2008 Sunrise Free Radical School Presentation by: Bruce Freeman, Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Abner Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2008 Sunrise Free Radical School Presentation by: Bruce Freeman, Ph.D.
2 Lipid xidation Bruce Freeman, PhD Department of Pharmacology and Chemical Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
3 Brief History Milestones in Lipid xidation BCE Fat was subjected to base hydrolysis to make soap 1800 Walnut oil shown to consume 150x its volume in oxygen 1818 Cholesterine described in gallstones 1827 Fat, in addition to protein and CH, reported as key dietary constituent 1834 Chloroform, diethyl ether utilized for lipid extractions Free fatty acids purified, chain length/unsaturation described 1860 French patent awarded for margarine 1861 Lipases first described in plant seeds, pancreatic fluids 1881 Hydroxy fatty acid derivatives i first described d 1886 Diene nature of linoleic acid (18:2) and triene nature of linolenic acid (18:3) first described 1895 Diesel built first engine that ran on peanut oil 1895 First proposal red cell membranes made of lipids, 2 molecules thick 1899 Acetone used to separate phospholipids p p from cholesterol, glycerides
4 Brief History Milestones in Lipid xidation 1902 Patent issued for conversion of unsaturated fatty acids and glycerides into saturated fats 1903 Cobra venom shown to hydrolyze phosphatidylcholine 1909 Arachidonic acid (20:4) first isolated from liver lipids 1913 Lipid soluble vitamins first recognized as necessary 1922 Antioxygenes" identified as phenolic substances preventing the oxidation butter and other vegetable oils 1926 Term lipid first used 1930 Dietary essentiality of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids recognized 1932 Description of a fatty acid oxidase activity ("lipoxydase") in soybean 1935 Eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic (20:5, 22:6) first identified in sardine oil, term steroids first coined, tocopherol structure ID ed 1939 Inositol and inositol phosphate lipids first described 1943 Hydroperoxides identified as constituents of rancid fat :2 observed to be a precursor of 20:4 fatty acid elongation
5 Brief History Milestones in Lipid xidation 1951 TLC, GLC, alumina column chromatography and rotavaps used!! 1952 Trans fatty acids were detected in biological specimens 1953 Acetylcholine was observed to initiate diglyceride release from membrane PL, mitochondrial β-oxidation described 1957 First detection of prostaglandins, :4 conversion to PGE Artificial membranes (liposomes) produced 1972 Serum cholesterol, LDL and triglyceride levels linked with CAD, platelet activating factor (PAF, alkyl acetyl PC) first described, fluid mosaic model of cell membrane proposed 1975 Phosphatidyl inositol effect linked with regulation of cell Ca levels 1978 EPA (20:5) linked with inhibition of thrombosis, atherosclerosis 1979 Leukotrienes (H derivatives of 20:4, SRS-A) first described 1980 Free radical oxidation of membrane phospholipids described xidation of lipoproteins results in pro-atherogenic foam cell formation 1982 Nobel Prize for prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes 1985 Nobel Prize for regulation of cholesterol metabolism
6 Brief History Milestones in Lipid xidation 1985 Fish oil reported to reduce intimal proliferation after vein grafting 1987 Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) described as anti-cancer, cardioprotective 1990 Isoprostanes described as free radical oxidation products of 20: Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors and other nuclear lipid receptors described arachidonyl glycerol described as ligand for cannabinoid receptor F4-neuroprostanes, isothromboxanes and F3-isoprostanes described 1999 Nitrogen dioxide observed to induce cis-trans isomerization of 20: Hydroxytriene derivatives of 20:5, 20:6 shown to be anti-inflammatory Electrophilic FA shown to be anti-inflammatory, PPARγ ligands
7 Lipids First Viewed as Metabolic Intermediates And Membrane Structural Components
8 New View Enzymatic and Autocatalytic xidation of Lipids Yields Products that Mediate Cell Signaling via Discrete Reactions with Receptors, Transcription Factors, Protein Kinases and Key Enzymes of Intermediary Metabolism Peroxisome Proliferator Activated G-Protein Coupled Receptors Receptor Retinoid X Receptor Heterodimer
9 Fatty Acids Fatty Acids have common and IUPAC names and numerous acronyms Linoleic Acid ctadeca-9,12-dienoic acid H 18:2 m/z 279 LA H Arachidonic Acid Eicosatetraenoic Acid Dodeca-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid 20:4 m/z 303 AA Myristic i acid (14:0) m/z 227 Linolenic i Acid (18:3) m/z 277 Palmitic acid (16:0) m/z 255 Arachidic Acid (20:0) m/z 311 Stearic acid (18:0) m/z 283 Eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5) m/z 301 leic acid (18:1) m/z 281 Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6) m/z 327 m/z values for negative ion mode
10 Lipids - ~180,000 different species/cell Fatty Acids Steroids Lipid Vitamins Terpenes Eicosanoids Triglycerides Waxes Sphingolipids Glycerophospholipids Ceramides Ether Phospholipids Sphingomyelins Cerebrosides Gangliosides Plasmalogens Diacyl-Linked Phospholipids p Platelet- Activating Factor ther Glycosphingo- lipids Phosphatidyl- Phosphatidyl- Phosphatidyl- Phosphatidyl- ther cholines ethanolamines serines Inositols Phospholipids
11 Phospholipid Structures Polar Head Group R 2 C C P - R 1 Phosphatidylcholine C R 1 R 2 C H H H N+ P - Phosphatidylinositol H H C R 1 R C 2 R 2 C P + NH 3 - Phosphatidylethanolamine C P - - R 1 Phosphatidic acid R 2 C C P - R 1 + NH 3 R 2 C C- Phosphatidyl h serine C R 1 P - H H Phosphatidylglycerol
12 Glycerolipid Bond Type at the sn-1 Carbon R-C- -C-R R-C- CH 2 CH 2 -R R-C- CH=CH-R P -Base P -Base P -Base Diacyl- 1--alkyl-2-acyl- 1--alk-1 -enyl-2-acyl- (plasmalogen) H 3 C-C- CH 2 CH 2 -R 1 PC
13 Glycerolipid Bond Type at the sn-1 Carbon R-C- -C-R R-C- CH 2 CH 2 -R R-C- CH=CH-R P -Base P -Base P -Base Diacyl- 1--alkyl-2-acyl- 1--alk-1 -enyl-2-acyl- (plasmalogen) H 3 C-C- CH 2 CH 2 -R 1 Phospholipase A 2 PC Preferentially hydrolyzes oxfa at sn-2 position FRBM 1985, 1:
14 5-oxo-ETE 5-HETE H H H H H Palmitate Arachidonate PC PLA 2 Arachidonic Acid Metabolites are, in general, pro-inflammatory 5-HpETE 5-L Arachidonic Acid H H LTA 4 LTC 4 LTD 4 LTE 4 H H H SCH2 HCH 2CHNCHC NHC(CH2) 2CHCH NH 2 H H SCH2 HCH2CHNCHC NH2 H H SCH2 HHC NH2 H LTB 4 H PGD 2 H H PGE 2 PGHS H H H H PGG 2 H H H H H H TXA 2 H H H PGF 2α xidation H H H H H H PGI 2 H H H H H H H H H H Type III H Type IV Type V Type VI
15 Peroxidation of Unsaturated Fatty Acids 18:2 H-abstraction conjugated diene 2 Propagation (k = M -1 s -1 ) α-th - L. (k = M -1 s -1 ) N. - L. (k = M -1 s -1 ) 18:2 propagation Fe +2 Fe +3 -tocopherol termination H propagation
16 Principal Peroxidation Products 18:2 H-abstraction conjugated diene 2 18:2 propagation -tocopherol termination H Fe +2 Fe +3 propagation
17 Iron Enhances Lipid Peroxidation Iron and other transition metals catalyze the oxidation of biomolecules Iron oxidizes unsaturated fatty acids indirectly via the generation of iron-oxo complexes, partially reduced oxygen species and lipid alkoxyl and peroxyl radicals Agents that reduce Fe(II) to Fe(II) accelerate lipid oxidation Peroxynitrite-induced lipid oxidation is Fe-independent Fe (II) + 2 Fe (III) H + H H +H Fe (II) Fe(III) + H RH + X-Fe (II) R + H - + X-Fe(III) R + LH RH + L L + 2 L
18 Free radical-mediated reactions Two epimeric ChHs are generated: 3β-hydroxycholest-5-ene-7α-hydroperoxide (7α-H) 3β-hydroxycholest-5-ene-7β-hydroperoxide (7β-H). These are accompanied by: cholest-5-ene-3β,7α-diol (7α-H) cholest-5-ene-3β,7β-diol (7β-H) 5,6-epoxide epimers, and the 7-ketone. CE oxidation can give rise to species modified in either the cholesteryl or fatty acyl moiety, or both. Singlet oxygen-mediated reactions Cholesterol xidation Three ChHs are formed via ene-type addition: 3β-hydroxy-5α-cholest-6-ene-5-hydroperoxide ene 5 hydroperoxide (5α-H, major) 3β-hydroxycholest-4-ene-6α-hydroperoxide (6α-H) 3β-hydroxycholest-4-ene-6β-hydroperoxide (6β-H). 5α-H, 6α-H and 6β-H can be chemically or enzymatically reduced to 5α-H, 6α-H and 6β-H, respectively. Thanks to A. Girotti
19 Nitric xide Plays an Inextricable Role in Regulating Lipid xidation N accelerates the rate and increases the breadth of reactions that transduce redox signaling N promotes covalent target molecule modification by serving as a precursor for oxidizing, nitrosating and nitrating species N is lipophilic, p concentrates in membranes, lipoproteins p N modulates both the gene expression and catalytic activity of cyclooxygenases and and lipoxygenases N participates in reactions that both stimulate and inhibit lipid peroxidation, depending on the underlying oxidative mileu Lipid peroxidation processes catalytically consume N and can impact on cgmp-dependent d signaling
20 Nitric xide Modulates.- 2 /H 2 2 /Fe Induced Fatty Acid xidation X LN 2 Formation N switches from oxidative to nitrosative/nitrative chemistry 2 N N - H + N H C 2 N C 2 N + L LN LH, LN 2, L()N 2, N - 2 J Biol Chem 269: , 1994
21 xygen is Consumed by Lipid xidation 300 Azo α -Tocopherol (1 µm) xy ygen (µm M) T inhibition N (1 µm) T inhibition Time (seconds) Biochemistry 1997, 36:15216
22 Lipoxygenase Consumes. N via Reaction With Enzyme-Bound Peroxyl Radical Intermediate Peroxide Activation E ox LH E red L red LH LH 2 Dioxygenase Reaction E red E red L LN N Radical Termination N E red LN LH, N 2 - JBC 274: , 1999; PNAS 98: , 2001
23 New Perspective Lipid xidation Products Modulate the Expression of Adaptive Genes rganisms have evolved a set of proteins that sense oxidized, electrophilic species (such as lipid oxidation products) that in turn activate adaptive signaling mechanisms mediated by receptors, transcription factors and protein kinases
24 Electrophilic Fatty Acids Inhibit NF-κB Signaling P 4 = IκB IκB kinase IκB-Pi ubiquitination and proteosomal degradation P50/p65 Cys38-SH P50/p65 Cys38-SH EFA NS2 Cytokines Chemokines S-EFA SH
25 Electrophilic Fatty Acids Induce Phase II Gene Expression Keap1 SH EFA S-EFA Keap1 ubiquitination proteosomal degradation Nrf2 Electrophile and Antioxidant Response Elements EpRE, ARE Nrf2 Phase II Gene Expression H-1 GSH GSH biosynthetic enzymes GSH peroxidase GSH reductase Epoxide hydrolase NADPH-generating enzymes
26 Electrophilic FA Induce H-1 Expression Rodent Aorta Heme H-1 C, Bilirubin, Biliverdin Control No Ab Nitrolinoleate PNAS 103: , 2006 PNAS 2006, 103:4299
27 Electrophilic Fatty Acids Induce Heat Shock Factor-Dependent Gene Expression Electrophiles H 2 2 Cys35, Cys105 HSF-60 HSF-70 HSF-90
28 Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors Bind lipophilic ligands, regulate nuclear transcription of genes encoding metabolic, inflammatory proteins Saturated fatty acids xidized fatty acids Sat/Unsat Fatty Acids Fibrates Thiazolidinediones (Rosiglitazone) Tyr analogs with carboxylate, acyl, N-substituents
29 PPAR-Dependent Genes Cytoplasm u u Degradation PPAR Ligands Co-repressor Nucleus P PPAR Coactivator RXR AGGTCA (N) AGGTCA PPRE Target genes 9-cis-RA
30 PPARγ Helix 12 Ligand alters Helix 12 conformation Helix 12 directs ligand-specific corepressor dissociation, co-activator binding patterns Co-regulator protein interactions define nature of transcriptional complex and thus ligand-specific gene expression patterns Ligand EC50 Unsaturated Fatty acids (18-22 C, 1-6 C=C) >25 μm 9 and 13-hydroxy-octadecadienoic acids >10 μm Various hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acids >10 μm 15-d-PGJ 2, LTB 4 > 1 μm PAF, lyso-pc > 1 μmm Rosiglitazone 50 nm Nitro derivatives of 18:1, 18: nm Various oxo derivatives of 20:5, 22:6? μmm
31 PPARγ Helix 12 Covalent binding of electrophilic fatty acid ligands (via Michael addition i to Cys285) uniquely alters Helix 12 conformation, displays non-traditional binding kinetics and ultimately induces unique gene expression patterns Nature Struct Mol Biol, 2008
32 Detection of Lipid xidation xygen consumption Loss of unsaturated fatty acids by GC- or HPLC-MS Conjugated diene formation by UV detection Schiff s base fluorophores Malonyldialdehyde (thiobarbituric acid-reactive) Ethane (n-3), pentane (n-6) Isoprostanes, neuroprostanes, isoketals HPLC-MS detection of specific oxidation products
33
34 Cool and Useful Lipid Links PPAR Helix info nih fatty acids aspx uk/iupac/lipid/ Ligand induces Helix 12 conformational change Helix 12 directs ligand-specific patterns of co-repressor dissociation and co-activator html binding Determines ligand-specific gene expression patterns wikipedia Challenge for PPARγ ligand pharmacology increase insulin sensitivity without fluid retention, weight gain, blood pressure edu/cellbio/membrane increase intro htm
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Detection of Lipid Peroxidation Products From Free Radical and Enzymatic Processes. Jason D. Morrow M.D. Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 Detection of Lipid Peroxidation Products From Free Radical and Enzymatic Processes Jason D. Morrow M.D. Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Question? Which one of the following is the most accurate
Detection of Lipid Peroxidation Products From Free Radical and Enzymatic Processes Jason D. Morrow M.D. Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Question? Which one of the following is the most accurate
Fats and Lipids (Ans570)
 Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Organic molecules highly hydrophobic and water insoluble.
 UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
OXIDIZED LIPIDS FORMED NON-ENZYMATICALLY BY REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES
 JBC Papers in Press. Published on February 19, 2008 as Manuscript R800006200 The latest version is at http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/10.1074/jbc.r800006200 OXIDIZED LIPIDS FORMED NON-ENZYMATICALLY BY REACTIVE
JBC Papers in Press. Published on February 19, 2008 as Manuscript R800006200 The latest version is at http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/10.1074/jbc.r800006200 OXIDIZED LIPIDS FORMED NON-ENZYMATICALLY BY REACTIVE
26.1 Acetyl Coenzyme A
 Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Microreview. A.-F. Miller, 2008, pg
 Microreview Polysaccharides: a vast diversity based on stereochemistry. Stereochemical differences are associated with secondary and tertiary structural differences: nature s huge and plentiful polymers.
Microreview Polysaccharides: a vast diversity based on stereochemistry. Stereochemical differences are associated with secondary and tertiary structural differences: nature s huge and plentiful polymers.
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
Reactivity and Biological Functions of Oxidized Lipids
 Reactivity and Biological Functions of Oxidized Lipids Matthew J. Picklo, Sr. Outline 1. Lipid Oxidation Mechanisms and Products 2. Biological Mechanisms 3. n-3 vs n-6 PUFA Oxidation 1. Fatty acids 2.
Reactivity and Biological Functions of Oxidized Lipids Matthew J. Picklo, Sr. Outline 1. Lipid Oxidation Mechanisms and Products 2. Biological Mechanisms 3. n-3 vs n-6 PUFA Oxidation 1. Fatty acids 2.
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Chapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids
 common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Nitrated Fatty Acids Formation and Actions Bruce Freeman, PhD Department of Pharmacology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
 Nitrated Fatty Acids Formation and Actions Bruce Freeman, PhD Department of Pharmacology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Sunrise Free Radical School SFRBM 2005 Austin,Tx Bruce Freeman 1 Objectives
Nitrated Fatty Acids Formation and Actions Bruce Freeman, PhD Department of Pharmacology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Sunrise Free Radical School SFRBM 2005 Austin,Tx Bruce Freeman 1 Objectives
Chapter 20 Lipids. Organic and Biochem
 Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition. phospholipids. Sphingolipids. Cholesterol. db=books&itool=toolbar
 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry. General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4. Lipids
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
Types of Free Radicals
 Terminology Lipid Oxidation and Lipid peroxidation Free Radicals and Reactive oxygen species Fatty acyl group and methylene group Hydroperoxides and lipid peroxides Peroxyl radicals and alkoxyl radicals
Terminology Lipid Oxidation and Lipid peroxidation Free Radicals and Reactive oxygen species Fatty acyl group and methylene group Hydroperoxides and lipid peroxides Peroxyl radicals and alkoxyl radicals
Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15
 Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15 Principle: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long (usually > 14) carbon chains which can be saturated (no carbon-carbon double bonds) are unsaturated
Chem 5 PAL Worksheet Lipids Smith text Chapter 15 Principle: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long (usually > 14) carbon chains which can be saturated (no carbon-carbon double bonds) are unsaturated
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Chapter 11: Lipids. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Lipids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8
 Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Nonessential fatty acids ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism A. Synthesized completely by the fatty acid synthase reaction (e.g., myristic and palmitic acid). B. Produced by the modification of
I. Nonessential fatty acids ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism A. Synthesized completely by the fatty acid synthase reaction (e.g., myristic and palmitic acid). B. Produced by the modification of
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
4 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 24 th 2013 Ahmad Moayd 1 Definition and general properties refer to slide no. 2 Lipids: macromolecules made from Alcohol and Fatty acid bonded by ester linkage. Amphipathic
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
Ahmad O. Olimat. Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh. Dr.Mamoun
 10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
Optimising. membranes
 Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202
 General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
General Biochemistry-1 BCH 202 1 I would like to acknowledge Dr. Farid Ataya for his valuable input & help in this course. 2 Outline Lipids Definition, function, fatty acids, classification: simple lipids:
Enzymatic oxidation of lipids: mechanisms and functions.
 Enzymatic oxidation of lipids: mechanisms and functions. Valerie B. O Donnell, PhD. Cardiff University. Enzymatic lipid oxidation: involves an enzyme catalyst, and gives very specific stereo- and regiospecific
Enzymatic oxidation of lipids: mechanisms and functions. Valerie B. O Donnell, PhD. Cardiff University. Enzymatic lipid oxidation: involves an enzyme catalyst, and gives very specific stereo- and regiospecific
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM. BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
CH 3. Lipids CHAPTER SUMMARY
 H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
Chapter 10 Homework Assignment
 hapter 10 Homework Assignment I have decided to alter the homework assignment for hapter 10. The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 2, 4, 5, 6, 9 Lipids are Good (and not always
hapter 10 Homework Assignment I have decided to alter the homework assignment for hapter 10. The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 2, 4, 5, 6, 9 Lipids are Good (and not always
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Thin layer absorption chromatography can achieve very good separation of small lipid samples
 Abbreviations Preface Acknowledgements Lipids: definition, isolation, separation and detection p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Definitions p. 1 Structural chemistry and nomenclature p. 1 Extraction of lipids from
Abbreviations Preface Acknowledgements Lipids: definition, isolation, separation and detection p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Definitions p. 1 Structural chemistry and nomenclature p. 1 Extraction of lipids from
BIOCATALYTIC CONVERSION OF OTHER LIPIDS
 Chapter 6 BIOCATALYTIC CONVERSION OF OTHER LIPIDS In Chapters 4 and 5, lipase-mediated conversion of acylglycerols were presented. The Chapter 6 deals with biocatalytic modification of phospholipids, sphingolipids,
Chapter 6 BIOCATALYTIC CONVERSION OF OTHER LIPIDS In Chapters 4 and 5, lipase-mediated conversion of acylglycerols were presented. The Chapter 6 deals with biocatalytic modification of phospholipids, sphingolipids,
Prostaglandins And Other Biologically Active Lipids
 Prostaglandins And Other Biologically Active Lipids W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student will: 1. Draw the structure of a prostaglandin, name the fatty
Prostaglandins And Other Biologically Active Lipids W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student will: 1. Draw the structure of a prostaglandin, name the fatty
Lipids and Biological Membranes
 Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Lipids. Lipids. Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague
 Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Cholesterol Oxidation. Mechanisms and Signature Products
 : Mechanisms and Signature Products Albert W. Girotti, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee, WI 53226, USA Tel: 414-456-8432 Fax: 414-456-6510 E-mail: agirotti@mcw.edu
: Mechanisms and Signature Products Albert W. Girotti, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee, WI 53226, USA Tel: 414-456-8432 Fax: 414-456-6510 E-mail: agirotti@mcw.edu
Lipid Chemistry. Presented By. Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair
 Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Chemistry Chapter 21
 Chemistry 2100 Chapter 21 Lipids Fa3y Acids CH oleic acid (mp 4 C) CH stearic acid (mp 70 C) Triacylglycerols Fatty Acids! The fatty acid components of triglycerides have certain things in common: 1.
Chemistry 2100 Chapter 21 Lipids Fa3y Acids CH oleic acid (mp 4 C) CH stearic acid (mp 70 C) Triacylglycerols Fatty Acids! The fatty acid components of triglycerides have certain things in common: 1.
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
Lipids. Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals. Storage Lipids: derivatives of fatty acids. 11/21/10
 1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
DIETARY LIPIDS, IMMUNE FUNCTION AND PATHOGENESIS OF DISEASE IN FISH
 DIETARY LIPIDS, IMMUNE FUNCTION AND PATHOGENESIS OF DISEASE IN FISH Santosh P. Lall and Joyce E. Milley National Research Council Canada, Institute for Marine Biosciences, 1411 Oxford Street, Halifax,
DIETARY LIPIDS, IMMUNE FUNCTION AND PATHOGENESIS OF DISEASE IN FISH Santosh P. Lall and Joyce E. Milley National Research Council Canada, Institute for Marine Biosciences, 1411 Oxford Street, Halifax,
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM. Fatty Acid Elongation and Desaturation
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
Organism. Organ and organ systems. Tissue. Cells. Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids
 hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
hemistry of Life rganism rgan and organ systems Tissue ells arbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Thiols, Aldehydes, Ketones, arboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines,
ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS - RED CELL
 Healthscope Functional Pathology 1868 Dandenong Road, Clayton, Victoria 3168, Australia www.functionalpathology.com.au ABN 62 006 823 089 T 1300 55 44 80 F 03 8540 5555 infofp@healthscope.com.au LAB No:
Healthscope Functional Pathology 1868 Dandenong Road, Clayton, Victoria 3168, Australia www.functionalpathology.com.au ABN 62 006 823 089 T 1300 55 44 80 F 03 8540 5555 infofp@healthscope.com.au LAB No:
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids Storage lipids: TG lipid 의기능 : 1 Energy source 3 Electrical insulator 2 Thermal insulator 4 Membrane 의구성성분, 방수, 부력, cofactor, signaling 등 지방대사이상 : obesity, atherosclerosis,
Dr. Mamoun. Loai Azar
 13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
13 Dr. Mamoun Loai Azar Lipids (2) - To get the best of this sheet PLEASE study it side by side with the doctor s slides. - In this lecture the doctor continued talking about Eicosanoids. Derived Fatty
Biomolecules: lipids
 Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
LIPIDS Introduction - complex lipids. Marek Vecka
 LIPIDS Introduction - complex lipids Marek Vecka CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS IV - biosynthetic route Lipid class Fatty acyls Glycerolipids Glycerophospholipids Sphingolipids Sterol lipids Prenol lipids Other
LIPIDS Introduction - complex lipids Marek Vecka CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS IV - biosynthetic route Lipid class Fatty acyls Glycerolipids Glycerophospholipids Sphingolipids Sterol lipids Prenol lipids Other
FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS
 FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS Dicarboxylic acids, ketone bodies. Department of General Chemistry Structure and classification of lipids Lipids can be divided into five categories, on the
FATTY ACIDS (FAs) SIMPLE AND COMPLEX LIPIDS Dicarboxylic acids, ketone bodies. Department of General Chemistry Structure and classification of lipids Lipids can be divided into five categories, on the
Objectives By the end of lecture the student should:
 Objectives By the end of lecture the student should: Illustrate α oxidation of fatty acids. Understand ω oxidation of fatty acids. List sources and fates of active acetate. Discuss eicosanoids. 2- α Oxidation
Objectives By the end of lecture the student should: Illustrate α oxidation of fatty acids. Understand ω oxidation of fatty acids. List sources and fates of active acetate. Discuss eicosanoids. 2- α Oxidation
Membrane Lipids & Cholesterol Metabolism
 Membrane Lipids & Cholesterol Metabolism Learning Objectives 1. How Are Acylglycerols and Compound Lipids Produced? 2. The synthesis of Sphingolipids from Ceramide 3. Diseases due to Disruption of Lipid
Membrane Lipids & Cholesterol Metabolism Learning Objectives 1. How Are Acylglycerols and Compound Lipids Produced? 2. The synthesis of Sphingolipids from Ceramide 3. Diseases due to Disruption of Lipid
PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA
 PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Alena Buretić-Tomljanović 1, Jasminka Giacometti 1, Sergej Nadalin 1, Gordana Rubeša 2, Mirjana Vulin 3, Draško
PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Alena Buretić-Tomljanović 1, Jasminka Giacometti 1, Sergej Nadalin 1, Gordana Rubeša 2, Mirjana Vulin 3, Draško
: Overview of EFA metabolism
 Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
Lipids. Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids.
 Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
STRUCTURE AND METABOLISM Of LIPIDS AND LIPOPROTEINS. R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty
 STRUCTURE AND METABOLISM Of LIPIDS AND LIPOPROTEINS R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty STRUCTURE OF LIPIDS AND LIPOPROTEINS DEFINTITION: Compounds Insoluble in water But
STRUCTURE AND METABOLISM Of LIPIDS AND LIPOPROTEINS R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty STRUCTURE OF LIPIDS AND LIPOPROTEINS DEFINTITION: Compounds Insoluble in water But
Roles of Lipids in the body
 Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Nebal Al - Gallab. Shatha Al - Jabri. Mamoon Ahram
 10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
Seminar 6 Theoretical part
 Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
Seminar 6 Theoretical part Lipids are a heterogeneous group of naturally occurring organic compounds, classified together on the basis of their common solubility properties. Lipids are insoluble in water,
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY
 BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
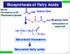 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids CH 511 ource b-oxidation of FA Glycolysis of glucose n H CoA Acetyl CoA CoA Malonyl CoA Carboxylation of acetyl CoA H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 n-1 CoA aturated thioesters aturated fatty
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids CH 511 ource b-oxidation of FA Glycolysis of glucose n H CoA Acetyl CoA CoA Malonyl CoA Carboxylation of acetyl CoA H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 n-1 CoA aturated thioesters aturated fatty
Lipids Analysis. Lipids
 Lipids Analysis Stephen Barnes 3 5 15 Lipids Lipids are mostly very hydrophobic Most are conjugates of fatty acids of a variety of chain lengths, which have different degrees of unsaturation, cis trans
Lipids Analysis Stephen Barnes 3 5 15 Lipids Lipids are mostly very hydrophobic Most are conjugates of fatty acids of a variety of chain lengths, which have different degrees of unsaturation, cis trans
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LOOKING FOR LIPID PEROXIDATION IN VITRO AND IN VIVO: IS SEEING BELIEVING? Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Jason D.
 LOOKING FOR LIPID PEROXIDATION IN VITRO AND IN VIVO: IS SEEING BELIEVING? Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Jason D. Morrow MD Which of the following assays of lipid peroxidation may be useful and
LOOKING FOR LIPID PEROXIDATION IN VITRO AND IN VIVO: IS SEEING BELIEVING? Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Jason D. Morrow MD Which of the following assays of lipid peroxidation may be useful and
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY
 FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
Introduction to Lipid Chemistry
 Introduction to Lipid Chemistry Benjamin Schwartz Ontario SCC Education Day September 18, 2018 Lipid knowledge for the personal care industry What is a Lipid? Lipids are fatty acids and their derivatives,
Introduction to Lipid Chemistry Benjamin Schwartz Ontario SCC Education Day September 18, 2018 Lipid knowledge for the personal care industry What is a Lipid? Lipids are fatty acids and their derivatives,
Important reactions of lipids
 Taif University College of Medicine Preparatory Year Students Medical chemistry (2) Part II (Lipids) week 4 lectures 1435-36 Important reactions of lipids Lectures outlines Definition and importance of
Taif University College of Medicine Preparatory Year Students Medical chemistry (2) Part II (Lipids) week 4 lectures 1435-36 Important reactions of lipids Lectures outlines Definition and importance of
Fats Can Be Good For You!
 Fats Can Be Good For You! Fat Quiz (True or False) 1. Excess fat in the diet is a major cause of heart disease. 2. Saturated fats raise cholesterol levels. 3. The saturated fats in butter and coconut oil
Fats Can Be Good For You! Fat Quiz (True or False) 1. Excess fat in the diet is a major cause of heart disease. 2. Saturated fats raise cholesterol levels. 3. The saturated fats in butter and coconut oil
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Nitric Oxide and Lipid Peroxidation
 Nitric Oxide and Lipid Peroxidation Valerie B. O Donnell a, Neil Hogg b and Victor M. Darley Usmar c a Dept of Med. Biochem. University of Wales College of Medicine, Heath Park, Cardiff CF14 4XN, UK. Ph:
Nitric Oxide and Lipid Peroxidation Valerie B. O Donnell a, Neil Hogg b and Victor M. Darley Usmar c a Dept of Med. Biochem. University of Wales College of Medicine, Heath Park, Cardiff CF14 4XN, UK. Ph:
Eicosanoid synthesis
 Seminar 12 Eicosanoid synthesis Examples of eicosanoids prostaglandins prostacyclins thromboxanes leukotrienes epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EET) They have roles in: inflammation fever regulation of blood
Seminar 12 Eicosanoid synthesis Examples of eicosanoids prostaglandins prostacyclins thromboxanes leukotrienes epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EET) They have roles in: inflammation fever regulation of blood
INTEGRATIVE MEDICINE BLOOD - EDTA Result Range Units
 D Collected : 00-00-0000 INTEGRATIVE MEDICINE BLOOD - EDTA Result Range Units RED CELL FATTY ACID PROFILE Red Cell Fatty Acid Summary Saturated Fats, Total 36.99 19.30-39.40 Monounsaturated Fats, Total
D Collected : 00-00-0000 INTEGRATIVE MEDICINE BLOOD - EDTA Result Range Units RED CELL FATTY ACID PROFILE Red Cell Fatty Acid Summary Saturated Fats, Total 36.99 19.30-39.40 Monounsaturated Fats, Total
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics
 Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
0 P a g e. Done by: Amani Nofal
 0 P a g e Done by: Amani Nofal *acid and base* 1- All of the following will cause mild or severe acidosis except: A) the presence of ketone bodies in untreated diabetic patient b) The production of acids
0 P a g e Done by: Amani Nofal *acid and base* 1- All of the following will cause mild or severe acidosis except: A) the presence of ketone bodies in untreated diabetic patient b) The production of acids
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
 LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
LIPIDS OF PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE Original slides. Important. 436 Notes 438 notes Extra information رابط التعديل: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1wvdec1atp7j- ZKWOUSukSLsEcosjZ0AqV4z2VcH2TA0/edit?usp=sharing
Saba Al Fayoumi. Nour Hamdan. Bann Khraisat. Dr. Mamoun Ahram
 9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
9 Saba Al Fayoumi Nour Hamdan Bann Khraisat Dr. Mamoun Ahram Proteoglycans and glycoproteins have been previously discussed and the differences between them have been noted. Protein glycosylation (protein-linked
