Association of Tightly Spiraled Bacterial Infection and Gastritis in Pigs
|
|
|
- Katrina Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FULL PAPER Pathology Association of Tightly Spiraled Bacterial Infection and Gastritis in Pigs Jong-Hwan PARK, Beom-Jun LEE 1), Yong-Soon LEE 1) and Jae-Hak PARK* Departments of Laboratory Animal Medicine and 1) Veterinary Public Health, College of Veterinary Medicine and School of Agricultural Biotechnology, Seoul National University, Suwon , Korea (Received 14 December 1999/Accepted 13 March 2000) ABSTRACT. Tightly spiral bacteria were observed only in the pyloric mucosa of 4 (8.0%) of 50 swine stomachs, mainly in the surface of epithelia, the gastric pits and the lumen of gastric glands. The presence of the spiral bacteria was significantly associated with chronic pyloric gastritis (p<0.05). Mean gastritis score of the bacteria-positive pyloric mucosa was 3.25 ± 0.25, whereas that of the bacterianegative pyloric mucosa was 2.37 ± Parakeratosis and hyperkeratosis were spontaneously seen in the mucosa layer of pars oesophagea, regadless of the bacterial infection. Marked infiltration of mononuclear cells and granulocytes were seen in the cardiac mucosa, regardless of the bacterial infection. Mean gastritis score of the bacteria-positive cardiac mucosa was 3.27 ± 0.32, whereas that of the bacteria-negative cardiac mucosa was 2.84 ± There was no significant difference between the bacteria-positive and negative cardiac mucosa (p>0.05). Inflammatory response in the fundic mucosa was rare (gastritis score=0.75 ± 0.08). The tightly spiraled bactera were not cultured with various culture media. These results suggest that the presence of tightly spiraled bacteria is associated with only the pyloric gastritis in pigs. KEY WORDS: chronic gastritis, gastric mucosa, swine, tightly spiraled bacteria. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 62(7): , 2000 Gastrospirillum suis, a tightly spiral bacterium, colonizes the gastric mucosa of swine [1, 4, 7, 8]. By 16S rrna sequencing, the bacterium is known to belong to the genus Helicobacter and is 99.5% similar to G. hominis type 1 [3, 6]. A possible link between such bacteria and gastric diseases of pig has been evoked [1, 12]. Such diseases contribute an important problem in veterinary medicine leading to significant economic consequences, with up to 2.5% of mortality in pigs due to gastrointestinal hemorrhage [14]. Ulceration of the gastric pars esophagus is also a common problem in intensive pig production [1, 12]. Several factors have been suspected in the pathogenesis of these lesions, but the etiology still remains unknown. In the present report, we investigated naturally occurring swine gastritis in Korea. In addition, the gastritis scores in the cardiac, fundic, and pyloric mucosa of swine stomach were calculated and analyzed for an association of the gastritis with the tightly spiraled bacterial infection. MATERIALS AND METHODS *CORRESPONDENCE TO: PARK, J.-H., Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, 103 Seodun-dong, Kwonsun-gu, Suwon , Korea. Sample preparation: Stomach samples were obtained from 50 apparently healthy pigs (about 5 months old) weighing about kg after slaughter at a slaughterhouse in Suwon, Korea. The stomach samples were transported to the laboratory in individual ice box (4 C) and cut open along the greater curvature from the pylorus to the diverticulum, and the contents were discarded. The stomachs were then washed gently in tap water, taking care to remove food particles only. The mucosal surfaces were examined and assessed for macroscopic lesions. Histopathological and microbiological examination: Fragments of the pars esophagea, cardia, fundus and pylorus were fixed in 10% neutral formalin for over 24 hr, dehydrated in alcohol-xylene series, and embedded in paraffin wax. From each block, sections 2-µm thick were prepared, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histological examination. The sections were also stained with modified Steiner s silver for the detection of spiral bacteria. Briefly, after deparaffinization, the slides were soaked in 1% uranyl nitrate for 15 min and then 1% silver nitrate for 90 min at 60 C. After washing three times with distilled water, the slides were soaked twice in 95% and 100%, respectively, followed by 2.5% gum mastic solution for 5 min at room temperature. After drying the slides in air, they were soaked in a reducing solution (10 ml of 2.5% gum mastic solution, 25 ml of 2% hydroquinone, 5 ml of 100% alcohol, and 0.2 ml of 1% silver nitrate) for 25 min at 45 C and observed by light microscopy. According to the microbiological examination, the stomachs were divided into two groups, bacteria-positive group and bacteria-negative group. The degree of gastritis in the cardiac, fundic and pyloric mucosa was evaluated by the scoring criteria shown in Table 1. Bacterial culture: Fragments of the fundic and pyloric mucosa were cut to very small pieces with a sterilized knife. The tissue pieces were inoculated into chocolate agar (BBL, U.S.A.) plate containing 5% horse serum, GC modified chocolate agar (DIFCO, U.S.A.) plate containing 10% horse serum and antibiotics (amphotericin B, trimethoprim, polymixin B, and vancomycin), or brain heart infusion agar (BBL, U.S.A.) plate. The plates were incubated in an incubator with Gaspak (GasPakPlus', BBL, U.S.A.) for 4 7 days. Statistical analysis: An ANOVA program for statistical analysis was performed on data for the gastritis score and the significant difference between the bacteria-positive and nega-
2 726 J-H. PARK, B-J LEE Y-S. LEE AND J-H PARK Table 1. Evaluation of gastritis in the cardiac, fundic, and pyloric mucosa of pigs Score Histopathological findings 0 No infiltration of inflammatory cells 1 Mild infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and some eosinophils 2 Moderately dense infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells but no lymphoid follicles 3 Moderately dense infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells and presence of lymphoid follicles 4 Very dense infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells and presence of lymphoid follicles Fig. 1. The presence of tightly spiral bacteria in the surface of pyloric mucosa (a) and the lumen of gastric glands (b). Steiner s silver stain. (a) 330, (b) 167. tive mucosa was analyzed by the student s t test at the level of p<0.05. RESULTS Macroscopically, proliferation of gastric fold and severe congestion were observed in the fundic region of 5 samples (10%), and focal necrosis of the gastric fold was also observed in the fundic region of 2 samples (4%). Congestion of gland pits and hyperkeratosis of the pars esophagea were seen in 6 samples (12%) and 2 samples (4%), respectively. With Steiner s silver stains, tightly spiraled bacteria were observed only in the pyloric mucosa of 4 (8%) out of a total of 50 stomachs, but not in the pars esophagus, the cardiac mucosa, and the fundic mucosa. The spiral bacteria were mainly seen in the mucus, the gastric pits, and the lumen of gastric glands (Fig. 1a, b). Microorganisms were not seen in lymphoid follicles, macrophages, or the laminar propria. In addition, the cultivation of the tightly spiral bacteria was not successful with various culture media. In the pars esophagus, hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis were spontaneously seen in the mucosa layer of the pars oesophagea, regadless of bacterial infection (Fig. 2a). The epithelial hyperkeratosis and the epithelial parakeratosis were observed in 11 samples (22%) and in 21 samples (42%), respectively (Table 2). However, no glanulomatous lesion and ulcer were seen. In the cardia, a moderate to marked infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils was observed in 47 (94%) of 50 samples (Fig. 2b, Table 2) and the average gastric score from a total of 50 samples was 2.86 ± 0.09 (Table 3). The average gastritis score of the bacteria-positive cardiac mucosa form a total of 4 samples was 3.27 ± 0.32, whereas that of the bacteria-negative cardiac mucosa from a total 46 samples was 2.84 ± 0.13 (Table 3). Epithelial hyperplasia was also seen in 3 samples (6%). In the fundus, the mild inflammatory response, showing a slight to moderate infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells, was mainly observed in the gastric pits (Fig. 2c). Epithelial degeneration in 8 samples (16%) and cystic dilatation in 2 samples (4%) were also observed (Table 2), and the gastritis score from a total of 50 samples was 0.75 ± 0.08 (Table 3). In the pylorus, a dense infiltration of lymphocytes and lymphoid follicles in the laminar propria were observed in all (100%) of 4 bacteria-positive samples, whereas 19 (41.3%) of the 46 bacteria-negative samples (Fig. 2d, Table 2). The average gastritis scores in the bacteria-positive samples and the bacteria-negative samples were 3.25 ± 0.25 and 2.37 ± 0.12, respectively (Table 3). There was a significant difference between the bacteria-positive and negative samples (p<0.05). DISCUSSION Many spiral bacteria have been demonstrated in the stomachs of many animal species [2, 9, 10]. In this study, tightly spiral bacteria were found only in the pyloric mucosa in pigs, but not in the cardiac and fundic mucosa. In addition, our results reported by the gastritis score showed a significant
3 BACTERIA INFECTION AND GASTRITIS IN PIGS 727 Fig. 2. Representative histopathological findings in the pars esophagus (a), cardia (b), fundus (c), and pylorus (d). Hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis were seen in the mucosa of the pars oesophagus. A large lymphoid follicle was observed in the cardiac and pyloric mucosa of a pig infected with tightly spiral bacteria. H&E stain, 50. association between the presence of spiral bacteria in the pyloric mucosa and chronic pyloric gastritis in pigs. The histological findings were similar to those reported in man and gnotobiotic piglets colonized by H. pylori [5, 11]. There was also a significant association between the presence of Gastrospirillum suis and lymphoid follicles [8]. In some G. suispositive pigs, the fundic mucosa was normal despite the presence of pyloric gastritis. This is also common in H. pylori infection in man [11]. Gastrospirillum suis is an uncultured tightly spiraled bacterium that colonizes the gastric mucosa of swine. We also tried to culture the bacteria using various culture media under several conditions. However, the spiralled bacteria were not cultured, which is consistent with other reports [8, 13]. Mendes et al. [8] reported that tightly spiraled bacteria were seen in the pyloric mucosa of the stomach of 13 (10.8%) of 120 pigs and in the fundic mucosa of three (5.0%) out of 60 pigs. In this study, the tightly spiraled bacteria were observed only in the pyloric mucosa of the stomach of 4 (8.0%) of 50 pigs that appeared clinically healthy at slaughter. Mendes et al. [8] also reported that chronic gastritis was observed more frequently in the pyloric region than fundic region and that the pyloric gastritis was significantly associated with the presence of the spiral bacteria. In this study, the chronic gastritis was observed most frequently in the cardiac region. However, the tightly spiraled bacteria were not seen in the cardiac region. The inflammatory response was not severe in the fundic region. Barbosa et al. [1] reported that there was no association between the Gastrospirillum suis and gastritis, Nevertheless, the diagnosis of gastritis in each type of gastric mucosa was based on the different areas out of the four examined. In this study we found a more striking inflammatory reaction in cardiac mucosa, in which bacteria were not found, than in the pyloric or fundic mucosa. However, there was no association between the tightly spiral bacteria infection and the cardiac gastritis. Probably there are many causes of chronic gastritis in swine, e.g., dietary habits and parasites such as Hyostrongylus rubidus, Ascarops spp., Physocephalus spp. and Simondsia spp. Chronic gastritis or gastric ulcer in the cardiac region and in the pars esophagus of the stomach is thought to occur sporad-
4 728 J-H. PARK, B-J LEE Y-S. LEE AND J-H PARK Table 2. Histopathological findings of pig stomachs infected with and without tightly spiral bacteria (TSB) Number of pigs Histological findings TSB-negative TSB-positive Pars esophagus hyperkeratinization 10 1 parakeratosis 20 1 lymphocytes 19 0 eosinophils 12 0 lymphoid follicles 8 0 Cardia epithelial degeneration 14 1 erosion 10 0 lymphocytes 43 4 eosinophils 40 2 lymphoid follicles 34 2 epithelial hyperplasia 3 0 eosinophils 2 1 Muscularis lymphocytes 1 0 eosinophils 1 0 Fundus epithelial degeneration 7 1 erosion 2 1 lymphocytes 27 1 eosinophils 7 0 lymphoid follicles 3 0 cystic dilatation 1 1 eosinophils 10 0 Muscularis lymphocytes 2 0 eosinophils 5 0 Pylorus epithelial degeneration 26 3 erosion 8 1 lymphocytes 41 4 eosinophils 36 3 lymphoid follicles 19 4 epithelial hyperplasia 3 0 eosinophils 3 0 The infiltration of lymphocytes and eosinophils was not seen in the muscularis of the pylorus. Table 3. Gastritis score of cardiac and pyloric mucosa Portion of stomach No. of stomach Gastritis score Cardiac mucosa (total) ± 0.09 Bacteria-positive ± 0.32 Bacteria-negative ± 0.13 Pyloric mucosa (total) ± 0.11 Bacteria-positive ± 0.25* Bacteria-negative ± 0.12 Fundic mucosa (total) ± 0.08 The gastritis score in the fundic mucosa was calculated only on the base of a total of 50 stomachs because there is no enough number of the bacteria-positive samples. *Significantly different from the average score of bacteria-negative pyloric mucosa (p<0.05). ically in pigs, but the cause remains unclear [1]. Although several functions are involved in the pathogenesis, the presence of the spiral bacteria is also considered as a possible factor for swine gastric ulcer [12]. They found Gastrospirillum spp. in the most regions of the stomach including antral, oxyntic, fundic, cardiac mucosa. In this study, the presence of tightly spiralled bacteria was not associated with the gastric ulcer in the pars esophagus of the stomach. In conclusion, although an inflammatory response was found most frequently in the cardiac mucosa, there was no association between tightly spiral bacteria infection and cardiac gastritis, whereas there was a close association between the presence of tightly spiral bacteria and pyloric gastritis. REFERENCES 1. Barbosa, A. J. A., Silva, J. C. P., Nogueira, A. M. M. F., Paulino, E. and Miranda, C. R Higher incidence of Gastrospirillum sp. in swine with gastric ulcer of the Pars oesophagea. Vet. Pathol. 32: Cantet, F., Magras, C., Marais, A., Federighi, M. and Megraud, F Helicobacter species colonizing pig stomach: molecular characterization and determination of prevalence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: De Groote, D., Van Doorn, L. J., Ducatelle, R., Verschuuren, A., Haesebrouck, F., Quint, W. G., Jalava, K. and Vandamme, P Candidatus Helicobacter suis, a gastric helicobacter from pigs, and its phylogenetic relatedness to other gastrospirilla. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: Grasso, G. M., Ripabelli, G., Sammarco, M. L., Ruberto, A. and Iannitto, G Prevalence of Helicobacter-like organisms in porcine gastric mucosa: a study of swine slaughtered in Italy. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 19: Krakowka, S., Morgab, D. R., Kraft, W. G. and Lunk, R. D Establishment of gastric Campylobacter pylori infection in the neonatal gnotobiotic piglet. Infect. Immun. 55: Mendes, E. N., Queiroz, D. M. M., Coimbra, R. S., Moura, S. B., Barbosa, A. J. A. and Rocha, G. A Experimental infection of Wistar rats with Gastrospirillum suis. J. Med. Microbiol. 44: Mendes, E. N., Queiroz, D. M. M., Rocha, G. A., Moura, S. B., Leite, V. H. R. and Fonseca, M. E. F Ultrastructure of a spiral micro-organism from pig gastric mucosa ( Gastrospirillum suis ). J. Med. Microbiol. 33: Mendes, E. N., Queiroz, D. M. M., Rocha, G. A., Nogueira, A. M. M. F., Carvalho, A. C. T., Lage, A. P. and Barbosa, A. J. A Histopathological study of porcine gastric mucosa with and without a spiral bacterium ("Gastrospirillum suis"). J. Med. Microbiol. 35: Neiger, R., Dieterich, C., Burnens, A., Waldvogel, A., Corthesy-Theulaz, I., Halter, F., Lauterburg, B. and Schmassmann, A Detection and prevalence of Helicobacter infection in pet cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36: Otto, G., Hazell, S. H., Fox, J. G., Howlett, C. R., Murphy, J. C., O Rourke, J. L. and Lee, A Animal and public
5 BACTERIA INFECTION AND GASTRITIS IN PIGS 729 health implications of gastric colonization of cats by Helicobacter-like organisms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 32: Queiroz, D. M. M., Dewhirst, F. E., Paster, B. J., Carvalho, S. D., Magnago, A. G. P., Moura, S. B., Rocha, G. A. and Oliveira, A. M. R Reservoir hosts for human Gastrospirillum infection. In: VIIIth International Workshop on Gastro-duodenal Pathology and Helicobacter pylori, July, (European Helicobacter pylori Study Group, Gut), Queiroz, D. M., Rocha, G.A., Mendes, E.N., De Moura, S.B., De Oliveira, A. M. and Miranda, D Association between Helicobacter and gastric ulcer disease of the pars esophagea in swine. Gastroenterology 111: Utriainen, M. and Hanninen, M. -L Detection of Helicobacter-like bacteria in porcine gastric biopsy samples by amplification of 16S rrna, ureb, vaca and caga genes by PCR. Vet. Res. Communs. 22: Yeomans, N. D Helicobacter heilmannii (formerly Gastrospirillum): association with pig and human gastric pathology. Gastroenterology 111:
Sponsors. Logo Design Ruth Cronje, and Jan Swanson; based on the original design by Dr. Robert Dunlop. Cover Design Sarah Summerbell
 Sponsors University of Minnesota College of Veterinary Medicine College of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Sciences Extension Service Swine Center Editors W. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas Layout
Sponsors University of Minnesota College of Veterinary Medicine College of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Sciences Extension Service Swine Center Editors W. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas Layout
Helicobacter-like organisms in the stomach of pigs with and without gastric ulceration
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Melnichouk SI, Friendship RM, Dewey CE, et al. Helicobacter-like organisms in the stomach of pigs with and without gastric ulceration. Swine Health Prod. 1999;7(5):201 205. Helicobacter-like
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Melnichouk SI, Friendship RM, Dewey CE, et al. Helicobacter-like organisms in the stomach of pigs with and without gastric ulceration. Swine Health Prod. 1999;7(5):201 205. Helicobacter-like
HELICOBACTER SP. MICROORGANISMS DO NOT ALTER PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY OF GASTRIC EPITHELIAL CELLS IN NATURALLY INFECTED SWINE
 Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 55, 9-14, 2011 HELICOBACTER SP. MICROORGANISMS DO NOT ALTER PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY OF GASTRIC EPITHELIAL CELLS IN NATURALLY INFECTED SWINE RAFAŁ SAPIERZYŃSKI, MICHAŁ FABISIAK, MAGDALENA
Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 55, 9-14, 2011 HELICOBACTER SP. MICROORGANISMS DO NOT ALTER PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY OF GASTRIC EPITHELIAL CELLS IN NATURALLY INFECTED SWINE RAFAŁ SAPIERZYŃSKI, MICHAŁ FABISIAK, MAGDALENA
Detection of Helicobacter spp. in gastric, fecal and saliva samples from swine affected by gastric ulceration
 pissn 1229-845X, eissn 1976-555X J. Vet. Sci. (2010), 11(3), 221-225 DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.3.221 Received: 22 Dec. 2009, Accepted: 10 Mar. 2010 Original Article JOURNAL OF Veterinary Science Detection
pissn 1229-845X, eissn 1976-555X J. Vet. Sci. (2010), 11(3), 221-225 DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.3.221 Received: 22 Dec. 2009, Accepted: 10 Mar. 2010 Original Article JOURNAL OF Veterinary Science Detection
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
Gastric Helicobacters in Domestic Animals and Nonhuman Primates and Their Significance for Human Health
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 202 223 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00041-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Gastric Helicobacters
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 202 223 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00041-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Gastric Helicobacters
Association Between Helicobacter and Gastric Ulcer Disease of the Pars Esophagea in Swine
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1996;111:19 27 Association Between Helicobacter and Gastric Ulcer Disease of the Pars Esophagea in Swine DULCIENE MARIA DE MAGALHÃES QUEIROZ,* GIFONE AGUIAR ROCHA,* EDILBERTO NOGUEIRA
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1996;111:19 27 Association Between Helicobacter and Gastric Ulcer Disease of the Pars Esophagea in Swine DULCIENE MARIA DE MAGALHÃES QUEIROZ,* GIFONE AGUIAR ROCHA,* EDILBERTO NOGUEIRA
The role of IFN-γ and IL-4 in gastric mucosa inflammation associated with Helicobacter heilmannii type 1 infection
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 253-261 Th1 response in H. heilmannii infection ISSN 0100-879X 253 The role of IFN-γ and IL-4 in gastric mucosa inflammation associated with
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 253-261 Th1 response in H. heilmannii infection ISSN 0100-879X 253 The role of IFN-γ and IL-4 in gastric mucosa inflammation associated with
Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Key words : low-grade MALT lymphoma, epithelial change, empty lamina propria, B-cell clonality, H. pylori, eradication, long-term follow-up
 Department of Pathology, The University of Tokushima School of Medicine, Tokushima, Japan ; Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, The University of Tokushima School of Dentistry, Tokushima, Japan
Department of Pathology, The University of Tokushima School of Medicine, Tokushima, Japan ; Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, The University of Tokushima School of Dentistry, Tokushima, Japan
Identification of Non-Helicobacter pylori Spiral Organisms in Gastric Samples from Humans, Dogs, and Cats
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 2005, p. 2256 2260 Vol. 43, No. 5 0095-1137/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.43.5.2256 2260.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 2005, p. 2256 2260 Vol. 43, No. 5 0095-1137/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.43.5.2256 2260.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Colonization of the Porcine Gastrointestinal Tract by Lactobacilli
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1989, p. 279-283 0099-2240/89/020279-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1989, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 55, No. 2 Colonization of the Porcine Gastrointestinal
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1989, p. 279-283 0099-2240/89/020279-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1989, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 55, No. 2 Colonization of the Porcine Gastrointestinal
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI DETECTION IN CHRONIC GASTRITIS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, HEMATOXYLIN & EOSIN AND GEIMSA STAIN FOR HELICOBACTER
Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen
 Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH HELICOBACTER PYLORI IN RATS
 Buletin USAMV-CN, 63/2006 (34-38) ISSN 1454-2382 EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH HELICOBACTER PYLORI IN RATS Cătoi C. 1, A. Gal 1, E. Dombay 1, I.V. Rus 1, Sorina Iacob 1, Adriana Florinela Cătoi 2 1 University
Buletin USAMV-CN, 63/2006 (34-38) ISSN 1454-2382 EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH HELICOBACTER PYLORI IN RATS Cătoi C. 1, A. Gal 1, E. Dombay 1, I.V. Rus 1, Sorina Iacob 1, Adriana Florinela Cătoi 2 1 University
Diagnosing Gastric Helicobacter Infections in Dogs and Cats
 Article #4 CE Diagnosing Gastric Helicobacter Infections in Dogs and Cats Michael S. Leib, DVM, MS, DACVIM Robert B. Duncan, DVM, PhD, DACVP Virginia Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine (Virginia
Article #4 CE Diagnosing Gastric Helicobacter Infections in Dogs and Cats Michael S. Leib, DVM, MS, DACVIM Robert B. Duncan, DVM, PhD, DACVP Virginia Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine (Virginia
Animal and Public Health Implications of Gastric Colonization
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 1994, p. 1043-1049 Vol. 32, No. 4 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Animal and Public Health Implications of Gastric Colonization of Cats by Helicobacter-Like Organisms G. OTTO,1t
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 1994, p. 1043-1049 Vol. 32, No. 4 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Animal and Public Health Implications of Gastric Colonization of Cats by Helicobacter-Like Organisms G. OTTO,1t
Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
Characterization of elongated Helicobacter pylori isolated from a patient with gastric-mucosaassociated lymphoid-tissue lymphoma
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 207 212 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.05281-0 Characterization of elongated Helicobacter pylori isolated from a patient with gastric-mucosaassociated lymphoid-tissue lymphoma
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 207 212 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.05281-0 Characterization of elongated Helicobacter pylori isolated from a patient with gastric-mucosaassociated lymphoid-tissue lymphoma
GASTRIC PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATED WITH DIFFERENT SPECIES OF HELICOBACTER IN PETS
 UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND VETERINARY MEDICINE CLUJ-NAPOCA FACULTY OF VETERINARY MEDICINE MARIAN TAULESCU SUMMARY OF THE Ph-D THESIS GASTRIC PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATED WITH DIFFERENT SPECIES OF
UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AND VETERINARY MEDICINE CLUJ-NAPOCA FACULTY OF VETERINARY MEDICINE MARIAN TAULESCU SUMMARY OF THE Ph-D THESIS GASTRIC PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATED WITH DIFFERENT SPECIES OF
Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
Ultrastructure of a spiral micro-organism from pig gastric mucosa ( Gastrospirillum suis )
 J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 33 (1990), 6146 0 1990 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland Ultrastructure of a spiral micro-organism from pig gastric mucosa ( Gastrospirillum suis ) 0022-261
J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 33 (1990), 6146 0 1990 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland Ultrastructure of a spiral micro-organism from pig gastric mucosa ( Gastrospirillum suis ) 0022-261
Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa:
 J Clin Pathol 1984;37:1002-1006 Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies DM JONES,* AM LESSELLS,t JOAN ELDRIDGE* From the *Public Health Laboratory
J Clin Pathol 1984;37:1002-1006 Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies DM JONES,* AM LESSELLS,t JOAN ELDRIDGE* From the *Public Health Laboratory
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL
 EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLA INFECTIONS: CHARACTERISTICS OF A FATAL INFECTION PRODUCED IN GUINEA PIGS' SAMUEL B. FORMAL, GUSTAVE J. DAMMIN, E. H. LABREC, AND H. SCHNEIDER Walter Reed Army Institute of Research,
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
The Resolution of Helicobacter suis-associated Gastric Lesions after Eradication Therapy
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8971-17 Intern Med 57: 203-207, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Resolution of Helicobacter suis-associated Gastric Lesions after Eradication Therapy Satoru Nakagawa
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8971-17 Intern Med 57: 203-207, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT The Resolution of Helicobacter suis-associated Gastric Lesions after Eradication Therapy Satoru Nakagawa
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005
 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
Helicobacter pylori Gastric Infection in Gnotobiotic Beagle Dogs
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 1990, p. 2606-2612 0019-9567/90/082606-07$02.00/0 Copyright X 1990, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 8 Helicobacter pylori Gastric Infection in Gnotobiotic Beagle
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 1990, p. 2606-2612 0019-9567/90/082606-07$02.00/0 Copyright X 1990, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 8 Helicobacter pylori Gastric Infection in Gnotobiotic Beagle
Gastric MALT-lymphoma and Helicobacter pylori infection
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 11 (Suppl. 1): 89 94. Gastric MALT-lymphoma and Helicobacter pylori infection E. BAYERDO RFFER, S. MIEHLKE, A. NEUBAUER & M. STOLTE* Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 11 (Suppl. 1): 89 94. Gastric MALT-lymphoma and Helicobacter pylori infection E. BAYERDO RFFER, S. MIEHLKE, A. NEUBAUER & M. STOLTE* Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology
Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2007; 41: 289-95 Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis Jeong Eun Hwang Young Ok Hong Dong Eun Song Se Jin Jang Eunsil Yu Department of Pathology, University
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2007; 41: 289-95 Clinicopathologic Analysis of Lymphocytic Gastritis Jeong Eun Hwang Young Ok Hong Dong Eun Song Se Jin Jang Eunsil Yu Department of Pathology, University
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY. Robin Warren
 - Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
 PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Campylobacter. Helicobacter. Arcobacter 10/14/2011. General. Difference from Vibrio. Difference from Vibrio. Vibrio. Campylobacter
 Helicobacter Gram-negative Short, curved (comma shaped), spiral or S forms May turn coccoid in old cultures Oxidase + Urease negative cf. Helicobacter mostly urease positive Microaerophilic (3% - 15% O
Helicobacter Gram-negative Short, curved (comma shaped), spiral or S forms May turn coccoid in old cultures Oxidase + Urease negative cf. Helicobacter mostly urease positive Microaerophilic (3% - 15% O
Original Article The Frequency of Lymphocytic and Reflux Esophagitis in Non-Human Primates
 www.ijcep.com/ijcep710008 Original Article The Frequency of Lymphocytic and Reflux Esophagitis in Non-Human Primates Carlos A. Rubio, Edward J. Dick Jr, Abiel Orrego and Gene B. Hubbard Southwest National
www.ijcep.com/ijcep710008 Original Article The Frequency of Lymphocytic and Reflux Esophagitis in Non-Human Primates Carlos A. Rubio, Edward J. Dick Jr, Abiel Orrego and Gene B. Hubbard Southwest National
Induction of ulceration and severe gastritis in Mongolian gerbil by Helicobacter pylori infection
 J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 46 (1997), 391-397 1997 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland MODEL OF INFECTION Induction of ulceration and severe gastritis in Mongolian gerbil by Helicobacter
J. Med. Microbiol. - Vol. 46 (1997), 391-397 1997 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland MODEL OF INFECTION Induction of ulceration and severe gastritis in Mongolian gerbil by Helicobacter
Experimental Helicobacter pylori gastric infection in miniature pigs
 J. Med. Microbiol. Ð Vol. 51 2002), 238±246 # 2002 Society for General Microbiology ISSN 0022-2615 MODELS OF INFECTION Experimental Helicobacter pylori gastric infection in miniature pigs T. KOGA, Y. SHIMADA,
J. Med. Microbiol. Ð Vol. 51 2002), 238±246 # 2002 Society for General Microbiology ISSN 0022-2615 MODELS OF INFECTION Experimental Helicobacter pylori gastric infection in miniature pigs T. KOGA, Y. SHIMADA,
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications
 594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
Helicobacter suis induces changes in gastric inflammation and acid secretion markers in pigs of different ages
 Helicobacter suis induces changes in gastric inflammation and acid secretion markers in pigs of different ages C. De Witte, B. Devriendt, B. Flahou, I. Bosschem, R. Ducatelle, A. Smet, F. Haesebrouck To
Helicobacter suis induces changes in gastric inflammation and acid secretion markers in pigs of different ages C. De Witte, B. Devriendt, B. Flahou, I. Bosschem, R. Ducatelle, A. Smet, F. Haesebrouck To
Gastric Polyps. Bible class
 Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Associations between the Plasticity Region Genes of Helicobacter pylori and Gastroduodenal Diseases in a High-Prevalence Area
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 4, No. 3, September 2010, pp. 345-350 original article Associations between the Plasticity Region Genes of Helicobacter pylori and Gastroduodenal Diseases in a High-Prevalence Area
Gut and Liver, Vol. 4, No. 3, September 2010, pp. 345-350 original article Associations between the Plasticity Region Genes of Helicobacter pylori and Gastroduodenal Diseases in a High-Prevalence Area
(Received September 12, Accepted April 23, 1997) Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol., 50, 55-62, 1997.
 Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol., 50, 55-62, 1997. EVALUATION OF CULTURE, HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION, SEROLOGY AND THE RAPID UREASE TEST FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI IN PATIENTS WITH DYSPEPSIA IN BANGLADESH
Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol., 50, 55-62, 1997. EVALUATION OF CULTURE, HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION, SEROLOGY AND THE RAPID UREASE TEST FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI IN PATIENTS WITH DYSPEPSIA IN BANGLADESH
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
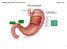 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
D. Bērziņa, E. Birģele Detection of Gastric Helicobacter-like Microorganisms in Dogs
 Detection of Gastric Helicobacter-like Microorganisms in Feral Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes Procyonoides) and Domestic Dogs (Canis Familiaris) Kuņģa helikobaktēriju noteikšana savvaļas jenotsuņiem (Nyctereutes
Detection of Gastric Helicobacter-like Microorganisms in Feral Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes Procyonoides) and Domestic Dogs (Canis Familiaris) Kuņģa helikobaktēriju noteikšana savvaļas jenotsuņiem (Nyctereutes
Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute
 J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
J Clin Pathol 1987;40:13-18 Histopathogenesis of intestinal metaplasia: minute lesions of intestinal metaplasia in ulcerated stomachs K MUKAWA, T NAKAMURA, G NAKANO, Y NAGAMACHI From the First Department
Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS
 SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
Helicobacter Connections. Barry Marshall
 Helicobacter Connections Barry Marshall The greatest obstacle to knowledge is not ignorance, it is the illusion of knowledge. Daniel Boorstein - Historian Peptic Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer (DU) Gastric Ulcer
Helicobacter Connections Barry Marshall The greatest obstacle to knowledge is not ignorance, it is the illusion of knowledge. Daniel Boorstein - Historian Peptic Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer (DU) Gastric Ulcer
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
Helicobacter suis Causes Severe Gastric Pathology in Mouse and Mongolian Gerbil Models of Human Gastric Disease
 Helicobacter suis Causes Severe Gastric Pathology in Mouse and Mongolian Gerbil Models of Human Gastric Disease Bram Flahou 1 *, Freddy Haesebrouck 1, Frank Pasmans 1, Katharina D Herde 2, Ann Driessen
Helicobacter suis Causes Severe Gastric Pathology in Mouse and Mongolian Gerbil Models of Human Gastric Disease Bram Flahou 1 *, Freddy Haesebrouck 1, Frank Pasmans 1, Katharina D Herde 2, Ann Driessen
Effect of Enterococcus faecium on immune system of chickens challenged against Salmonella Minnesota
 Effect of Enterococcus faecium on immune system of chickens challenged against Salmonella Minnesota Published on: 09/10/2012 Author/s : Leandro NagaeKuritza, Leonardo BozziMiglino, Mariana Camargo Lourenço,
Effect of Enterococcus faecium on immune system of chickens challenged against Salmonella Minnesota Published on: 09/10/2012 Author/s : Leandro NagaeKuritza, Leonardo BozziMiglino, Mariana Camargo Lourenço,
The surface mucous cells and the cardiac and pyloric glands secrete mucus which protects the stomach from self-digestion.
 PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION A Pol rat Wilairatana I, Mario Riganti2, Sornchai Looareesuwan I, Benjanee Punpoowong2, Preeya Srisopark2 and Preecha Charoenlarpl
DYSPEPSIA IN ACUTE FALCIPARUM MALARIA CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION A Pol rat Wilairatana I, Mario Riganti2, Sornchai Looareesuwan I, Benjanee Punpoowong2, Preeya Srisopark2 and Preecha Charoenlarpl
by authors and SVSBT.
 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2016 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastric atrophy: use of OLGA staging system in practice Mahsa
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Surface morphology of the gastroduodenal mucosa in duodenal ulceration
 Gut, 1984, 25, 1203-1210 Surface morphology of the gastroduodenal mucosa in duodenal ulceration H W STEER From the Southampton General Hospital, Southampton SUMMARY Endoscopic biopsies from the duodenal
Gut, 1984, 25, 1203-1210 Surface morphology of the gastroduodenal mucosa in duodenal ulceration H W STEER From the Southampton General Hospital, Southampton SUMMARY Endoscopic biopsies from the duodenal
Pathogenesis Most individuals with the infection also have the associated gastritis but are asymptomatic
 STOMACH Chronic Gastritis The presence of chronic inflammatory changes in the mucosa leading eventually to mucosal atrophy and epithelial metaplasia. In the Western world the prevalence of chronic gastritis
STOMACH Chronic Gastritis The presence of chronic inflammatory changes in the mucosa leading eventually to mucosal atrophy and epithelial metaplasia. In the Western world the prevalence of chronic gastritis
Review article: have we found the source of Helicobacter pylori?
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14 (Suppl. 3): 7±12 Review article: have we found the source of Helicobacter pylori? F. ME GRAUD & N. BROUTET Laboratoire de BacteÂriologie, Universite Victor Segalen Bordeaux
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14 (Suppl. 3): 7±12 Review article: have we found the source of Helicobacter pylori? F. ME GRAUD & N. BROUTET Laboratoire de BacteÂriologie, Universite Victor Segalen Bordeaux
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Definition gastritis
 Gastritis Definition The term gastritis is used to denote inflammation associated with mucosal injury Gastritis is mostly a histological term that needs biopsy to be confirmed Gastritis is usually due
Gastritis Definition The term gastritis is used to denote inflammation associated with mucosal injury Gastritis is mostly a histological term that needs biopsy to be confirmed Gastritis is usually due
Research Article Correlation between the Intensity of Helicobacter pylori Colonization and Severity of Gastritis
 Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 8320496, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8320496 Research Article Correlation between the Intensity of Helicobacter pylori Colonization
Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 8320496, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8320496 Research Article Correlation between the Intensity of Helicobacter pylori Colonization
Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report.
 Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report. Alan Shienbaum, DO; AndriyPavlenko, MD; Jun Liu, MD, PhD; Janusz J Godyn, MD. Pathology Department, Kennedy University Hospitals,
Lymphocytic Gastritis, Isolated Type Occurring in Family Members. A Case Report. Alan Shienbaum, DO; AndriyPavlenko, MD; Jun Liu, MD, PhD; Janusz J Godyn, MD. Pathology Department, Kennedy University Hospitals,
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Histological and immunohistochemical detection of different Helicobacter species in the gastric mucosa of cats
 J Vet Diagn Invest 13:3 12 (2001) Histological and immunohistochemical detection of different Helicobacter species in the gastric mucosa of cats Eugenio Scanziani, Kenneth W. Simpson, Silvia Monestiroli,
J Vet Diagn Invest 13:3 12 (2001) Histological and immunohistochemical detection of different Helicobacter species in the gastric mucosa of cats Eugenio Scanziani, Kenneth W. Simpson, Silvia Monestiroli,
Presentation Outline. Periweaning Failure to Thrive Syndrome
 Periweaning Failure to Thrive Syndrome Terri O Sullivan APV Conference June 6 8, 2012 Shanghai, China 2700 km Presentation Outline PFTS introduction and background PFTS clinical presentation Hypotheses
Periweaning Failure to Thrive Syndrome Terri O Sullivan APV Conference June 6 8, 2012 Shanghai, China 2700 km Presentation Outline PFTS introduction and background PFTS clinical presentation Hypotheses
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) PATHOLOGY LAB #1. January 06, 2012
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) PATHOLOGY LAB #1 GOAL: January 06, 2012 Faculty Copy 1. Describe the basis morphologic and pathophysiologic changes which occur in
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) PATHOLOGY LAB #1 GOAL: January 06, 2012 Faculty Copy 1. Describe the basis morphologic and pathophysiologic changes which occur in
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
JJBS Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences
 JJBS Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences Volume 4, Number 2, June 2011 ISSN 1995-6673 Pages 71-76 Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis at the North of Jordan N. M. Abu-Ahmad, A. Odeh and A-K.
JJBS Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences Volume 4, Number 2, June 2011 ISSN 1995-6673 Pages 71-76 Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Gastritis at the North of Jordan N. M. Abu-Ahmad, A. Odeh and A-K.
H. pylori IgM CLIA kit
 H. pylori IgM CLIA kit Cat. No.:DEEL0251 Pkg.Size:96 tests Intended use Helicobacter pylori IgM Chemiluminescence ELISA is intended for use in evaluating the serologic status to H. pylori infection in
H. pylori IgM CLIA kit Cat. No.:DEEL0251 Pkg.Size:96 tests Intended use Helicobacter pylori IgM Chemiluminescence ELISA is intended for use in evaluating the serologic status to H. pylori infection in
PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 40 (1): 15-19, 2006 PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS Shilpa Sood 1 and P.C. Verma CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar - 125 004, India ABSTRACT The
Indian J. Anim. Res., 40 (1): 15-19, 2006 PATHOLOGY OF PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA INFECTION IN CHICKENS Shilpa Sood 1 and P.C. Verma CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar - 125 004, India ABSTRACT The
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
H. pylori IgM. Cat # H. pylori IgM ELISA. ELISA: Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. ELISA - Indirect; Antigen Coated Plate
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com H. pylori
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com H. pylori
Gastrin cells and fasting serum gastrin levels in duodenal ulcer patients A quantitative study based on multiple biopsy specimens
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 171-178 Gastrin cells and fasting serum gastrin levels in duodenal ulcer patients A quantitative study based on multiple biopsy specimens JUAN PIRIS AND R. WHITEHEADI
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 171-178 Gastrin cells and fasting serum gastrin levels in duodenal ulcer patients A quantitative study based on multiple biopsy specimens JUAN PIRIS AND R. WHITEHEADI
SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PATHOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Program SAM PROVIDER TOOLKIT Developing Self-Assessment Modules (SAMs) www.abpath.org The American Board of Pathology (ABP) approves educational
ARTICLES. An Epizootic of Lymphoplasmacytic Gastritis Attributed to Helicobacter pylori Infection in Cynomolgus Monkeys (Macaca fascicularis)
 Vet Pathol 36:1 13 (1999) ARTICLES An Epizootic of Lymphoplasmacytic Gastritis Attributed to Helicobacter pylori Infection in Cynomolgus Monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) J. F. REINDEL, A. L. FITZGERALD, M.
Vet Pathol 36:1 13 (1999) ARTICLES An Epizootic of Lymphoplasmacytic Gastritis Attributed to Helicobacter pylori Infection in Cynomolgus Monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) J. F. REINDEL, A. L. FITZGERALD, M.
Iranian Journal of Veterinary Research, Shiraz University, Vol. 12, No. 4, Ser. No. 37, 2011
 Morphological and histochemical investigation of the camel (Camelus dromedarius) abomasal mucous membrane by light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Raji, A. R. Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty
Morphological and histochemical investigation of the camel (Camelus dromedarius) abomasal mucous membrane by light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Raji, A. R. Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty
Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions MULAZIM HUSSAIN BUKHARI, SAMINA QAMAR*, SHAHBAZ AHMAD QURESHI*, MALIK MAQSOOD ANWAR** ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histopathological study of Helicobacter Pylori bearing Gastric Biopsies for Gastric Lesions MULAZIM HUSSAIN BUKHARI, SAMINA QAMAR*, SHAHBAZ AHMAD QURESHI*, MALIK MAQSOOD ANWAR** ABSTRACT
Original Article Increased lysozyme expression in gastric biopsies with intestinal metaplasia and pseudopyloric metaplasia
 www.ijcem.com/ijcem908003 Original Article Increased lysozyme in gastric biopsies with intestinal metaplasia and pseudopyloric metaplasia Carlos A Rubio, Ragnar Befrits Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology
www.ijcem.com/ijcem908003 Original Article Increased lysozyme in gastric biopsies with intestinal metaplasia and pseudopyloric metaplasia Carlos A Rubio, Ragnar Befrits Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology
Framing Helicobacter pylori: The Etiology of Peptic Ulcers and Gastritis
 Framing Helicobacter pylori: The Etiology of Peptic Ulcers and Gastritis By Aja Dunn Gastritis (inflammation of the stomach); Etiologic agent - Helicobacter pylori (1). Transmission H. pylori infection
Framing Helicobacter pylori: The Etiology of Peptic Ulcers and Gastritis By Aja Dunn Gastritis (inflammation of the stomach); Etiologic agent - Helicobacter pylori (1). Transmission H. pylori infection
Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 17: 1051-1055, 2007 Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma SUN-YOUNG LEE 1, HYE SEUNG HAN 2, KYUNG YUNG LEE 3, TAE SOOK HWANG 2, JEONG HWAN KIM 1, IN-KYUNG SUNG
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 17: 1051-1055, 2007 Sonic hedgehog expression in gastric cancer and gastric adenoma SUN-YOUNG LEE 1, HYE SEUNG HAN 2, KYUNG YUNG LEE 3, TAE SOOK HWANG 2, JEONG HWAN KIM 1, IN-KYUNG SUNG
Brachyspira & Lawsonia
 General Brachyspira & Lawsonia Gram-negative Anaerobic but with aerotolerance Colonize the large intestine of mammals and birds Infections with Brachyspira species are important in pigs Species & Disease
General Brachyspira & Lawsonia Gram-negative Anaerobic but with aerotolerance Colonize the large intestine of mammals and birds Infections with Brachyspira species are important in pigs Species & Disease
H.Pylori IgG Cat # 1503Z
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
HELICOBACTER THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY
 HELICOBACTER THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Nobel Lecture, December 8, 2005 by J. Robin Warren Perth, WA 6000, Australia. PREFACE This is the story of my discovery of Helicobacter. At various
HELICOBACTER THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Nobel Lecture, December 8, 2005 by J. Robin Warren Perth, WA 6000, Australia. PREFACE This is the story of my discovery of Helicobacter. At various
Post-immunisation gastritis and Helicobacter infection in the mouse: a long term study
 Gut 2001;49:467 473 467 PAPERS School of Microbiology and Immunology, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia P Sutton S J Danon L J Thompson J Wilson T Kosaka A Lee Department of Histopathology,
Gut 2001;49:467 473 467 PAPERS School of Microbiology and Immunology, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia P Sutton S J Danon L J Thompson J Wilson T Kosaka A Lee Department of Histopathology,
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA
 A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF NONSTEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS (NSAIDs) ON THE GASTRIC AND DUODENAL MUCOSA Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 287 To 290 Naheed Moghal, N.A. Jafarey
H.Pylori IgM Cat # 1504Z
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------
 A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------ The pain can be relieved by food or antiacids------ He denies taking aspirin or NSAID------ Lab
A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------ The pain can be relieved by food or antiacids------ He denies taking aspirin or NSAID------ Lab
CIRRHOSIS; HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN GASTRIC MUCOSA OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS PATIENTS.
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4146 ORIGINAL PROF-4146 CIRRHOSIS; HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN GASTRIC MUCOSA OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS PATIENTS. 1. MBBS, M.Phil Professor Isra University 2.
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.29309/TPMJ/18.4146 ORIGINAL PROF-4146 CIRRHOSIS; HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN GASTRIC MUCOSA OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS PATIENTS. 1. MBBS, M.Phil Professor Isra University 2.
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States
 Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
