Membrane Structure and Function
|
|
|
- Abigayle Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function Lecture Outline Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, controls traffic into and out of the cell. Like all biological membranes, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable, allowing some substances to cross more easily than others. Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins The main macromolecules in membranes are lipids and proteins, but carbohydrates are also important. The most abundant lipids are phospholipids. Phospholipids and most other membrane constituents are amphipathic molecules. Amphipathic molecules have both hydrophobic regions and hydrophilic regions. The arrangement of phospholipids and proteins in biological membranes is described by the fluid mosaic model. Membrane models have evolved to fit new data. Models of membranes were developed long before membranes were first seen with electron microscopes in the 1950s. In 1915, membranes isolated from red blood cells were chemically analyzed and found to be composed of lipids and proteins. In 1925, E. Gorter and F. Grendel reasoned that cell membranes must be a phospholipid bilayer two molecules thick. The molecules in the bilayer are arranged such that the hydrophobic fatty acid tails are sheltered from water while the hydrophilic phosphate groups interact with water. Actual membranes adhere more strongly to water than do artificial membranes composed only of phospholipids. One suggestion was that proteins on the surface of the membrane increased adhesion. In 1935, H. Davson and J. Danielli proposed a sandwich model in which the phospholipid bilayer lies between two layers of globular proteins. Early images from electron microscopes seemed to support the Davson-Danielli model, and until the 1960s, it was widely accepted as the structure of the plasma membrane and internal membranes. Further investigation revealed two problems. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-1
2 First, not all membranes were alike. Membranes differ in thickness, appearance when stained, and percentage of proteins. Membranes with different functions differ in chemical composition and structure. Second, measurements showed that membrane proteins are not very soluble in water. Membrane proteins are amphipathic, with hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. If membrane proteins were at the membrane surface, their hydrophobic regions would be in contact with water. In 1972, S. J. Singer and G. Nicolson presented a revised model that proposed that the membrane proteins are dispersed and individually inserted into the phospholipid bilayer. In this fluid mosaic model, the hydrophilic regions of proteins and phospholipids are in maximum contact with water, and the hydrophobic regions are in a nonaqueous environment within the membrane. A specialized preparation technique, freeze-fracture, splits a membrane along the middle of the phospholipid bilayer. When a freeze-fracture preparation is viewed with an electron microscope, protein particles are interspersed in a smooth matrix, supporting the fluid mosaic model. Membranes are fluid. Membrane molecules are held in place by relatively weak hydrophobic interactions. Most of the lipids and some proteins drift laterally in the plane of the membrane, but rarely flip-flop from one phospholipid layer to the other. The lateral movements of phospholipids are rapid, about 2 microns per second. A phospholipid can travel the length of a typical bacterial cell in 1 second. Many larger membrane proteins drift within the phospholipid bilayer, although they move more slowly than the phospholipids. Some proteins move in a very directed manner, perhaps guided or driven by motor proteins attached to the cytoskeleton. Other proteins never move and are anchored to the cytoskeleton. Membrane fluidity is influenced by temperature. As temperatures cool, membranes switch from a fluid state to a solid state as the phospholipids pack more closely. Membrane fluidity is also influenced by its components. Membranes rich in unsaturated fatty acids are more fluid that those dominated by saturated fatty acids because the kinks in the unsaturated fatty acid tails at the locations of the double bonds prevent tight packing. The steroid cholesterol is wedged between phospholipid molecules in the plasma membrane of animal cells. At warm temperatures (such as 37 C), cholesterol restrains the movement of phospholipids and reduces fluidity. At cool temperatures, it maintains fluidity by preventing tight packing. Thus, cholesterol acts as a temperature buffer for the membrane, resisting changes in membrane fluidity as temperature changes. To work properly with active enzymes and appropriate permeability, membranes must be about as fluid as salad oil. Cells can alter the lipid composition of membranes to compensate for changes in fluidity caused by changing temperatures. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-2
3 For example, cold-adapted organisms such as winter wheat increase the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in their membranes in the autumn. This prevents membranes from solidifying during winter. Membranes are mosaics of structure and function. A membrane is a collage of different proteins embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer. Proteins determine most of the membrane s specific functions. The plasma membrane and the membranes of the various organelles each have unique collections of proteins. There are two major populations of membrane proteins. Peripheral proteins are not embedded in the lipid bilayer at all. Instead, they are loosely bound to the surface of the protein, often connected to integral proteins. Integral proteins penetrate the hydrophobic core of the lipid bilayer, often completely spanning the membrane (as transmembrane proteins). The hydrophobic regions embedded in the membrane s core consist of stretches of nonpolar amino acids, often coiled into alpha helices. Where integral proteins are in contact with the aqueous environment, they have hydrophilic regions of amino acids. On the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, some membrane proteins connect to the cytoskeleton. On the exterior side of the membrane, some membrane proteins attach to the fibers of the extracellular matrix. The proteins of the plasma membrane have six major functions: 1. Transport of specific solutes into or out of cells. 2. Enzymatic activity, sometimes catalyzing one of a number of steps of a metabolic pathway. 3. Signal transduction, relaying hormonal messages to the cell. 4. Cell-cell recognition, allowing other proteins to attach two adjacent cells together. 5. Intercellular joining of adjacent cells with gap or tight junctions. 6. Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix, maintaining cell shape and stabilizing the location of certain membrane proteins. Membrane carbohydrates are important for cell-cell recognition. The plasma membrane plays the key role in cell-cell recognition. Cell-cell recognition, the ability of a cell to distinguish one type of neighboring cell from another, is crucial to the functioning of an organism. This attribute is important in the sorting and organization of cells into tissues and organs during development. It is also the basis for rejection of foreign cells by the immune system. Cells recognize other cells by binding to surface molecules, often carbohydrates, on the plasma membrane. Membrane carbohydrates are usually branched oligosaccharides with fewer than 15 sugar units. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-3
4 They may be covalently bonded to lipids, forming glycolipids, or more commonly to proteins, forming glycoproteins. The oligosaccharides on the external side of the plasma membrane vary from species to species, from individual to individual, and even from cell type to cell type within the same individual. This variation distinguishes each cell type. The four human blood groups (A, B, AB, and O) differ in the external carbohydrates on red blood cells. Membranes have distinctive inside and outside faces. Membranes have distinct inside and outside faces. The two layers may differ in lipid composition. Each protein in the membrane has a directional orientation in the membrane. The asymmetrical orientation of proteins, lipids and associated carbohydrates begins during the synthesis of membrane in the ER and Golgi apparatus. Membrane lipids and proteins are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. Carbohydrates are added to proteins in the ER, and the resulting glycoproteins are further modified in the Golgi apparatus. Glycolipids are also produced in the Golgi apparatus. When a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, the outside layer of the vesicle becomes continuous with the inside layer of the plasma membrane. In that way, molecules that originate on the inside face of the ER end up on the outside face of the plasma membrane. Concept 7.2 Membrane structure results in selective permeability A steady traffic of small molecules and ions moves across the plasma membrane in both directions. For example, sugars, amino acids, and other nutrients enter a muscle cell, and metabolic waste products leave. The cell absorbs oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. It also regulates concentrations of inorganic ions, such as Na +, K +, Ca 2+, and Cl, by shuttling them across the membrane. However, substances do not move across the barrier indiscriminately; membranes are selectively permeable. The plasma membrane allows the cell to take up many varieties of small molecules and ions and exclude others. Substances that move through the membrane do so at different rates. Movement of a molecule through a membrane depends on the interaction of the molecule with the hydrophobic core of the membrane. Hydrophobic molecules, such as hydrocarbons, CO 2, and O 2, can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and cross easily. The hydrophobic core of the membrane impedes the direct passage of ions and polar molecules, which cross the membrane with difficulty. This includes small molecules, such as water, and larger molecules, such as glucose and other sugars. An ion, whether a charged atom or molecule, and its surrounding shell of water also has difficulty penetrating the hydrophobic core. Proteins assist and regulate the transport of ions and polar molecules. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-4
5 Specific ions and polar molecules can cross the lipid bilayer by passing through transport proteins that span the membrane. Some transport proteins, called channel proteins, have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or ions can use as a tunnel through the membrane. For example, the passage of water through the membrane can be greatly facilitated by channel proteins known as aquaporins. Other transport proteins, called carrier proteins, bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane. Each transport protein is specific as to the substances that it will translocate. For example, the glucose transport protein in the liver will carry glucose into the cell but will not transport fructose, its structural isomer. Concept 7.3 Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment Diffusion is the tendency of molecules of any substance to spread out in the available space. Diffusion is driven by the intrinsic kinetic energy (thermal motion or heat) of molecules. Movements of individual molecules are random. However, movement of a population of molecules may be directional. Imagine a permeable membrane separating a solution with dye molecules from pure water. If the membrane has microscopic pores that are large enough, dye molecules will cross the barrier randomly. The net movement of dye molecules across the membrane will continue until both sides have equal concentrations of the dye. At this dynamic equilibrium, as many molecules cross one way as cross in the other direction. In the absence of other forces, a substance will diffuse from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated, down its concentration gradient. No work must be done to move substances down the concentration gradient. Diffusion is a spontaneous process that decreases free energy and increases entropy by creating a randomized mixture. Each substance diffuses down its own concentration gradient, independent of the concentration gradients of other substances. The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane is passive transport because it requires no energy from the cell to make it happen. The concentration gradient itself represents potential energy and drives diffusion. Because membranes are selectively permeable, the interactions of the molecules with the membrane play a role in the diffusion rate. Diffusion of molecules of limited permeability through the lipid bilayer may be assisted by transport proteins. Osmosis is the passive transport of water. Differences in the relative concentration of dissolved materials in two solutions can lead to the movement of ions from one to the other. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-5
6 The solution with the higher concentration of solutes is hypertonic relative to the other solution. The solution with the lower concentration of solutes is hypotonic relative to the other solution. These are comparative terms. Tap water is hypertonic compared to distilled water but hypotonic compared to seawater. Solutions with equal solute concentrations are isotonic. Imagine that two sugar solutions differing in concentration are separated by a membrane that will allow water through, but not sugar. The hypertonic solution has a lower water concentration than the hypotonic solution. More of the water molecules in the hypertonic solution are bound up in hydration shells around the sugar molecules, leaving fewer unbound water molecules. Unbound water molecules will move from the hypotonic solution, where they are abundant, to the hypertonic solution, where they are rarer. Net movement of water continues until the solutions are isotonic. The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. The direction of osmosis is determined only by a difference in total solute concentration. The kinds of solutes in the solutions do not matter. This makes sense because the total solute concentration is an indicator of the abundance of bound water molecules (and, therefore, of free water molecules). When two solutions are isotonic, water molecules move at equal rates from one to the other, with no net osmosis. The movement of water by osmosis is crucial to living organisms. Cell survival depends on balancing water uptake and loss. An animal cell (or other cell without a cell wall) immersed in an isotonic environment experiences no net movement of water across its plasma membrane. Water molecules move across the membrane but at the same rate in both directions. The volume of the cell is stable. The same cell in a hypertonic environment will lose water, shrivel, and probably die. A cell in a hypotonic solution will gain water, swell, and burst. For organisms living in an isotonic environment (for example, many marine invertebrates), osmosis is not a problem. The cells of most land animals are bathed in extracellular fluid that is isotonic to the cells. Organisms without rigid walls have osmotic problems in either a hypertonic or hypotonic environment and must have adaptations for osmoregulation, the control of water balance, to maintain their internal environment. For example, Paramecium, a protist, is hypertonic to the pond water in which it lives. In spite of a cell membrane that is less permeable to water than other cells, water still continually enters the Paramecium cell. To solve this problem, Paramecium cells have a specialized organelle, the contractile vacuole, which functions as a bilge pump to force water out of the cell. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-6
7 The cells of plants, prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists have walls that contribute to the cell s water balance. A plant cell in a hypotonic solution will swell until the elastic cell wall opposes further uptake. At this point the cell is turgid (very firm), a healthy state for most plant cells. Turgid cells contribute to the mechanical support of the plant. If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no movement of water into the cell. The cell becomes flaccid (limp), and the plant may wilt. The cell wall provides no advantages when a plant cell is immersed in a hypertonic solution. As the plant cell loses water, its volume shrinks. Eventually, the plasma membrane pulls away from the wall. This plasmolysis is usually lethal. Specific proteins facilitate passive transport of water and selected solutes. Many polar molecules and ions that are normally impeded by the lipid bilayer of the membrane diffuse passively with the help of transport proteins that span the membrane. The passive movement of molecules down their concentration gradient via transport proteins is called facilitated diffusion. Two types of transport proteins facilitate the movement of molecules or ions across membranes: channel proteins and carrier proteins. Some channel proteins simply provide hydrophilic corridors for the passage of specific molecules or ions. For example, water channel proteins, aquaporins, greatly facilitate the diffusion of water. Many ion channels function as gated channels. These channels open or close depending on the presence or absence of a chemical or physical stimulus. If chemical, the stimulus is a substance other than the one to be transported. For example, stimulation of a receiving neuron by specific neurotransmitters opens gated channels to allow sodium ions into the cell. When the neurotransmitters are not present, the channels are closed. Some transport proteins do not provide channels but appear to actually translocate the solutebinding site and solute across the membrane as the transport protein changes shape. These shape changes may be triggered by the binding and release of the transported molecule. In certain inherited diseases, specific transport systems may be defective or absent. Cystinuria is a human disease characterized by the absence of a protein that transports cysteine and other amino acids across the membranes of kidney cells. An individual with cystinuria develops painful kidney stones as amino acids accumulate and crystallize in the kidneys. Concept 7.4 Active transport uses energy to move solutes against their gradients Some transport proteins can move solutes across membranes against their concentration gradient, from the side where they are less concentrated to the side where they are more concentrated. This active transport requires the cell to expend metabolic energy. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-7
8 Active transport enables a cell to maintain its internal concentrations of small molecules that would otherwise diffuse across the membrane. Active transport is performed by specific proteins embedded in the membranes. ATP supplies the energy for most active transport. ATP can power active transport by transferring a phosphate group from ATP (forming ADP) to the transport protein. This may induce a conformational change in the transport protein, translocating the solute across the membrane. The sodium-potassium pump actively maintains the gradient of sodium ions (Na + ) and potassium ions (K + ) across the plasma membrane of animal cells. Typically, K + concentration is low outside an animal cell and high inside the cell, while Na + concentration is high outside an animal cell and low inside the cell. The sodium-potassium pump maintains these concentration gradients, using the energy of one ATP to pump three Na + out and two K + in. Some ion pumps generate voltage across membranes. All cells maintain a voltage across their plasma membranes. Voltage is electrical potential energy due to the separation of opposite charges. The cytoplasm of a cell is negative in charge compared to the extracellular fluid because of an unequal distribution of cations and anions on opposite sides of the membrane. The voltage across a membrane is called a membrane potential, and ranges from 50 to 200 millivolts (mv). The inside of the cell is negative compared to the outside. The membrane potential acts like a battery. The membrane potential favors the passive transport of cations into the cell and anions out of the cell. Two combined forces, collectively called the electrochemical gradient, drive the diffusion of ions across a membrane. One is a chemical force based on an ion s concentration gradient. The other is an electrical force based on the effect of the membrane potential on the ion s movement. An ion does not simply diffuse down its concentration gradient but diffuses down its electrochemical gradient. For example, there is a higher concentration of Na + outside a resting nerve cell than inside. When the neuron is stimulated, a gated channel opens and Na + diffuse into the cell down their electrochemical gradient. The diffusion of Na + is driven by their concentration gradient and by the attraction of cations to the negative side of the membrane. Special transport proteins, electrogenic pumps, generate the voltage gradient across a membrane. The sodium-potassium pump in animals restores the electrochemical gradient not only by the active transport of Na + and K +, setting up a concentration gradient, but because it pumps two K + inside for every three Na + that it moves out, setting up a voltage across the membrane. The sodium-potassium pump is the major electrogenic pump of animal cells. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-8
9 In plants, bacteria, and fungi, a proton pump is the major electrogenic pump, actively transporting H + out of the cell. Proton pumps in the cristae of mitochondria and the thylakoids of chloroplasts concentrate H + behind membranes. These electrogenic pumps store energy that can be accessed for cellular work. In cotransport, a membrane protein couples the transport of two solutes. A single ATP-powered pump that transports one solute can indirectly drive the active transport of several other solutes in a mechanism called cotransport. As the solute that has been actively transported diffuses back passively through a transport protein, its movement can be coupled with the active transport of another substance against its concentration gradient. Plants commonly use the gradient of hydrogen ions generated by proton pumps to drive the active transport of amino acids, sugars, and other nutrients into the cell. One specific transport protein couples the diffusion of protons out of the cell and the transport of sucrose into the cell. Plants use the mechanism of sucrose-proton cotransport to load sucrose into specialized cells in the veins of leaves for distribution to nonphotosynthetic organs such as roots. Concept 7.5 Bulk transport across the plasma membrane occurs by exocytosis and endocytosis Small molecules and water enter or leave the cell through the lipid bilayer or by transport proteins. Large molecules, such as polysaccharides and proteins, cross the membrane via vesicles. During exocytosis, a transport vesicle budded from the Golgi apparatus is moved by the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane. When the two membranes come in contact, the bilayers fuse and spill the contents to the outside. Many secretory cells use exocytosis to export their products. During endocytosis, a cell brings in macromolecules and particulate matter by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane. Endocytosis is a reversal of exocytosis, although different proteins are involved in the two processes. A small area of the plasma membrane sinks inward to form a pocket. As the pocket deepens, it pinches in to form a vesicle containing the material that had been outside the cell. There are three types of endocytosis: phagocytosis ( cellular eating ), pinocytosis ( cellular drinking ), and receptor-mediated endocytosis. In phagocytosis, the cell engulfs a particle by extending pseudopodia around it and packaging it in a large vacuole. The contents of the vacuole are digested when the vacuole fuses with a lysosome. In pinocytosis, a cell creates a vesicle around a droplet of extracellular fluid. All included solutes are taken into the cell in this nonspecific process. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-9
10 Receptor-mediated endocytosis allows greater specificity, transporting only certain substances. This process is triggered when extracellular substances, or ligands, bind to special receptors on the membrane surface. The receptor proteins are clustered in regions of the membrane called coated pits, which are lined on their cytoplasmic side by a layer of coat proteins. Binding of ligands to receptors triggers the formation of a vesicle by the coated pit, bringing the bound substances into the cell. Receptor-mediated endocytosis enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific materials that may be in low concentrations in the environment. Human cells use this process to take in cholesterol for use in the synthesis of membranes and as a precursor for the synthesis of steroids. Cholesterol travels in the blood in low-density lipoproteins (LDL), complexes of protein and lipid. These lipoproteins act as ligands to bind to LDL receptors and enter the cell by endocytosis. In an inherited disease called familial hypercholesterolemia, the LDL receptors are defective, leading to an accumulation of LDL and cholesterol in the blood. This contributes to early atherosclerosis. Lecture Outline for Campbell/Reece Biology, 7 th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc. 7-10
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Section B: Traffic Across Membranes 1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability 2. Passive transport is diffusion across a membrane
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Section B: Traffic Across Membranes 1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability 2. Passive transport is diffusion across a membrane
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Chapter 8 KEY CONCEPTS Cellular s are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Membrane structure results in selective permeability Passive transport is diffusion of a substance
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Chapter 8 KEY CONCEPTS Cellular s are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Membrane structure results in selective permeability Passive transport is diffusion of a substance
What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast.
 1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Membrane Structure and Function
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast.
 1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
1. A membrane s molecular organization results in selective permeability What kind of things must pass into and out of cells?? Be careful not to go too fast. Permeability of a molecule through a membrane
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function Lecture Outline Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell from its surroundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, controls traffic
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function Lecture Outline Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell from its surroundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, controls traffic
BIOLOGY. Membrane Structure and Function CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 7 Membrane Structure and Function Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life at the Edge The plasma
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 7 Membrane Structure and Function Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life at the Edge The plasma
Membrane Structure and Function
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. Phospholipids are amphipathic. Explain what this means. Name Period Amphipathic means
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. Phospholipids are amphipathic. Explain what this means. Name Period Amphipathic means
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Membrane Structure and Function. Cell Membranes and Cell Transport
 Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membranes and Cell Transport 1895 1917 1925 Membrane models Membranes are made of lipids Phospholipids can form membranes Its actually 2 layers - there are proteins
Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membranes and Cell Transport 1895 1917 1925 Membrane models Membranes are made of lipids Phospholipids can form membranes Its actually 2 layers - there are proteins
Membrane Structure and Function
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
How Things Get In and Out of Cells, or gummy bears, zip lock bags or whatever!
 How Things Get In and Out of Cells, or gummy bears, zip lock bags or whatever! SC.912.L.14.3 Benchmark Clarifications: Students will compare and/or contrast the structures found in plant cells and in animal
How Things Get In and Out of Cells, or gummy bears, zip lock bags or whatever! SC.912.L.14.3 Benchmark Clarifications: Students will compare and/or contrast the structures found in plant cells and in animal
Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins.
 Study Guide e Plasma Membrane You should be able to write out the definitions to each of the following terms in your own words: plasma membrane fluid mosaic integral proteins peripheral proteins receptor
Study Guide e Plasma Membrane You should be able to write out the definitions to each of the following terms in your own words: plasma membrane fluid mosaic integral proteins peripheral proteins receptor
Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
 Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Lipids: Non-polar substances such as fat that contain C, H, O. Phospholipids: Lipid with phosphate group, very abundant in plasma
Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Lipids: Non-polar substances such as fat that contain C, H, O. Phospholipids: Lipid with phosphate group, very abundant in plasma
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function. Key Terms:
 Key Terms: Selectively permeable Fluid mosaic model Amphipathic Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Phosphate head Fatty acid tail Davson-Danielli Singer-Nicolson Freeze-Fracture EM Unsaturated
Key Terms: Selectively permeable Fluid mosaic model Amphipathic Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Phosphate head Fatty acid tail Davson-Danielli Singer-Nicolson Freeze-Fracture EM Unsaturated
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Image from: http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/ge22/03.gif Slide show modified from: http://www.explorebiology.com/pptap/2005/ http://facstaff.bloomu.edu/gdavis/links%20100.htm
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Image from: http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/ge22/03.gif Slide show modified from: http://www.explorebiology.com/pptap/2005/ http://facstaff.bloomu.edu/gdavis/links%20100.htm
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 LECTURE RESENTATIONS For CAMBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, eter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Membrane Structure and Function
Chapter 7 LECTURE RESENTATIONS For CAMBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, eter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Membrane Structure and Function
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222
 Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily than
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily than
The Cell Membrane. Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit. Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia
 The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
The Cell Membrane. Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings. Controls traffic in & out of the cell
 The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function 1. Membrane Structure 2. Transport Across Membranes 1. Membrane Structure Chapter Reading pp. 125-129 What are Biological Membranes? Hydrophilic head WATER They
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function 1. Membrane Structure 2. Transport Across Membranes 1. Membrane Structure Chapter Reading pp. 125-129 What are Biological Membranes? Hydrophilic head WATER They
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function. 1. Membrane Structure. What are Biological Membranes? 10/21/2015. Why phospholipids? 1. Membrane Structure
 Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function 1. Membrane Structure 2. Transport Across Membranes 1. Membrane Structure Chapter Reading pp. 125-129 What are Biological Membranes? Hydrophilic head WATER They
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function 1. Membrane Structure 2. Transport Across Membranes 1. Membrane Structure Chapter Reading pp. 125-129 What are Biological Membranes? Hydrophilic head WATER They
Diffusion across cell membrane
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
The Cell Membrane AP Biology
 The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
Membrane Structure and Function - 1
 Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
CWDHS Mr. Winch Grade 12 Biology
 The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
AP Biology. Overview. The Cell Membrane. Phospholipids. Phospholipid bilayer. More than lipids. Fatty acid tails. Phosphate group head
 Overview The Cell Membrane Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
Overview The Cell Membrane Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
Cell Transport & the Cell Membrane
 Cell Transport & the Cell Membrane I. Cell Membrane A. Structure Structure of the cell membrane is referred to as the Fluid Mosaic Model. It is made up of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. The membrane
Cell Transport & the Cell Membrane I. Cell Membrane A. Structure Structure of the cell membrane is referred to as the Fluid Mosaic Model. It is made up of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. The membrane
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 LECTURE RESENTATIONS For CAMBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, eter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Membrane Structure and Function
Chapter 7 LECTURE RESENTATIONS For CAMBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, eter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Membrane Structure and Function
BSC Exam I Lectures and Text Pages
 BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages I. Intro to Biology (2-29) II. Chemistry of Life Chemistry review (30-46) Water (47-57) Carbon (58-67) Macromolecules (68-91) III. Cells and Membranes Cell structure
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes. Reading Assignments. Selective and Semi-permeable Barriers
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Cell Membranes Valencia college
 6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
Monday, September 30 th :
 Monday, September 30 th : QUESTION TO PONDER: Differentiate between a pro- and eukaryotic organism. List 4 organelles that each type of organism has in common. The Cell Membrane Modified from Kim Foglia
Monday, September 30 th : QUESTION TO PONDER: Differentiate between a pro- and eukaryotic organism. List 4 organelles that each type of organism has in common. The Cell Membrane Modified from Kim Foglia
Movement across the Membrane
 Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane 2003-2004 1 Cell membrane Cells have an inside & an outside Cell membrane is the boundary Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO! Why not? The cell needs materials
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane 2003-2004 1 Cell membrane Cells have an inside & an outside Cell membrane is the boundary Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO! Why not? The cell needs materials
CONCEPT 5.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
 Ch 5 Membrane Transport and Signaling Overview The plasma separates the living cell from its surroundings The plasma exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than
Ch 5 Membrane Transport and Signaling Overview The plasma separates the living cell from its surroundings The plasma exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than
The Cell Membrane. Phospholipids. Chapter 7: Arranged as a Phospholipid bilayer. Cell membrane defines cell! Cell membrane separates living cell from
 Chapter 7: The Cell Membrane Phospholipids! Amphipathic Molecules: " Phosphate head! hydrophilic " Fatty acid tails! Hydrophobic! Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled
Chapter 7: The Cell Membrane Phospholipids! Amphipathic Molecules: " Phosphate head! hydrophilic " Fatty acid tails! Hydrophobic! Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Membrane Structure and Function. Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function
 Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function. The plasma membrane surrounds the living cells from their surroundings.
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane surrounds the living cells from their surroundings. Only 8 nm thick (8,000 to equal the thickness of a sheet of paper) Controls passage of
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane surrounds the living cells from their surroundings. Only 8 nm thick (8,000 to equal the thickness of a sheet of paper) Controls passage of
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Division Ave High School Ms. Foglia AP Biology
 The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water 2007-2008 Aaaah, one of those structure
The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water 2007-2008 Aaaah, one of those structure
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function What You Must Know: Why membranes are selectively permeable. The role of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in membranes. How water will move if a cell is placed
Membrane Structure and Function What You Must Know: Why membranes are selectively permeable. The role of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in membranes. How water will move if a cell is placed
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION selective permeability permits some substances to cross it more easily than others Figure 7.1 Scientists studying the plasma Reasoned that it must be a phospholipid bilayer
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION selective permeability permits some substances to cross it more easily than others Figure 7.1 Scientists studying the plasma Reasoned that it must be a phospholipid bilayer
Chapter 7. Movement across the Cell Membrane
 Chapter 7 Movement across the Cell Membrane 2005-2006 Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems u Universe tends towards disorder Diffusion u movement from high low concentration Diffusion
Chapter 7 Movement across the Cell Membrane 2005-2006 Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological systems u Universe tends towards disorder Diffusion u movement from high low concentration Diffusion
Phospholipids. Phosphate head. Fatty acid tails. Arranged as a bilayer. hydrophilic. hydrophobic. Phosphate. Fatty acid. attracted to water
 The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water I want you to remember: Structure
The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water I want you to remember: Structure
The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11
 1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries
 Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Membrane Structure & Function (Learning Objectives)
 Membrane Structure & Function (Learning Objectives) Review the basic function and biochemical composition of the plasma membrane. Learn the fluid state of membranes and the movement of its lipids and proteins.
Membrane Structure & Function (Learning Objectives) Review the basic function and biochemical composition of the plasma membrane. Learn the fluid state of membranes and the movement of its lipids and proteins.
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane. diffusion. Diffusion of 2 solutes. Cell (plasma) membrane. Diffusion 9/7/2012
 Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane Diffusion Diffusion of 2 solutes Each substance diffuses down its own concentration gradient, independent of concentration gradients of other substances Diffusion
Chapter 8. Movement across the Cell Membrane Diffusion Diffusion of 2 solutes Each substance diffuses down its own concentration gradient, independent of concentration gradients of other substances Diffusion
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Cell Membrane Structure and Function. What is the importance of having a cell membrane?
 Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
Diffusion. Chapter 7. Movement across the Cell Membrane. Cell (plasma) membrane. diffusion. Building a membrane. Diffusion of 2 solutes
 WH Chapter 7 Diffusion Move for HIGH to LOW concentration passive transport no energy needed Movement across the Cell Membrane 2005-2006 diffusion osmosis Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological
WH Chapter 7 Diffusion Move for HIGH to LOW concentration passive transport no energy needed Movement across the Cell Membrane 2005-2006 diffusion osmosis Diffusion 2nd Law of Thermodynamics governs biological
The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11
 1 The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid mosaic model
1 The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid mosaic model
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function CELL MEMBRANE: Basics: Regulates flow in and out of the cell Composed of phospholipids and proteins - some carbohydrates and lipids SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE - allows
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function CELL MEMBRANE: Basics: Regulates flow in and out of the cell Composed of phospholipids and proteins - some carbohydrates and lipids SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE - allows
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules. Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine
 Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer. Membrane Structure and Function. Fluid Mosaic Model. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Chapter 5. The Working Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
The Plasma Membrane. 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane. Phospholipid Bilayer. The Plasma Membrane
 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins
 1 Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins 2 Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Amphipathic Phosphate attracted to
1 Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins 2 Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Amphipathic Phosphate attracted to
Membrane Structure and Function
 BIOL1040 Page 1 Membrane Structure and Function Friday, 6 March 2015 2:58 PM Cellular Membranes Fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids - abundant Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules (has
BIOL1040 Page 1 Membrane Structure and Function Friday, 6 March 2015 2:58 PM Cellular Membranes Fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids - abundant Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules (has
The Cell Membrane. Lecture 3a. Overview: Membranes. What is a membrane? Structure of the cell membrane. Fluid Mosaic Model. Membranes and Transport
 Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
What do you remember about the cell membrane?
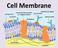 Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Chapter 5Membrane Structure and. Function
 Chapter 5Membrane Structure and Function Cell (plasma) membrane Cells need an inside & an outside separate cell from its environment ability to discriminate chemical exchanges Phospholipid Bilayer A membrane
Chapter 5Membrane Structure and Function Cell (plasma) membrane Cells need an inside & an outside separate cell from its environment ability to discriminate chemical exchanges Phospholipid Bilayer A membrane
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment
 Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
Comprehensive and Easy Course Notes for BIOL1040 Exams and Assessment MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF CELL FUNCTION Membrane Structure & Function Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids
I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids. Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule. Amphiphatic:
 I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule Amphiphatic: a) The amphiphatic nature & cylindrical shape of phospholipids contributes to their ability to assume bilayers in an
I. Chemical Properties of Phospholipids Figure 1: Phospholipid Molecule Amphiphatic: a) The amphiphatic nature & cylindrical shape of phospholipids contributes to their ability to assume bilayers in an
Biology Kevin Dees. Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane surrounds the living cells from their surroundings. Only 8 nm thick (8,000 to equal the thickness of a sheet of paper) Controls passage of
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane surrounds the living cells from their surroundings. Only 8 nm thick (8,000 to equal the thickness of a sheet of paper) Controls passage of
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane. Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5
 Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
I. Membrane Structure Figure 1: Phospholipid. Figure 1.1: Plasma Membrane. Plasma Membrane:
 I. Membrane Structure Figure 1: Phospholipid Figure 1.1: Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane: 1 II. Early Plasma Membrane Models Figure 2: Davson-Danielli Sandwich Model In the 1960 s new evidence suggested
I. Membrane Structure Figure 1: Phospholipid Figure 1.1: Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane: 1 II. Early Plasma Membrane Models Figure 2: Davson-Danielli Sandwich Model In the 1960 s new evidence suggested
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Transport. Slide 1 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 & Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
& Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membrane structure.
 Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membranebound organelles. In this topic, we will examine the structure and
Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membranebound organelles. In this topic, we will examine the structure and
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life at the Edge
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life at the Edge
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222
 Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Molecules with hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts are called Ampipathic molecules
 Plasma Membrane The membrane at the boundary of every cell Functions as a selective barrier for the passage of materials in and out of cells Membrane Composition Phospholipids Proteins Carbohydrates Cholesterol
Plasma Membrane The membrane at the boundary of every cell Functions as a selective barrier for the passage of materials in and out of cells Membrane Composition Phospholipids Proteins Carbohydrates Cholesterol
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 100-119. There are many great figures in this chapter. Make sure you study all
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 100-119. There are many great figures in this chapter. Make sure you study all
