Cell Membrane And Transport Study Guide Answers
|
|
|
- Sheryl Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CELL MEMBRANE AND TRANSPORT STUDY GUIDE ANSWERS PDF - Are you looking for cell membrane and transport study guide answers Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time cell membrane and transport study guide answers PDF is available at our online library. With our complete resources, you could find cell membrane and transport study guide answers PDF or just found any kind of Books for your readings everyday. We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell membrane and transport study guide answers. To get started finding cell membrane and transport study guide answers, you are right to find our website which has a comprehensive collection of manuals listed. Our library is the biggest of these that have literally hundreds of thousands of different products represented. You will also see that there are specific sites catered to different product types or categories, brands or niches related with cell membrane and transport study guide answers. So depending on what exactly you are searching, you will be able to choose ebooks to suit your own need Need to access completely for Ebook PDF cell membrane and transport study guide answers You could find and download any of books you like and save it into your disk without any problem at all. We also provide a lot of books, user manual, or guidebook that related to cell membrane and transport study guide answers PDF, such as ; Cell Membrane And Cell Transport Webquest Active And... cell membrane and cell transport webquest active and passive... which part of the membrane might function to transport hydophilic or water loving substances into the cell? 4. what are two reasons why a substance cannot make it through the lipid bilayer?... draw what a cell membrane looks like and label the two components of the cell Cell Transport - Weebly 7.3 cell transport lesson objectives describe passive transport. describe active transport. lesson summary passive transport the movement of materials across the cell membrane 1 / 7
2 without using cellular energy is called passive transport. diffusion is the process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower... Osmosis, Diffusion And Cell Transport osmosis, diffusion and cell transport. types of transport there are 3 types of transport in cells: bulk transport involves the cell membrane making vesicles to bring materials in and out of... merges with the cell membrane and the materials are released into the outside environment. Biology 12 - Cell Membrane & Transport Review Worksheet b. if a red blood cell is placed in distilled water, it will shrink c. if a plant cell is placed in distilled water, the cell membrane will move away from the cell wall d. if a red blood cell is placed in a salt solution, salt will enter the cells, giving them a strange appearance e. Module 3 Lecture 1 Transport Across Cell Membrane membrane proteins called carriers, permeases, channels and transporters. unlike active transport, this process does not involve chemical energy. so the passive mediated transport is totally dependent upon the permeability nature of cell membrane, which in turn, is function of organization and characteristics of membrane lipids and proteins. Ap Biology- The Cell / Plasma Membrane And Cellular Processes ap biology- the cell / plasma membrane and cellular processes the cell / plasma membrane: made up of phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and other lipids.... they serve as transport channels for particles to enter and leave the cell they produce vesicles containing proteins that will fuse with the cell membrane and Cells And Cell Transport - Centennial School District cells and cell transport p. 19 p. 21 p. 23 p. 25 p. 20 p. 22 p. 24 vocabulary cell tissue cell membrane (plasma membrane) nucleus ribosome mitochondrion chloroplast protein synthesis active transport carrier (transport) proteins concentration gradient diffusion endocytosis endoplasmic reticulum endosymbiosis Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure And Function chapter 4: membrane structure and function cell membrane proteins: 1) transport proteins: regulate movement of hydrophilic molecules through membrane a) channel proteins (e.g. na+ channels) b) carrier proteins (e.g. glucose transporter) 2) receptor proteins: trigger cell activity when molecule from outside environment binds to protein Chapter 5: Cell Membrane Structure And Function chapter 5: cell membrane structure and function chapter 5: membrane structure and function plasma membrane: thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from the outside environment function: 1) isolate cell?s content from outside environment 2) regulate exchange of substances between inside / outside cell 3) communicate with other cells Cell Transport Practice Test d. move across the membrane to the inside of the cell. 6. the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called a. osmotic pressure. b. osmosis. c. pinocytosis. d. 2 / 7
3 active transport. 7. an animal cell that is surrounded by fresh water will burst because the osmotic pressure causes a. water to move into the cell. b... The Cell Membrane - Library.vcc.ca transport in/out of the cell through the cell membrane: passive transport (no atp is expended) diffusion the net movement of a substance (atoms, molecules, or ions) down Membrane Transport And Cell Signaling - Anderson.k12.ky.us membrane transport and cell signaling. overview: life at the edge the plasma membrane separates the living cell from its surroundings... substances across the membrane some transport proteins, called channel proteins, have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or Cell Transport Webquest - Sjsd.k12.mo.us cell membrane & cell transport webquest press next 28. define osmosis: 29. draw a before and after for a cell in a hypotonic solution. show the change in size of the cell. 30. draw a before and after for a cell in a hypertonic solution. show the change in size of... Lab. Cell Membranes - Explore Biology lab. cell membranes the cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also aids in the protection... the cell membrane is composed of several kinds of molecules. the most important of these are... proteins serve as transport proteins acting as channels or tunnels through which molecules Cell Membranes, Transport, And Communication Teacher Packet cell membranes, transport, and communication free response 1. the cell membrane is much more than a passive barrier of the cell. (a) describe in detail the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. (6 pt maximum) phospholipid description (polar head, nonpolar tails) phospholipid bilayer (must explain significance with reference to polarity) Name: Block: Date - Homework c. of active transport the concentration ([]) of na is greater outside a cell, the [] of k is greater inside a cell 7. list 3 ways in which active transport differs from the process of diffusion across a cell membrane. Cancer Cell Membranes And Metastasis - Njms.rutgers.edu cancer cell membranes and metastasis - lecture outline 1. changes at the cancer cell surface... cell membrane composition the chief membrane components are lipids, proteins, glycoproteins,... transport of nutrients has been observed with cultured cells. after transformation of mammalian or avian fibroblasts by oncogenic dna Transport Across Cell Membrane - Mar Athanasius College membrane proteins called carriers, permeases, channels and transporters. unlike active transport, this process does not involve chemical energy. so the passive mediated transport is totally dependent upon the permeability nature of cell membrane, which in turn, is function of 3 / 7
4 Cell Membrane And Transport Review Sheet - Indianhills.edu cell membrane and transport review sheet transport of nutrients, ions, and excretory substances from one side to the other is a major function of the cell membrane. a number of different means have been developed to fulfill this function. generally, the permeation of small molecules across the membrane is quite different from engulfing Membrane Transport - Guido Li Volsi membrane transport if all body fluids were identical in composition, it would be easy to maintain body fluids. but, intracellular and extracellular fluids are very different. differences are maintained by pumps in plasma membrane selective permeability of plasma membrane. 2 Membrane Transport New - Faculty.mtsac.edu membrane transport cell membranes are selectively permeable some solutes can freely diffuse across the membrane some solutes have to be selectively moved across the membrane facilitated by a carrier or transport protein carrier mediated transport (passive transport) active transport Orise Lesson Plan: The Cell Membrane selectively permeable membrane. the cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that can be found in all cells. it allows some substances to pass through freely without the use of energy. this is known as passive transport. the passage of substances through the membrane with use of energy is known as active transport. Chapter 4 Cells, Cell Structure & Cell Transport chapter 4 cells, cell structure & cell transport cell theory 1.all organisms are composed of one or more cells... cell membrane) to freely diffuse in/out of the cell. these channels come into greatest use with small ions like k+, na+, and cl-. the speed of facilitated Membrane Structure And Function - Phoenix College plasma membrane: active transport active transport is a protein-mediated transport of molecules across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient (low to high solute concentration areas). it requires a boost of energy (atp) to occur. as facilitated diffusion, is very selective glucose is actively transported through the plasma... Name Date Period - Copley list 4 functions of the cell or plasma membrane: a. cell signaling b. selective transport c. excretion of wastes d. structural support correctly color code and identify the name for each part of the cell membrane. letter name/color letter name/color a phospholipid bilayer (no color) h peripheral protein (red) Cell Transport And Plasma Membrane Structure cell transport and plasma membrane structure pogilguided inquiry learning targets explain the importance of the plasma membrane. compare and contrast different types of passive transport. explain how materials diffuse across a semipermeable membrane. Transport And The Cell Membrane - Moodle.northport.k12.ny.us 4 / 7
5 cell membrane structure: fluid mosaic model fluid mosaic model - the plasma membrane is composed of a double lipid layer in which large proteins float. the cell membrane the entry and exit of materials. Cell Membrane Transport - Modesto Junior College cell membrane transport: passive processes the cell membrane forms a boundary that is essential for life. this boundary supports life by controlling the movement of molecules and substances across it. some molecules and substances are transported across the cell membrane by processes that require the expenditure of energy. The Cell Membrane - Thieme Medical Publishers 2 the cell membrane i 11 several micrometers per second. several membrane transport processes and enzyme activities depend on the optimum fluidity of the cellular membrane. as membrane fluidity increases, there is a rise in membrane permeability to water and small hydrophilic solutes. the fluidity of a cell membrane de Biology Transport Webquest - Sjsd.k12.mo.us cell membrane & cell transport webquest press next 22. define osmosis: 23. draw a before and after for a cell in a hypotonic solution. show the change in size of the cell. 24. draw a before and after for a cell in a hypertonic solution. show the change in size of... Cell Transport Worksheet - Lhsblogs.typepad.com cell transport review cell transport movement of molecules in and out of the cell match the definition on the left with the term on the right. 1. large wastes or cell products are released from inside to outside a cell 2. diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. 3. Cellular Transport Review - Neshaminy School District cellular transport review osmosis label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments)... the shrinking of plant cells when water leaves so the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall is called plasmolysis cell transport lesson objectives describe passive transport. describe active transport. lesson summary class date passive transport the movement of materials across the cell membrane without using cellular energy is called passive transport. (diffusion is the process by which panicles move from an area of high concentration to an Name Lab Time/date Review Sheet The Cell: Transport... a transport system that requires that the cell provide atp. one such system moves substances across the cell membrane attached to a carrier molecule called a solute pump. engulfment of extracellular particles by pseudopod formation. cell eating. intake of extracellular fluids by vesicle formation. cell drinking. Ap 2006 Biology Form B Frq - College Board (c) cell membrane structure/signal transduction (d) membrane protein structure/active transport 5 / 7
6 or facilitated diffusion 2006 ap biology free-response questions (form b) Diffusion: Molecular Transport Across Membranes diffusion: molecular transport across membranes... special proteins embedded in the cell membrane can act as pumps to move molecules from a region of lower concentration through the cell membrane to a region of higher concentration. this type of active transport requires energy. Diffusion, Osmosis, And Membrane Transport - Jocha-biology cell membrane allows some materials to pass trough it, but prevent the movement of others. materials may move across the plasma membrane in two ways: passive transport and active transport, with the name indicating the Lab 2 Cell Structure And Cell Membrane observations of passive transport in rbc the plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the cell. the passive movement of water and dissolved... embedded into the cell membrane which act to equalize the internal pressures within the cell to inhibit major changes in their shape. red blood cells lack these proteins in... Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport - Biologymad active transport is the energy-demanding transfer of a substance across a cell membrane against its concentration gradient, i.e., from lower concentration to higher concentration. special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein carriers. Biology 4a Laboratory: Membrane Transport - Saddleback.edu biology 4a lab membrane transport page 1 of 5 biology 4a laboratory: membrane transport objectives... plant cells are surrounded by rigid cell walls, and under normal conditions, the cell membrane is pressed tightly against these cell walls. when plant cells are placed into an iso-osmotic (equal... Why? Model 1: Movement Of Water A Type Of Diffusion. spi the pogil project 3 limited use by permission only not for distribution transport in cells b1yvm2 read this! 6. predict the net direction of movement of the molecule that crosses the membrane by drawing an arrow into or out of the cell on the diagram in model 2. Topic 1.4: Membrane Transport - Bioninja.com.au vesicular transport the fluidity of the plasma membrane allows it to break and reform around certain materials (this process requires atp) exocytosis: materials released from a cell via vesicles endocytosis: materials internalised within a vesicle intracellular vesicles can move materials between cell organelles Chapter 4 Cell Membrane Transport - Lavc.edu chapter 4 cell membrane transport plasma membrane review o functions separate icf / ecf allow exchange of materials between icf / ecf such as obtaining o. 2. and nutrients and getting rid of waste products property of a membrane o permeable or semipermeable. 6 / 7
7 Transport Across Cell Membranes - Weebly transport across cell membranes. cell membrane structure a phospholipidbilayermakes up the main part of the cell membrane each phospholipidmolecule contains a charged polar head... passive transport: diffusion/osmosis diffusion is the movement of particles from an area Biological Membranes And Transport - Academic.mu.edu what types of molecules move across the cell membrane by passive transport or facilitated diffusion? 1. describe the kinetics of movement by passive transport. d. what types of molecules move across the cell membrane by active transport? 1. describe the different types of active transport Biology 102 Lecture 6: Cell Membranes biology 102 lecture 6: cell membranes 11.. physical isolation separates inside of cell from extracellular fluid cell membrane functions 2. regulates intracellular2. regulates intracellular--extracellular exchange extracellular exchange controls ions, nutrients, waste, and secretory product exchange cell membrane functions 3. Chapter 7: Cell Membrane Structure And Function biology i. chapter 7 cell membrane structure and function evelyn i. milian - instructor 2 plasma membrane (cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) the plasma membrane is the cell s flexible outer limiting barrier that separates the cell s internal environment from the external (extracellular) environment. Chapter Membrane Structure And Function How Do... channels remain permanently open and are used to transport ions and water across the cell membrane. 22. discuss with your group why the type of protein channel in model 3 is called a gated channel. Cell Membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi cell membrane to enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. to protect the cell. to allow substances into and out of the cell. to have metabolic reactions on its surface. "fluid mosaic model suggests" that the phospholipids form a bilayer framework, with their hydrophilic (polar) heads on the 7 / 7
Cell Membrane Transport Lab Answers
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell membrane transport
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cell membrane transport
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure And Function
 CHAPTER 7 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 7 membrane structure and function Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 7 membrane structure and function PDF
CHAPTER 7 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 7 membrane structure and function Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 7 membrane structure and function PDF
Transport. Slide 1 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 & Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
& Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells
 Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane. Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5
 Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Equilibrium when two areas have the same concentration or are filled evenly
 Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Cytology I Study of Cells
 Cytology I Study of Cells Biology 20 Which cell type has organelles such as mitochondria, nuclues, Golgi bodies, etc? A) prokaryotic B) eukaryotic C) bacterial D) viral E) none of these Cellular Basis
Cytology I Study of Cells Biology 20 Which cell type has organelles such as mitochondria, nuclues, Golgi bodies, etc? A) prokaryotic B) eukaryotic C) bacterial D) viral E) none of these Cellular Basis
The Cell Membrane. Why cells must control materials. Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival.
 The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
Membrane Structure and Function - 1
 Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3
 Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE. SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion).
 CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
Slide 2 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. End Show
 2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Plasma Membrane Function
 Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
BELLRINGER DAY In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane?
 BELLRINGER DAY 01 1. In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane? THE CELL MEMBRANE S T R U C T U R E A N D F U N C T I O N CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS Cell
BELLRINGER DAY 01 1. In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane? THE CELL MEMBRANE S T R U C T U R E A N D F U N C T I O N CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS Cell
9/20/2016 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES. Section Objectives. Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions.
 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function. Biology 12 Chapter 4
 Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT
 CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT Homeostasis: Maintaining a Balance Organisms must adjust to changes in their environment. If not DEATH! A formal definition is maintaining a stable internal condition despite
CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT Homeostasis: Maintaining a Balance Organisms must adjust to changes in their environment. If not DEATH! A formal definition is maintaining a stable internal condition despite
Outline. Membrane Structure and Function. Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
Cells: The Living Units
 Cells: The Living Units Introduction Life in general occurs in an aqueous environment All chemical processes essential to life occur within the aqueous environment of the cell and surrounding fluids contained
Cells: The Living Units Introduction Life in general occurs in an aqueous environment All chemical processes essential to life occur within the aqueous environment of the cell and surrounding fluids contained
Name Class Date. cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell. MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
 Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membrane structure.
 Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membranebound organelles. In this topic, we will examine the structure and
Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membranebound organelles. In this topic, we will examine the structure and
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries
 Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
The Cell Membrane. Lecture 3a. Overview: Membranes. What is a membrane? Structure of the cell membrane. Fluid Mosaic Model. Membranes and Transport
 Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
The Cell Membrane. Also known as the Plasma Membrane
 Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function
 Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Cell Boundaries. Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h
 Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
The Plasma Membrane. 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane. Phospholipid Bilayer. The Plasma Membrane
 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer. Membrane Structure and Function. Fluid Mosaic Model. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment. Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane
 Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Looking forward to an awesome year in IB Biology!
 WESTLAKE HIGH SCHOOL IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS IB Biology will be a very intensive course. Though we will have 90 minute periods every other day, there is still a lot of new material to
WESTLAKE HIGH SCHOOL IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS IB Biology will be a very intensive course. Though we will have 90 minute periods every other day, there is still a lot of new material to
Example - Paramecium contain contractile vacuoles that collect and remove excess water, thereby helping to achieve homeostasis
 Homeostasis Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment; All organisms have ranges that are tolerated (i.e. ph and temperature) Example - Paramecium contain contractile
Homeostasis Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment; All organisms have ranges that are tolerated (i.e. ph and temperature) Example - Paramecium contain contractile
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism
 5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism Concentration of a substance Number of atoms or molecules in a given volume Concentration gradient of a substance A difference in concentration between two regions
5.6 Diffusion, Membranes, and Metabolism Concentration of a substance Number of atoms or molecules in a given volume Concentration gradient of a substance A difference in concentration between two regions
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8. Cell Membrane Section 1
 Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes All cells have a cell membrane Functions: a. Controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b. Provides protection
Membrane Structure and Function. Cell Membranes and Cell Transport
 Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membranes and Cell Transport 1895 1917 1925 Membrane models Membranes are made of lipids Phospholipids can form membranes Its actually 2 layers - there are proteins
Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membranes and Cell Transport 1895 1917 1925 Membrane models Membranes are made of lipids Phospholipids can form membranes Its actually 2 layers - there are proteins
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function. Chapter 7, Section 3 Cell Boundaries and Transport
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7, Section 3 Cell Boundaries and Transport 1 7.3 A. Cell Membrane Is Described Three Ways: 1. Selectively Permeable Membrane: Limits what enters and exits
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7, Section 3 Cell Boundaries and Transport 1 7.3 A. Cell Membrane Is Described Three Ways: 1. Selectively Permeable Membrane: Limits what enters and exits
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Discovery of the Cell
 The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
Biology. Membranes.
 1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
Membrane structure & function
 Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
Written Response #1: True/False
 Written Response #1: True/False 1. Osmosis means to absorb something. 2. Cells are able to excrete waste. 3. Cells obtain energy by gaining nutrition from food. 4. Plants use sunlight for food. 5. Plants
Written Response #1: True/False 1. Osmosis means to absorb something. 2. Cells are able to excrete waste. 3. Cells obtain energy by gaining nutrition from food. 4. Plants use sunlight for food. 5. Plants
Cell membrane & Transport. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function
 Section 1: Cell Discovery and Theory Section 2: The Plasma Membrane Section 3: Structures and Organelles Section 4: Cellular Transport Click on a lesson name to select. 7.2 The Plasma/Cell Membrane Thin,
Section 1: Cell Discovery and Theory Section 2: The Plasma Membrane Section 3: Structures and Organelles Section 4: Cellular Transport Click on a lesson name to select. 7.2 The Plasma/Cell Membrane Thin,
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Chapter 8 KEY CONCEPTS Cellular s are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Membrane structure results in selective permeability Passive transport is diffusion of a substance
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Chapter 8 KEY CONCEPTS Cellular s are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Membrane structure results in selective permeability Passive transport is diffusion of a substance
Movement across the Membrane
 Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane 2003-2004 1 Cell membrane Cells have an inside & an outside Cell membrane is the boundary Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO! Why not? The cell needs materials
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane 2003-2004 1 Cell membrane Cells have an inside & an outside Cell membrane is the boundary Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO! Why not? The cell needs materials
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function
 Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
Cell Biology. The Plasma Membrane
 Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
Cell Biology The Plasma Membrane recall Fluid Mosiac Model S.J. Singer Semipermeable membrane fluid portion is double layer of phospholipids (=phospholipid bilayer) mosaic portion is the proteins and carbohydrates
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Chapter 5 Ground Rules of Metabolism Sections 6-10
 Chapter 5 Ground Rules of Metabolism Sections 6-10 5.6 Cofactors in Metabolic Pathways Most enzymes require cofactors Energy in ATP drives many endergonic reactions Table 5-1 p86 Cofactors and Coenzymes
Chapter 5 Ground Rules of Metabolism Sections 6-10 5.6 Cofactors in Metabolic Pathways Most enzymes require cofactors Energy in ATP drives many endergonic reactions Table 5-1 p86 Cofactors and Coenzymes
7.3 Cell Boundaries. Regents Biology. Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham
 7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
Equilibrium is a condition of balance. Changes in temperature, pressure or concentration can cause a shift in the equilibrium.
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Passive Transport Objectives Relate concentration gradients, diffusion, and equilibrium. Predict the direction of water
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Passive Transport Objectives Relate concentration gradients, diffusion, and equilibrium. Predict the direction of water
The Cell Membrane AP Biology
 The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC. Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC Cell Membrane Structure and Function 4.1 How Is the Structure of a Membrane Related to Its Function? 4.1.1 The Plasma Membrane Isolates the Cell While Allowing Communication
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC Cell Membrane Structure and Function 4.1 How Is the Structure of a Membrane Related to Its Function? 4.1.1 The Plasma Membrane Isolates the Cell While Allowing Communication
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
The Cell Membrane. Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings. Controls traffic in & out of the cell
 The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
Cell membranes. Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102
 Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution
![[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution [S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution](/thumbs/88/115710711.jpg) Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
CWDHS Mr. Winch Grade 12 Biology
 The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
Monday, September 30 th :
 Monday, September 30 th : QUESTION TO PONDER: Differentiate between a pro- and eukaryotic organism. List 4 organelles that each type of organism has in common. The Cell Membrane Modified from Kim Foglia
Monday, September 30 th : QUESTION TO PONDER: Differentiate between a pro- and eukaryotic organism. List 4 organelles that each type of organism has in common. The Cell Membrane Modified from Kim Foglia
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Bio Chapter 7.3 Notes. Cellular Movement
 Bio Chapter 7.3 Notes Cellular Movement I.Background Information A. Solution- a mixture in which the solute (molecules being dissolved) never settle out in the solvent (water). B. In a 25% Koolaid solution,
Bio Chapter 7.3 Notes Cellular Movement I.Background Information A. Solution- a mixture in which the solute (molecules being dissolved) never settle out in the solvent (water). B. In a 25% Koolaid solution,
Controlled via the Cell Membrane
 CELL TRANSPORT 1 Controlled via the Cell Membrane Passive Transport Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations Active Transport DOES require energy, moves from LOW concentrations
CELL TRANSPORT 1 Controlled via the Cell Membrane Passive Transport Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations Active Transport DOES require energy, moves from LOW concentrations
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
Cellular Transport Notes. Ch. 7.3
 Cellular Transport Notes Ch. 7.3 About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions: a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides
Cellular Transport Notes Ch. 7.3 About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions: a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides
What do you remember about the cell membrane?
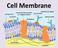 Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
 Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Lipids: Non-polar substances such as fat that contain C, H, O. Phospholipids: Lipid with phosphate group, very abundant in plasma
Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Lipids: Non-polar substances such as fat that contain C, H, O. Phospholipids: Lipid with phosphate group, very abundant in plasma
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
11/30/18 CELL TRANSPORT: POGIL
 11/30/18 CELL TRANSPORT: POGIL DO NOW Study for quiz for 3 minutes AGENDA Quiz (15 min) Membrane Structure and Function POGIL Share out QUIZ You will have 15 minutes to complete the quiz When you are finished,
11/30/18 CELL TRANSPORT: POGIL DO NOW Study for quiz for 3 minutes AGENDA Quiz (15 min) Membrane Structure and Function POGIL Share out QUIZ You will have 15 minutes to complete the quiz When you are finished,
AP Biology. Overview. The Cell Membrane. Phospholipids. Phospholipid bilayer. More than lipids. Fatty acid tails. Phosphate group head
 Overview The Cell Membrane Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
Overview The Cell Membrane Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes
 BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
BIOLOGY 12 - Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Function: Chapter Notes The cell membrane is the gateway into the cell, and must allow needed things such as nutrients into the cell without letting them escape.
Passive Cellular Transport. Unit 2 Lesson 4
 Unit 2 Lesson 4 Students will be able to: Define passive transport Enumerate the three types of passive transport Described each type of passive transport: osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Students will be able to: Define passive transport Enumerate the three types of passive transport Described each type of passive transport: osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Cells & Transport. Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4
 Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
