4) Which one of the following is not found in prokaryotic cells? 4) A) ribosomes B) a membrane-bound nucleus C) a cell wall D) a capsule E) pili
|
|
|
- Maurice Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are told that the cells on a microscope slide are plant, animal, or bacterial. You look at them through a microscope and see cell walls and membrane-bound organelles. You conclude that the cells 2) A) are plant cells. B) could be either plant or bacterial. C) are animal cells. D) could be plant, animal, or bacterial. E) are bacteria. 3) Cells acquire LDLs by 3) A) receptor-mediated endocytosis. B) pinocytosis. C) phagocytosis. D) osmosis. E) diffusion. 4) Which one of the following is not found in prokaryotic cells? 4) A) ribosomes B) a membrane-bound nucleus C) a cell wall D) a capsule E) pili 5) A scientist wants to examine living cells lining the respiratory tract to determine how the cells use tiny hairs to move dirt and mucus away from the lungs. Which one of the following instruments would be best, and why? 5) A) a transmission electron microscope, because it has high resolving power B) a light microscope, because it allows observations of whole, live cells C) a transmission electron microscope, because it is capable of very high magnification D) a scanning electron microscope, because it can reveal structures on cell surfaces E) a scanning electron microscope, because it can be used to observe whole cells without slicing them 7) Diffusion does not require the cell to expend ATP. Therefore, diffusion is considered a type of 7) A) endocytosis. B) exocytosis. C) active transport. D) passive transport. E) phagocytosis. 8) Which of the following is not a true statement about diffusion? Diffusion 8) A) requires no input of energy into the system. B) is driven by entropy. C) is a result of the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. D) proceeds until equilibrium is reached. E) occurs when particles spread from areas where they are less concentrated to areas where they are more concentrated. 9) You are adrift in the Atlantic Ocean, and, being thirsty, drink the surrounding seawater. As a result, 9) A) you dehydrate yourself. B) you quench your thirst. C) your cells lyse, due to the excessive intake of salt. D) your cells become turgid.
2 10) Osmosis can be defined as 10) A) the diffusion of nonpolar molecules. B) endocytosis. C) the diffusion of a solute. D) the diffusion of water. E) active transport. 11) Cilia differ from flagella in that 11) A) cilia are composed of microfilaments and flagella are composed of intermediate filaments. B) cilia contain nine microtubule doublets surrounding a central pair of microtubules; flagella contain only nine microtubule doublets. C) cilia are anchored only in the proteins of the cell membrane; flagella are anchored in a special structure called the basal body. D) cilia are typically more numerous and shorter than flagella. E) the protein filaments of cilia are "naked"; those of flagella are wrapped in an extension of the cell membrane. 12) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum 12) A) helps assemble ribosomes for protein synthesis. B) stores calcium ions in muscle cells. C) produces proteins for cell membranes. D) is the major site of carbohydrate synthesis in eukaryotic cells. E) produces antibodies. 13) The diameter of most animal and plant cells ranges from 13) A) 1.0 to 10 microns. B) 0.01 to 0.1 microns. C) 10 to 100 microns. D) 100 to 1000 microns. E) 0.1 to 1.0 microns. 14) A bacterial cell's DNA is found in its 14) A) capsule. B) nucleoid region. C) nucleus. D) peroxisome. E) ribosomes. 15) Insulin is a protein that is produced by pancreatic cells and secreted into the bloodstream. Which of the following choices best describes the route of insulin from its production to its exit from the cell? 15) A) rough ER, transport vesicles, cell membrane B) rough ER, transport vesicles, Golgi apparatus, transport vesicles, cell membrane C) rough ER, lysosomes, transport vesicles, cell membrane D) rough ER, Golgi apparatus, smooth ER, cell membrane 16) Plasmodesmata 16) A) carry nutrients between plant cells. B) carry chemical messages between plant cells. C) are one type of cell junction in plants. D) penetrate plant cell walls. 17) Lysosomes 17) A) destroy harmful bacteria engulfed by white blood cells.
3 B) help to digest worn-out or damaged organelles. C) recycle materials within the cell. D) fuse with food vacuoles to expose nutrients to lysosomal enzymes. 18) The function of chloroplasts is 18) A) intracellular transport of proteins. B) intracellular digestion. C) lipid synthesis. D) photosynthesis. E) cellular respiration. 19) Cells that lack a membrane-bound nucleus are cells. 19) A) plant B) animal C) fungal D) prokaryotic E) eukaryotic 20) The function of the nucleolus is 20) A) intracellular digestion. B) to manufacture polypeptides. C) to produce H with subscript((2) ) O with subscript((2) ). D) to store chromatin. E) to help manufacture ribosomes. 21) A cell that neither gains nor loses water when it is immersed in a solution is 21) A) isotonic to its environment. B) dead. C) hypotonic to its environment. D) metabolically inactive. E) hypertonic to its environment. 22) The nucleus of a cell 22) A) is the region of the cell where ribosomes are degraded. B) contains DNA. C) is contained within the nucleolus. D) is surrounded by a single layer of membrane. E) both is contained within the nucleolus and contains DNA. 23) Microfilaments differ from microtubules in that microfilaments 23) A) help to anchor organelles, whereas microtubules primarily function to help cells change shape and move. B) are found only in plants whereas microtubules are found in plants and animal cells. C) are larger than microtubules. D) form the inner core of cilia and flagella whereas microtubules regulate metabolism. E) are mainly composed of actin whereas microtubules are composed of tubulin. 24) In lab, you use a special balloon that is permeable to water but not sucrose to make an "artificial cell." The balloon is filled with a solution of 20% sucrose and 80% water and is immersed in a beaker containing a solution of 40% sucrose and 60% water. Which of the following will occur? 24) A) Water will enter the balloon. B) Sucrose will enter the balloon. C) Sucrose will leave the balloon. D) Water will leave the balloon. E) None of the choices will occur.
4 25) The two main functions of the rough endoplasmic reticulum are the production of 25) A) mitochondria and proteins that are to be secreted by the cell. B) ribosomes and steroid hormones. C) hydrogen peroxide and steroid hormones secreted by the cell. D) chromatin and mitochondria. E) membrane and proteins to be secreted by the cell. 26) Which one of the following is not a function of the plasma membrane? The plasma membrane 26) A) has receptors for chemical messages. B) plays a role in signal transduction. C) is involved in self-recognition. D) is the control center of the cell. E) forms a selective barrier around the cell. 27) If placed in tap water, an animal cell will undergo lysis, whereas a plant cell will not. What accounts for this difference? 27) A) the fact that plant cells are isotonic to tap water B) expulsion of water by the plant cell's central vacuole C) the relative impermeability of the plant cell wall to water D) the relative inelasticity and strength of the plant cell wall E) the relative impermeability of the plant cell membrane to water 28) The nucleoid region of a prokaryotic cell 28) A) contains the cell's nucleoli. B) is surrounded by a nucleoid membrane. C) separates the RNA from the cytoplasm. D) contains the cell's DNA. E) is the site of organelle production. 29) A major function of glycoproteins and glycolipids in the cell membrane is to 29) A) allow the cells of an embryo to sort themselves into tissues and organs. B) help the cell retain its shape. C) help the cell resist swelling. D) glue cells together to form tissues. E) attach the cell membrane to the cytoskeleton. 30) The act of a white blood cell engulfing a bacterium is 30) A) phagocytosis. B) osmosis. C) diffusion. D) pinocytosis. E) receptor-mediated endocytosis. 31) Contractile vacuoles 31) A) allow organisms to avoid dehydration by absorbing water from the environment. B) help in the excretion of excess salt. C) are generally found in protists that inhabit salt water. D) prevent cells from bursting as a result of the influx of excess water. 32) A scientist wants to magnify a pollen grain 8,000 times and examine the ridges and pores on its surface. Which one of the following instruments would be best? 32) A) a scanning electron microscope B) an inverted light microscope
5 C) a transmission light microscope D) a scanning light microscope E) a transmission electron microscope 33) Which of these is not a component of the endomembrane system? 33) A) transport vesicles B) mitochondria C) endoplasmic reticulum D) Golgi apparatus E) nuclear envelope 34) Many of the enzymes that control a firefly's ability to produce light energy from chemical energy are located 34) A) in the nucleus. B) within mitochondria. C) within chloroplasts. D) in membranes. E) outside of cells. 35) As cell size increases, the 35) A) volume and surface area decrease. B) volume increases faster than the surface area. C) surface area and volume increase at the same rate. D) surface area increases faster than the volume. 36) Certain cells that line the stomach synthesize a digestive enzyme and secrete it into the stomach. This enzyme is a protein. Which of the following processes could be responsible for its secretion? 36) A) diffusion B) pinocytosis C) exocytosis D) passive transport E) endocytosis 37) Which one of the following cells would have the greatest surface-to-volume ratio? 37) A) ostrich egg B) human red blood cell C) bacterium D) human muscle cell E) frog egg 38) The membranous compartmentalization of a cell 38) A) allows different metabolic processes to occur simultaneously. B) divides the cell into two equal-sized halves. C) requires the presence of a cell wall. D) is common in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. E) requires the presence of a large central vacuole. 39) Secretory proteins are 39) A) chemically modified in the nucleus. B) produced by ribosomes on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. C) produced by the cell for internal use. D) incorporated into the mitochondrial membrane. E) released from the cell through the plasma membrane.
6 40) Chronic administration of a drug (such as a barbiturate or an antibiotic) may cause the liver to 40) A) increase the production of enzymes that break down certain other drugs or foreign substances. B) produce additional smooth endoplasmic reticulum. C) increase the production of enzymes that detoxify the drug in question. D) increase the body's tolerance to the drug. 41) The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as consisting of 41) A) two layers of phospholipids with protein sandwiched between them. B) a protein bilayer with embedded phospholipids. C) individual proteins and phospholipids that can drift in a phospholipid bilayer. D) a phospholipid bilayer with embedded carbohydrates. E) carbohydrates, proteins, and phospholipids that can drift in the membrane. 42) In a hypotonic solution, an animal cell will 42) A) experience turgor. B) neither gain nor lose water. C) shrivel. D) lyse. E) lose water. 43) Unlike animal cells, plant cells have and. Unlike plant cells, animal cells have. 43) A) chloroplasts... cell walls... cell membranes B) centrioles... cell walls... large central vacuoles C) chloroplasts... cell walls... a nucleus D) centrioles... chloroplasts... cell walls E) chloroplasts... cell walls... centrioles 44) One centimeter = millimeters. 44) A) 0.10 B) 10 C) 1,000 D) 100 E) ) Which one of the following processes could result in the net movement of a substance into a cell, if the substance is more concentrated in the cell than in the surroundings? 45) A) active transport B) diffusion C) osmosis D) facilitated diffusion 46) Which one of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system? 46) A) ribosomes B) smooth ER C) nucleus D) Golgi apparatus E) lysosomes 47) All cells on Earth 47) A) are enclosed in a membrane that maintains internal conditions different from the surroundings. B) can interconvert chemical materials. C) have DNA as the genetic material. D) can interconvert forms of energy.
7 48) When a cell is deprived of oxygen, its lysosomes tend to burst and release their contents into the cell. As a result of this, that cell will 48) A) undergo self-digestion and die. B) recycle damaged organelles. C) produce additional ER. D) undergo cell division. E) produce replacement lysosomes. 49) An inherited lack (or shortage) of functional LDL receptors causes 49) A) cystic fibrosis. B) hypercholesterolemia. C) Marfan's syndrome. D) hyperbilirubinemia. E) type I diabetes. 50) Which of the following cell structures is not associated with the breakdown of harmful substances or substances that are no longer needed by the cell? 50) A) peroxisomes B) mitochondria C) vacuoles D) lysosomes E) All of the choices play a role in these functions. 51) Which one of the following statements about cellular metabolism is false? Cellular metabolism 51) A) often occurs on the surfaces of internal membranes. B) can occur within organelles. C) occurs in animal but not plant cells. D) includes different processes that require different conditions. E) can involve the synthesis of steroid hormones. 52) Most animal cells are 52) A) attached to each other via plasmodesmata. B) embedded in an endomembrane system. C) embedded in an extracellular matrix. D) surrounded by a cell wall. E) embedded in a lipid matrix. 53) The of a mitochondrion is/are an adaptation that increases the surface area and enhances a mitochondrion's ability to produce ATP. 53) A) stroma B) intermembrane space C) grana D) matrix E) cristae 54) Which of the following structures are used by prokaryotes for attaching to surfaces? 54) A) pili B) anchoring junctions C) capsules D) flagella E) both pili and capsules 55) When two aqueous solutions that differ in solute concentration are placed on either side of a semipermeable membrane, and osmosis is allowed to take place, the water will 55) A) exhibit a net movement to the side with lower water concentration.
8 B) exhibit a net movement to the side with higher water concentration. C) exhibit a net movement to the side with lower solute concentration. D) not cross the membrane. E) exhibit an equal movement in both directions across the membrane. 56) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes 56) A) provide additional area where many metabolic processes occur. B) form membranous compartments called organelles. C) contain proteins essential for metabolic processes. D) greatly increase a cell's total membrane area. 57) Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell is called 57) A) self-recognition. B) selective permeability. C) inhibition. D) competition. E) signal transduction. 58) Which of these processes can move a solute against its concentration gradient? 58) A) active transport B) passive transport C) facilitated diffusion D) diffusion E) osmosis 59) A plant cell in a hypotonic solution 59) A) lyses. B) is flaccid. C) is turgid. D) wilts. E) shrivels. 60) Active transport 60) A) can move solutes up a concentration gradient. B) requires the cell to expend energy. C) uses ATP as an energy source. D) is necessary to allow nerves to function properly. 61) The Golgi apparatus 61) A) forms fats from glycerols and fatty acids. B) is composed of stacks of membranous vesicles that are continuous with one another. C) is the site of carbohydrate breakdown. D) stores, modifies, and packages proteins. E) strings together amino acids to produce proteins. 62) Which one of the following statements is true about electron microscopes? 62) A) Scanning electron microscopes are used to study the details of internal cell structure. B) Electron microscopes use glass lenses to focus and magnify the image. C) Electron beams are focused to create a magnified image of an object. D) Transmission electron microscopes are mainly used to study cell surfaces. E) Specimens must be sectioned to be viewed under a scanning electron microscope.
9 63) The idea that all living things are composed of cells and that all cells come from other cells defines: 63) A) inheritance of acquired characteristics. B) the laws of inheritance. C) central dogma. D) cell theory. E) organelle theory. 64) Facilitated diffusion across a biological membrane requires and moves a substance its concentration gradient. 64) A) transport proteins... against B) energy... down C) energy and transport proteins... down D) transport proteins... down E) energy and transport proteins... against 65) A cell is exposed to a substance that prevents it from dividing. The cell becomes larger and larger. This situation 65) A) should be beneficial since the cell will be able to divert the ATP normally used for cell division to other processes. B) should present no problem to the cell because the surface area of the cell will increase as the volume of the cell increases. C) should present no problem to the cell since it can continue to perform all other necessary functions. D) will eventually be problematic since the cell's ability to absorb nutrients through its outer membrane will not keep increasing as quickly as its cytoplasmic needs. 66) A scanning electron microscope is used to study, whereas a transmission electron microscope is used to study. 66) A) plant tissue... animal tissue B) internal cell structures... cell surfaces C) cell surfaces... internal cell structures D) live cells... dead cells E) dead cells... live cells 67) The cholesterol associated with cell membranes 67) A) is attached to membrane proteins and extends into the watery environment surrounding the cell. B) helps to stabilize the cell membrane at body temperature. C) is an abnormality resulting from a diet high in cholesterol. D) makes the cell membrane fluid at room temperature. 68) In lab, you use a special balloon that is permeable to water but not sucrose to make an "artificial cell." The balloon is filled with a solution of 20% sucrose and 80% water and is immersed in a beaker containing a solution of 40% sucrose and 60% water. The solution in the balloon is relative to the solution in the beaker. 68) A) hypertonic B) hydrophilic C) isotonic D) hypotonic E) hydrophobic 69) The molecules responsible for membrane transport are 69) A) carbohydrates. B) ATP. C) steroids.
10 D) phospholipids. E) proteins. 70) Most of the functions of a cell membrane are performed by 70) A) proteins. B) cholesterol. C) phospholipids. D) nucleotides. E) glycolipids. 71) Which one of the following is not a function of membrane proteins? Membrane proteins 71) A) provide cellular identification tags. B) attach the membrane to the cytoskeleton. C) serve as enzymes. D) form junctions between cells. E) All of the choices are membrane protein functions. 72) Long fibers of DNA and protein are called a 72) A) lysosome. B) chromatin. C) ribosome. D) central vacuole. E) nucleolus. 73) Some protozoans have special organelles called contractile vacuoles that continually eliminate excess water from the cell. The presence of these organelles tells you that the environment 73) A) is isotonic to the protozoan. B) is hypertonic to the protozoan. C) contains a higher concentration of solutes than the protozoan. D) is hypotonic to the protozoan. 74) Your throat is dry, and you want the last cough drop in the box to last a long time in your mouth. What should you do? 74) A) Break the cough drop into little pieces and put them all in your mouth. This decreases the surface-tovolume ratio, and slows the dissolution of the cough drop. B) Break the cough drop into little pieces and put them all in your mouth. Since each little piece must be dissolved separately, the drop will last longer. C) Keep the cough drop whole. This maintains the largest surface-to-volume ratio, and slows the dissolution of the cough drop. D) It doesn't matter if the cough drop is in one piece or many pieces; the total amount of cough drop is all that matters. E) Break the cough drop into little pieces, put them all in your mouth, and drink plenty of water. 76) Which one of the following is a typical feature of an ATP-driven active transport mechanism? 76) A) The transport protein is irreversibly phosphorylated as transport takes place. B) The solute must be phosphorylated before it can bind to the transport protein. C) The transport protein must cross to the correct side of the membrane before the solute can bind to it. D) The transport protein catalyzes the conversion of ADP to ATP. 78) Resolving power is the 78) A) ability of an optical instrument to show two close objects as separate. B) size of an image. C) distance between the lenses of a microscope.
11 D) ability of an optical instrument to magnify an image. E) ability of an optical instrument to estimate the size of an image. 79) Which of the following pieces of evidence would prove that a substance enters a cell by active rather than passive transport? 79) A) The substance is moved across the cell membrane by a carrier protein. B) The breakdown of ATP is needed for transport to occur. C) The substance enters the cell when its concentration is higher outside the cell than inside. D) All of the choices are correct. 80) When physicians perform an organ transplant, they choose a donor whose tissues match those of the recipient as closely as possible. Which of the following cell components are being matched? 80) A) plasma membrane phospholipids B) cell-surface carbohydrates C) plasma membrane proteins D) cytoskeletal elements E) plasma membrane cholesterols 81) Which one of the following statements is false? The endomembrane system 81) A) includes the nuclear envelope. B) is involved in the synthesis, storage, and export of important molecules. C) is a system of interrelated membranes that are all physically connected. D) includes the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. E) divides the cell into compartments. 83) Membrane phospholipids 83) A) have hydrophobic heads that face the center of the membrane and are shielded from water. B) remain fluid because they are tightly packed against one another. C) have hydrophilic tails that face outward and are exposed to water. D) often have "kinks" in their tails caused by the presence of a single rather than a double bond between carbons. 84) The function of mitochondria is 84) A) intracellular transport of proteins. B) photosynthesis. C) intracellular digestion. D) cellular respiration. E) lipid synthesis. 85) Which one of the following statements is false? The Golgi apparatus 85) A) works closely with the endoplasmic reticulum. B) modifies chemicals received from the endoplasmic reticulum. C) sorts molecules according to their destination. D) decreases in size when a cell increases its protein production. E) serves as a molecular warehouse and finishing factory. 87) Plasma membranes are selectively permeable. This means that 87) A) glucose cannot enter the cell. B) cholesterol cannot enter the cell. C) anything can pass into or out of a cell as long as the membrane is intact and the cell is healthy. D) the plasma membrane allows some substances to enter or leave a cell more easily than others. E) plasma membranes must be very thick. 88) The functions of the central vacuoles of plant cells include 88)
12 A) storing pigments that will help attract pollinating insects. B) storing poisons. C) storing waste products. D) helping increase the size of cells by absorbing water. 89) The cells that produce hair contain a lot of. The cells that produce the oils that coat the hair contain a lot of. 89) A) nuclei... chromatin B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum... lysosomes C) rough endoplasmic reticulum... smooth endoplasmic reticulum D) microbodies... lysosomes E) smooth endoplasmic reticulum... rough endoplasmic reticulum 90) Intermediate filaments can be found 90) A) within cilia and flagella. B) supporting the inner mitochondrial membrane. C) guiding the movements of chromosomes. D) guiding the movements of organelles. E) surrounding a nucleus. 91) Light microscopes 91) A) work by reflecting electrons off the surface of an object being studied. B) can generally magnify objects about 10,000 times without blurring. C) use light and glass lenses to magnify an image. D) typically provide more resolution than an electron microscope.
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Cell Transport Unit Test
 Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about cells is true? A) All cells have cell walls.
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about cells is true? A) All cells have cell walls.
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Cell Structure & Interactions
 Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cells. Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function. Cells. Plasma Membrane
 Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Peroxisomes. Endomembrane System. Vacuoles 9/25/15
 Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
3UNIT. Photosynthesis and. Cellular Respiration. Unit PreQuiz? General Outcomes. Unit 3 Contents. Focussing Questions
 3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell
 Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and function
 Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Chapters 4 & 5: The Cell
 Chapters 4 & 5: The Cell Honors Biology 2011 1 The History of the Microscope and Cell Theory 1665 - Robert Hooke uses a simple microscope to look at cork. 1668 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed single celled
Chapters 4 & 5: The Cell Honors Biology 2011 1 The History of the Microscope and Cell Theory 1665 - Robert Hooke uses a simple microscope to look at cork. 1668 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed single celled
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
Cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Euakryotic cells are generally one to one hundred times bigger than prokaryotic cells
 Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
1/18/2018. BIO 1101 Lecture 4 Chapters 4 & 5: Cells & The Working Cell. What is a Cell?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BIO 1101 Lecture 4 Chapters 4 & 5: Cells & The Working Cell What is a Cell? The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life. All organisms are made of cells
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BIO 1101 Lecture 4 Chapters 4 & 5: Cells & The Working Cell What is a Cell? The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life. All organisms are made of cells
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Review for Quiz on the Structure and Function of Eukaryotic Cells, Answers
 2. Label the diagram of a typical cell membrane: a) phospholipid b) phospholipid bilayer c) carbohydrate group d) cholesterol molecules e) channel or carrier protein (aka. integral or transmembrane protein)
2. Label the diagram of a typical cell membrane: a) phospholipid b) phospholipid bilayer c) carbohydrate group d) cholesterol molecules e) channel or carrier protein (aka. integral or transmembrane protein)
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 4. Most cells are microscopic. Cells vary in size and shape
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head
 CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
The Cell. The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK
 NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2010, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Cells Most basic unit of living system Arise by cell division from existing cell Make up
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2010, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Cells Most basic unit of living system Arise by cell division from existing cell Make up
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells eye 100 mm (10 cm) Chicken egg aid n 10 mm
 Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
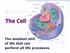 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided.
 Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY
 BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
A Tour of the Cell Period
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
