: a comparison in quail animal mode. Nagamine, Masaru; Takei, Hiroshi. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Effects of dietary lard and fish oi : a comparison in quail animal mode Toda, Takayoshi; Hokama, Seitetsu; Nagamine, Masaru; Takei, Hiroshi Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34 Issue Date URL Right This document is downloaded
2 Acta Med. Nagasaki 34: Effects of dietary lard and fish oil on the serum lipid level and aortic tissue : a comparison in quail animal model Takayoshi TODA 1, Seitetsu HOKAMA 1, Nobuhiro FIKUDA 2, Kyoko TERUYA 2, Masaru NAGAMINE 3 and Hiroshi TAKEI 3 1 Depertment of Clinical Laboratory, University Hospital, 2 Laboratory of Nutrition Chemistry, School of Agriculture, and 3 Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, University of the Ryukyus, Okinawa 903, Japan Received for publication, December 26, 1987 SUMMARY : A total of twenty-five 40-day-old, male, Japanese quails were fed with either basal diet, a diet containing 15% butter fat and 2% cholesterol, or a diet containing 15% fish oil and 2% cholesterol for 3 months. The birds which were fed with the diet containing lard and cholesterol showed marked hypercholesterolemia and severe lipid-rich aortic lesions. In accordance to serum cholesterol level, the lard fed group had numerous fibroblasts with or without lipid droplets in the thickened intima of the ascending aorta. The birds fed with the fish oil and cholesterol had no significant increase in their serum cholesterol level or lipid-rich aortic lesions. These data clearly indicate that fish oil is less atherogenic than lard. INTRODUCTION Elevated blood lipids have been statistically established as a risk factor in the development of atherosclerosis (9). Therefore, most of the attempts to regulate blood lipids by diet has been centered on the fat in the diet. It has been reported that diets rich in saturated fatty acids are usually associated with increase in serum cholesterol levels and severe atherosclerosis in man (6) and experimental animals (13,19). On the other hand, it has long been considered that polyunsaturated fatty acids lower cholesterol level, and are anti-atherogenic and essential for the growth and proper nutrition of humans and animals (6). We have been working on experimental atherosclerosis using chicken which is susceptible to atherosclerosis as well as economical than the other animal model (16). In the present study, we chose Japanese quail as animal model because it can thrive in small laboratory cages and is economical and easy to maintain for long-term experiment (1). The first objective of the present study was to determine the degree of atherosclerosis produced by the atherogenic diet rich in saturated fatty acids. We chose lard as a fat rich in saturated fatty acids. A second objective was to compare the atherogenecity of fish oil and lard because fish oil rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids of n- 3 family has been reported to be anti-atherogenic (4,21). MATERIALS AND METHODS Twenty-five 40-day-old male Japanese quails were used in this study and divided into, three groups as shown in Table 2. One group was fed with a basal diet and the other two groups were fed with the test diets which contain 2%
3 cholesterol and 15% fat of either lard or fish oil. The birds were allowed ad lib. access to both food and water throughout the threemonth experiment. The basal diet (Kyoei Co. Ltd. Okinawa) contained 18% protein, 3.8% fat, 6.3% ash, 3.5% fiber, and 2842 Kcal/Kg. The fatty acid composition of test diets was analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography as described elsewhere (15). Serum cholesterol and trigyceride were determined by the enzymatic methods (TC-S 736, Kyowa Tokyo, and TG-V3 Nishin Shozi Osaka. ). The hearts and the proximal one cm of the ascending aorta and its large branches were collected. These tissues were fixed in 10% formaldehyde solution, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4 micrometer, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin, elastica van Gieson, and Mallory Azan. As previously reported (17), intimal thickening was measured on the representative three to four arteries in each quail using an ocular micrometer. The severity of arteriosclerosis was expressed as the average degree of intimal thickening of the arteries in each group. Small pieces of thoracic aortas were fixed in 3 % glutaraldehyde solution for electon microscopic examination. These tiny specimens were postfixed in phosphate-buffered 1 % osmium tetroxide, serially dehydrated in increasing concentrations of ethanol, embedded in spur resin and sectioned with diamond knife. Ultrathin sections were, stained with uranyl acetate, and examined with a JEM 20 00EX electron microscope. RESULTS Biochemistry : The percent composition of fatty acids in the diet of each experimental group is shown in Table 1. All the diets contained enough amounts of linoleic acid to fulfil the minimum requirement of essential fatty acids (3). Table 2 shows body weight and lipid profile in each experimental group. There was no significant difference in final body weight among all the experimental groups. Serum cholesterol levels in quails on the diet containing lard and cholesterol showed a sharp increase. Serum triglyceride level in the lard and fish oil groups were lower than that in the basal group. Histology : The control birds showed no lipid-rich arterial lesions (Fig. 1), while the quails fed with the lard-containing diet showed moderate to severe lipid-rich intimal lesions in the ascending and proximal thoracic aortas (Fig. 2). The quails fed with the fish oilcontaining diet developed slight intimal thickening in the aortas (Fig. 3). Table 3 shows a comparison of the incidence and degree of Table 1. Percent fatty acid composition of the diet used in each experimental group 12:0 14:0 16:0 16:1 18:0 18:1 18:2 18:3 20:4 20:5 Sat. Mono. Poly. Control Lard Fish oil Table 2. Dietary groups, number of quails, body weights and mean serum cholesterol and triglycerides concentrations No. of Final body Serum lipids (mg/dl ) quail weight (g) TG TC Control 8 113±6 173±27 182± 14 Lard 8 107±4 61± ±156 Fish oil 9 105±3 39± 5 261± 7 TG : tryglyceride TC : total cholesterol Data are expressed as mean ± standard error
4 Fig. 1. Aorta from a quail fed with a basal diet. Alternating lamellae of medial smooth muscle cells (SM) are shown (elastica van Gieson X 180). Fig. 2. Photomicrograph of a aorta from a quail fed with a lard-containing diet showing marked intimal thickening (Mallory Azan X 180). intimal thickening of the ascending aorta and its large branches which were found in birds fed with the control diet, lard-containing diet and fish oil-containing diet. Quails fed with the lard-containing diet had the most fre- Fig. 3. Photomicrograph of a aorta from a quail fed with a fish oil-containing diet showing slight intimal thickening (elastica van Gieson X180). quent and severe intimal thickening of the ascending aorta and its large branches among all the experimental groups.. Electron microscopy : In control quails, the intima consisted of a single layer of elongate endothelial cells. The connective tissue layer beneath the endothelium consisted of a loose reticular network with banded collagen fibers. The media was composed of alternating layer of smooth muscle cells and fibroblastic cells. Intercellular space contained elastic fibers as well as collagen fibers (Fig. 4). In contrast to the aortas of quails fed with a basal diet, aortas from quails receiving a lard-containing diet had remarkable lipid-rich aortic lesions. The thickened intima was mainly composed of lipid-containing fibroblastic cells (Fig. 5 ). Deeper portions of the thickened intima contained smooth muscle cells with or without lipid droplets (Fig.6). Smooth muscle cells in the middle layer of the tunics media showed a normal fusiform appearance. Inter- Table 3. Effects of control, lard-containing diet and fish oil-containing diet on aortic lesions in quails Groups Parameter Control Lard Fish oil Incidence of 5/31 9/29 4/33 thickened intima Average of intimal 0.8± ± ±0.4 thickeness (x 10-2mm)
5 The lesions observed in quails receiving a fish oil-containing diet were small and mild. The subendothelial space was slightly and focally expanded, and contained a few foam cells and a small amount of extracellular lipid granules. DISCUSSION Fig. 4. Fibroblasts (F) and smooth muscle cells (S) are seen in the tunica media ( X2,600). F - elastic fiber. Fig. 5. Lipid-containing fibroblasts (F) are shown. E : elastic fiber (X6,500). Fig. 6. Lipid inclusions (I) are more numerous in fibroblastics than in smooth muscle cells (S) ( x4,300). cellular spaces were slightly widened and contained a small amount of lipid granules. Feeding trial of a diet containing 189/o saturated fatty acid-rich lard without cholesterol produced moderate increase in the level of serum cholesterol and the thickness of coronary arterial intima of swine (14). In this experiment, we fed a diet containing 15% lard 2 % cholesterol to quails, and found that this diet induces hypercholesterolemia and significant degree of atherosclerotic lesions in the ascending aortic arch, proximal thoracic aorta and their large branches. These results demonstrate that lard enriched with saturated fatty acid is highly atherogenic in quails as observed in other animals (18) and the Japanese quail is as useful as the chicken as an animal model for the study of atherosclerosis (16). Polyunsaturated fatty acids are categorized into the three major families of unsaturated fatty acids including the oleic acid(n-9) family, the linoleic acid (n-6) family, and the linolenic acid (n-3) family (6). Fish oils contain a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids of the n-3 series such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Many studies have reported various effects upon platelet aggregability (5, 8 ), blood lipid (12,20), blood pressure (11), and inflammatory or immunological processes (10). Concerning the effects of fish oils on arteries, several reports of animal experiments (4, 21). have been published. It is speculated that the benificial, and preventive effect of fish oil to atherosclerosis is achieved through prostaglandin metabolism and platelet function instead of lipid metabolism. In the present study, fish oil fed with group had significantly lower levels of serum cholesterol and less atherosclerosis than the lard fed group. The factors which regulate serum cholesterol level have been known to include : 1) cholesterol absorption ; 2) excretion of neutral and acidic steroids ; 3) cholesterol synthesis ; 4) transfer
6 of cholesterol from plasma to tissues ; 5 ) changes in the cholesterol-to-protein ratio in LDL, and 6) changes in membrane fluidity (2, 7). Goodnight et al. (6), proposed that changes in the fluidity of lipoproteins and/or cellular plasma membranes are the most promising mechanisms governing the serum cholesterol level. However, the profound hypolipidemic action of fish oil remains as yet unexplained. REFERENCES 1) BAYER,R.C., RINGER,R.K., and COGGER,E.A : The influence of dietary vitamin A on atherogenesis in Japanese quail. Poult Sci. 51 : (1972). 2) CONNOR, W.E., WrAK, D.T., STONE, D.B., and ARMSTRONG,M.L. : Cholesterol balance and fecal neutral steroid and bile acid excretion in normal men fed dietary fats of different fatty acid composition. J Clin Invest 48: (1969). 3) CUTHBERTSON, W.F.J. : Essential fatty acid requirements in infancy. Am J Clin Nutr. 29: (1976). 4) DAVIS,H.R., VESSELINOVITCH,D., and WISSLER,R. W. : Fish oil inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in rhesus monkeys. Circulation (Suppl) 74 : (1986). 5) DYERBERG, J. and BANG, H.O. : Haemostatic function and platelet polyunsaturated fatty acids in Eskimos. Lancet 2 : (1979). 6) GooDNIGHT,S.H., HARRIs,Jr.W.S.,CoNNoR,W.E., and Illingworth, D. R. : Polyunsaturated fatty acids, hyperlipidemia, and thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis. 2 : (1982). 7) GRuNDY, S.M., and AHRENS, E.H.: The effect of unsaturated dietary fats on absorption, excretion, synthesis and distribution of cholesterol in man. J Clin Invest 49 : (1970). 8) HARY,C.R.M., DuBER,A.P., and SAYNOR,R. Effect of fish oil on platelet kinetics in patients with ischemic heart disease. Lancet (1982). 9) KRITHCEVSKY,D. : Diet and atherosclerosis. Am J Patho 184 : (1976). 10) LEE, T.H., HOOVER, R.L., WILLIAM; J.D., SPERLING, R.I., RAVALESE, J., SPPuR, B.W., RIBINSON,D.R., CoREY,E.J., LEWIS, R.A., and AUSTEN,K.F. : Effect of dietary enrichment with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on in vitro neutrophil and monocyte leukotriene generation and neutrophil function. NEng JMed. 312 : (1985). 11) LORENZ,R., SPENGLER,U., FISCHER,S., DUHM,J., and WEBER,P.C. : Platelet function, thromboxane formation and blood pressure control during supplementation of the Western diet with cod liver oil. Circulation 67 : (1983). 12) PHILLIPSON,B.E., ROTHROCK, D.W., CONNOR,W. E., HARRIS,W.S., and ILLINGWORTH,D.R.. Reduction of plasma lipids, lipoproteins and apoproteins by dietary fish oils in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. NEng JMed 312: (1985). 13) ROWSELL,H.C., DOWNIE,H.G., and MUSTARD,J. F. : The experimental production of atherosclerosis in swine following the feeding of butter and margarine. Can Med Ass J. 79 : (1958). 14) SUGAMATA, M., TODA, T., NAGAMINE, M., NAKASHIMA,Y., TAKEI,H., andkummerow,f.a. : Comparative study of the athrogenecity of culinary fats in swine coronary arteries. J Jpn Atheroscler Soc. 15 : (1987). 15) SUGANO,M., WATANABE,M., KOHNO,M., CHO,Y.- J., and IDE,T. : Effects of dietary trans-fats on biliary and fecal steroid excretion and serum lipoproteins in rats. Lipids 18 : (1983). 16) ToDA, T., NISHIMORI, I., and KUMMEROW, F. Animal model of atherosclerosis. Experimental atherosclerosis in the chicken animal model. J Jpn Atheroscler Soc. 11 : (1983). 17) ToDA,T., MAHFUZ,M.M., and KuMMEROW,F.A. : Influence of dietary fats on ultrastructure and fatty acid composition of swine arterial tissue. Acta Pathol Jpn. 34 : (1984). 18) ToDA, T., ToDA, Y., YAMAMOTO, V.K., and KuMMEROW,F.A. : Comparative study of the atherogenecity of dietary trans, saturated and unsaturated fatty acids on swine coronary arteries. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 31 ; (1985). 19) VESSELINOVITCH,D., GETZ,G.S., HUGHES,R.H., and WISSLER,R.W. : Atherosclerosis in. the rhesus monkey fed three food fats. Atherosclerosis 20 : (1974). 20) Von LossoNCZY,T.O., RUITER,A., BRONSGEEST- ScHOUTE,H.C., van GENT,C.H., and HERMUS,R. J.J.: The effect of a fish diet on serum lipids in healthy human patient. Am J Clin Nutr 31 : (1978). 21) WEINER, B.H., OCKENE, I.S., LEVINE, P.H.,
7 CUENOUD, H.F., FrsHER, M., JOHNSON, B.F., DAOUD, A.S., JARMELYCH, J., HosrvrER, D., JOHNSON, M. H., NATALE,A., VAUNDREUIL,C., and Hoogasian,J.J. :Inhibition of atherosclerosis by cod-liver oil in a hyperlipidemic swine model. NEng JMed 315 : (1986).
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases
 Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
The Role of Fats. Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because
 The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
The Role of Fats Fat provides flavour and texture to foods. Fat contributes to making us feel satiated because Fats are more energy dense than carbohydrates or protein Fats take longer to digest Emulsion
Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit
 Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit RAPID PUBLICATIONS J. B. RODGERS, E. C. KYRIAKIDES, B. KAPUSCINSKA, S. K. PENG, and W. J. BOCHENEK, Department of Medicine, Albany
Hydrophobic Surfactant Treatment Prevents Atherosclerosis in the Rabbit RAPID PUBLICATIONS J. B. RODGERS, E. C. KYRIAKIDES, B. KAPUSCINSKA, S. K. PENG, and W. J. BOCHENEK, Department of Medicine, Albany
Review. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Hyperlipidemia, and Thrombosis
 Review Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Hyperlipidemia, and Thrombosis Scott H. Goodnight, Jr., William S. Harris, William E. Connor, and D. Roger Illlngworth CONTENTS Introduction Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid
Review Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Hyperlipidemia, and Thrombosis Scott H. Goodnight, Jr., William S. Harris, William E. Connor, and D. Roger Illlngworth CONTENTS Introduction Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid
13/09/2012. Dietary fatty acids. Triglyceride. Phospholipids:
 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different?
 Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Composition and Structure of Oil and Fats and its Relationship to Health and Nutrition
 Composition and Structure of Oil and Fats and its Relationship to Health and Nutrition SB Neoh* & K. Sundram** * Managing Director, Soon Soon Oilmills Sdn Bhd, Malaysia **Deputy CEO and Director, Science
Composition and Structure of Oil and Fats and its Relationship to Health and Nutrition SB Neoh* & K. Sundram** * Managing Director, Soon Soon Oilmills Sdn Bhd, Malaysia **Deputy CEO and Director, Science
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Atherosclerosis as a Proliferative ultrastructural, immunohistochemica Toda, Takayoshi; Nagamine, Masaru; Hokama, Seitetsu Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Atherosclerosis as a Proliferative ultrastructural, immunohistochemica Toda, Takayoshi; Nagamine, Masaru; Hokama, Seitetsu Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
Maintain Cholesterol
 Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions
 Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Roles of Lipids in the body
 Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Replacement Of Partially Hydrogenated Soybean Oil By Palm Oil In Margarine Without Unfavorable Effects On Serum Lipoproteins
 Replacement Of Partially Hydrogenated Soybean Oil By Palm Oil In Margarine Without Unfavorable Effects On Serum Lipoproteins Muller H, Jordal O, et al. (998) Replacement of partially hydrogenated soybean
Replacement Of Partially Hydrogenated Soybean Oil By Palm Oil In Margarine Without Unfavorable Effects On Serum Lipoproteins Muller H, Jordal O, et al. (998) Replacement of partially hydrogenated soybean
Lipids are used to store and excess energy from extra carbohydrates in animals
 Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
4. Essential fatty acids
 4. Essential fatty acids Physiology and metabolism Dietary fat is a major source of energy and also provides fat soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids. The properties of dietary fat are primarily
4. Essential fatty acids Physiology and metabolism Dietary fat is a major source of energy and also provides fat soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids. The properties of dietary fat are primarily
ANSC/NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Dietary fat and Cardiovascular Disease
 ANSC/NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Dietary fat and Cardiovascular Disease I. Investigations in humans relating dietary fat intake to serum cholesterol A. Ansel Keys: the Keys Formula Cholesterol
ANSC/NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Dietary fat and Cardiovascular Disease I. Investigations in humans relating dietary fat intake to serum cholesterol A. Ansel Keys: the Keys Formula Cholesterol
Fats and Other Lipids
 Fats and Other Lipids Chapter 6 Chapter 6: Fats and other Lipids 1 6.1 Understanding Lipids Lipids include: 1. Fatty acids 2. Triglycerides 3. Phospholipids 4. Cholesterol Oil and Water Don t Mix Because
Fats and Other Lipids Chapter 6 Chapter 6: Fats and other Lipids 1 6.1 Understanding Lipids Lipids include: 1. Fatty acids 2. Triglycerides 3. Phospholipids 4. Cholesterol Oil and Water Don t Mix Because
Heart Health and Fats
 ww Heart Health and Fats By Marie Spano, M.S., R.D., C.S.C.S., Contributing Editor Dietary-fat recommendations for heart health are more specific now then ever, breaking down different types of polyunsaturated
ww Heart Health and Fats By Marie Spano, M.S., R.D., C.S.C.S., Contributing Editor Dietary-fat recommendations for heart health are more specific now then ever, breaking down different types of polyunsaturated
Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble
 Lipids Lipids Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble Lipids They act like this because of their molecular structure (non-polar) Lipids are made mostly of C and H atoms, with O
Lipids Lipids Lipids do not like water! (aka: hydrophobic) Generally insoluble Lipids They act like this because of their molecular structure (non-polar) Lipids are made mostly of C and H atoms, with O
Nutrition and Health Benefits of Rice Bran Oil. Dr. B. Sesikeran, MD, FAMS Former Director National Institute of Nutrition (ICMR) Hyderabad
 Nutrition and Health Benefits of Rice Bran Oil Dr. B. Sesikeran, MD, FAMS Former Director National Institute of Nutrition (ICMR) Hyderabad 1 Fats are needed for life Energy 9 K Cals/g Low fat intakes in
Nutrition and Health Benefits of Rice Bran Oil Dr. B. Sesikeran, MD, FAMS Former Director National Institute of Nutrition (ICMR) Hyderabad 1 Fats are needed for life Energy 9 K Cals/g Low fat intakes in
Inhibition of Low Density Lipoprotein Synthesis by Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Humans
 Inhibition of Low Density Lipoprotein Synthesis by Dietary Omega- Fatty Acids in Humans D. Roger Illingworth, William S. Harris, and William E. Connor Diets rich in omega- fatty acids derived from fish
Inhibition of Low Density Lipoprotein Synthesis by Dietary Omega- Fatty Acids in Humans D. Roger Illingworth, William S. Harris, and William E. Connor Diets rich in omega- fatty acids derived from fish
Dietary Effects of Fish Oils on Human Health: A Review of Recent Studies
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 60 (1987), 37-44 Dietary Effects of Fish Oils on Human Health: A Review of Recent Studies SACHI. SRI KANTHA, Ph.D. Department offood Science, University ofillinois,
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 60 (1987), 37-44 Dietary Effects of Fish Oils on Human Health: A Review of Recent Studies SACHI. SRI KANTHA, Ph.D. Department offood Science, University ofillinois,
Can seal oil contribute to better human health?
 Can seal oil contribute to better human health? Bjarne Østerud and Edel O. Elvevoll, Faculty of Medicine and NFH, University of Tromsø E-mail: bjarne@fagmed. Historical background Old food lore of seafood
Can seal oil contribute to better human health? Bjarne Østerud and Edel O. Elvevoll, Faculty of Medicine and NFH, University of Tromsø E-mail: bjarne@fagmed. Historical background Old food lore of seafood
STUDY QUESTIONS, Chapter 5: The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols
 STUDY QUESTIONS, Chapter 5: The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols To answer the next questions, read the introductory paragraphs, Introducing the Lipids and A Close Look at Lipids in Ch. 5.
STUDY QUESTIONS, Chapter 5: The Lipids: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids and Sterols To answer the next questions, read the introductory paragraphs, Introducing the Lipids and A Close Look at Lipids in Ch. 5.
FAT. Dr. Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology
 FAT Dr. Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology OBJECTIVES LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define what is lipid/fat
FAT Dr. Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology OBJECTIVES LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define what is lipid/fat
Where are we heading?
 Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: What s in your food? Unit 2: How does your body use food? Unit 3: What is metabolic disease? Unit 4: How do I identify good and bad food? Unit
Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: What s in your food? Unit 2: How does your body use food? Unit 3: What is metabolic disease? Unit 4: How do I identify good and bad food? Unit
A Review on Causes and Risk Factors of Hyperlipidemia
 Human Journals Review Article June 2017 Vol.:9, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by TREESA VARGHESE et al. A Review on Causes and Risk Factors of Hyperlipidemia Keywords: Lipids, Lipoproteins, Hyperlipidemia,
Human Journals Review Article June 2017 Vol.:9, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by TREESA VARGHESE et al. A Review on Causes and Risk Factors of Hyperlipidemia Keywords: Lipids, Lipoproteins, Hyperlipidemia,
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O
 PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O Basic Facts on Oil Palm Originated from West Africa, palm oil is the rich source of edible oil and has become important resource of vegetable oil in the
PALM OLEIN BLENDING FOR TEMPERATE MARKET L/O/G/O Basic Facts on Oil Palm Originated from West Africa, palm oil is the rich source of edible oil and has become important resource of vegetable oil in the
Dietary influences on serum lipids and lipoproteins
 Dietary influences on serum lipids and lipoproteins Scott M. Grundy and Margo A. Denke Center for Human Nutrition, Departments of Internal Medicine, Biochemistry, and Clinical Nutrition, University of
Dietary influences on serum lipids and lipoproteins Scott M. Grundy and Margo A. Denke Center for Human Nutrition, Departments of Internal Medicine, Biochemistry, and Clinical Nutrition, University of
Dietary Reference Values: a Tool for Public Health
 HOGE GEZONDHEISRAAD Dietary Reference Values: a Tool for Public Health CONSEIL SUPERIEUR DE LA SANTE Belgian Dietary Reference Values for Energy and Macronutrients: FATS G. De Backer Brussels, February
HOGE GEZONDHEISRAAD Dietary Reference Values: a Tool for Public Health CONSEIL SUPERIEUR DE LA SANTE Belgian Dietary Reference Values for Energy and Macronutrients: FATS G. De Backer Brussels, February
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules CARBON BASED MOLECULES
 CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
CARBON BASED MOLECULES KEY CONCEPTS Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Lipids are one class of organic molecules. This group includes fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids are made of
Cardiovascular risk potential of dietary saturated fats: an update and some implications
 Cardiovascular risk potential of dietary saturated fats: an update and some implications Gerard Hornstra, PhD Med" Prof. Em. of Experimental Nutrition" Maastricht University" The Netherlands" Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular risk potential of dietary saturated fats: an update and some implications Gerard Hornstra, PhD Med" Prof. Em. of Experimental Nutrition" Maastricht University" The Netherlands" Cardiovascular
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA. Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD
 ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
AHA Medical/Scientific Statement. Special Report. A Definition of Initial, Fatty Streak, and Intermediate Lesions of Atherosclerosis
 840 AHA Medical/Scientific Statement Special Report A Definition of Initial, Fatty Streak, and Intermediate Lesions of Atherosclerosis A Report From the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on
840 AHA Medical/Scientific Statement Special Report A Definition of Initial, Fatty Streak, and Intermediate Lesions of Atherosclerosis A Report From the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on
Facts on Fats. Ronald P. Mensink
 Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE
 Page 1 of 6 Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE By Yousry Naguib, PhD Essential fatty acids (EFAs) must be obtained through the diet and cannot be synthesized by the human body. EFAs are
Page 1 of 6 Essential Fatty Acids Essential for Good Health SIE By Yousry Naguib, PhD Essential fatty acids (EFAs) must be obtained through the diet and cannot be synthesized by the human body. EFAs are
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12
 BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
Are you eating a balanced diet?
 Are you eating a balanced diet? Do you know WHAT A BALANCED DIET IS? Eating a balanced diet means choosing a variety of foods & drinks from all the food groups Health Canada recommends 2-3 Tbsp of oil/day
Are you eating a balanced diet? Do you know WHAT A BALANCED DIET IS? Eating a balanced diet means choosing a variety of foods & drinks from all the food groups Health Canada recommends 2-3 Tbsp of oil/day
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
Future directions for nutritional and therapeutic research in omega-3 3 lipids
 Future directions for nutritional and therapeutic research in omega-3 3 lipids Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University of Southampton Aim To review dietary sources and intakes of long
Future directions for nutritional and therapeutic research in omega-3 3 lipids Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University of Southampton Aim To review dietary sources and intakes of long
Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats
 J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought
 Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Effects of Regression of Atherosclerotic Lesions on the Content and Ester if ication of Cholesterol by Cell-Free Preparations of Pigeon Aorta
 Effects of Regression of Atherosclerotic Lesions on the Content and Ester if ication of Cholesterol by Cell-Free Preparations of Pigeon Aorta By Richard W. St. Clair, Thomas B. Clarkson, and Hugh B. Lofland
Effects of Regression of Atherosclerotic Lesions on the Content and Ester if ication of Cholesterol by Cell-Free Preparations of Pigeon Aorta By Richard W. St. Clair, Thomas B. Clarkson, and Hugh B. Lofland
OUTLINE. The need for fat. What is fat? Types of fats. Dietary sources of the different types of fat
 DIETARY FATS OUTLINE The need for fat What is fat? Types of fats Dietary sources of the different types of fat Evidence for cardiovascular health benefit of fish omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids Possible
DIETARY FATS OUTLINE The need for fat What is fat? Types of fats Dietary sources of the different types of fat Evidence for cardiovascular health benefit of fish omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids Possible
Lec 4a- BPK 110 Human Nutrition: Current Iss.
 Lec 4a- BPK 110 Human Nutrition: Current Iss. TOPICS FOR Lec 4a: 1. Introduction to Lipids 2. Lipid Structure 3. Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fatty Acid Chains 4. Phospholipids and Sterols (Other Lipids)
Lec 4a- BPK 110 Human Nutrition: Current Iss. TOPICS FOR Lec 4a: 1. Introduction to Lipids 2. Lipid Structure 3. Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fatty Acid Chains 4. Phospholipids and Sterols (Other Lipids)
THE SAME EFFECT WAS NOT FOUND WITH SPIRITS 3-5 DRINKS OF SPIRITS PER DAY WAS ASSOCIATED WITH INCREASED MORTALITY
 ALCOHOL NEGATIVE CORRELATION BETWEEN 1-2 DRINKS PER DAY AND THE INCIDENCE OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE SOME HAVE SHOWN THAT EVEN 3-4 DRINKS PER DAY CAN BE BENEFICIAL - WHILE OTHERS HAVE FOUND IT TO BE HARMFUL
ALCOHOL NEGATIVE CORRELATION BETWEEN 1-2 DRINKS PER DAY AND THE INCIDENCE OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE SOME HAVE SHOWN THAT EVEN 3-4 DRINKS PER DAY CAN BE BENEFICIAL - WHILE OTHERS HAVE FOUND IT TO BE HARMFUL
PLATELET FATTY ACIDS IN CORONARY HEART DISEASE, DYSLIPIDEMIA, HYPERTENSION AND HEALTHY CONTROLS
 PLATELET FATTY ACIDS IN CORONARY HEART DISEASE, DYSLIPIDEMIA, HYPERTENSION AND HEALTHY CONTROLS Kanjana Hongtong 1, Dolaya Boonnim 2, Ratana Pakpeankitwatana 3, Talabporn Harnroongroj 1, Yaowamarn Chantaranipapong
PLATELET FATTY ACIDS IN CORONARY HEART DISEASE, DYSLIPIDEMIA, HYPERTENSION AND HEALTHY CONTROLS Kanjana Hongtong 1, Dolaya Boonnim 2, Ratana Pakpeankitwatana 3, Talabporn Harnroongroj 1, Yaowamarn Chantaranipapong
Summary and Conclusions
 Summary and Conclusions 125 Summary The thesis entitled Studies on Anti-hyperlipidemic and Anti-atherosclerotic activities of selected Indian Medicinal Plants incorporated the study of antioxidant, antihyperlipidemic
Summary and Conclusions 125 Summary The thesis entitled Studies on Anti-hyperlipidemic and Anti-atherosclerotic activities of selected Indian Medicinal Plants incorporated the study of antioxidant, antihyperlipidemic
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Effects of Dietary Fat Intake on HDL Metabolism
 Elmer ress Review J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(3):145-149 Effects of Dietary Fat Intake on HDL Metabolism Hidekatsu Yanai a, c, Hisayuki Katsuyama a, Hidetaka Hamasaki a, Shinichi Abe b, Norio Tada b, Akahito
Elmer ress Review J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(3):145-149 Effects of Dietary Fat Intake on HDL Metabolism Hidekatsu Yanai a, c, Hisayuki Katsuyama a, Hidetaka Hamasaki a, Shinichi Abe b, Norio Tada b, Akahito
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System
 Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Alison L. Bailey MD, FACC Erlanger Heart and Lung Institute/University of Tennessee COM
 Omega-3 Fatty Acids Alison L. Bailey MD, FACC Erlanger Heart and Lung Institute/University of Tennessee COM Chattanooga @a_l_bailey Disclosures None Objectives Describe omega-3 fatty acids Review the historic
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Alison L. Bailey MD, FACC Erlanger Heart and Lung Institute/University of Tennessee COM Chattanooga @a_l_bailey Disclosures None Objectives Describe omega-3 fatty acids Review the historic
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy
 Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 2: The Chemistry of Life Biological Molecules
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 2: The Chemistry of Life Biological Molecules The Chemistry of Life : Learning Outcomes 2.4) Describe the significance of carbon in forming the basis of the four classes of biological
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 2: The Chemistry of Life Biological Molecules The Chemistry of Life : Learning Outcomes 2.4) Describe the significance of carbon in forming the basis of the four classes of biological
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
 LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
Fat & Human Health. Types of Fats & their effect on Human Health
 Fat & Human Health Why do we need Fats/Oils? Fat is an important ingredient of human diet. The functional role of fat in the diet is manifold. Fat is a most concentrated source of energy. One gram of fat
Fat & Human Health Why do we need Fats/Oils? Fat is an important ingredient of human diet. The functional role of fat in the diet is manifold. Fat is a most concentrated source of energy. One gram of fat
LIP I I P D I S & PROTEINS
 LIPIDS & PROTEINS I. LIPIDS: Foods: butter, oil, Crisco, lard Commonly called fats & oils Contain more C-H bonds and less O atoms than carbohydrates. Ex: C 57 H 110 O 6 Nonpolar; therefore repel water
LIPIDS & PROTEINS I. LIPIDS: Foods: butter, oil, Crisco, lard Commonly called fats & oils Contain more C-H bonds and less O atoms than carbohydrates. Ex: C 57 H 110 O 6 Nonpolar; therefore repel water
FATTY ACIDS COMPOSITION OF FISH, LINSEED AND RAPESEED OILS
 Short Communication FATTY ACIDS COMPOSITION OF FISH, LINSEED AND RAPESEED OILS S. Ezhil Valavan 1, B Mohan, P Selvaraj, S. C. Edwin, K. Mani, R. Amutha and A. Bharathidhasan Directorate of Distance Education
Short Communication FATTY ACIDS COMPOSITION OF FISH, LINSEED AND RAPESEED OILS S. Ezhil Valavan 1, B Mohan, P Selvaraj, S. C. Edwin, K. Mani, R. Amutha and A. Bharathidhasan Directorate of Distance Education
The WorkCare Group, Inc. Content used with permission. StayWell is a registered trademark of The StayWell Company. All rights reserved.
 Know Your Cholesterol Numbers Checklist for Lowering Your Cholesterol Cholesterol Questions to Ask Your Doctor Misconceptions about Cholesterol LDL and HDL Lowering Your Cholesterol CHECKLIST Cut down
Know Your Cholesterol Numbers Checklist for Lowering Your Cholesterol Cholesterol Questions to Ask Your Doctor Misconceptions about Cholesterol LDL and HDL Lowering Your Cholesterol CHECKLIST Cut down
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Effect in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Volume 1, Issue no. 1, DOI 10.18502/ajne.v1i1.1220 Production and Hosting by Knowledge E Research Article Omega-3 Fatty Acid Effect in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Alketbi Fatima Mohammed, Bolaji
Volume 1, Issue no. 1, DOI 10.18502/ajne.v1i1.1220 Production and Hosting by Knowledge E Research Article Omega-3 Fatty Acid Effect in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Alketbi Fatima Mohammed, Bolaji
SUMMARY. Introduction. Study design. Summary
 SUMMARY Introduction The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing rapidly and nowadays affects almost 250 million people. Cardiovascular disease is the most prevalent complication of type 2 diabetes,
SUMMARY Introduction The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing rapidly and nowadays affects almost 250 million people. Cardiovascular disease is the most prevalent complication of type 2 diabetes,
Lipids. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m44401 1 Lipids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
The most concentrated source of food energy. There are 9 calories in every gram of fat
 Fat Is The most concentrated source of food energy There are 9 calories in every gram of fat Fats that are liquid at room temperature are called oils. (Examples: vegetable oil, canola oil, olive oil, etc.)
Fat Is The most concentrated source of food energy There are 9 calories in every gram of fat Fats that are liquid at room temperature are called oils. (Examples: vegetable oil, canola oil, olive oil, etc.)
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
EAT GOOD FATS TO MEET YOUR HEALTH GOALS!
 EAT GOOD FATS TO MEET YOUR HEALTH GOALS! THE POWER OF GOOD FATS Did you know healthy fats provide a wealth of health benefits? At almost any age, replacing saturated fats* with polyunsaturated fats (omega-3,
EAT GOOD FATS TO MEET YOUR HEALTH GOALS! THE POWER OF GOOD FATS Did you know healthy fats provide a wealth of health benefits? At almost any age, replacing saturated fats* with polyunsaturated fats (omega-3,
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver)
 I. TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF CHOLESTEROL Choose the correct answer. 1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver) 2. Only
I. TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF CHOLESTEROL Choose the correct answer. 1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver) 2. Only
Your cholesterol levels. Questions or concerns
 Because you have high cholesterol you should: Know your cholesterol levels Take the medicine to lower cholesterol that your doctor has told you to take Follow your doctor s treatment plan Keep your appointments
Because you have high cholesterol you should: Know your cholesterol levels Take the medicine to lower cholesterol that your doctor has told you to take Follow your doctor s treatment plan Keep your appointments
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
Victor Tambunan. Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia
 Victor Tambunan Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia 1 Handbook of Clinical Nutrition 4th ed., 2006, by D. C. Heimburger & J. A. Ard Krause s Nutrition & Diet Therapy 12th
Victor Tambunan Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia 1 Handbook of Clinical Nutrition 4th ed., 2006, by D. C. Heimburger & J. A. Ard Krause s Nutrition & Diet Therapy 12th
HDL-C. J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart
 Online publication March 25, 2009 48 6 2007 2007 HDL-C LDL-C HDL-C J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: 463 470 NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart 1987 NIPPON DATA80 Iso 10 MRFIT
Online publication March 25, 2009 48 6 2007 2007 HDL-C LDL-C HDL-C J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: 463 470 NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart 1987 NIPPON DATA80 Iso 10 MRFIT
Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke. Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital
 Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital Outline Why are we interested in cholesterol What is a heart attack and how does it
Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital Outline Why are we interested in cholesterol What is a heart attack and how does it
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs
 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Hyperlipidemias. Hyperlipoproteinemias. Hyperlipemia. Hypercholestrolemia. Direct relationship with acute pancreatitis and atherosclerosis Structure Lipoprotein Particles Types
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Hyperlipidemias. Hyperlipoproteinemias. Hyperlipemia. Hypercholestrolemia. Direct relationship with acute pancreatitis and atherosclerosis Structure Lipoprotein Particles Types
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
The Lipids: Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols
 The Lipids: Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Chapter 5 The Lipids-Triglycerides, Phospholipids, and Sterols The Lipid Family Triglycerides (fats and oils) Predominate in the body (99%) and in foods
The Lipids: Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Chapter 5 The Lipids-Triglycerides, Phospholipids, and Sterols The Lipid Family Triglycerides (fats and oils) Predominate in the body (99%) and in foods
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Chapter 5 Reading Guide Note: please read my supplemental lecture (part I) before going through these questions.
 Chapter 5 Reading Guide Note: please read my supplemental lecture (part I) before going through these questions. 1. Which has more oxygen atoms (O), carbohydrates or lipids? 2. What 2 chemical groups are
Chapter 5 Reading Guide Note: please read my supplemental lecture (part I) before going through these questions. 1. Which has more oxygen atoms (O), carbohydrates or lipids? 2. What 2 chemical groups are
Bio 12 Important Organic Compounds: Biological Molecules NOTES Name:
 Bio 12 Important Organic Compounds: Biological Molecules NOTES Name: Many molecules of life are.(means many molecules joined together) Monomers: that exist individually Polymers: Large organic molecules
Bio 12 Important Organic Compounds: Biological Molecules NOTES Name: Many molecules of life are.(means many molecules joined together) Monomers: that exist individually Polymers: Large organic molecules
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids?
 Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
There is more scientific evidence behind the cardiovascular benefits of fish oil than nearly any other nutritional supplement
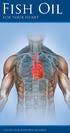 n Provides optimal support for heart health n Reduces triglyceride levels n Reduces cardiovascular risk factors 7, 8 n Complements statin drug therapy n Optimizes circulation and blood vessel function
n Provides optimal support for heart health n Reduces triglyceride levels n Reduces cardiovascular risk factors 7, 8 n Complements statin drug therapy n Optimizes circulation and blood vessel function
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Case of Primary Trabecular Carcin Toda, Takayoshi; Shiroma, Hajime; T Yamada, Mamoru; Nakama, Benjamin Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34 Issue
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Case of Primary Trabecular Carcin Toda, Takayoshi; Shiroma, Hajime; T Yamada, Mamoru; Nakama, Benjamin Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34 Issue
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought
 Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
