Interphotoreceptor Retinoid-Binding Protein in the Golgi Apparatus of Monkey Foveal Cones
|
|
|
- Randell McDowell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 33, No. 5, April 1992 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Interphotoreceptor Retinoid-Binding Protein in the Golgi Apparatus of Monkey Foveal Cones Electron Microscopic Immunocyrochemicol Locolizorion Louvenia Carrer-Dawson and Michael Burroughs The presence of interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) in the Golgi apparatus of monkey cone photoreceptors was examined by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Intracellular labeling for IRBP was light to moderate over the Golgi complex of foveal and peripheral cones in the retinas of all four monkeys examined. Composite drawings of two to seven serial sections of inner segments indicated that the highest density of intracellular labeling occurred over the Golgi apparatus. The labeling density over the Golgi complex was fold higher than that over a comparable area of inner segment cytoplasm. The presence of immunolabel for IRBP in the Golgi apparatus supported the findings of in situ hybridization studies that cone photoreceptors can synthesize IRBP. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33: ,1992 Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) is an extracellular protein found largely in the interphotoreceptor matrix (IPM). 1 " 6 This protein may be involved in the transfer of retinoids between the photoreceptors and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) 34 or may serve as a buffer protein. 7 Rod photoreceptors are thought to be responsible for the synthesis and secretion of IRBP. Studies using complementary DNA (cdna) probes and in situ hybridization showed IRBP messenger RNA localized mainly to rod photoreceptors. 8 Electron microscopic immunocytochemical studies also have shown IRBP localized intracellularly to rod photoreceptors. 910 Although intracellular labeling for IRBP has not been reported for cones, predominately cone retinas contain IRBP in the IPM. 11 It also has been detected in the all-cone fovea of the monkey. 6 Either the neighboring rods or both rods and cones synthesize the IRBP seen in the IPM of the fovea and cone-dominant retinas. A recent in situ hybridization study 12 showed the From the Sensory Sciences Center, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, Texas. Supported by National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, Maryland) grant EY05596 (LC-D), and National Science Foundation (Washington DC) grant BSN (LC-D). Presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, Sarasota, Florida, May 1-6, Submitted for publication: August 27, 1990; accepted November 8, Reprint requests: Louvenia Carter-Dawson, PhD, 6420 Lamar Fleming Avenue, Room 316, Sensory Sciences Center, The University of Texas Health Science, Center at Houston, Houston, TX presence of IRBP messenger RNA in the cones of humans and cone-dominant squirrel retinas. The protein IRBP should pass through the Golgi apparatus for glycosylation and packaging because it is a glycoprotein. We examined the Golgi complex of foveal and peripheral cones in monkey retinas for IRBP immunoreactivity using a postembedded immunogold-labeling procedure. The presence of immunoreactivity for this glycoprotein in the Golgi apparatus would provide supporting evidence that cones synthesize IRBP. Materials and Methods One eye from each of four monkeys (Macacafascicularis) was provided by Dr. M. L. J. Crawford (University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston) after vascular perfusion with a mixture of paraformaldehyde 2% and glutaraldehyde 0.5% (ph 7.3, 0.1 M phosphate buffer). The animals were handled in conformance with the ARVO Resolution on the Use of Animals in Research. The anterior segments were removed, and the eyecups were fixed further, and processed for embedding in LR white (E. F. Fullam, Latham, NY). 10 Ultrathin sections of foveal and peripheral retina were mounted on Butvar-coated (BioRad, Cambridge, MA) grids and incubated with goat serum 5% to block nonspecific binding of primary antisera, followed by incubation in 30-/*l drops of rabbit anti-monkey IRBP immunoglobulin G (0.009 ng/ix\ or 30 n\ of affinity-purified rabbit antimonkey IRBP serum. Polyclonal antibodies to purified IRBP were gifts from Drs. B. Wiggert and G. 1589
2 1590 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY & VISUAL SCIENCE / April 1992 Vol. 33 Chader, National Eye Institute, Bethesda, MD) using the two-stage labeling method. 10 Control specimens consisted of sections incubated in rabbit immunoglobulin G instead of rabbit anti-monkey immunoglobulin G. All sections were washed in Tris buffer, incubated in goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G conjugated to 5-nm gold. The grids were washed, and the sections were counterstained with uranyl acetate and exposed to osmium vapor as previously described. 10 The sections were examined and photographed with a JEOL (Peabody, MA) 100B electron microscope. Foveal and peripheral cones, rods, and RPE cells with prominent Golgi regions were photographed in two to seven consecutive sections and printed to a final magnification of 40,000. Four to eight foveal cones, three peripheral cones, three rods, and four RPE cells were examined in each of four, two, and three monkeys, respectively. Composite drawings were made of the inner segments or RPE cell bodies, including outlines of the Golgi apparatus and membranous vesicles and all gold particles. The area of the inner segments or RPE cell bodies and the Golgi apparatus was determined using the Hewlett Packard (Fort Collins, CO) area program and digital tablet (model 9111 A). The area of the inner segments or RPE cytoplasm included only the region surrounding the Golgi complex. The number of gold particles were counted for each area, and the number per 0.25 /xm 2 area was determined. (Vesicles heavily labeled for IRBP were excluded from the analysis because it was not clear whether they were secretory or endocytotic.) Results Examination of the Golgi regions of foveal cones in a single section showed unlabeled, lightly labeled, or moderately labeled areas. Composite drawings (two M2 FOVEAL CONE IPM QLM Fig. 1. A composite drawing and representative section of a cone from monkey 2. (A) The distribution of labeling for IRBP in two consecutive sections is seen in this composite drawing. The highest density of label is present over the Golgi region (arrows). (B) Labeling over the Golgi region (arrows) is seen in a portion of one section used in the drawing (sections incubated with nonaffinity purified antiserum). OLM, outer limiting membrane; IPM, interphotoreceptor matrix. Original magnification X 40,000; bar = 0.5 Mm.
3 No. 5 IRBP LOCALIZATION IN MONKEY CONE5 / Correr-Dowson and Durroughs 1591 to four sections) of representative cells that were unlabeled to lightly labeled in one section showed most of the label localized to the Golgi apparatus and membranous vesicles. This pattern of labeling was observed in sections that reacted with nonaffinity (Figs. 1A-1B) or affinity-purified antiserum (Figs. 2A-B). The Golgi apparatus of peripheral cones and rods also were unlabeled to lightly labeled in single sections, but they were heavily labeled in composite drawings (Fig. 3, seven serial sections; Fig. 4, two serial sections). This pattern of labeling was seen in the cones of all monkeys examined. The Golgi region of RPE cells were labeled at background levels. Quantitation of the number of gold particles, representing IRBP labeling of inner segments, showed the highest labeling over the Golgi complex. The density of label over the Golgi and inner segment in representative foveal cones was fold higher than in the inner segment cytoplasmic region (range, 0.93/ /0.1 per 0.25 ^m 2 ). Over peripheral cones, the labeling density for Golgi and inner segment cytoplasm was fold higher (range, 2.51/ /0.18 per 0.25 /urn 2 ). The Golgi regions of peripheral rod inner segments were labeled fold higher than other cytoplasmic regions (rod range, 2.5/ /0.06 per 0.25 jim 2, excluding membranous vesicles and rough endoplasmic reticulum). Similar quantitation of IRBP labeling over the Golgi region in RPE cells showed the labeling density over the Golgi region to be only fold higher than that over other cytoplasmic regions (range, 0.09/ /0.06 per 0.25 ftm 2 ). The labeling for IRBP over the Golgi region in control samples was similar to that over cytoplasmic regions (range, 0.16/ /0.24 per fim 2 ). Discussion Our findings provide supporting evidence that cones may synthesize IRBP. We found IRBP immunoreactivity associated with the Golgi complex and M2 FOVEAL CONE (affinity purified serum) V IPM 2A Fig. 2. Localization of IRBP in foveal cones with affinity purified serum. (A) Similar to Figure 1A, the composite drawing shows labeling concentrated in the region of the Golgi (arrows), except for a heavily labeled vesicle (arrow head). (B) The Golgi region is moderately labeled in one of the sections used for the composite drawing (arrows). The heavily labeled membranous vesicle seen in the composite drawing is present in one of the sections used in the drawing (arrow head). M2, monkey 2; IPM, interphotoreceptor matrix. Original magnification X4O,OOO; bar = 0.5 Mm.
4 1592 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY 6 VISUAL SCIENCE / April 1992 Vol. 30 M3 PERIPHERAL CONE 1PM iv QLM \ : 3B NUC Fig. 3. Composite drawing and a representative section of a peripheral cone from monkey 3. (A) The composite drawing shows the distribution of label for IRBP in seven serial sections. Label is associated with the Golgi region (arrows) and other membranous vesicles. (B) A portion of the Golgi region from one of seven sections is lightly labeled for IRBP in this micrograph (arrows; nonaffinity purified antiserum was used). NUC, nucleus; OLM, outer limiting membrane; IPM, interphotoreceptor matrix. Original magnification X4O,OOO; bar = 0.5 ^m. membranous vesicles in cone and rod inner segments. The labeling in rods was similar to that described earlier. 9 In addition, the Golgi apparatus of foveal and peripheral cones were labeled for IRBP. Single sections through the Golgi apparatus of cones appeared unlabeled, lightly labeled, or moderately labeled. Most often the Golgi region appeared unlabeled to lightly labeled. Therefore, if only a single section is examined and background labeling is high, the Golgi region will appear unlabeled. This may explain why labeling of the Golgi region was not detected previously. The labeling of the Golgi complex in cones and rods appeared to be specific for IRBP. The IRBP labeling of the Golgi region was observed with affinity- and nonaffinity-purified antisera. However, labeling for IRBP in the Golgi region of RPE cells by affinity- or nonaffinity-purified antiserum was only one to threefold higher than background. This slightly elevated labeling density in the RPE may represent an error related to the identification of the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi in the RPE is not recognized as easily as it is in the photoreceptor inner segment. Some non-golgi apparatus membranous structures may have been included in the analysis. The absence of a high density of labeling in the Golgi region of RPE cells and cone inner segments of control cells for IRBP suggested that the antibody was not recognizing a protein component common to all Golgi apparatus, but rather was recognizing IRBP in the Golgi. We used a secondary antibody conjugated to 5-nm gold particles to increase the labeling density and examined two to seven serial sections of cones through the Golgi region. Composite drawings of the labeling in serial sections also were made. The combination of high density and specificity of labeling, low background, the use of serial sections, composite drawings, and quantitative analysis of labeling densities made it clear that the Golgi apparatus of monkey cones showed labeling for IRBP. Does the label for IRBP in the Golgi apparatus represent synthesis or recycling of protein that had undergone endocytosis? Recent studies have shown cellsurface proteins that have undergone endocytosis to be translocated to the trans-golgi network for resialylation. 13 In this study, label for IRBP was not restricted to one or two cisternae, as might be expected for labeling in the trans-golgi area. Because label was
5 No. 5 IRBP LOCALIZATION IN MONKEY CONES / Correr-Dawson and Burroughs 1593 M3 PERIPHERAL ROD IPM 4B S OLM 4A Fig. 4. IRBP labeling in rod photoreceptors of monkey 3 (M3). (A) The composite drawing of two serial sections shows most of the label associated with the Golgi region (arrows) and membranous vesicles. (B) A micrograph of one serial section shows IRBP labeling associated with the Golgi region (arrows) and membranous vesicles (nonaffinity purified IRBP antiserum). OLM, outer limiting membrane; 1PM, interphotoreceptor matrix. Original magnification X 40,000; bar = 0.5 pm. present in most cisternae, some of it probably was related to IRBP synthesis. Our findings of IRBP immunoreactivity in the Golgi region of monkey cone photoreceptors supported cdna hybridization studies 12 that cone photoreceptors can synthesize IRBP. Key words: interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein, retina, immunocytochemistry, monkey, cones, rods, Golgi apparatus Acknowledgments The authors thank Drs. B. Wiggert and G. Chader for their generous supply of IRBP antibodies and purified protein and Dr. M. L. J. Crawford for the monkey eyes. References 1. Adler AJ and Martin KJ: Retinol-binding proteins in bovine interphotoreceptor matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 108:1601, Bunt-Milam AH and Saari JC: Immunocytochemical localization of two retinoid-binding proteins in vertebrate retina. J Cell Biol 97:703, Chader GJ, Wiggert B, Lai Y-L, Lee L, and Fletcher R: Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein: A possible role in retinoid transport to the retina. In Progress in Retinal Research, Osborne N and Chader GJ, editors. Oxford, Pergamon Press, 1983, pp Okajima T-I, Pepperberg DR, Ripps H t Wiggert B, and Chader GJ: Interphotoreceptors retinoid-binding protein promotes rhodopsin regeneration in toad photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6907, 1990.
6 1594 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY & VISUAL SCIENCE / April 1992 Vol Fong S-L, Liou GI, Landers RA, Alvarez RA, Gonzalez-Fernandez F, Glazebrook PA, Lam DMK, and Bridges CDB: The characterization, localization, and biosynthesis of an interstitial retinol-binding glycoprotein in the human eye. J Neurochem 42:1667, Wiggert B, Lee L, Rodrigues M, Hess H, Redmond TM, and Chader GJ: Immunochemical distribution of interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein in selected species. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 27:1041, Ho M-T, Massey H, Pownall RE, Anderson RE, and Hollyfield JG: Mechanism of vitamin A movement between rod outer segments, interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein, and liposomes. J Biol Chem 26:928, van Veen T, Katial A, Shinohara T, Barrett D, Wiggert B, Chader GJ, and Nickerson J: Retinal photoreceptor neurons and pinealocytes accumulate mrna for interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP). FEBS Lett 208:133, Rodrigues M, Hackett J, Wiggert B, Gery I, Spiegel A, Krishna G, Stein P, and Chader G: Immunoelectron microscopic localization of photoreceptor-specific markers in the monkey retina. Curr Eye Res 6:369, Carter-Dawson L and Burroughs M: Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) in the postnatal developing rds mutant retina: EM immunocytochemical localization. Exp Eye Res 49:829, Anderson DH, Neitz JC, Saari JC, Kaska DD, Fenwick J, Jacobs GH, and Fisher SK: Retinoid-binding proteins in conedominant retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 27:1015, Porrello K, Bhat SP, and Bok D: Detection of Interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein (IRBP) mrna in human and cone-dominant squirrel retinas by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem 29:171, Gruenberg J and Howell KE: Membrane traffic in endocytosis: Insights from cell-free assays. Annu Rev Cell Biol 5:453, 1989.
Confocal immunolocalization of bovine serum albumin, serum retinol-binding protein, and interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein in bovine retina
 Received 29 August 2006 Accepted 14 December 2006 Published 22 December 2006 Confocal immunolocalization of bovine serum albumin, serum retinol-binding protein, and interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding
Received 29 August 2006 Accepted 14 December 2006 Published 22 December 2006 Confocal immunolocalization of bovine serum albumin, serum retinol-binding protein, and interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding
Identification of Proteins in Retinas and IPM From Eyes With Retinitis Pigmentosa
 ovember 988 Vol. 9/ Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science Articles Identification of Proteins in Retinas and IPM From Eyes With Retinitis Pigmentosa Susan Y. Schmidt,* Cynthia A. Heth,* Ross D.
ovember 988 Vol. 9/ Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science Articles Identification of Proteins in Retinas and IPM From Eyes With Retinitis Pigmentosa Susan Y. Schmidt,* Cynthia A. Heth,* Ross D.
Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid
 Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid Roland K. Herrmann,* W. Gerald Robison, Jr.,* and John G. Dieri-)- The effects of vitamin E and A deficiencies on the
Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid Roland K. Herrmann,* W. Gerald Robison, Jr.,* and John G. Dieri-)- The effects of vitamin E and A deficiencies on the
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
You and plants have something in common! 1
 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure & Function These are micrographs of cells you will see in this week's lab. One is plant (onion epithelium), the other animal (human cheek epithelium). Determine which is which
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure & Function These are micrographs of cells you will see in this week's lab. One is plant (onion epithelium), the other animal (human cheek epithelium). Determine which is which
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy
 7.4 - Translation 7.4.1 - Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy Each amino acid has a specific trna-activating
7.4 - Translation 7.4.1 - Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy Each amino acid has a specific trna-activating
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope.
 1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope. Select your answers from the list below. 10x 40x 100x light microscope... x transmission
1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope. Select your answers from the list below. 10x 40x 100x light microscope... x transmission
Regulation of retinalaldehydes isomerization in the chicken inner retina.
 Regulation of retinalaldehydes isomerization in the chicken inner retina. Name of fellow: Nicolas Diaz Laboratory USA: Dr. Andrew Tsin, Department of Biology, University of Texas at San Antonio Laboratory
Regulation of retinalaldehydes isomerization in the chicken inner retina. Name of fellow: Nicolas Diaz Laboratory USA: Dr. Andrew Tsin, Department of Biology, University of Texas at San Antonio Laboratory
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Endomembrane system 11/1/2018. Endomembrane System. Direct physical continuity. Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles. Outer Nuclear envelope
 Endomembrane system Endomembrane System Outer Nuclear envelope Direct physical continuity Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles Endoplasmic reticulum BUT membranes are not identical in structure and
Endomembrane system Endomembrane System Outer Nuclear envelope Direct physical continuity Transfer of membrane segments as vesicles Endoplasmic reticulum BUT membranes are not identical in structure and
Vitamin A storage and peroxisomes in retinal pigment epithelium and liver. W. Gerald Robison, Jr., and Toichiro Kuwabara
 Vitamin A storage and peroxisomes in retinal pigment epithelium and liver W. Gerald Robison, Jr., and Toichiro Kuwabara Retinas and livers were studied with histochemical methods for catalase combined
Vitamin A storage and peroxisomes in retinal pigment epithelium and liver W. Gerald Robison, Jr., and Toichiro Kuwabara Retinas and livers were studied with histochemical methods for catalase combined
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science
 DECEMBER 1982 Vol. 23/6 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science A Journal of Clinical and Basic Research Articles Identification and distribution of coated vesicles in the retinal pigment epithelium
DECEMBER 1982 Vol. 23/6 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science A Journal of Clinical and Basic Research Articles Identification and distribution of coated vesicles in the retinal pigment epithelium
(A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids. A. Incorrect! Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have cell membranes.
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
Starch grains - excess sugars
 (a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
(a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
visual-pigment bleaching in isolated photoreceptors (vision/dark adaptation/11-cis retinoid/interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 86, pp. 966-961, December 1989 Neurobiology Retinoid requirements for recovery of sensitivity after visual-pigment ing in isolated photoreceptors (vision/dark adaptation/11-cis
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 86, pp. 966-961, December 1989 Neurobiology Retinoid requirements for recovery of sensitivity after visual-pigment ing in isolated photoreceptors (vision/dark adaptation/11-cis
Eye physiology and phototransduction. Zoran Đogaš
 Eye physiology and phototransduction Zoran Đogaš Eye geometry Nervus opticus Pupillary reflex and accommodation Clinical Sy Myopia Hypermetropia Photoreceptors ROD CONE Photoreceptors The photoreceptor
Eye physiology and phototransduction Zoran Đogaš Eye geometry Nervus opticus Pupillary reflex and accommodation Clinical Sy Myopia Hypermetropia Photoreceptors ROD CONE Photoreceptors The photoreceptor
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Ferritin-Conjugated Antibodies Used for Labeling of Organelles Involved
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 71, No. 5, pp. 2033-2037, May 1974 Ferritin-Conjugated Antibodies Used for Labeling of Organelles Involved in the Cellular Synthesis and Transport of Procollagen (ferritin-antibody
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 71, No. 5, pp. 2033-2037, May 1974 Ferritin-Conjugated Antibodies Used for Labeling of Organelles Involved in the Cellular Synthesis and Transport of Procollagen (ferritin-antibody
The pinealocytes of the human pineal gland: a light and electron microscopic study
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 65, No. 3, pp. 181 187 Copyright 2006 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The pinealocytes of the human pineal gland: a light and electron microscopic
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 65, No. 3, pp. 181 187 Copyright 2006 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The pinealocytes of the human pineal gland: a light and electron microscopic
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae.
 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Cell Structure. Present in animal cell. Present in plant cell. Organelle. Function. strength, resist pressure created when water enters
 Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina
 High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina Greg D. Field 1, Martin Greschner 1, Jeffrey L. Gauthier 1, Carolina Rangel 2, Jonathon Shlens 1,3, Alexander
High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina Greg D. Field 1, Martin Greschner 1, Jeffrey L. Gauthier 1, Carolina Rangel 2, Jonathon Shlens 1,3, Alexander
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
lsomerization reactions of retinoids in the visual system
 Pure & Appl. Chem., Vol. 66, No. 5, pp. 989-994, 1994. Printed in Great Britain. 0 1994 IUPAC lsomerization reactions of retinoids in the visual system Robert R. Rando Harvard Medical School, Biological
Pure & Appl. Chem., Vol. 66, No. 5, pp. 989-994, 1994. Printed in Great Britain. 0 1994 IUPAC lsomerization reactions of retinoids in the visual system Robert R. Rando Harvard Medical School, Biological
Age-related decrease in rod bipolar cell density of the human retina: an immunohistochemical study
 Rod bipolar cells in ageing human retina 293 Age-related decrease in rod bipolar cell density of the human retina: an immunohistochemical study P AGGARWAL, T C NAG and S WADHWA* Department of Anatomy,
Rod bipolar cells in ageing human retina 293 Age-related decrease in rod bipolar cell density of the human retina: an immunohistochemical study P AGGARWAL, T C NAG and S WADHWA* Department of Anatomy,
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Analysis of the Visual Cycle in Cellular Retinol-Binding Protein Type I (CRBPI) Knockout Mice
 Analysis of the Visual Cycle in Cellular Retinol-Binding Protein Type I (CRBPI) Knockout Mice John C. Saari, 1,2 Maria Nawrot, 1 Gregory G. Garwin, 1 Matthew J. Kennedy, 2 James B. Hurley, 2,3 Norbert
Analysis of the Visual Cycle in Cellular Retinol-Binding Protein Type I (CRBPI) Knockout Mice John C. Saari, 1,2 Maria Nawrot, 1 Gregory G. Garwin, 1 Matthew J. Kennedy, 2 James B. Hurley, 2,3 Norbert
Construction of the Visual Image
 Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
:1c.c :& Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* structure with rounded ends and a striated lamella
 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Deng et al. 0.073/pnas.09038206 SI Text Animals and Subretinal Injections. Tr / mice were a gift from Dr. Janis Lem. GNAT2 cpfl3, rd7 and wildtype ALR/LtJ mice were purchased from
Supporting Information Deng et al. 0.073/pnas.09038206 SI Text Animals and Subretinal Injections. Tr / mice were a gift from Dr. Janis Lem. GNAT2 cpfl3, rd7 and wildtype ALR/LtJ mice were purchased from
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department
 Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Cell Biology 1.2- Ultrastructure of Cells
 Essential idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure than prokaryotes. Cell Biology 1.2- Ultrastructure of Cells Nature of science: Developments in scientific research follow improvements
Essential idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure than prokaryotes. Cell Biology 1.2- Ultrastructure of Cells Nature of science: Developments in scientific research follow improvements
INDEX. Genetics. French poodle progressive rod-cone degeneration,
 INDEX Acuity in Stargardt's macular dystrophy, 25-34 ADRP (Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa), see Retinitis pigmentosa and Genetics afgf, 294, 296 Age-related maculopathy, see Macular degeneration
INDEX Acuity in Stargardt's macular dystrophy, 25-34 ADRP (Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa), see Retinitis pigmentosa and Genetics afgf, 294, 296 Age-related maculopathy, see Macular degeneration
10 The Golgi Apparatus: The First 100 Years
 2 Structure With no cell compartment or organelle has morphology served such a pivotal role in its discovery and investigation as with the apparatus of Golgi. The original description of the apparato reticulo
2 Structure With no cell compartment or organelle has morphology served such a pivotal role in its discovery and investigation as with the apparatus of Golgi. The original description of the apparato reticulo
Processing and Transport of Retinoids by the Retinal Pigment Epithelium
 Eye (1990) 4, 326-332 Processing and Transport of Retinoids by the Retinal Pigment Epithelium DEAN BOK Los Angeles Summary Recent developments regarding our understanding of retinoid processing and transport
Eye (1990) 4, 326-332 Processing and Transport of Retinoids by the Retinal Pigment Epithelium DEAN BOK Los Angeles Summary Recent developments regarding our understanding of retinoid processing and transport
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology
 3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The Protective Effect of Ascorbic Acid in Retinal Light Damage of Rats Exposed to Intermittent Light
 July 1990 Vol. 31/7 Investigative Ophthalmology G Visual Science Articles The Protective Effect of Ascorbic Acid in Retinal Light Damage of Rats Exposed to Intermittent Light Daniel T. Organisciak, Yih-ling
July 1990 Vol. 31/7 Investigative Ophthalmology G Visual Science Articles The Protective Effect of Ascorbic Acid in Retinal Light Damage of Rats Exposed to Intermittent Light Daniel T. Organisciak, Yih-ling
BIOSC 041. v Today s lecture. v Today s lab. v Note- Monday is a holiday good time to do some reading!
 BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Detection of Hepatitis A Antigen in Human Liver
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1982, p. 320-324 0019-9567/82/040320-05$02.00/0 Vol. 36, No. 1 Detection of Hepatitis A Antigen in Human Liver YOHKO K. SHIMIZU,'* TOSHIO SHIKATA,' PAUL R. BENINGER,2 MICHIO
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1982, p. 320-324 0019-9567/82/040320-05$02.00/0 Vol. 36, No. 1 Detection of Hepatitis A Antigen in Human Liver YOHKO K. SHIMIZU,'* TOSHIO SHIKATA,' PAUL R. BENINGER,2 MICHIO
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Identification and Characterization of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Immunoreactive Amacrine Cells
 Identification and Characterization of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Immunoreactive Amacrine Cells Nicholas C. Brecho,* Clyde W. Oyster,f and Ellen S. Takahashrf- Using immunohistochemical techniques and antiserum
Identification and Characterization of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Immunoreactive Amacrine Cells Nicholas C. Brecho,* Clyde W. Oyster,f and Ellen S. Takahashrf- Using immunohistochemical techniques and antiserum
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
The Discovery of the Cell
 The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Cell Physiology
 Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
The finding of mutations in the gene encoding the trabecular
 mrna In Situ Hybridization of TIGR/MYOC in Human Trabecular Meshwork Xiaofang Wang and Douglas H. Johnson PURPOSE. To determine the distribution of mrna expression of the trabecular meshwork induced glucocorticoid
mrna In Situ Hybridization of TIGR/MYOC in Human Trabecular Meshwork Xiaofang Wang and Douglas H. Johnson PURPOSE. To determine the distribution of mrna expression of the trabecular meshwork induced glucocorticoid
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
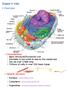 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 8, 339-346 (1984) C by Japan Society for Cell Biology Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice Ikuo Yamaoka, Sumie Katsuta and Yoshimi
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 8, 339-346 (1984) C by Japan Society for Cell Biology Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice Ikuo Yamaoka, Sumie Katsuta and Yoshimi
Questions in Cell Biology
 Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Immunohistochemical Localization For Aldose Reductase in Diabetic Lenses
 Immunohistochemical Localization For Aldose Reductase in Diabetic Lenses Yoshio Akagi, Pefer F. Kador, ond Jin H. Kinoshira Sugar cataract formation has been demonstrated to result from lenticular sorbitol
Immunohistochemical Localization For Aldose Reductase in Diabetic Lenses Yoshio Akagi, Pefer F. Kador, ond Jin H. Kinoshira Sugar cataract formation has been demonstrated to result from lenticular sorbitol
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
The Visual System. Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems
 The Visual System Basic anatomy of the eye The retina Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems Phototransduction Conversion of energy of light into changes in V m Adaptation and expansion
The Visual System Basic anatomy of the eye The retina Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems Phototransduction Conversion of energy of light into changes in V m Adaptation and expansion
Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) is a 135
 Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Exaggerated Eye Growth in IRBP-Deficient Mice in Early Development Jeffrey Wisard, 1 Amanda Faulkner, 2 Micah A. Chrenek, 1 Timothy Waxweiler, 1 Weston Waxweiler, 1 Christy
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Exaggerated Eye Growth in IRBP-Deficient Mice in Early Development Jeffrey Wisard, 1 Amanda Faulkner, 2 Micah A. Chrenek, 1 Timothy Waxweiler, 1 Weston Waxweiler, 1 Christy
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Fundus Autofluorescence. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Fundus Autofluorescence Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) has many important functions including phagocytosis of the photoreceptor outer segments Cone Rod
Fundus Autofluorescence Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) has many important functions including phagocytosis of the photoreceptor outer segments Cone Rod
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University
 SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
