FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS
|
|
|
- Roderick Cobb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS PART I QUALITY ASSESSMENT 1 PATIENT-DEPENDENT FACTORS 3 REVIEW OF IMPORTANT ANATOMY 7 LUNGS AND PLEURA 11 DIAPHRAGMS 13 BONES AND SOFT TISSUES 14 A BRIEF LOOK AT THE LATERAL CXR 16 When interpreting a CXR it is important to make an assessment of whether the x-ray is of diagnostic quality. In order to facilitate this, first pay attention to two radiographic parameters prior to checking for pathology; namely the quality of the film and patient-dependent factors. A suboptimal x-ray can mask or even mimic underlying disease. Quality assessment Is the film correctly labelled? This may seem like an obvious statement to make. However, errors do occur and those relating to labelling of the radiograph are the most common. What to check for? Does the x-ray belong to the correct patient? Check the patient s name on the film. Have the left and right side markers been labelled correctly, or does the patient really have dextrocardia? Lastly has the projection of the radiograph (PA vs. AP) been documented?
2 IFundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics Assessment of exposure quality Is the film penetrated enough? On a high quality radiograph, the vertebral bodies should just be visible through the heart. If the vertebral bodies are not visible, then an insufficient number of x-ray photons have passed through the patient to reach the x-ray film. As a result the film will look whiter leading to potential overcalling of pathology. Similarly, if the film appears too black, then too many photons have resulted in overexposure of the x-ray film. This blackness results in pathology being less conspicuous and may lead to undercalling. The effect of varied exposure on the quality of the final image. 2 Is the film PA or AP Most CXRs are taken in a PA position; that is, the patient stands in front of the x-ray film cassette with their chest against the cassette and their back to the radiographer. The x-ray beam passes through the patient from back to front (i.e. PA) onto the film. The heart and mediastinum are thus closest to the film and therefore not magnified. When an x-ray is taken in an AP position, such as when the patient is unwell in bed, the heart and mediastinum are distant from the cassette and are therefore subject to x-ray magnification. As a result it is very difficult to make an accurate assessment of the cardiomediastinal contour on an AP film.
3 I The cardiomediastinal contour is significantly magnified on this AP film. This needs to be appreciated and not overcalled. Fundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics On the PA film, taken only an hour later, the mediastinum appears normal. Patient-dependent factors Assessment of patient rotation Identifying patient rotation is important. Patient rotation may result in the normal thoracic anatomy becoming distorted; cardiomediastinal structures, lung parenchyma and the bones and soft tissues may all 3
4 IFundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics A well centred x-ray. Medial ends of clavicles are equidistant from the spinous process. 4 This patient is rotated to the left. Note the spinous process is close to the right clavicle and the left lung is blacker than the right, due to the rotation.
5 appear more, or less, conspicuous. To the uninitiated, failure to appreciate this could easily lead to overcalling pathology. On a high-quality CXR, the medial ends of both clavicles should be equidistant from the spinous process of the vertebral body projected between the clavicles. If this is not the case then the patient is rotated, either to the left or to the right. If there is rotation, the side to which the patient is rotated is assessed by comparing the densities of the two hemi-thoraces. The increase in blackness of one hemi-thorax is always on the side to which the patient is rotated, irrespective of whether the CXR has been taken PA or AP. Assessment of adequacy of inspiratory effort Ensuring the patient has made an adequate inspiratory effort is important in the initial assessment of the CXR. Assessment of inspiratory adequacy is a simple process. It is ascertained by counting either the number of visible anterior or posterior ribs. If six complete anterior or ten posterior ribs are visible then the patient has taken an adequate inspiratory effort. Conversely, fewer than six anterior ribs implies a poor inspiratory effort and more than six anterior ribs implies hyper-expanded lungs. I Fundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics Six complete anterior ribs (and ten posterior ribs) are clearly visible. 5
6 IFundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics An example of poor inspiratory effort. Only four complete anterior ribs are visible. This results in several spurious findings: cardiomegaly, a mass at the aortic arch and patchy opacification in both lower zones. 6 Same patient following an adequate inspiratory effort. The CXR now appears normal.
7 If a poor inspiratory effort is made or if the CXR is taken in expiration, then several potentially spurious findings can result: apparent cardiomegaly apparent hilar abnormalities apparent mediastinal contour abnormalities the lung parenchyma tends to appear of increased density, i.e. white lung. Needless to say any of these factors can lead to CXR misinterpretation. Review of important anatomy Heart and mediastinum Assessment of heart size The cardiothoracic ratio should be less than 0.5. i.e. A/B < 0.5. A cardiothoracic ratio of greater than 0.5 (in a good quality film) suggests cardiomegaly. I Fundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics 7
8 IFundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics Assessment of cardiomediastinal contour Right side: SVC RA Anterior aspect: RV Cardiac apex: LV Left side: LV Left atrial appendage Pulmonary trunk Aortic arch. 8
9 Assessment of hilar regions Both hilar should be concave. This results from the superior pulmonary vein crossing the lower lobe pulmonary artery. The point of intersection is known as the hilar point (HP). Both hilar should be of similar density. The left hilum is usually superior to the right by up to 1 cm. I Fundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics Assessment of the trachea The trachea is placed usually just to the right of the midline, but can be pathologically pushed or pulled to either side, providing indirect support for an underlying abnormality. The right wall of the trachea should be clearly seen as the so-called right para-tracheal stripe. 9
10 IFundamentals of CXR interpretation the basics The para-tracheal stripe is visible by virtue of the silhouette sign: air within the tracheal lumen and adjacent right lung apex outline the softtissue-density tracheal wall. Loss or thickening of the para-tracheal stripe intimates adjacent pathology. The trachea is shown in its normal position, just to the right of centre. The right para-tracheal stripe is clearly seen. Evaluation of mediastinal compartments It is useful to consider the contents of the mediastinum as belonging to three compartments: Anterior mediastinum: anterior to the pericardium and trachea. Middle mediastinum: between the anterior and posterior mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum: posterior to the pericardial surface. 10
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
X-Rays. Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM
 X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai
 Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Disclosure. Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I
 Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma Surgery
Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma Surgery
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Approach to CXR. Terminology. 1.Identification. Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow. Correct patient Correct date and time Correct examination
 Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
The External Anatomy of the Lungs. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
Interpretation of the chest radiograph Elizabeth Puddy MB ChB FCARCSI Catherine Hill MB ChB MRCP FRCR
 Interpretation of the chest radiograph Elizabeth Puddy MB ChB FCARCSI Catherine Hill MB ChB MRCP FRCR The traditional technique used in the acquisition and development of a chest radiograph uses methods
Interpretation of the chest radiograph Elizabeth Puddy MB ChB FCARCSI Catherine Hill MB ChB MRCP FRCR The traditional technique used in the acquisition and development of a chest radiograph uses methods
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Cardiac Radiography. Jared D. Christensen, M.D.
 Cardiac Radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Cardiac radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Overview Basic Concepts Technique Normal anatomy Cases Technique 3 Standard Views Posterior-Anterior (PA) Anterior-Posterior
Cardiac Radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Cardiac radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Overview Basic Concepts Technique Normal anatomy Cases Technique 3 Standard Views Posterior-Anterior (PA) Anterior-Posterior
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shades of Gray Interpretation of Perioperative Imaging
 Stanford Hospital and Clinics DEPARTMENT OF CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY-THORACIC AORTIC SURGERY UNIT FALK CARDIOVASCULAR RESEARCH CENTER STANFORD, CALIFORNIA 94305-5407 MICHAEL SHEEHAN, MSN, RNFA, NPC TELEPHONE
Stanford Hospital and Clinics DEPARTMENT OF CARDIOTHORACIC SURGERY-THORACIC AORTIC SURGERY UNIT FALK CARDIOVASCULAR RESEARCH CENTER STANFORD, CALIFORNIA 94305-5407 MICHAEL SHEEHAN, MSN, RNFA, NPC TELEPHONE
CT Chest. Verification of an opacity seen on the straight chest X ray
 CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017
 CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017 1. Sample x-rays 2. Basic chest x-ray interpretation skills 3. Chest x-ray
CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017 1. Sample x-rays 2. Basic chest x-ray interpretation skills 3. Chest x-ray
ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA. Dr Oluwadiya KS
 ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA Dr Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Introduction The thoracic cavity is divided mainly into: Right pleural cavity Mediastinum Left Pleural cavity Pleural cavity The pleural
ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA Dr Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Introduction The thoracic cavity is divided mainly into: Right pleural cavity Mediastinum Left Pleural cavity Pleural cavity The pleural
Signs in Chest Radiology
 Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
TIPS AND PITFALLS IN PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION
 TIPS AND PITFALLS IN PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION Dr Philip Touska MBBS, BMedSci(Hons), MRCS, DO-HNS, FRCR Radiology Fellow Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals LEARNING OBJECTIVES Where do we go wrong? Common pitfalls
TIPS AND PITFALLS IN PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION Dr Philip Touska MBBS, BMedSci(Hons), MRCS, DO-HNS, FRCR Radiology Fellow Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals LEARNING OBJECTIVES Where do we go wrong? Common pitfalls
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Chest X-Ray in Clinical Practice
 Chest X-Ray in Clinical Practice Rita Joarder Neil Crundwell Editors Chest X-Ray in Clinical Practice 123 Editors Dr. Rita Joarder Conquest Hospital The Ridge St. Leonards-On-Sea East Sussex United Kingdom
Chest X-Ray in Clinical Practice Rita Joarder Neil Crundwell Editors Chest X-Ray in Clinical Practice 123 Editors Dr. Rita Joarder Conquest Hospital The Ridge St. Leonards-On-Sea East Sussex United Kingdom
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum. Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes
 Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity.
 Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
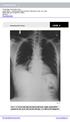 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th & 12 th Eds.)
 PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
X-rays. Dr Will Dooley
 X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Lab #3. Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Jumana Jihad. Ammar Ramadan. 0 P a g e
 Lab #3 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Jumana Jihad Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Last anatomy lab: Lungs and structure on the mediastinal surfs: 1-the right lung: How do we know it s the right lung??? -the 3 lobes
Lab #3 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Jumana Jihad Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Last anatomy lab: Lungs and structure on the mediastinal surfs: 1-the right lung: How do we know it s the right lung??? -the 3 lobes
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Lines and tubes. 1 Nasogastric tubes Endotracheal tubes Central lines Permanent pacemakers Chest drains...
 Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Sectional Anatomy Quiz II
 Sectional Anatomy II Rashid Hashmi Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales, Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 3 Aug 2017
Sectional Anatomy II Rashid Hashmi Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales, Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 3 Aug 2017
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Anterior Mediastinal Masses: The 4 T s
 May 2001 Anterior Mediastinal Masses: The 4 T s Rachel Van Sambeek, Harvard Medical School, Year III 1 Mediastinal Compartments 3 arbitrary divisions that do not correlate with anatomic planes: Anterior
May 2001 Anterior Mediastinal Masses: The 4 T s Rachel Van Sambeek, Harvard Medical School, Year III 1 Mediastinal Compartments 3 arbitrary divisions that do not correlate with anatomic planes: Anterior
Imaging of Respiratory Disorders: M2 Pathology correlated with Radiology
 Imaging of Respiratory Disorders: M2 Pathology correlated with Radiology by (c) Dr Goh Poh Sun MBBS(Melb), FRCR(UK), FAMS(Singapore), MHPE(Maastricht) Senior Consultant Radiologist and Associate Professor
Imaging of Respiratory Disorders: M2 Pathology correlated with Radiology by (c) Dr Goh Poh Sun MBBS(Melb), FRCR(UK), FAMS(Singapore), MHPE(Maastricht) Senior Consultant Radiologist and Associate Professor
Objectives. What is a Chest X Ray? CXR Workshop. Definition (diagnostic tool/internal PE) Types. Cost
 Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Radiology of the respiratory disease
 Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
PULMONARY COLLAPSE Whole lung collapse: There is complete opacity of the L hemi-thorax. The mediastinum is invisible and displaced into
 1 PULMONARY COLLAPSE: A cause of opacity on chest X-ray but there are several features to distinguish it from alveolar shadowing or interstitial lung disease. The loss of lung volume may affect the position
1 PULMONARY COLLAPSE: A cause of opacity on chest X-ray but there are several features to distinguish it from alveolar shadowing or interstitial lung disease. The loss of lung volume may affect the position
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results
 AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
Inter InterpretIng Chest X-rays
 Stephen Ellis Interpreting Chest X-Rays Interpreting Chest X-Rays Stephen Ellis Consultant Thoracic Radiologist St Bartholomew s Hospital and The London Chest Hospital, London, UK Scion Publishing Ltd,
Stephen Ellis Interpreting Chest X-Rays Interpreting Chest X-Rays Stephen Ellis Consultant Thoracic Radiologist St Bartholomew s Hospital and The London Chest Hospital, London, UK Scion Publishing Ltd,
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
Anatomy Lecture 8. In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy:
 Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
11.1 The Aortic Arch General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta
 456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Theme 30. Structure, topography and function of the lungs and pleura. Mediastinum and its contents. X -ray films digestive and respiratory systems.
 Theme 30. Structure, topography and function of the lungs and pleura. Mediastinum and its contents. X -ray films digestive and respiratory systems. STRUCTURE, TOPOGRAPHY AND FUNCTІON OF LUNGS AND PLEURA.
Theme 30. Structure, topography and function of the lungs and pleura. Mediastinum and its contents. X -ray films digestive and respiratory systems. STRUCTURE, TOPOGRAPHY AND FUNCTІON OF LUNGS AND PLEURA.
A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology. Outline. Technique. Technique. Principles of interpretation. Case Examples. Optimize image quality
 A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology Kacie Schmitt Felber, DVM, DACVIM Cardiology Thursday, May 17 th, 2018 Mid Atlantic States Veterinary Clinic Conference Outline Technique Principles of interpretation
A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology Kacie Schmitt Felber, DVM, DACVIM Cardiology Thursday, May 17 th, 2018 Mid Atlantic States Veterinary Clinic Conference Outline Technique Principles of interpretation
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
Bony Thorax. Anatomy and Procedures of the Bony Thorax Edited by M. Rhodes
 Bony Thorax Anatomy and Procedures of the Bony Thorax 10-526-191 Edited by M. Rhodes Anatomy Review Bony Thorax Formed by Sternum 12 pairs of ribs 12 thoracic vertebrae Conical in shape Narrow at top Posterior
Bony Thorax Anatomy and Procedures of the Bony Thorax 10-526-191 Edited by M. Rhodes Anatomy Review Bony Thorax Formed by Sternum 12 pairs of ribs 12 thoracic vertebrae Conical in shape Narrow at top Posterior
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
J Somerville and V Grech. The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jan-Mar; 12(1): 1 8.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p
 Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Penetrating Neck Injuries. Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010
 Penetrating Neck Injuries Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010 CASE PRESENTATION 19 YO M 3 Stab Wounds Right zone I neck SW 2 SW anterior abdomen Left epigastrium anterior axillary line
Penetrating Neck Injuries Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010 CASE PRESENTATION 19 YO M 3 Stab Wounds Right zone I neck SW 2 SW anterior abdomen Left epigastrium anterior axillary line
Mediastinal lines, stripes and interfaces on PA chest radiograph with CT correlations
 Mediastinal lines, stripes and interfaces on PA chest radiograph with CT correlations Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Bystrická,
Mediastinal lines, stripes and interfaces on PA chest radiograph with CT correlations Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Bystrická,
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
REVIEW. Radiographic Features of Mediastinal Anatomy* RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES OF MEDIAmNAl ANATOMY 609
 REVIEW Radiographic Features of Mediastinal Anatomy* Eric A.Hyson, M.D., andcarl E. Ravin, M.D., F.C.C.P. The increasing use of higher kilovoltage techniques and shorter exposure times in chest radiography
REVIEW Radiographic Features of Mediastinal Anatomy* Eric A.Hyson, M.D., andcarl E. Ravin, M.D., F.C.C.P. The increasing use of higher kilovoltage techniques and shorter exposure times in chest radiography
THE DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
 Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Case N 1. Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds. Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania
 Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Atlases for Organs at Risk (OARs) in Thoracic Radiation Therapy
 Atlases for Organs at Risk (OARs) in Thoracic Radiation Therapy Feng-Ming (Spring) Kong MD PhD Leslie Quint MD Mitchell Machtay MD Jeffrey Bradley MD 1 Outline of Content Atlas for lung, esophagus, and
Atlases for Organs at Risk (OARs) in Thoracic Radiation Therapy Feng-Ming (Spring) Kong MD PhD Leslie Quint MD Mitchell Machtay MD Jeffrey Bradley MD 1 Outline of Content Atlas for lung, esophagus, and
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP. October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18
 Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized
 Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
SERRATUS ANTERIOR MUSCLE
 AND THE SERRATUS ANTERIOR MUSCLE James D. Collins, MD, Richard K. J. Los Angeles, California Brown, MD, and Poonam Batra, MD Twenty-seven patients with a history of asbestos exposure were reviewed at the
AND THE SERRATUS ANTERIOR MUSCLE James D. Collins, MD, Richard K. J. Los Angeles, California Brown, MD, and Poonam Batra, MD Twenty-seven patients with a history of asbestos exposure were reviewed at the
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer lymph node map Lymph node stations Imaging CT
 Review of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lymph Node Classification System Localization of Lymph Node Stations on CT Imaging Hamza Jawad, MBBS a, Arlene Sirajuddin, MD b, Jonathan
Review of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lymph Node Classification System Localization of Lymph Node Stations on CT Imaging Hamza Jawad, MBBS a, Arlene Sirajuddin, MD b, Jonathan
Sheet lab 5 Anatomy: CT Scans
 Sheet lab 5 Anatomy: CT Scans In the orientation we see the picture from downward to upward. The first picture is a CT scan at the level of the heart. Left border of the heart is the left ventricle and
Sheet lab 5 Anatomy: CT Scans In the orientation we see the picture from downward to upward. The first picture is a CT scan at the level of the heart. Left border of the heart is the left ventricle and
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
