Mass Spectrometric Imaging of GABA in the Drosophila melanogaster Adult Head
|
|
|
- Harriet Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES SEPTEMBER 2018, VOL The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry Notes Mass Spectrometric Imaging of GABA in the Drosophila melanogaster Adult Head Yosuke ENOMOTO,* Phan NT. AN,** Masamitsu YAMAGUCHI,*** Eiichiro FUKUSAKI,* and Shuichi SHIMMA* * Department of Biotechnology, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University, 2-1 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka , Japan ** Institute of Applied Microbiology, Aachen Biology and Biotechnology, RWTH Aachen University, Worringer Weg 1, 52074, Aachen, Germany *** Department of Applied Biology, Kyoto Institute of Technology, Matsugasaki, Sakyo, Kyoto , Japan Drosophila melanogaster is a model organism in neurodegenerative disease research. In neurodegenerative study, the direct spatial information of neurotransmitters such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain of Drosophila melanogaster is important to understand the role of GABA. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI-IMS) is an attractive method for direct visualization of neurotransmitters. In this paper, we describe methods to visualize GABA in the brain and head of Drosophila melanogaster using MALDI-IMS. Keywords Imaging mass spectrometry, Drosophila melanogaster, GABA, on-tissue derivatization (Received April 29, 2018; Accepted July 17, 2018; Advance Publication Released Online by J-STAGE July 27, 2018) Introduction Drosophila melanogaster is widely used in studies of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer s disease, Parkinson s disease, repeat expansion diseases and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, based on the many advantages compared to other model organisms. 1 For example, the life cycle is short (10 days), gene manipulation methods have already been established, and it is relatively inexpensive to rear Drosophila as well as produce new strains. As a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) has important roles in many behaviors and neurodegenerative diseases. 2 While measuring the neurotransmitter concentration in the whole brain is important, visualizing the localization of neurotransmitters would provide critical information about its functions. Therefore, information about the distribution of GABA in the head of Drosophila melanogaster can contribute to our understanding of this neurotransmitter. Immunohistochemistry and fluorescent imaging methods are commonly used to study the spatial distribution of GABA in the heads of Drosophila melanogaster. These conventional methods mainly visualize either the enzymes required to produce GABA (GAD1), 3 or GABA transporters, 4 instead of visualizing GABA directly. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI-IMS) is an attractive alternative as a direct imaging method. GABA has already been visualized in mouse brain sections using MALDI-IMS. 5 However, this method has not been applied to Drosophila, since there are some obstacles to visualizing GABA in the Drosophila head. In MALDI-IMS, it is difficult to use samples that are fixed using To whom correspondence should be addressed. sshimma@bio.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp methods such as formalin fixation and paraffin embedment (FFPE). During the FFPE process, small molecules are washed out. On the other hand, cryosectioning the head of Drosophila melanogaster is challenging, as it is very small in size (less than 1 mm 3 ). 6 Another obstacle to visualization is the difference in hardness between the head and brain. In addition, the Drosophila melanogaster head is covered by hard cuticles, and its cells, which lack intermediate filaments, are softer than mammalian cells. These features make it quite difficult to generate sections of the Drosophila head. Moreover, the GABA detection is also difficult due to low ionization efficiency in MALDI 5 and the small amount. In this study, we developed a head sectioning method of Drosophila melanogaster and applied on-tissue derivatization to improve the GABA ionization efficiency. Experimental Chemicals The matrix α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) and derivatization agent 2,4-diphenyl-pyranylium tetrafluoroborate (DPP-TFB), trans-ferulic acid (trans-fa) and 4-hydroxy-3- methoxycinnamic acid (CA) were purchased from Sigma- Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). GABA, ethanol, methanol, acetonitrile, formic acid, ultrapure water, 2-propanol, triethylamine, Mayer s hematoxylin solution, 1% eosin Y solution, xylene, and Softmount were purchased from Wako (Osaka, Japan). The embedding material 4% carboxymethyl cellulose (4% CMC) was purchased from Leica Microsystems (Wetzlar, Germany). Fly strain and sample collection Canton S, a wild type strain of Drosophila melanogaster (Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, Bloomington, IN,
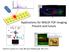
2 1056 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES SEPTEMBER 2018, VOL. 34 Fig. 1 Comparison between sections taken with cryofilm and an anti-roll plate. The comparison between sections taken with an anti-roll plate (A) and using cryofilm (B). GABA intensity was compared between the two methods (C). Scale bar is 200 μm USA), was reared at 25 C on standard food (0.7% agar, 10% glucose, 4% dry yeast, 5% cornmeal, 3% rice bran), and female Drosophila melanogaster were selected for experiments. Tissue sectioning Drosophila heads were dissected and immediately soaked in 70% ethanol. Then, the heads were placed into a mold filled with 4% CMC, which was subsequently frozen using liquid nitrogen. The CMC blocks were stored at 20 C for 1 h and then sectioned to a thickness of 15 μm using a cryomicrotome (CM1950, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). The chamber temperature and sample holder temperature were 18 and 16 C, respectively. We tried two sectioning methods, using either Cryofilm type C (10) (Leica) or an anti-roll plate (Leica). The sections were then thaw mounted onto indium-tin-oxide (ITO)-coated glass slides (100 Ω/m 2 without anti-peeling coating, Matsunami Glass, Osaka, Japan). For sections acquired using the cryofilm, double-sided conductive tape (Shielding Non-woven Fabric Tape, 3M, St. Paul, MN, USA) was utilized to attach the tissue sections onto the glass slides. Sample preparation for IMS DPP-TFB was dissolved in methanol to prepare 10 mg/ml stock solutions. DPP-TFB solutions used for derivatization contained 6 μl of the stock solution, 69 μl of 60% methanol, and 1 μl of triethylamine. After sectioning, on-tissue derivatization was performed with 50 μl of DPP-TFB solution deposited onto each section manually using an airbrush (PS-270, GSI Creos, Tokyo, Japan). The tissue sections were then incubated in a box saturated with the vapor of 50% methanol for 60 min to facilitate the derivatization reaction. To acidify the tissue sections, 20 μl of 10% acetic acid was sprayed onto each section. Another derivatization method was also evaluated to recognize GABA structural isomers. 7 A methanol solution consisting of 11.5 mg/ml CA and 4.25 mg of trans-fa was used as another derivatization reagent. The solution was also deposited onto each section manually using an airbrush. The tissue sections were then incubated at room temperature for 10 min. To detect DPP-GABA and CA-GABA, we performed an imaging experiment without matrix, however the obtained ion intensity was dramatically low. Once the matrix was applied, we obtained a much higher peak intensity. Although this method was different from that reported in previous papers, 7,8 we proactively applied matrix using the following procedures. Matrix was deposited onto the tissue by the two-step matrix application method, 9 which combines sublimation and spraying of the matrix solution. The CHCA was deposited using imlayer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) at 250 C until a thickness of 0.5 μm was achieved. Following sublimation, 50 μl of matrix solution (10 mg/ml CHCA in a solution containing 30% acetonitrile, 10% 2-propanol, and 0.1% formic acid) was sprayed onto each section with a manual airbrush. H&E staining The tissue sections were soaked in hematoxylin for 1 min and washed with water for 1 min. The tissue sections were then placed in 1% eosin for 3 s and washed with water for 1 min. Tissue sections were subsequently dehydrated in ethanol for 1 min; this was repeated 3 times. Sections were then immersed in xylene twice for 1 min. The tissue was sealed with coverslips (20 20 mm, Matsunami Glass, Osaka, Japan) using Softmount. Imaging mass spectrometry Imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) analyses were performed using imscope TRIO (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). This instrument has a sample chamber to observe with a microscope and a MALDI ionization source with an Nd:YAG laser (λ = 355 nm and 1 khz) under atmospheric pressure. The tissue surface was irradiated with the laser, with 200 shots for each data point. Mass spectra for DPP derivatization and CA derivatization were acquired in the positive ion detection mode in the mass range of m/z and , respectively. In the MALDI-IMS experiments, constant voltages for the sample stage and detector were applied at 3.50 and 2.1 kv, respectively. The laser power was kept at a constant of 25 (arbitrary unit in imscope TRIO). To obtain a DPP-GABA and CA-GABA signal, MS/MS analysis was performed using selected precursor ions of DPP-GABA ([M] ) and CA- GABA ([M] ). Results and Discussion Optimization and evaluation of sectioning method Generating sections of Drosophila melanogaster head with good morphology is challenging because of the small size as well as the difference in hardness between the external and internal head anatomy. For IMS, sections with good morphology are critical for obtaining accurate spatial information. To our knowledge, there is no Drosophila head sectioning method standardized for MALDI-IMS, especially for detecting small metabolites. Here, we present an optimized sectioning method appropriate for use in MALDI-IMS. In the field of tissue sectioning, embedding materials are commonly used to help section small samples. However, Drosophila bristles prevent the attachment of embedding
3 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES SEPTEMBER 2018, VOL Fig. 2 GABA distribution in head sections of Drosophila melanogaster. (A) Obtained product ion spectrum of m/z (DPP-GABA). (B) The distribution of DPP-GABA (m/z > ) in the brain of Drosophila melanogaster (pitch 20 μm). (C) Signal intensity map in the whole head (pitch 15 μm). The white line indicates the area of the Drosophila brain. The peak at m/z (derivatization reagent side) was mainly observed in this derivatization. Scale bars: 200 μm. material to the tissue. We observed that Drosophila head tissue could attach well to 4% CMC following a short immersion in 70% ethanol, which might be due to the solubility of cuticular lipids in a polar solvent. To prevent tissue damage from ice crystal formation, the CMC blocks containing Drosophila heads were frozen in liquid nitrogen. We then compared two sectioning methods, one using an anti-roll plate and the other using cryofilm. In both methods, we could obtain sections with good morphology by optimizing the thickness and the temperature in microtome (Figs. 1A and 1B). We found that the method using cryofilm was less technically challenging. The cryofilm could attach to the tissue section surface and preserve the morphology. Hence better sections with their morphology preserved could be obtained using this method (Fig. 1B). We compared peak intensity of GABA (DPP-GABA described in the next section) in the tissue sections obtained by the two different sectioning methods described above. Three biological replicates were performed. Even though the method using cryofilm yielded superior tissues with well-preserved morphology, the GABA intensity was significantly lower (p < 0.01) (Fig. 1C). Since this cryofilm acted as an insulator, it interfered with the electric field that introduces generated ions into the mass spectrometer. Therefore, the method using an anti-roll plate without films is more suitable for generating Drosophila head sections for MALDI-IMS analysis. Visualizing GABA in the Drosophila melanogaster brain and head by DPP derivatization The analysis of GABA by MALDI-IMS is difficult because GABA ionization efficiency is low and the ion peak of the matrix used to facilitate analytes desorption/ionization interferes with the GABA ion peak. 5 To solve these problems, on-tissue derivatization is commonly used. First, we developed a MALDI- IMS method to detect DPP derivatized GABA (DPP-GABA) using a standard GABA solution. This method was performed to directly visualize DPP-GABA in Drosophila brain tissue sections; unfortunately, no signal was detected. This might be due to the inhibition of derivatization or ionization by the high lipid content of the Drosophila brain. We then optimized the derivatization reaction conditions for Drosophila melanogaster. We facilitated the derivatization reaction by performing in 50% methanol vapor. Moreover, 10% acetic acid was sprayed to acidify the tissue to ensure that derivatized GABA maintained a positive charge. 8 Using these procedures, the peak at m/z was clearly observed (Fig. 2A), which was the peak derived from DPP-GABA. In addition, the distribution in the brain and head of Drosophila melanogaster was successfully visualized using MALDI-IMS (Figs. 2B and 2C) from the obtained product ion spectrum. Following optimization of the sectioning and derivatization method, we interpreted the distribution of GABA in the
4 1058 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES SEPTEMBER 2018, VOL. 34 Fig. 3 CA-GABA distribution in head sections of Drosophila melanogaster. (A) Obtained product ion spectrum of m/z In this product ion mass spectrum, peak at m/z was specific peak to separate structural isomers of GABA. The distribution of CA-GABA (m/z > ) in the brain of Drosophila melanogaster (pitch 20 μm) (B) and in the whole head (pitch 15 μm) (C). The white line indicates the area of the Drosophila brain. Scale bars are 80 μm in (B) and 90 μm in (C). Drosophila head. GABA was distributed all over the brain (Fig. 2B). It is known that GABA is produced by glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and it is distributed all over the brain. 3 Moreover, when we examined the entire head section, GABA was observed in the brain surrounding tissues and very low GABA signal was detected in the Drosophila retina (Fig. 2C). To meet its high energy and oxygen demand, the Drosophila brain is supported by vessels from the vascular system and the tracheae from the tracheal system. 10 A previous study of Drosophila larvae suggested that GABA is secreted into the circulating hemolymph. 11 This phenomenon may also occur in adult Drosophila. Specific visualization of GABA in Drosophila melanogaster brain and head by CA derivatization We successfully visualized GABA using DPP derivatization. However, it is impossible to distinguish GABA from its structural isomers such as 2-aminobutyric acid, 2-aminoisobutyric acid, and 3-aminobutyric acid, 7 using DPP reagent. This is because the m/z is the fragment ion of DPP. According to Manier et al., 7 the isomers of GABA can be distinguished by using CA as the derivatization method. When the authors derivatized GABA with CA, they obtained the precursor ion of m/z and the specific product ion of m/z Therefore, we also applied CA as another derivatization method to support our results (Fig. 3). In CA-GABA measurement, the obtained product ion spectrum (Fig. 3A) and distribution of m/z > in the brain and whole head are shown in Figs. 3B and 3C, respectively. As predicted, we observed similar distribution of GABA while applying CA and DPP derivatization methods. We further examined the product ions of m/z by scanning m/z in brain tissue. No specific peaks derived from 2-aminobutyric acid and 2-aminoisobutyric acid (m/z 218.2) as well as 3-aminoisobutyric acid (m/z ) were observed (Fig. 3A). This result indicated that 2-aminobutyric acid, 2-aminoisobutyric acid, and 3-aminobutyric acid in the Drosophila brain either do not exist or exist at very low levels (under detection limits). Together, we confirmed the specificity of GABA in MALDI- IMS analysis. Since we could not detect 2-aminobutyric acid, 2-aminoisobutyric acid, and 3-aminobutyric acid in the Drosophilabrain, both DPP and CA can be used as derivatization methods to visualize GABA using MALDI-IMS. Conclusions To the best of our knowledge, we have developed the first optimized method for visualizing GABA in the Drosophila head
5 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES SEPTEMBER 2018, VOL using MALDI-IMS. Sections with well-preserved morphology were obtained using our sectioning method. GABA was visualized in the head of Drosophila melanogaster by applying on-tissue derivatization. We observed that GABA was distributed all over the head except for in the retina. In the future, MALDI-IMS can be applied in Drosophila research, including in work on neurodegenerative diseases, to examine the GABA level in the brain. References 1. U. B. Pandey and C. D. Nichols, Pharmacol. Rev., 2011, 63, J. W. Blaszczyk, Front. Neurosci., 2016, 10, A. C. Paulk, Y. Zhou, P. Stratton, L. Liu, and B. van Swinderen, J. Neurophysiol., 2013, 110(7), L. Enell, Y. Hamasaka, and A. Kolodziejczyk, J. Comp. Neurol., 2007, 505, C. Esteve, E. A. Tolner, R. Shyti, A. M. J. M. van der Maagdenberg, and L. A. McDonnell, Metabolomics, 2016, 12(2), N. T. N. Phan, A. S. Mohammadi, M. D. Pour, and A. G. Ewing, Anal. Chem., 2016, 88, M. L. Manier, J. M. Spraggins, M. L. Reyzer, J. L. Norris, and R. M. Caprioli, J. Mass Spectrom., 2014, 49, M. Shariatgorji, A. Nilsson, P. Källback, O. Karlsson, Z. Zhang, P. Svenningsson, and P. E. Andren, Neuron, 2014, 84(4), S. Shimma, Y. Takashima, J. Hashimoto, K. Yonemori, K. Tamura, and A. Hamada, J. Mass Spectrom., 2013, 48, W. Pereanu, S Spindler, L. Cruz, and V. Hartenstein, Dev. Biol., 2007, 302(1), J. Shim, T. Mukherjee, B. C. Mondal, T. Liu, G. C. Young, D. P. Wijewarnasuriya, and U. Banerjee, Cell, 2013, 155, 1141.
Sequence Identification And Spatial Distribution of Rat Brain Tryptic Peptides Using MALDI Mass Spectrometric Imaging
 Sequence Identification And Spatial Distribution of Rat Brain Tryptic Peptides Using MALDI Mass Spectrometric Imaging AB SCIEX MALDI TOF/TOF* Systems Patrick Pribil AB SCIEX, Canada MALDI mass spectrometric
Sequence Identification And Spatial Distribution of Rat Brain Tryptic Peptides Using MALDI Mass Spectrometric Imaging AB SCIEX MALDI TOF/TOF* Systems Patrick Pribil AB SCIEX, Canada MALDI mass spectrometric
The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device
 Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
Visualization of Asparaptine in Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) Using MALDI-IMS
 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES SEPTEMBER 2018, VOL. 34 997 2018 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry Visualization of Asparaptine in Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) Using MALDI-IMS Kohei MIYOSHI, Yosuke ENOMOTO,
ANALYTICAL SCIENCES SEPTEMBER 2018, VOL. 34 997 2018 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry Visualization of Asparaptine in Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) Using MALDI-IMS Kohei MIYOSHI, Yosuke ENOMOTO,
MALDI-IMS (MATRIX-ASSISTED LASER DESORPTION/IONIZATION
 MALDI-IMS (MATRIX-ASSISTED LASER DESORPTION/IONIZATION IMAGING MASS SPECTROMETER) IN TISSUE STUDY YANXIAN CHEN MARCH 8 TH, WEDNESDAY. SEMINAR FOCUSING ON What is MALDI imaging mass spectrometer? How does
MALDI-IMS (MATRIX-ASSISTED LASER DESORPTION/IONIZATION IMAGING MASS SPECTROMETER) IN TISSUE STUDY YANXIAN CHEN MARCH 8 TH, WEDNESDAY. SEMINAR FOCUSING ON What is MALDI imaging mass spectrometer? How does
Supporting information for: Memory Efficient. Principal Component Analysis for the Dimensionality. Reduction of Large Mass Spectrometry Imaging
 Supporting information for: Memory Efficient Principal Component Analysis for the Dimensionality Reduction of Large Mass Spectrometry Imaging Datasets Alan M. Race,,, Rory T. Steven,, Andrew D. Palmer,,,
Supporting information for: Memory Efficient Principal Component Analysis for the Dimensionality Reduction of Large Mass Spectrometry Imaging Datasets Alan M. Race,,, Rory T. Steven,, Andrew D. Palmer,,,
Data Independent MALDI Imaging HDMS E for Visualization and Identification of Lipids Directly from a Single Tissue Section
 Data Independent MALDI Imaging HDMS E for Visualization and Identification of Lipids Directly from a Single Tissue Section Emmanuelle Claude, Mark Towers, and Kieran Neeson Waters Corporation, Manchester,
Data Independent MALDI Imaging HDMS E for Visualization and Identification of Lipids Directly from a Single Tissue Section Emmanuelle Claude, Mark Towers, and Kieran Neeson Waters Corporation, Manchester,
Small Molecule Drug Imaging of Mouse Tissue by MALDI-TOF/TOF Mass Spectrometry and FTMS
 Bruker Daltonics Application Note # MT-93/FTMS-38 Small Molecule Drug Imaging of Mouse Tissue by MALDI-TOF/TOF Mass Spectrometry and FTMS Introduction Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI)
Bruker Daltonics Application Note # MT-93/FTMS-38 Small Molecule Drug Imaging of Mouse Tissue by MALDI-TOF/TOF Mass Spectrometry and FTMS Introduction Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI)
Three Dimensional Mapping and Imaging of Neuropeptides and Lipids in Crustacean Brain
 Three Dimensional Mapping and Imaging of Neuropeptides and Lipids in Crustacean Brain Using the 4800 MALDI TOF/TOF Analyzer Ruibing Chen and Lingjun Li School of Pharmacy and Department of Chemistry, University
Three Dimensional Mapping and Imaging of Neuropeptides and Lipids in Crustacean Brain Using the 4800 MALDI TOF/TOF Analyzer Ruibing Chen and Lingjun Li School of Pharmacy and Department of Chemistry, University
Mass spectrometry imaging. What does MS imaging offer?
 BMG 744 Mass spectrometry imaging Stephen Barnes, PhD With sincere acknowledgments to David Stella, PhD and Kyle A. Floyd, MS, former students in the Barnes Laboratory (2005 2012) and Kevin Schey, PhD,
BMG 744 Mass spectrometry imaging Stephen Barnes, PhD With sincere acknowledgments to David Stella, PhD and Kyle A. Floyd, MS, former students in the Barnes Laboratory (2005 2012) and Kevin Schey, PhD,
Supporting information for
 Supporting information for Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-doped Carbon Dots-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Profiling Bisphenol S Distribution in Mouse Tissues
Supporting information for Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-doped Carbon Dots-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Profiling Bisphenol S Distribution in Mouse Tissues
MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: A New Rapid ID Method in Clinical Microbiology
 MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: A New Rapid ID Method in Clinical Microbiology Patrick R. Murray, PhD WW Director, Scientific Affairs BD Diagnostic Systems Outline MALDI-TOF is the most important innovation
MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: A New Rapid ID Method in Clinical Microbiology Patrick R. Murray, PhD WW Director, Scientific Affairs BD Diagnostic Systems Outline MALDI-TOF is the most important innovation
Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry
 Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Basic principles An attractive feature of the time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer is its
Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Basic principles An attractive feature of the time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer is its
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Microwave-assisted Kochetkov amination followed by permanent charge derivatization: A facile strategy for glycomics Xin Liu a,b, Guisen Zhang* a, Kenneth Chan b and
Electronic Supplementary Information Microwave-assisted Kochetkov amination followed by permanent charge derivatization: A facile strategy for glycomics Xin Liu a,b, Guisen Zhang* a, Kenneth Chan b and
An optical dosimeter for the selective detection of gaseous phosgene with ultra-low detection limit
 Supporting information for An optical dosimeter for the selective detection of gaseous phosgene with ultra-low detection limit Alejandro P. Vargas, Francisco Gámez*, Javier Roales, Tània Lopes-Costa and
Supporting information for An optical dosimeter for the selective detection of gaseous phosgene with ultra-low detection limit Alejandro P. Vargas, Francisco Gámez*, Javier Roales, Tània Lopes-Costa and
Fizzy Extraction of Volatile and Semivolatile Compounds into the Gas Phase
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Fizzy Extraction of Volatile and Semivolatile Compounds into the Gas Phase Cheng-Hao Chang, Pawel L. Urban* Department of Applied Chemistry, National Chiao Tung University 1001 University
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Fizzy Extraction of Volatile and Semivolatile Compounds into the Gas Phase Cheng-Hao Chang, Pawel L. Urban* Department of Applied Chemistry, National Chiao Tung University 1001 University
MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry
 MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry Nan Kleinholz Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Facility The Ohio State University Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Workshop What is MALDI Imaging? MALDI: Matrix Assisted
MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry Nan Kleinholz Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Facility The Ohio State University Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Workshop What is MALDI Imaging? MALDI: Matrix Assisted
Future Directions: Tissue and Cell Imaging Robert C. Murphy
 LIPID MAPS Lipidomics Workshop April 19, 2009 www.lipidmaps.org m/z 806 (16:0a/22:6-PC) [M+H] + Future Directions: Tissue and Cell Imaging Robert C. Murphy 16:0/22:6 PC m/z 806.4 Department of Pharmacology
LIPID MAPS Lipidomics Workshop April 19, 2009 www.lipidmaps.org m/z 806 (16:0a/22:6-PC) [M+H] + Future Directions: Tissue and Cell Imaging Robert C. Murphy 16:0/22:6 PC m/z 806.4 Department of Pharmacology
Characterization of Noncovalent Complexes of Polyelectrolytes by Mass Spectrometry
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Characterization of Noncovalent Complexes of Polyelectrolytes by Mass
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Characterization of Noncovalent Complexes of Polyelectrolytes by Mass
Analysis of Triglycerides in Cooking Oils Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry and Principal Component Analysis
 Analysis of Triglycerides in Cooking Oils Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry and Principal Component Analysis Kevin Cooley Chemistry Supervisor: Kingsley Donkor 1. Abstract Triglycerides are composed of
Analysis of Triglycerides in Cooking Oils Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry and Principal Component Analysis Kevin Cooley Chemistry Supervisor: Kingsley Donkor 1. Abstract Triglycerides are composed of
Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery. against melanoma
 Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
MALDI Imaging Drug Imaging Detlev Suckau Head of R&D MALDI Bruker Daltonik GmbH. December 19,
 MALDI Imaging Drug Imaging Detlev Suckau Head of R&D MALDI Bruker Daltonik GmbH December 19, 2014 1 The principle of MALDI imaging Spatially resolved mass spectra are recorded Each mass signal represents
MALDI Imaging Drug Imaging Detlev Suckau Head of R&D MALDI Bruker Daltonik GmbH December 19, 2014 1 The principle of MALDI imaging Spatially resolved mass spectra are recorded Each mass signal represents
Imaging Mass Microscope
 Imaging Mass Microscope imscope C146-E220 Introducing the New Era of Imaging Mass Spectrometry Imaging mass spectrometry is a revolutionary new technology. The instrument is a combination of an optical
Imaging Mass Microscope imscope C146-E220 Introducing the New Era of Imaging Mass Spectrometry Imaging mass spectrometry is a revolutionary new technology. The instrument is a combination of an optical
Solving practical problems. Maria Kuhtinskaja
 Solving practical problems Maria Kuhtinskaja What does a mass spectrometer do? It measures mass better than any other technique. It can give information about chemical structures. What are mass measurements
Solving practical problems Maria Kuhtinskaja What does a mass spectrometer do? It measures mass better than any other technique. It can give information about chemical structures. What are mass measurements
INTRODUCTION TO MALDI IMAGING
 INTRODUCTION TO MALDI IMAGING Marten F. Snel, Emmanuelle Claude, Thérèse McKenna, and James I. Langridge Waters Corporation, Manchester, UK INT RODUCTION The last few years have seen a rapid increase in
INTRODUCTION TO MALDI IMAGING Marten F. Snel, Emmanuelle Claude, Thérèse McKenna, and James I. Langridge Waters Corporation, Manchester, UK INT RODUCTION The last few years have seen a rapid increase in
Mass Spectrometry. Actual Instrumentation
 Mass Spectrometry Actual Instrumentation August 2017 See also http://www.uni-bielefeld.de/chemie/analytik/ms f additional infmation 1. MALDI TOF MASS SPECTROMETRY ON THE ULTRAFLEX 2 2. ESI MASS SPECTROMETRY
Mass Spectrometry Actual Instrumentation August 2017 See also http://www.uni-bielefeld.de/chemie/analytik/ms f additional infmation 1. MALDI TOF MASS SPECTROMETRY ON THE ULTRAFLEX 2 2. ESI MASS SPECTROMETRY
Desorption Electrospray Ionization Coupled with Ultraviolet Photodissociation for Characterization of Phospholipid Isomers in Tissue Sections
 Desorption Electrospray Ionization Coupled with Ultraviolet Photodissociation for Characterization of Phospholipid Isomers in Tissue Sections Dustin R. Klein, Clara L. Feider, Kyana Y. Garza, John Q. Lin,
Desorption Electrospray Ionization Coupled with Ultraviolet Photodissociation for Characterization of Phospholipid Isomers in Tissue Sections Dustin R. Klein, Clara L. Feider, Kyana Y. Garza, John Q. Lin,
Ionization Methods. Neutral species Charged species. Removal/addition of electron(s) Removal/addition of proton(s)
 Ionization Methods Neutral species Charged species Removal/addition of electron(s) M + e - (M +. )* + 2e - electron ionization Removal/addition of proton(s) M + (Matrix)-H MH + + (Matrix) - chemical ionization
Ionization Methods Neutral species Charged species Removal/addition of electron(s) M + e - (M +. )* + 2e - electron ionization Removal/addition of proton(s) M + (Matrix)-H MH + + (Matrix) - chemical ionization
Ozonolysis of phospholipid double bonds during electrospray. ionization: a new tool for structure determination
 Ozonolysis of phospholipid double bonds during electrospray ionization: a new tool for structure determination Michael C. Thomas, Todd W. Mitchell, Stephen J. Blanksby Departments of Chemistry and Biomedical
Ozonolysis of phospholipid double bonds during electrospray ionization: a new tool for structure determination Michael C. Thomas, Todd W. Mitchell, Stephen J. Blanksby Departments of Chemistry and Biomedical
Application Note # MT-91. High Quality MALDI Imaging of Proteins and Peptides in Small Rodent Organ Tissues. Bruker Daltonics.
 Bruker Daltonics Application Note # MT-91 18385 Da 6230 Da 7843 Da High Quality MALDI Imaging of Proteins and Peptides in Small Rodent Organ Tissues New developments in MALDI instrumentation, laser technology
Bruker Daltonics Application Note # MT-91 18385 Da 6230 Da 7843 Da High Quality MALDI Imaging of Proteins and Peptides in Small Rodent Organ Tissues New developments in MALDI instrumentation, laser technology
Lipid Imaging Mass Spectrometry.
 Lipid Imaging Mass Spectrometry. NH 2 P H H H H P H H P H N N Advanced Graduate Course in Metabolomics 3-11-2015 Janusz Kabarowski, Dept. of Microbiology, UAB. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization
Lipid Imaging Mass Spectrometry. NH 2 P H H H H P H H P H N N Advanced Graduate Course in Metabolomics 3-11-2015 Janusz Kabarowski, Dept. of Microbiology, UAB. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization
DIRECT EXTRACTION OF BENZODIAZEPINE METABOLITE WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLUID FROM WHOLE BLOOD
 DIRECT EXTRACTION OF BENZODIAZEPINE METABOLITE WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLUID FROM WHOLE BLOOD Kenichi TAKAICHI, Shuji SAITOH, Yoshio KUMOOKA, Noriko TSUNODA National Research Institute of Police Science, Chiba,
DIRECT EXTRACTION OF BENZODIAZEPINE METABOLITE WITH SUPERCRITICAL FLUID FROM WHOLE BLOOD Kenichi TAKAICHI, Shuji SAITOH, Yoshio KUMOOKA, Noriko TSUNODA National Research Institute of Police Science, Chiba,
[ Care and Use Manual ]
![[ Care and Use Manual ] [ Care and Use Manual ]](/thumbs/91/107423451.jpg) MALDI Calibration Kit I. Introduction The MALDI Calibration Kit is a conveniently packaged selection of MALDI matrices and calibration standards (includes high-purity Neg Ion Mode Calibrant for accurate
MALDI Calibration Kit I. Introduction The MALDI Calibration Kit is a conveniently packaged selection of MALDI matrices and calibration standards (includes high-purity Neg Ion Mode Calibrant for accurate
Isolation of pure cell populations from healthy and
 Direct Analysis of Laser Capture Microdissected Cells by MALDI Mass Spectrometry Baogang J. Xu and Richard M. Caprioli Department of Chemistry, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, USA Melinda
Direct Analysis of Laser Capture Microdissected Cells by MALDI Mass Spectrometry Baogang J. Xu and Richard M. Caprioli Department of Chemistry, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, USA Melinda
(III) MALDI instrumentation
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava (I) Basics of MALDI-TF (II) Sample preparation In-gel digestion Zip-tip sample clean-up Matrix and sample plating (III) MALDI instrumentation 2 1 (I) Basics of MALDI-TF Analyte
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava (I) Basics of MALDI-TF (II) Sample preparation In-gel digestion Zip-tip sample clean-up Matrix and sample plating (III) MALDI instrumentation 2 1 (I) Basics of MALDI-TF Analyte
Mass spectrometry Technologies in Lipid chemistry
 Mass spectrometry Technologies in Lipid chemistry Rabah Soliymani University Of Helsinki Protein Chemistry Unit Biomedicum Helsinki Rabah.soliymani@helsinki.fi Complex_&_dynamic_mixtures (few copies to
Mass spectrometry Technologies in Lipid chemistry Rabah Soliymani University Of Helsinki Protein Chemistry Unit Biomedicum Helsinki Rabah.soliymani@helsinki.fi Complex_&_dynamic_mixtures (few copies to
Development of Laser Ionization Techniques for Evaluation of the Effect of Cancer Drugs Using Imaging Mass Spectrometry
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 214, 15, 11234-11244; doi:1.339/ijms15711234 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Development of Laser Ionization Techniques
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 214, 15, 11234-11244; doi:1.339/ijms15711234 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Development of Laser Ionization Techniques
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Glycan Reductive Isotope-coded Amino Acid Labeling (GRIAL) for Mass Spectrometry-based
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Glycan Reductive Isotope-coded Amino Acid Labeling (GRIAL) for Mass Spectrometry-based
Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit
 Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601510 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Dienes Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601510 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria Xi Liu a,b,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria Xi Liu a,b,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Molecular imaging of brain localization of liposomes in mice using MALDI mass spectrometry Annabelle Fülöp 1,2, Denis A. Sammour 1,2, Katrin Erich 1,2, Johanna von Gerichten 4,
Supplementary Information Molecular imaging of brain localization of liposomes in mice using MALDI mass spectrometry Annabelle Fülöp 1,2, Denis A. Sammour 1,2, Katrin Erich 1,2, Johanna von Gerichten 4,
Biological Mass Spectrometry. April 30, 2014
 Biological Mass Spectrometry April 30, 2014 Mass Spectrometry Has become the method of choice for precise protein and nucleic acid mass determination in a very wide mass range peptide and nucleotide sequencing
Biological Mass Spectrometry April 30, 2014 Mass Spectrometry Has become the method of choice for precise protein and nucleic acid mass determination in a very wide mass range peptide and nucleotide sequencing
UPLC-MS/MS Analysis of Azole Antifungals in Serum for Clinical Research
 Stephen Balloch and Gareth Hammond Waters Corporation, Wilmslow, UK APPLICATION BENEFITS Analytical selectivity afforded by mass selective detection Wide linear measuring range Simple, inexpensive sample
Stephen Balloch and Gareth Hammond Waters Corporation, Wilmslow, UK APPLICATION BENEFITS Analytical selectivity afforded by mass selective detection Wide linear measuring range Simple, inexpensive sample
Applications for MALDI-TOF Imaging Present and Future
 Y Position 8563 / (3000-30000) 12124 / (3000-30000) 14044 / (3000-30000) 10158 35 / (3000-30000) 15012 / (3000-30000) 10894 / (3000-30000) 4964 / (3000-30000) 12414 / (3000-30000) Area Chromatogram - All
Y Position 8563 / (3000-30000) 12124 / (3000-30000) 14044 / (3000-30000) 10158 35 / (3000-30000) 15012 / (3000-30000) 10894 / (3000-30000) 4964 / (3000-30000) 12414 / (3000-30000) Area Chromatogram - All
The J105 SIMS. A New Instrument for 3-Dimensional Imaging and Analysis. Paul Blenkinsopp, Ionoptika Ltd
 The J105 SIMS A New Instrument for 3-Dimensional Imaging and Analysis Paul Blenkinsopp, Ionoptika Ltd The J105 SIMS Why a new ToF Mass Spectrometer? The J105 ToF has been designed to allow us to separate
The J105 SIMS A New Instrument for 3-Dimensional Imaging and Analysis Paul Blenkinsopp, Ionoptika Ltd The J105 SIMS Why a new ToF Mass Spectrometer? The J105 ToF has been designed to allow us to separate
CAMAG TLC-MS INTERFACE
 CAMAG TLC-MS INTERFACE 93.1 249.2 40 30 97.1 20 10 250.2 0 200 400 m/z WORLD LEADER IN PLANAR-CHROMATOGRAPHY Identification and elucidation of unknown substances by hyphenation of TLC / HPTLC and MS The
CAMAG TLC-MS INTERFACE 93.1 249.2 40 30 97.1 20 10 250.2 0 200 400 m/z WORLD LEADER IN PLANAR-CHROMATOGRAPHY Identification and elucidation of unknown substances by hyphenation of TLC / HPTLC and MS The
Nanostructured ZnO as a solution-processable transparent electrode material for low-cost photovoltaics
 Nanostructured ZnO as a solution-processable transparent electrode material for low-cost photovoltaics Investigators P.I: Alberto Salleo, Assistant Professor, Materials Science and Engineering Dr. Ludwig
Nanostructured ZnO as a solution-processable transparent electrode material for low-cost photovoltaics Investigators P.I: Alberto Salleo, Assistant Professor, Materials Science and Engineering Dr. Ludwig
A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting
 Supporting Information A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting Naoko Wakabayashi 1, Yoshiaki Yano 1, Kenichi Kawano 1, and Katsumi Matsuzaki 1 1 Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Supporting Information A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting Naoko Wakabayashi 1, Yoshiaki Yano 1, Kenichi Kawano 1, and Katsumi Matsuzaki 1 1 Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics. Outlines
 The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
Nanoglassified, Optically-Active Monolayer Films of Gold Nanoparticles for in situ Orthogonal Detection by LSPR and SALDI-MS
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Nanoglassified, Optically-Active Monolayer Films of Gold Nanoparticles for in situ Orthogonal Detection by LSPR and SALDI-MS Chih-Yuan Chen,, Samuel S. Hinman,, Jicheng Duan,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Nanoglassified, Optically-Active Monolayer Films of Gold Nanoparticles for in situ Orthogonal Detection by LSPR and SALDI-MS Chih-Yuan Chen,, Samuel S. Hinman,, Jicheng Duan,
Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS. Application. Authors. Abstract. Experimental. Introduction. Food Safety
 Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS Application Food Safety Authors Masahiko Takino Agilent Technologies 9-1 Takakura-Cho Hachiouji-Shi, Tokyo Japan Toshitsugu Tanaka Kobe Institute of Health
Determination of Aflatoxins in Food by LC/MS/MS Application Food Safety Authors Masahiko Takino Agilent Technologies 9-1 Takakura-Cho Hachiouji-Shi, Tokyo Japan Toshitsugu Tanaka Kobe Institute of Health
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
MALDI-TOF analysis of whole blood: its usefulness and potential in the assessment of HbA1c levels
 MALDI-TOF analysis of whole blood: its usefulness and potential in the assessment of HbA1c levels Jane Y. Yang, David A. Herold Department of Pathology, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman
MALDI-TOF analysis of whole blood: its usefulness and potential in the assessment of HbA1c levels Jane Y. Yang, David A. Herold Department of Pathology, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman
Supporting Information. Evolution of atomically precise silver clusters to superlattices
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2012. Supporting Information for Part. Part. Sys. Charact., DOI: 10.1002/ppsc.((please add manuscript number)) Evolution of atomically
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2012. Supporting Information for Part. Part. Sys. Charact., DOI: 10.1002/ppsc.((please add manuscript number)) Evolution of atomically
Analysis of Peptides via Capillary HPLC and Fraction Collection Directly onto a MALDI Plate for Off-line Analysis by MALDI-TOF
 Analysis of Peptides via Capillary HPLC and Fraction Collection Directly onto a MALDI Plate for Off-line Analysis by MALDI-TOF Application Note 219 Joan Stevens, PhD; Luke Roenneburg; Kevin Fawcett (Gilson,
Analysis of Peptides via Capillary HPLC and Fraction Collection Directly onto a MALDI Plate for Off-line Analysis by MALDI-TOF Application Note 219 Joan Stevens, PhD; Luke Roenneburg; Kevin Fawcett (Gilson,
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Thin layer chromatography is the best known technique of plant biochemistry. TLC is used for preliminary separation and determination of plant constituents. It is helpful for
ANALYTICAL SCIENCES JULY 2010, VOL The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry
 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES JULY 2010, VOL. 26 743 2010 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry MALDI Mass Spectrometry Using 2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone and 2,4-Dihydroxyacetophenone with Cyclodextrins: Suppression
ANALYTICAL SCIENCES JULY 2010, VOL. 26 743 2010 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry MALDI Mass Spectrometry Using 2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone and 2,4-Dihydroxyacetophenone with Cyclodextrins: Suppression
Supporting information
 1 2 3 Supporting information SO 2 Uptake on Oleic Acid: A New Formation Pathway of Organosulfur Compounds in the Atmosphere 4 5 Jing Shang, Monica Passananti, Yoan Dupart, Raluca Ciuraru, Liselotte Tinel,
1 2 3 Supporting information SO 2 Uptake on Oleic Acid: A New Formation Pathway of Organosulfur Compounds in the Atmosphere 4 5 Jing Shang, Monica Passananti, Yoan Dupart, Raluca Ciuraru, Liselotte Tinel,
2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis
 2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis Direct Mass Selective Detection of a Pharmaceutical Peptide from an MS-Incompatible USP Method Application Note Biologics and Biosimilars Author Sonja
2D-LC as an Automated Desalting Tool for MSD Analysis Direct Mass Selective Detection of a Pharmaceutical Peptide from an MS-Incompatible USP Method Application Note Biologics and Biosimilars Author Sonja
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR: CONCENTRATIONS OF POLYBROMINATED DIPHENYL ETHERS, HEXABROMOCYCLODODECANES AND TETRABROMOBISPHENOL-A IN BREAST MILK FROM
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR: CONCENTRATIONS OF POLYBROMINATED DIPHENYL ETHERS, HEXABROMOCYCLODODECANES AND TETRABROMOBISPHENOL-A IN BREAST MILK FROM UNITED KINGDOM WOMEN DO NOT DECREASE OVER TWELVE MONTHS
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR: CONCENTRATIONS OF POLYBROMINATED DIPHENYL ETHERS, HEXABROMOCYCLODODECANES AND TETRABROMOBISPHENOL-A IN BREAST MILK FROM UNITED KINGDOM WOMEN DO NOT DECREASE OVER TWELVE MONTHS
Development of a Cell-penetrating Peptide that Exhibits Responsive. Changes in its Secondary Structure in the Cellular Environment
 Development of a Cell-penetrating Peptide that Exhibits Responsive Changes in its Secondary Structure in the Cellular Environment iroko Yamashita, 1 Takuma Kato, 2 Makoto ba, 2 Takashi Misawa, 1 Takayuki
Development of a Cell-penetrating Peptide that Exhibits Responsive Changes in its Secondary Structure in the Cellular Environment iroko Yamashita, 1 Takuma Kato, 2 Makoto ba, 2 Takashi Misawa, 1 Takayuki
O O H. Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL. LC /MS conditions
 Simplifying Qual/Quan Analysis in Discovery DMPK using UPLC and Xevo TQ MS Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION The determination of the drug metabolism
Simplifying Qual/Quan Analysis in Discovery DMPK using UPLC and Xevo TQ MS Robert S. Plumb and Paul D. Rainville Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, U.S. INTRODUCTION The determination of the drug metabolism
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2419 Diversification of Self-Replicating Molecules Jan W. Sadownik, Elio Mattia, Piotr Nowak, Sijbren Otto* University of Groningen, Center for Systems Chemistry, Stratingh Institute
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2419 Diversification of Self-Replicating Molecules Jan W. Sadownik, Elio Mattia, Piotr Nowak, Sijbren Otto* University of Groningen, Center for Systems Chemistry, Stratingh Institute
Hiroya Hidaka *1), Masaki Takiwaki 2), Mine Yamashita 2), Shinya Otsuki 1), Kenji Kawasaki 3), Mitsutoshi Sugano 3) and Takayuki Honda 4)
 Mild acid hydrolysis of sphingolipids yields lysosphingolipids: a matrix-assisted laser desorption and ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry study Hiroya Hidaka *1), Masaki Takiwaki 2), Mine Yamashita
Mild acid hydrolysis of sphingolipids yields lysosphingolipids: a matrix-assisted laser desorption and ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry study Hiroya Hidaka *1), Masaki Takiwaki 2), Mine Yamashita
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities by LC/MS. Application Note. Christine Miller Agilent Technologies.
 Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
Using Software Tools to Improve the Detection of Impurities Application Note Christine Miller Introduction The analysis of raw materials and finished products for or impurities presents a challenge in
Concentrations of drugs of abuse found in brain
 Quantitative MALDI-MS n Analysis of Cocaine in the Autopsied Brain of a Human Cocaine User Employing a Wide Isolation Window and Internal Standards Richard F. Reich, Kasia Cudzilo, Joseph A. Levisky, and
Quantitative MALDI-MS n Analysis of Cocaine in the Autopsied Brain of a Human Cocaine User Employing a Wide Isolation Window and Internal Standards Richard F. Reich, Kasia Cudzilo, Joseph A. Levisky, and
Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme
 P-CN1716E Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme ASMS 2017 MP-406 Tsuyoshi Nakanishi 1, Masaki Yamada 1, Ningombam Sanjib Meitei 2, 3 1 Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan,
P-CN1716E Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme ASMS 2017 MP-406 Tsuyoshi Nakanishi 1, Masaki Yamada 1, Ningombam Sanjib Meitei 2, 3 1 Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan,
Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium. Application. Authors. Abstract.
 Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium Application Natural Product Chemistry Authors Hideaki Uchida Agilent Technologies Japan, Ltd. Tokyo
Time-of-Flight LC/MS Identification and Confirmation of a Kairomone in Daphnia magna Cultured Medium Application Natural Product Chemistry Authors Hideaki Uchida Agilent Technologies Japan, Ltd. Tokyo
LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell 120 EC C18 Column
 Application Note Clinical Research LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell EC C8 Column Authors Rongjie Fu and Zhiming Zhang Agilent Technologies
Application Note Clinical Research LC/MS/MS Separation of Cholesterol and Related Sterols in Plasma on an Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell EC C8 Column Authors Rongjie Fu and Zhiming Zhang Agilent Technologies
Protein and peptides in pictures: Imaging with MALDI mass spectrometry
 Proteomics 2008, 8, 3785 3800 DOI 10.1002/pmic.200800320 3785 REVIEW Protein and peptides in pictures: Imaging with MALDI mass spectrometry Richard J. A. Goodwin 1, Stephen R. Pennington 2 and Andrew R.
Proteomics 2008, 8, 3785 3800 DOI 10.1002/pmic.200800320 3785 REVIEW Protein and peptides in pictures: Imaging with MALDI mass spectrometry Richard J. A. Goodwin 1, Stephen R. Pennington 2 and Andrew R.
Sulfate Radical-Mediated Degradation of Sulfadiazine by CuFeO 2 Rhombohedral Crystal-Catalyzed Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Effects and Mechanisms
 Supporting Information for Sulfate Radical-Mediated Degradation of Sulfadiazine by CuFeO 2 Rhombohedral Crystal-Catalyzed Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Effects and Mechanisms Submitted by Yong Feng, Deli
Supporting Information for Sulfate Radical-Mediated Degradation of Sulfadiazine by CuFeO 2 Rhombohedral Crystal-Catalyzed Peroxymonosulfate: Synergistic Effects and Mechanisms Submitted by Yong Feng, Deli
SPE-LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Nicotine, Cotinine, and Trans-3-hydroxycotinine in Urine
 SPE-LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Nicotine, Cotinine, and Trans-3-hydroxycotinine in Urine J. Jones, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Application Note 709 Key Words SPE, SOLA
SPE-LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Nicotine, Cotinine, and Trans-3-hydroxycotinine in Urine J. Jones, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Application Note 709 Key Words SPE, SOLA
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics
 Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
Determination of N-Nitrososarcosine (NSAR) in tobacco
 JTI-Ökolab Vienna, Austria Determination of N-Nitrososarcosine (NSAR) in tobacco Madeleine Werneth, Jutta Pani, Bernhard Mayer-Helm 2014 CORESTA CONGRESS - ST46 Québec City, Canada 12-16 October 2014 Background
JTI-Ökolab Vienna, Austria Determination of N-Nitrososarcosine (NSAR) in tobacco Madeleine Werneth, Jutta Pani, Bernhard Mayer-Helm 2014 CORESTA CONGRESS - ST46 Québec City, Canada 12-16 October 2014 Background
Fatty Acid Mass Spectrometry Protocol Updated 10/11/2007 By Daren Stephens
 Fatty Acid Mass Spectrometry Protocol Updated 10/11/2007 By Daren Stephens Synopsis: This protocol describes the standard method for extracting and quantifying free fatty acids found in cells and media
Fatty Acid Mass Spectrometry Protocol Updated 10/11/2007 By Daren Stephens Synopsis: This protocol describes the standard method for extracting and quantifying free fatty acids found in cells and media
Components of a Mass Spectrometer
 Components of a Mass Spectrometer Sample Introduction Inlet GC LC Direct Insertion (Syringe/Probe) Ionization Ion Separation Ion Detection Ion Source EI,CI,,, MALDI Mass Analyzer Under vacuum TOF, Quadrupole,
Components of a Mass Spectrometer Sample Introduction Inlet GC LC Direct Insertion (Syringe/Probe) Ionization Ion Separation Ion Detection Ion Source EI,CI,,, MALDI Mass Analyzer Under vacuum TOF, Quadrupole,
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences SPECIAL TOPIC January 2011 Vol.54 No.1: 48 53 RESEARCH PAPERS doi: 10.1007/s11427-010-4119-9 Whole-cell matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-offlight mass spectrometry
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences SPECIAL TOPIC January 2011 Vol.54 No.1: 48 53 RESEARCH PAPERS doi: 10.1007/s11427-010-4119-9 Whole-cell matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-offlight mass spectrometry
Fundamentals of Soft Ionization and MS Instrumentation
 Fundamentals of Soft Ionization and MS Instrumentation Ana Varela Coelho varela@itqb.unl.pt Mass Spectrometry Lab Analytical Services Unit Index Mass spectrometers and its components Ionization methods:
Fundamentals of Soft Ionization and MS Instrumentation Ana Varela Coelho varela@itqb.unl.pt Mass Spectrometry Lab Analytical Services Unit Index Mass spectrometers and its components Ionization methods:
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Artepillin C, is it a good marker for quality control of Brazilian Green Propolis? Cui-ping Zhang 1, Xiao-ge Shen 1, Jia-wei Chen 1, Xia-sen Jiang 1, Kai Wang 2, Fu-liang Hu 1 *
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Artepillin C, is it a good marker for quality control of Brazilian Green Propolis? Cui-ping Zhang 1, Xiao-ge Shen 1, Jia-wei Chen 1, Xia-sen Jiang 1, Kai Wang 2, Fu-liang Hu 1 *
Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) for the Retention of Highly Polar Analytes
 Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) for the Retention of Highly Polar Analytes Eric S. Grumbach,, Diane M. Diehl and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo 2003 Waters Corp. Outline Introduction HILIC Definition
Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) for the Retention of Highly Polar Analytes Eric S. Grumbach,, Diane M. Diehl and Jeffrey R. Mazzeo 2003 Waters Corp. Outline Introduction HILIC Definition
Supporting Information
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 011 Supporting Information Vertically-Aligned ZnO Nanorods Doped with Lithium for Polymer Solar Cells: Defect Related Photovoltaic Properties Pipat Ruankham,
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 011 Supporting Information Vertically-Aligned ZnO Nanorods Doped with Lithium for Polymer Solar Cells: Defect Related Photovoltaic Properties Pipat Ruankham,
Automated Sample Preparation/Concentration of Biological Samples Prior to Analysis via MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy Application Note 222
 Automated Sample Preparation/Concentration of Biological Samples Prior to Analysis via MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy Application Note 222 Joan Stevens, Ph.D.; Luke Roenneburg; Tim Hegeman; Kevin Fawcett
Automated Sample Preparation/Concentration of Biological Samples Prior to Analysis via MALDI-TOF Mass Spectroscopy Application Note 222 Joan Stevens, Ph.D.; Luke Roenneburg; Tim Hegeman; Kevin Fawcett
Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application
 Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application Environmental Author Paul Zavitsanos and Christine Miller Agilent Technologies, Inc. Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 9- USA Abstract
Identification of Steroids in Water by Ion Trap LC/MS/MS Application Environmental Author Paul Zavitsanos and Christine Miller Agilent Technologies, Inc. Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 9- USA Abstract
LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES. Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016
 LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016 1 MOLECULAR ANALYSES Which focus? LOCALIZATION of molecules by Mass Spectrometry
LOCALISATION, IDENTIFICATION AND SEPARATION OF MOLECULES Gilles Frache Materials Characterization Day October 14 th 2016 1 MOLECULAR ANALYSES Which focus? LOCALIZATION of molecules by Mass Spectrometry
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2],
![Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2], Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2],](/thumbs/86/93801604.jpg) Supplementary information Methods Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2], and A/Hong Kong/213/03 [H5N1]) were grown in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells
Supplementary information Methods Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2], and A/Hong Kong/213/03 [H5N1]) were grown in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells
Analysis of Testosterone, Androstenedione, and Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate in Serum for Clinical Research
 Analysis of Testosterone, Androstenedione, and Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate in Serum for Clinical Research Dominic Foley, Michelle Wills, and Lisa Calton Waters Corporation, Wilmslow, UK APPLICATION
Analysis of Testosterone, Androstenedione, and Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate in Serum for Clinical Research Dominic Foley, Michelle Wills, and Lisa Calton Waters Corporation, Wilmslow, UK APPLICATION
Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040 A method for the determination of amantadine in chicken was established using Shimadzu Triple Quadrupole
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Determination of Amantadine Residues in Chicken by LCMS-8040 A method for the determination of amantadine in chicken was established using Shimadzu Triple Quadrupole
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry. Supporting Information
 Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
Characterization of Disulfide Linkages in Proteins by 193 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation (UVPD) Mass Spectrometry M. Montana Quick, Christopher M. Crittenden, Jake A. Rosenberg, and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
MS-IMS (MALDI-IMAGING)?
 MS-IMS (MALDI-IMAGING)? Protein Chemistry/Proteomics and Peptide Synthesis and Array Unit Biomedicum Helsinki and Haartman Institute E-Mail: marc.baumann@helsinki.fi (http://research.med.helsinki.fi/corefacilities/proteinchem)
MS-IMS (MALDI-IMAGING)? Protein Chemistry/Proteomics and Peptide Synthesis and Array Unit Biomedicum Helsinki and Haartman Institute E-Mail: marc.baumann@helsinki.fi (http://research.med.helsinki.fi/corefacilities/proteinchem)
Methods in Mass Spectrometry. Dr. Noam Tal Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry School of Chemistry, Tel Aviv University
 Methods in Mass Spectrometry Dr. Noam Tal Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry School of Chemistry, Tel Aviv University Sample Engineering Chemistry Biology Life Science Medicine Industry IDF / Police Sample
Methods in Mass Spectrometry Dr. Noam Tal Laboratory of Mass Spectrometry School of Chemistry, Tel Aviv University Sample Engineering Chemistry Biology Life Science Medicine Industry IDF / Police Sample
Appendix 1. A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for
 Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
[application note] DIRECT TISSUE IMAGING AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS USING A MALDI SYNAPT HDMS SYSTEM
![[application note] DIRECT TISSUE IMAGING AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS USING A MALDI SYNAPT HDMS SYSTEM [application note] DIRECT TISSUE IMAGING AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS USING A MALDI SYNAPT HDMS SYSTEM](/thumbs/93/111965378.jpg) DIRECT TISSUE IMAGING AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS USING A MALDI SYNAPT HDMS SYSTEM Emmanuelle Claude, Marten Snel, Thérèse McKenna, and James Langridge INTRODUCTION The last decade has seen a
DIRECT TISSUE IMAGING AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS USING A MALDI SYNAPT HDMS SYSTEM Emmanuelle Claude, Marten Snel, Thérèse McKenna, and James Langridge INTRODUCTION The last decade has seen a
Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus
 University of Groningen Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus Published in: Chemistry DOI: 10.1002/chem.201001816
University of Groningen Tunable Hydrophobicity in DNA Micelles Anaya, Milena; Kwak, Minseok; Musser, Andrew J.; Muellen, Klaus; Herrmann, Andreas; Müllen, Klaus Published in: Chemistry DOI: 10.1002/chem.201001816
Introduction. This paper
 Rahul Narayanan 29/11/2014 Introduction Mass spectrometry (MS) has been demonstrated to be a powerful tool for chemical and biological analysis. The high specificity, high sensitivity, and high precision
Rahul Narayanan 29/11/2014 Introduction Mass spectrometry (MS) has been demonstrated to be a powerful tool for chemical and biological analysis. The high specificity, high sensitivity, and high precision
NAS Workshop on the Industrialization of Biology
 High throughput chemical characterization using mass spectrometry NAS Workshop on the Industrialization of Biology Jonathan V. Sweedler University of Illinois Urbana, IL USA May 2014 Funding: DOE, NSF
High throughput chemical characterization using mass spectrometry NAS Workshop on the Industrialization of Biology Jonathan V. Sweedler University of Illinois Urbana, IL USA May 2014 Funding: DOE, NSF
Oxysterol Derivatization MaxSpec Kit
 Oxysterol Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601540 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Oxysterol Derivatization MaxSpec Kit Item No. 601540 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Biomass Oxidation to Formic Acid in Aqueous Media Using Polyoxometalate Catalysts Boosting FA Selectivity by In-situ Extraction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Biomass Oxidation to Formic Acid in Aqueous Media Using Polyoxometalate Catalysts
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Biomass Oxidation to Formic Acid in Aqueous Media Using Polyoxometalate Catalysts
Protein Analysis using Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectroscopy *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m38341 1 Protein Analysis using Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectroscopy * Wilhelm Kienast Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m38341 1 Protein Analysis using Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectroscopy * Wilhelm Kienast Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
On the Dynamics of Kefir Volatome
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (E.S.I.) On the Dynamics of Kefir Volatome Jie-Bi Hu,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (E.S.I.) On the Dynamics of Kefir Volatome Jie-Bi Hu,
PosterREPRINT A NOVEL APPROACH TO MALDI-TOF-MS SAMPLE PREPARATION. Presented at ABRF 2002, Austin, Texas, USA, 9th - 12th March 2002.
 Introduction A NOVEL APPROACH TO MALDI-TOF-MS SAMPLE PREPARATION Ed Bouvier 2, Jeff Brown 1, Emmanuelle Claude 1, John L. Gebler 2, Weibin Chen 2, *Dominic Gostick 1, Kevin Howes 1, James Langridge 1,
Introduction A NOVEL APPROACH TO MALDI-TOF-MS SAMPLE PREPARATION Ed Bouvier 2, Jeff Brown 1, Emmanuelle Claude 1, John L. Gebler 2, Weibin Chen 2, *Dominic Gostick 1, Kevin Howes 1, James Langridge 1,
