Introduction: Alprazolam is a triazolobenzodiazepine used in panic disorders and other anxiety
|
|
|
- Reynold Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /medarh Med Arh Dec; 67(6): Received: June 18th 2013 Accepted: October 15th 2013 Published online: 28/12/2013 Published print: 12/2013 ORIGINAL PAPER Chromosomal and Nuclear Alterations in Root Tip Cells of Allium Cepa L. Induced by Alprazolam Hilada Nefic 1, Jasmin Musanovic 2, Azra Metovic 2, Kemajl Kurteshi 3 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 1 Department for Biology and Human Genetics, Medical Faculty, University of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 2 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Prishtina 3 Introduction: Alprazolam is a triazolobenzodiazepine used in panic disorders and other anxiety states. Target organ of Alprazolam is CNS, causing depression of respiration and consciousness. Aim: This study aimed to estimate the genotoxic potential of Alprazolam using Allium cepa test. Methods: Allium cepa is one of the most suitable plants for detecting different types of xenobiotics. The test enables the assessment of different genetic endpoints making possible damage to the DNA of humans to be predicted. Results: Alprazolam induced chromosomal (anaphase bridges, breaks, lagging and stickiness, abnormal spiralisation, multipolarity and polyploidy) and cytological aberrations, especially nuclear alterations (nuclear buds, fragmented nucleus and apoptotic bodies, cells without nucleus, binucleated and micronucleated cells), morphological alterations in shape and size of cells, spindle disturbance and polar deviation in root tip meristem cells of Allium cepa at all tested concentrations. Alprazolam also caused significant inhibition of mitotic index in these cells. Conclusion: These changes in cells are indicators of genotoxic potential of Alprazolam suggesting a need for further in vitro studies on animal and human lymphocytes as well as in vivo studies. Key words: Allium cepa test, Alprazolam, Genotoxicity, Apoptotic bodies Corresponding author: Prof. Hilada Nefic, PhD. Department of Biology of the Faculty of Science in Sarajevo, Zmaja od Bosne 33-35, Sarajevo 71000, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Phone: (0) ; Fax: (0) addresses: hnefic@pmf.unsa.ba; hnefic@gmail.com 1. INTRODUCTION The root tips several of plant species have been used for the study of induced chromosomal aberrations (CAs) and presence of micronuclei (MNi). Root tips of different Allium species are used the most frequent as experimental material. The plants possess some advantages over other organisms in certain circumstances. The plants usually have the large chromosomes and the low chromosome number. The root meristem contains a high proportion of cells in mitosis (1-3). Plant systems had a major part in early investigations of the genetic changes caused by mutagenic chemicals and radiation. One of the most suitable plants for detecting different types of xenobiotics is Allium cepa L. The first modification of the Allium cepa test for environmental monitoring was introduced by Fiskesjö (4, 5). The chromosome assays on plants are rapid and inexpensive and do not require elaborate laboratory facilities and a wide range of genetic endpoints is available. The chromosomes of plants and animals are morphologically similar, and appear to respond to treatment with mutagens in a similar way to those of mammals and other eukaryotes. There are some important limitations as well, such as the longer life cycle of most plants than bacteria, yeast or Drosophila and some biochemical differences between plants and mammals. There are also fundamental differences in structure between plant and mammalian cells. The growing root tips of the onion, Allium cepa provide a readily available source of material for studying the damaging effects of chemicals on chromosomes. This plant is useful for evaluating DNA damages that express such as CAs, disturbances in the mitotic cycle, nuclear alterations (NAs) and presence of MNi in meristem cells. The decrease in the mitotic index (MI) of Allium cepa meristem cells can be considered as a reliable method to determine the presence of cytotoxic agents in the environment. CAs are including changes in either chromosomal structure or in the total number of chromosomes. Structural chromosomal alterations may be induced by DNA breaks, inhibition of DNA synthesis and replication of altered DNA. The CAs, such as chromosome bridges and breaks, are indicators of a clastogenic action. The numerical CAs (aneuploidy and polyploidy) are consequences of abnormal segregation of chromosomes (chromosome losses, delays, adherence, multipolarity and C-metaphases) which can occur either spontaneously or by the action of aneugenic agents. Chromosome without telomeres become sticky and may fuse with other broken chromosome ends. The result of these chromosomal rearrangements are acentric fragments, dicentric bridges that can be observed in mitotic cells of the first cell cycle after mutagenic treatment or MNi in the interphase cell in the next cell cycle. 388 Med Arh Dec; 67(6): ORIGINAL PAPER
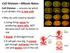
2 The Allium cepa test is used for screening and monitoring environmental chemicals with mutagenic and carcinogenic potential (6-10). Alprazolam is a newer benzodiazepine that is being used more commonly in overdose. Overdose in adults frequently involves co-ingestion of other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, which act synergistically to increase toxicity. Alprazolam is assumed to be capable of causing fatal harm and an increased risk if congenital abnormalities when administered to a pregnant woman during the first trimester. The aim of this study was to evaluate the genotoxic potential of benzodiazepine drug Alprazolam. For estimate the genotoxicity of this benzodiazepine and for assessment of risks from exposure to Alprazolam we used the Allium cepa test. 2. MATERIAL AND METHODS Alprazolam (Xanax, Helex, Alpronax) is a triazolobenzodiazepine used in panic disorder and other anxiety states. Alprazolam, like other benzodiazepines, binds to specific sites on the GABA A (gamma-amino-butyric acid) receptor. The chemical name of Alprazolam is 8-chloro-1-methyl-6- phenyl-4h-s-triazolo [4,3-a] [1,4] benzodiazepine. The molecular formula is C 17 H 13 ClN 4 which corresponds to a molecular weight of The root tip cells of onion were used to test the potentially genotoxic effects of Alprazolam. The test was carried out according to Fiskesjö protocol (4, 11-12) with some modifications. Common onion (Allium cepa L.) has eight pairs of relatively large chromosomes (2n = 16) that allows for the easy detection of CAs. The plant material is available all the year round, it is inexpensive and easily to grow and handled. The size of chromosomes makes Allium cepa tips as favourable material for the study of the effects of chemicals on frequency of CAs which are biomarkers of damage of genetic material. The root tip cells have a very low spontaneous aberration frequency and a stable chromosome number. To perform this test we used onion bulbs that cultivated without the application of herbicides or fungicides. Healthy young onion bulbs that were the same size were used in the test. The outer scales are removed from bulbs and they scraped at the root to promote the emergence of new roots. Onion bulbs then have been grown in water at room temperature. The bulbs should remain in the dark. When the newly emerged roots are 2 cm in length, they are ready for treatment with the test drug. Adequate root growth should be obtained in 3-4 days. The bulbs should be transferred to petri dish with 30 ml of Alprazolam solution appropriate concentration for the treatments. We use group of 6 bulbs of Allium cepa for each treatment. Roots of Allium cepa have been treated with a series of concentration 100, 150, 200, 250 and 500μg/ml for 24h. Freshly prepared solutions of Alprazolam should be used. Treatments took place in the dark. A negative control has been treated with distilled water. After 24h, the roots of each bulb were extracted and fixed in freshly prepared and cool mixture (4-10 C) containing 3 parts of methanol and 1 part of glacial acetic acid (3:1, v/v) for 24h. Roots can be stored in fixative for several days or weeks. For preparation root tip chromosome slides acetorcein squash technique has been used to analyse MI, cytotoxic effects and CAs. The root tips of bulbs hydrolysed in 1N hydrochloric acid (HCl) at 60 ºC for 4-5 min. The cell wall has to dissolve by hydrolysis with acid. From HCl the roots are transferred to distilled water and left for a few minutes. The roots then were transferred on clean slide. Three roots tips were used for each slide. On the slide, tips were crushed in drop of 2% acetorcein (Gurr Orcein, BDH Chemicals Ltd., Poole, England) with the flat end of metal rod (taper) and squashed under a cover slip. The pressure was applied under several thickness of blotting filter paper during sideways movements of cover slip must be avoided. The two slides prepared for each of bulbs in each experimental group (concentration of the test drug). A thousand cell for MI and a hundred metaphase cells (except for concentration of 500μg/ml due to reduction in MI) for CAs were counted for each bulb per treatment group. Twelve slides were prepared for each concentration of Alprazolam and the control. For cytogenetic examination of mitotic cells was used a microscope (Jenaval) at1000x magnification. The Mitotic Index (MI) represents the total number of dividing cells in relation to the number of analysed cells in cell cycle. A minimum of 1,000 cells were scored for MI and expressed as a percentage of total number of examined cells undergoing mitosis. The frequency of CAs was expressed as the number of aberrant cells per 100 cells examined. A hundred metaphase cells were scored for each bulb in experimental group and the number of aberrant cells in each experimental group is compared with the values from the control group. The Allium cepa test enables to estimate CAs in all phases of the cell cycle. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of the means for MI and frequency of aberrant cells. For statistical analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used. Relationships between different concentrations of Alprazolam and MI or frequency of aberrant cells were investigated using Pearson s correlation analysis and/or Spearman s rank correlation. Analyses were done at P<0.05 and 95% confidence level using MedCalc Version statistical software package. 3. RESULTS The results this study showed concentration-dependent reduction in MI of Allium cepa root tip meristem cells treated with different concentrations of Alprazolam for 24h (Table 1). This difference was significant in Pearson s correlation analysis where correlation coefficient (r) was with significance level P< and 95% confidence interval (CI) for r to The similar results we obtained after using Spearman s rank correlation. Spearman s coefficient of rank correlation (rho) was with significance level P< and 95% CI for rho to Based on the statistical analysis using ANOVA test we observed inhibition of MI in meristem cells that was statistically significant at all tested concentrations (P<0.05) but not significant at 150μg/ml when compared with the control. Med Arh Dec; 67(6): ORIGINAL PAPER 389
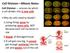
3 Concentration Number of Phase index MI (%) of Alprazolam dividing cells P PM M A T Control (0) 86.78± ± ± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 61.50±24.19* 6.2±2.42* 16.67± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 63.00± ± ± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 50.20±20.62* 5.0±2.06* 13.00± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 40.00±1.83* 4.0±0.18* 10.25± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 8.62±20.23* 1.57±2.02* 6.67± ± ± ± ±1.73 Legend: P: prophase, PM: prometaphase, M: metaphase, A: anaphase, T: telophase. Table 1. Mitotic index (MI) of Allium cepa root tip cells exposed to different concentrations of Alprazolam (mean ± SD) observed at cell cycle after the treatments with Alprazolam were different NAs (nuclear buds, ghost cells cells without nucleus, fragmented nucleus and apoptotic bodies), binucleated cells and micronucleus formation (Table 3). MNi were present in the different phases of cell cycle in root meristem cells of Allium cepa. The spindle disturbance and polar deviation can lead to abnormal kinetics of chromosome and prolonged prophase. Figure 2 shows nuclear abnormalities that can be found in Allium cepa meristem cells exposed to Alprazolam. Statistically positive Concentration of Alprazolam Chromosomal aberrations (CAs) The CAs in Allium cepa root tip meristem cells after 24h exposure to Alprazolam were anaphase bridges, breaks, chromosome lagging and stickiness, abnormal spiralisation of chromosomes, multipolarity and polyploidy (Table 2). Statistically significant increased number of CAs in the meristem cells with increasing concentration of Alprazolam was observed in Spearman s rank correlation analysis (rho=0.524, P= and 95% CI: to 0.741). Statistically significant higher number of CAs were at all tested concentrations (P<0.05) except at 100μg/ml in comparison with the control when analysed with the ANOVA test. In this analysis we excluded cells treated with Alprazolam of 500μg/ml because a little number of dividing cells at this concentration. Figure 1 shows CAs at all phases of cell cycle that can be observed by the Allium cepa test. Cytological aberrations Bridges Breaks Lagging Stickiness Polyploidy Abnormal spiralisation Multipolarity Abnormal kinetics Total number of aberrant cells Control (0) 0.00± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 1.00± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 0.75± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±4.35* 200μg/ml 3.60± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±17.40* 250μg/ml 6.00± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±5.06* 500μg/ml 0.00± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±7.51 Table 2. Chromosome aberration assay in Allium root cells exposed to Alprazolam (100, 150, 200, 250 and 500μg/ml for 24h) Concentration of Alprazolam Cytological aberrations Nuclear buds Cells without nucleus Morphological alterations of cell Cells with apoptotic bodies BNC MNC Total number of aberrant cells Control (0) 0.00± ± ± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 1.33± ± ± ± ± ± ± μg/ml 1.75± ± ± ± ± ± ±4.50* 200μg/ml 3.00± ± ± ± ± ± ±6.35* 250μg/ml 2.75± ± ± ± ± ± ±3.86* 500μg/ml 0.00± ± ± ± ± ± ±22.94* Legend: MNC: micronucleated cells, BNC: binucleated cells. Table 3. Cytological effects of different concentrations of Alprazolam on root tip cells of Allium cepa (mean ± SD) Figure 1. Photomicrographs of CAs induced by Alprazolam in root tip cells of Allium cepa; (a) prolonged prophase and abnormal kinetics; (b) and (c) chromosome laggards and spindle disturbance at metaphase; (d) disturbed anaphase in a polyploid cell; (e) anaphase with chromosome laggards; (f) multipolar anaphase and spindle disturbance (magnification: 1000x). correlations were found between concentrations Alprazolam and NAs after using Pearson s correlation analysis (r=0.7866, P< and 95% CI: to ) and Spearman s rank correlation (rho=0.811, P< and 95% CI: to 0.905). These results were statistically significant except for concentration 100μg/ml when analysed with the ANOVA test (P<0.05) in comparison with the control. 4. DISCUSSION The Allium cepa test is important test in vivo, where the roots grow in direct contact with the substance of interest enabling possible damage to DNA of humans to be predicted. In this study, test enables the assessment of different genetic endpoints which occur as a result from exposure to Alprazolam. Alprazolam caused significant inhibition of MI in Allium cepa meristem cells and 390 Med Arh Dec; 67(6): ORIGINAL PAPER
4 induced CAs, nuclear abnormalities and micronucleated cells (MNCs). The decrease in the MI as the concentration of Alprazolam increased. The changes in MI of Allium cepa cells are indicators of cytotoxic and genototoxic potential and mitodepressive activity of Alprazolam. The number of CAs increased as concentration of Alparzolam increased. The analysis of the different CA types, in all phases of the cell cycle, enables a better investigation of the effects of Alprazolam, concerning its clastogenic, aneugenic and tubergenic effects. Breakages may occur and subsequent inhibition of repair mechanisms may lead to base mismatch, mutation and CAs such as fragment chromosomes and DNA breaks (12-14). Examination of anaphase chromosomes for fragments and bridges is a useful for obtaining information on clastogenic activity. The presence of dicentric chromosomes and unequally exchanged chromatids undergoing translocation has been reported to be responsible for chromosomal bridges at anaphase. The bridges, breaks, lagging and multipolar anaphase chromosomes were observed at all concentrations, except at the highest tested concentration. The results showed that higher concentrations were able to inhibit significantly cell division. Alprazolam cause lethal CAs in Allium cepa at higher concentrations. Stickiness is due to interchromosomal linkages of sub-chromatid strands coupled with excessive formation of nucleoproteins and inappropriate protein-protein interaction. Nuclear abnormalities are characterized by morphological alterations in the interphase nuclei as a result from the exposure to Alprazolam. Aberrations observed at interphase stage of cell cycle were different NAs (nuclear buds, cells without nucleus ghost cells, fragmented nuclei and apoptotic bodies), BNCs and micronucleus formation. Also, we observed alterations in shape Figure 2. Photomicrographs of cytological aberrations in Allium cepa meristem cells exposed to Alprazolam; (a b) cells with fragmented nucleus and apoptotic bodies, morphological alterations in shape and size of cells; (c) extended interphase and telophase cell, dislocation of spindle, stickiness; (d) extended cells, disturbed spindle and cytoplasm destruction; (e) micronucleus in prophase, stickiness; (f) cells with nuclear bud (magnification: 1000x). and size of cells (gigantic and extended cells). The presence of fragmented nuclei and polynuclear cells can indicate a cell death process and this may lead to aneuploidy and then to cell death. The number of cytological aberrations increased with increasing concentration. MNi are formed as a consequence of chromosome breakage (clastogenic agent) or whole chromosomes (aneugenic agent) that were not incorporated to the main nucleus during the cell division cycle (15-16). The frequency of cells with MNi is indicator of the cytogenetic effects of tested chemicals. MNi were observed to be mostly caused by Alprazolam at 500μg/ml suggesting its greater genotoxic and tubergenic effects on Allium cepa when compared with lower concentrations of drug. Inhibition of cytokinesis following telophase is responsible for binucleated cell formation. Long half-life benzodiazepines, such as diazepam or clonazepam, accumulate with repeated doses and clearance is significantly increased with age. Alprazolam is intermediate halflife benzodiazepine and it s the usual starting dose varies between 0.5 and 1 mg per day. Benzodiazepines produce dose-dependent adverse effect and long half-life benzodiazepines use may induce physiological dependence (17). Musanovic et al. (18) reported cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of lower concentrations of Alprazolam against Allium cepa root meristem cells. According to Isbister et al. (19) Alprazolam was significantly more toxic than other benzodiazepines. 5. CONCLUSION In conclusion, the results of this study indicate that benzodiazepine drug Alprazolam induced chromosomal (anaphase bridges, breaks, lagging and stickiness, abnormal spiralisation, multipolarity and polyploidy) and cytological aberrations, especially nuclear alterations (nuclear buds, fragmented nucleus and apoptotic bodies, cells without nucleus, binucleated and micronucleated cells), morphological alterations in shape and size of cells, spindle disturbances and polar deviation in root tip meristem cells of Allium cepa at all tested concentrations. Alprazolam also caused significant inhibition of mitotic index in these cells and almost stopped the cell proliferation at the highest tested concentration. The changes in Allium cepa meristem cells are indicators of genotoxic potential of Alprazolam suggesting a need for safe dose administration of the drug in human medicine and further in vitro studies on animal and human lymphocytes as well as in vivo studies. CONFLICT OF INTEREST: NONE DECLARED REFERENCES 1. Kihlman BA. Root tips of Vicia faba for the study of the induction of chromosomal aberrations. In: Kilbey BJ, Legator M, Nichols W, Ramel C. eds. Handbook of mutagenicity test procedures. Elsevier scientific publishing company, Amsterdam, New York, Oxford, 1977: Grant WF. The present status of higher plant bioassays for detection of environmental mutagens. Mutat Res. 1994; 310: Leme DM, Marin-Morales MA. Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: A review on its application. Mutat Res. 2009; 682(1): Fiskesjö G. The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas. 1985; 102: Trushin MV, Ratushnyak AY, Arkharova IA, Ratushnyak AA. Genetic Alterations Revealed in Allium cepa-test System under the Action of Some Xenobiotics. World Applied Sciences Journal Med Arh Dec; 67(6): ORIGINAL PAPER 391
5 2013; 22(3): Sofradžija A, Hadžiselimovic R, Maslic E. Genotoksicnost pesticida. Svjetlost, Sarajevo, Knasmuller S, Gottmann E, Steinkellner H, Fomin A, Pickl C, Paschke A, God R, Kundi M. Detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metals contaminted soils with plant bioassays. Mutat Res. 1998; 420: Ma TH. The role of plant systems for the detection of environmental mutagens and carcinogens. Mutat Res. 1999; 437: Cabaravdic M. Induction of Chromosome Aberrations in the Allium cepa Test System Caused by the Exposure of Cells to benzo(a)pyrene. Med Arh. 2010; 64(4): Sharma S, Vig AP. Genotoxicity of Atrazine, Avenoxan, Diuron and Quizalofop- P-ethyl Herbicides using the Allium cepa Root Chromosomal Aberration Assay. Terrestrial and Aquatic Environmental Toxicology 2012; 6(2): Fiskesjö G. A 2-3 day plant test for toxicity assessment by measuring the mean root growth of onions (Allium cepa L.). Environ Toxicol Water Quality. 1993; 8: Fiskesjö G. Allium Test For Screening Chemicals; Evaluation of Cytological Parameters, In: Wang W, Gorsuch JW, Hughes JS (Eds.). Plants for Environmental Studies, Lewis, New York, USA, 1997: Türkoğlu S. Genotoxicity of five food preservatives tested on root tips of Allium cepa L. Mutat Res. 2007; 626: Badr A, Ibrahim AG. Effect of herbicide Glean on mitosis, chromosomes and nucleic acids in Alium cepa and Vicia faba root meristems. Cytol. 1987; 52: Fenech M, Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay, Nature protocols. 2007; 2(5): Leme DM, de Franceschi de Angelis D, Marin-Morales MA. Action mechanisms of petroleum hydrocarbons present in waters impacted by an oil spill on the genetic material of Allium cepa root cells. Aquatic Toxicology. 2008; 88: Yousif WB. Microscopic Studies on the Effect of Alprazolam (Xanax) on the Liver of Mice. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences. 2002; 5(1): Musanovic J, Ramic N, Nefic H, Dzubur A. Chromosome aberration and irregular cell cycle in Allium cepa root cells caused by different concentrations of Alprazolam. International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health. 2013; 5(6): Isbister GK, O Regan L, Sibbritt D, Whyte IM. Alprazolam is relatively more toxic than other benzodiazepines in overdose. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004; 58(1): Med Arh Dec; 67(6): ORIGINAL PAPER
Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion
 Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Available online:
 VOL.3 NO.2September 2014 - ISSN 2233 1859 Southeast Europe Journal of Soft Computing Available online: www.scjournal.com.ba GENOTOXICITY ANALYSIS OF FROMILID AND METHOTREXATE USING ALLIUM TEST Merisa Ćenanović
VOL.3 NO.2September 2014 - ISSN 2233 1859 Southeast Europe Journal of Soft Computing Available online: www.scjournal.com.ba GENOTOXICITY ANALYSIS OF FROMILID AND METHOTREXATE USING ALLIUM TEST Merisa Ćenanović
Chromosome aberration and irregular cell cycle in Allium cepa root cells caused by different concentrations of Alprazolam
 407 Chromosome aberration and irregular cell cycle in Allium cepa root cells caused by different concentrations of Alprazolam Jasmin Musanovic 1*, Nerman Ramic 2, Hilada Nefić 3, Amela Dzubur 4 1 Department
407 Chromosome aberration and irregular cell cycle in Allium cepa root cells caused by different concentrations of Alprazolam Jasmin Musanovic 1*, Nerman Ramic 2, Hilada Nefić 3, Amela Dzubur 4 1 Department
Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE
 ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis
 Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test
 Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION. Cytokinesis. centromere. DNA Replication S-Phase. One Chromosome Two Chromatids. One Chromosome No Chromatids 10.
 MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
Cytogenetic Effects of Fungicide Afugan on the Meristematic Cells of Allium cepa L.
 2003 The Japan Mendel Society Cytologia 68(3): 237 243, 2003 Cytogenetic Effects of Fungicide Afugan on the Meristematic Cells of Allium cepa L. Deniz Yüzbaşıoǧlu* Gazi Üniversitesi, Fen-Edebiyat Fakültesi,
2003 The Japan Mendel Society Cytologia 68(3): 237 243, 2003 Cytogenetic Effects of Fungicide Afugan on the Meristematic Cells of Allium cepa L. Deniz Yüzbaşıoǧlu* Gazi Üniversitesi, Fen-Edebiyat Fakültesi,
LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L.
 South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa
 Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle
 Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: 1. Understand the meaning of mitotic index and duration of stages (phases) 2. Calculate
Mitotic index and Duration of the cell cycle Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: 1. Understand the meaning of mitotic index and duration of stages (phases) 2. Calculate
Genotoxicity of Euphorbia hirta: An Allium cepa Assay
 Molecules 2012, 17, 7782-7791; doi:10.3390/molecules17077782 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Genotoxicity of Euphorbia hirta: An Allium cepa Assay Kwan Yuet
Molecules 2012, 17, 7782-7791; doi:10.3390/molecules17077782 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules Genotoxicity of Euphorbia hirta: An Allium cepa Assay Kwan Yuet
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE
 Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn)
 EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn) Pechlada Rochanabanthit 1 and Peeranuch Jompuk 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, Faculty of Science,
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC GAMMA IRRADIATION ON SHALLOT CHROMOSOMES (Allium ascalonicum Linn) Pechlada Rochanabanthit 1 and Peeranuch Jompuk 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, Faculty of Science,
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
(i) List these events in the correct order, starting with D.... (1)... (1)... (1)
 Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
Q1. (a) Boxes A to E show some of the events of the cell cycle. A Chromatids seperate B Nuclear envelopes disappears C Cytoplasm divides D Chromosomes condense and become visible E Chromosomes on the equator
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Lecture -2- Environmental Biotechnology
 Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m43135 1 1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis * Daniel Williamson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 The cell cycle and
OpenStax-CNX module: m43135 1 1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis * Daniel Williamson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 The cell cycle and
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS
 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical.
 Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA MUNGO (L.) HEPPER
 EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
Comparative effects of colchicine, 8-hydroxyquinoline and paradichlorobenzene on arm ratio of mitotic chromosomes of Allium cepa L.
 International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell)
 Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
Corresponding Readings: Lab title: Cell Division author: Dr. Ruth Dahlquist-Willard (modified by D. Bell) Campbell Ch. 8 BIOL-100L Safety Information: We will be using laboratory glassware such as microscope
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. A B C D ... (1) ... (1)
 1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
1. The diagram shows four stages in mitosis. Only one pair of homologous chromosomes is shown. X A B C D (a) Place stages A, B, C and D in the correct order.... (b) Name the structures labelled X.... Describe
Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1
 Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
 Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
Chapter 10 Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Chromosomes Organisms grow by dividing of cells Binary Fission form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring (Bacteria) Eukaryotes have two
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Mutagenic effects of glyphosate (IPA) herbicides using the Vicia faba L. Root tip
 World Journal of Biology and Biological Sciences Vol. 2 (2), pp. 044-048, March 2014 Available online at http://wsrjournals.org/journal/wjbbs ISSN 2331-1894 2014 World Science Research Journals Full Length
World Journal of Biology and Biological Sciences Vol. 2 (2), pp. 044-048, March 2014 Available online at http://wsrjournals.org/journal/wjbbs ISSN 2331-1894 2014 World Science Research Journals Full Length
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab
 Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab Names: Period # Reproduction of most cells in plants and animals uses the type of cell division called Mitosis. In this activity, you will study mitosis in plant cells by examining
Mitosis in Plant Cells Lab Names: Period # Reproduction of most cells in plants and animals uses the type of cell division called Mitosis. In this activity, you will study mitosis in plant cells by examining
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division
 2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
2.1 The Importance of Cell Division Functions of cell division Growth Repair Reproduction Growth All organisms begin as a single cell. Cell divisions will increase as an organism s size increases. There
Genotoxic evaluations of Allium cepa L. using different concentrations of synthesized butenolide
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 213, 3(4):8-12 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Genotoxic evaluations of Allium cepa L. using different
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 213, 3(4):8-12 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY Genotoxic evaluations of Allium cepa L. using different
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 Genetics and Information Transfer Big Idea 3 INVESTIGATION 7 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS How do eukaryotic cells divide to produce genetically identical cells or to produce gametes with half the
Genetics and Information Transfer Big Idea 3 INVESTIGATION 7 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS How do eukaryotic cells divide to produce genetically identical cells or to produce gametes with half the
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Genotoxic Effects of Lead Acetate Employing Allium sativum Root Chromosomal Aberration Assay
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com Research Article Genotoxic Effects of Lead Acetate Employing Allium sativum Root Chromosomal Aberration
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com Research Article Genotoxic Effects of Lead Acetate Employing Allium sativum Root Chromosomal Aberration
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
The Cell Cycle. Materials 2 pipe cleaners of one color and 2 of another color Drawing paper
 The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Objective: Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction and normal functions. APK: Why do
Cytological Effects of 5- Amino Uracil on Allium cepa L. roots
 2017; 5(1): 96-100 ISSN 2320-3862 JMPS 2017; 5(1): 96-100 2017 JMPS Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 16-12-2016 Saswati Bhattacharya Department of Botany, Dr A.P.J Abdul Kalam Govt. College, New Town, Rajarhat,
2017; 5(1): 96-100 ISSN 2320-3862 JMPS 2017; 5(1): 96-100 2017 JMPS Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 16-12-2016 Saswati Bhattacharya Department of Botany, Dr A.P.J Abdul Kalam Govt. College, New Town, Rajarhat,
Ploidy and Human Cell Types. Cell Cycle and Mitosis. DNA and Chromosomes. Where It All Began 11/19/2014. Chapter 12 Pg
 Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes
 Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
_??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: , Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler
 _??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: 647-652, 1987 Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler Accepted July, 28, 1986 R. K. Somashekar Department
_??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: 647-652, 1987 Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler Accepted July, 28, 1986 R. K. Somashekar Department
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division
 Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
Science 10-Biology Activity 12 Experiment on Observing Cell Division Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe and sketch plant cells and animal cells in various
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation
 B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
Guided Notes: Chromosomes. What type of macromolecule is DNA? DNA stands for: DNA is made up of repeating (the monomer of nucleic acids!
 Guided Notes: Chromosomes The Structure of DNA What type of macromolecule is DNA? DNA stands for: DNA is made up of repeating (the monomer of nucleic acids!) 1) Where is it found (use figures 1 and 2 to
Guided Notes: Chromosomes The Structure of DNA What type of macromolecule is DNA? DNA stands for: DNA is made up of repeating (the monomer of nucleic acids!) 1) Where is it found (use figures 1 and 2 to
The Cell Cycle Guided Reading
 Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
Name Date Period 1. List three things that multi-celled organisms need cell division for. a. b. c. 2. Why do single-celled organisms need to go through cell division? 3. What is the cell cycle? 4. True
LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project
 LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project I. Researching Mitosis and Cellular Function For this research project, your team should choose some aspect of mitosis,
LABORATORY INQUIRY Part 2 Practicing Procedures and Developing Your Research Project I. Researching Mitosis and Cellular Function For this research project, your team should choose some aspect of mitosis,
Genotoxic Effects of Avenoxan on Allium cepa L. and Allium sativum L.
 CARYOLOGIA Vol. 59, no. 3: 241-247, 2006 Genotoxic Effects of Avenoxan on Allium cepa L. Allium sativum L. Tartar Gul, Fisun Kaymak 1* Fulya D. Gokalp Muranli 2 1 Trakya University, Faculty of Arts Sciences,
CARYOLOGIA Vol. 59, no. 3: 241-247, 2006 Genotoxic Effects of Avenoxan on Allium cepa L. Allium sativum L. Tartar Gul, Fisun Kaymak 1* Fulya D. Gokalp Muranli 2 1 Trakya University, Faculty of Arts Sciences,
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials. What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think.
 Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Cell Division Questions. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Cell Division Questions Mitosis and Meiosis 1 10 Do not write outside the box 5 Figure 3 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 3 E E e e F F f f 5 (a)
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Mitosis. Cell Cycle. interphase. Five Phases. prophase. metaphase
 Mitosis Have you ever wondered how living things grow? Living things are made of cells. To grow bigger, they need more cells. Where do the new cells come from? Each cell divides, turning into two cells.
Mitosis Have you ever wondered how living things grow? Living things are made of cells. To grow bigger, they need more cells. Where do the new cells come from? Each cell divides, turning into two cells.
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
Cell Division. Introduction. Chromatin, Chromosomes, and Chromatids, Oh My! The Cell Cycle
 Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Introduction Cell Division Just like a butterfly passes through different phases (such as caterpillar, chrysalis, and adult butterfly) there are a series of phases in a cell's life as it gets ready to
Effect of Nano-Silver on Cell Division and Mitotic Chromosomes: A Prefatory Siren
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nanotechnology Volume 2 Number 2 Effect of Nano-Silver on Cell Division and Mitotic Chromosomes: A Prefatory Siren K Babu, M Deepa, S Shankar, S Rai Citation K Babu, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nanotechnology Volume 2 Number 2 Effect of Nano-Silver on Cell Division and Mitotic Chromosomes: A Prefatory Siren K Babu, M Deepa, S Shankar, S Rai Citation K Babu, M
Cytotoxicity of two common pesticides using Allium cepa (onion) Assay
 CURRENT STUDIES IN COMPARATIVE EDUCATION, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, 2016, PP. 211-221 Cytotoxicity of two common pesticides using Allium cepa (onion) Assay JAMES, O. E. & ADELEKE, M.
CURRENT STUDIES IN COMPARATIVE EDUCATION, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, 2016, PP. 211-221 Cytotoxicity of two common pesticides using Allium cepa (onion) Assay JAMES, O. E. & ADELEKE, M.
GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L
 J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468 Vol. 93 (1 & 2) 2014 : 135-139 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L VISHNU SHANKAR SINHA AND NANDJEE KUMAR*
J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468 Vol. 93 (1 & 2) 2014 : 135-139 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L VISHNU SHANKAR SINHA AND NANDJEE KUMAR*
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1
 Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
Genes and Proteins. Key points: The DNA must be copied and then divided exactly so that each cell gets an identical copy.
 Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
Mitosis Genes and Proteins Proteins do the work of the cell: growth, maintenance, response to the environment, reproduction, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in each
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
