by authors and SVSBT.
|
|
|
- Amie Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, ISSN (Print) : : ISSN (Print and online) : , abbreviated as IJVSBT /ijvsbt.v13i Submitted : Accepted : Published : Histomorphological, Micrometrical and Histochemical Characteristics of Abomasum in Gaddi Sheep (Ovis aries) Shabir Ahmad Malik *, Rajesh Rajput, Uiase Bin Farooq and Mohd Rafiq Department of Anatomy & Histology, Department of Surgery & Radiology DGCN College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, CSKHPKV, Palampur , India Corresponding Author: malikshabir21@gmail.com This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License ( creativecommons.org/licenses /by/4.0/p), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited by authors and SVSBT. Abstract The present study was conducted to know the histoarchitecture and histochemical characteristics of abomasum of adult Gaddi sheep (n=6). Lamina propria of the tunica mucosa was occupied by cardiac, fundic and pyloric glands. Lamina epithelialis consisted of tall columnar epithelial cells. The number of chief cells was greater compared to parietal cells in the gastric glands and showed basophilic reaction. However parietal cells were comparatively larger than chief cells or mucous neck cells and showed strong eosinophilic reaction. Fundic glands were simple tubular whereas pyloric glands were simple, straight, branched tubular glands which opened into the gastric pits. Depth of gastric pits in the pyloric region was higher than in cardiac and fundic regions. The predominant cells of pyloric glands were the mucous neck cells. Tunica submucosa was composed of a network of collagen, reticular and elastic fibres. Tunica muscularis was composed of an inner circular and outer longitudinal layer. Histochemical reactions were mainly demonstrated in surface epithelium, gastric pit epithelium and gastric gland cells of abomasum. Abundant acid mucopolysaccharides were localized in the pyloric region of abomasum which indicated the predominance of mucous neck cells in pyloric region. Key Words: Gaddi, Abomasum, Histology, Histochemistry, Chief cells, Parietal cells, Mucous neck cells Introduction The abomasum is the most aboral and first glandular compartment of the ruminant stomach. In the typical ruminant, the first three compartments (rumen, reticulum and omasum) are nonglandular, whereas the fourth part abomasum, as glandular stomach, contains typical cardiac, fundic and pyloric glands (Eurell and Frappier, 2006). The Gaddi breed of sheep plays a very important role in the livelihood of Gaddi tribe of people in the Himalayan region. The present study sought to chart the histomorphology and histochemistry of the abomasum in Gaddi sheep using histological and histochemical techniques. The objectives of this study were: (a) to provide a description of the histology of the abomasum in Gaddi sheep, (b) to demonstrate histochemical reactions, and (c) to measure various micrometrical parameters of abomasal wall and gastric gland cells. Indian J. Vet Sci. Biotech (2018) Vol. 13 No. 4 20
2 Materials and Methods The abomasums of adult healthy Gaddi sheep of either sex (n=6) were collected from the local slaughter house. Tissue specimens from different regions of abomasums were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. The tissues were processed by routine paraffin embedding technique (Luna, 1968) and tissue sections of 5 to 7 μm were cut. The sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin for routine histology, Masson s trichome for collagen fibres, Gomori s for reticular fibres and Verhoeff s for elastic fibres. For histochemical studies the sections were stained for carbohydrates by PAS stain, acid mucopolysaccharides by Alcian blue method, and for fat by Sudan Black B (Luna, 1968). The data were analyzed statistically using independent samples T test (SPSS Statistics 17.0). Result and Discussion Histologically the abomasum in Gaddi sheep was composed of four different layers, i.e., tunica mucosa, tunica submucosa, tunica muscularis and tunica serosa (Fig. 1). Micrometrical parameters of these four layers were recorded (Table 1). Tunica mucosa consisted of lamina epithelialis, lamina propria and lamina muscularis mucosa. The lamina epithelialis consisted of tall columnar epithelial cells. The lining cells were mucous secreting. Surface epithelium was uniquely distinguished from the glandular epithelium in that the mucin is not preserved by the routine histological preparations, thus a clear zone is present in the apical portion of the surface epithelium (Fig. 2). Considerable amount of lymphoid tissue was observed in the lamina propria of the abomasum. Height of epithelial Table 1: Micrometrical parameters of different layers of abomasum in cardiac, fundic and pyloric region in Gaddi sheep Parameters Measurement (µm) Cardiac region Fundic region Pyloric region Tunica mucosa a ± ( ) b ± ( ) c ± ( ) Tunica submucosa a ± 8.33 (70-240) b ± 9.40 ( ) c ± ( ) Tunica muscularis a ± ( ) b ± ( ) c ± ( ) Tunica serosa 57 a ± 6.12 (35-83) 60 a ± 6.42 (38-85) b ± 9.50 (65-145) Values with different superscripts (a, b) within the row vary significantly (P < 0.05). Table 2: Micrometrical parameters of abomasal glands in cardiac, fundic and pyloric region in Gaddi sheep Measurement (µm) Parameters (µm) Cardiac region Fundic region Pyloric region Depth of gastric pits a ± 2.25 (37-83) b ± 3.30 (40-160) c ± 3.84 (80-240) Epithelial height 6.25 a ± 0.34 (4-12) 5.97 a ± 0.29 (3-12) b ± 0.44 (10-22) Diameter of nuclei of epithelial cells 3.07 a ± 0.15 (3-5) 2.87 a ± 0.15 (2-5) 5.00 b ± 0.15 (3-8) Diameter of gastric pits a ± 0.78 (9-25) a ± 0.98 (7-27) b ± 0.26 (15-36) Values with different superscripts (a, b) within the row vary significantly (P < 0.05). Indian J. Vet Sci. Biotech (2018) Vol. 13 No. 4 21
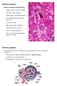
3 cells and diameter of nuclei of columnar epithelial cells were measured in cardiac, fundic and pyloric gland region (Table 2). Lamina propria mucosa consisted of a loose connective tissue and a network of reticular, collagen and elastic fibres were interspersed between the extensive gastric glands (Fig. 3 & 4). Longitudinal smooth muscle fibres constituted the lamina muscularis mucosa. Cardiac gland region occupied a narrow strip at the junction of the glandular and non-glandular mucosae. Mucous secreting neck cells which were cuboidal line the neck and upper portion of the body of cardiac glands. The cardiac glands were relatively short, coiled and tubular. Morphology of the fundic gland region was similar to the cardiac region; however the extent of the fundic gland region varies in different species (Banks, 1981). Fundic glands were straight, tubular glands that extended to the lamina muscularis. Three different types of cells were found in the fundic gland mucosa: chief cells, parietal cells and mucous neck cells (Fig. 5). However, Eurell and Frappier (2006) have observed four cell types. The chief cells lining the body and fundus were cuboidal. The chief cells were the most numerous of the gastric gland cells and showed basophilia towards the basal portion. Chief cells are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of gastric enzymes like pepsin, rennin and gastric lipase (Banks, 1981). The basophilia of the chief cells towards the basal portion is because of the abundance of rough endoplasmic reticulum required for peptide and enzyme synthesis like pepsin. Parietal cells were comparatively larger than chief cells or mucous neck cells. Parietal cells occurred singly and their cytoplasm stained deeply with eosin, i.e. showed strong eosinophilia. The pyramidal configuration with a round nucleus is a distinctive feature of parietal cells (Fig. 5). Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid required for food digestion. Mucous neck cells line the neck of the gland and are distributed among the parietal cells. The secretory product of the mucous neck cells protect the fundic gland from the proteolytic and hydrolytic activity of the proteases and hydrochloric acid, respectively (Banks, 1981). Depth of gastric pits varied significantly in the cardiac, fundic and pyloric region and was maximum in the pyloric region (Table 2). Pyloric glands were simple, straight, branched tubular glands which opened into the gastric pits (Fig. 6 & 7). Gastric pits in pyloric gland region were comparatively deeper than the gastric pits in cardiac or fundic region. The pit and neck were lined with tall, columnar mucous cells. The predominant cells of pyloric glands were the mucous neck cells. Lamina muscularis mucosa was S L C TS TM Fig. 1. Abomasal wall showing tunica serosa (S), longitudinal muscle (L), circular muscle (C), tunica submucosa (TS) and tunica mucosa (TM). Massons trichome x 40X; Fig. 2. Mucosal columnar epithelilial cells lining the gastric glands and the surface epithelium. H & E x 1000X; Fig. 3. Collagen fibres (red) present in the lamina propria and in the tunica submucosa of abomasum. Van Giesons stain x 200X Indian J. Vet Sci. Biotech (2018) Vol. 13 No. 4 22
4 present as a thin layer of smooth muscle in the cardiac and fundic region however it was very prominent in the pyloric gland region (Fig. 8). Tunica submucosa was composed of a network of collagen and elastic fibres. Many small and large blood vessels and lymphatic vessels were also present in tunica submucosa. Thickness of tunica submucosa increased from cardiac region towards pyloric region. Tunica muscularis was composed of an inner circular and outer longitudinal layer (Fig. 8). The inner circular layer was very much thicker in the pyloric region and formed the pyloric sphincter. Eurell and Frappier (2006) observed the tunica muscularis consisted of an inner oblique layer, middle circular layer and outer longitudinal layer in small ruminants, this arrangement however in the present study was not observed. Thickness of tunica muscularis increased from cardiac to pyloric region similar to the observations by Agge et al. (2006). Tunica serosa consisted of mesothelium overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. Histochemically mucins are classified into two types: Epithelial mucins (mucins/ mucosubstances) and connective tissue mucins (mucopolysaccharides). Epithelial mucins are further classified as neutral and acidic (Reid and Clamp, 1978). Epithelial mucins were demonstrated in the present study with Alcian blue (AB) ph 2.5 reaction. Further Periodic-Acid-Schiff (PAS) reaction demonstrates neutral polysaccharides like glycogen, simple polysaccharides and non-ionic homoglycans. In the present study, histochemical reactions were mainly demonstrated in surface epithelium, gastric pit epithelium and gastric gland cells of abomasum. The pyloric gland region showed more intense histochemical reaction compared to cardiac and fundic region. The gastric glands present near the superficial region of mucosa showed a strong reaction for PAS as well as AB ph 2.5 indicating presence of glycogen and acid mucopolysaccharides, respectively (Fig. 9 & 10). Glands present near the basal region showed negligible PAS and AB ph 2.5 reaction similar to the observations by Raji (2011) in camel. Surface epithelium and gastric pit epithelial cells showed strong PAS reaction. Glandular epithelial cells of fundic glands showed PAS reaction as well as AB ph 2.5 reaction in their supranuclear zone (Fig. 11). Parietal cells showed a mild PAS positive reaction. Karakoc et al., (2016) reported that neutral and acidic mucins were present in the mucosa and the glands of the pars cardiaca, fundus, and pars pylorica of the abomasums of both bulls and rams. Surface epithelial cells and gastric pit Fig. 4. Pyloric glands surrounded by reticular fibres (black). Gomori s reticulum x 200X; Fig. 5. Fundic glands showing eosinophilic parietal cells (P), basophilic chief cells (C) and mucous neck cells (M) H & E x 200X; Fig. 6. Deep gastric pits (GP) in the pyloric region H & E x 200X; Indian J. Vet Sci. Biotech (2018) Vol. 13 No. 4 23
5 Fig. 7. Branched tubular glands lined by columnar epithelial cells in the pyloric region. H & E x 200X; Fig. 8. Lamina musularis mucosa (LMM), tunica submucosa (TS) and tunica muscularis (TM) in the pyloric gland region H & E x 40X Fig. 9. Pyloric glands showing PAS positive reaction in the surface epithelial cells and gastric pit epithelial cells. Parietal cells show mild PAS reaction. 200X; Fig. 10. Pyloric glands showing strong alcian blue reaction by epithelial cells of gastric pits. 200X; Fig. 11. Fundic glands showing PAS positive reaction by the glandular epithelial cells in their supranuclear zone. 1000X Fig. 12. Sudan Black B reaction by epithelial cells of gastric pits and pyloric gland cells. 200X; Indian J. Vet Sci. Biotech (2018) Vol. 13 No. 4 24
6 epithelial cells showed moderate Sudan Black B reaction however gastric gland cells showed strong Sudan Black B reaction indicating the presence of lipids (Fig.12). Cells at the base of gastric pits showed strong reaction for Sudan Black B. Fat droplets were deposited in the basal region of the gastric pits in the pyloric gland region, whereas the cells in the superficial layer of gastric pits showed weak reaction. Abundance of acid mucopolysaccharides in the gastric glands indicated the high secretory activity of mucous neck cells to counteract the acid digestion of the abomasal wall. Acknowledgements This study was supported by research fellowship from ICAR. The authors thank faculty members and supporting staff of the department of Anatomy and Histology of the College for their suggestions and cooperation. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest References: Agge, H.M., Bhosle, N.S. and Kapadnis, P.J. (2006). Microscopic study of abomasum in sheep. Indian J. Anim. Res., 42(2): Banks, W.J. (1981). Digestive System, In: Applied Veterinary Histology. Waverly Press, Inc. pp 389. Eurell, J.A. and Frappier, B.L. (2006). Dellmann s Text Book of Veterinary Histology. 3 rd ed, Blackwell Publishing Limited. pp 190. Karakoc, Z., Sagsoz, H. and Ketani, M.A. (2016). Mucin profiles of the abomasum in bulls and rams: A comparative study. Microscopic Res. Tech., 79: Luna, L.G. (1968). Manual of Histologic Staining Methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. 3 rd edn., McGraw Hill Book Co., New York, pp Raji, A.R. (2011). Morphological and histochemical investigation of the camel (Camelus dromedarius) abomasal mucous membrane by light and scanning electron microscopy. Iranian J. Vet. Res., 12(4): 3. Reid, J. and Clamp, J.R. (1978). The biochemical and histochemical nomenclature of mucus. British Med. J., 38: 1-8. Indian J. Vet Sci. Biotech (2018) Vol. 13 No. 4 25
Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep
 DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Iranian Journal of Veterinary Research, Shiraz University, Vol. 12, No. 4, Ser. No. 37, 2011
 Morphological and histochemical investigation of the camel (Camelus dromedarius) abomasal mucous membrane by light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Raji, A. R. Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty
Morphological and histochemical investigation of the camel (Camelus dromedarius) abomasal mucous membrane by light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Raji, A. R. Department of Basic Sciences, Faculty
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE GALL BLADDER OF THE CHUKAR PARTRIDGE (ALECTORIS CHUKAR)
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 2, 73 78 MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF TH GALL BLADDR OF TH CHUKAR PARTRIDG (ALCTORIS CHUKAR) Summary B. MOBINI Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 2, 73 78 MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF TH GALL BLADDR OF TH CHUKAR PARTRIDG (ALCTORIS CHUKAR) Summary B. MOBINI Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dana Alrafaiah. Dareen Abu Shalbak. Mohammad Almuhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture:
 السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Urinary system. Urinary system
 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Esophagus. Transport is achieved by peristaltic contractions and relaxation of the esophageal sphincters (upper and lower)
 GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
 VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Behzad Mobini* Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran. Received: 25 October 2010, Accepted: 4 January 2011
 Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN:
 Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Iranian Journal of Veterinary Research, Shiraz University, Vol. 13, No. 1, Ser. No. 38, 2012
 Histological and histomorphometrical changes of different regions of oviduct during follicular and luteal phases of estrus cycle in adult Azarbaijan buffalo Ayen, E. 1* ; Shahrooz, R. 2 and Kazemie, S.
Histological and histomorphometrical changes of different regions of oviduct during follicular and luteal phases of estrus cycle in adult Azarbaijan buffalo Ayen, E. 1* ; Shahrooz, R. 2 and Kazemie, S.
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Micromorphological Observations on the Ductular System of Mammary Gland in Sheep During Various Age Groups
 Micromorphological Observations on the Ductular System of Mammary Gland in Sheep During Various Age Groups S. Paramasivan*, Geetha Ramesh, S. Ushakumary, A. Kumaravel, O.R. Sathyamoorthy, and S. Sivagnanam
Micromorphological Observations on the Ductular System of Mammary Gland in Sheep During Various Age Groups S. Paramasivan*, Geetha Ramesh, S. Ushakumary, A. Kumaravel, O.R. Sathyamoorthy, and S. Sivagnanam
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
Histology Lab. looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira book and you can use BlueHistolgy website
 Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Gastrointestinal Tract
 CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Histological Features of the Renal Arteries in Indian Goat (Capra hircus)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
الله الر ح م ن الر ح يم مسب
 بسم رلا هللارلا هللا This is the second histology lecture in the GI system. In this lecture, we will discuss the histology of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine so prepare yourself.this sheet
بسم رلا هللارلا هللا This is the second histology lecture in the GI system. In this lecture, we will discuss the histology of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine so prepare yourself.this sheet
Histological Observations on the Infundibulum of Kuttanad Duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestics) during Postnatal Period
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2013 1 Histological Observations on the Infundibulum of Kuttanad Duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestics) during Postnatal
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2013 1 Histological Observations on the Infundibulum of Kuttanad Duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestics) during Postnatal
Lab 8: Digestive System
 BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
Digestion and Absorption. Food:
 Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
Gut Integrity of Neonatal Piglets: A Histomorphological Analysis
 DOI: 10.5958/2277-940X.2017.00167.X Journal of Animal Research: v.7 n.6, p. 1115-1121. December 2017 Gut Integrity of Neonatal Piglets: A Histomorphological Analysis Arup Kalita 1 *, Kabita Sarma 2, M.
DOI: 10.5958/2277-940X.2017.00167.X Journal of Animal Research: v.7 n.6, p. 1115-1121. December 2017 Gut Integrity of Neonatal Piglets: A Histomorphological Analysis Arup Kalita 1 *, Kabita Sarma 2, M.
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
HISTOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS OF STOMACH IN DIFFERENT MAMMALS Ramanuj Singh and Ajay Babu. Kannabathula*
 Research Article INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT MEDICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH ISSN: 2395-6429, Impact Factor: SJIF: 4.656 Available Online at www.journalcmpr.com Volume 4; Issue 4(A); April 2018;
Research Article INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT MEDICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH ISSN: 2395-6429, Impact Factor: SJIF: 4.656 Available Online at www.journalcmpr.com Volume 4; Issue 4(A); April 2018;
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas
 Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA)
 Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA) Original article Anatomical and histological studies of esophagus of one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) Adel Jabbar Hussein 1 ;Muntdhur
Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA) Original article Anatomical and histological studies of esophagus of one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) Adel Jabbar Hussein 1 ;Muntdhur
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Stomach. Stomach. Nerve supply. Blood supply. Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system
 Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
Stomach Nerve supply Sympathe0c and parasympathe0c fibers of the autonomic nervous system Blood supply Celiac trunk, and corresponding veins (part of the hepa0c portal system) Stomach Figure 23.14a Chapter
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
Histology. Marcello Malpighi ( ) is regarded as Father of Histology.
 Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
Comparative Histochemical Study of Mucin in Colonic Goblet Cells of Albino Rat, Goat & Dog
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 48-53 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Histochemical Study of Mucin
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 48-53 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Histochemical Study of Mucin
HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE ADRENAL GLAND OF HORSE
 Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2016 ISSN Prasanth 2321 9602 Babu www.iajavs.com A et al., 2016 Vol. 4, No. 1, February 2016 2016 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Research Paper HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES
Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2016 ISSN Prasanth 2321 9602 Babu www.iajavs.com A et al., 2016 Vol. 4, No. 1, February 2016 2016 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Research Paper HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Anatomy PHL 212. Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan. -
 Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Special Staining (I)
 Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Anatomical studies on the cystic artery of sheep (Ovis aries)
 2018; 7(3): 650-655 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(3): 650-655 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 20-01-2018 Accepted: 21-02-2018 B Venkatesh PG Scholar,
2018; 7(3): 650-655 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(3): 650-655 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 20-01-2018 Accepted: 21-02-2018 B Venkatesh PG Scholar,
The Stomach. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although a minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach. An expansion of the alimentary canal that lies immediately
Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16. Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36. Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73
 Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. during postnatal period and to provide elasticity during prenatal and early
 CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Lingual Tonsil of Young Pigs
 VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Lingual Tonsil of Young Pigs Ranjit, Pawan
VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Lingual Tonsil of Young Pigs Ranjit, Pawan
川北医学院讲稿. Under low power note the testis is enclosed by a strong fibrous. layer of serous epithelium. These fibrous tissue
 川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Histological and Morphometrical Studies on the Ampulla of the Deferent Duct of Donkey (Equus Asinus) in Different Seasons
 Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research Volume 3 (2013) 135-141 Original Research Histological and Morphometrical Studies on the Ampulla of the Deferent Duct of Donkey (Equus Asinus) in Different Seasons
Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research Volume 3 (2013) 135-141 Original Research Histological and Morphometrical Studies on the Ampulla of the Deferent Duct of Donkey (Equus Asinus) in Different Seasons
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
Class XI Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Biology
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Alimentary Canal (I) Salivatory Glands. (Esophagus and Stomach) Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra..
 Alimentary Canal (I) (Esophagus and Stomach) Salivatory Glands Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: 1. By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic
Alimentary Canal (I) (Esophagus and Stomach) Salivatory Glands Color index: Slides.. Important..Notes..Extra.. Objectives: 1. By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Gross, histological and histochemical studies on the ovary and oviduct of Kendrapada sheep (Ovis aries) at different age groups
 2017; 5(6): 2319-2324 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(6): 2319-2324 2017 JEZS Received: 25-09-2017 Accepted: 28-10-2017 SK Sahu RK Das S Sathapathy UK Mishra SK Dash Department of AGB,
2017; 5(6): 2319-2324 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(6): 2319-2324 2017 JEZS Received: 25-09-2017 Accepted: 28-10-2017 SK Sahu RK Das S Sathapathy UK Mishra SK Dash Department of AGB,
A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove.
 By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1671 1681 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOMORPHOLOGY OF SKIN EPIDERMIS OF CATTLE BREEDS OF MAHARASHTRA IN DIFFERENT
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1671 1681 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOMORPHOLOGY OF SKIN EPIDERMIS OF CATTLE BREEDS OF MAHARASHTRA IN DIFFERENT
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
