WOUND MANAGEMENT. HOW WOUNDS HEAL And Why Some Don t Heal Quality Pharmacy Training Chronic Wound Delayed Healing 4/20/2017
|
|
|
- Jodie Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WOUND MANAGEMENT Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences HOW WOUNDS HEAL And Why Some Don t Heal Quality Pharmacy Training 2017 Associate Professor Geoff Sussman Clayton Campus PRIMUM NON NOCERE The first thing, do no harm! "The Provision of the Appropriate Environment for Healing by both Direct and Indirect Methods Together with the Prevention of Skin Breakdown Sussman Geoff Sussman Austin & Repatriation Medical Centre Phases of Healing Inflammatory phase shortest phase bleeding clotting for haemostasis surrounding erythema, heat, pain (may not be infection) exudate manifest Destructive actions Phagocytosis protease destruction of tissue growth factor release Proliferative phase angiogenesis collagen deposition fibroblast activity contraction, granulation, epithelisation Maturation tensile strength develops may take many months Normal Wound Healing Acute tissue Platelet degranulation Release of GF injury Inflammation with influx of neutrophils and macrophages Kill Bacteria Release of Proteases from Neutrophils Activation of macrophages with release of cytokines and growth factors Debridement TNF and IL-1 Growth Factors Influx of Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells Collagen Synthesis Angiogenesis Scar formation, Epithelialization, Remodeling Mast BA & Schultz GS ( 1996 ) Repeated Trauma Local Tissue Ischemia Necrotic Tissue Heavy Bacterial Burden Tissue Breakdown Degrades ECM impaired cell migration impaired connective tissue deposition Degrades Growth Factors Chronic Wound Delayed Healing Prolonged Inflammation Stimulation of macrophage and neutrophils to wound bed Activation of macrophages with release of cytokines TNF and IL-1 WOUND MANAGEMENT TRADITIONAL THEORY 1. WOUNDS SHOULD BE KEPT CLEAN AND DRY SO THAT A SCAB FORMS OVER THE WOUND 2. WOUNDS SHOULD BE EXPOSED TO AIR AND SUNLIGHT AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE 3. WHERE TISSUE LOSS IS PRESENT THE WOUND SHOULD BE PACKED TO PREVENT SURFACE CLOSURE BEFORE THE CAVITY IS FILLED 4. WOUNDS SHOULD BE COVERED WITH A DRY DRESSING 3 Mast BA & Schultz GS (1996 ) Production MMPs and TIMPs 1
2 TRADITIONAL THEORY DISADVANTAGES MOIST WOUND MANAGEMENT GEORGE WINTER Nature 20/1/62 1. THE SCAB(DEHYDRATED EXUDATE AND DYING DERMIS) IS A PHYSICAL BARRIER TO HEALING THE DELAY BECAUSE EPIDERMAL CELLS CANNOT MOVE EASILY UNDER THE SCAB THERE MAY BE POOR COSMETIC RESULTS AND SCARRING. 2. EXPOSURE TO AIR REDUCES SURFACE TEMPERATURE OF THE WOUND AND DRIES THE WOUND CAUSING FURTHER DELAYS HEALING 3. GAUZE PACKING IMPAIRES THE QUALITY OF HEALING 4. THE DRESSING MAY ADHERE TO THE WOUND AND CAUSE TRAUMA WHEN IT IS REMOVED. FORMATION OF THE SCAB & THE RATE OF EPITHELIZATION OF SUPERFICIAL WOUNDS IN THE SKIN OF YOUNG DOMESTIC PIGS "THE DEMONSTRATION THAT A SIMPLE CHANGE IN PHYSICAL CONDITIONS AT THE WOUND SURFACE CAN HAVE SUCH A MARKED EFFECT ON THE RATE OF EPITHELIZATION,HAS AN IMPORTANT BEARING ON EXPERIMENTAL METHODS IN WOUND HEALING" EPITHELIZATION Under Normal(Dry) and Experimental(Moist) Conditions TIME -WOUND LENGTH EPIDERMIS (mm x 10-2) WINTER 1962 LENGTH SECTION (mm x 10-2) % EPIDERMIS DRY WOUNDS 1 DAYS 1 1,608 71, DAYS 7 26,212 77, DAYS 3 55,524 77, DAYS 9 77,902 78, Also at 9 and 11 days 100 MOIST WOUNDS 1 DAY 2 11,327 66, DAYS 8 77,598 78, DAYS 4 71,721 71, Also at 7,9 and 11 days 100 MOIST WOUND MANAGEMENT HINMAN C.D et AL Nature 26/10/63 EFFECT OF AIR EXPOSURE AND OCCLUSION ON EXPERIMENTAL HUMAN SKIN WOUNDS "MOST OCCLUDED SPECIMENS SHOWED SO MUCH MORE EPITHELIZATION THAN THE AIR-EXPOSED WOUNDS THAT THE DIFFERENCE WAS OBVIOUS WITHOUT BENEFIT OF MEASUREMENT" "EXPERIMENTAL SPLIT SKIN WOUNDS IN HUMAN VOLUNTEERS,RE-EPITHELIZATION WAS MORE RAPID IN THE OCCLUDED THAN IN THE AIR-EXPOSED CONTROL." EPITHELIZATION DAY SUBJECT WOUND No and GROUP TOTAL LENGTH SECTION TOTAL NEW EPIDERMIS % NEW GROWTH 3 DAYS A 51 E* 17,599 2, O# 5,693 1, B 53 E 22,656 2, O 12,411 5, C 116 E 8,902 1, O 6,639 1, D 120 E 7,960 1, O 1,942 1, DAYS E E 3,509 1, O 3,746 1, C 118 E 5, O 2,551 1, D E 2, O 2,730 1, [mmx10-2] [mmx10-2] *,CONTROL AIR EXPOSED #,OCCLUDED HINMAN
3 Wound Management Aims Maintain moist wound environment Control exudate and debris -moisture management (absorb/donate) -facilitate autolytic debridement -physically/chemically debride Maintain/improve circulation Insulate and protect Wound Bed Preparation Debridement Bacterial Balance Exudate Management? 3
4 Edge of wound TIME acronym Tissue Moisture imbalance Inflammation Infection Developed by the International Advisory Board on Wound Bed Preparation, 2002/3 Goal to describe the observable characteristics of chronic wounds within the framework of the scientific basis of Wound Bed Preparation Schultz GS, Sibbald RG, Falanga V, et al. Wound bed preparation: a systematic approach to wound management. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2003; 11:1 28 Biofilms impacted both T & I components Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) impacted T I and M components New topical dressings impacted I component silver new antiseptic dressings -PHMB DNA-based identification of bacteria impacted I Diagnostics for proteases impacted E Major Developments last 10 years What has changed? Reintroduction of traditional non-surgical debridement methods (i.e. larval, enzymatic) New debridement methods (i.e. hydrosurgery, ultrasound) NPWT in combination with debridement and instillation of antiseptic solutions T: Tissue IWII Curriculum E+08 1.E+07 1.E+06 1.E+05 1.E+04 1.E+03 1.E+02 1.E+01 1.E+00 CFU / 5mm Biopsy Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01 SA35556 Staphylococcus aureus Larval Debridement Therapy Before treatment Before treatment After 24hr treatment L. Cowan, J. Stechmiller, P. Phillips, Q.P. Yang and G. Schultz. Chronic Wounds, Biofilms and Use of Medicinal Larvae, Ulcers, Article ID , 7 pages;
5 What has changed? I: Infection & Inflammation What has changed? E: Edge Greater understanding of the different effects of antibiotics on planktonic and biofilm bacteria in wounds New developments in our understanding of how antimicrobial agents work (i.e. PHMB, iodine, honey, silver-containing dressings) Tobramycin rapidly kills planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa ( ) very effectively, but is not effective against biofilm Pseudomonas ( ). Costerton, Sci Am, 2001 The importance of accurate wound measurement is critical in relation to the other clinical actions of TIME E should also represent evaluation, using assessment tools and adjunctive therapies If E also represents evaluation Expanding: TIME Then we should expand our focus outwards from the wound to consider the wellbeing and quality of life of the patient The TIME acronym should not just focus on the wound bed A more holistic approach is needed TIME should be considered in relation to the patient, healing and therapeutic services environments TIME: expanding Patient the environment focus Epithelial edge Extending TIME Holistically Tissue debridement Wound bed preparation Moisture balance Inflammation Infection Surrounding skin Therapeutic services environment Cost benefit & QoL issues Holistic & systemic evaluation Healing environment D. Leaper and D. Smith Wound Needs Wound Needs 5
6 Cardiovascular Decreased vascular elasticity Coronary blood flow and cardiac output Peripheral vascular resistance Gastrointestinal Protein synthesis by liver Teeth, saliva taste sensation Gut innervation & peristalsis Blood is less efficiently pumped around the body therefore possible problems of oxygen supply to tissues Protein metabolism may cause protein deficiencies, no enjoyment in eating, all food tastes the same, ability to digest is slow so often they complain of always feeling full and so not interested in food. Genitourinary Nephrons and renal blood flow Bladder strength and capacity Glomerular filtration rate Continence issues, so they do not want to drink as much fluid as we would like and regularly suffer from bladder/renal infections, which make them very unwell and at risk of other problems. Also when incontinent urine may contaminate lower leg dressings. Pulmonary Elasticity of lungs and chest wall Alveoli, capillaries, cilia Vital capacity Poor lung capacity means they may have poor oxygen supply to the tissues and thus wound. Musculoskeletal Muscle power and coordination Erosion and ossification of joints Thinner muscle fibres Nervous Vision and hearing acuity Skeletal reflex time & pain threshold Neural control of circulation and velocity of nerve impulse conduction Decreased strength means less energy, lack of exercise means poorer oxygenation of tissues and again possibly the wound. With these changes 6
7 Immunologic Delayed hypersensitivity reaction T-cell and antibody responses Autoantibodies This means the elderly patient is at more risk of infection, but also more prone to sensitivities. Factors What influences wound healing in a negative way? Intrinsic Factors Affecting Healing HEALTH STATUS Circulation :- Arterial & Venous Anaemia IMMUNE FUNCTION Normal Immune Function help cleansing the wound CO-MORBIDITIES Diabetes, RA & other Diseases will impact on wound Healing Intrinsic Factors Affecting Healing AGE FACTORS Skin changes with Age Loss of Hair Follicles, Blood Supply Fragility, Loss of Sebaceous Glands, Receptors Skin become dry, Tissue-paper thin Intrinsic Factors Affecting Healing NUTRITIONAL STATUS Balanced diet Protein {Arginine}, Carbohydrates, Fats, Fluid Essential :- Vitamins A,B, K and C Minerals :- Iron, Copper and Zinc Extrinsic Factors Affecting Healing MECHANICAL STRESS Pressure Friction Shearing Forces 7
8 Extrinsic Factors Affecting Healing DEBRIS Slough, Necrotic Tissue, Eschar, Scab, Dressing Residue, Sutures Extrinsic Factors Affecting Healing DESICCATION If the wound Surface dries the Surface cells die MACERATION Excess Moisture will retard Healing and damage periskin TEMPERATURE The Body needs about 37 o Typical Leg Ulcer Note Maceration to the peri-skin Extrinsic Factors Affecting Healing INFECTION Will Retard Healing CHEMICAL STRESS Topical Agents may have a -ve effect on the wound and Cells e.g. Antiseptics OTHER FACTORS Smoking Radio-therapy Alcohol Drugs Typical Infected Leg Ulcer Note Erythema Drugs and Wound Healing Negative effects Prednisolone and other steroids Oral/systemic steroids Topical steroids NSAIDs Antibiotics (topical) Anti-neoplastics Hydroxyurea Positive effects Haemorrheologics (Pentoxifylline) Retinoids Phenytoin Antibiotics (Oral/systemic) 8
9 Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing - Corticosteroids Drugs in this class include prednisolone, prednisone, hydrocortisone, etc Inhibit nearly every aspect of wound healing! Inhibit acute wound healing only when given prior to or immediately after injury Due to inhibition of inflammatory phase Inhibit initial increase in vascular permeability and vasodilation (normal post trauma) due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing - Corticosteroids Chronic wounds During inflammatory phase - macrophages Affects chemotaxis and proliferation of fibroblasts collagen production, inhibition of angiogenesis Reduce wound contraction during proliferative phase due to effects on fibroblasts Inhibit epithelial migration, poor quality tissue Decreased tensile strength of healed tissue in maturation phase Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing - Corticosteroids Chronic wounds Immune system effects (immunosppressive) susceptibility to infection chemotaxis and proliferation of T lymphocytes protein synthesis (modulation of gene transcription) - TGF-ß (cytokine involved with broad range of wound repair activities) Complex and detailed events more details in: Roberts, A. and Sporn, M. Transforming Growth Factor- ß in Clark, R. (Ed), The Molecular and Cellular Biology of Wound Repair, (2 nd edition), Plenum Press, New York, 1996 Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing - Corticosteroids Topically applied steroids used to treat Eczema or other dermatologic conditions Will cause vascoconstriction at the edge of a Wound if inadvertently applied. Caution should be used to separate the wound edge from the product used to treat the skin rash. Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing Antineoplastic drugs General points about antineoplastics Cytotoxic - not cancer cell-specific Range of classes and pharmacological actions generally exert effect on rapidly replicating cells ire cancer cells Wound cells may be replicating more rapidly than normal cells and so at risk Risk of extravasation injury Haematological changes may affect healing Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing Antineoplastic drugs Specific points about antineoplastics Haematological changes may affect healing Impact Red Blood Cells ( most) Impact White Blood Cells ( most) Myelosupression ( most) Neurotoxic (cis-platinum, Vinblastine, Vincristine, Carboplatin, Vindesine, Hexamethylamine) 9
10 Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing Antineoplastic drugs Hydroxyurea (Hydrea ) Non-nucleoside anti-metabolite Associated with causation of ulcers, esp malleolar, with long term use or high doses Lichenoid eruptions called hydroxyurea dermopathy after long periods of therapy Damage basal keratinocytes leading to dermal atrophy Platelet mediated inflammatory response leading to micro-thrombi formation Tobacco - a major cause of death Tobacco causes more illness and death than any other drug. In the financial year , 14,900 people died from smoking related diseases; around 89% of all drug caused deaths. Research estimates that one in two lifetime smokers will die from a disease caused by their smoking. Every year around 3,940 Victorians die from diseases caused by smoking Smoking Cigarettes are not the simple mixtures of tobacco leaves they appear to be. They are in fact very complex products containing an estimated 4000 chemicals. 43 carcinogens have been identified in tobacco smoke. Some of the major chemicals in cigarette smoke include Tar Nicotine Carbon Monoxide Hydrogen Peroxide Metals (eg. nickel, arsenic and cadmium) Radioactive compounds Agricultural chemicals and additives Smoking What is less well understood is the effect of smoking on wound healing. It was Mosley and Finseth in 1977 who concluded in their published study that cigarette smoking impairs Digital blood flow and wound healing. Mosley LH, Finseth F. Cigarette smoking:impairment of digital blood flow and wound healing in the hand. HAND 1977;9: Smoking The following year Mosley,Finseth &Goody showed, in an experimental animal model, that Nicotine systemically administered impairs Wound Healing. Since then a number of papers have been published demonstrating the negative effects on wound healing of cigarette smoking. Nicotine is a cutaneous vasoconstrictor this action is achieved by the release of adrenal and peripheral catecholamines, which also increases heart rate, blood pressure and oxygen demand. Nicotine also increases platelet adhesiveness increasing the risk of micro-vascular occlusion and tissue ischemia 10
11 As a result of this reduced blood flow there is a reduction in the flow of nutrients to the wound and a lower oxygen level. Nicotine will diminish red blood cells, fibroblast and macrophages. The red blood cells are essential in the transport of oxygen to the tissues via hemoglobin. The macrophages are involved in phagocytosis of the wound by removing bacteria that have the potential of resultant infection in the wound. Nicotine from smoking reaches the brain and muscle tissue soon after being inhaled resulting in: Increased heart rate (Pulse) Increased blood pressure and slowing of circulation in smaller vessels. Combined with vasoconstriction lowers skin temperature Nicotine can both relax skeletal muscles and increase muscle tension eg. Increase hand tremor after smoking Nicotine stomach secretions & changes brain activity Carbon monoxide has an affinity for haemoglobin 200 times that of oxygen. This will have a major effect in decreasing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the hemoglobin subsequently reducing the amount of oxygen available to the tissues. The combination of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin result in carboxyhemoglobin instead of oxy-hemoglobin. It will also lead to cellular hypoxia and impact on wound healing. The lack of oxygen will then contribute to the lack of collagen deposition, as oxygen is essential for the hydroxylation of proline. to ultimately produce collagen. Carbon Monoxide is quickly absorbed into the Blood reducing the capacity to carry oxygen. Passive smoking has the same effect. This results in a need for more effort to achieve the same physical result as in non-smokers, The heart must work harder for the same effect, especially when doing rigorous exercise. Studies have shown levels of CO in the blood of a 20 a day smoker can impair vision, perception of time and coordination. Hydrogen cyanide inhibits enzyme-systems necessary for oxygen transport at the cellular level. as well as oxidative metabolism. Once again the additive affect on the transport of oxygen to the tissue as with carbon monoxide will impact on wound healing. Without the availability of adequate amounts of oxygen cellular hypoxia will occur impacting of the ability of tissue to heal. 11
12 Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing Nicotine- Direct effects A study by Roseby Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne examined the effects of one cigarette on a group of young smokers who had not smoked for 12 hours. The tests studied pre and post one cigarette were: Blood Pressure, Lung Function, Carbon Monoxide in the Lungs, Laser Doppler arterial circulation, Muscle Tension Hand Tremor Error Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing Nicotine- Direct effects Test Area Pre-Smoking Post-Smoking Blood Pressure 110/70 135/85 Lung Function Normal Abnormal Carbon Monoxide in the Lungs 1 PPM 16 PPM Laser Doppler arterial circulation Muscle Tension Hand Tremor Error % 14.37% Roseby Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Roseby Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Conclusion Smoking and Tissue are incompatible Smoking is one of the major factors for non-healing wounds. I know it is not always simple however it is Essential that your patients be encouraged to quit smoking it will require an extreme Effort on all parties But it is worth it in the end Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing - Anti-platelet drugs Class includes Aspirin and other NSAIDs Inhibits inflammatory response and acid mucopolysaccharide synthesis in wounds Inhibit inflammatory mediators derived from arachidonic acid metabolism and platelet aggregation Inhibition of Cox-1 by NSAIDS could increase the local ischaemia and hypoxia associated with chronic venous ulcers Abd-El-Aleem et al 2001 Drugs with a negative effect on wound healing - Anti-platelet drugs Impact of COX-II inhibitors is unclear Reduction of scar formation Wilgus et al 2003 without disrupting epithelialization Delay gastric ulcer healing Baatar et al 2001 Reduced Ligament repair and strength in surgically incised medial collateral ligament in 50 SD rats half treated post op with a Cox-2 inhibitor when compared with the non-treated rats a 32% lower load to failure. Elder et al Delayed re-epithelialization in the early phase of wound healing Inhibition of angiogenesis Futagami et al 2002 Drugs with a negative effect on Wound Healing Anti-coagulants These Drugs are used to reduce blood viscosity and include Warfarin and Heparin. They inhibit proper coagulation and can adversely affect wounds by increasing the risk of haematomas and seroma formation. They can cause tissue necrosis purple toe syndrome There is some evidence of risk in terms of wound healing. 12
13 Sometimes we don t get what we expect 13
Wound Healing Basic Concept
 Department of Orthopaedic & Traumatology The Chinese University of Hong Kong Wound Healing Basic Concept Dr TSE Lung Fung ( 謝龍峰醫生 ) MBChB(CUHK),FRCS(Edin),FRCSEd(Orth),FHKCOS,FHKAM(Ortho) Tissue Damage
Department of Orthopaedic & Traumatology The Chinese University of Hong Kong Wound Healing Basic Concept Dr TSE Lung Fung ( 謝龍峰醫生 ) MBChB(CUHK),FRCS(Edin),FRCSEd(Orth),FHKCOS,FHKAM(Ortho) Tissue Damage
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment
 Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
After this presentation and discussion, the participants should be able to:
 Tissue Repair Robert F. Diegelmann, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After this presentation and discussion, the participants should be able to: 1. Define the biochemical responses to tissue injury 2. Describe the mechanisms
Tissue Repair Robert F. Diegelmann, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After this presentation and discussion, the participants should be able to: 1. Define the biochemical responses to tissue injury 2. Describe the mechanisms
Hemostasis Inflammatory Phase Proliferative/rebuilding Phase Maturation Phase
 The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Wound Care in the Community. Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts
 Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
RN Cathy Hammond. Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch
 RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
Mechanisms of disease
 PP Mechanisms of disease Stress and disease Homeostasis - Responsible for maintaining a constant, safe internal environment - Controlled by feedback loops o Negative feedback loop: temperature, blood glucose
PP Mechanisms of disease Stress and disease Homeostasis - Responsible for maintaining a constant, safe internal environment - Controlled by feedback loops o Negative feedback loop: temperature, blood glucose
Disclosures for Tarik Alam. Wound Bed Preparation. Wound Prognosis. Session Objectives. Debridement 4/26/2015
 Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice BY Christine Pearson Christine Pearson, RN, IIWCC, is a wound clinician for Vancouver Coastal Health and has worked in
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice BY Christine Pearson Christine Pearson, RN, IIWCC, is a wound clinician for Vancouver Coastal Health and has worked in
We will dose your Gentamycin. We will dose your Vancomycin
 We will dose your Gentamycin We will dose your Vancomycin We will dose your Heparin We will dose your Warfarin We will do your wound care Animal models show that wounds, including chronic wounds, heal
We will dose your Gentamycin We will dose your Vancomycin We will dose your Heparin We will dose your Warfarin We will do your wound care Animal models show that wounds, including chronic wounds, heal
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds
 Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS
 WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
SAMPLE. HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care. Learner resource. HLT07 Health Training Package. Version 2
 HLT07 Health Training Package HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care Learner resource Version 2 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Acknowledgments The TAFE NSW Training and Education
HLT07 Health Training Package HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care Learner resource Version 2 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Acknowledgments The TAFE NSW Training and Education
Skin Integrity and Wound Care
 Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED
 WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
Surgical Wounds & Incisions
 Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
Galen ( A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing
 Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Tissue repair. (3&4 of 4)
 Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Venous. Arterial. Neuropathic (e.g. diabetic foot ulcer) Describe Wound Types & Stages of. Pressure Ulcers. Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care
 A dressing the situation at hand Describe Wound Types & Stages of Pressure Ulcers Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care Goals Clarify Referral Protocol Lacerations- The goal is nearest to complete approximation
A dressing the situation at hand Describe Wound Types & Stages of Pressure Ulcers Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care Goals Clarify Referral Protocol Lacerations- The goal is nearest to complete approximation
Healing & Repair. Tissue Regeneration
 Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice.
 Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Fundamentals Of Wound Management. Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse
 Fundamentals Of Wound Management Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse Wound Management What are we trying to achieve? Maintaining a controlled set of local conditions that is able to sustain the
Fundamentals Of Wound Management Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse Wound Management What are we trying to achieve? Maintaining a controlled set of local conditions that is able to sustain the
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey
 Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
WOUND CARE UPDATE. -Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products For Wound. -Total Contact Casting. Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C. ped.
 WOUND CARE UPDATE -Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products For Wound Closure -Total Contact Casting Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C. ped. Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products for Wound Closure why are they
WOUND CARE UPDATE -Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products For Wound Closure -Total Contact Casting Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C. ped. Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products for Wound Closure why are they
DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED
 10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
Wound Healing: General Principles. Mansour Dib MD
 Wound Healing: General Principles Mansour Dib MD Normal Wound Healing Chronic Wounds: Stuck Where does it get stuck? Mostly Proliferation Sometimes Remodeling Why? Systemic factors Local factors How do
Wound Healing: General Principles Mansour Dib MD Normal Wound Healing Chronic Wounds: Stuck Where does it get stuck? Mostly Proliferation Sometimes Remodeling Why? Systemic factors Local factors How do
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
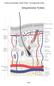 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected dressings enhance the body s ability to heal the wound. Progression Towards Healing
 Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Wound Management. E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP
 Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE
 SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
ULCERS 1/12/ million diabetics in the US (2012) Reamputation Rate 26.7% at 1 year 48.3% at 3 years 60.7% at 5 years
 Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use!
 I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use! Introduction: Originating from battlefield medicine much of what we use today is an evolution of material science combined with our understanding
I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use! Introduction: Originating from battlefield medicine much of what we use today is an evolution of material science combined with our understanding
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types. Summary
 Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Understanding Debridement
 Understanding Debridement Figure 1. Wound Healing Process Wound Blood Clot Blood Blood Vessel Fat Tissue The wound in the skin exposes deep tissue layers to the air. Scab Scab Exudate Granulation Tissue
Understanding Debridement Figure 1. Wound Healing Process Wound Blood Clot Blood Blood Vessel Fat Tissue The wound in the skin exposes deep tissue layers to the air. Scab Scab Exudate Granulation Tissue
dr. Elida Ilyas, SpRM
 dr. Elida Ilyas, SpRM INTRODUCTION Skin is a complex organ whose basic function is holocrine secretion for it self Being composed of epidermis and dermis Its 20.000 cm square of surface in an adult and
dr. Elida Ilyas, SpRM INTRODUCTION Skin is a complex organ whose basic function is holocrine secretion for it self Being composed of epidermis and dermis Its 20.000 cm square of surface in an adult and
DEBRIDEMENT. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment. Michelle Greenwood. Lorraine Grothier. Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust
 Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know?
 Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know? Laura Owen European Specialist in Small Animal Surgery Lecturer in Small Animal Surgery, University of Cambridge The Acute Open Wound PPE
Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know? Laura Owen European Specialist in Small Animal Surgery Lecturer in Small Animal Surgery, University of Cambridge The Acute Open Wound PPE
Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development
 Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR
 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
The Risk. Background / Bias. Integrating Wound Care into a Limb Preservation Initiative 4/24/2009
 Stimulating Wound Granulation: Advances in NPWT and other Measures (Wound Bed Preparation) Charles Andersen MD, FACS, FAPWCA Clinical Prof of Surgery UW, USUHS Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation
Stimulating Wound Granulation: Advances in NPWT and other Measures (Wound Bed Preparation) Charles Andersen MD, FACS, FAPWCA Clinical Prof of Surgery UW, USUHS Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation
Chapter 7 Wound Healing
 Chapter 7 Wound Healing 長庚皮膚科 2015.12.11 R2 劉人鳳 CHAPTER SUMMARY Wound healing occurs in orderly, overlapping phases: the inflammatory, the proliferative, and the remodeling phases. The depth of the wound
Chapter 7 Wound Healing 長庚皮膚科 2015.12.11 R2 劉人鳳 CHAPTER SUMMARY Wound healing occurs in orderly, overlapping phases: the inflammatory, the proliferative, and the remodeling phases. The depth of the wound
Prontosan. Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing
 Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Four Types of Vertebrate Tissue
 BIO 121 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture Section IV A. Cells in the Context of Tissue, Organ and Organismal Architecture B. Wound Healing Four Types of Vertebrate Tissue 1.Epithelium 2.Connective Tissue
BIO 121 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture Section IV A. Cells in the Context of Tissue, Organ and Organismal Architecture B. Wound Healing Four Types of Vertebrate Tissue 1.Epithelium 2.Connective Tissue
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT
 TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
Acute and Chronic WOUND ASSESSMENT. Wound Assessment OBJECTIVES ITEMS TO CONSIDER
 WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management
 Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM. Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS
 BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Contamination Presence of non-replicating microorganisms on the wound surface that evoke no clinical host response - All
BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Contamination Presence of non-replicating microorganisms on the wound surface that evoke no clinical host response - All
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation
 Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
We look forward to serving you.
 ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
Foam dressings have frequently
 The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
Acute Soft Tissue Injuries
 Acute Soft Tissue Injuries Classic Soft-Tissue Injury Response Sequence: v inflammatory phase v proliferative phase v maturation phase Inflammation v pathologic process consisting of dynamic complex of
Acute Soft Tissue Injuries Classic Soft-Tissue Injury Response Sequence: v inflammatory phase v proliferative phase v maturation phase Inflammation v pathologic process consisting of dynamic complex of
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 46 Caring for Clients with Burns Types of Burns Thermal Dry heat flame Moist heat steam or hot liquid
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 46 Caring for Clients with Burns Types of Burns Thermal Dry heat flame Moist heat steam or hot liquid
Understanding and Managing
 Understanding and Managing MM s in Wound Bed Brock Liden DM, ABM, FAWCA Learning Objectives Review the four sequential phases of normal wound healing and recognize the BENEFICIAL effects of CONTROLLED
Understanding and Managing MM s in Wound Bed Brock Liden DM, ABM, FAWCA Learning Objectives Review the four sequential phases of normal wound healing and recognize the BENEFICIAL effects of CONTROLLED
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Biofilm and Advanced Wound Management Strategies
 Biofilm and Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org 1 Objectives What are Biofilms How Biofilms
Biofilm and Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org 1 Objectives What are Biofilms How Biofilms
Making the Most of your Dressing Products Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE
 Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
Emerging Use of Topical Biologics in Limb Salvage Role of Activated Collagen in Multimodality Treatment
 9 th Annual New Cardiovascular Horizons New Orleans September 12, 2008 Emerging Use of Topical Biologics in Limb Salvage Role of Activated Collagen in Multimodality Treatment Gary M. Rothenberg, DPM, CDE,
9 th Annual New Cardiovascular Horizons New Orleans September 12, 2008 Emerging Use of Topical Biologics in Limb Salvage Role of Activated Collagen in Multimodality Treatment Gary M. Rothenberg, DPM, CDE,
Wound Jeopardy: Name That Wound Session 142 Saturday, September 10 th 2011
 Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products Version 9 March 2018 Surgical Dressing Manufacturers Association 2018 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Wound Dressings Swabs Taping Traditional Wound
Venous Leg Ulcers. Care for Patients in All Settings
 Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
Advanced Wound Care. Cut Shape Innovate
 Advanced Wound Care Cut Shape Innovate Vacutex incorporates a patented three layer construction of poly-cotton elements that promotes an accelerated capillary action on wound interfaces. Effectively lifting,
Advanced Wound Care Cut Shape Innovate Vacutex incorporates a patented three layer construction of poly-cotton elements that promotes an accelerated capillary action on wound interfaces. Effectively lifting,
Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell
 Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell Objectives Identify the stages of pressure ulcer according to the depth of tissue destruction. Discuss the differences
Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell Objectives Identify the stages of pressure ulcer according to the depth of tissue destruction. Discuss the differences
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Spinal Cord Injury Info Sheet An information series produced by the Spinal Cord Program at GF Strong Rehab Centre.
 Spinal Cord Injury Info Sheet An information series produced by the Spinal Cord Program at GF Strong Rehab Centre. What does skin do? 1. It protects you. 2. It provides sensory information. 3. It helps
Spinal Cord Injury Info Sheet An information series produced by the Spinal Cord Program at GF Strong Rehab Centre. What does skin do? 1. It protects you. 2. It provides sensory information. 3. It helps
MANAGEMENT OF LEG WOUNDS/ULCERS WITH HONEY. Ms. Irny Hidaya Binte Muhammad Raffles Hospital Nurse Clinician (Wound Care)
 MANAGEMENT OF LEG WOUNDS/ULCERS WITH HONEY Ms. Irny Hidaya Binte Muhammad Raffles Hospital Nurse Clinician (Wound Care) Outline: Normal Phases of Wound Healing Wound Infection Continuum Non-healing wounds
MANAGEMENT OF LEG WOUNDS/ULCERS WITH HONEY Ms. Irny Hidaya Binte Muhammad Raffles Hospital Nurse Clinician (Wound Care) Outline: Normal Phases of Wound Healing Wound Infection Continuum Non-healing wounds
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Advazorb. Hydrophilic foam dressing range
 Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Scott E. Palmer, V.M.D. Diplomate, A.B.V.P., Eq. Practice New Jersey Equine Clinic
 Scott E. Palmer, V.M.D. Diplomate, A.B.V.P., Eq. Practice New Jersey Equine Clinic spalmer@njequine.com Hemostasis Inflammation Proliferation Remodeling Inflammation Matrix production Angiogenesis Epithelialization
Scott E. Palmer, V.M.D. Diplomate, A.B.V.P., Eq. Practice New Jersey Equine Clinic spalmer@njequine.com Hemostasis Inflammation Proliferation Remodeling Inflammation Matrix production Angiogenesis Epithelialization
Type of Injury & Repair. Wound Healing 10/6/2009. Complex and dynamic process. Wound location influences healing. Surgical Incisions.
 Wound Healing & Wound Healing Complex and dynamic process Results in restoration of anatomic continuity and function Need adequate nutrition, blood flow, and oxygen Type of Injury & Repair Surgical Incisions
Wound Healing & Wound Healing Complex and dynamic process Results in restoration of anatomic continuity and function Need adequate nutrition, blood flow, and oxygen Type of Injury & Repair Surgical Incisions
WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets
 AMERIGEL WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets P R O D U C T I N F O R M AT I O N MSDS APPLICATION PROTOCOLS AmeriGel WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets A HYDROGEL WITH A UNIQUE AUTOLYTIC DEBRIDER Diabetic
AMERIGEL WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets P R O D U C T I N F O R M AT I O N MSDS APPLICATION PROTOCOLS AmeriGel WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets A HYDROGEL WITH A UNIQUE AUTOLYTIC DEBRIDER Diabetic
Nonspecific Host Resistance. Counter attack (Specific Host Resistance) A. Nonspecific (Innate) Resistance (Page 362)
 Pages 361-382 Nonspecific Host Resistance 1. Introduction A. Resistance i. Resistance by defense Resistance by alliance Counter attack (Specific Host Resistance) B. Susceptibility 2. Resistance A. Nonspecific
Pages 361-382 Nonspecific Host Resistance 1. Introduction A. Resistance i. Resistance by defense Resistance by alliance Counter attack (Specific Host Resistance) B. Susceptibility 2. Resistance A. Nonspecific
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge. Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN
 Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN Projects and Posters These resources were developed by creative VA nurses who had no special
Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN Projects and Posters These resources were developed by creative VA nurses who had no special
What is histology? HISTOLOGY
 Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Embrace the Call to Wound Prevention and Care
 CONCLUSION Embrace the Call to Wound Prevention and Care A challenging career Be part of an interprofessional team Help patients, families, communities Commit to lifelong learning To cure occasionally,
CONCLUSION Embrace the Call to Wound Prevention and Care A challenging career Be part of an interprofessional team Help patients, families, communities Commit to lifelong learning To cure occasionally,
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing
 Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Innate vs Adaptive Response
 General Immunology Innate vs Adaptive Response Innate- non-specific (4 types of barriers) anatomic- ato mechanical ca (skin), ph, mucous, normal flora Physiologic- temperature, ph, chemicals (lysozyme,
General Immunology Innate vs Adaptive Response Innate- non-specific (4 types of barriers) anatomic- ato mechanical ca (skin), ph, mucous, normal flora Physiologic- temperature, ph, chemicals (lysozyme,
Managing Wounds. Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse
 Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
Managing Wounds Esther White Tissue Viability Nurse First things first.. Assess, measure and photograph Know what you re dealing with, look at anatomical position and the bigger picture to look for extra
Essential intervention No. 2 Wound management
 Essential intervention No. 2 Wound management Essential intervention No. 2 Wound management KEY OBJECTIVES To know the function of skin and understand the phases of normal tissue repair in the healing
Essential intervention No. 2 Wound management Essential intervention No. 2 Wound management KEY OBJECTIVES To know the function of skin and understand the phases of normal tissue repair in the healing
45 min. Name Assoc Prof presenter Bill McGuiness PhD, RN, FAWMA. xx College Month of 201x Science, Health & Engineering
 45 min Title Skin integrity of presentation the cellular level? Name Assoc Prof presenter Bill McGuiness PhD, RN, FAWMA Title Head of of presenter School School / of Faculty Nursing / Division & Midwifery
45 min Title Skin integrity of presentation the cellular level? Name Assoc Prof presenter Bill McGuiness PhD, RN, FAWMA Title Head of of presenter School School / of Faculty Nursing / Division & Midwifery
SDMA Categorisation of Wound Care and Associated Products
 Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
Version 7 - February 2015 TAPES AND TRADITIONAL DRESSINGS Traditional Wound Dressings Wound Dressings Packs Swabs Swabs Swab Products Adhesive Tapes Taping Sheets Absorbent Wadding Absorbent Dressings
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite
 Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Wound Dressing. Choosing the Right Dressing
 Wound Dressing Choosing the Right Dressing Benefits of using the correct Drsg Helps create the optimal wound environment Increases healing rates Reduces pain Decreases infection rates Cost effective Care
Wound Dressing Choosing the Right Dressing Benefits of using the correct Drsg Helps create the optimal wound environment Increases healing rates Reduces pain Decreases infection rates Cost effective Care
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Choosing an appropriate dressing for chronic wounds Denise Bell BSc, RGN and Dot Hyam RGN, DipHE
 Choosing an appropriate dressing for chronic wounds Denise Bell BSc, RGN and Dot Hyam RGN, DipHE Chronic wounds are nonhealing with a sometimes complex aetiology, and dressing such wounds can be difficult
Choosing an appropriate dressing for chronic wounds Denise Bell BSc, RGN and Dot Hyam RGN, DipHE Chronic wounds are nonhealing with a sometimes complex aetiology, and dressing such wounds can be difficult
New approach to the wounds by moist wound healing in Japan. Yoshihiko Mochizuki Japan
 New approach to the wounds by moist wound healing in Japan. Yoshihiko Mochizuki M.D. @Tokyo Japan What is the meaning of wound healing? I think there are two types of wound healing. 1. True healing moist
New approach to the wounds by moist wound healing in Japan. Yoshihiko Mochizuki M.D. @Tokyo Japan What is the meaning of wound healing? I think there are two types of wound healing. 1. True healing moist
7/2/2015 A.Shahrokhi 1
 7/2/2015 A.Shahrokhi 1 PRESSURE ULCER MANAGEMENT A.Shahrokhi,MSc Qazvin University of Medical Sciences 7/2/2015 A.Shahrokhi 3 Noticeable Facts Significant Prevalence 10% to 18% in acute care Cause of Death
7/2/2015 A.Shahrokhi 1 PRESSURE ULCER MANAGEMENT A.Shahrokhi,MSc Qazvin University of Medical Sciences 7/2/2015 A.Shahrokhi 3 Noticeable Facts Significant Prevalence 10% to 18% in acute care Cause of Death
Vacuumed Assisted Closure
 Vacuumed Assisted Closure Louise Morris Lead Nurse in Tissue Viability Jackie Stephen-Haynes Consultant Nurse and senior Lecturer in Tissue Viability 2009 Aims and Objectives To develop an awareness of
Vacuumed Assisted Closure Louise Morris Lead Nurse in Tissue Viability Jackie Stephen-Haynes Consultant Nurse and senior Lecturer in Tissue Viability 2009 Aims and Objectives To develop an awareness of
