Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and
|
|
|
- Mitchell Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut, 1978, 19, Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and total CO2 in bile D. JUNE SUTOR AND LYNETTE I. WILKIE From the Department of Chemistry, University College London, London SUMMARY Measurement of total CO2 concentrations in bile from patients undergoing cholecystectomy because of gallstones has shown that the presence of calcium carbonate in the stones can be associated with a raised total CO2 concentration in the common duct bile. In bile from functioning and poorly-functioning gallbladders, total CO2 was nearly always related to ph irrespective of stone composition. The different forms of calcium carbonate (vaterite aragonite, and calcite) are important constituents of gallstones (Sutor and Wooley, 1971). At University College Hospital, London, we are finding that a higher proportion of patients have gallstones consisting of cholesterol + calcium carbonate than of pure cholesterol, and we want to determine how and why calcium carbonate crystallises from bile. In the first instance, the concentrations of the relevant ions have been measured in bile from different types of stone-formers, to see if they are higher in patients with calcium carbonate in their gallstones. Only this kind of comparison was possible because bile from normal persons was not available. So far, we have found no significant difference in calcium concentrations in bile from calcium carbonate stoneformers and from patients with cholesterol gallstones (Sutor and Wilkie, 1977). In this paper we have investigated some factors influencing the concentration of the carbonate ion. Over the biliary ph range, which is 6-8-8&5 (Sutor and Wilkie, 1976), the carbonate concentration is approximately 1-2 to 1-3 of the bicarbonate concentration and is, therefore, too small to measure. The bicarbonate concentration can be measured directly by titration but this was not possible for the small amount of bile, particularly common duct bile, collected at operation. We have, therefore, measured the amount of total CO2 present Present address of authors: Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, Rayne Institute, University Street, London WC1E 6JJ. Received for publication 1 October 1977 which is the sumof theconcentrations of bicarbonate, carbonic acid, dissolved C2, and carbonate. On searching the literature for bicarbonate concentrations measured by other workers, we have found that they too have measured total C2 and called it bicarbonate, or calculated a theoretical bicarbonate value using constants derived for serum. This is not correct as the solubility of CO2 in bile has not been determined, the pressure of CO2 with which bile is in equilibrium is not known, and the pki value for the dissociation of carbonic acid in bile is unknown. Until these factors have been investigated, and they could vary from one patient to another, such results should be presented in terms of total C2. Methods COLLECTION AND SELECTION OF BILE SAMPLES Bile was collected anaerobically at 37 C from patients undergoing surgery, usuallycholecystectomy, at University College Hospital, London, during the period A previously reported technique was used by the surgeons to collect common duct and gallbladder bile and to minimise contamination of the former by the latter (Antsaklis et al., 1975). For the anaerobic collection, bile was drawn into a closed sterile syringe and air from the Luer fitting was immediately expelled. The gallbladder was completely aspirated to minimise stratification effects (Tera, 196). For technical reasons, common duct bile was not always obtained. The syringe was sealed by bending the needle and insulated to prevent heat loss till it could be placed, generally within 3 minutes, in a constant temperature box at 37 C. In order that bile could be handled relatively 22 Gut: first published as /gut on 1 March Downloaded from on 28 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
2 Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and total C2 in bile easily at 37 C, the box used was a dry box fitted withaheating element, fan, and variable transformer. Work on the bile was started immediately. Eighty-two patients presented for operation, but material suitable for analysis was not always obtained. In the case of gallbladder bile, 11 patients had bile too thick to handle, 13 had no bile in their gallbladders, four had had previous cholecystectomies, and five biles contained blood and were discarded. The remaining 49 samples were analysed. Forty samples of common duct bile were collected but to obtain data as 'normal' as possible, the following were excluded: bile containing blood, bile from patients with an obstructed or dilated duct, bile obviously containing mucus which suggested it was contaminated with gallbladder bile, and samples less than 2,ll which were unlikely to be anaerobic. These restrictions left 28 samples for analysis. Both common duct and gallbladder bile suitable for analysis were obtained from 15 patients. PH MEASUREMENTS The ph was measured using microelectrodes in the constant temperature box and a Radiometer ph meter. The meter was standardised with Radiometer buffer, ph = 7-38 ± 2 at 38 C, the reliability of the electrodes being checked regularly. Exposure to air of bile in the glass electrode did not affect the measurement, which was stable for at least 1 minutes. Two measurements were made on each bile. After each determination, the glass electrode was flushed out with saline and water, and the standardisation of the meter was checked. Millipore filtration of bile (described below) did not affect the ph, which could therefore be determined on filtered and unfiltered samples. Most of our ph measurements were made on unfiltered bile. MILLIPORE FILTRATION OF BILE To remove any stone debris, precipitate, and soluble and insoluble mucus of high molecular weight, the bile was filtered anaerobically at 37 C through a prefilter and Millipore filter (pore size, 45,um) by attaching to the syringe containing the sample a Millipore stainless steel microsyringe filter-holder with the dead space filled in. All biles analysed were forced through the filters by hand pressure and the filtrate passed into a piece of silicone rubber tubing attached to the outlet on the filter-holder. Samples for analysis were withdrawn through the wall of the tubing using a microsyringe. The first 5,A would have been in contact with air in the filter-holder and was not used. MEASUREMENT OF TOTAL C2 Total CO2 was determined at room temperature 221 with a Technicon Auto-Analyser using a micro CO2 procedure (Technicon Methodology N-19a). This method is for serum and the following modifications were made for bile: 1. Hydrochloric acid was used instead of sulphuric acid to prevent any calcium sulphate being precipitated, because the calcium concentration in bile is frequently higher than in serum (Sutor and Wilkie, 1977). 2. Water free of CO2 (made by degassing distilled water) was used as a diluent for the bile instead of saline, as water added to bile does not precipitate proteins or other substances at the dilutions used below. 3. Standardised sodium carbonate solution was added to bile samples having a low ph, which experience showed corresponds to a low total C2 concentration, to bring the concentration into the range covered by the standards (1-4 mmol/l). Samples for measurement were prepared by adding gallbladder bile (1,ul and 2,ul together with sodium carbonate solution if necessary) or common duct bile (1 pl) to a small amount of water free of CO2 in 2 ml volumetric flasks and making to volume with such water. Measurements were made on unfiltered bile not containing crystals and its Millipore filtrate to confirm that the total C2 content was unaffected by this process. SUBDIVISION OF DATA The data were considered in relation to two variables. Gallbladderfunction Patients were always divided according to their gallbladder function, which was usually known and had been assessed by oral x-ray cholecystography. Three groups were recognised: patients with functioning, poorly-functioning, and non-functioning gallbladders depending on whether the gallbladder gave good concentration, some concentration, or no concentration of the dye respectively. All patients with an obstructed duct were taken as having nonfunctioning gallbladders. Data for five patients whose gallbladder function was not determined have not been included and this reduced the number of gallbladder bile samples to 44. Stone composition Most patients had gallstones, and the crystalline constituents present were determined by the x-ray powder method (Sutor and Wooley, 1971). Patients were classified according to the surface composition of their gallstones as this area is most likely to be related to the present bile composition. The following grouping was made: (1) pure cholesterol, (2) some Gut: first published as /gut on 1 March Downloaded from on 28 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
3 222 calcium carbonate, usually with cholesterol, (3) calcium salt other than calcium carbonate. STATISTICAL TESTS Statistical significance of differences between two groups was determined using the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-test (Siegel, 1956). To determine if two variables were related, the significance of the correlation coefficient (r) was tested (Pearson and Hartley, 1966). The 5% level was adopted for significance tests. Results The estimated errors in the measurements were ± 2 mmol/l for total CO2 and ± '5 for the ph. Measurements made on biles free of crystals and their filtrates showed that, as expected, the concentration of total CO2 was not affected by Millipore filtration. so E E (,1J -6 45r 4k COMMON DUCT BILE In the case of common duct bile, patients with functioning and poorly-functioning gallbladders were taken together, as the values were unlikely to be affected by the degree of function. Total CO2 was within the range 22'5-27'7 mmol/l and the mean was 24'5 (SEM, '5) for the 1 patients with only cholesterol on the stone surface (Fig. 1). Nine of the gallbladders were functioning and one was poorly- 35r- 3k Cholesterol Some CaCO3 Stones in Stones Fig. 1 Total CO2 in common duct bilefor patients with functioning or poorly-functioning gallbladders and gallstones of different composition. D. June Sutor and Lynette L Wilkie functioning. Total CO2 was within the range 29'1-42'5 mmol/l and the mean was 33'9 (SEM, 1'5) for the 11 patients having some calcium carbonate on the stone surface (Fig. 1). Ten of these gallbladders were functioning and one was poorly-functioning. These two groups of stone-formers differ significantly (p < O'O1). Only one patient had a total CO2 concentration in the higher range and no calcium carbonate in the gallstone, which consisted entirely of calcium bilirubinate. This was the only patient from whom common duct bile had been obtained and who had a calcium salt other than calcium carbonate on the stone surface. Total CO2 for one patient with no gallbladder and one patient with no stone at operation and a functioning gallbladder was 26'6 and 27'6 mmol/l respectively. These values were comparable with those for the cholesterol stone-formers. For the four patients with nonfunctioning gallbladders, total CO2 was within the range '4 mmol/l and the gallstone surfaces consisted of cholesterol. The ph of common duct bile from all patients was within the range 7'5-8'. There was no statistically significant correlation between ph and total CO2 for either the cholesterol or calcium carbonate stone-formers with functioning or poorly-functioning gallbladders (p < O16 and P < O66 respectively). GALLBLADDER BILE Total CO2 was always less in gallbladder bile than in the corresponding common duct bile irrespective of gallbladder function and stone composition. Table 1 gives values for the 15 pairs of measurements. Table 1 Total C2 concentrations in corresponding common duct and gallbladder bile Total CO. (mmol/l) Composition Gallbladder group function Common Gallbladder duct bile bile f f f f f f f f f f f pf nf nf ns f Key to composition of gallstones: 1 = cholesterol, 2 = some calcium carbonate, 3 = calcium salt other than calcium carbonate, ns = no stone. Key to gallbladder function: f = functioning, pf = poorlyfunctioning, nf = non-functioning. Gut: first published as /gut on 1 March Downloaded from on 28 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 Calcium carbonate in human gallstones and total CO2 in bile In Fig. 2, total CO2 for bile from functioning gallbladders is plotted against ph. Measurements were available only for the cholesterol and calcium carbonate stone-formers. For these patients, the correlation coefficient for total CO2 regressed on ph was significant (r = 9, n = 27, p < 1). -5 t-' U E CY -a F 25 F 2 F 15F Table 2 ph and total CO2 concentrations in gallbladder bile from patients with poorly-functioning or nonfunctioning gallbladders ph Total C2 Stone composition (mmol/l) group and comments Poorly-functioning gallbladders Non-functioning gallbladders (blocked duct) (watery bile) (white bile) Composition of surface of stones: 1 = cholesterol, 2 = some calcium carbonate, 3 = calcium salt other than calcium carbonate. Discussion. lo1 Although data are limited because of the problems / Stone Composition associated with collecting bile from human subjects, Cholesterol some highly significant results have been obtained..5 = Some CaC3 For patients with functioning or poorly-functioning gallbladders, the presence of calcium carbonate in gallstones was related to a raised concentration of L, I, total CO2 in common duct bile. Values were within the range mmol/l for cholesterol stone-formers ph and they are within the normal range for serum (2-28 mmol/l, University College Hospital values). Fig. 2 Plot of total CO2 against phfor bilefrom It is suggested they represent normal concentrations functioning g,allbladders. The regression line has a slope of for common duct bile. Values greater than 29 mmol/l 22-2 and inte rcept of The three points lying well were almost invariably associated with the presence above the lingrewere not included in this calculation. of calcium carbonate on the stone surface and are referred to as raised concentrations. Only one patient The slope of the line was 22-2 and the intercept had a raised value for total CO2 and no calcium ThLree patients with some calcium carbonate carbonate in the gallstone which was composed of on the surf; ace of their stones had values well above calcium bilirubinate. This would suggest that, in the line anci these were not included in this calcula- solutions supersaturated with calcium bilirubinate tion. Therie was also a statistically significant and calcium carbonate, the former is deposited. correlation for total CO2 regressed on ph for bile The reason for the raised total C2 values in these from the siix poorly-functioning gallbladders (r = biles is not known, but it could result from a dis- -84, n = ( 5, p < 4). The slope of the regression turbance in the secretion of secretin. In a study of line was 37'*7 and the intercept was All of the rate of bile flow and the electrolyte composition these patients had gallstones with some calcium of human hepatic bile in cholecystectomised patients carbonate, c-alciumphosphate, or calcium bilirubinate with T-tubes in the common duct, the administration on the surfsace. There was no statistically significant of secretin augmented the flow of common duct bile difference between the regression coefficients corres- with a fluid rich in total CO2 (Waitman et al., 1969). ponding to measurements for patients with func- These workers reported that the fluid was rich in tioning anci poorly-functioning gallbladders. Data bicarbonate, but they, too, measured total CO2. for the latt er group are given in Table 2 together In patients with non-functioning gallbladders, with values for patients with non-functioning two of the total CO2 concentrations in common duct gallbladderss. bile (17 4 and 2-4 mmol/l) were below the values 223 Gut: first published as /gut on 1 March Downloaded from on 28 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
5 224 D. June Sutor and Lynette L Wilkie found for patients with functioning or poorlyfunctioning gallbladders. This may indicate that the suggested normal range is too small, or that some of the molecules or ions responsible for the total C2 concentration have been lost by diffusion through the duct walls. One patient in this group had a total C2 concentration of 29-4 mmol/l and this did not lead to the precipitation of calcium carbonate. However, if an increase in the concentration of total C2 occurred after the gallbladder became non-functioning, and if this bile could not enter the gallbladder, the gallstone composition would not reflect this abnormality in the composition of the common duct bile. In the gallbladder, there was a decrease in the total C2 concentration and this is consistent with the active transport of bicarbonate ions from the gallbladder. However, passive diffusion through the gallbladder wall of molecules and ions, such as dissolved C2 and bicarbonate, may also be occurring during concentration of bile in the gallbladder. Although there was no correlation between total C2 and ph in common duct bile, these two variables were related in bile from functioning and from poorly-functioning gallbladders, irrespective of the composition of the gallstones formed. Three of the calcium carbonate stone-formers had values lying above the regression line for data from patients with functioning gallbladders. These high concentrations could have resulted from the gallbladder having emptied not long before the samples were taken, or the gallbladder function may have deteriorated between the time of the cholecystogram and the time of the operation. Our studies suggest that an important factor in the deposition of calcium carbonate in gallstones is the raised level of total C2 in common duct bile. Precipitation would occur when such bile enters the gallbladder before the relationship between ph and total C2 has been attained. We thank Professor C. G. Clark and the surgeons at University College Hospital for providing the bile specimens, Mr K. Piper for helpful discussions concerning the measurement of total C2, and the Medical Research Council for financial support. References Antsaklis, G., Lewin, M. R., Sutor, D. J., Cowie, A. G. A., and Clark, C. G. (1975). Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition. Gut, 16, Pearson, E. S., and Hartley, H.. (1966). Biometrika Tables for Statisticians, vol. 1, 3rd edn, p. 21. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge. Siegel, S. (1956). Nonparametric Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences. McGraw-Hill: New York. Sutor, D. J., and Wilkie, L. I. (1976). Diurnal variations in the ph of pathological gallbladder bile. Gut, 17, Sutor, D. J., and Wilkie, L. I. (1977). Calcium in bile and calcium salts in gallstones. Clinica Chimica Acta, 79, Sutor, D. J., and Wooley, S. E. (1971). A statistical survey of the composition of gallstones in eight countries. Gut, 12, Tera, H. (196). Stratification of human gallbladder bile in vivo. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica, suppl., 256, Waitman, A. M., Dyck, M. P., and Janowitz, H. D. (1969). Effect of secretin and acetazolamide on the volume and electrolyte composition of hepatic bile in man. Gastroenterology, 56, Gut: first published as /gut on 1 March Downloaded from on 28 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition
 Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition Gut, 1975, 16, 937-942 G. ANTSAKLIS, M. R. LEWIN1, D. JUNE SUTOR, A. G. A. COWIE, AND C. G. CLARK From the Department of Surgery, University
Gallbladder function, cholesterol stones, and bile composition Gut, 1975, 16, 937-942 G. ANTSAKLIS, M. R. LEWIN1, D. JUNE SUTOR, A. G. A. COWIE, AND C. G. CLARK From the Department of Surgery, University
The organic matrix of gallstones
 Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
Gut, 1974, 15, 487-491 The organic matrix of gallstones D. JUNE SUTOR AND SUSAN E. WOOLEY From the Department of Chemistry, University College, London SUMMARY Dissolution of gallstones consisting of cholesterol,
Change to read: BRIEFING
 BRIEFING Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate, USP 29 page 359. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Dibasic
BRIEFING Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate, USP 29 page 359. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia is the coordinating pharmacopeia for the international harmonization of the compendial standards for the Dibasic
human gall bladder bile
 Gut, 1986, 27, 1382-1386 Effect of binding of ionised calcium on the in vitro nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirubinate in human gall bladder bile S GALLINGER, P R C HARVEY, C N PETRUNKA, AND
Gut, 1986, 27, 1382-1386 Effect of binding of ionised calcium on the in vitro nucleation of cholesterol and calcium bilirubinate in human gall bladder bile S GALLINGER, P R C HARVEY, C N PETRUNKA, AND
EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH
 Practical Manual Food Chemistry and Physiology EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4.2 Experiment 4a: Reducing
Practical Manual Food Chemistry and Physiology EXPERIMENT 4 DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, TOTAL REDUCING SUGARS, SUCROSE AND STARCH Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4.2 Experiment 4a: Reducing
ENZYME CONCENTRATIONS AND ENZYME ACTIVITY: PLANNING SHEET
 Activity 2.11 Student Sheet ENZYME CONCENTRATIONS AND ENZYME ACTIVITY: PLANNING SHEET To investigate how enzyme concentration can affect the initial rate of reaction. Wear eye protection, lab coats and
Activity 2.11 Student Sheet ENZYME CONCENTRATIONS AND ENZYME ACTIVITY: PLANNING SHEET To investigate how enzyme concentration can affect the initial rate of reaction. Wear eye protection, lab coats and
RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
Compliance. Should you have any questions, please contact Behnaz Almasi, Associate Scientific Liaison ( or
 Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 30 Mar 2018 Official Date 01 Apr 2018 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 3 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 30 Mar 2018 Official Date 01 Apr 2018 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 3 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
This revision also necessitates a change in the table numbering in the test for Organic Impurities.
 Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 27 Jul 2018 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert Committee Chemical
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 27 Jul 2018 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert Committee Chemical
contents of the monograph in effect today. Please refer to the current edition of the USP NF for official text.
 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 26 Jan 2018, revised 12 Feb 2018 1 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert
Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 26 Jan 2018, revised 12 Feb 2018 1 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert
Identification and qualitative Analysis. of Renal Calculi
 Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
It is recommended to use titanium coils. ph meter to control ph of the process. It is advised to use an automatic dosage for the maintenance products.
 CRODA III Decorative Trivalent Chrome Process CRODA III is a hexavalent free chrome process, allowing to obtain slightly blue and bright deposits, optimal for decorative applications. ADVANTAGES Depuration
CRODA III Decorative Trivalent Chrome Process CRODA III is a hexavalent free chrome process, allowing to obtain slightly blue and bright deposits, optimal for decorative applications. ADVANTAGES Depuration
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Pathak, 1959; Hunt & Pathak, 1960). This slowing of gastric emptying is
 34 J. Phy8iol. (1962), 163, pp. 34-45 With 2 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain THE REGULATION OF GASTRIC EMPTYING OF MEALS CONTAINING CITRIC ACID AND SALTS OF CITRIC ACID BY J. N. HUNT AND M. T. KNOX
34 J. Phy8iol. (1962), 163, pp. 34-45 With 2 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain THE REGULATION OF GASTRIC EMPTYING OF MEALS CONTAINING CITRIC ACID AND SALTS OF CITRIC ACID BY J. N. HUNT AND M. T. KNOX
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Experiment 2: Melting Points and the Identification of an Unknown and Cholesterol from Human Gallstones
 1 Experiment 2: Melting Points and the Identification of an Unknown and Cholesterol from Human Gallstones Part 1. Melting Points and the Identification of an Unknown Read pp 211-220, Chapter 14, (especially
1 Experiment 2: Melting Points and the Identification of an Unknown and Cholesterol from Human Gallstones Part 1. Melting Points and the Identification of an Unknown Read pp 211-220, Chapter 14, (especially
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
HAGEDORN AND JENSEN TO THE DETER- REDUCING SUGARS. MINATION OF LARGER QUANTITIES OF XIV. AN APPLICATION OF THE METHOD OF
 XIV. AN APPLICATION OF THE METHOD OF HAGEDORN AND JENSEN TO THE DETER- MINATION OF LARGER QUANTITIES OF REDUCING SUGARS. By CHARLES SAMUEL HANES (Junior Scholar of the Exhibition of 1851). From the Botany
XIV. AN APPLICATION OF THE METHOD OF HAGEDORN AND JENSEN TO THE DETER- MINATION OF LARGER QUANTITIES OF REDUCING SUGARS. By CHARLES SAMUEL HANES (Junior Scholar of the Exhibition of 1851). From the Botany
Transport of Iodide Ion in Compacted Bentonite Containing Ag 2 O
 Transport of Iodide Ion in Compacted Bentonite Containing Ag 2 O - 12111 Sung Paal Yim*, Ji-Hyun Lee*, Heui-Joo Choi*, Jong-Won Choi*, Cheo Kyung Lee** Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Yusong, Daejon,
Transport of Iodide Ion in Compacted Bentonite Containing Ag 2 O - 12111 Sung Paal Yim*, Ji-Hyun Lee*, Heui-Joo Choi*, Jong-Won Choi*, Cheo Kyung Lee** Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Yusong, Daejon,
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 8
 CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 8 DETERMINATION OF WATER IN THE MAINSTREAM SMOKE OF CIGARETTES BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS (August 1991) 1. FIELD OF APPLICATION The method is applicable to the particulate
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 8 DETERMINATION OF WATER IN THE MAINSTREAM SMOKE OF CIGARETTES BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS (August 1991) 1. FIELD OF APPLICATION The method is applicable to the particulate
What is the Acid Source? Where is Acid Rain Falling? Chemistry of Acid Rain Formation. What Determines Lake Susceptibility to Acidification?
 Acid Precipitation and Remediation of Acid Lakes What is the Acid Source? Acid Rain Peristaltic Pump ph Probe Lake Data source: www.usepa.gov. Chemistry of Acid Rain Formation Where is Acid Rain Falling?
Acid Precipitation and Remediation of Acid Lakes What is the Acid Source? Acid Rain Peristaltic Pump ph Probe Lake Data source: www.usepa.gov. Chemistry of Acid Rain Formation Where is Acid Rain Falling?
XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES.
 XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES. II. THE PREPARATION OF GLUCOSE UREIDE. BY ALEXANDER HYND. From the Department of Physiology, University of St Andrews. (Received
XXVI. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION. OF AMINO-COMPOUNDS AND CARBOHYDRATES. II. THE PREPARATION OF GLUCOSE UREIDE. BY ALEXANDER HYND. From the Department of Physiology, University of St Andrews. (Received
PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS
 PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS INTRODUCTION Parenteral (Gk, para enteron, beside the intestine) dosage forms differ from all other drug dosage forms, because they are injected directly into body tissue through
PARENTERAL PREPARATIONS INTRODUCTION Parenteral (Gk, para enteron, beside the intestine) dosage forms differ from all other drug dosage forms, because they are injected directly into body tissue through
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Package leaflet: information for the user. Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration
 Package leaflet: information for the user Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Calcium chloride dihydrate/ magnesium chloride hexahydrate/ glucose monohydrate/ lactic
Package leaflet: information for the user Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium Solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Calcium chloride dihydrate/ magnesium chloride hexahydrate/ glucose monohydrate/ lactic
Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (3) Vol., No. 3, Issue 7, 3-7 Controversies in the management of acute pancreatitis Singh DR 1, Mehta A, Dangol UMS 3 1 Lecturer, Medical Officer, 3 Lecturer, Dept.
2. is a set of principles intended to help sustain a habitable planet.
 Chapter 2 Tools of the Trade 1 Multiple Choice 2-1 Safe, Ethical Handling of Chemicals and Waste 1. Which of the following statements are TRUE? I Organic solvents, concentrated acids, and concentrated
Chapter 2 Tools of the Trade 1 Multiple Choice 2-1 Safe, Ethical Handling of Chemicals and Waste 1. Which of the following statements are TRUE? I Organic solvents, concentrated acids, and concentrated
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
Topic Objectives. Physical Examination LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE. Appearance. Odor Specific Gravity Volume
 LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
MONOGRAPHS (USP) Saccharin Sodium
 Vol. 31(4) [July Aug. 2005] HARMONIZATION 1225 MONOGRAPHS (USP) BRIEFING Saccharin Sodium, USP 28 page 1745 and page 612 of PF 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating
Vol. 31(4) [July Aug. 2005] HARMONIZATION 1225 MONOGRAPHS (USP) BRIEFING Saccharin Sodium, USP 28 page 1745 and page 612 of PF 31(2) [Mar. Apr. 2005]. The United States Pharmacopeia is the coordinating
FREEZING POINTS OF ANTI-COAGULANT SALT SOLUTIONS
 Published Online: 20 March, 1935 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.18.4.485 Downloaded from jgp.rupress.org on October 21, 2018 FREEZING POINTS OF ANTI-COAGULANT SALT SOLUTIONS B~ DAVID I. HITCI~OCK
Published Online: 20 March, 1935 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.18.4.485 Downloaded from jgp.rupress.org on October 21, 2018 FREEZING POINTS OF ANTI-COAGULANT SALT SOLUTIONS B~ DAVID I. HITCI~OCK
The Nitrofurantoin Capsules Revision Bulletin supersedes the currently official monograph.
 Nitrofurantoin Capsules Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 28 Dec 2018 Official Date 01 Jan 2019 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 1 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
Nitrofurantoin Capsules Type of Posting Revision Bulletin Posting Date 28 Dec 2018 Official Date 01 Jan 2019 Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs 1 Reason for Revision Compliance In accordance
» Croscarmellose Sodium is a cross linked polymer of carboxymethylcellulose sodium.
 BRIEFING Croscarmellose Sodium, NF 22 page 2856 and page 702 of PF 30(2) [Mar. Apr. 2004]. A modification is made in the test for Degree of substitution to correct the endpoint color to agree with the
BRIEFING Croscarmellose Sodium, NF 22 page 2856 and page 702 of PF 30(2) [Mar. Apr. 2004]. A modification is made in the test for Degree of substitution to correct the endpoint color to agree with the
Pectins. Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Pectins This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive Specifications.
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Pectins This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive Specifications.
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN BY JOHN H. NORTHROP. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, iv. J.
 CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN III. PREPARATION OF ACTIVE CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM INACTIVE DENATURED PEPSIN BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton,
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN III. PREPARATION OF ACTIVE CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM INACTIVE DENATURED PEPSIN BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton,
Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects
 12 LI T. C. Northfield, N. F. LaRusso, A. F. Hofmann, and J. L. Thistle Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects T. C. NORTHFIELD, N. F. LaRUSSO, A. F. HOFMANN, AND J. L. THISTLE
12 LI T. C. Northfield, N. F. LaRusso, A. F. Hofmann, and J. L. Thistle Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects T. C. NORTHFIELD, N. F. LaRUSSO, A. F. HOFMANN, AND J. L. THISTLE
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP
 CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN V. ISOLATION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN FROM BOVINE GASTRIC JUICE BY JOHN H. NORTHROP (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J.) (Accepted
Experimental Techniques Question Paper 2
 Experimental Techniques Question Paper 2 Level IGCSE Subject Chemistry Exam Board CIE Topic Experimental Techniques Sub-Topic Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper 2 Time Allowed:
Experimental Techniques Question Paper 2 Level IGCSE Subject Chemistry Exam Board CIE Topic Experimental Techniques Sub-Topic Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper 2 Time Allowed:
LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 298-303, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE BILE ACID METABOLISM IN CIRRHOSIS III. Biliary lipid secretion
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 298-303, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.2 Printed in U.S.A. LIVER PHYSIOLOGY AND DISEASE BILE ACID METABOLISM IN CIRRHOSIS III. Biliary lipid secretion
Most of the ethanol that is used as a biofuel in this country is produced from corn.
 Chem 251 Ethanol from Corn Most of the ethanol that is used as a biofuel in this country is produced from corn. In this experiment you will make ethanol from frozen corn kernels using a process similar
Chem 251 Ethanol from Corn Most of the ethanol that is used as a biofuel in this country is produced from corn. In this experiment you will make ethanol from frozen corn kernels using a process similar
Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. NCERT
 Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
Exercise 28 Aim: To study the effect of ph on the action of salivary amylase. Principle: Optimal activity for most of the enzymes is generally observed between ph 5.0 and 9.0. However, a few enzymes, e.g.,
For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Surname. Candidate. Number. Other Names
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Surname Other Names Notice to Candidate. The work you submit for assessment must be your own. If you copy from someone else or allow another
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Surname Other Names Notice to Candidate. The work you submit for assessment must be your own. If you copy from someone else or allow another
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Biochemical Techniques 06 Salt Fractionation of Proteins. Biochemistry
 . 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
. 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
Organic Molecule Composition of Milk: Lab Investigation
 Name: Organic Molecule Composition of Milk: Lab Investigation Introduction & Background Milk & milk products have been a major food source from earliest recorded history. Milk is a natural, nutritionally
Name: Organic Molecule Composition of Milk: Lab Investigation Introduction & Background Milk & milk products have been a major food source from earliest recorded history. Milk is a natural, nutritionally
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
REEF CARE PROGRAM / Reef Colors. Reef Foundation. Testing and Supplementing
 GB REEF CARE PROGRAM / Reef Colors Reef Foundation Testing and Supplementing Red Sea s Reef Care Program The complete Reef Care program is the result of years of research into the physiological demands
GB REEF CARE PROGRAM / Reef Colors Reef Foundation Testing and Supplementing Red Sea s Reef Care Program The complete Reef Care program is the result of years of research into the physiological demands
CHAPTER VI FACTORIAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECTS OF CYCLODEXTRINS AND SOLUTOL HS15 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF EFAVIRENZ AND RITONAVIR
 CHAPTER VI FACTORIAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECTS OF CYCLODEXTRINS AND SOLUTOL HS15 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF EFAVIRENZ AND RITONAVIR Efavirenz and ritonavir, two widely prescribed anti retroviral
CHAPTER VI FACTORIAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECTS OF CYCLODEXTRINS AND SOLUTOL HS15 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF EFAVIRENZ AND RITONAVIR Efavirenz and ritonavir, two widely prescribed anti retroviral
EFFECT OF HIGH SALT CONCENTRATIONS ON COLOR PRODUCTION OF THE BIURET REACTION FOR PROTEIN ANALYSIS
 EFFECT OF HIGH SALT CONCENTRATIONS ON COLOR PRODUCTION OF THE BIURET REACTION FOR PROTEIN ANALYSIS HAROLD L. ROSENTHAL, PH.D., AND TOYOKO KAWAKAMI, M.T. (ASC1>) Division of Biochemistry, Department of
EFFECT OF HIGH SALT CONCENTRATIONS ON COLOR PRODUCTION OF THE BIURET REACTION FOR PROTEIN ANALYSIS HAROLD L. ROSENTHAL, PH.D., AND TOYOKO KAWAKAMI, M.T. (ASC1>) Division of Biochemistry, Department of
Potentiality of Yeast Strain On Cement Concrete specimen
 Potentiality of Yeast Strain On Cement Concrete specimen N.Bharathi * and RM. Meyyappan Bio-Electrochemical Laboratory, Annamalai University, Chidambaram, Tamilnadu. Abstract The objective of the present
Potentiality of Yeast Strain On Cement Concrete specimen N.Bharathi * and RM. Meyyappan Bio-Electrochemical Laboratory, Annamalai University, Chidambaram, Tamilnadu. Abstract The objective of the present
THE COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF PHOSPHORUS.
 XXX. THE COLORMETRC DETERMNATON OF PHOSPHORUS. By EARL JUDSON KNG. Department of Medical Research, Banting nstitute, University of Toronto. (Received January 12th, 1932.) OF the several colorimetric methods
XXX. THE COLORMETRC DETERMNATON OF PHOSPHORUS. By EARL JUDSON KNG. Department of Medical Research, Banting nstitute, University of Toronto. (Received January 12th, 1932.) OF the several colorimetric methods
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical. Amylase is harmful, avoid contact with eyes and skin.
 Practical 3 - The identification of biological chemicals present in solutions This practical focuses on making decisions about measurements and observations, recording and presenting data and observations,
Practical 3 - The identification of biological chemicals present in solutions This practical focuses on making decisions about measurements and observations, recording and presenting data and observations,
Revision Bulletin 28 Jul Aug 2017 Chemical Medicines Monographs 3
 Oxybutynin Chloride Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Posting Date Official Date Expert Committee Reason for Revision Revision Bulletin 28 Jul 2017 01 Aug 2017 Chemical Medicines Monographs 3 Compliance
Oxybutynin Chloride Extended-Release Tablets Type of Posting Posting Date Official Date Expert Committee Reason for Revision Revision Bulletin 28 Jul 2017 01 Aug 2017 Chemical Medicines Monographs 3 Compliance
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Significance of Ca-soap formation for calcium
 Gut, 1977, 18, 64-68 Significance of Ca-soap formation for calcium absorption in the rat G. GACS AND D. BARLTROP' From the Paediatric Unit, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The significance
Gut, 1977, 18, 64-68 Significance of Ca-soap formation for calcium absorption in the rat G. GACS AND D. BARLTROP' From the Paediatric Unit, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The significance
School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR
 1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
1 School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PLB SEMINAR URINARY (RENAL) STONE FORMATION An Overview What are Urinary (Renal)
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Unit 2b: EXCRETION OF DRUGS. Ms.M.Gayathri Mpharm (PhD) Department of Pharmaceutics Krishna Teja Pharmacy college Subject code: 15R00603 (BPPK)
 Unit 2b: EXCRETION OF DRUGS By Ms.M.Gayathri Mpharm (PhD) Department of Pharmaceutics Krishna Teja Pharmacy college Subject code: 15R00603 (BPPK) Excretion, along with metabolism and tissue redistribution,
Unit 2b: EXCRETION OF DRUGS By Ms.M.Gayathri Mpharm (PhD) Department of Pharmaceutics Krishna Teja Pharmacy college Subject code: 15R00603 (BPPK) Excretion, along with metabolism and tissue redistribution,
SOME ASPECTS OF GASTRIC FUNCTION IN THE NEWBORN
 SOME ASPECTS OF GASTRIC FUNCTION IN THE NEWBORN BY SEYMOUR MASON From the Children's Department, St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JANUARY 23, 1962) Gastric digestion of protein
SOME ASPECTS OF GASTRIC FUNCTION IN THE NEWBORN BY SEYMOUR MASON From the Children's Department, St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JANUARY 23, 1962) Gastric digestion of protein
GlucCell TM SYSTEM USER S GUIDE ver 2.3 CELL CULTURE GLUCOSE METER. Important Information. Intended Use. Caution. About the System
 GlucCell TM SYSTEM USER S GUIDE ver 2.3 Intended Use The GlucCell TM Cell Culture Glucose Monitoring System (The GlucCell TM System) is designed to quantitatively measure the concentration of glucose during
GlucCell TM SYSTEM USER S GUIDE ver 2.3 Intended Use The GlucCell TM Cell Culture Glucose Monitoring System (The GlucCell TM System) is designed to quantitatively measure the concentration of glucose during
Experimental. Schmidt, in his experiments, boiled his solutions
 PROTECTION OF TRYPSIN FROM DESTRUCTION BY HEAT. BY D. IL DE SOUZA. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) E. W. SCHMIDT' has recently claimed: that trypsin in the presence of peptone,
PROTECTION OF TRYPSIN FROM DESTRUCTION BY HEAT. BY D. IL DE SOUZA. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) E. W. SCHMIDT' has recently claimed: that trypsin in the presence of peptone,
Gallstones Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Gutscharity.org.uk
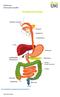 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
CHAPTER 3: MATERIALS AND METHODS
 CHAPTER 3: MATERIALS AND METHODS Materials and Methods. The from different husks, fruits, and vegetables peels were estimated quantitatively by the following volumetric procedure s such as Bertrand s,
CHAPTER 3: MATERIALS AND METHODS Materials and Methods. The from different husks, fruits, and vegetables peels were estimated quantitatively by the following volumetric procedure s such as Bertrand s,
Part 1 The Cell and the Cellular Environment
 1 Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 The Cell and the Cellular Environment 2 The Human Cell The is the fundamental unit of the human body. Cells contain all the necessary for life functions. 3 Cell
1 Chapter 3 Anatomy and Physiology Part 1 The Cell and the Cellular Environment 2 The Human Cell The is the fundamental unit of the human body. Cells contain all the necessary for life functions. 3 Cell
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
TECHNICAL METHODS GASTRIC CONTENTS AND URINE THE IDENTIFICATION OF BARBITURATE DRUGS IN. aspirated and examined as well.
 J. clin. Path. (1950), 3, 152. TECHNICAL METHODS THE IDENTIFICATION OF BARBITURATE DRUGS IN GASTRIC CONTENTS AND URINE BY From the Pathological Depariment, Salisbury General Infirmary (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
J. clin. Path. (1950), 3, 152. TECHNICAL METHODS THE IDENTIFICATION OF BARBITURATE DRUGS IN GASTRIC CONTENTS AND URINE BY From the Pathological Depariment, Salisbury General Infirmary (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION
contents of the currently official monograph. Please refer to the current edition of the USP NF for official text.
 Estradiol Transdermal System Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 28 Sep 2018 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs
Estradiol Transdermal System Type of Posting Notice of Intent to Revise Posting Date 28 Sep 2018 Targeted Official Date To Be Determined, Revision Bulletin Expert Committee Chemical Medicines Monographs
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
THE RING STRUCTURE OF THYMIDINE
 THE RING STRUCTURE OF THYMIDINE BY P. A. LEVENE AND R. STUART TIPSON (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York) (Received for publication, March 13, 1935) The 2-desoxy-ribose
THE RING STRUCTURE OF THYMIDINE BY P. A. LEVENE AND R. STUART TIPSON (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York) (Received for publication, March 13, 1935) The 2-desoxy-ribose
preliminaryfinding. Current theories of iron metabolism would explain dispute over urinary iron, which is agreed by all to be very small and
 148 J. Physiol. (I938) 94, I48-I54 6I5.739.I3:6I2.386 THE ABSORPTION AND EXCRETION OF IRON FOLLOWING ORAL AND INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION BY R. A. McCANCE AND E. M. WIDDOWSON From the Biochemical Laboratory,
148 J. Physiol. (I938) 94, I48-I54 6I5.739.I3:6I2.386 THE ABSORPTION AND EXCRETION OF IRON FOLLOWING ORAL AND INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION BY R. A. McCANCE AND E. M. WIDDOWSON From the Biochemical Laboratory,
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET GROWCLEAR PLUS
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET GROWCLEAR PLUS CATHODIC ELECTROPHORETIC CLEAR / TINTED LACQUERING PROCESS Introduction Growclear Plus is an advanced version of the earlier popular electrophoretic Clearlyte lacquer.
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET GROWCLEAR PLUS CATHODIC ELECTROPHORETIC CLEAR / TINTED LACQUERING PROCESS Introduction Growclear Plus is an advanced version of the earlier popular electrophoretic Clearlyte lacquer.
THE ESTIMATION OF TRYPSIN WITH HEMOGLOBIN
 THE ESTIMATION OF TRYPSIN WITH HEMOGLOBIN BY M. L. ANSON Am) A. E. MIRSKY (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J., and the Hospital of The Rockefeller
THE ESTIMATION OF TRYPSIN WITH HEMOGLOBIN BY M. L. ANSON Am) A. E. MIRSKY (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, Princeton, N. J., and the Hospital of The Rockefeller
DIASTASE ACTIVITY IN HONEY ASSAY PROCEDURE K-AMZHY 04/05
 DIASTASE ACTIVITY (α-amylase) IN HONEY ASSAY PROCEDURE K-AMZHY 04/05 Megazyme International Ireland Limited 2004 INTRODUCTION: The traditional method for the measurement of diastase activity in honey isthe
DIASTASE ACTIVITY (α-amylase) IN HONEY ASSAY PROCEDURE K-AMZHY 04/05 Megazyme International Ireland Limited 2004 INTRODUCTION: The traditional method for the measurement of diastase activity in honey isthe
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis
 Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-R1-4.6x150 Ludger Document # LS-R1-DMB-Guide-v5.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-R1-4.6x150 Ludger Document # LS-R1-DMB-Guide-v5.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United
STUDIES ON THE CALCIUM-PROTEIN RELATIONSHIP WITH THE AID OF THE ULTRACENTRIFUGE
 STUDIES ON THE CALCIUM-PROTEIN RELATIONSHIP WITH THE AID OF THE ULTRACENTRIFUGE II. OBSERVATIONS ON SERUM BY STEPHAN LUDEWIG, ALFRED CHANUTIN, AND A. V. MASKETt (From the Biochemical Laboralory, University
STUDIES ON THE CALCIUM-PROTEIN RELATIONSHIP WITH THE AID OF THE ULTRACENTRIFUGE II. OBSERVATIONS ON SERUM BY STEPHAN LUDEWIG, ALFRED CHANUTIN, AND A. V. MASKETt (From the Biochemical Laboralory, University
EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006
 EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006 PAPER A CHEMISTRY This paper comprises: * Letter from the applicant 2006/A(Ch)/e/1-6 * Document 1 2006/A(Ch)/e/7 * Document 2 2006/A(Ch)/e/8-10 2006/A(Ch)/e - 1 - LETTER
EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006 PAPER A CHEMISTRY This paper comprises: * Letter from the applicant 2006/A(Ch)/e/1-6 * Document 1 2006/A(Ch)/e/7 * Document 2 2006/A(Ch)/e/8-10 2006/A(Ch)/e - 1 - LETTER
RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS. Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012)
 July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
July 2012 RITONAVIRI COMPRESSI RITONAVIR TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2012) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-sixth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications
Unit 1, Section C.1. In which you will learn about: Solutions Electrolytes Saturation Solubility curves
 Unit 1, Section C.1 In which you will learn about: Solutions Electrolytes Saturation Solubility curves Some Definitions A solution is a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances in a single phase. One
Unit 1, Section C.1 In which you will learn about: Solutions Electrolytes Saturation Solubility curves Some Definitions A solution is a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances in a single phase. One
Experiment 3. Potentiometric Titration Using a ph Electrode. information necessary for both purposes by monitoring the ph of the solution as the
 Experiment 3 Potentiometric Titration Using a Electrode Introduction Titrations are most commonly performed either to find out how much analyte is present or to measure equilibrium constants of the analyte.
Experiment 3 Potentiometric Titration Using a Electrode Introduction Titrations are most commonly performed either to find out how much analyte is present or to measure equilibrium constants of the analyte.
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: GALLSTONES Document Purpose To ensure patients with gallstones disease are managed appropriately in primary/ secondary care Oxford Radcliffe Hospital Surgical Department Surgical Registrar
IJPAR Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 Journal Home page:
 IJPAR Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 Journal Home page: ISSN: 2320-2831 Research article Open Access Method development and validation of tenofovir disoproxil fumerate and emtricitabine in combined tablet
IJPAR Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 Journal Home page: ISSN: 2320-2831 Research article Open Access Method development and validation of tenofovir disoproxil fumerate and emtricitabine in combined tablet
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM ur2 UHPLC Column for DMB Sialic Acid Analysis
 Product Guide for LudgerSep TM ur2 UHPLC Column for DMB Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-UR2-2.1x100 Ludger Document # LS-uR2-DMB-Guide-v2.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United Kingdom
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM ur2 UHPLC Column for DMB Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-UR2-2.1x100 Ludger Document # LS-uR2-DMB-Guide-v2.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United Kingdom
CHAPTER 5 CRYSTALLISATION OF HYDRATED AND ANHYDROUS URIC ACID AND AMMONIUM ACID URATE CRYSTALS IN GEL
 61 CHAPTER 5 CRYSTALLISATION OF HYDRATED AND ANHYDROUS URIC ACID AND AMMONIUM ACID URATE CRYSTALS IN GEL 5.1 INTRODUCTION Uric acid is an important constituent of human stones. Under normal circumstances
61 CHAPTER 5 CRYSTALLISATION OF HYDRATED AND ANHYDROUS URIC ACID AND AMMONIUM ACID URATE CRYSTALS IN GEL 5.1 INTRODUCTION Uric acid is an important constituent of human stones. Under normal circumstances
چهارمین کنگره مهندسی نفت ایران. Lab Investigation of Inorganic Scale Removal Using Chelating Agents and Hydrochloric Acid Solutions.
 Lab Investigation of Inorganic Scale Removal Using Chelating Agents and Hydrochloric Acid Solutions Abstract One of the most important damages to the oil and gas reservoirs, are inorganic scales resulted
Lab Investigation of Inorganic Scale Removal Using Chelating Agents and Hydrochloric Acid Solutions Abstract One of the most important damages to the oil and gas reservoirs, are inorganic scales resulted
A modification of Fiske and Subbarow's method for determination of phosphocreatine 1,
 A modification of Fiske and Subbarow's method for determination of phosphocreatine 1, By N.-O. Abdon (Lund) and Erik Jacobsen (Copenhagen). (From the Pharmacological Department, University of Lund, Sweden.)
A modification of Fiske and Subbarow's method for determination of phosphocreatine 1, By N.-O. Abdon (Lund) and Erik Jacobsen (Copenhagen). (From the Pharmacological Department, University of Lund, Sweden.)
Inhibitive properties of some chelates and their ligands in acid corrosion of zinc
 Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib., 2014, 3, no. 3, 204 214 Inhibitive properties of some chelates and their ligands in acid corrosion of zinc V. P. Grigor ev, 1. A. Belousova, 1 E. V. Plekhanova 1 and A.S.
Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib., 2014, 3, no. 3, 204 214 Inhibitive properties of some chelates and their ligands in acid corrosion of zinc V. P. Grigor ev, 1. A. Belousova, 1 E. V. Plekhanova 1 and A.S.
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
A MICRO TIME METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, AND ITS APPLICATION TO ANALYSIS OF BLOOD AND URINE.
 A MICRO TIME METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, AND ITS APPLICATION TO ANALYSIS OF BLOOD AND URINE. BY JAMES A. HAWKINS. (From Ike Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research,
A MICRO TIME METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF REDUCING SUGARS, AND ITS APPLICATION TO ANALYSIS OF BLOOD AND URINE. BY JAMES A. HAWKINS. (From Ike Hospital of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research,
Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen Colorimetric Testing for Discrete and Segmented Flow Analyzers. NEMC 2017 Sarah Leibenguth Technical Support Chemist
 Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen Colorimetric Testing for Discrete and Segmented Flow Analyzers NEMC 2017 Sarah Leibenguth Technical Support Chemist Topics for Discussion Method Principle Digestion Protocol Temperature
Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen Colorimetric Testing for Discrete and Segmented Flow Analyzers NEMC 2017 Sarah Leibenguth Technical Support Chemist Topics for Discussion Method Principle Digestion Protocol Temperature
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 39
 CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 39 DETERMINATION OF THE PURITY OF NICOTINE AND NICOTINE SALTS BY GRAVIMETRIC ANALYSIS - TUNGSTOSILICIC ACID METHOD (November 1994) 0. INTRODUCTION Several methods for checking
CORESTA RECOMMENDED METHOD N 39 DETERMINATION OF THE PURITY OF NICOTINE AND NICOTINE SALTS BY GRAVIMETRIC ANALYSIS - TUNGSTOSILICIC ACID METHOD (November 1994) 0. INTRODUCTION Several methods for checking
EFFECT OF CARBENOXOLONE ON THE GASTRIC MUCOSAL BARRIER IN MAN AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF TAUROCHOLIC ACID
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1101-1105, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64 No.6 Printed in U.S.A. EFFECT OF CARBENOXOLONE ON THE GASTRIC MUCOSAL BARRIER IN MAN AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF TAUROCHOLIC
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1101-1105, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64 No.6 Printed in U.S.A. EFFECT OF CARBENOXOLONE ON THE GASTRIC MUCOSAL BARRIER IN MAN AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF TAUROCHOLIC
satisfactorily as a means of altering experimentally the ph of the upper
 THE REACTION QF HUMAN DUODENAL CONTENTS TO ACID AND ALKALINE MEAT MIXTURES By STACY R. METTIER (From I1e Thorndike Memorial Laboratory, Boston City Hospital, and the Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
THE REACTION QF HUMAN DUODENAL CONTENTS TO ACID AND ALKALINE MEAT MIXTURES By STACY R. METTIER (From I1e Thorndike Memorial Laboratory, Boston City Hospital, and the Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
The system: calcium oxalate - sulphuric acid
 Scholars' Mine Masters Theses Student Research & Creative Works 1927 The system: calcium oxalate - sulphuric acid Joseph Maple Wilson Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsmine.mst.edu/masters_theses
Scholars' Mine Masters Theses Student Research & Creative Works 1927 The system: calcium oxalate - sulphuric acid Joseph Maple Wilson Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarsmine.mst.edu/masters_theses
