Cellular Biochemistry
|
|
|
- Regina Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cellular Biochemistry Fall Semester 2013 Sept. 23 Benoit Kornmann Institute of Biochemistry
2 Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry Membrane proteins Integral proteins Lipid-anchored proteins Peripheral proteins Distribution and signaling Phosphoinositides (Vesicular transport) Transporter Main textbook Molecular Biology of the Cell 5th edition Alberts et al. Garlands eds. 2
3 c Function of the biological membranes Allow COMPARTIMENTALIZATION Plasma membrane defines the boundary of the cell Intracellular membranes subdivide the cell into different compartments (organelles) that differ in composition (proteins, ions, ph, redox potential, electrochemical potential) These compartments carry out different cellular functions Favor biochemical reactions 2D instead of 3D diffusion favors encounter of metabolites 3
4 Biological membranes 200 ms in the life of aquaporin (B.L. de Groot and H. Grubmüller: Science 294, (2001) From BM/0C ps/de_groot/gallery.html Media 10.1 Membranes are thin (5-7 nm), strong, non-elastic, self-sealing, flexible, deformable, hydrophobic barriers between aqueous compartments Composed of amphiphilic lipids (phospholipids) arranged as a bilayer. The bilayers also contain non-membrane-forming lipids, and proteins many of which carry carbohydrate moieties or covalently bound lipids. The bilayer is usually fluid, mostly liquid 4
5 Challenges in membrane biology Membranes derive from membranes membranes inherited from sperm and oocyte how to make new membranes? Growth: one molecule at a time (lipid/protein) Fusion/fission How to make the right amount of membrane? How can the cell differentiate between two membranes? E.g. what differs between an early and late endosome, how is that difference generated and maintained? How can a protein be targeted to the right membrane? Limited permeability How to selectively transport metabolites and nutrients when needed? How to communicate across membranes? 5
6 Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry Membrane proteins Integral proteins Lipid-anchored proteins Peripheral proteins Membrane Identity Phosphoinositides Microdomains Exemples 6
7 Glycero-phospholipids 7
8 Glycero-phospholipids Figure 10-3 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 8
9 Glycero-phospholipids Figure 10-3 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 9
10 Sphingolipids Glycolipids Figure 10-3 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 10
11 sterols Figure 10-4 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 11
12 sterols Figure 10-5 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 12
13 Lipid composition varies with membrane Table 10-1 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 13
14 Asymmetry in the membranes Phospholipids with choline head groups enriched in extracytosolic leaflet (PC,SPH) Phospholipids with terminal amino group enriched in head group in cytosolic leaflet(pe, PS and also PI) Glycolipids in the outer leaflet Cholesterol in both Charge difference: majority of negative phospholipids (PS, PI) face inside Asymmetry is generated by flippases and counteracted by 'scramblases' 14
15 Lateral differentiation of membranes: phase separation Lipids in a mixtures in a single membrane may spontaneously segregate into different liquid phases Different fluidity Different dynamic properties Allows lateral partitioning of membrane components including proteins Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 15
16 Lipid rafts 16
17 Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry Membrane proteins transmembrane proteins Lipid-anchored proteins Peripheral proteins Distribution and signaling Phosphoinositides (Vesicular transport) Transporter 17
18 Membrane proteins Integral proteins Single pass trans-membrane protein; type I and II Polytopic (many passes through the membrane) Tail-anchored (ex. SNAREs) Loop-anchored (ex. Caveolin-1, reticulon homology domain) Lipid-anchored Peripheral proteins Lipid-associated proteins Protein-associated proteins 18
19 Transmembrane proteins α-helical TM domains can be detected on a hydrophobicity plot TM β-barrel protein (in bacterial and mitochondrial outer membranes) are more difficult to predict 19
20 Integral proteins that do not span the membrane include 20
21 Lipidated proteins (cytosolic face) Myristylation Fatty Acylation Prenylation Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 21
22 Lipidated protein (cytosolic face) C14 fatty acid via amide bond to amino group of N-terminal glycin Added to cotranslationally to cytosolic non membrane proteins, a permanent modification. Sufficient for membrane binding only when combined with:1) Positive charge cluster,2) FA alkyl group, or 3) proteinprotein interactions Arf1 and c-src Exposed or hidden after reversible conformational change. Fatty acylation Typically C16 i.e. palmitic acid By thioester to cystein Reversible modification in cis-golgi, on soluble proteins and endodomains of transmembrane proteins Double FA-acyl group direct many proteins to lipid rafts Caveolin, influenza hemagglutinin. Prenylation Farnesyl (C15) or geranylgeranyl (C20) By thioether to cystein Added to cytosolic non membrane proteins. So called CaaX box usually at the Cterminus, a permanent modification Often combined with nearby FA acyl groups Two Ras isoforms: H ras farnesyl plus two FA acyl chains. K-ras Farnesyl plus cluster of positive charges Myristylation 22
23 Importance of protein lipidation They allow proteins to come on and off membranes and thus support dynamic processes during signal transduction, molecular sorting, membrane bending, vesicle formation, membrane recognition, etc. Functions and dynamics can be strictly regulated in time and place. Allow interaction of proteins with specific membranes only and with specific lipid micro-domains such as lipid rafts. 23
24 GPI-anchored proteins (extra-cytosolic) Chemical composition: PI phosphatidyl Several sugar inositol (GPI) anchor residues (N-acetyl glucose addition amine and mannose plus others) Phosphoethanolam ine connected by amide bond to Cterminus of protein. Glyco Topology: In the extracellular leaflet. The GPI anchor provides the only connection with the membrane. Distribution: Enriched in apical membranes of epithelial cells, Enriched in lipid rafts. Tail can be removed by phospholipase C, releasing the proteins. Examples: Thy-1 antigen Alkaline phosphatase Acetyl-choline esterase 24
25 Peripheral proteins Non-covalently attached to lipid head-groups or proteins in the membrane Complex mixture of proteins on both sides of a membrane Interactions are often transient and regulated Cytosolic side of PM is particularly rich in peripheral proteins: an extensive, dynamic cortex of actin, adaptor proteins, and other proteins (needed for membrane stability; local membrane specializations; connections with cytoskeleton; transmission of signals; trafficking of vesicles; cell shape and polarity determination; membrane curvature; endocytosis.) 25
26 Cytosolic face of the plasma membrane 26
27 Focal adhesion complex 27
28 Peripheral protein binding to the membrane Binding to other proteins Lipid-binding domain PIPs PH-domain FYVE motif C2-domain Curvature sensing domain BAR-domain ALPS-motif 28
29 Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry Membrane proteins Integral proteins Lipid-anchored proteins Peripheral proteins Distribution and signaling Phosphoinositides (Vesicular transport) Transporter 29
30 Phosphatidylinositol phosphate(s) Inositol= cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6cyclohexanehexol Phosphoinositides (PIs) undergo phosphorylation/dephosphorylation through organelle-specific PI kinases and PI phosphatases in three positions of the inositol ring: 3,4 and 5. These combinations lead to different lipid products with distinct subcellular distributions. Phospholipases can cleave inositol-phosphate and release it in the cytosol as a second messenger 30
31 Phosphatidylinositol phosphate(s) In their specific locations, PIs control the correct timing and location of many important trafficking events. They do it via cytosolic proteins that bind to their inositol ring. These proteins include coat proteins, membrane fusion/fission proteins, membrane bending factors, enzymes, GTPase effectors, etc Most of these factors associate transiently with the membrane. 31
32 Phosphoinositides have preferred cellular locations PIP(4,5)P2 Plasma membrane PI(4)P Golgi complex PI(3)P Early endosomes PI(3,5)P2 Late endosomes They face the cytosolic compartment 32
33 PI-phosphorylation/ dephosphorylation pathways. s Mediated by a large family of PI-kinases and phosphatases s s From: Maria Antonietta De Matteis & Anna Godi Nature Cell Biology 6, (2004) s 33
34 Phosphoinositide binding domains 34
35 Lipid transporters Can extract any kind of lipid from a membrane and deliver it to another membrane Bind lipid in hydrophobic pocket From: Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol Oct;11(10):
36 Osh4p structure Sterol-bound PI4P-bound 36
37 Example: generation of sterol gradient From: J Cell Biol(2011) 195,
Cell Membranes. Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Cell and Molecular Biology
 Cell Membranes Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Cell and Molecular Biology Organelles 2Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids DNA
Cell Membranes Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Cell and Molecular Biology Organelles 2Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids DNA
Models of the plasma membrane - from the fluid mosaic to the picket fence model. Mario Schelhaas Institute of Cellular Virology
 Models of the plasma membrane - from the fluid mosaic to the picket fence model Mario Schelhaas Institute of Cellular Virology Today s lecture Central Question: How does the plasma membrane fulfil its
Models of the plasma membrane - from the fluid mosaic to the picket fence model Mario Schelhaas Institute of Cellular Virology Today s lecture Central Question: How does the plasma membrane fulfil its
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes. Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment.
 Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Rama Abbady. Odai Bani-Monia. Diala Abu-Hassan
 5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7)
 The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7) Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water Aaaah, one of those structure
The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7) Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water Aaaah, one of those structure
Biomembranes structure and function. B. Balen
 Biomembranes structure and function B. Balen All cells are surrounded by membranes Selective barrier But also important for: 1. Compartmentalization 2. Biochemical activities 3. Transport of dissolved
Biomembranes structure and function B. Balen All cells are surrounded by membranes Selective barrier But also important for: 1. Compartmentalization 2. Biochemical activities 3. Transport of dissolved
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 8. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
Lecture 36: Review of membrane function
 Chem*3560 Lecture 36: Review of membrane function Membrane: Lipid bilayer with embedded or associated proteins. Bilayers: 40-70% neutral phospholipid 10-20% negative phospholipid 10-30% cholesterol 10-30%
Chem*3560 Lecture 36: Review of membrane function Membrane: Lipid bilayer with embedded or associated proteins. Bilayers: 40-70% neutral phospholipid 10-20% negative phospholipid 10-30% cholesterol 10-30%
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane
 Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
Division Ave High School Ms. Foglia AP Biology
 The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water 2007-2008 Aaaah, one of those structure
The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water 2007-2008 Aaaah, one of those structure
Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments
 Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular Compartments and
Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular Compartments and
The Cell Membrane AP Biology
 The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
Diffusion across cell membrane
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
Phospholipids. Phosphate head. Fatty acid tails. Arranged as a bilayer. hydrophilic. hydrophobic. Phosphate. Fatty acid. attracted to water
 The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water I want you to remember: Structure
The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water I want you to remember: Structure
membranes membrane functions basic structure membrane functions chapter 11-12
 membranes chapter - membrane functions Ca + hormone IP H + HO compartmentalization intracellular compartments scaffold for biochemical activities organize enzymes selectively permeable membrane allows
membranes chapter - membrane functions Ca + hormone IP H + HO compartmentalization intracellular compartments scaffold for biochemical activities organize enzymes selectively permeable membrane allows
CWDHS Mr. Winch Grade 12 Biology
 The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
The Cell Membrane Overview Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
Week 5 Section. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
The Cell Membrane. Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings. Controls traffic in & out of the cell
 The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
AP Biology. Overview. The Cell Membrane. Phospholipids. Phospholipid bilayer. More than lipids. Fatty acid tails. Phosphate group head
 Overview The Cell Membrane Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
Overview The Cell Membrane Cell separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances to cross more
The Cell Membrane. Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit. Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia
 The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry. The cell: Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell
 Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
CHAPTER 11 Membranes
 CHAPTER 11 Membranes Key topics The function of biological membranes The structure and composition of membranes Dynamics of membranes Structure and function of membrane proteins Transport across biological
CHAPTER 11 Membranes Key topics The function of biological membranes The structure and composition of membranes Dynamics of membranes Structure and function of membrane proteins Transport across biological
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Cell Membranes Valencia college
 6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
membranes cellular membranes basic structure basic structure chapter ECM CYTOPLASM
 membranes chapter 11-1 1 cellular membranes 3 compartmentalization intracellular compartments 1. receiving info membrane receptors recognition and interaction with other cells. import and export of molecules
membranes chapter 11-1 1 cellular membranes 3 compartmentalization intracellular compartments 1. receiving info membrane receptors recognition and interaction with other cells. import and export of molecules
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules. Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine
 Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
The Cell Membrane. Lecture 3a. Overview: Membranes. What is a membrane? Structure of the cell membrane. Fluid Mosaic Model. Membranes and Transport
 Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
PLASMA MEMBRANE. Submitted by:- DR.Madhurima Sharma PGGCG-II,Chandigarh
 PLASMA MEMBRANE Submitted by:- DR.Madhurima Sharma PGGCG-II,Chandigarh LIPID COMPONENTS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE The outer leaflet consists predominantly of phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, and glycolipids,
PLASMA MEMBRANE Submitted by:- DR.Madhurima Sharma PGGCG-II,Chandigarh LIPID COMPONENTS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE The outer leaflet consists predominantly of phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, and glycolipids,
The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on C number 3 of a triacylglycerol molecule O O CH 2 O C R CH 2 O P O X OH.
 Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins
 1 Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins 2 Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Amphipathic Phosphate attracted to
1 Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins 2 Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Amphipathic Phosphate attracted to
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005
 COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005 Cell membranes 1. What are the functions of cell membranes? 2. What is the current model of membrane structure? 3. Evidence supporting the fluid mosaic
COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005 Cell membranes 1. What are the functions of cell membranes? 2. What is the current model of membrane structure? 3. Evidence supporting the fluid mosaic
Monday, September 30 th :
 Monday, September 30 th : QUESTION TO PONDER: Differentiate between a pro- and eukaryotic organism. List 4 organelles that each type of organism has in common. The Cell Membrane Modified from Kim Foglia
Monday, September 30 th : QUESTION TO PONDER: Differentiate between a pro- and eukaryotic organism. List 4 organelles that each type of organism has in common. The Cell Membrane Modified from Kim Foglia
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents:
 Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Membrane transport. Pharmacy Dr. Szilvia Barkó
 Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
Lipids: Membranes Testing Fluid Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure: Cellular Fusion
 Models for Membrane Structure NEW MODEL (1972) Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer & Nicholson Lipids form a viscous, twodimensional solvent into which proteins are inserted and integrated more or less
Models for Membrane Structure NEW MODEL (1972) Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer & Nicholson Lipids form a viscous, twodimensional solvent into which proteins are inserted and integrated more or less
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Cell membranes. Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102
 Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer. Membrane Structure and Function. Fluid Mosaic Model. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222
 Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Chapters 9 and 10 Lipids and Membranes
 Chapters 9 and 10 Lipids and Membranes Lipids- a class of biological molecules defined by low solubility in water and high solubility in nonpolar solvents. Lipids contain or are derived from fatty acids.
Chapters 9 and 10 Lipids and Membranes Lipids- a class of biological molecules defined by low solubility in water and high solubility in nonpolar solvents. Lipids contain or are derived from fatty acids.
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Lipids are macromolecules, but NOT polymers. They are amphipathic composed of a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol
 d 1 2 Lipids are macromolecules, but NOT polymers. They are amphipathic composed of a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol backbone. The phosphate head group is hydrophilic water
d 1 2 Lipids are macromolecules, but NOT polymers. They are amphipathic composed of a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol backbone. The phosphate head group is hydrophilic water
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
 Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Main Functions maintain homeostasis
 The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
10/28/2013. Double bilayer of lipids with imbedded, dispersed proteins Bilayer consists of phospholipids, cholesterol, and glycolipids
 Structure of a Generalized Cell MEMBRANES Figure 3.1 Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model Separates intracellular fluids from extracellular fluids Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity Glycocalyx is
Structure of a Generalized Cell MEMBRANES Figure 3.1 Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model Separates intracellular fluids from extracellular fluids Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity Glycocalyx is
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Protein-lipid interactions and the lipid raft hypothesis
 Protein-lipid interactions and the lipid raft hypothesis or? Fivaz & Meyer 2003 euron 40, 319-30 Munro 2003 Cell 115, 377-88 How to target proteins to membranes? 1 Covalent lipid modification of proteins
Protein-lipid interactions and the lipid raft hypothesis or? Fivaz & Meyer 2003 euron 40, 319-30 Munro 2003 Cell 115, 377-88 How to target proteins to membranes? 1 Covalent lipid modification of proteins
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
40s 50s. 70s. Membrane Rafts
 40s 50s 70s Membrane Rafts Membrane Microdomains Raft is a specific type of microdomain sphingolipid/cholesterol rich region Separation of discrete liquid-ordered and liquid-disordered phase domains occurring
40s 50s 70s Membrane Rafts Membrane Microdomains Raft is a specific type of microdomain sphingolipid/cholesterol rich region Separation of discrete liquid-ordered and liquid-disordered phase domains occurring
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
Principles of membrane organization, membrane proteins
 Module 1 Lecture 3 Principles of membrane organization, membrane proteins Introduction All living cells possess a cell membrane. These membranes serve to contain and protect cell components from the surroundings
Module 1 Lecture 3 Principles of membrane organization, membrane proteins Introduction All living cells possess a cell membrane. These membranes serve to contain and protect cell components from the surroundings
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 8, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 April 8, 2013 1 / 41 Outline Questions and answers Shipunov (MSU)
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 8, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 April 8, 2013 1 / 41 Outline Questions and answers Shipunov (MSU)
Lecture 15. Membrane Proteins I
 Lecture 15 Membrane Proteins I Introduction What are membrane proteins and where do they exist? Proteins consist of three main classes which are classified as globular, fibrous and membrane proteins. A
Lecture 15 Membrane Proteins I Introduction What are membrane proteins and where do they exist? Proteins consist of three main classes which are classified as globular, fibrous and membrane proteins. A
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Cell Boundaries. Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h
 Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Membrane Structure and Function. Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function
 Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes. Reading Assignments. Selective and Semi-permeable Barriers
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Chapter 5 Cell Membrane Structure and Organelles
 Part II Principles of Individual Cell Function Chapter 5 Cell structures consist of biological membranes essentially mobile lipid bilayers to which many membrane proteins attach. The cell membrane separates
Part II Principles of Individual Cell Function Chapter 5 Cell structures consist of biological membranes essentially mobile lipid bilayers to which many membrane proteins attach. The cell membrane separates
CONCEPT 5.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
 Ch 5 Membrane Transport and Signaling Overview The plasma separates the living cell from its surroundings The plasma exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than
Ch 5 Membrane Transport and Signaling Overview The plasma separates the living cell from its surroundings The plasma exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than
Membrane Structure and Function - 1
 Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment. Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane
 Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Name: Multiple choice questions. Pick the BEST answer (2 pts ea)
 Exam 1 202 Oct. 5, 1999 Multiple choice questions. Pick the BEST answer (2 pts ea) 1. The lipids of a red blood cell membrane are all a. phospholipids b. amphipathic c. glycolipids d. unsaturated 2. The
Exam 1 202 Oct. 5, 1999 Multiple choice questions. Pick the BEST answer (2 pts ea) 1. The lipids of a red blood cell membrane are all a. phospholipids b. amphipathic c. glycolipids d. unsaturated 2. The
Introduction and protein sorting
 Introduction and protein sorting Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids (50% of mass of plasma membranes, 30% of mitochondrial membranes, 80% of myelin
Introduction and protein sorting Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids (50% of mass of plasma membranes, 30% of mitochondrial membranes, 80% of myelin
Membranes & Membrane Proteins
 School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11
 1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
Chapter 5: Cell Membranes and Signaling
 Chapter Review 1. For the diagram below, explain what information you would use to determine which side of the membrane faces the inside of the cell and which side faces the extracellular environment.
Chapter Review 1. For the diagram below, explain what information you would use to determine which side of the membrane faces the inside of the cell and which side faces the extracellular environment.
Signal-Transduction Cascades - 2. The Phosphoinositide Cascade
 Signal-Transduction Cascades - 2 The Phosphoinositide Cascade Calcium ion as a second messenger Tyrosine kinase and receptor dimerization scribd.com Faisal Khatib JU The Phosphoinositide Cascade Used by
Signal-Transduction Cascades - 2 The Phosphoinositide Cascade Calcium ion as a second messenger Tyrosine kinase and receptor dimerization scribd.com Faisal Khatib JU The Phosphoinositide Cascade Used by
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
What do you remember about the cell membrane?
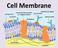 Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28
 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University March 30, 2012 Outline Questions and answers Outline Questions and answers Questions and answers Previous final question: the answer How to make a transgenic organism
Alexey Shipunov Minot State University March 30, 2012 Outline Questions and answers Outline Questions and answers Questions and answers Previous final question: the answer How to make a transgenic organism
Introduction to biomembranes
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry Biomembranes and Cell Signaling (BCH 452) Chapter 1 Introduction to biomembranes Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry Biomembranes and Cell Signaling (BCH 452) Chapter 1 Introduction to biomembranes Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya
Cell Membranes. Q: What components of the cell membrane are in a mosaic pattern?
 Cell Membranes The cell / plasma membrane is. Selective in that it allows things in and some things out of the cell. Recall that phospholipids have hydrophobic and hydrophilic. The term to describe this
Cell Membranes The cell / plasma membrane is. Selective in that it allows things in and some things out of the cell. Recall that phospholipids have hydrophobic and hydrophilic. The term to describe this
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
1.4 Page 1 Cell Membranes S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport Page 1 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport from your syllabus l. Cell Membrane Structure 1. Read and
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport Page 1 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport from your syllabus l. Cell Membrane Structure 1. Read and
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Classification of Lipids
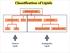 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cell membrane & Transport. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Cell membrane, transport. Prof. Gábor Szabó, 2017
 Cell membrane, transport Prof. Gábor Szabó, 2017 This lecture: Essential Cell Biology: chapters 11-12 All the pages are required, except: ion channels, the pumps and mechanisms relevant to Ca, osmo- and
Cell membrane, transport Prof. Gábor Szabó, 2017 This lecture: Essential Cell Biology: chapters 11-12 All the pages are required, except: ion channels, the pumps and mechanisms relevant to Ca, osmo- and
