Protein-lipid interactions and the lipid raft hypothesis
|
|
|
- Austen Gray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Protein-lipid interactions and the lipid raft hypothesis or? Fivaz & Meyer 2003 euron 40, Munro 2003 Cell 115, How to target proteins to membranes? 1
2 Covalent lipid modification of proteins Palmitoylation (16 C acyl chain) (Cys) thioester bonds The most abundant The only reversible (can be cleaved by thioesterases) -myristoylation (14 C acyl chain) In most cases not enough to anchor a protein to membrane Prenylation (farnesyl or geranylgeranyl) Thioether linkage to a C-terminal Cys Protein binding domains Polybasic domains Short cluster of basic amino acids (<30) non-specific binding to acidic lipids Act synergistically with lipid modifications Phospho inositides binding modules Low affinity lipid interaction modules that regulate transient association w/cellular membranes Examples: PH, FERM, ETH [PI(4,5)P 2 ] FYVE, PX [PI(3)P] C1 and C2 domains 2
3 How fast are proteins localized to they targets in the cell? 3
4 Suggested roles for Rafts Signal transduction pathways (Leah, Paejonette, Daniel) Apoptosis (Sait) Cell adhesion and migration (Casey) Synaptic transmission (Kathryn, Andrew, Khursheed) rganization of cytoskeleton (Ban-Yoon, Kristina) Protein sorting during exo- and endocytosis (at) Point of entry of viruses, bacteria, and toxins (William, Fabian) Site of viral assembly and formation of prion and Alzheimer amyloid (Dorota, Adriana) Alicja, David, Krovi, Paul (?) Kevin, avin However Current knowledge does not unequivocally support the existence of rafts Alternative models for the structure of the plasma membrane are equally plausible 4
5 Mixtures of lipids form lipid phases 'Rafts' in the Plasma Membrane Liquid-Disordered d) (l Bilayer Liquid-rdered o) (l Domain ('Raft') Liquid-Disordered d) (l Bilayer Glycosphingolipids Transmembrane Proteins Multiply Acylated Proteins (Cytoplasm) 5
6 Detergent/Low Temperature Method to Isolate and Characterize 'Rafts' Triton X o C 100,000 x g (0-4 o C) 'Raft' Fraction Cell or Membrane Suspension Apply under Density Gradient 6
7 Detergent-resistant membranes There are a number of reasons why it cannot be assumed that detergent resistance reflects a protein being present in a microdomain that was present before triton was added. A number of nonphysiological rearrangements of the bilayer could occur during detergent solubilization Reduction in T can alter lipid organization The highly asymmetric nature will lead to anomalous processes Triton actually promotes the formation of ordered domains in model bilayers (Heerklotz 2002, Biophys. J. 83, 2693) Lipid phase behavior is highly temperature dependent (Dietrich et al., Biophys. J. 2001) 7
8 Relative Affinities of Different Bimane-labeled Diacyl PE Probes for Lc vs. Ld Domains in 1:1:1 Spin-labeled PC/Sphingomyelin/Cholesterol Bilayers Relative Affinities of Bimane-labeled Diacyl PEs for Liquid-ordered Domains 1.4 Bimta-di16:0-PE Bimta-di18:1c-PE - P - P H H S S Relative Affinity for l o Domains (Sphingomyelin/Spin-labeled PC Cholesterol Bilayers, 37 o C) di18:1 18:0/18:1 di14:0 di16:0 di18:0 di20:0 Acyl Chains of Bimane-labeled PE 8
9 The Detergent-Solubilization and Fluorescence Assays Can Give Divergent Pictures of Molecular Partitioning into 'Raft' Domains 1.2 Relative Fraction in l o Phase (di18:0-bimtape = 1.0) Detergent Fluorescence 0 di18:1c- Bimanyl-PE 18:0/18:1c- Bimanyl-PE di-14:0- Bimanyl-PE di-18:0- Bimanyl-PE Sensitivity to cholesterol depletion Cholesterol affects a number of physical properties of the membranes Cellular processes are sensitive to changes in any one physical property Any consequences would not necessarily be due to the loss of rafts 9
10 Conclusion The existence of lipid rafts cannot be taken as a established fact We should proceed with caution and open mind to alternative mechanisms for phenomena currently attributed to rafts 10
40s 50s. 70s. Membrane Rafts
 40s 50s 70s Membrane Rafts Membrane Microdomains Raft is a specific type of microdomain sphingolipid/cholesterol rich region Separation of discrete liquid-ordered and liquid-disordered phase domains occurring
40s 50s 70s Membrane Rafts Membrane Microdomains Raft is a specific type of microdomain sphingolipid/cholesterol rich region Separation of discrete liquid-ordered and liquid-disordered phase domains occurring
Cellular Biochemistry
 Cellular Biochemistry Fall Semester 2013 Sept. 23 Benoit Kornmann Institute of Biochemistry Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry
Cellular Biochemistry Fall Semester 2013 Sept. 23 Benoit Kornmann Institute of Biochemistry Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry
Cell Membranes. Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Cell and Molecular Biology
 Cell Membranes Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Cell and Molecular Biology Organelles 2Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids DNA
Cell Membranes Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Cell and Molecular Biology Organelles 2Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids DNA
Biophysical Journal Volume 79 August
 Biophysical Journal Volume 79 August 2000 919 933 919 Fluorescence-Based Evaluation of the Partitioning of Lipids and Lipidated Peptides into Liquid-Ordered Lipid Microdomains: A Model for Molecular Partitioning
Biophysical Journal Volume 79 August 2000 919 933 919 Fluorescence-Based Evaluation of the Partitioning of Lipids and Lipidated Peptides into Liquid-Ordered Lipid Microdomains: A Model for Molecular Partitioning
Rama Abbady. Odai Bani-Monia. Diala Abu-Hassan
 5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
Chapter 12. Part II. Biological Membrane
 Chapter 12 Part II. Biological Membrane Single-tailed lipids tend to form micelles Critical micelle concentration (cmc): minimum concentration that forms micelles e.g.) cmc for SDS 1mM; cmc for phospholipids
Chapter 12 Part II. Biological Membrane Single-tailed lipids tend to form micelles Critical micelle concentration (cmc): minimum concentration that forms micelles e.g.) cmc for SDS 1mM; cmc for phospholipids
Lipid raft-a gateway for passing through the cell membrane for pathogens
 16 3 2004 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 16, No. 3 Jun., 2004 10040374(2004)03014404 200031 / GPI (GPI) Q241 Q257 R37 A Lipid rafta gateway for passing through the cell membrane for pathogens
16 3 2004 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 16, No. 3 Jun., 2004 10040374(2004)03014404 200031 / GPI (GPI) Q241 Q257 R37 A Lipid rafta gateway for passing through the cell membrane for pathogens
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 8. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
Models of the plasma membrane - from the fluid mosaic to the picket fence model. Mario Schelhaas Institute of Cellular Virology
 Models of the plasma membrane - from the fluid mosaic to the picket fence model Mario Schelhaas Institute of Cellular Virology Today s lecture Central Question: How does the plasma membrane fulfil its
Models of the plasma membrane - from the fluid mosaic to the picket fence model Mario Schelhaas Institute of Cellular Virology Today s lecture Central Question: How does the plasma membrane fulfil its
Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments
 Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular Compartments and
Lecture 2 I. Membrane Proteins II. Intracellular Compartments Ref: MBoC (5th Edition), Alberts Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Chapter 10 Membrane Structure Chapter 12 Intracellular Compartments and
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane
 Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
Molecular Organization of the Cell Membrane A walk from molecules to a functional biostructure Cell Membrane Definition An ultrastructure separating connecting the cell to the environment 1 Coarse chemical
Ras plasma membrane signalling platforms
 Biochem. J. (2005) 389, 1 11 (Printed in Great Britain) 1 REVIEW ARTICLE Ras plasma membrane signalling platforms John F. HANCOCK* 1 and Robert G. PARTON* *Institute for Molecular Bioscience, University
Biochem. J. (2005) 389, 1 11 (Printed in Great Britain) 1 REVIEW ARTICLE Ras plasma membrane signalling platforms John F. HANCOCK* 1 and Robert G. PARTON* *Institute for Molecular Bioscience, University
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
The effect of hydrostatic pressure on membrane-bound proteins
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2005) 38: 1203-1208 High pressure studies on membrane-associated proteins ISSN 0100-879X Review 1203 The effect of hydrostatic pressure on membrane-bound
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2005) 38: 1203-1208 High pressure studies on membrane-associated proteins ISSN 0100-879X Review 1203 The effect of hydrostatic pressure on membrane-bound
ALLOSTERIC REGULATION OF GPCR ACTIVITY BY PHOSPHOLIPIDS
 Supplementary Information ALLOSTERIC REGULATION OF GPCR ACTIVITY BY PHOSPHOLIPIDS Rosie Dawaliby 1, Cataldo Trubbia 1, Cédric Delporte 3,4, Matthieu Masureel 2, Pierre Van Antwerpen 3,4, Brian K. Kobilka
Supplementary Information ALLOSTERIC REGULATION OF GPCR ACTIVITY BY PHOSPHOLIPIDS Rosie Dawaliby 1, Cataldo Trubbia 1, Cédric Delporte 3,4, Matthieu Masureel 2, Pierre Van Antwerpen 3,4, Brian K. Kobilka
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Plasma membrane structure and dynamics explored via a combined AFM/FCS approach
 Plasma membrane structure and dynamics explored via a combined AFM/FCS approach Salvatore Chiantia Molekulare Biophysik, Dept. Of Biology Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Dresden nanoseminar, May 2013 Outline
Plasma membrane structure and dynamics explored via a combined AFM/FCS approach Salvatore Chiantia Molekulare Biophysik, Dept. Of Biology Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Dresden nanoseminar, May 2013 Outline
Introductory comments. Structure of lipid bilayers
 Introductory comments Today we review the structural properties of biological membranes and discuss a few of the ways in which these structures influence cytomechanics and biochemistry. We will then start
Introductory comments Today we review the structural properties of biological membranes and discuss a few of the ways in which these structures influence cytomechanics and biochemistry. We will then start
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
GCD3033:Cell Biology. Plasma Membrane Dynamics
 Plasma Membrane Dynamics Membrane Structure I) Lipid Bilayer A) Membrane Lipids B) Membrane Flexibility & Composition C) Phospholipids II) Membrane Proteins A) association with membranes B) membrane solubilization
Plasma Membrane Dynamics Membrane Structure I) Lipid Bilayer A) Membrane Lipids B) Membrane Flexibility & Composition C) Phospholipids II) Membrane Proteins A) association with membranes B) membrane solubilization
Lecture 36: Review of membrane function
 Chem*3560 Lecture 36: Review of membrane function Membrane: Lipid bilayer with embedded or associated proteins. Bilayers: 40-70% neutral phospholipid 10-20% negative phospholipid 10-30% cholesterol 10-30%
Chem*3560 Lecture 36: Review of membrane function Membrane: Lipid bilayer with embedded or associated proteins. Bilayers: 40-70% neutral phospholipid 10-20% negative phospholipid 10-30% cholesterol 10-30%
Membranes & Membrane Proteins
 School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES. Lipid rafts in neurodegenerative diseases. Nigel M.
 Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Lipid rafts in neurodegenerative diseases Nigel M. Hooper Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Lipid rafts in neurodegenerative diseases Nigel M. Hooper Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Effects of Cholesterol on Membranes: Physical Properties
 Effects of Cholesterol on Membranes: Physical Properties Removes gel to liquid crystal phase transition New intermediate phase called liquid ordered - ordering of the membrane lipids due to condensation
Effects of Cholesterol on Membranes: Physical Properties Removes gel to liquid crystal phase transition New intermediate phase called liquid ordered - ordering of the membrane lipids due to condensation
(multiple answers) This strain of HIV uses a different chemokine coreceptor for entry into cells.
 LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4 100 points total all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in TF 1. (20 points) To further investigate HIV infection you decide to study the process of the
LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4 100 points total all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in TF 1. (20 points) To further investigate HIV infection you decide to study the process of the
Chapter 12: Membranes. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
CHAPTER 11 Membranes
 CHAPTER 11 Membranes Key topics The function of biological membranes The structure and composition of membranes Dynamics of membranes Structure and function of membrane proteins Transport across biological
CHAPTER 11 Membranes Key topics The function of biological membranes The structure and composition of membranes Dynamics of membranes Structure and function of membrane proteins Transport across biological
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which of the following statements about passive and primary active transport proteins is FALSE?
 Biological Membranes 1. Which of the following statements about passive and primary active transport proteins is FALSE? A. They are both integral membrane proteins. B. They both show a high degree of selectivity.
Biological Membranes 1. Which of the following statements about passive and primary active transport proteins is FALSE? A. They are both integral membrane proteins. B. They both show a high degree of selectivity.
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Principles of membrane organization, membrane proteins
 Module 1 Lecture 3 Principles of membrane organization, membrane proteins Introduction All living cells possess a cell membrane. These membranes serve to contain and protect cell components from the surroundings
Module 1 Lecture 3 Principles of membrane organization, membrane proteins Introduction All living cells possess a cell membrane. These membranes serve to contain and protect cell components from the surroundings
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Week 5 Section. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Sheet #5 Dr. Mamoun Ahram 8/7/2014
 P a g e 1 Protein Structure Quick revision - Levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary. - Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids residues. It determines the other
P a g e 1 Protein Structure Quick revision - Levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary. - Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids residues. It determines the other
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes. Reading Assignments. Selective and Semi-permeable Barriers
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222
 Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
Theory of Raft Formation by the Cross-Linking of Saturated or Unsaturated Lipids in Model Lipid Bilayers
 Biophysical Journal Volume 96 June 2009 4935 4940 4935 Theory of Raft Formation by the Cross-Linking of Saturated or Unsaturated Lipids in Model Lipid Bilayers G. Garbès Putzel and M. Schick* Department
Biophysical Journal Volume 96 June 2009 4935 4940 4935 Theory of Raft Formation by the Cross-Linking of Saturated or Unsaturated Lipids in Model Lipid Bilayers G. Garbès Putzel and M. Schick* Department
Biophysical Analysis of Membrane Functions by Laser Tweezers
 Biophysical Analysis of Membrane Functions by Laser Tweezers Plasma Membrane Functions (Control by PIP2 Levels in Plasma Membrane) Cell Motility Endocytosis (Cell Volume regulation) Membrane resealing
Biophysical Analysis of Membrane Functions by Laser Tweezers Plasma Membrane Functions (Control by PIP2 Levels in Plasma Membrane) Cell Motility Endocytosis (Cell Volume regulation) Membrane resealing
Looking at lipid rafts?
 One of the most intriguing issues in membrane biology is whether non-caveolar glycosphingolipid (GSL)-enriched domains 1 actually exist in the plane of the plasma membrane. One reason for the high interest
One of the most intriguing issues in membrane biology is whether non-caveolar glycosphingolipid (GSL)-enriched domains 1 actually exist in the plane of the plasma membrane. One reason for the high interest
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine
 Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
STUDYING MEMBRANE ANCHOR ORGANIZATION IN LIVING CELL MEMBRANES
 STUDYING MEMBRANE ANCHOR ORGANIZATION IN LIVING CELL MEMBRANES by Hector H. Huang A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Molecular
STUDYING MEMBRANE ANCHOR ORGANIZATION IN LIVING CELL MEMBRANES by Hector H. Huang A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Molecular
LIPIDS. Docent Tuomo Glumoff. Faculty of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine P Biomolecules for Biochemists (8 op)
 Faculty of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine 740143P Biomolecules for Biochemists (8 op) 740147P Biomolecules for Bioscientists (8 op) 740148P Biomolecules (5 op) LIPIDS Docent Tuomo Glumoff LIPIDS lectures
Faculty of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine 740143P Biomolecules for Biochemists (8 op) 740147P Biomolecules for Bioscientists (8 op) 740148P Biomolecules (5 op) LIPIDS Docent Tuomo Glumoff LIPIDS lectures
BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Prof. J.H.P. Bayley, Dr. R.M. Adlington and Dr. L. Smith Trinity Term First Year. Lecture 2 Hagan Bayley
 BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Prof. J.H.P. Bayley, Dr. R.M. Adlington and Dr. L. Smith Trinity Term 2007 - First Year Lecture 2 Hagan Bayley Introduction to the macromolecules of life and cell structures. Introduction
BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Prof. J.H.P. Bayley, Dr. R.M. Adlington and Dr. L. Smith Trinity Term 2007 - First Year Lecture 2 Hagan Bayley Introduction to the macromolecules of life and cell structures. Introduction
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Methods of studying membrane structure
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry Biomembranes and Cell Signaling (BCH 452) Chapter 2 Methods of studying membrane structure Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry Biomembranes and Cell Signaling (BCH 452) Chapter 2 Methods of studying membrane structure Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
BCMB 3100 Lipids (Text Chapters 11, 12, 13)
 BCMB 3100 Lipids (Text Chapters 11, 12, 13) Definition Major classes Fatty acids Triacylglycerol Glycerophospholipids Sphingolipids Cholesterol : water insoluble organic compounds in living organisms Lipids
BCMB 3100 Lipids (Text Chapters 11, 12, 13) Definition Major classes Fatty acids Triacylglycerol Glycerophospholipids Sphingolipids Cholesterol : water insoluble organic compounds in living organisms Lipids
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Protein regulation Protein motion
 Lecture 13 Protein regulation Protein motion Antoine van Oijen BCMP201 Spring 2008 04/02 Section IV 04/09 Hands-on methods session / PS 4 due 1 Today s lecture 1) Mechanisms of protein regulation 2) Molecular
Lecture 13 Protein regulation Protein motion Antoine van Oijen BCMP201 Spring 2008 04/02 Section IV 04/09 Hands-on methods session / PS 4 due 1 Today s lecture 1) Mechanisms of protein regulation 2) Molecular
MODEL SYSTEMS, LIPID RAFTS, AND CELL MEMBRANES 1
 Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2004. 33:269 95 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141803 Copyright c 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on
Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2004. 33:269 95 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141803 Copyright c 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 8, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 April 8, 2013 1 / 41 Outline Questions and answers Shipunov (MSU)
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 8, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28 April 8, 2013 1 / 41 Outline Questions and answers Shipunov (MSU)
LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4
 LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4 Due Friday 10/27 at noon in your TF s drop box on the 2 nd floor of the Science Center all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in 1. To further investigate
LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4 Due Friday 10/27 at noon in your TF s drop box on the 2 nd floor of the Science Center all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in 1. To further investigate
The Cell Membrane. Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit. Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia
 The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
Greasing Their Way: Lipid Modifications Determine Protein Association with Membrane Rafts
 Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6305 6316 6305 DOI: 10.1021/bi100882y Greasing Their Way: Lipid Modifications Determine Protein Association with Membrane Rafts Ilya Levental, Michal Grzybek, and Kai Simons* Max
Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6305 6316 6305 DOI: 10.1021/bi100882y Greasing Their Way: Lipid Modifications Determine Protein Association with Membrane Rafts Ilya Levental, Michal Grzybek, and Kai Simons* Max
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 28
 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University March 30, 2012 Outline Questions and answers Outline Questions and answers Questions and answers Previous final question: the answer How to make a transgenic organism
Alexey Shipunov Minot State University March 30, 2012 Outline Questions and answers Outline Questions and answers Questions and answers Previous final question: the answer How to make a transgenic organism
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Lipid Rafts: Bringing Order to Chaos
 JLR Papers In Press. Published on February 1, 2003 as Manuscript R200021-JLR200 Lipid Rafts: Bringing Order to Chaos Linda J. Pike, Ph.D. Washington University School of Medicine Dept. of Biochemistry
JLR Papers In Press. Published on February 1, 2003 as Manuscript R200021-JLR200 Lipid Rafts: Bringing Order to Chaos Linda J. Pike, Ph.D. Washington University School of Medicine Dept. of Biochemistry
The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7)
 The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7) Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water Aaaah, one of those structure
The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7) Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water Aaaah, one of those structure
04_polarity. The formation of synaptic vesicles
 Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
membranes membrane functions basic structure membrane functions chapter 11-12
 membranes chapter - membrane functions Ca + hormone IP H + HO compartmentalization intracellular compartments scaffold for biochemical activities organize enzymes selectively permeable membrane allows
membranes chapter - membrane functions Ca + hormone IP H + HO compartmentalization intracellular compartments scaffold for biochemical activities organize enzymes selectively permeable membrane allows
Chapter 5: Cell Membranes and Signaling
 Chapter Review 1. For the diagram below, explain what information you would use to determine which side of the membrane faces the inside of the cell and which side faces the extracellular environment.
Chapter Review 1. For the diagram below, explain what information you would use to determine which side of the membrane faces the inside of the cell and which side faces the extracellular environment.
Introduction and protein sorting
 Introduction and protein sorting Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids (50% of mass of plasma membranes, 30% of mitochondrial membranes, 80% of myelin
Introduction and protein sorting Membrane proteins Major components of cells Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids (50% of mass of plasma membranes, 30% of mitochondrial membranes, 80% of myelin
The Amyloid Precursor Protein Has a Flexible Transmembrane Domain and Binds Cholesterol
 The Amyloid Precursor Protein Has a Flexible Transmembrane Domain and Binds Cholesterol Science 336, 1171 (2013) Coach Prof. : Dr. Chung-I Chang Sit-in Prof.: Dr. Wei Yuan Yang Presenter: Han-Ying Wu Date:
The Amyloid Precursor Protein Has a Flexible Transmembrane Domain and Binds Cholesterol Science 336, 1171 (2013) Coach Prof. : Dr. Chung-I Chang Sit-in Prof.: Dr. Wei Yuan Yang Presenter: Han-Ying Wu Date:
Lipids: Membranes Testing Fluid Mosaic Model of Membrane Structure: Cellular Fusion
 Models for Membrane Structure NEW MODEL (1972) Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer & Nicholson Lipids form a viscous, twodimensional solvent into which proteins are inserted and integrated more or less
Models for Membrane Structure NEW MODEL (1972) Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer & Nicholson Lipids form a viscous, twodimensional solvent into which proteins are inserted and integrated more or less
AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes. Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment.
 Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Chapter 9 - Biological Membranes www.gsbs.utmb.edu/ microbook/ch037.htmmycoplasma Membranes form a semi-permeable boundary between a cell and its environment. Membranes also permit subcellular organization
Biology 4410 First Examination Version B
 Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition. phospholipids. Sphingolipids. Cholesterol. db=books&itool=toolbar
 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11
 1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
Cells: The Living Units
 Cells: The Living Units Introduction Life in general occurs in an aqueous environment All chemical processes essential to life occur within the aqueous environment of the cell and surrounding fluids contained
Cells: The Living Units Introduction Life in general occurs in an aqueous environment All chemical processes essential to life occur within the aqueous environment of the cell and surrounding fluids contained
Cholesterol modulates amyloid beta peptide 1-42 channel formation in planar lipid membranes
 Cholesterol modulates amyloid beta peptide 1-42 channel formation in planar lipid membranes Meleleo D., Notarachille G., Gallucci E. and Micelli S. Dept. Farmaco-Biologico, Università degli Studi di Bari,
Cholesterol modulates amyloid beta peptide 1-42 channel formation in planar lipid membranes Meleleo D., Notarachille G., Gallucci E. and Micelli S. Dept. Farmaco-Biologico, Università degli Studi di Bari,
Biomembranes structure and function. B. Balen
 Biomembranes structure and function B. Balen All cells are surrounded by membranes Selective barrier But also important for: 1. Compartmentalization 2. Biochemical activities 3. Transport of dissolved
Biomembranes structure and function B. Balen All cells are surrounded by membranes Selective barrier But also important for: 1. Compartmentalization 2. Biochemical activities 3. Transport of dissolved
Lecture 1, Fall 2014 The structure of the eukaryotic cell, as it relates to cells chemical and biological functions.
 Lecture 1, Fall 2014 The structure of the eukaryotic cell, as it relates to cells chemical and biological functions. There are several important themes that transcends just the chemistry and bring the
Lecture 1, Fall 2014 The structure of the eukaryotic cell, as it relates to cells chemical and biological functions. There are several important themes that transcends just the chemistry and bring the
Biology 4410 First Examination Version B
 Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Lipid-dependent Targeting of G Proteins into Rafts*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 275, No. 3, Issue of January 21, pp. 2191 2198, 2000 2000 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Lipid-dependent
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 275, No. 3, Issue of January 21, pp. 2191 2198, 2000 2000 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Lipid-dependent
What do you remember about the cell membrane?
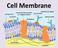 Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
 LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
Lipidne mikrodomene. funkcija
 Lipidne mikrodomene funkcija 1 Cellular processes involving lipid rafts - Signal transduction - Protein and lipid trafficking and sorting - Endosome(clathrin)-independent endocytosis: - potocytosis and
Lipidne mikrodomene funkcija 1 Cellular processes involving lipid rafts - Signal transduction - Protein and lipid trafficking and sorting - Endosome(clathrin)-independent endocytosis: - potocytosis and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Membrane Domains and the Lipid Raft Concept
 Send rders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae 4 Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2013, 20, 4-21 Membrane Domains and the Lipid Raft Concept S. Sonnino and A. Prinetti* Department of Medical Biotechnology
Send rders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae 4 Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2013, 20, 4-21 Membrane Domains and the Lipid Raft Concept S. Sonnino and A. Prinetti* Department of Medical Biotechnology
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
2
 1 2 What defines all living systems is the ability to generate a chemical environment inside the cell that is different from the extracellular one. The plasma membrane separates the inside of the cell
1 2 What defines all living systems is the ability to generate a chemical environment inside the cell that is different from the extracellular one. The plasma membrane separates the inside of the cell
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson
 Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
