human gall bladder bile
|
|
|
- Neal Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut, 1986, 27, Effect of binding of ionised calcium on the in vitro nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirubinate in human gall bladder bile S GALLINGER, P R C HARVEY, C N PETRUNKA, AND S M STRASBERG From the Department of Surgery, University of Toronto and Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada SUMMARY Biliary calcium may be a nucleating agent in cholesterol cholelithiasis. A study was designed to determine the effect of binding of ionised calcium on in vitro nucleation time. Ultracentrifuged and microscopically clear gall bladder bile from cholesterol gall stone patients was divided into two aliquots. One aliquot served as control and ionised calcium was bound in the second aliquot by addition of EDTA. Nucleation time was observed for the two groups. Addition of EDTA had no effect on lipid composition of the biles. EDTA bound all ionised calcium. Calcium bilirubinate precipitated from all controls on day 1 but was absent in all samples with EDTA. Addition of EDTA had no effect on cholesterol crystal nucleation time; nucleation time was rapid in both the controls and samples with EDTA. lonised calcium is essential for calcium bilirubinate precipitation but is not responsible for the rapid nucleation time of bile from cholesterol gall stone patients. Nucleation of cholesterol from bile is an important early step in cholesterol gall stone formation. 1 Gall bladder bile of patients with cholesterol gall stones has a rapid in vitro nucleation time compared with equally supersaturated bile from control patients.2- Bile appears to contain antinucleating5 and pronucleating substances.4 6- Calcium is a candidate pronucleating substance as calcium bilirubinate is at the centre of many cholesterol gall stones;912 also calcium might contribute to vesicle aggregation'3 and thus accelerate nucleation of cholesterol monohydrate crystals. On the other hand we have previously shown total and free calcium concentration to be similar in bile from cholesterol gall stone patients and controls.3 Unconjugated bilirubin concentrations are not higher in cholesterol gall stones biles3 and total bilirubin concentrations are higher in controls than in cholesterol stone patients.3 14 These studies, however, do not exclude the possibility that calcium ions or calcium bilirubinate are necessary for rapid in vitro nucleation of bile. The purpose of the present studv was to determine the effect of binding of Address for correspondence: Dr S M Strasberg, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Suite 1142, 6(X) University Avenue, Toronto, Canada M5G IX5. Received for publication 1If March calcium ions with EDTA on in vitro nucleation time. If calcium was an important pronucleator considerable lengthening of the nucleation time under these conditions would be expected. Methods PATIENTS Gall bladder bile was collected at surgery from 10 patients undergoing elective cholecystectomy for cholesterol cholelithiasis.3 The patients were otherwise well and had normal liver function tests including SGOT, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin. The age (±SD) of the patients was 52-6 years±19-1 and weight 67-3 kg±10-4. There were nine women and one male in the patient group. Each patient gave informed consent for bile collection. This study was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of the University of Toronto. BILE PREPARATION Fresh bile samples were divided into 6-0 ml aliquots. One aliquot served as control and the second aliquot was added to sterile vacutainers containing EDTA (K3) in water (Becton Dickinson, Mississauga, Canada). The final concentration of EDTA in the biles was 3-5 mg/ml. This concentration is about 1382
2 Binding of ionised calcium on the in vitro nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirlubinate three times that required to bind calcium in blood (approximately 1 mg/ml)'5 and was chosen because gall bladder bile contains three to four times more calcium than blood As expected, the ph of the bile samples fell to after addition of EDTA; therefore the samples were buffered with il IN NaOH to raise the ph to within 0.1 ph units of that of the parent control bile. Both the control and EDTA aliquots were then ultracentrifuged at g for two hours to generate a bile specimen containing no crystals or other particulate matter by light microscopy.2 3 NUCLEATION TIME TECHNIQUE The control aliquots and those with added EDTA were observed daily for nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirubinate crystals using a modification3 of the technique of Holan et al. The appearance of cholesterol crystals marks the nucleation time (in days) of a bile sample. During bile preparation and nucleation time assay the samples were handled using sterile techniques and all containers and instruments were prewarmed to 37 C. The sterility of the controls and mixtures was assured by aerobic and anaerobic culture of the biles on the day of collection and upon nucleation. Only samples which were sterile were included in the studies. CHEMICAL METHODS Bile salts,'7 cholesterol'8 and phospholipid'9 were measured in all samples and in some of the mixtures. Cholesterol saturation is expressed as the cholesterol saturation index (CSI).Po In some controls and mixtures, total calcium was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry (aa/ae spectrophotometer, Instrumentation Laboratory Inc, Lexington, Mass.). lonised calcium was measured with an ion-selective electrode (ICA ionised calcium analyser, Radiometer, Copenhagen). The ph of the samples was measured with a ph meter (Corning ph meter 125, Corning Science Products, Medfield, Ma.). The ionised calcium concentrations reported in this study are based on the ph of each particular sample - that is, not corrected to standard ph. Gall stones were obtained from all the study patients. The stones were dried, crushed, weighed, extracted in hexane and cholesterol measured by GLC.'x All patients had cholesterol gall stones (>70(% cholesterol by weight). STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Nucleation times of the gall bladder biles with and without added EDTA were compared by Wilcoxon's test.2' Results EFFECTS OF EDTA ON LIPID COMPOSITION OF GALL BLADDER BILE The lipid composition of the control gall bladder biles are shown in Table 1. The values are within the range of previous reports.2-5 Addition of EDTA had no discernible effects on lipid composition in four patients in whom lipid composition was measured both before and after addition of EDTA (Table 1). EFFECTS OF EDTA ON IONISED CAL CIUM CONCENTRATION OF GALL BLADDER BILE In samples from the first four patients, total calcium Table 1 Lipid composition, * total lipid concentration and cholesterol saturation index of gall bladder bile samples Patient with EDTAt with EDTA 9 9 with EDTA with EDTA Bile salts (mmrolldl) ) (02 12t07 10(20) Cholesterol (mmnolldl) 147 (069 3X87 0(68 ( I (50 Phl.spholipid (mnmolldl) X ) Total lipid concentration (gldl) 7X87 4X X Cholesterol saturatiotn index *To convert bile salt, cholesterol, and phospholipid concentration to mg/dl, multiply by 491, 387 and 775 rcspectively. tconccntration of EDTA in mixturcs=3 5 mg/mi (199 It) I
3 1384 concentrations were measured in the controls and ionised calcium concentrations in the controls and mixtures. The results are shown in Table 2. The values for total and ionised calcium concentrations in the control biles are within the range of previous reports.2 16 As shown, there was no detectable ionised calcium after mixing with EDTA. lonised calcium was not measured in samples from the other six patients because it was assumed from the preceeding results that the dose of EDTA was sufficient to reduce concentrations to very low levels. EFFECT OF EDTA ON NUCLEATION OF CHOLESTEROL MONOHYDRATE CRYSTALS AND CALCIUM BILIRUBINATE CRYSTALS Binding of calcium with EDTA had no effect on the in vitro nucleation time of cholesterol monohydrate. Table 2 Effects of EDTA on ionised calcium concentration of gall bladder bile* Gall bladder Control gall bladder bile bile + ED TA Total lonised lonised Patient calcium calcium calcium pht *All calcium concentrations are mmol/l. To convert to mg/dl multiply by 4-0. tph of bile samples after EDTA and NaOH added (Samples were buffered with IN NaOH to raise the ph to within 0-1 ph unit of the controls). Table 3 Effects of EDTA on nucleation time of cholesterol crystals from gall bladder bile Nucleation time (d) Patient Control bile Bile + EDTA t p=not significant (Wilcoxon's test). 3allinger, Harvey, Petrunka, and Strasberg Biles with added EDTA nucleated cholesterol monohydrate crystals on the same day as control biles, or one day earlier or one day later than control biles (Table 3). There was no difference in appearance of the crystals which precipitated from biles containing EDTA (Fig. 1). We have previously reported that calcium bilirubinate crystals appear in bile samples on day one of the in vitro nucleation time test. This occurs in almost all biles whether from patients with cholesterol gall stones or from controls without biliary tract disease. Calcium bilirubinate precipitates were present in all control aliquots on day one in this study. None of the EDTA containing aliquots precipitated calcium bilirubinate. The observation for calcium bilirubinate crystals was continued for two days after the nucleation of cholesterol crystals. Discussion Calcium is present in bile in ionised form or bound to bile salts or proteins Calcium salts are major constituents of pigment stones and their importance in pigment stone formation is well documented.24 Calcium may also be important in cholesterol gall stone formation. Calcium salts are found in the centre of cholesterol gall stones912 and it has been proposed that the nidus for cholesterol nucleation is made of calcium salts.23 Recently vesicles have been shown to be a second cholesterol carrier in human bile25 and calcium ions can act as a vesicle aggregating agent13 and might accelerate nucleation of cholesterol from bile by this mechanism. Patients with cholesterol gall stones are readily distinguished from controls without gall stones and from patients with pigment gall stones by the in vitro nucleation time test.-4 EDTA can reduce ionised calcium to undetectable levels in human bile but this has no effect on the in vitro nucleation time. Thus this study cannot support a role for calcium ions in the nucleation of cholesterol from bile. Other studies from this laboratory have also looked for and failed to find a connection between biliary calcium and the rapid in vitro nucleation time of gall bladder bile from patients with stones. Gollish et al3 found that calcium bilirubinate crystals precipitate equally rapidly in abnormal and normal bile and that there was no correlation between the time for calcium bilirubinate precipitation and cholesterol crystal nucleation time. The levels of total and ionised calcium are not higher in the gall bladder bile of cholesterol stone patients compared with normal subjects Unconjugated bilirubin, the anion which complexes with ionised calcium to form calcium bilirubinate, is present in similar concentrations in cholesterol gall stone and normal
4 Binding of ionised calcium on the in vitro nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirubinate Fig. 1 Photomicrographs ofhuman gall bladder bile with (top and bottom right panels) and without (top and bottom left panels) addition of EDTA. Note typical polarising cholesterol monohydrate crystals in all samples but lack ofcalcium bilirubinate precipitates (granular background precipitates) in bile samples with added EDTA. Binding ofionised calcium with EDTA did not affect cholesterol crystal nucleation time. Magnification x250 with polarised light. gall bladder bile.3 Only in pigment gall stone bile are concentrations of unconjugated bilirubin abnormally high.24 As opposed to cholesterol, the precipitation of calcium bilirubinate was very sensitive to chelation of ionised calcium. To our knowledge this is the first demonstration that precipitation of these typical crystals can be prevented in human gall bladder bile by EDTA. This finding provides encouragement to those seeking to prevent or treat pigment stones by reducing calcium levels in bile. Finally, it is now known that cholesterol is transported in human bile both by mixed micelles and unilamellar vesicles.25 The latter are not removed by the short period of ultracentrifugation used in these studies and are too small to be seen by light microscopy. The specimens used in this study were free of crystals or other particulate matter by 1385 light microscopy. This had been previously referred to as the isotropic phase in the in vitro nucleation time technique.2 5 Although isotropic by light microscopy, it is not truly isotropic and we have avoided the term. There is some evidence that nucleation occurs from the vesicular phase.27 This study indicates that Ca++ is not necessary for this to occur. In summary, ionised calcium does not appear responsible for the rapid in vitro nucleation time of bile from cholesterol gall stone patients. We have reaffirmed the importance of ionised calcium in the precipitation of calcium bilirubinate from bile. This study was supported by the Physicians' Services Incorporated and the Medical Research Council of Canada. Dr Gallinger is a fellow of the Canadian Liver Foundation. Dr Harvey is a career scientist
5 1386 Gallinger, Harvey, Petrunka, and Strasberg for the Ontario Ministry of Health, Health Research Personnel Development Program. The authors would like to acknowledge Mrs JoAnn Gold for secretarial assistance and Dr B Hoffman and Dr M D'Costa for assistance with measurement of biliary calcium. References 1 Sedaghat A, Grundy SM. Cholesterol crystals and the formation of cholesterol gallstones. N Engl J Med 1980; 302: Holan KR, Holzbach RT, Hermann RE, Cooperman AM, Claffey WJ. Nucleation time: a key factor in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstone disease. Gastroenterology 1979; 77: Gollish SH, Burnstein MJ, Ilson RG, Petrunka CN, Strasberg SM. Nucleation of cholesterol monohydrate crystals from hepatic and gall-bladder bile of patients with cholesterol gallstones. Gut 1983; 24: Burnstein MJ, Ilson RG, Petrunka CN, Taylor RD, Strasberg SM. Evidence for a potent nucleating factor in the gallbladder bile of patients with cholesterol gallstones. Gastroenterology 1983; 85: Holzbach RT, Kibe A, Thiel E, Howell JH, Marsh M, Hermann RE. Biliary proteins. Unique inhibitors of cholesterol crystal nucleation in human gallbladder bile. J Clin Invest 1984; 73: Gallinger S, Taylor RD, Harvey PRC, Petrunka CN, Strasberg SM. The effect of mucous glycoprotein on nucleation time of human bile. Gastroenterology 1985; 89: Levy PF, Smith BF, LaMont JT. Human gallbladder mucin accelerates nucleation of cholesterol in human bile. Gastroeniterolog, 1984; 87: 27(-5. 8 Gallinger S, Harvey PRC, Strasberg SM. Human gallbladder bile proteins: evidence for a role in the nucleation defect of cholesterol gallstone disease [Abstract]. Gastroenterology 1985; 88: Sutor JD, Wooley SE. The sequential deposition of crystalline material in gallstones: evidence for changing gallbladder bile composition during the growth of some stones. Gut 1974; 15: 13( Bills PM, Lewis D. A structural study of gallstones. Gut 1975; 16: Been JM, Bills PM, Lewis D. Microstructure of gallstones. Gastroeniterology 1979; 76: Srivastava AK, Lal K, Tandon RK. A layerwise quantitation of human cholesterol gallstone constituents. Indian J Med Res 1983; 77: Ohki S, Leonards K. Effects of proteins on phospholipid vesicle aggregation and lipid vesicle-monolayer interactions. Chem Phys Lipids 1982; 31: Masuda H, Nakayama F. Composition of bile pigment in gallstones and bile and their etiological significance. J Lab Clin Med 1979; 93: Alper CR. Specimen collection and preservation. In: Henry RJ, Cannon DC, Winkelman JW, eds. Clinical chemistry. Principles and technics. Maryland: Harper & Row, 1974: Sutor JD, Wilkie LI, Jackson MJ. Ionised calcium in pathological human bile. J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: Talalay P. Enzymatic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods Biochem Anal 1960; 8: Morin RJ, Elms NJ. Rapid microanalysis of cholesterol in bile and serum by gas chromatography. Ann Clin Lab Sci 1977; 5: Bartlett GR. Phosphorous assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem 1959; 234: Carey MC. Critical tables for calculating the cholesterol saturation of native bile. J Lipid Res 1978; 19: Snedecor GW, Cochran WG. Statistical methods. 7th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, Moore EW, Celic L, Ostrow JD. Interactions between ionized calcium and sodium taurocholate: bile salts are important buffers for prevention of calcium-containing gallstones. Gastroenterology 1982; 83: Moore EW. The role of calcium in the pathogenesis of gallstones: Ca++ electrode studies of model bile salt solutions and other biologic systems. Hepatology 1984; 4: suppl 228S-43S. 24 Ostrow JD. The etiology of pigment gallstones. Hepatology 1984; 4: suppl 215S-22S. 25 Somjen GJ, Gilat T. A non-micellar mode of cholesterol transport in human bile. FEBS Letters 1983; 156: Harvey RC, Taylor D, Petrunka CN, Murray AD, Strasberg SM. Quantitative analysis of major, minor and trace elements in gallbladder bile of patients with and without gallstones. Hepatology 1985; 5: Halpern Z, Dudley MA, Lynn MP, Nader JM, Breuer AC, Holzbach RT. Vesicle aggregation in model solutions of supersaturated bile: Relation to crystal nucleation and lipid composition of the vesicular phase. [Abstract]. Hepatology 1985; 5: 963.
A rapid, simple high capacity cholesterol crystal growth assay
 A rapid, simple high capacity cholesterol crystal growth assay P. Robert C. Harvey,l.*.fand G. Aravinda Upadhya* Departments of Surgery* and Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics,+Washington, University,
A rapid, simple high capacity cholesterol crystal growth assay P. Robert C. Harvey,l.*.fand G. Aravinda Upadhya* Departments of Surgery* and Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics,+Washington, University,
A rapid, simple high capacity cholesterol crystal growth assay
 A rapid, simple high capacity cholesterol crystal growth assay P. Robert C. Harvey,l.*.fand G. Aravinda Upadhya* Departments of Surgery* and Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics,+Washington, University,
A rapid, simple high capacity cholesterol crystal growth assay P. Robert C. Harvey,l.*.fand G. Aravinda Upadhya* Departments of Surgery* and Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics,+Washington, University,
Contribution of vesicular and micellar carriers to cholesterol transport in human bile
 Contribution of vesicular and micellar carriers to cholesterol transport in human bile Giora J. Somjen and Tuvia Gilat Department of Gastroenterology, Ichilov Hospital and Sackler Faculty of Medicine,
Contribution of vesicular and micellar carriers to cholesterol transport in human bile Giora J. Somjen and Tuvia Gilat Department of Gastroenterology, Ichilov Hospital and Sackler Faculty of Medicine,
Measurement of cholesterol gallstone growth in vitro
 Measurement of cholesterol gallstone growth in vitro A. Andre van den Berg, 1 Jaap D. van Buul, J. Donald Ostrow, 2 and Albert K. Groen Department of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases, Academic Medical
Measurement of cholesterol gallstone growth in vitro A. Andre van den Berg, 1 Jaap D. van Buul, J. Donald Ostrow, 2 and Albert K. Groen Department of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases, Academic Medical
Dieter Jungst, Thomas Lang, Peter Huber, Volker Lange: and Gustav Paumgartner
 Effect of phospholipids and bile acids on cholesterol nucleation time and vesicular/micellar cholesterol in gallbladder bile of patients with cholesterol stones Dieter Jungst, Thomas Lang, Peter Huber,
Effect of phospholipids and bile acids on cholesterol nucleation time and vesicular/micellar cholesterol in gallbladder bile of patients with cholesterol stones Dieter Jungst, Thomas Lang, Peter Huber,
FEBS Letters 340 (1994) FEBS 13698
 FEBS Letters 340 (1994) 78-82 IHHH LETTERS FEBS 13698 Direct visualization of lipid aggregates in native human bile by light- and cryo-transmission electron-microscopy Alon Kaplun, Yeshayahu Talmona, Fred
FEBS Letters 340 (1994) 78-82 IHHH LETTERS FEBS 13698 Direct visualization of lipid aggregates in native human bile by light- and cryo-transmission electron-microscopy Alon Kaplun, Yeshayahu Talmona, Fred
Defective acid base regulation by the gall bladder epithelium and its significance for gall stone formation
 Gut 1995; 37: 127-131 127 PROGRESS REPORT Liver Research Laboratories, Department of Medicine, The Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, Edinburgh J N Plevris I A D Bouchier Correspondence to: Dr J N Plevris,
Gut 1995; 37: 127-131 127 PROGRESS REPORT Liver Research Laboratories, Department of Medicine, The Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, Edinburgh J N Plevris I A D Bouchier Correspondence to: Dr J N Plevris,
IMAGING AND MONITORING CHOLESTEROL CRYSTALLIZATION IN BILE
 Scanning Microscopy Vol. 13, No. 2-3, 1999 (Pages 381-393) 0891-7035/99$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago (AMF Biliary O Hare), cholesterol IL 60666 crystallization USA IMAGING AND MONITORING
Scanning Microscopy Vol. 13, No. 2-3, 1999 (Pages 381-393) 0891-7035/99$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago (AMF Biliary O Hare), cholesterol IL 60666 crystallization USA IMAGING AND MONITORING
gall stone formation after subtotal or total
 1760 Departnent of Surgery 1, Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka, Japan I Makino K Chijiiwa H Higashijima S Nakahara M Kishinaka S Kuroki R Mibu Correspondence to: Dr Chijiiwa, Department of
1760 Departnent of Surgery 1, Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka, Japan I Makino K Chijiiwa H Higashijima S Nakahara M Kishinaka S Kuroki R Mibu Correspondence to: Dr Chijiiwa, Department of
The organic matrix of gallstones
 Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
H ydrop ho bic/hyd rop h i I ic balance of proteins: a major determinant of cholesterol crystal formation in model bile
 H ydrop ho bic/hyd rop h i I ic balance of proteins: a major determinant of cholesterol crystal formation in model bile H. A. Ahmed, M. L. Petroni, M. Abu-Hamdiyyah, R. P. Jazrawi, and T. C. Northfield
H ydrop ho bic/hyd rop h i I ic balance of proteins: a major determinant of cholesterol crystal formation in model bile H. A. Ahmed, M. L. Petroni, M. Abu-Hamdiyyah, R. P. Jazrawi, and T. C. Northfield
The role of cholestanol in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstones. Review: Hypothesis and Conception (1991)
 The role of cholestanol in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstones. Review: Hypothesis and Conception (1991) Jacob L. Turumin Department of Experimental Surgery, Irkutsk Institute of Surgery, Scientific
The role of cholestanol in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstones. Review: Hypothesis and Conception (1991) Jacob L. Turumin Department of Experimental Surgery, Irkutsk Institute of Surgery, Scientific
Mucin and phospholipids determine viscosity of gallbladder bile in patients with gallstones
 P.O.Box 2345 Beijing 100023, China World J Gastroentero, 2001; 7(2):203-207 Fax. 0086 10 65891893 Tel. 0086 10 65897901 World Journal of Gastroenterology E-mail.wcjd public.bta.net.cn www.wd.org.cn Copyright
P.O.Box 2345 Beijing 100023, China World J Gastroentero, 2001; 7(2):203-207 Fax. 0086 10 65891893 Tel. 0086 10 65897901 World Journal of Gastroenterology E-mail.wcjd public.bta.net.cn www.wd.org.cn Copyright
Human gallbladder mucin binds biliary lipids and promotes cholesterol crystal nucleation in model bile
 Human gallbladder mucin binds biliary lipids and promotes cholesterol crystal nucleation in model bile Bernard F. Smith Section of Gastroenterology and Evans Memorial Department of Clinical Research, University
Human gallbladder mucin binds biliary lipids and promotes cholesterol crystal nucleation in model bile Bernard F. Smith Section of Gastroenterology and Evans Memorial Department of Clinical Research, University
Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and
 Gut, 1978, 19, 22-224 Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and total CO2 in bile D. JUNE SUTOR AND LYNETTE I. WILKIE From the Department of Chemistry, University College London, London SUMMARY Measurement
Gut, 1978, 19, 22-224 Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and total CO2 in bile D. JUNE SUTOR AND LYNETTE I. WILKIE From the Department of Chemistry, University College London, London SUMMARY Measurement
Quantitative and qualitative comparison of gall bladder mucus glycoprotein from patients with and without gall stones
 Gut, 1986, 27, 374-381 Quantitative a qualitative comparison of gall bladder mucus glycoprotein from patients with a without gall stones P R C HARVEY, C A RUPAR, S GALLINGER, C N PETRUNKA, AND S M STRASBERG
Gut, 1986, 27, 374-381 Quantitative a qualitative comparison of gall bladder mucus glycoprotein from patients with a without gall stones P R C HARVEY, C A RUPAR, S GALLINGER, C N PETRUNKA, AND S M STRASBERG
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
 GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
Characterization of model bile using fluorescence energy transfer from dehydroergosterol to dansylated lecithin
 Characterization of model bile using fluorescence energy transfer from dehydroergosterol to dansylated lecithin Steven P. Wrenn, 1, * Manasa Gudheti,* Anka N. Veleva, Eric W. Kaler, and Sum P. Lee Chemical
Characterization of model bile using fluorescence energy transfer from dehydroergosterol to dansylated lecithin Steven P. Wrenn, 1, * Manasa Gudheti,* Anka N. Veleva, Eric W. Kaler, and Sum P. Lee Chemical
Pathogenesis of Calcium-containing Gallstones Canine Ductular Bile, but Not Gallbladder Bile, Is Supersaturated with Calcium Carbonate
 Pathogenesis of Calcium-containing Gallstones Canine Ductular Bile, but Not Gallbladder Bile, Is Supersaturated with Calcium Carbonate Robert V. Rege and Edward W. Moore Department ofsurgery, Northwestern
Pathogenesis of Calcium-containing Gallstones Canine Ductular Bile, but Not Gallbladder Bile, Is Supersaturated with Calcium Carbonate Robert V. Rege and Edward W. Moore Department ofsurgery, Northwestern
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 298-303, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE BILE ACID METABOLISM IN CIRRHOSIS III. Biliary lipid secretion
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 298-303, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE BILE ACID METABOLISM IN CIRRHOSIS III. Biliary lipid secretion
A novel vesicular assay to study factors affecting cholesterol crystallization in vitro
 A novel vesicular assay to study factors affecting cholesterol crystallization in vitro A. Ingrid M. Zijlstra,l,* Bert J. M. Van de Heijning,? Merian van Overveld,* and Albert K. Groen* Department of Gastroenterology
A novel vesicular assay to study factors affecting cholesterol crystallization in vitro A. Ingrid M. Zijlstra,l,* Bert J. M. Van de Heijning,? Merian van Overveld,* and Albert K. Groen* Department of Gastroenterology
Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition
 Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition Gut, 1975, 16, 937-942 G. ANTSAKLIS, M. R. LEWIN1, D. JUNE SUTOR, A. G. A. COWIE, AND C. G. CLARK From the Department of Surgery, University
Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition Gut, 1975, 16, 937-942 G. ANTSAKLIS, M. R. LEWIN1, D. JUNE SUTOR, A. G. A. COWIE, AND C. G. CLARK From the Department of Surgery, University
Biliary Proteins Unique Inhibitors of Cholesterol Crystal Nucleation in Human Gallbladder Bile
 Biliary Proteins Unique Inhibitors of Cholesterol Crystal Nucleation in Human Gallbladder Bile R. T. Holzbach, A. Kibe, E. Thiel, J. H. Howell, M. Marsh, and R. E. Hermann Gastrointestinal Research Unit,
Biliary Proteins Unique Inhibitors of Cholesterol Crystal Nucleation in Human Gallbladder Bile R. T. Holzbach, A. Kibe, E. Thiel, J. H. Howell, M. Marsh, and R. E. Hermann Gastrointestinal Research Unit,
The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man
 The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man William H. Admirand, Donald M. Small J Clin Invest. 1968;47(5):1043-1052. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci105794. Research Article The concentrations
The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man William H. Admirand, Donald M. Small J Clin Invest. 1968;47(5):1043-1052. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci105794. Research Article The concentrations
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences CORRELATION OF SERUM LIPIDS AND GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN CHOLELITHIASIS
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO CHEMISTRY CORRELATION OF SERUM LIPIDS AND GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN CHOLELITHIASIS Corresponding Author DEVAKI R.N Department of Biochemistry,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO CHEMISTRY CORRELATION OF SERUM LIPIDS AND GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST IN CHOLELITHIASIS Corresponding Author DEVAKI R.N Department of Biochemistry,
Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
 MORPHOLOGY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE AND CHEMICAL MEDICAL JOURNAL COMPOSITION GALLSTONES VOL.10, NO.1, 2011 Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
MORPHOLOGY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE AND CHEMICAL MEDICAL JOURNAL COMPOSITION GALLSTONES VOL.10, NO.1, 2011 Prevalence, Morphology and Chemical Composition of Gallstones in 150 Cholecystectomised Patients
Inhibition and promotion of cholesterol crystallization by protein fractions from normal human gallbladder bile
 Inhibition and promotion of cholesterol crystallization by protein fractions from normal human gallbladder bile N. Busch,' N. Matiuck,' S. Sahlix~,~ S. P. Pilla~,~ and R. Thomas Holzbach' Gastrointestinal
Inhibition and promotion of cholesterol crystallization by protein fractions from normal human gallbladder bile N. Busch,' N. Matiuck,' S. Sahlix~,~ S. P. Pilla~,~ and R. Thomas Holzbach' Gastrointestinal
Influence of total lipid concentration, bile salt: lecithin ratio, and cholesterol content on inter-mixed
 Influence of total lipid concentration, bile salt: lecithin ratio, and cholesterol content on inter-mixed micellarhesicular (non-lecithin-associated) bile salt concentrations in model bile Joanne M. Donovan,.**t
Influence of total lipid concentration, bile salt: lecithin ratio, and cholesterol content on inter-mixed micellarhesicular (non-lecithin-associated) bile salt concentrations in model bile Joanne M. Donovan,.**t
Biliary proteins: assessment of quantitative techniques and comparison in gallstone and nongallstone subjects
 Biliary proteins: assessment of quantitative techniques and comparison in gallstone and nongallstone subjects Kiyoshi Yamazaki, Stephen P. Powers, and Nicholas F. LaRusso Gastroenterology Research Unit,
Biliary proteins: assessment of quantitative techniques and comparison in gallstone and nongallstone subjects Kiyoshi Yamazaki, Stephen P. Powers, and Nicholas F. LaRusso Gastroenterology Research Unit,
Microstructural Evolution of Lipid Aggregates in Nucleating Model and Human Biles Visualized by Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy
 Original Articles Microstructural Evolution of Lipid Aggregates in Nucleating Model and Human Biles Visualized by Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy FRED M. KONIKOFF, 1 DGANIT DANINO, 2 DAPHNA
Original Articles Microstructural Evolution of Lipid Aggregates in Nucleating Model and Human Biles Visualized by Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy FRED M. KONIKOFF, 1 DGANIT DANINO, 2 DAPHNA
Obesity is an important risk factor in the development
 Changes in Gallbladder Bile Composition and Crystal Detection Time in Morbidly Obese Subjects After Bariatric Surgery Ulf Gustafsson, 1 Lisbet Benthin, 2 Lars Granström, 1 Albert K. Groen, 3 Staffan Sahlin,
Changes in Gallbladder Bile Composition and Crystal Detection Time in Morbidly Obese Subjects After Bariatric Surgery Ulf Gustafsson, 1 Lisbet Benthin, 2 Lars Granström, 1 Albert K. Groen, 3 Staffan Sahlin,
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Hepatobiliary lipids איך טיפול נולד... from bench to bedside. Fred M Konikoff, MD, MSc, FAASLD
 Hepatobiliary lipids איך טיפול נולד... from bench to bedside Fred M Konikoff, MD, MSc, FAASLD Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Meir Medical Center, Kfar Saba, and Research Laboratory of Cholesterol
Hepatobiliary lipids איך טיפול נולד... from bench to bedside Fred M Konikoff, MD, MSc, FAASLD Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Meir Medical Center, Kfar Saba, and Research Laboratory of Cholesterol
Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion
 Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion Martin C. Carey, D.Sc., M.D. Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women s Hospital and Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, U.S.A. Functions
Pathophysiology of Bile Secretion Martin C. Carey, D.Sc., M.D. Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women s Hospital and Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, U.S.A. Functions
Minerals composition of different types of gallstones in Sudanese population
 Open Science Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2014; 1(1): 1-5 Published online January 30, 2014 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjac) Minerals composition of different types of gallstones in
Open Science Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2014; 1(1): 1-5 Published online January 30, 2014 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjac) Minerals composition of different types of gallstones in
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lipid vesicle fusion induced by phospholipase C activity in model bile
 Lipid vesicle fusion induced by phospholipase C activity in model bile Timothy E. Little,* Hassan Madani,t Sum P. Lee,* and Eric W. Kalert Departments of Medicine* and Chemical Engineering,t University
Lipid vesicle fusion induced by phospholipase C activity in model bile Timothy E. Little,* Hassan Madani,t Sum P. Lee,* and Eric W. Kalert Departments of Medicine* and Chemical Engineering,t University
Masato Abei, Jorg Schwarzendrube, Hannu Nuutinen, Thomas A. Broughan, Paul Kawczak, Carlumandarlo Williams, and R.
 Cholesterol crystallization-promoters in human bile: comparative potencies of immunoglobulins, al-acid glycoprotein, phospholipase C, and aminopeptidase N1 Masato Abei, Jorg Schwarzendrube, Hannu Nuutinen,
Cholesterol crystallization-promoters in human bile: comparative potencies of immunoglobulins, al-acid glycoprotein, phospholipase C, and aminopeptidase N1 Masato Abei, Jorg Schwarzendrube, Hannu Nuutinen,
Cholangitis. John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California, San Francisco. Greek Symmetry of the Universe and Humanity
 Cholangitis John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California, San Francisco Greek Symmetry of the Universe and Humanity The Four Humors the Medieval European Concept Gentile
Cholangitis John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California, San Francisco Greek Symmetry of the Universe and Humanity The Four Humors the Medieval European Concept Gentile
Effects of Fenofibrate on Bile Lipid Composition
 Effects of on Bile Lipid Composition Robert H. Palmer In humans, clofibrate increases the degree of bile cholesterol saturation and predisposes patients to cholesterol gallstone formation. To determine
Effects of on Bile Lipid Composition Robert H. Palmer In humans, clofibrate increases the degree of bile cholesterol saturation and predisposes patients to cholesterol gallstone formation. To determine
10 Essential Blood Tests PART 1
 Presents 10 Essential Blood Tests PART 1 The Blood Chemistry Webinars With DR. DICKEN WEATHERBY Creator of the Blood Chemistry Software Essential Blood Test #1: Basic Chem Screen and CBC http://bloodchemsoftware.com
Presents 10 Essential Blood Tests PART 1 The Blood Chemistry Webinars With DR. DICKEN WEATHERBY Creator of the Blood Chemistry Software Essential Blood Test #1: Basic Chem Screen and CBC http://bloodchemsoftware.com
Serum Lipid Profile in Pre and Post Cholecystectomy Patients
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27123:2267 Surgery Section Original Article Serum Lipid Profile in Pre and Post Cholecystectomy Patients Kuldip Singh Ahi, Rajinder Pal Singh, Harpreet Kaur, Ashish Moudgil ABSTRACT
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27123:2267 Surgery Section Original Article Serum Lipid Profile in Pre and Post Cholecystectomy Patients Kuldip Singh Ahi, Rajinder Pal Singh, Harpreet Kaur, Ashish Moudgil ABSTRACT
GASTROENTEROIJOGY. Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association COPYRIGHT 1967 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS CO.
 GASTROENTEROIJOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association COPYRIGHT 1967 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS CO. VOLUME 52 March 1967 NUMBER 3 CONCENTRATIONS OF BILE SALTS AT THE CRITICAL
GASTROENTEROIJOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association COPYRIGHT 1967 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS CO. VOLUME 52 March 1967 NUMBER 3 CONCENTRATIONS OF BILE SALTS AT THE CRITICAL
Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic
 Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic substances. Describe the formation of bile,its constitents
Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic substances. Describe the formation of bile,its constitents
cholesterol saturation in patients with liver cirrhosis
 Gut, 1986, 27, 23-28 Effect of small doses of deoxycholic acid on bile cholesterol saturation in patients with liver cirrhosis PAOLA DI DONATO, FRANCESCA CARUBBI, M PONZ DE LEON, AND N CARULLI From Semeiotica
Gut, 1986, 27, 23-28 Effect of small doses of deoxycholic acid on bile cholesterol saturation in patients with liver cirrhosis PAOLA DI DONATO, FRANCESCA CARUBBI, M PONZ DE LEON, AND N CARULLI From Semeiotica
BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS
 1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
1 BILE FORMATION, ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & BILE SALTS Color index Important Further explanation 2 Mind map...3 Functions of bile & stages of bile secretion... 4 Characteristics & composition of bile...5
Sustained Gallbladder Stasis Promotes Cholesterol Gallstone Formation in the Ground Squirrel
 Sustained Gallbladder Stasis Promotes Cholesterol Gallstone Formation in the Ground Squirrel QI-WEI XU, MICHÈLE MANTLE, JÜRGEN G. PAULETZKI, AND ELDON A. SHAFFER Although gallbladder stasis exists in most
Sustained Gallbladder Stasis Promotes Cholesterol Gallstone Formation in the Ground Squirrel QI-WEI XU, MICHÈLE MANTLE, JÜRGEN G. PAULETZKI, AND ELDON A. SHAFFER Although gallbladder stasis exists in most
Dr. R. Pradheep. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern. Railway. Hospital.
 Hyperbilirubinemia in an Infant Pradheep Railway Dr. R. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern Hospital. A 2 ½ month old male baby born out of 3 rd degree consanguinity presented to us with c/o yellow discolouration
Hyperbilirubinemia in an Infant Pradheep Railway Dr. R. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern Hospital. A 2 ½ month old male baby born out of 3 rd degree consanguinity presented to us with c/o yellow discolouration
The gallbladder. Bile secretion:
 The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
Clinical Chemistry
 Western Technical College 10513155 Clinical Chemistry Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 5.00 Introduces Clinical Chemistry techniques
Western Technical College 10513155 Clinical Chemistry Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 5.00 Introduces Clinical Chemistry techniques
Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects
 12 LI T. C. Northfield, N. F. LaRusso, A. F. Hofmann, and J. L. Thistle Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects T. C. NORTHFIELD, N. F. LaRUSSO, A. F. HOFMANN, AND J. L. THISTLE
12 LI T. C. Northfield, N. F. LaRusso, A. F. Hofmann, and J. L. Thistle Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects T. C. NORTHFIELD, N. F. LaRUSSO, A. F. HOFMANN, AND J. L. THISTLE
Cholesterol monohydrate growth in model -bile solutions (cholelithiasis/crystal morphology/diumal variation/solubility)
 Proc. NatI. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 75, No. 12, pp. 6230-6234, December 1978 Medical Sciences Cholesterol monohydrate growth in model -bile solutions (cholelithiasis/crystal morphology/diumal variation/solubility)
Proc. NatI. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 75, No. 12, pp. 6230-6234, December 1978 Medical Sciences Cholesterol monohydrate growth in model -bile solutions (cholelithiasis/crystal morphology/diumal variation/solubility)
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Bile acid metabolism. doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc.
 Bile acid metabolism doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc. Bile acid metabolism Importance: Availability for fat & cholesterol absorption Regulates total body pool of cholesterol Factors that synthesis promote
Bile acid metabolism doc. Ing. Zenóbia Chavková, CSc. Bile acid metabolism Importance: Availability for fat & cholesterol absorption Regulates total body pool of cholesterol Factors that synthesis promote
Steven P. Wrenn,* Eric W. Kaler, 1, * and Sum P. Lee
 A fluorescence energy transfer study of lecithincholesterol vesicles in the presence of phospholipase C Steven P. Wrenn,* Eric W. Kaler, 1, * and Sum P. Lee Center for Molecular and Engineering Thermodynamics,
A fluorescence energy transfer study of lecithincholesterol vesicles in the presence of phospholipase C Steven P. Wrenn,* Eric W. Kaler, 1, * and Sum P. Lee Center for Molecular and Engineering Thermodynamics,
Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Cholelithiasis Patients in Bikaner, Rajasthan (India)
 Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Cholelithiasis Patients in Bikaner, Rajasthan (India) Original Research Article Kedar Nath 1, Ashok Kumar 2, Jitendra Acharya 3 1Senior Specialist, 2 CAS PG Resident, Department
Prevalence of Hypothyroidism in Cholelithiasis Patients in Bikaner, Rajasthan (India) Original Research Article Kedar Nath 1, Ashok Kumar 2, Jitendra Acharya 3 1Senior Specialist, 2 CAS PG Resident, Department
Ex : Butter contain large proportion of short chains of fatty acids, so it has high saponification number while margarine with more long fatty acids,
 Lec 2 1. Saponification number Definition : The number of m gms of KOH required to saponify the free and combined fatty acids in one gram of a given fat. Uses : The amount of alkali needed to saponify
Lec 2 1. Saponification number Definition : The number of m gms of KOH required to saponify the free and combined fatty acids in one gram of a given fat. Uses : The amount of alkali needed to saponify
Applicable To Employees of the Gundersen Boscobel Area Hospital Laboratory and Gundersen Palmer Lutheran Hospital and Clinics laboratories.
 Subject Calcium C311 Index Number Lab-8810 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Judy Dayton Last Revised 4/11/2017 References Required document for Laboratory
Subject Calcium C311 Index Number Lab-8810 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Judy Dayton Last Revised 4/11/2017 References Required document for Laboratory
Hormonal control of cholesterol cholelithiasis in the female hamster
 Hormonal control of cholesterol cholelithiasis in the female hamster Nariman Ayyad,* Bertram I. Cohen,* Erwin H. Mosbach,l3* Takahiro Mikami,29* Yasuko Mikam%* and Akira Ohshimaz** Departments of Surgery,*
Hormonal control of cholesterol cholelithiasis in the female hamster Nariman Ayyad,* Bertram I. Cohen,* Erwin H. Mosbach,l3* Takahiro Mikami,29* Yasuko Mikam%* and Akira Ohshimaz** Departments of Surgery,*
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Characterisation of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-bile salts aggregation and its impact on poorly water-soluble drug solubilisation in the gut.
 Characterisation of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-bile salts aggregation and its impact on poorly water-soluble drug solubilisation in the gut. Claudia Pigliacelli School of Pharmacy, University of East
Characterisation of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-bile salts aggregation and its impact on poorly water-soluble drug solubilisation in the gut. Claudia Pigliacelli School of Pharmacy, University of East
Arachidyl Amido Cholanoic Acid (Aramchol) Is a Cholesterol Solubilizer and Prevents the Formation of Cholesterol Gallstones in Inbred Mice 1
 Arachidyl Amido Cholanoic Acid (Aramchol) Is a Cholesterol Solubilizer and Prevents the Formation of Cholesterol Gallstones in Inbred Mice 1 Tuvia Gilat a,b, *, Alicia Leikin-Frenkel b, Ilana Goldiner
Arachidyl Amido Cholanoic Acid (Aramchol) Is a Cholesterol Solubilizer and Prevents the Formation of Cholesterol Gallstones in Inbred Mice 1 Tuvia Gilat a,b, *, Alicia Leikin-Frenkel b, Ilana Goldiner
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* Previous studies (1, 2) have shown that after the ingestion of caffeine
 A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
A STUDY OF THE METABOLISM OF THEOBROMINE, THEOPHYLLINE, AND CAFFEINE IN MAN* BY HERBERT H. CORNISH AND A. A. CHRISTMAN (From the Department of Biological Chemistry, Medical School, University of Michigan,
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION
 DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
Screening Conditions for NMR of Integral Membrane Proteins Updated 1/2015
 Screening Conditions for NMR of Integral Membrane Proteins Updated 1/2015 Charles R. Sanders, Vanderbilt University chuck.sanders@vanderbilt.edu phone: 615-833-2586 Background Reading Solution NMR of membrane
Screening Conditions for NMR of Integral Membrane Proteins Updated 1/2015 Charles R. Sanders, Vanderbilt University chuck.sanders@vanderbilt.edu phone: 615-833-2586 Background Reading Solution NMR of membrane
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
: Disease of extrahepatic biliary tract. : Jumana Abu Hamour : 6/12/2015. : Dr. Samir Bashir. 1 P a g e
 21 : Disease of extrahepatic biliary tract : Jumana Abu Hamour : 6/12/2015 : Dr. Samir Bashir 1 P a g e *Check last page please before you start. Cholelithiasis: -Small, round stones in the gallbladder.
21 : Disease of extrahepatic biliary tract : Jumana Abu Hamour : 6/12/2015 : Dr. Samir Bashir 1 P a g e *Check last page please before you start. Cholelithiasis: -Small, round stones in the gallbladder.
Biliary cholesterol crystallization characterized by single-crystal cryogenic electron diffraction
 Biliary cholesterol crystallization characterized by single-crystal cryogenic electron diffraction Daphne Weihs, 1, * Judith Schmidt,* Ilana Goldiner, Dganit Danino, 2, * Moshe Rubin, Yeshayahu Talmon,
Biliary cholesterol crystallization characterized by single-crystal cryogenic electron diffraction Daphne Weihs, 1, * Judith Schmidt,* Ilana Goldiner, Dganit Danino, 2, * Moshe Rubin, Yeshayahu Talmon,
Clinical and Nutritional Study on Gallstone. Disease in Japan. Haruo Kameda, MD, Fumitake Ishihara, MD, Koji Shibata, MDand Eiichi Tsukie, MD
 Original Article Clinical and Nutritional Study on Gallstone Haruo Kameda, MD, Fumitake Ishihara, MD, Koji Shibata, MDand Eiichi Tsukie, MD The dietary factors, as a cause on increasing incidence of gallstones
Original Article Clinical and Nutritional Study on Gallstone Haruo Kameda, MD, Fumitake Ishihara, MD, Koji Shibata, MDand Eiichi Tsukie, MD The dietary factors, as a cause on increasing incidence of gallstones
Etiology Bacteria Sand particles Particles of ingesta / intestinal contents Desquamated epithelium
 10 CONCRETIONS Concretions Calculi o Urinary Calculi o Biliary Calculi o Salivary Calculi o Pancreatic Calculi o Enteric Calculi Piliconcretions Phytoconcretions Polyconcretions Model Questions CONCRETIONS
10 CONCRETIONS Concretions Calculi o Urinary Calculi o Biliary Calculi o Salivary Calculi o Pancreatic Calculi o Enteric Calculi Piliconcretions Phytoconcretions Polyconcretions Model Questions CONCRETIONS
COLLECTION TUBES FOR PHLEBOTOMY
 COLLECTION TUBES FOR PHLEBOTOMY Red Top None Blood clots, and the serum is separated by centrifugation Chemistries, Immunology and Serology, Blood Bank (Crossmatch) Gold Top None Serum separator tube (SST)
COLLECTION TUBES FOR PHLEBOTOMY Red Top None Blood clots, and the serum is separated by centrifugation Chemistries, Immunology and Serology, Blood Bank (Crossmatch) Gold Top None Serum separator tube (SST)
Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Pharmacopeial Forum 818 INTERIM REVISION ANNOUNCEMENT Vol. 35(4) [July Aug. 2009] ERRATA
![Pharmacopeial Forum 818 INTERIM REVISION ANNOUNCEMENT Vol. 35(4) [July Aug. 2009] ERRATA Pharmacopeial Forum 818 INTERIM REVISION ANNOUNCEMENT Vol. 35(4) [July Aug. 2009] ERRATA](/thumbs/85/92881277.jpg) 818 INTERIM REVISION ANNOUNCEMENT Vol. 35(4) [July Aug. 2009] ERRATA Following is a list of errata and corrections to USP NF. The page number indicates where the item is found and in which official or
818 INTERIM REVISION ANNOUNCEMENT Vol. 35(4) [July Aug. 2009] ERRATA Following is a list of errata and corrections to USP NF. The page number indicates where the item is found and in which official or
Disclosures. Overview. Case 1. Common Bile Duct Sizes 10/14/2016. General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis
 Disclosures General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis 123 Blank Blank, LLC Aldo Maspons, MD Assistant Professor Director of Endoscopy Department of Pediatrics Texas Tech University Health
Disclosures General GI + Advanced Endoscopy: NAFLD/Stones/Pancreatitis 123 Blank Blank, LLC Aldo Maspons, MD Assistant Professor Director of Endoscopy Department of Pediatrics Texas Tech University Health
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
STUDIES ON THE CALCIUM-PROTEIN RELATIONSHIP WITH THE AID OF THE ULTRACENTRIFUGE
 STUDIES ON THE CALCIUM-PROTEIN RELATIONSHIP WITH THE AID OF THE ULTRACENTRIFUGE II. OBSERVATIONS ON SERUM BY STEPHAN LUDEWIG, ALFRED CHANUTIN, AND A. V. MASKETt (From the Biochemical Laboralory, University
STUDIES ON THE CALCIUM-PROTEIN RELATIONSHIP WITH THE AID OF THE ULTRACENTRIFUGE II. OBSERVATIONS ON SERUM BY STEPHAN LUDEWIG, ALFRED CHANUTIN, AND A. V. MASKETt (From the Biochemical Laboralory, University
Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds
 Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds Objectives: 1) List the major groups of inorganic chemicals common in cells. 2) Describe the functions of various types of inorganic chemicals in cells.
Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds Objectives: 1) List the major groups of inorganic chemicals common in cells. 2) Describe the functions of various types of inorganic chemicals in cells.
DEPARTMENT: Regulatory Compliance Support
 PAGE: 1 of 5 REPLACES POLICY DATED: 1/16/98, 3/1/99, SCOPE: All Company-affiliated hospitals performing and/or billing laboratory services. Specifically, the following departments: Business Office Admitting/Registration
PAGE: 1 of 5 REPLACES POLICY DATED: 1/16/98, 3/1/99, SCOPE: All Company-affiliated hospitals performing and/or billing laboratory services. Specifically, the following departments: Business Office Admitting/Registration
DETERMINING LINAMARIN IN CASSAVA, USING THE ENZYME- IMMOBILIZED MICROPLATE METHOD
 DETERMINING LINAMARIN IN CASSAVA, USING THE ENZYME- IMMOBILIZED MICROPLATE METHOD H.-H. Yeoh and C.-K. C. Tan Abstract Glutaraldehyde and polyethylene imine were used to bind cassava leaf ß-glucosidase
DETERMINING LINAMARIN IN CASSAVA, USING THE ENZYME- IMMOBILIZED MICROPLATE METHOD H.-H. Yeoh and C.-K. C. Tan Abstract Glutaraldehyde and polyethylene imine were used to bind cassava leaf ß-glucosidase
URINARY CRYSTALS. by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown
 URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
MINI-REVIEW. Gallstone Etiopathogenesis, Lith and Mucin Genes and New Treatment Approaches. Vedat Goral. Abstract. Risk Factors.
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.2.467 MINI-REVIEW Gallstone Etiopathogenesis, Lith and Mucin Genes and New Treatment Approaches Vedat Goral Abstract Gallstones constitute one of the more common
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.2.467 MINI-REVIEW Gallstone Etiopathogenesis, Lith and Mucin Genes and New Treatment Approaches Vedat Goral Abstract Gallstones constitute one of the more common
Gallstones Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Gutscharity.org.uk
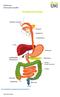 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood
 Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood BCH 471 [Practical] BLOOD COMPOSITION Other names to blood cells Red blood cells (erythrocytes) White blood cells (leukocytes) Platelets
Separation of Plasma and Serum and Their Proteins from Whole Blood BCH 471 [Practical] BLOOD COMPOSITION Other names to blood cells Red blood cells (erythrocytes) White blood cells (leukocytes) Platelets
rabbit, 45 min for dog) and more slowly for dehydrocholic acid (25- decrease, questioning the mechanism by which bile acids increase bile
 J. Physiol. (1972), 224, pp. 259-269 259 With 6 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain SPECIES DIFFERENCES IN THE CHOLERETIC RESPONSE TO BILE SALTS BY CURTIS D. KLAASSEN From the Clinical Pharmacology and
J. Physiol. (1972), 224, pp. 259-269 259 With 6 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain SPECIES DIFFERENCES IN THE CHOLERETIC RESPONSE TO BILE SALTS BY CURTIS D. KLAASSEN From the Clinical Pharmacology and
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
EH1008 Biomolecules. Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Water. Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry.
 EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
72 hour Fast Protocol
 Page 1 of 5 Principle This procedure provides instruction on how to conduct a prolonged fast. During the fast, a careful record must be kept of exactly what was done, what blood samples were taken and
Page 1 of 5 Principle This procedure provides instruction on how to conduct a prolonged fast. During the fast, a careful record must be kept of exactly what was done, what blood samples were taken and
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
BILIARY LIPID SECRETION BEFORE AND AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY IN AMERICAN INDIANS WITH CHOLESTEROL GALLSTONES
 (; l\~thoe~teholor.y 6(l:1~1 ~ - 1 ~ 1-;. I ~J74 COiJ\Tight l'l,~ I,, TllP Wi ll ia m, &: Wilki ils Co. V(II. 6'3. ~(l. f) Printed ill ( r.sa. BILIARY LIPID SECRETION BEFORE AND AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY IN
(; l\~thoe~teholor.y 6(l:1~1 ~ - 1 ~ 1-;. I ~J74 COiJ\Tight l'l,~ I,, TllP Wi ll ia m, &: Wilki ils Co. V(II. 6'3. ~(l. f) Printed ill ( r.sa. BILIARY LIPID SECRETION BEFORE AND AFTER CHOLECYSTECTOMY IN
601 S. College Avenue Kaitlin L. Siela Columbia, MO Telephone: (816)
 Jane M. Jackson Department of Chemistry Telephone: (816) 695-8701 University of Missouri Columbia Email: jmj9q7@mail.missouri.edu 105 Chemistry Building 601 S. College Avenue Kaitlin L. Siela Columbia,
Jane M. Jackson Department of Chemistry Telephone: (816) 695-8701 University of Missouri Columbia Email: jmj9q7@mail.missouri.edu 105 Chemistry Building 601 S. College Avenue Kaitlin L. Siela Columbia,
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Session Outline. Routine Urinalysis a historical perspective. Unit 2; Session 8
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
PPBio Australasia Metadata SOIL PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS
 PPBio Australasia Metadata SOIL PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS Title: Soil Characteristics at Karawatha Forest Chemical and Physical Analysis Responsibility: Sarah Butler Clay Simpkins APro Jean-Marc
PPBio Australasia Metadata SOIL PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS Title: Soil Characteristics at Karawatha Forest Chemical and Physical Analysis Responsibility: Sarah Butler Clay Simpkins APro Jean-Marc
Hepatic esterification rate of cholesterol and biliary lipids in human obesity
 Hepatic esterification rate of cholesterol and biliary lipids in human obesity Staffan Sahlin,' Lars Granstrom, Ulf Gustafsson, Dagny Stalberg, Lars Backman, and Kurt Einarsson Department of Surgery, Danderyd
Hepatic esterification rate of cholesterol and biliary lipids in human obesity Staffan Sahlin,' Lars Granstrom, Ulf Gustafsson, Dagny Stalberg, Lars Backman, and Kurt Einarsson Department of Surgery, Danderyd
Separation of Main Proteins in Plasma and Serum
 BCH 471 Experiment (2) Separation of Main Proteins in Plasma and Serum PLASMA PROTEINS Mw The main plasma proteins are: þ Albumin (36-50 g/l), Mw 66.241kDa. þ Globulins (18-32 g/l), Mw of globulins Cover
BCH 471 Experiment (2) Separation of Main Proteins in Plasma and Serum PLASMA PROTEINS Mw The main plasma proteins are: þ Albumin (36-50 g/l), Mw 66.241kDa. þ Globulins (18-32 g/l), Mw of globulins Cover
Influence of Legume Intake on Biliary Lipids and Cholesterol Saturation in Young Chilean Men
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1989;96:825-30 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Influence of Legume Intake on Biliary Lipids and Cholesterol Saturation in Young Chilean Men Identification of a Dietary Risk Factor for
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1989;96:825-30 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Influence of Legume Intake on Biliary Lipids and Cholesterol Saturation in Young Chilean Men Identification of a Dietary Risk Factor for
Liver Function Tests. Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy
 Liver Function Tests Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Metabolic function Excretory function Synthetic fuction Detoxification function Storage function
Liver Function Tests Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Metabolic function Excretory function Synthetic fuction Detoxification function Storage function
A novel approach for differentiating etiology of gallstone formation: Sistocholedochal angle
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences A novel approach for differentiating etiology of gallstone formation: Sistocholedochal angle M. SIPAHI 1, M.F. ERKOÇ 2, H.I. SERIN 2, H. BÖREKÇI
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences A novel approach for differentiating etiology of gallstone formation: Sistocholedochal angle M. SIPAHI 1, M.F. ERKOÇ 2, H.I. SERIN 2, H. BÖREKÇI
