Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition
|
|
|
- Jeremy Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition Gut, 1975, 16, G. ANTSAKLIS, M. R. LEWIN1, D. JUNE SUTOR, A. G. A. COWIE, AND C. G. CLARK From the Department of Surgery, University College Hospital Medical School, London, and the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Gallbladder bile obtained at operation from five patients with no symptoms of biliary disease was undersaturated with cholesterol in every case. However, gallbladder bile from patients with stones composed of % crystalline cholesterol was on average just saturated with cholesterol when the gallbladder was functioning and undersaturated when it was not. Regardless of gallbladder function, the patients with stones had on average significantly more cholesterol in their bile than the control group, but the differences between the mean composition of bile from functioning and non-functioning gallbladders were not significant. Common duct bile from patients with non-functioning and functioning gallbladders was on average supersaturated with cholesterol, but there was significantly more bile salt and significantly less cholesterol in the bile from patients with non-functioning gallbladders. Only in the case of patients with functioning gallbladders did the mean composition of the common duct and gallbladder biles differ significantly. The former contained significantly more cholesterol and less bile salt than the latter. It is suggested that patients with non-functioning gallbladders may be 'autocholecystectomised' with the duct bile reverting to a more 'normal' composition. Small and Rapo (1970) and Vlahcevic et al. (1970) showed that hepatic bile in their group of patients undergoing cholecystectomy for cholesterol gallstones was always supersaturated with cholesterol. Other workers, however, have sometimes found hepatic bile of normal composition in similar stoneformers under the same conditions (Mackay et al., 1972; Smallwood et al., 1972; Cahlin et al., 1973). Such different results could reflect variations in the methods used in measuring gallstone and bile composition, or, represent real differences in the groups of patients studied, since production of a supersaturated bile by the liver may not always be the primary abnormality in cholesterol gallstone formation. In order to understand gallstone formation, bile composition must be known in different circumstances. Few (Bell et al., 1973; Cahlin et al., 1973) studies have attempted to relate bile composition and gallbladder function, so we have investigated this in patients with pure cholesterol stones (97-100% crystalline cholesterol). 'Address for correspondence: M. R. L., Department of Surgery, University College Hospital Medical School, University Street, London WCI. Received for publication 14 October 1975 Methods Thirty-two patients undergoing surgery for cholesterol gallstones formed the basis of this study. Preoperatively, liver function tests and serum cholesterol estimations were performed on all patients. Gallbladder function was assessed by oral cholecystography. At operation the gallbladder was aspirated completely to avoid stratification errors (Tera, 1960), having first clamped the cystic duct to minimize mixing of ga!lbladder bile with that from the common duct. Thereafter, the cystic duct was divided and bile obtained by cannulation of the common duct before the performance of operative cholangiography. Of 32 gallbladders aspirated, four contained insufficient bile for analysis, and another five contained white bile and these were excluded from this study. Bile from the common bile duct was not obtained from 18 patients for technical reasons. After cholecystectomy, stones were removed from the"gallbladder for subsequent analysis. At the conclusion of the operation, bile samples were stored at -14 'C. Before chemical analysis, all the samples were thawed slowly to room temperature and vigorously shaken. Total bile salts were estimated by the steroid dehydrogenase method 937
2 938 of Talalay (1960) as modified by Admirand and Small (1968). Cholesterol concentrations were estimated by the methods described by Babson et al. (1962) and Leffler and McDougald (1963). Phospholipids were estimated as inorganic phosphorus (Fiske and Subbarrow, 1925), after extraction of the bile with chloroform and methanol, and digestion of the lipids with sulphuric acid. The results were expressed as percentages of the total molar concentration of cholesterol, phospholipid, and bile salts, and plotted on a three-component diagram showing the micellar zone of cholesterol solubility as determined by Admirand and Small (1968). The gallstones were soaked in formaldehyde for 24 hours, washed well with water and air dried. They were analysed by the x-ray powder method using the techniques described by Sutor and Wooley (1969, 1971). Phospholipid and bile salt results were statistically analysed by multiple comparisons at the 5% level G. Antsaklis, M. R. Lewin, D. June Sutor, A. G. A. Cowie, and C. G. Clark (Scheffe, 1959), while the cholesterol results were analysed using Welch's approximate t test on the transformed data (Scheffe, 1970). Bile was obtained only from the gallbladders of five patient undergoing operations for other conditions-namely, duodenal ulceration, Crohn's disease, carcinoma of the stomach, and pancreatic disease (two cases). None of these patients had symptoms of biliary disease. Results No patient had any biochemical evidence of altered or impaired liver function or an abnormal serum cholesterol. CONTROLS The mean molar percentage composition of gallbladder bile from the five control subjects is given in Table 1 together with other results from the Author No. Origin ofsample Percentage molar lipid composition (mean ± SEM) - Bile salts Cholesterol Phospholipids Present study 5 Gallbladder bile ± Simmons et al. (1972) 10 Duodenal aspirate ± Mackay et al. (1972) 21 Duodenal aspirate t Heller and Bouchier* (1973) 12 Gallbladder bile ±10 ± Vlahcevic et al. (1972) 7 Duodenal aspirate Table 1 Percentage molar lipid composition in control subjects *SEM calculated from original data. Authors Gallbladder No. Percentage molar lipid composition (mean + SEM) function Gallbladder bile Common duct bile Cholesterol Phospholipids Bile salts No. Cholesterol Phospholipids Bile salts Present study Yes ±24 t ±49 Present study No ± t Vlahcevic et al.* (1970) Not specified ± 15 t SmallandRapo(1970) Yes ±05 ±04 t06 ±12 ± Mackayetal.(1972) Yes t ±07 ± Vlahcevicet al. (1972) Yes t ± 45 t ± 65 Simmons et al. (1972) Yes ± Heller and Bouchier* (1973) Yes ± Table 2 Percentage molar lipid composition in gallbladder and common duct bile of cholesterol stone-formers *SEM calculated from original data.
3 Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition */. BILE SALTS Fig. 1 Mean ± SEM and individual resultsfor biliary lipid composition in gallbladder bilefromfive control subjects ers 939 Fig. 2 Mean ± SEMfor biliary lipid composition in gallbladder and common duct bilefrom patients with cholesterolgallstones Gut: first published as /gut on 1 December Downloaded from */. BILE SALTS literature. Only one of these refers to bile obtained by the same method, the remainder being an analysis of duodenal aspirate. The individual results are plotted in Fig. 1 together with the mean and one standard error. All of these points were within the micellar zone representing the composition of solutions undersaturated with respect to cholesterol. STONE-FORMERS The mean molar percentages for the three main on 24 September 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 940 biliary lipids in gallbladder and common duct bile for patients with functioning and non-functioning gallbladders are given in Table 2 together with some other published results. Our mean values with one standard error are plotted in Fig. 2. The points representing the mean composition of the common duct biles from patients with either functioning or non-functioning gallbladders fell outside the micellar zone, the latter point lying closer to the boundary. Bile from functioning gallbladders had a mean value which was on the boundary of the micellar zone and was thus just saturated with cholesterol, while that from non-functioning gallbladders had a mean composition represented by a point lying just within the micellar zone. There was, however, considerable variation in the individual values. In the group with functioning gallbladders, the composition of 60% gallbladder biles and 100% common duct biles fell outside the micellar zone, while, in the group with non-functioning gallbladders, the composition of 50% gallbladder biles and 78% common duct biles were outside this area. Table 3 shows the statistical significance in a comparison of the mean molar percentages of the three main biliary lipids. There was significantly more cholesterol in the gallbladder bile of stoneformers than in that of the controls regardless of gallbladder function (p < for patients with functioning and P < 0.05 for those with nonfunctioning gallbladders). Comparing the bile from the common duct and the bile from the gallbladder in stone-formers with functioning gallbladders, there was significantly more cholesterol (p < 0.01) Compared groups G. Antsaklis, M. R. Lewin, D. June Sutor, A. G. A. Cowie, and C. G. Clark Level ofsignificance Cholesterol Phospho- Bile salts lipids Control, GB-bile vs p < NS NS Functioning GB, GB-bile Control, GB-bile vs p < 005 NS NS Non-functioning GB, GB-bile Functioning GB, GB-bile vs p<oo1 NS p<0-05 Functioning GB, CBD-bile Non-functioning GB, GB-bile vs NS NS NS Non-functioning GB, CBD-bile Functioning GB, CBD-bile vs p < 005 NS p <O05 Non-functioning GB, CBD-bile Functioning GB, GB-bile vs NS NS NS Non-functioning GB, GB-bile GB: gallbladder; CBD: common bile duct Table 3 Statistical testing between individual groups GB: gall bladder. CBD: common bile duct. and less bile salt (P < 0.05) in the common duct bile. Similarly, there was significantly more cholesterol (p < 0.05) and less bile salt (p < 0.05) in the common duct bile of stone-formers with functioning gallbladders as compared with common duct bile from patients with non-functioning gallbladders. Discussion This study shows that the composition of the common duct bile in patients with cholesterol gallstones is potentially lithogenic, as is the composition of the gallbladder bile of those patients whose gallbladder is functioning. However, if the gallbladder is nonfunctioning, the bile contained within it is more 'normal'. When points representing the molar ratios of the lipids in these biles are plotted on triangular coordinates, only the biles from the gallbladders of patients with non-functioning gallbladders fall within the micellar zone of cholesterol solubility. Despite considerable variation in individual cases, it is evident from our results that the difference chiefly responsible for this abnormality is a relative increase in the proportion of cholesterol and a fall in the proportion of bile salt from the more normal levels seen in the controls. The molar ratios seen in this series for control patients are similar to those reported by others (Table 1), although there is a somewhat higher proportion of bile salt and lower proportion of phospholipid. However, the analyses in other series were performed chiefly on bile obtained by duodenal aspiration and are not strictly comparable. Table 2 shows that the biles from patients with cholesterol stones also have rather more bile salt and rather less phospholipid but otherwise compare well in most circumstances with bile compositions reported by others. The striking difference is the considerable increase in the cholesterol content of the bile from the common duct in our patients with functioning gallbladders. This finding is unlikely to be due to differences in methodology, since the analyses compare well in other circumstances. However, it is possible that cholesterol crystals may have been present in the bile from the common duct of patients with functioning gallbladders and not filtered before analysis. Van der Linden and Nakayama (1974) have shown that an excess of crystals may be present in the hepatic bile of such patients compared with patients whose gallbladder is not functioning. In patients forming cholesterol gallstones, the cholesterol content of gallbladder bile is significantly greater than normal controls whether the gallbladder is functioning (p < 0-001) or non-functioning (p < 0-05). Normal common duct bile dould not be obtained. Common duct bile from patients with
5 Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition functioning gallbladders contained significantly more cholesterol than the gallbladder bile (p < 0 01), but no such difference occurred in patients with non-functioning gallbladders (Table 3). These statistical differences, however, do not necessarily indicate the lithogenic potential of bile. It is only on consideration of the phase diagrams (Figs. 1 and 2), that it is evident that the most grossly lithogenic bile comes from the common duct in patients with functioning gallbladders. Since all patients had virtually pure cholesterol stones-and can therefore be presumed to be a population virtually with the same defect of bile composition-the conclusion must be that progressive deterioration in gallbladder function has the effect of reducing the lithogenic potential of common duct bile. Admirand and Small (1968) suggested that the lithogenic changes in gallbladder bile composition could be detected in all cases, but others have been unable to confirm this (Smallwood et al., 1972; Heller and Bouchier, 1973). In this series only 60% of the gallbladder biles tested were potentially lithogenic, although 78 % of the common duct biles when the gallbladder was non-functioning and 100 % of the common duct biles wh-n the gallbladder was functioning had molar ratios which could be plotted above the micellar line. These findings do, however, support the view that the primary biochemical abnormality occurs during the hepatic production of bile (Small and Rapo, 1970; Vlahcevic et al., 1970). Mackay et al. (1972), while supporting this view, point out that there must be other factors of importance since, although most abnormal biles contain more cholesterol and less bile salt, many have a composition still within the micellar zone. Malagelada et al. (1973) showed that cholecystectomy, which changes the dynamics of the enterohepatic circulation from an intermittent process to a continuous one, results in a 24 hour output of bile which exceeds that which occurred preoperatively. This was disputed by Adler et al. (1974) who reported no change in secretion rates but their study was confined to a very small group of American Indians. Support for Malagelada's view came from Shaffer et al. (1972) who reported that interference with the enterohepatic circulation resulted in a fourfold increase in bile salt synthesis. The importance of the rate of bile salt secretion was shown recently by Schersten et al. (1974) who showed that a minimum rate of secretion existed below which the bile became saturated with cholesterol. Fasting is known to affect bile composition in Rhesus monkeys (Redinger et al., 1971), although the bile never becomes oversaturated, and in man (Metzger et al., 1973), in whom the bile becomes more lithogenic. This may be a function of the fall in bile salt secretion rate or 94t a rise in cholesterol. After cholecystectomy, the composition of common duct bile becomes more normal (Nilsson and Scherstdn, 1969; Small and Rapo, 1970; Schersten et al., 1971; Simmons et al., 1972) and this is probably a result of the change in enterohepatic circulation dynamics. Recently, Nakayama and Van der Linden (1974) have again reported this finding and in their cases the gallbladder bile at operation was not oversaturated, while the common duct bile was. They suggested that preoperative fasting might account for this difference. Recently, Pederson et al. (1974) reported the effect of small doses of chenodeoxycholate given to four patients with radiolucent gallstones and functioning gallbladders. It was shown that there was on average a 40 % reduction in the 'input of cholesterol into the rapidly miscible pool'. If this effect of bile salt on cholesterol metabolism is confirmed, it might explain the findings in the present series of a lower cholesterol level in bile if the gallbladder is non-functioning and the findings of a 'normalisation' of bile composition as reported by others after cholecystectomy. We thank Mr I. Robertson, MRC Statistics Unit, for analysing the data, and the Medical Research Council for financial assistance. References Adler, R. D., Metzger, A. L., and Grundy, S. M. (1974). Biliary lipid secretion before and after cholecystectomy in American Indians with cholesterol gallstones. Gastroenterology, 66, Admirand, W. H., and Small, D. M. (1968). The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man. Journal ofclinical Investigation, 47, Babson, A. L., Shapiro, P. O., and Phillips, G. E. (1962). A new assay for cholesterol and cholesterol esters in serum which is not affected by bilirubin. Clinica et Chimica Acta, 7, Bell, G. D., Sutor, D. J., and Dowling, R. H. (1973). Relationship between bile and gallstone composition to the rate of gallstone dissolution in the Rhesus monkey and in man. 9th International Congress of Gastroenterology, Paris Archives Franpais des Maladies de l'appareil Digestif, 6, Cahlin, E., Jonsson, J., Nilsson, S., and Scherst6n, T. (1973). Biliary lipid composition in normolipidemic and prebeta hyperlipoproteinemic gallstone patients. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 8, Fiske, C. H., and Subbarrow, Y. (1925). The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 66, Heller, F., and Bouchier, I. A. D. (1973). Cholesterol and bile salt studies on the bile of patients with cholesterol gallstones. Gut, 14, Leffler, H. H., and McDougald, C. H. (1963). Estimation of cholesterol in serum. American Journal ofclinical Pathology, 39, Mackay, C., Crook, J. N., Smith, D. C., and McAllister,
6 942 G. Antsaklis, M. R. Lewin, D. June Sutor, A. G. A. Cowie, and C. G. Clark R. A. (1972). The composition of hepatic and gallbladder bile in patients with gallstones. Gut, 13, Malagelada, J. R., Go, V. L. W., Summerskill, W. H. J., and Gamble, W. S. (1973). Bile acid secretion and biliary bile acid composition altered by cholecystectomy. American Journal of Digestive Diseases, 18, Metzger, A. L., Adler, R. D., Heymsfield, S., and Grundy, S. M. (1973). Diurnal variation in biliary lipid composition. New England Journal of Medicine, 288, Nakayama, F., and Van der Linden, W. (1974). Role of gallbladder in gallstone formation. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica, 140, Nilsson, S., and Schersten, T. (1969). Importance of bile acids for phospholipid secretion into human hepatic bile. Gastroenterology, 57, Pedersen, L., Arnfred, T., and Hess Thaysen, E. (1974). Cholesterol kinetics in patients with cholesterol gallstones before and during chenodeoxycholic acid treatment. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 9, Redinger, R. N., Herman, A. H., and Small, D. M. (1971). Effect of diet on bile composition in the Rhesus monkey. Gastroenterology, 60, 198. Scheffe, H. (1959). The Analysis of Variance. Wiley: New York. Scheffe, H. (1970). Practical solutions of the Behrens-Fisher problem. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 65, Schersten, T.. Cahlin, E., Jonsson, J., Lindblad, L., and Nilsson, S. (1974). Supersaturated bile-is it due to a metabolic disorder or to an impaired gallbladder. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 9, Scherst6n, T., Nilsson, S., Cahlin, E., Filipson, M., and Brodin-Persson, G. (1971). Relationship between the biliary excretion of bile acids and the excretion of water, lecithin, and cholesterol in man. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 1, Shaffer, E. A., Braasch, J. W., and Small, D. M. (1972). Bile composition at and after surgery in normal persons and patients with gallstones. New England Journal of Medicine, 287, Simmons, F., Ross, A. P. J., and Bouchier, I. A. D. (1972). Alterations in hepatic bile composition after cholecystectomy. Gastroenterology, 63, Small, D. M., and Rapo, S. (1970). Source of abnormal bile in patients with cholesterol gallstones. New England Journal of Medicine, 283, Smallwood, R. A., Jablonski, P., and Watts, J. McK. (1972). Intermittent secretion of abnormal bile in patients with cholesterol gall stones. British Medical Journal, 4, Sutor, D. J., and Wooley, S. E. (1969). X-ray diffraction studies of the composition of gallstones from English and Australian patients. Gut, 10, Sutor, D. J., and Wooley, S. E. (1971). A statistical survey of the composition of gallstones in eight countries. Gut, 12, Talalay, P. (1960). Enzymic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods in Biochemical Analysis, 8, Tera, H. (1960). Stratification of human gallbladder bile in vivo. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica, Suppl. 256, Van der Linden, W. and Nakayama, F. (1974). Occurrence of cholesterol crystal, in human bile. Gut, 15, Vlahcevic, Z. R., Bell, C. C., Jr., Gregory, D. H., Buker, G., Juttijudata, P., and Swell, L. (1972). Relationship of bile acid pool size to the formation of lithogenic bile in female Indians of the southwest. Gastroenterology, 62, Vlahcevic, Z. R., Bell, C. C., Jr., and Swell, L. (1970). Significance of the liver in the production of lithogenic bile in man. Gastroenterology, 59, Gut: first published as /gut on 1 December Downloaded from on 24 September 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 298-303, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE BILE ACID METABOLISM IN CIRRHOSIS III. Biliary lipid secretion
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 298-303, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE BILE ACID METABOLISM IN CIRRHOSIS III. Biliary lipid secretion
Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and
 Gut, 1978, 19, 22-224 Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and total CO2 in bile D. JUNE SUTOR AND LYNETTE I. WILKIE From the Department of Chemistry, University College London, London SUMMARY Measurement
Gut, 1978, 19, 22-224 Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and total CO2 in bile D. JUNE SUTOR AND LYNETTE I. WILKIE From the Department of Chemistry, University College London, London SUMMARY Measurement
BILIARY LIPID SECRETION BEFORE AND AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY IN AMERICAN INDIANS WITH CHOLESTEROL GALLSTONES
 (; l\~thoe~teholor.y 6(l:1~1 ~ - 1 ~ 1-;. I ~J74 COiJ\Tight l'l,~ I,, TllP Wi ll ia m, &: Wilki ils Co. V(II. 6'3. ~(l. f) Printed ill ( r.sa. BILIARY LIPID SECRETION BEFORE AND AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY IN
(; l\~thoe~teholor.y 6(l:1~1 ~ - 1 ~ 1-;. I ~J74 COiJ\Tight l'l,~ I,, TllP Wi ll ia m, &: Wilki ils Co. V(II. 6'3. ~(l. f) Printed ill ( r.sa. BILIARY LIPID SECRETION BEFORE AND AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY IN
Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects
 12 LI T. C. Northfield, N. F. LaRusso, A. F. Hofmann, and J. L. Thistle Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects T. C. NORTHFIELD, N. F. LaRUSSO, A. F. HOFMANN, AND J. L. THISTLE
12 LI T. C. Northfield, N. F. LaRusso, A. F. Hofmann, and J. L. Thistle Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects T. C. NORTHFIELD, N. F. LaRUSSO, A. F. HOFMANN, AND J. L. THISTLE
carbohydrate diets on bile cholesterol saturation and bile acid metabolism
 Gut, 1983, 24, 2-6 and gall stones: effects of refined and unrefined carbohydrate diets on bile cholesterol saturation and bile acid metabolism J R THORNTON, P M EMMETT, and K W HEATON From the University
Gut, 1983, 24, 2-6 and gall stones: effects of refined and unrefined carbohydrate diets on bile cholesterol saturation and bile acid metabolism J R THORNTON, P M EMMETT, and K W HEATON From the University
The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man
 The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man William H. Admirand, Donald M. Small J Clin Invest. 1968;47(5):1043-1052. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci105794. Research Article The concentrations
The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man William H. Admirand, Donald M. Small J Clin Invest. 1968;47(5):1043-1052. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci105794. Research Article The concentrations
Progress report. The present position concerning gallstone dissolution. changes in bile which lead to the formation of cholesterol gallstones
 Progress report The present position concerning gallstone dissolution Gut, 1974, 15, 913-929 In prelisterian times, when conservative measures were the only means available to the doctor for the relief
Progress report The present position concerning gallstone dissolution Gut, 1974, 15, 913-929 In prelisterian times, when conservative measures were the only means available to the doctor for the relief
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences CORRELATION OF SERUM LIPIDS AND GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN CHOLELITHIASIS
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO CHEMISTRY CORRELATION OF SERUM LIPIDS AND GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN CHOLELITHIASIS Corresponding Author DEVAKI R.N Department of Biochemistry,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO CHEMISTRY CORRELATION OF SERUM LIPIDS AND GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN CHOLELITHIASIS Corresponding Author DEVAKI R.N Department of Biochemistry,
Mechanisms of Lithogenic Bile Formation in American Indian Women with Cholesterol Gallstones
 Mechanisms of Lithogenic Bile Formation in American Indian Women with Cholesterol Gallstones ScoTT M. GRUNDY, ALLAN L. MEIZGER, and RONALD D. ADLER From the Phoenix Clinical Research Section, National
Mechanisms of Lithogenic Bile Formation in American Indian Women with Cholesterol Gallstones ScoTT M. GRUNDY, ALLAN L. MEIZGER, and RONALD D. ADLER From the Phoenix Clinical Research Section, National
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64:1156-1162, 1973 Copyright by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No. 6 Printed in U.S. A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE INTERRELATIONSHIP OF BILE SALTS, PHOSPHOLIPIDS, AND CHOLESTEROL
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64:1156-1162, 1973 Copyright by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No. 6 Printed in U.S. A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE INTERRELATIONSHIP OF BILE SALTS, PHOSPHOLIPIDS, AND CHOLESTEROL
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 68: 326-334, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 68, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE EFFECTS OF LOW DOSE CHENODEOXYCHOLIC ACID FEEDING ON BILIARY
GASTROENTEROLOGY 68: 326-334, 1975 Copyright 1975 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 68, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE EFFECTS OF LOW DOSE CHENODEOXYCHOLIC ACID FEEDING ON BILIARY
BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS
 1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
J. clin. Path., 26, suppl. (Ass. Clin. Path.), 5, ACTIVE TRANSPORT DIFFLS1ON. Fig 1. The normal bile acid enterohepatic circulation.
 J. clin. Path., 26, suppl. (Ass. Clin. Path.), 5, 59-67 The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids as they relate to lipid disorders R. HERMON DOWLING From the MRC Intestinal Malabsorption Group, Department
J. clin. Path., 26, suppl. (Ass. Clin. Path.), 5, 59-67 The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids as they relate to lipid disorders R. HERMON DOWLING From the MRC Intestinal Malabsorption Group, Department
Start Module 2: Physiology: Bile, Bilirubin. Liver and the Lab
 Start Module 2: Physiology: Bile, Bilirubin Liver and the Lab Bile Physiology WYNTKFTB (Intro to Pathology) Applied Anatomy Components Function Synthesis Enterohepatic circulation Imbalance of components
Start Module 2: Physiology: Bile, Bilirubin Liver and the Lab Bile Physiology WYNTKFTB (Intro to Pathology) Applied Anatomy Components Function Synthesis Enterohepatic circulation Imbalance of components
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
Serum Squalene in Patients with Gallstones*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 32, No. 2, June, 1983 HIJM 32-24 157 Serum Squalene in Patients with Gallstones*) Goro KAJIYAMA, Itaru HORIUCHI, Shoji NISHIMURA, Fumiaki HINO, Hiroshi SASAKI
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 32, No. 2, June, 1983 HIJM 32-24 157 Serum Squalene in Patients with Gallstones*) Goro KAJIYAMA, Itaru HORIUCHI, Shoji NISHIMURA, Fumiaki HINO, Hiroshi SASAKI
The effect of coeliac disease upon bile salts
 Gut, 1973, 14, 24-2 T. S. LOW-BEER,1 K. W. HEATON, E. W. POMARE, AND A. E. READ From the University Department of Medicine, Bristol Royal Infirmary SUMMARY The size and composition of the bile salt pool
Gut, 1973, 14, 24-2 T. S. LOW-BEER,1 K. W. HEATON, E. W. POMARE, AND A. E. READ From the University Department of Medicine, Bristol Royal Infirmary SUMMARY The size and composition of the bile salt pool
Cholesterol Solubility in Bile
 Cholesterol Solubility in Bile EVDENCE THAT SUPERSATURATED BLE S FREQUENT N HEALTHY MAN R. THOMAS HOLZBACH, MrrsuKo MARSH, MONCA OLSZEWS, and KTr Hoi" From the Gastrointestinal Research Unit, Department
Cholesterol Solubility in Bile EVDENCE THAT SUPERSATURATED BLE S FREQUENT N HEALTHY MAN R. THOMAS HOLZBACH, MrrsuKo MARSH, MONCA OLSZEWS, and KTr Hoi" From the Gastrointestinal Research Unit, Department
Henry Y. I. Mok, Klaus von Bergmann, and Scott M. Grundy
 Effects of continuous and intermittent feeding on biliary lipid outputs in man: application for measurements of intestinal absorption of cholesterol and bile acids Henry Y. I. Mok, Klaus von Bergmann,
Effects of continuous and intermittent feeding on biliary lipid outputs in man: application for measurements of intestinal absorption of cholesterol and bile acids Henry Y. I. Mok, Klaus von Bergmann,
Hepatobiliary lipids איך טיפול נולד... from bench to bedside. Fred M Konikoff, MD, MSc, FAASLD
 Hepatobiliary lipids איך טיפול נולד... from bench to bedside Fred M Konikoff, MD, MSc, FAASLD Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Meir Medical Center, Kfar Saba, and Research Laboratory of Cholesterol
Hepatobiliary lipids איך טיפול נולד... from bench to bedside Fred M Konikoff, MD, MSc, FAASLD Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Meir Medical Center, Kfar Saba, and Research Laboratory of Cholesterol
The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids during continuous liquid formula perfusion of the duodenum
 The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids during continuous liquid formula perfusion of the duodenum P. Rutgeerts, Y. Ghoos, and G. Vantrappen Department of Medical Research, University of Leuven, University
The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids during continuous liquid formula perfusion of the duodenum P. Rutgeerts, Y. Ghoos, and G. Vantrappen Department of Medical Research, University of Leuven, University
Serum Lipid Profile in Pre and Post Cholecystectomy Patients
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27123:2267 Surgery Section Original Article Serum Lipid Profile in Pre and Post Cholecystectomy Patients Kuldip Singh Ahi, Rajinder Pal Singh, Harpreet Kaur, Ashish Moudgil ABSTRACT
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27123:2267 Surgery Section Original Article Serum Lipid Profile in Pre and Post Cholecystectomy Patients Kuldip Singh Ahi, Rajinder Pal Singh, Harpreet Kaur, Ashish Moudgil ABSTRACT
Enterohepatic circulation rates of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid in man
 Gut, 1979, 20, 1078-1082 Enterohepatic circulation rates of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid in man K. A. EINARSSON,' S. M. GRUNDY, AND W. G. M. HARDISON From the Department of Meaicine, School of
Gut, 1979, 20, 1078-1082 Enterohepatic circulation rates of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid in man K. A. EINARSSON,' S. M. GRUNDY, AND W. G. M. HARDISON From the Department of Meaicine, School of
cholesterol gall stone formation
 Liver and biliary Effects of dietary sucrose on factors influencing cholesterol gall stone formation D WERNER, P M EMMETT, AND K W HEATON From the University Department of Medicine, Bristol Royal Infirmary,
Liver and biliary Effects of dietary sucrose on factors influencing cholesterol gall stone formation D WERNER, P M EMMETT, AND K W HEATON From the University Department of Medicine, Bristol Royal Infirmary,
Effects of feeding cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on cholesterol absorption and hepatic secretion of biliary lipids in man
 Effects of feeding cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on cholesterol absorption and hepatic secretion of biliary lipids in man Kurt Einarsson and Scott M. Grundy Department of Medicine, Veterans Administration
Effects of feeding cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on cholesterol absorption and hepatic secretion of biliary lipids in man Kurt Einarsson and Scott M. Grundy Department of Medicine, Veterans Administration
The Formation of Abnormal Bile and Cholesterol Gallstones from Dietary Cholesterol in the Prairie Dog
 The Formation of Abnormal Bile and Cholesterol Gallstones from Dietary Cholesterol in the Prairie Dog D. E. BRENNEMAN, WnIAM E. CONNOR, E. L. FoRKER, and LARmY DENBESTEN From the Clinical Research Center
The Formation of Abnormal Bile and Cholesterol Gallstones from Dietary Cholesterol in the Prairie Dog D. E. BRENNEMAN, WnIAM E. CONNOR, E. L. FoRKER, and LARmY DENBESTEN From the Clinical Research Center
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
 GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy and biliary lipidsa dose-response study
 Gut, 1980, 21, 305-310 Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy and biliary lipidsa dose-response study M C BATESON, P E ROSS, J MURISON, J H B SAUNDERS, AND I A D BOUCHIER From the Department of Medicine, Ninewells
Gut, 1980, 21, 305-310 Ursodeoxycholic acid therapy and biliary lipidsa dose-response study M C BATESON, P E ROSS, J MURISON, J H B SAUNDERS, AND I A D BOUCHIER From the Department of Medicine, Ninewells
human gall bladder bile
 Gut, 1986, 27, 1382-1386 Effect of binding of ionised calcium on the in vitro nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirubinate in human gall bladder bile S GALLINGER, P R C HARVEY, C N PETRUNKA, AND
Gut, 1986, 27, 1382-1386 Effect of binding of ionised calcium on the in vitro nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirubinate in human gall bladder bile S GALLINGER, P R C HARVEY, C N PETRUNKA, AND
The organic matrix of gallstones
 Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
Effects of Polyunsaturated Fats on Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia
 Effects of Polyunsaturated Fats on Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia SCOTr M. GRUNDY From the Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, University of California, San Diego and Veterans
Effects of Polyunsaturated Fats on Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia SCOTr M. GRUNDY From the Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, University of California, San Diego and Veterans
Circadian distribution of bile acid in the enterohepatic circulatory system in hamsters
 Circadian distribution of bile acid in the enterohepatic circulatory system in hamsters Kang-Jey Ho Department of Pathology, Medical Center, University of Alabama in Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama 35294
Circadian distribution of bile acid in the enterohepatic circulatory system in hamsters Kang-Jey Ho Department of Pathology, Medical Center, University of Alabama in Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama 35294
Table 1 Clinical findings of diabetics. hypoglycemic agent
 Table 1 Clinical findings of diabetics 1)oral hypoglycemic agent Fig. 3 The ratio of primary bile acid to total bile acid Fig. 1 Fecal wet weight Fig. 4 Fecal fatty acid Fig. 2 Fecal bile acid excretion
Table 1 Clinical findings of diabetics 1)oral hypoglycemic agent Fig. 3 The ratio of primary bile acid to total bile acid Fig. 1 Fecal wet weight Fig. 4 Fecal fatty acid Fig. 2 Fecal bile acid excretion
The gallbladder is a digestive organ located under the right side of the liver and connected to the common bile duct.
 The gallbladder is a digestive organ located under the right side of the liver and connected to the common bile duct. Bile is a digestive juice secreted by the liver that helps digest fats and has other
The gallbladder is a digestive organ located under the right side of the liver and connected to the common bile duct. Bile is a digestive juice secreted by the liver that helps digest fats and has other
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Ursodeoxycholic acid 250mg Hard Capsules 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each hard gelatin capsule contains Ursodeoxycholic
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Ursodeoxycholic acid 250mg Hard Capsules 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each hard gelatin capsule contains Ursodeoxycholic
Clinical and Nutritional Study on Gallstone. Disease in Japan. Haruo Kameda, MD, Fumitake Ishihara, MD, Koji Shibata, MDand Eiichi Tsukie, MD
 Original Article Clinical and Nutritional Study on Gallstone Haruo Kameda, MD, Fumitake Ishihara, MD, Koji Shibata, MDand Eiichi Tsukie, MD The dietary factors, as a cause on increasing incidence of gallstones
Original Article Clinical and Nutritional Study on Gallstone Haruo Kameda, MD, Fumitake Ishihara, MD, Koji Shibata, MDand Eiichi Tsukie, MD The dietary factors, as a cause on increasing incidence of gallstones
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION
 DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
Gallstones & Other Biliary Disorders
 Gallstones & Other Biliary Disorders Jason Smith MD DMI FRCS(Gen.Surg) Consultant General & Colorectal Surgeon Introduction Gallstones are found in 12% men and 24% women Prevalence increases with advancing
Gallstones & Other Biliary Disorders Jason Smith MD DMI FRCS(Gen.Surg) Consultant General & Colorectal Surgeon Introduction Gallstones are found in 12% men and 24% women Prevalence increases with advancing
Gallstones Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Gutscharity.org.uk
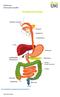 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
Bile acid metabolism. doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc.
 Bile acid metabolism doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc. Bile acid metabolism Importance: Availability for fat & cholesterol absorption Regulates total body pool of cholesterol Factors that synthesis promote
Bile acid metabolism doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc. Bile acid metabolism Importance: Availability for fat & cholesterol absorption Regulates total body pool of cholesterol Factors that synthesis promote
Biliary MRI w Eovist
 Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic
 Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic substances. Describe the formation of bile,its constitents
Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic substances. Describe the formation of bile,its constitents
Ali Yaghi. Yaseen Fatayer. M.Khatatbeh
 6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
from Mentha piperidis, the peppermint plant or the German (Blumenberg, 1957), Japanese (Kameda, 1960; Okabe, 1960; Noda et al., 1965), and English
 Gut, 1979, 20, 312-317 Clinical trial Rowachol - a possible treatment for cholesterol gallstones' J. DORAN, M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, AND G. D. BELL From the University Department of Therapeutics, City Hospital,
Gut, 1979, 20, 312-317 Clinical trial Rowachol - a possible treatment for cholesterol gallstones' J. DORAN, M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, AND G. D. BELL From the University Department of Therapeutics, City Hospital,
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
Significance of Ca-soap formation for calcium
 Gut, 1977, 18, 64-68 Significance of Ca-soap formation for calcium absorption in the rat G. GACS AND D. BARLTROP' From the Paediatric Unit, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The significance
Gut, 1977, 18, 64-68 Significance of Ca-soap formation for calcium absorption in the rat G. GACS AND D. BARLTROP' From the Paediatric Unit, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The significance
Effect of Oral Chenodeoxycholic Acid on Bile Acid Kinetics
 Effect of Oral Chenodeoxycholic Acid on Bile Acid Kinetics and Biliary Lipid Composition in Women with Cholelithiasis RUDY C. DANZINGER, ALAN F. HOFMANN, JOHNSON L. THISTLE, and LESLIE J. SCHOENFIELD From
Effect of Oral Chenodeoxycholic Acid on Bile Acid Kinetics and Biliary Lipid Composition in Women with Cholelithiasis RUDY C. DANZINGER, ALAN F. HOFMANN, JOHNSON L. THISTLE, and LESLIE J. SCHOENFIELD From
THE NATURAL COURSE OF GALLSTONE DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, 3 Printed in U.S.A. THE NATURAL COURSE OF GALLSTONE DISEASE Eleven-year review of 781 nonoperated cases ANDERS WENCKERT, M.D., AND
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, 3 Printed in U.S.A. THE NATURAL COURSE OF GALLSTONE DISEASE Eleven-year review of 781 nonoperated cases ANDERS WENCKERT, M.D., AND
Gallbladder and Small Intestinal Regulation of Biliary Lipid Secretion during Intraduodenal Infusion of Standard Stimuli
 Gallbladder and Small Intestinal Regulation of Biliary Lipid Secretion during Intraduodenal Infusion of Standard Stimuli GREGORY T. EVERSON, MICHAEL J. LAWSON, CAROL MCKINLEY, RADENE SHOWALTER, and FRED
Gallbladder and Small Intestinal Regulation of Biliary Lipid Secretion during Intraduodenal Infusion of Standard Stimuli GREGORY T. EVERSON, MICHAEL J. LAWSON, CAROL MCKINLEY, RADENE SHOWALTER, and FRED
Effects of lovastatin and dietary cholesterol on bile acid kinetics and bile lipid composition in healthy male subjects
 Effects of lovastatin and dietary cholesterol on bile acid kinetics and bile lipid composition in healthy male subjects William C. Duane Department of Medicine, Veterans Affairs Medical Center and University
Effects of lovastatin and dietary cholesterol on bile acid kinetics and bile lipid composition in healthy male subjects William C. Duane Department of Medicine, Veterans Affairs Medical Center and University
Cholangitis. John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California, San Francisco. Greek Symmetry of the Universe and Humanity
 Cholangitis John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California, San Francisco Greek Symmetry of the Universe and Humanity The Four Humors the Medieval European Concept Gentile
Cholangitis John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California, San Francisco Greek Symmetry of the Universe and Humanity The Four Humors the Medieval European Concept Gentile
cholesterol saturation in patients with liver cirrhosis
 Gut, 1986, 27, 23-28 Effect of small doses of deoxycholic acid on bile cholesterol saturation in patients with liver cirrhosis PAOLA DI DONATO, FRANCESCA CARUBBI, M PONZ DE LEON, AND N CARULLI From Semeiotica
Gut, 1986, 27, 23-28 Effect of small doses of deoxycholic acid on bile cholesterol saturation in patients with liver cirrhosis PAOLA DI DONATO, FRANCESCA CARUBBI, M PONZ DE LEON, AND N CARULLI From Semeiotica
Department of Internal Medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at Dallas, Dallas, TX Supplementary key words phospholipid
 Regulation of biliary cholesterol output in the rat: dissociation from the rate of hepatic cholesterol synthesis, the size of the hepatic cholesteryl ester pool, and the hepatic uptake of chylomicron cholesterol
Regulation of biliary cholesterol output in the rat: dissociation from the rate of hepatic cholesterol synthesis, the size of the hepatic cholesteryl ester pool, and the hepatic uptake of chylomicron cholesterol
Fecal fat, bile acid, and sterol excretion and biliary lipid changes in jejunoileostomy patients1 2
 Fecal fat, acid, and sterol excretion and biliary lipid changes in jejunoileostomy patients1 2 William W. Faloon, M.D.,3 Albert Rubulis, Ph.D.,4 John Knipp, M.D.,5 Char/es D. Sherman, M.D.,6 and Mary S.
Fecal fat, acid, and sterol excretion and biliary lipid changes in jejunoileostomy patients1 2 William W. Faloon, M.D.,3 Albert Rubulis, Ph.D.,4 John Knipp, M.D.,5 Char/es D. Sherman, M.D.,6 and Mary S.
SIMULTANEOUS MEASUREMENT OF THE PANCREATIC AND BILIARY RESPONSE TO CCK AND SECRETIN
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:403-407, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. SIMULTANEOUS MEASUREMENT OF THE PANCREATIC AND BILIARY RESPONSE TO CCK AND SECRETIN Primate
GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:403-407, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. SIMULTANEOUS MEASUREMENT OF THE PANCREATIC AND BILIARY RESPONSE TO CCK AND SECRETIN Primate
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
ACID-BASE COMPOSITION OF PANCREATIC JUICE AND BILE.
 ACID-BASE COMPOSITION OF PANCREATIC JUICE AND BILE. BY JAMES L. GAMBLE, M.D., AND MONROE A. McIVER, M.D. WI~r ~a~ ASSlSTANC~ OF PAULINE MARSII AND MAURICE M. TOL~.N. (From the Departments of Pediatrics
ACID-BASE COMPOSITION OF PANCREATIC JUICE AND BILE. BY JAMES L. GAMBLE, M.D., AND MONROE A. McIVER, M.D. WI~r ~a~ ASSlSTANC~ OF PAULINE MARSII AND MAURICE M. TOL~.N. (From the Departments of Pediatrics
Bile composition. Pathophysiology of Gallstone Formation and Pancreatitis. Bile
 Bile composition Pathophysiology of Gallstone Formation and Pancreatitis Robert F. Schwabe rfs2102@columbia.edu Phospholipids Miscellaneous (Pigment, Protein) (Lecithin) Bile Salts 0.7% 4% H 2 0 1% 12%
Bile composition Pathophysiology of Gallstone Formation and Pancreatitis Robert F. Schwabe rfs2102@columbia.edu Phospholipids Miscellaneous (Pigment, Protein) (Lecithin) Bile Salts 0.7% 4% H 2 0 1% 12%
Lipid Digestion. An Introduction to Lipid Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins.
 Digestion An Introduction to Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins By Noel Ways Suspension and Nutralization of Chyme ph Boli containing lipids enters
Digestion An Introduction to Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins By Noel Ways Suspension and Nutralization of Chyme ph Boli containing lipids enters
Lipid Digestion. and Human Nutrition. An Introduction to Lipid Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins
 Digestion and Human Nutrition An Introduction to Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins By Noel Ways Emulsification of s and release of Pancreatic Lipase
Digestion and Human Nutrition An Introduction to Transport and Digestion with consideration of High Density and Low Density Lipoproteins By Noel Ways Emulsification of s and release of Pancreatic Lipase
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF BILE ACIDS FOR BILE FLOW AND BILIARY LIPID SECRETION IN MAN
 CM Det här verket är upphovrättskyddat enligt Lagen (1960:729) om upphovsrätt till litterära och konstnärliga verk. Det har digitaliserats med stöd av Kap. 1, 16 första stycket p 1, för forskningsändamål,
CM Det här verket är upphovrättskyddat enligt Lagen (1960:729) om upphovsrätt till litterära och konstnärliga verk. Det har digitaliserats med stöd av Kap. 1, 16 första stycket p 1, för forskningsändamål,
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Cholesterol Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels
 Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Effects of lovastatin and chenodiol on bile acid synthesis, bile lipid composition, and biliary lipid secretion in healthy human subjects
 Effects of lovastatin and chenodiol on bile acid synthesis, bile lipid composition, and biliary lipid secretion in healthy human subjects David S. Hanson and William C. Duane' Department of Medicine, Veterans
Effects of lovastatin and chenodiol on bile acid synthesis, bile lipid composition, and biliary lipid secretion in healthy human subjects David S. Hanson and William C. Duane' Department of Medicine, Veterans
Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Cholelithiasis Patients in Bikaner, Rajasthan (India)
 Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Cholelithiasis Patients in Bikaner, Rajasthan (India) Original Research Article Kedar Nath 1, Ashok Kumar 2, Jitendra Acharya 3 1Senior Specialist, 2 CAS PG Resident, Department
Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Cholelithiasis Patients in Bikaner, Rajasthan (India) Original Research Article Kedar Nath 1, Ashok Kumar 2, Jitendra Acharya 3 1Senior Specialist, 2 CAS PG Resident, Department
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
What you should know about gallstone treatment. The informed patient
 What you should know about gallstone treatment The informed patient Publisher 2018 Falk Foundation e.v. All rights reserved. 15th revised edition 2018 The informed patient What you should know about gallstone
What you should know about gallstone treatment The informed patient Publisher 2018 Falk Foundation e.v. All rights reserved. 15th revised edition 2018 The informed patient What you should know about gallstone
Effect of synthetic oestrogens and progestagens in oral contraceptives on bile lipid composition
 Guit, 1983, 24, 253-259 Effect of synthetic oestrogens and progestagens in oral contraceptives on bile lipid composition R H L DOWN, M J WHITING, J McK WATTS, AND W JONES From the Departments of Surgery
Guit, 1983, 24, 253-259 Effect of synthetic oestrogens and progestagens in oral contraceptives on bile lipid composition R H L DOWN, M J WHITING, J McK WATTS, AND W JONES From the Departments of Surgery
Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (2004), 50(7):
 TitleRole of the urinary calcium in the Author(s) Murayama, Tetsuo; Sakai, Naoki; Tak Tetsuo Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (24), 5(7): 451-455 Issue Date 24-7 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/113414 Right Type Departmental
TitleRole of the urinary calcium in the Author(s) Murayama, Tetsuo; Sakai, Naoki; Tak Tetsuo Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (24), 5(7): 451-455 Issue Date 24-7 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/113414 Right Type Departmental
GASTROENTEROIJOGY. Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association COPYRIGHT 1967 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS CO.
 GASTROENTEROIJOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association COPYRIGHT 1967 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS CO. VOLUME 52 March 1967 NUMBER 3 CONCENTRATIONS OF BILE SALTS AT THE CRITICAL
GASTROENTEROIJOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association COPYRIGHT 1967 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS CO. VOLUME 52 March 1967 NUMBER 3 CONCENTRATIONS OF BILE SALTS AT THE CRITICAL
Serum immunoreactive trypsin concentration after a Lundh meal Its value in the diagnosis of pancreatic disease
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 1003-1008 Serum immunoreactive trypsin concentration after a Lundh meal Its value in the diagnosis of pancreatic disease G. LAKE-BAKAAR, S. McKAVANAGH, M. REDSHAW,
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 1003-1008 Serum immunoreactive trypsin concentration after a Lundh meal Its value in the diagnosis of pancreatic disease G. LAKE-BAKAAR, S. McKAVANAGH, M. REDSHAW,
Gallbladder And Biliary Tract Diseases (Gastroenterology And Hepatology, Number By Afdhal
 Gallbladder And Biliary Tract Diseases (Gastroenterology And Hepatology, Number By Afdhal If searched for a book Gallbladder and Biliary Tract Diseases (Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Number by Afdhal
Gallbladder And Biliary Tract Diseases (Gastroenterology And Hepatology, Number By Afdhal If searched for a book Gallbladder and Biliary Tract Diseases (Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Number by Afdhal
The economy of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in the baboon. 1. Studies of controlled enterohepatic circulation of bile acids'
 The economy of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in the baboon. 1. Studies of controlled enterohepatic circulation of bile acids' Richard N. Rediner: James W. Hawkins, and D. Michael Grace Department
The economy of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in the baboon. 1. Studies of controlled enterohepatic circulation of bile acids' Richard N. Rediner: James W. Hawkins, and D. Michael Grace Department
gall stone formation after subtotal or total
 1760 Departnent of Surgery 1, Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka, Japan I Makino K Chijiiwa H Higashijima S Nakahara M Kishinaka S Kuroki R Mibu Correspondence to: Dr Chijiiwa, Department of
1760 Departnent of Surgery 1, Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka, Japan I Makino K Chijiiwa H Higashijima S Nakahara M Kishinaka S Kuroki R Mibu Correspondence to: Dr Chijiiwa, Department of
CLASS XI BIOLOGY. Digestion And Absorption. Finish Line & Beyond send your queries to
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do?
 ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
Acute Pancreatitis. What is the Pancreas? What does it do? What is acute pancreatitis? What causes acute pancreatitis? What symptoms do you get?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Acute Pancreatitis www.corecharity.org.uk What is the Pancreas? What does it do? What is acute pancreatitis? What causes
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Acute Pancreatitis www.corecharity.org.uk What is the Pancreas? What does it do? What is acute pancreatitis? What causes
Moh Tarek + Suhayb. Tamara Al-Azzeh + Asmaa Aljeelani ... Faisal
 28 Moh Tarek + Suhayb Tamara Al-Azzeh + Asmaa Aljeelani... Faisal Digestion of dietary lipids Lipid digestion and absorption are complex processes. They involve soluble enzymes, substrates with different
28 Moh Tarek + Suhayb Tamara Al-Azzeh + Asmaa Aljeelani... Faisal Digestion of dietary lipids Lipid digestion and absorption are complex processes. They involve soluble enzymes, substrates with different
in Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency
 Studies of the Hepatic Excretory Defects in Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency THEIR POSSIBLE RELATIONSHIP TO THE GENESIS OF CHOLESTEROL GALLSTONES I. J. SARAm, D. A. BEELER, D. H. TREBLE, and J. A. BALiNr
Studies of the Hepatic Excretory Defects in Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency THEIR POSSIBLE RELATIONSHIP TO THE GENESIS OF CHOLESTEROL GALLSTONES I. J. SARAm, D. A. BEELER, D. H. TREBLE, and J. A. BALiNr
Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
 MORPHOLOGY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE AND CHEMICAL MEDICAL JOURNAL COMPOSITION GALLSTONES VOL.10, NO.1, 2011 Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
MORPHOLOGY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE AND CHEMICAL MEDICAL JOURNAL COMPOSITION GALLSTONES VOL.10, NO.1, 2011 Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
Relationship between bile acid malabsorption and
 Gut, 1976, 17, 295-299 Relationship between bile acid malabsorption and pancreatic insufficiency in cystic fibrosis A. M. WEBER1, C. C. ROY, L. CHARTRAND, G. LEPAGE,. L. DUFOUR, C. L. MORN, AND R. LASALLE
Gut, 1976, 17, 295-299 Relationship between bile acid malabsorption and pancreatic insufficiency in cystic fibrosis A. M. WEBER1, C. C. ROY, L. CHARTRAND, G. LEPAGE,. L. DUFOUR, C. L. MORN, AND R. LASALLE
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1983;84:253-64
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1983;84:253-64 Alteration of the Degree of Biliary Cholesterol Saturation in the Hamster and Rat by Manipulation of the Pools of Preformed and Newly Synthesized Cholesterol STEPHEN D.
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1983;84:253-64 Alteration of the Degree of Biliary Cholesterol Saturation in the Hamster and Rat by Manipulation of the Pools of Preformed and Newly Synthesized Cholesterol STEPHEN D.
ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT OF A BILE DUCT
 HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 3, pp. 67-71 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORT
Gastric, intestinal and colonic absorption of metoprolol in
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1985), 19, 85S-89S Gastric, intestinal and colonic absorption of metoprolol in the rat J. DOMENECH', M. ALBA', J. M. MORERA', R. OBACH' & J. M. PLA DELFINA2 'Department of Pharmaceutics,
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1985), 19, 85S-89S Gastric, intestinal and colonic absorption of metoprolol in the rat J. DOMENECH', M. ALBA', J. M. MORERA', R. OBACH' & J. M. PLA DELFINA2 'Department of Pharmaceutics,
Gallstone Disease. PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017
 PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Gallstone Disease Dr. Muhammad Fayyaz Consultant Gastroenterologist Saidu Group of Teaching Hospitals, Saidu sharif Swat, Pakistan Abstract Gallstone disease is one
PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Gallstone Disease Dr. Muhammad Fayyaz Consultant Gastroenterologist Saidu Group of Teaching Hospitals, Saidu sharif Swat, Pakistan Abstract Gallstone disease is one
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
In this edition we will take a look at Cholelithiasis diagnoses and illustrate the increased specificity under the ICD-10-CM nomenclature.
 On October 1, 2015, the ICD-9-CM code set that is used to report medical diagnoses in the United States will be replaced with the ICD-10-CM code set. The new code set provides more than 68,000 codes, compared
On October 1, 2015, the ICD-9-CM code set that is used to report medical diagnoses in the United States will be replaced with the ICD-10-CM code set. The new code set provides more than 68,000 codes, compared
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion
 Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion Martin C. Carey, D.Sc., M.D. Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women s Hospital and Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, U.S.A. Functions
Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion Martin C. Carey, D.Sc., M.D. Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women s Hospital and Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, U.S.A. Functions
Per-operative conversion of laparoscopic cholecystectomy to open surgery: prospective study at JSS teaching hospital, Karnataka, India
 International Surgery Journal Raza M et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jan;4(1):81-85 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20163977
International Surgery Journal Raza M et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jan;4(1):81-85 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20163977
Cholesterol monohydrate growth in model -bile solutions (cholelithiasis/crystal morphology/diumal variation/solubility)
 Proc. NatI. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 75, No. 12, pp. 6230-6234, December 1978 Medical Sciences Cholesterol monohydrate growth in model -bile solutions (cholelithiasis/crystal morphology/diumal variation/solubility)
Proc. NatI. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 75, No. 12, pp. 6230-6234, December 1978 Medical Sciences Cholesterol monohydrate growth in model -bile solutions (cholelithiasis/crystal morphology/diumal variation/solubility)
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
