Original Article Comparison of immunofluorescence and immunohistochemical staining with anti-insulin antibodies on
Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies. Traditional Hypothesis Stress
 3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1
 Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features
 Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supplementary Methods: Omalizumab Trial This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the University of Utah Hospital and
 Supplementary Methods: Omalizumab Trial This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the University of Utah Hospital and Primary Children s Hospital, Salt Lake City, UT, both
Supplementary Methods: Omalizumab Trial This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the University of Utah Hospital and Primary Children s Hospital, Salt Lake City, UT, both
Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System
 Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which one of the following is non-encapsulated and less organized secondary lymphoid organ? Question
Immunology - Problem Drill 04: Structure and Functions of the Immune System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which one of the following is non-encapsulated and less organized secondary lymphoid organ? Question
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
4. TEXTBOOK: ABUL K. ABBAS. ANDREW H. LICHTMAN. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY. 5 TH EDITION. Chapter 2. pg
 LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples.
 ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Except for the extraocular conjunctiva, 1,2 the human eye is
 Intraocular Lymphangiogenesis in Malignant Melanomas of the Ciliary Body with Extraocular Extension Ludwig M. Heindl, 1 Tanja N. Hofmann, 1 Harald L. J. Knorr, 1 Carmen Rummelt, 1 Falk Schrödl, 2 Ursula
Intraocular Lymphangiogenesis in Malignant Melanomas of the Ciliary Body with Extraocular Extension Ludwig M. Heindl, 1 Tanja N. Hofmann, 1 Harald L. J. Knorr, 1 Carmen Rummelt, 1 Falk Schrödl, 2 Ursula
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody to NFkB p65 (v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian))
 Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
label the basement membrane). Different fixation methods of EB-perfused P8 mice to optimize the combination
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimization of the tissue fixation protocol to combine EB perfusion and IB4 endothelial tip cell staining in the postnatal mouse brain. a-l Labeling of EB-perfused P8 mice with
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimization of the tissue fixation protocol to combine EB perfusion and IB4 endothelial tip cell staining in the postnatal mouse brain. a-l Labeling of EB-perfused P8 mice with
NEW IHC A n t i b o d i e s
 NEW IHC Antibodies TABLE OF CONTENTS NEW IHC ANTIBODIES from Cell Marque CITED1 (5H6).... 1 Claudin 7 (5D10F3).... 1 GATA1 (4F5).... 1 Transgelin (2A10C2).... 1 NEW IHC ANTIBODIES using RabMAb Technology
NEW IHC Antibodies TABLE OF CONTENTS NEW IHC ANTIBODIES from Cell Marque CITED1 (5H6).... 1 Claudin 7 (5D10F3).... 1 GATA1 (4F5).... 1 Transgelin (2A10C2).... 1 NEW IHC ANTIBODIES using RabMAb Technology
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo. SI Figures and Legend
 Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to
 Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D.
 The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how ordered Ig gene rearrangements lead to the development
The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how ordered Ig gene rearrangements lead to the development
Lymphoedema in bariatric patients
 Lymphoedema in bariatric patients Lymfødemseminar 27. oktober 2016 Mungo Park, Kolding, Denmark Mieke Flour, Leuven, Belgium Morbid obesity and lymphedema Morbid obesity: definition and co-morbidities
Lymphoedema in bariatric patients Lymfødemseminar 27. oktober 2016 Mungo Park, Kolding, Denmark Mieke Flour, Leuven, Belgium Morbid obesity and lymphedema Morbid obesity: definition and co-morbidities
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel
 Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
