Homologous Series. Learning Outcomes :
|
|
|
- Candice Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 omologous Series N5 Learning Outcomes : Revision of homologous series including alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkanes, amines Reactions of alkenes including halogenoalkanes Systematic naming of hydrocarbons, including branched hydrocarbons.
2 ompounds in the same homologous series:- have a similar structure (functional group) fit a general formula have similar properties undergo the same reactions
3 omologous series Examples of homologous groups include: omologous series General formula Functional group Alkanes n 2n + 2 Alkenes n 2n = Alkynes n 2n - 2 = Alkanols n 2n + 1 O R O Alkanoic acids n 2n + 1 OO R OO Alkanals n 2n + 1 O R O
4 Alkanes General formula n 2n+2 Name Meth Eth Prop But Pent ex ept Oct No. s
5 Alkanes Full Structural formula Shortened structural formula 3 8 Molecular formula
6 Alkanes N5
7 Alkanes Alkanes contain only single carbon to carbon bonds they are described as saturated hydrocarbons. Alkanes are not very reactive (they do not react with acids, alkalis or bromine water). They do burn making them important fuels ½ O 2 2 O O = kj mol -1
8 Structural Isomers Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae. 3 butane 2-methylpropane ere, you can see that 2-methylpropane has a side chain.
9 Isomers or not isomers? Take care, the same molecule can be represented in different ways by: Drawing the branch below instead of above the carbon chain. Drawing the branch at the other end of the chain. By drawing a bend in the longest chain.
10 Isomers: Boiling points Use your understanding of structure and bonding to explain why the boiling point is increasing?
11 Isomers: Boiling points As the amount of branching increases, the tendency is for the boiling point to decrease. The structure is more compact, smaller surface area, weaker London's dispersion forces.
12 Naming ompounds of arbon Alkanes 1. Identify the longest chain 2. Identify the branches and name them. 3. Number the carbon atoms on the longest chain, at the end giving the lowest numbers for the branches. 4. Write the branches in alphabetical order. 5. If there are more branches with the same name use di, tri etc
13 N5 Naming Organic ompounds, Alkanes Worked examples
14 3 2-methylbutane
15 3 3 2,2-dimethylbutane
16 ethyl-3-methyldecane
17 Draw full structural formula for 2,3,3-trimethylpentane 3 3 3
18 ethyl-2,4-dimethylhexane
19 Problems for you to try: 1. Draw the shortened structural formulae of a) 2,4-dimethylhexane b) 4-ethyl-3-methyloctane c) 2,2,4,4-tetramethylpentane 2. Work out the systematic names of the following compounds. a) b) c)
20 ycloalkanes N5
21 ycloalkanes: have a ring structure and are saturated (contain only single bonds). Name yclopropane yclobutane yclopentane yclohexane ycloalkane Molecular Formula n 2n Structural Formula ( 2 ) n
22 Branched ycloalkanes methylcyclopentane 1,4-dimethylcyclohexane 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane
23 Alkenes N5
24 Alkenes Alkenes are hydrocarbons with the general formula n 2n Name No s Eth Prop But Pent ex ept Oct
25 Alkenes = 3 2 Full Structural formula Shortened structural formula 3 6 Molecular formula
26 Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon to carbon double bond they are described as unsaturated hydrocarbons.
27 Structural Isomers Ethene has no isomers. Propene is isomeric with cyclopropene Isomers of alkenes can arise for two reasons the position of the double bond in the chain can vary the chain can be straight or branched
28 Naming ompounds of arbon Alkenes 1. Identify the longest chain, that contains a double bond. 2. Identify the branches and name them. 3. Number the carbon atoms on the longest chain, starting from the end nearest the double bond. 4. Pick the lowest number and give the position of the double bond. 4. Write the branches in alphabetical order. 5. If there are more branches with the same name use di, tri etc
29 N5 Naming Organic ompounds, Alkenes Worked examples
30 Naming Organic ompounds, Alkenes = but-1-ene
31 Draw full structural formula for but-2-ene =
32 = 3 4-methylpent-2-ene
33 2 5 = 3 3 5,5-dimethylhept-2-ene
34 Problems for you to try: 1. Draw the shortened structural formulae of a) oct-4-ene b) 3-ethylpent-1-ene c) 4,4-dimethylhex-2-ene 2. Work out the systematic names of the following compounds.
35 Reactions of Alkenes Addition reactions involving: ydrogen (ydrogenation) alogens ydrogen alides Water (ydration)
36 Addition Reactions of Alkenes ydrogenation, the reaction of an alkene with hydrogen is an example of an addition reaction. + - Propene Propane
37 Addition Reactions of Alkenes alogenation, the reaction with halogens is another example of an addition reaction Br Br + Br-Br orange/red colourless colourless propene 1,2-dibromopropane This can be used for a test for unsaturation
38 Reaction of Alkenes Reaction with ydrogen alides + -I Normally the from the halide attaches to the which already has the most hydrogen s. I or 2 -iodopropane I 1 -iodopropane
39 Alkenes with water oncentrated sulphuric acid reacts with ethene The reaction is an example of ydration. The overall effect of the acid is to combine water with ethene. At one time, this was the most important method for manufacturing ethanol from ethene. Nowadays, direct catalytic hydration of ethene is used. onc Phosphoric acid 2 = O 3 2 O Draw the full structural formulae for the hydration of ethene above.
40 Addition reactions
41 Naming alogenoalkanes Worked examples
42 Br Br 1,2-dibromoethane
43 Br Br 1,1-dibromoethane
44 3 3 l 3-chloro-2,2-dimethylpentane
45 alogen Derivatives (aloalkanes) alogenalkanes and halogenalkenes l 3 hloroform l 2 =l 2 l 2 F 2 Freon l 4 3 l 3 F 2 =F 2 orrecting fluid Gortex, Teflon l =l Solvent for grease Degreasing agent Paint Stripper Vinyl chloride Anesthetic
46 hlorofluorocarbons: F s All F s are very unreactive, are not flammable and not toxic. They are used as flame retardants. l 2 F 2 l 3 F The first refrigerant, and in aerosols. Used as a blowing agent to make expanded foam Recently hydrofluorocarbons have replaced some F s. e.g. 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane is used as a refrigerant.
47 Ozone destruction O 3 F s are very stable, lasting for 100 years in the atmosphere. So over time, F s can reach the stratosphere. ere, UV radiation attacks the F s forming free radicals ( ). When UV light breaks bonds, free radicals are formed. Free radicals have unpaired electrons and, as a result, are highly reactive. U.V.light l 3 F l 2 F + l l + O 3 lo + O 2 lo + O l + O 2 Free radicals react with O 3, the reaction is complex, but one l free radical can catalyse the break down 1 million O 3 molecules. We will look at free radicals in more detail later in the unit!!!
48 Amines
49 Amines The structure of Amines is closely related to ammonia. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a carbon containing group Amines contain the Amino Functional Group. R Indicates any carbon groups.
50 Naming Amines Amines with small chains can be named with the carbon chains as branches. 3 N 2 Methylamine 3 2 N 2 Ethylamine 3 N 3 Dimethylamine 3 Larger chains use the prefix amino and the name of the alkane from which they are derived. N 3 N 2 3 Trimethylamine Pentane aminopentane
51 Amines Amines with low molecular mass are volatile gases and liquids. They resemble ammonia in having strong fishy smells. ethylamine trimethyl amine putrescine cadaverine 2 N( 2 ) 4 N 2 2 N( 2 ) 5 N 2 3,4-diaminobutane 1,5-diaminopentane
52 Reactions of Amines Amines are bases. Like ammonia they react with acids to form salts. N 3 + l N 4+ l - ammonia hydrochloric ammonium chloride acid 3 N 2 + l 3 N 3+ l - methylamine hydrochloric methylammonium chloride acid
53 Aromatics
54 Aromatic ydrocarbons Benzene is the simplest member of the class of aromatic hydrocarbons. 6 6 Benzene was originally thought to have the following structure. Kekulé suggested it contained alternating double and single bonds.
55 Aromatic compounds Although this structure was a good attempt in its time, there are serious problems with it: Benzene does not decolurise bromine water and does not undergo addition reactions. X ray analysis confirms all the bonds are the same length.
56 Aromatic compounds Although you will still come across the Kekulé structure for benzene, for most purposes we use the following structure. The hexagon shows the ring of six carbon atoms, each of which has one hydrogen attached. The circle represents a cloud of six delocalised electrons.
57 Aromatic compounds A benzene ring that has had a hydrogen removed is called a phenyl group Aromatic compounds are important feedstocks and are used in dyes, herbicides, insecticides fungicides, medicines and plastics
58 Aromatic compounds OO OO 3 NO 3 Aspirin 2-ethanoyloxybenzenecarboxcyclic acid O Paracetamol 4-hydroxyphenylethanamide
59 fe igher hemistry Unit 2: Natures hemistry Alcohols 24/01/2018
60 Alcohols Learning Outcomes : Give systematic names, structural formulae and isomers for branch chained alcohols. The structure of diols, triols and the effect of hydrogen bonding on properties of these molecules. lassification of alcohols as primary, secondary and tertiary.
61 Alcohols N5 omologous Series containing the hydroxyl (-O) functional group General formula: n 2n+1 O *Draw the full structural formula for: Methanol, 3 O Ethanol 2 5 O Propanol 3 7 O
62 Isomers * Draw the full structural formula of propanol* Straight chain isomers of Alkanols: Propanol has 2 isomers, propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol. O O propan-1-ol propan-2-ol
63 Practice Question Naming Alkanols O butan-1-ol
64 Practice Question Naming Alkanols 3 ( 2 ) 5 O 3 octan-2-ol
65 Practice Question Naming Alkanols ( 2 5 )O 3 3-ethylhexan-2-ol
66 Practice Question Naming Alkanols 3 O 3-methylbutan-1-ol
67 Other Alcohols ycloalcohols O yclohexanol Diols (dihydric) O O Ethan-1,2-diol (Anti freeze) Triols (trihydric) e.g. propan-1,2,3-triol or glycerol is used in cosmetics, paints and nitroglycerine explosives. *Draw the full structural formula for glycerol*
68 Ethanol 2 5 O O ydroxyl group R O δ - δ + δ + O δ - δ + Functional group -O ydrogen bonding allows ethanol to dissolve in water,( p 7. b.p. 78 o.) This effect decreases in alcohols as the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases. Ethanol is a good solvent, it behaves both like water and other hydrocarbon solvents.
69 Uses of Alcohols
70 Uses of Ethanol Solvents: In varnishes (as it evaporates easily), dyes, perfumes and drugs leaning products: Meths is ethanol with added methanol. Drinks: Ethanol is a natural product of fermentation. Ethanol cannot be more than 15% of the fermentation mixture, as ethanol is a poison and will kill the yeast. In the UK 8 g of ethanol is 1 UNIT.
71 Uses of ethanol Fuel: Increasingly seen as an important fuel. 3 2 O + 3 O 2 2 O O = kj mol -1 Ethanol can be used as a fuel in cars. Produced by fermentation e.g. sugar cane. It has an octane rating of 111. In Brazil about 20% of their petrol is ethanol
72 Uses of methanol Methanol again burns to form carbon dioxide and water. Methanol can be used as petrol additive or as a fuel in its own right. Octane rating of 114, also clean burning. Toxic and corrosive
73 lassification of Alcohols
74 lassification of Alkanols In alcohols the arbon attached to the O can be attached to 0, 1, 2 or 3 other arbon atoms 0 or 1 makes it primary as the O is on the end carbon 2 is secondary (the O is in the middle of a chain) 3 is tertiary (in the middle of a chain, opposite a branch) R 2 R 1 O R 3 R 1, R 2 and R 3 can represent ydrogens or any sized length of carbon chain, like a branch.they are referred to as alkyl groups
75 lassification of Alkanols O O O 3 primary secondary tertiary *Give the systematic name for each of the alcohols above*
76 Practice Question Problems for you to try: lassify the following as primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols: A O. B. O D.
77 ARBOXYLI AIDS Learning Outcomes : In this section you can learn about the characteristic chemical properties of the family of carboxylic acids, and find out how they are put to good use in everyday consumer products.
78 arboxylic Acids Vinegar s chemical name is ethanoic acid, sometimes called acetic acid. It is a member of a group of compounds called carboxylic acids, which contain the carboxyl functional group (-OO). If it is a straight chain hydrocarbon containing the carboxyl functional group it is known as an alkanoic or carboxylic acid.
79 arboxylic (Alkanoic) Acids They contain the ARBOXYL functional group OO They have the general formula n 2n+1 OO Because of the ability of lower molecular sized alkanoic acids to form hydrogen bonds, they are soluble in water. They have high b.p. s for the same reason. They also have a sharp smell. uman sweat contains a mixture of these compounds.
80 Testing arboxylic Acids ATIVITY: Testing carboxylic acids. Test a selection of carboxylic acids to for smell, p and reactivity. NOTES Show what functional group a carboxylic acid contains and what the members of the alkanoic acid homologous series look like by drawing the full structural formulae and chemical formulae for the first four members of the alkanoic acid homologous series. After completing the experiments make a note of your observations. In particular you should record any trends in smell, p and reactivity as the length of the carbon chain increases.
81 Reactions of arboxylic Acids ATIVITY: Neutralisation of carboxylic acids. Neutralise ethanoic acid using sodium hydroxide, using p paper to check it is no longer acidic. Evaporate off the water to leave the salt, sodium ethanoate. NOTES Write a note on the formation of salts from carboxylic acids. Write a word equation and a chemical equation for the formation of sodium ethanoate from the neutralisation of ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide.
82 Naming Organic ompounds, Alkanoic acids O - O propanoic acid
83 Naming Organic ompounds, Alkanoic acids 3 3 O O - 3-methylpentanoic acid
84 Naming Organic ompounds, Alkanoic acids 3 O - 3 O 3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid
85 Naming Organic ompounds, Alkanoic acids 3 ( 2 ) 5 OO heptanoic acid
86 Alkanoic Acids Properties: Acids have a p below 7. Alkanoic acids are weak acids, so can react with some metals and alkalis. 2 3 OO + Mg ( 3 OO) 2 Mg + 2 Magnesium ethanoate 3 OO + NaO 3 OONa + 2 O Sodium ethanoate 3 OO + K 2 O OOK + 2 O + O 2 Potassium ethanoate
87 Uses of arboxylic Acids
88 Uses for arboxylic acids arboxylic acids are used in: some food items. Vinegar is dilute ethanoic acid. This is used in preparations for pickles, salads, sauces, etc. the manufacture of soaps. Sodium salts of fatty acids are used in soap and detergent industries. medicines. Ethanoic acid is used in making aspirin. industrial solvents. preparing perfumes and artificial essences used in food manufacturing. are produced in your sweat glands. Dogs can track humans by detecting the characteristic blend of these acids in your sweat.
89 Food preservation Vinegar has been used for millennia to preserve foods. There are many other foods where a proportion of ethanoic acid is added not only to enhance flavour, but also to help prevent food spoilage.
90 Removing lime-scale The ability of carboxylic acids to react with carbonates to form salts is exploited in some lime-scale removers. Lime-scale forms when hard water (water containing soluble calcium and magnesium salts) is boiled or allowed to evaporate. Under these conditions the soluble salts are changed into insoluble ones. For example, a water supply containing calcium hydrogen carbonate will deposit calcium carbonate when boiled. a(o 3 ) 2 (aq) ao 3 (s) + 2 O(l) + O 2 (g)
S4 Chemistry National 5
 S4 hemistry National 5 Nature s hemistry Unit ourse Notes- ydrocarbons and onsumer Products Name lass 1 ydrocarbons ydrocarbons can be categorised into family groups known as OMOLOGOUS SERIES. A homologous
S4 hemistry National 5 Nature s hemistry Unit ourse Notes- ydrocarbons and onsumer Products Name lass 1 ydrocarbons ydrocarbons can be categorised into family groups known as OMOLOGOUS SERIES. A homologous
Fuels. 1. Combustion is an example of an exothermic reaction which will give out energy, endothermic reactions are the opposite
 Fuels 1. ombustion is an example of an exothermic reaction which will give out energy, endothermic reactions are the opposite overed ( ) ow well can you do this? 2. The energy given out by a fuel can be
Fuels 1. ombustion is an example of an exothermic reaction which will give out energy, endothermic reactions are the opposite overed ( ) ow well can you do this? 2. The energy given out by a fuel can be
Organic Chemistry. AQA Chemistry topic 7
 rganic hemistry AQA hemistry topic 7 7.1 arbon ompounds as fuels and feedstock rude il rude oil is a finite resource found in rocks. It s the remains of an ancient biomass consisting mainly of plankton
rganic hemistry AQA hemistry topic 7 7.1 arbon ompounds as fuels and feedstock rude il rude oil is a finite resource found in rocks. It s the remains of an ancient biomass consisting mainly of plankton
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH
 1 The alcohols form a homologous series. The first member is methanol and the fourth is butanol. 3 O methanol 3 2 2 2 O butanol (a) Give two general characteristics of a homologous series. (ii) alculate
1 The alcohols form a homologous series. The first member is methanol and the fourth is butanol. 3 O methanol 3 2 2 2 O butanol (a) Give two general characteristics of a homologous series. (ii) alculate
Alkane C-C single bond (propane) Alkene C=C double bond (propene) Alcohol - OH group (1-propanol) major. minor
 Functional group* and name? Alkane - single bond (propane) *alkanes not really regarded as a functional group Alkene = double bond (propene) Addition of an unsymmetrical reagent to unsymmetrical alkene
Functional group* and name? Alkane - single bond (propane) *alkanes not really regarded as a functional group Alkene = double bond (propene) Addition of an unsymmetrical reagent to unsymmetrical alkene
National 5 Unit Two : Nature s Chemistry
 National 5 Unit Two : Nature s Chemistry Fuels A fuel is a chemical which burns, giving off energy. Combustion is a reaction of a substance with oxygen giving off energy. The test for oxygen is it relights
National 5 Unit Two : Nature s Chemistry Fuels A fuel is a chemical which burns, giving off energy. Combustion is a reaction of a substance with oxygen giving off energy. The test for oxygen is it relights
Unit 2: Nature s Chemistry Topic 2 Consumer Products Summary Notes
 St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 2: Nature s Chemistry Topic 2 Consumer Products Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing this topic you should be able
St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 2: Nature s Chemistry Topic 2 Consumer Products Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing this topic you should be able
Topic 6 : Structures and Reactions of Hydrocarbons Revised April Alkanes (General formula : C x H 2x+2 )
 6/1 Topic 6 : Structures and Reactions of ydrocarbons Revised April 1995 ydrocarbons all contain arbon and ydrogen only. There are various families of hydrocarbons (subsets of the set of hydrocarbons)
6/1 Topic 6 : Structures and Reactions of ydrocarbons Revised April 1995 ydrocarbons all contain arbon and ydrogen only. There are various families of hydrocarbons (subsets of the set of hydrocarbons)
4. CARBON AND ITS COMPOUND
 . ARBN AND ITS MPUND rganic hemistry- The study of carbon compounds. rganic ompounds- The compounds of carbon (except the oxides of carbon, carbonates, hydro carbonates and carbides) are called organic
. ARBN AND ITS MPUND rganic hemistry- The study of carbon compounds. rganic ompounds- The compounds of carbon (except the oxides of carbon, carbonates, hydro carbonates and carbides) are called organic
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 23. Hill, Petrucci, McCreary & Perry 4 th. Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane CH 4 methyl CH 3
 hapter 23 rganic hemistry ill, Petrucci, Mcreary & Perry 4 th Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane 4 methyl 3 ethane 3 3 ethyl 3 2 propane 3 2 3 propyl 3 2 2 isopropyl ( 3 ) 2 or 3 3 butyl 3 2 2 2 butane
hapter 23 rganic hemistry ill, Petrucci, Mcreary & Perry 4 th Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane 4 methyl 3 ethane 3 3 ethyl 3 2 propane 3 2 3 propyl 3 2 2 isopropyl ( 3 ) 2 or 3 3 butyl 3 2 2 2 butane
CH [2] (ii) Give the structural formula of another hydrocarbon which is isomeric with the above.
![CH [2] (ii) Give the structural formula of another hydrocarbon which is isomeric with the above. CH [2] (ii) Give the structural formula of another hydrocarbon which is isomeric with the above.](/thumbs/75/72821632.jpg) 1 The alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. They form a homologous series, the members of which have the same chemical properties. They undergo addition reactions and are easily oxidised. (a) The following
1 The alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. They form a homologous series, the members of which have the same chemical properties. They undergo addition reactions and are easily oxidised. (a) The following
large molecules small molecules fuels carbon
 4 10 5 12 6 14 4 2 6 3 8 methane ethane propane butane, pentane & hexane n 2n+2 Saturated hydrocarbons Insoluble in water n 2n Unsaturated hydrocarbons Insoluble in water Burns in plentiful 2 with a clean
4 10 5 12 6 14 4 2 6 3 8 methane ethane propane butane, pentane & hexane n 2n+2 Saturated hydrocarbons Insoluble in water n 2n Unsaturated hydrocarbons Insoluble in water Burns in plentiful 2 with a clean
6/9/2015. Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.2: Substituted Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
 1-chloropropane 2-methylpropane 1-iodobutane Ethanoic Acid Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.2: Substituted Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups 43 It Ain t Just Hydrocarbons There are all sorts of organic
1-chloropropane 2-methylpropane 1-iodobutane Ethanoic Acid Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.2: Substituted Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups 43 It Ain t Just Hydrocarbons There are all sorts of organic
Fuels. 1. Fuel is a substance that burns to give energy? 2. There are 3 fossil fuels coal, oil and gas which are finite
 Fuels overed ( ) ow well can you do this? 1. Fuel is a substance that burns to give energy 2. There are 3 fossil fuels coal, oil and gas which are finite 3. rude oil is formed from dead marine life compressed
Fuels overed ( ) ow well can you do this? 1. Fuel is a substance that burns to give energy 2. There are 3 fossil fuels coal, oil and gas which are finite 3. rude oil is formed from dead marine life compressed
Esters. What intermolecular forces do you think esters have? δ + CH 3
 Esters What intermolecular forces do you think esters have? ow will these intermolecular forces affect their: Melting and boiling points compared to alkanes Solubility in water δ 3 δ + 3 Dipole dipole
Esters What intermolecular forces do you think esters have? ow will these intermolecular forces affect their: Melting and boiling points compared to alkanes Solubility in water δ 3 δ + 3 Dipole dipole
Alkenes. Isomerism in the alkenes
 Alkenes Alkenes are a family of hydrocarbons (compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only) containing a carbon-carbon double bond. The first two are: ethene 2 4 propene 3 6 You can work out the formula
Alkenes Alkenes are a family of hydrocarbons (compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only) containing a carbon-carbon double bond. The first two are: ethene 2 4 propene 3 6 You can work out the formula
Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl Chlorides
 R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
Summary Consumer Products
 Summary Consumer Products National 4 Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds which contain the elements Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen, with the Hydrogen and Oxygen in the ratio of two to one. Plants
Summary Consumer Products National 4 Carbohydrates are naturally occurring compounds which contain the elements Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen, with the Hydrogen and Oxygen in the ratio of two to one. Plants
Alkenes. Question Paper 1. Chemistry (0620/0971) Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) Topic. Organic chemistry Sub-Topic. Alkenes.
 or more awesome resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ lkenes Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Organic chemistry
or more awesome resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ lkenes Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Organic chemistry
Farr High School HIGHER CHEMISTRY. Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry. Question Booklet
 Farr igh School IGER EMISTRY Unit 2 Nature s hemistry Question Booklet 1 ydrocarbons 1. Write the systematic names for a) b) 3 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 3 2. Write the structural formulae and names of 3 isomers of
Farr igh School IGER EMISTRY Unit 2 Nature s hemistry Question Booklet 1 ydrocarbons 1. Write the systematic names for a) b) 3 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 3 2. Write the structural formulae and names of 3 isomers of
Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react. methyl pentanoate. Name the type of reaction used to make an ester
 1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
Carboxylic Acids and Esters
 arboxylic Acids and Esters N Goalby hemrevise.org - absorption IR Spectrum for arboxylic acids Butanoic acid 1 Solubility in Water The smaller carboxylic (up to 4) acids dissolve in water in all proportions
arboxylic Acids and Esters N Goalby hemrevise.org - absorption IR Spectrum for arboxylic acids Butanoic acid 1 Solubility in Water The smaller carboxylic (up to 4) acids dissolve in water in all proportions
Oxidizing Alcohols. Questions. Prediction. Analysis. Safety Precautions. Materials. Conclusions. Procedure. 74 MHR Unit 1 Organic Chemistry
 xidizing Alcohols SKILL FUS Predicting Performing and recording Analyzing and interpreting Acidified potassium permanganate solution, KMn 4(aq), acts as an oxidizing agent when it comes in contact with
xidizing Alcohols SKILL FUS Predicting Performing and recording Analyzing and interpreting Acidified potassium permanganate solution, KMn 4(aq), acts as an oxidizing agent when it comes in contact with
A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH
 1.6 Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Fats Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH These compounds are weak acids. Citrus fruits, crabapples, rhubarb,
1.6 Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Fats Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH These compounds are weak acids. Citrus fruits, crabapples, rhubarb,
Teacher s Tools Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Nomenclature and Isomerism
 1. Hydrocarbons: a) Naming of hydrocarbons is done based on the number of carbons. 1 = meth 6 = hex 2 = eth 7 = hept 3 = prop 8 = oct 4 = but 9 = non 5 = pent 10 = dec b) Alkanes are hydrocarbons without
1. Hydrocarbons: a) Naming of hydrocarbons is done based on the number of carbons. 1 = meth 6 = hex 2 = eth 7 = hept 3 = prop 8 = oct 4 = but 9 = non 5 = pent 10 = dec b) Alkanes are hydrocarbons without
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Alkenes.
 Save My Exams! The ome of Revision For more awesome GSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Alkenes Question Paper 3 Level IGSE Subject hemistry ExamBoard IE Topic Organic hemistry
Save My Exams! The ome of Revision For more awesome GSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Alkenes Question Paper 3 Level IGSE Subject hemistry ExamBoard IE Topic Organic hemistry
Carbon s unique bonding pattern arises from the hybridization of the electrons.
 Unit 8 Neptune, the 8 th planet of our solar system Organic Chemistry Organic: compound containing carbon, excluding oxides and carbonates Carbon is an allotrope, meaning it has different bonding patterns.
Unit 8 Neptune, the 8 th planet of our solar system Organic Chemistry Organic: compound containing carbon, excluding oxides and carbonates Carbon is an allotrope, meaning it has different bonding patterns.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Interchapter G Unsaturated ydrocarbons FPO aption TK. G. unsaturated ydrocarbons G1 In this Interchapter, we shall continue our introduction to organic chemistry by discussing unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Interchapter G Unsaturated ydrocarbons FPO aption TK. G. unsaturated ydrocarbons G1 In this Interchapter, we shall continue our introduction to organic chemistry by discussing unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Chapter 4 - Carbon Compounds
 Chapter 4 - Carbon Compounds Carbon compounds organic compounds are tied up with living organisms. So much so, that as we have seen, the presence of methane might be considered an indicator of life. Methane
Chapter 4 - Carbon Compounds Carbon compounds organic compounds are tied up with living organisms. So much so, that as we have seen, the presence of methane might be considered an indicator of life. Methane
Alcohols and Ethers. Alcohols
 Alcohols and Ethers A patient does not experience pain during surgery when given a general anesthetic. The earliest anesthetics, used during the Civil War, belonged to a class of chemical compounds called
Alcohols and Ethers A patient does not experience pain during surgery when given a general anesthetic. The earliest anesthetics, used during the Civil War, belonged to a class of chemical compounds called
H O. rapidly reduces. They dissolve. because they can hydrogen bond to the water molecules.
 3.9 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
3.9 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY SYSTEMATIC NOMENCLATURE
 ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY SYSTEMATIC NOMENCLATURE Organic compounds are carbon containing compounds. Carbon has the following unique bonding properties: 1) it has a covalence of four 2) carbon atoms
ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY SYSTEMATIC NOMENCLATURE Organic compounds are carbon containing compounds. Carbon has the following unique bonding properties: 1) it has a covalence of four 2) carbon atoms
Naming Organic Halide Organic Halide: is a compound that contains one or more halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I) as part of its molecular structure.
 Naming Organic Halide Organic Halide: is a compound that contains one or more halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I) as part of its molecular structure. Organic halides have many important uses including: fire retardation,
Naming Organic Halide Organic Halide: is a compound that contains one or more halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I) as part of its molecular structure. Organic halides have many important uses including: fire retardation,
Chapter 13: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
 Chapter 13: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS, AND ETHERS Hydroxy group the OH functional group An alcohol has an OH group attached to an aliphatic carbon. General formula: R-OH A phenol
Chapter 13: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS, AND ETHERS Hydroxy group the OH functional group An alcohol has an OH group attached to an aliphatic carbon. General formula: R-OH A phenol
The four levels of protein structure are: primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure.
 Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Chapter 3 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes. Classification Review. Alkenes: Structure and Stereochem Slide 3-2
 hapter 3 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes lassification Review Alkenes: Structure and Stereochem Slide 3-2 1 Alkane Structural Formulas All - single bonds Saturated with hydrogens (no pi bonds)
hapter 3 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes lassification Review Alkenes: Structure and Stereochem Slide 3-2 1 Alkane Structural Formulas All - single bonds Saturated with hydrogens (no pi bonds)
Topic 4.5 COMPOUNDS CONTAINING THE CARBONYL GROUP. Aldehydes and Ketones Carboxylic Acids and their Salts Esters Acyl Chlorides and Acid Anhydrides
 Topic 4.5 MPUNDS NTAINING TE ARBNYL GRUP Aldehydes and Ketones arboxylic Acids and their Salts Esters Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides ALDEYDES AND KETNES 1. Introduction Aldehydes and ketones are collectively
Topic 4.5 MPUNDS NTAINING TE ARBNYL GRUP Aldehydes and Ketones arboxylic Acids and their Salts Esters Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides ALDEYDES AND KETNES 1. Introduction Aldehydes and ketones are collectively
Chemistry B11 Chapters 14 Amines, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids
 Chapters 4 Amines, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids Amines: are derivatives from ammonia ( 3 ). Aliphatic amines: an amine in which nitrogen is bonded only to alkyl group or hydrogens. Aromatic
Chapters 4 Amines, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids Amines: are derivatives from ammonia ( 3 ). Aliphatic amines: an amine in which nitrogen is bonded only to alkyl group or hydrogens. Aromatic
School of Chemistry and Physics, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Westville Campus Chemical Reactivity 120R. Organic Reactions
 Boiling point (o) School of hemistry and Physics, University of KwaZulu-atal, Westville ampus hemical eactivity 120 rganic ALKAES Saturated hydrocarbons - contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, where
Boiling point (o) School of hemistry and Physics, University of KwaZulu-atal, Westville ampus hemical eactivity 120 rganic ALKAES Saturated hydrocarbons - contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, where
Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes. Organic and BioChem
 hapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Organic and Biohem Section 12.1 Introduction Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more carbon-carbon double or triple bonds 3 6? 2 2? Three lasses of Unsaturated ydrocarbons
hapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Organic and Biohem Section 12.1 Introduction Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more carbon-carbon double or triple bonds 3 6? 2 2? Three lasses of Unsaturated ydrocarbons
CfE Higher Chemistry Homework. Unit 2: Natures Chemistry. The Chemistry of Cooking and Oxidation of Food. 1. Which of the following is an aldehyde?
 CfE Higher Chemistry Homework Unit 2: Natures Chemistry The Chemistry of Cooking and Oxidation of Food 1. Which of the following is an aldehyde? 2. Which is true of a compound with the following formula?
CfE Higher Chemistry Homework Unit 2: Natures Chemistry The Chemistry of Cooking and Oxidation of Food 1. Which of the following is an aldehyde? 2. Which is true of a compound with the following formula?
Lesmahagow High School
 Lesmahagow High School Higher Chemistry Alcohols and Esters - Past Paper Homework Questions . Carbohydrates are an essential part of our diet. (a) Why are carbohydrates an important part of our diet? (b)
Lesmahagow High School Higher Chemistry Alcohols and Esters - Past Paper Homework Questions . Carbohydrates are an essential part of our diet. (a) Why are carbohydrates an important part of our diet? (b)
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
 hemistry 52 hapter 20 UNSATURATED YDROARBONS The unsaturated hydrocarbons consist of three families of homologous compounds that contain multiple bonds between carbon atoms. Alkenes contain carbon carbon
hemistry 52 hapter 20 UNSATURATED YDROARBONS The unsaturated hydrocarbons consist of three families of homologous compounds that contain multiple bonds between carbon atoms. Alkenes contain carbon carbon
Organic. Carbon Chemistry
 Today Organic Carbon Chemistry Organic You know more than you think already What you will need Lewis dot, VSEPR VB, hybrid orbitals, MO electronegativity intermolecular forces Two hurdles we will deal
Today Organic Carbon Chemistry Organic You know more than you think already What you will need Lewis dot, VSEPR VB, hybrid orbitals, MO electronegativity intermolecular forces Two hurdles we will deal
CHAPTER4 ANSWERS. Multiple Choice Questions. Short Answer Questions. 1. (b) 2. (d) 3. (a) 4. (c) 5. (c) 6. (b) 7. (a) 8. (b)
 CHAPTER4 ANSWERS Multiple Choice Questions 1. (b) 2. (d) 3. (a) 4. (c) 5. (c) 6. (b) 7. (a) 8. (b) 9. (a) 10. (d) 11. (a) 12. (d) 13. (b) 14. (a) 15. (c) 16. (c) 17. (c) 18. (d) 19. (c) 20. (a) 21. (b)
CHAPTER4 ANSWERS Multiple Choice Questions 1. (b) 2. (d) 3. (a) 4. (c) 5. (c) 6. (b) 7. (a) 8. (b) 9. (a) 10. (d) 11. (a) 12. (d) 13. (b) 14. (a) 15. (c) 16. (c) 17. (c) 18. (d) 19. (c) 20. (a) 21. (b)
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
OCR A GCSE Chemistry. Topic 6: Global challenges. Organic chemistry. Notes.
 OCR A GCSE Chemistry Topic 6: Global challenges Organic chemistry Notes C6.2a recognise functional groups and identify members of the same homologous series Prefixes (beginning of the name) o remember
OCR A GCSE Chemistry Topic 6: Global challenges Organic chemistry Notes C6.2a recognise functional groups and identify members of the same homologous series Prefixes (beginning of the name) o remember
Alkanes. 1. Predict the molecular formula of an alkane with 13 carbon atoms The table below lists the boiling points of some alkanes.
 Alkanes 1. Predict the molecular formula of an alkane with 13 carbon atoms.... [Total 1 mark]. The table below lists the boiling points of some alkanes. alkane number of carbon atoms molecular formula
Alkanes 1. Predict the molecular formula of an alkane with 13 carbon atoms.... [Total 1 mark]. The table below lists the boiling points of some alkanes. alkane number of carbon atoms molecular formula
This topic will look at six important chemicals found inside your kitchen cupboard.
 P & L. Johnson 2012 You may not realise it but everything is made of chemicals and therefore everything in your kitchen cupboard is a chemical. In fact some of the substances in your cupboard contain really
P & L. Johnson 2012 You may not realise it but everything is made of chemicals and therefore everything in your kitchen cupboard is a chemical. In fact some of the substances in your cupboard contain really
Alkenes and Alkynes: Structure and Nomenclature
 hapter 3 3 : Structure and Nomenclature APTER SUMMARY 3.1 Introduction to Alkenes are hydrocarbons in which there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond; alkynes have at least one carbon-carbon triple
hapter 3 3 : Structure and Nomenclature APTER SUMMARY 3.1 Introduction to Alkenes are hydrocarbons in which there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond; alkynes have at least one carbon-carbon triple
cyclobutane Benzene Ring phenyl
 ow many carbons and hydrogens in the following? More rganic Today eview hydrocarbons Functional Groups Condensation eaction Biopolymers A. 6 C, 14 B. 6 C, 15 C. 6 C, 16 3 1 2 D. 7 C, 15 3 1 1 3 E. 7 C,
ow many carbons and hydrogens in the following? More rganic Today eview hydrocarbons Functional Groups Condensation eaction Biopolymers A. 6 C, 14 B. 6 C, 15 C. 6 C, 16 3 1 2 D. 7 C, 15 3 1 1 3 E. 7 C,
Chapter 24. The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 24 The of Life: James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Organic and Biochemistry Chapter focus: the molecules that bridge chemistry & biology Most common elements:
Lecture Presentation Chapter 24 The of Life: James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Organic and Biochemistry Chapter focus: the molecules that bridge chemistry & biology Most common elements:
Lesmahagow High School
 Lesmahagow High School Higher hemistry Unit 2 Tutorial Questions 1 Multiple hoice 1. The conversion of linoleic acid, 18 H 32 O 2, into stearic acid, 18 H 36 O 2, is likely to be achieved by hydrogenation
Lesmahagow High School Higher hemistry Unit 2 Tutorial Questions 1 Multiple hoice 1. The conversion of linoleic acid, 18 H 32 O 2, into stearic acid, 18 H 36 O 2, is likely to be achieved by hydrogenation
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 bjectives: (A) To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure and (B) chemical tests will be performed to distinguish primary,
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 bjectives: (A) To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure and (B) chemical tests will be performed to distinguish primary,
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank.
 Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. 1. (3 points each) First set functional groups A. ether D. amine B.
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. 1. (3 points each) First set functional groups A. ether D. amine B.
B07 Alcohols, Corboxylic Acids & Esters.notebook. November 19, Alcohols
 Alcohols There is more to alcohol than just beverages. In fact, most alcohols are poisonous. THis is what makes them effective as disinfectants and cleaners. 1 What makes an alcohol and alcohol? If a hydrocarbon
Alcohols There is more to alcohol than just beverages. In fact, most alcohols are poisonous. THis is what makes them effective as disinfectants and cleaners. 1 What makes an alcohol and alcohol? If a hydrocarbon
UNIT 11 FURTHER ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 11 FURTER RGANI EMISTRY teacher version www.chemguide.co.uk ontents (a) Alcohols (alkanols) (b) arboxylic acids (alkanoic acids) and Alkanoates (c) Amines and Amino Acids (d) Addition and ondensation
UNIT 11 FURTER RGANI EMISTRY teacher version www.chemguide.co.uk ontents (a) Alcohols (alkanols) (b) arboxylic acids (alkanoic acids) and Alkanoates (c) Amines and Amino Acids (d) Addition and ondensation
Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid
 Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes and Ketones: Introduction Aldedydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain carbon-oxygen doule bonds. The general formula for aldehydes is O C R
Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes and Ketones: Introduction Aldedydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain carbon-oxygen doule bonds. The general formula for aldehydes is O C R
H y., are burned in 100 cm 3 of oxygen, which is an excess of oxygen.
 1 (a) Hydrocarbons are compounds which contain hydrogen and carbon only. 10 cm 3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon, C x H y, are burned in 100 cm 3 of oxygen, which is an excess of oxygen. After cooling to room
1 (a) Hydrocarbons are compounds which contain hydrogen and carbon only. 10 cm 3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon, C x H y, are burned in 100 cm 3 of oxygen, which is an excess of oxygen. After cooling to room
C. Correct! A compound that consists only of hydrogen and carbon is termed a hydrocarbon.
 Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 06: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes No. 1 of 10 1. What is a hydrocarbon? (A) A compound that consists of only carbon. (B) A compound that consists of nonmetals. (C) A compound
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 06: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes No. 1 of 10 1. What is a hydrocarbon? (A) A compound that consists of only carbon. (B) A compound that consists of nonmetals. (C) A compound
Downloaded from
 Question 16.1: Why do we need to classify drugs in different ways? The classification of drugs and the reasons for classification are as follows: (i) On the basis of pharmacological effect: This classification
Question 16.1: Why do we need to classify drugs in different ways? The classification of drugs and the reasons for classification are as follows: (i) On the basis of pharmacological effect: This classification
Calderglen High School CfE Higher Chemistry. Nature s Chemistry Esters, Fats and Oils. Page 1 of 11
 Calderglen High School CfE Higher Chemistry Nature s Chemistry Esters, Fats and Oils Page 1 of 11 No. Learning Outcome Understanding? 1 An ester can be identified from the name containing the -yl-oate
Calderglen High School CfE Higher Chemistry Nature s Chemistry Esters, Fats and Oils Page 1 of 11 No. Learning Outcome Understanding? 1 An ester can be identified from the name containing the -yl-oate
F322: Alcohols Methylpropan-2-ol ALLOW methylpropan-2-ol [1]
![F322: Alcohols Methylpropan-2-ol ALLOW methylpropan-2-ol [1] F322: Alcohols Methylpropan-2-ol ALLOW methylpropan-2-ol [1]](/thumbs/78/78045383.jpg) F322: Alcohols 1. 2-Methylpropan-2-ol ALLW methylpropan-2-ol [1] 2. as (bonds) R has hydroxyl (groups) R has hydroxy (groups) ALLW marks from a diagram of hydrogen bonding IGNRE reference to alcohol functional
F322: Alcohols 1. 2-Methylpropan-2-ol ALLW methylpropan-2-ol [1] 2. as (bonds) R has hydroxyl (groups) R has hydroxy (groups) ALLW marks from a diagram of hydrogen bonding IGNRE reference to alcohol functional
Acknowledgement. Copyright is held by Peter & Lesley Johnson ( P & L Johnson 2013.)
 P& L Johnson 2013 1 Acknowledgement The Shopping Trolley hemistry workbook and activities were developed and written by Peter Johnson, with the help of Graeme Mitchell and harlie Kerr of the Stewart s
P& L Johnson 2013 1 Acknowledgement The Shopping Trolley hemistry workbook and activities were developed and written by Peter Johnson, with the help of Graeme Mitchell and harlie Kerr of the Stewart s
Firrhill High School CfE Higher Chemistry
 Firrhill High School CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Homework Natures Chemistry 1 1. Write the general formula for the alkanols. Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids and Esters 2. Draw the structural formulae for each
Firrhill High School CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Homework Natures Chemistry 1 1. Write the general formula for the alkanols. Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids and Esters 2. Draw the structural formulae for each
Alcohol aldehydes cetones and carboxylic acids
 Alcohol aldehydes cetones and carboxylic acids 1 Classes of organic compounds 2 Alcohols Alcohols are organic compounds containing hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to C atom. In an alcohol, -OH group replaces
Alcohol aldehydes cetones and carboxylic acids 1 Classes of organic compounds 2 Alcohols Alcohols are organic compounds containing hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to C atom. In an alcohol, -OH group replaces
Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 5 Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 20 in Organic Chemistry,
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 5 Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 20 in Organic Chemistry,
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids. Introduction
 hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
Level 3 Chemistry, 2007
 Level 3 hemistry, 2007 Annotated answers to this organic paper. Q1 QUESTIN NE Give the proper name that gives the structure a unique name (a) Give the systematic IUPA names for the following molecules
Level 3 hemistry, 2007 Annotated answers to this organic paper. Q1 QUESTIN NE Give the proper name that gives the structure a unique name (a) Give the systematic IUPA names for the following molecules
13. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 1. ORGANIC EMISTRY III) ALKENES SYNOPSIS Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. These contain a C =C. They contain two hydrogens less than corresponding alkanes. Double bonded carbon undergoes hybridisation.
1. ORGANIC EMISTRY III) ALKENES SYNOPSIS Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. These contain a C =C. They contain two hydrogens less than corresponding alkanes. Double bonded carbon undergoes hybridisation.
1. The compound which reacts fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is
 1. The compound which reacts fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is (a) butan-1-ol (b) butan-2-ol (c) 2-methylpropan-1-ol (d) 2-methylpropan-2-ol 2. Chlorination of toluene in the presence of
1. The compound which reacts fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is (a) butan-1-ol (b) butan-2-ol (c) 2-methylpropan-1-ol (d) 2-methylpropan-2-ol 2. Chlorination of toluene in the presence of
Organic Chemistry Part 2
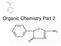 Organic Chemistry Part 2 Benzene Benzene is a special structure C 6 H 6 The carbon-carbon bonds aren t a single or double bond but something in-between Resonance bond CYCLIC HYDROCARBONS Carbon chains
Organic Chemistry Part 2 Benzene Benzene is a special structure C 6 H 6 The carbon-carbon bonds aren t a single or double bond but something in-between Resonance bond CYCLIC HYDROCARBONS Carbon chains
Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids
 The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
HIGHER CHEMISTRY. Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry. Homework exercises
 IGER CEMISTRY Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry omework exercises 1 ydrocarbons, alcohols and carboxylic acids (revision Nat 5) 1. Write the systematic names for a) b) C 2 C 3 C C 3 C C 2 C C 2 C 3 C C C C C C
IGER CEMISTRY Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry omework exercises 1 ydrocarbons, alcohols and carboxylic acids (revision Nat 5) 1. Write the systematic names for a) b) C 2 C 3 C C 3 C C 2 C C 2 C 3 C C C C C C
Chapter 24. The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 24 The of Life: James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Organic and Biochemistry Chapter focus: the molecules that bridge chemistry & biology Most common elements:
Lecture Presentation Chapter 24 The of Life: James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Organic and Biochemistry Chapter focus: the molecules that bridge chemistry & biology Most common elements:
Chapter 23. Functional Groups. Halogen Side Chains What is a halocarbon? How are organic compounds classified?
 23.1 Chapter 23 From a distance, the musicians in an orchestra may look alike, but each musician contributes a unique sound. In a similar way, one hydrocarbon is nearly identical to another until it picks
23.1 Chapter 23 From a distance, the musicians in an orchestra may look alike, but each musician contributes a unique sound. In a similar way, one hydrocarbon is nearly identical to another until it picks
Alkenes. IB Chemistry Topic 10.2
 Alkenes IB Chemistry Topic 10.2 What is the difference between alkanes and alkenes? Which do you think would be more reactive? The relationship between the number of bonds, bond length and bond strength
Alkenes IB Chemistry Topic 10.2 What is the difference between alkanes and alkenes? Which do you think would be more reactive? The relationship between the number of bonds, bond length and bond strength
Nature s Chemistry. Fragrances and Skin Care
 St Andrew s and St Bride s High School CfE Higher Chemistry Nature s Chemistry Page 1 of 12 Essential Oils Essential oils are concentrated extracts of the volatile, non-water soluble (hydrophobic) aroma
St Andrew s and St Bride s High School CfE Higher Chemistry Nature s Chemistry Page 1 of 12 Essential Oils Essential oils are concentrated extracts of the volatile, non-water soluble (hydrophobic) aroma
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1)
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
(b) The following two alcohols are members of an homologous series and they are isomers.
 1 The alcohols form an homologous series. (a) Give three characteristics of an homologous series. [3] (b) The following two alcohols are members of an homologous series and they are isomers. OH and ( )
1 The alcohols form an homologous series. (a) Give three characteristics of an homologous series. [3] (b) The following two alcohols are members of an homologous series and they are isomers. OH and ( )
level 6 (6 SCQF credit points)
 Nature s Chemistry SCQF: level 6 (6 SCQF credit points) Unit code: H21J 76 Unit outline The general aim of this Unit is to develop skills of scientific inquiry, investigation, analytical thinking, independent
Nature s Chemistry SCQF: level 6 (6 SCQF credit points) Unit code: H21J 76 Unit outline The general aim of this Unit is to develop skills of scientific inquiry, investigation, analytical thinking, independent
Chemistry 1120 Exam 1 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 1 Study Guide Chapter 3 3.1 a) Know that alcohols contain a hydroxy (-OH) group. Determine the IUPAC name for a given structure by determining the longest chain. b) Determine the number
Chemistry 1120 Exam 1 Study Guide Chapter 3 3.1 a) Know that alcohols contain a hydroxy (-OH) group. Determine the IUPAC name for a given structure by determining the longest chain. b) Determine the number
ALCOHOLS, ETHERS, PHENOLS, AND THIOLS
 C22 09/17/2013 11:27:34 Page 319 APTER 22 ALCLS, ETHERS, PHENLS, AND THILS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The question allows great freedom of choice. These shown here are very simple examples of each type.
C22 09/17/2013 11:27:34 Page 319 APTER 22 ALCLS, ETHERS, PHENLS, AND THILS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The question allows great freedom of choice. These shown here are very simple examples of each type.
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life. Chapter 4
 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Chapter 4 CARBON Carbon is has ability to form large and complex, molecules Aspirin molecular formula? A triglyceride Organic chemistry is study of carbon compounds
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Chapter 4 CARBON Carbon is has ability to form large and complex, molecules Aspirin molecular formula? A triglyceride Organic chemistry is study of carbon compounds
Ch14. Carboxylic Acids. Combining the hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups. To make more powerful functional groups. version 1.
 Ch14 Carboxylic Acids Combining the hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups. To make more powerful functional groups. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch14 Carboxylic Acids & Esters Carboxylic
Ch14 Carboxylic Acids Combining the hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups. To make more powerful functional groups. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch14 Carboxylic Acids & Esters Carboxylic
5124 SCIENCE (PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY)
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5124 SCIENCE (PHYSICS AND
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 5124 SCIENCE (PHYSICS AND
Chemistry. hsn.uk.net. Higher. HSN12000 Unit 2 All Topics
 Higher Chemistry Unit 2 All Topics This document was produced specially for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that any copies or derivative works attribute the work to us. For more details about the
Higher Chemistry Unit 2 All Topics This document was produced specially for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that any copies or derivative works attribute the work to us. For more details about the
Molecules of Life. Chapter 22. Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1
 Molecules of Life Chapter 22 Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1 Chapter Outline Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry Proteins: The Workhorses
Molecules of Life Chapter 22 Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1 Chapter Outline Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry Proteins: The Workhorses
CHY3F. (Jan11CHy3f01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January Unit Chemistry C3. Written Paper TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January 2011 1 2 Chemistry
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January 2011 1 2 Chemistry
Chap 7: Alcohols, Phenols, & Thiols
 Chap 7: Alcohols, Phenols, & Thiols Objectives: Chap 7: Alcohols, Phenols, & Thiols (Chapter 7 and pages 283-285 & 296-297, A-1 & A-2 in lab manual) 1. Identify molecules as an alcohol, phenol, glycol,
Chap 7: Alcohols, Phenols, & Thiols Objectives: Chap 7: Alcohols, Phenols, & Thiols (Chapter 7 and pages 283-285 & 296-297, A-1 & A-2 in lab manual) 1. Identify molecules as an alcohol, phenol, glycol,
Alkenes. 1. Isoprene is an alkene that can be tapped from some trees. It is the monomer in natural rubber.
 Alkenes 1. Isoprene is an alkene that can be tapped from some trees. It is the monomer in natural rubber. Limonene is a natural oil found in the rind of oranges and lemons. Both isoprene and limonene contain
Alkenes 1. Isoprene is an alkene that can be tapped from some trees. It is the monomer in natural rubber. Limonene is a natural oil found in the rind of oranges and lemons. Both isoprene and limonene contain
Structure of Alkenes In ethene (ethylene) each carbon is bonded to 3 other atoms, with zero nonbonding electrons => sp 2 hybridization.
 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Alkenes (olefins) are hydrocarbons which have carbon carbon double bonds. A double bond is a bond and a bond. Double bond B.D.E. bond B.D.E. = 146 kcal/mol = 83 kcal/mol
Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Alkenes (olefins) are hydrocarbons which have carbon carbon double bonds. A double bond is a bond and a bond. Double bond B.D.E. bond B.D.E. = 146 kcal/mol = 83 kcal/mol
Worksheet Chapter 17: Food chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 17.1 Chapter 17: Food chemistry glossary Aldehydes (alkanals) A homologous series of compounds with the general formula RCHO, where the CHO group (the aldehyde group) consists of a carbonyl group
Worksheet 17.1 Chapter 17: Food chemistry glossary Aldehydes (alkanals) A homologous series of compounds with the general formula RCHO, where the CHO group (the aldehyde group) consists of a carbonyl group
Chapter 7-2 Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 7-1 Carbon C atom - atomic # is 6; it has 6 protons and therefore 6 electrons - is in group 14; it has 4 valence electrons - atomic mass is 12; it has 6 neutrons - shares electrons when forming
Chapter 7-1 Carbon C atom - atomic # is 6; it has 6 protons and therefore 6 electrons - is in group 14; it has 4 valence electrons - atomic mass is 12; it has 6 neutrons - shares electrons when forming
Chapter 44. Typical reactions of various functional groups Introducing organic reactions Typical reactions of alkanes
 Chapter 44 Typical reactions of various functional groups 44.1 Introducing organic reactions 44.2 Typical reactions of alkanes 44.3 Typical reactions of alkenes 44.4 Typical reactions of haloalkanes 44.5
Chapter 44 Typical reactions of various functional groups 44.1 Introducing organic reactions 44.2 Typical reactions of alkanes 44.3 Typical reactions of alkenes 44.4 Typical reactions of haloalkanes 44.5
unit 9 practice test (organic and biochem)
 Name: Class: Date: unit 9 practice test (organic and biochem) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What s the correct formula for the simplest
Name: Class: Date: unit 9 practice test (organic and biochem) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What s the correct formula for the simplest
