SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU)
|
|
|
- Edwina Stevenson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting presentations and posters related to interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome and chronic pelviperineal pain, with studies presented on different methods of treating the pain aspect. Abstracts discussed sacral neuromodulation in IC/PBS patients as well as in patients suffering from both bowel and voiding problems; a study was presented on trying intravesical bupivacaine in IC/PBS patients who have failed to respond to intravesical lidocaine; there was a fascinating look at whether patients and their doctors are speaking the same language when it comes to LUTS terminology and what patients think the term urgency means; a study into the efficacy of using vaginal diazepam for pelvic floor dysfunction pain, IC and/or vulvar pain and much more besides. The full abstracts from this meeting can be found in Neurourology and Urodynamics, Volume 29, Issue 2, 2010 (DOI /nau). Below is a review of selected abstracts presented at SUFU in the field of IC/PBS and chronic pelviperineal pain. Poster# BS12 IMMUNIZATION WITH SELF UROPLAKIN II CAUSES AUTOIMMUNE CYSTITIS; NOVEL MURINE EXPERIMENTAL AUTOIMMUNE CYSTITIS MODEL. Altuntas CZ, Byrne LN, Sakalar C, Gulen MF, Bakhautdin E, Qin J, Li X, Tuohy VK, Daneshgari F. In this mouse study, the presenter explained that while we still know little about the pathophysiology of IC, it is hypothesized that defects in the urothelial cell layers may play a role and that an autoimmune mechanism may be involved. The aim of this basic science study was to examine whether immunizing mice to recombinant Uroplakin (rmupii) would provoke an autoimmune response to bladder urothelium that would be sufficient to create an IC phenotype in mice. The study showed a large immune response in mice immunized with UPII; this response is specific to bladder tissue. There was significant evidence of frequency with decreased volumes of urine voided in EAC (experimental autoimmune cystitis). It was concluded that further characterization of EAC should include evidence for pain and/or afferent hypersensitivity as well as evidence of urothelial cell layer damage. Poster# BS13 CATHETERIZING INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME (IC/PBS) PATIENTS FOR INTRAVESICAL INSTILLATION: DOES CATHETER SIZE MATTER? Ruzimovsky M, Rais-Bahrami S, Donlon K, Moldwin R. While IC/PBS patients often complain of urethral pain, they often require frequent catheterization for intravesical treatment. This prospective patient-blinded study with 30 male and female IC/PBS patients of varying ages and backgrounds examined whether the International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
2 size (diameter) of catheter use has an effect on the amount of pain felt by the patient during and after instillation treatments. All the patients had previously had multimodal treatment with at least two sessions of intravesical treatment. Two different sizes of catheter were used in the study - 10Fr and 16Fr - on two consecutive visits, two weeks apart. Before catheterization, on each visit lidocaine 2% gel was injected into the urethra. The pain was assessed on a scale of ) when the catheter was inserted into the urethra, 2) while the catheter was indwelling in the bladder and 3) immediately followed removal of the catheter. The results led to the conclusion that while the size of the catheter used for intravesical treatment appeared to have no impact on the amount of pain felt by the IC/PBS patient during the indwelling phase, a smaller size was tolerated better by some patients when inserted and also resulted in less pain immediately following withdrawal of the catheter. So this may be worth considering for some patients even though the differences were not really statistically significant. NB In practice, some patients who self-catheterize have in fact already been choosing to use smaller diameter catheters as they find this more comfortable. Poster# 1 THE IMPACT OF CHRONIC NEUROMODULATION ON CO-MORBID BOWEL SYMPTOMS IN PATIENTS WITH VOIDING DYSFUNCTION Peters KM, Killinger KA, Kangas JR, Boura JR. Many patients have coexisting bladder and bowel problems. The purpose of this prospective neuromodulation database study was to evaluate changes in bowel function in patients undergoing a staged neuromodulation procedure as a treatment for voiding symptoms. The enrolled patients had a history of IBS, constipation, diarrhoea or faecal incontinence and either overactive bladder with or without incontinence, IC/PBS or other disorder e.g. urinary retention. The patients received a tined lead at either the sacral or pudendal nerve, followed by generator implantation. It was concluded from the results that although bladder voiding improved as a result of the neuromodulation, improvement in bowel function was not so clear. More research is now needed to take a closer look at how neuromodulation can affect bowel symptoms that coexist with bladder disorders. Poster# 7 DOES BOWEL FUNCTION CHANGE IN IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME PATIENTS UNDERGOING NEUROMODULATION FOR VOIDING DYSFUNCTION? Peters KM, Killinger KA, Kangas JR, Boura JA. This study looked at the impact of staged neuromodulation on 35 female patients with voiding disorders but with coexisting IBS without faecal incontinence prior to starting neuromodulation. An evaluation was carried out of patients who had improvement in their bladder symptoms after placement of tined leads at the sacral or pudendal nerve and implantation with a permanent generator. Preliminary study data suggest that although voiding symptoms improved, changes in bowel function in IBS patients were less clear, although the average number of diarrhoea episodes per day improved more in sacral than pudendal neuromodulation. While some improvements were seen, more research is needed to explore this potential benefit of neuromodulation more fully. Poster# 12 BATTERY LONGEVITY AFTER SACRAL NEUROMODULATION Cameron AP, Anger JT, Madison R, Saigal CS, Clemens JQ. International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
3 Sacral neuromodulation is increasingly being used for patients who fail to respond to any medical treatment. The battery life is officially listed as being 7 years ( ) years. However, nobody knows how the batteries perform outside manufacturer trials and how many of these devices have to be removed due to inadequate functioning, damage or pain. Based on the results, it was concluded that while few sacral neuromodulation batteries are removed prematurely, IC patients are at very high risk of requiring removal of a battery due to pain or lack of efficacy of the device. Poster# 19 SACRAL NERVE ROOT NEUROMODULATION FOR THE TREATMENT OF INTRACTABLE PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME/INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (PBS/IC): 14 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF ONE CENTER Gajewski J, Al-Zahrani A. The purpose of this retrospective study from Canada with 78 PBS/IC patients ( ) was to evaluate long-term success and tolerability of the sacral neuromodulation (SNM) in the control of painful bladder syndrome/ interstitial cystitis (PBS/IC) symptoms. The researchers found that the presence of urgency was a very good predictor of long-term success. 28% of the devices were removed, mainly due to poor results. Revision rate was 50%, mainly due to lack of stimulation sensation and worsening of symptoms. It was concluded that SNM is an effective chronic treatment of PBS/IC and should be considered if all other medical treatment has failed and before any surgical intervention. While it may be described as safe, the revision rate in these patients is high and lifelong follow-up is necessary. Poster# 20 EFFICACY OF NEUROMODULATION FOR REFRACTORY INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Lenherr S, Smith G, Bresette J, Stoffel J. The aim of this retrospective study ( ) was to evaluate the efficacy of sacral neuromodulation (Interstim) for the treatment of 25 IC/PBS patients who had failed to respond to previous medical treatment. 23 patients went on to second stage implantation. On the basis of the results, it was concluded that in this series of patients neuromodulation for refractory IC/PBS demonstrated an initial statistical improvement in symptom and problem scores after second stage implantation. However, by 3 12 months the symptom scores returned to close to pre-operative baseline while problem scores remained improved. These findings now need to be validated in a large multi-institution study. Poster# 79 MENTAL DISTRESS PREDICTS PAIN SEVERITY, PHYSICAL IMPAIRMENT IN INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS AND CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN Baxter C, Bolus R, Lee U, Mayer E, Ackerman D, Rodriguez L. This study was aimed at evaluating correlations of mental distress with symptom severity in a selected group of IC/CPP patients using validated questionnaires. The study population comprised patients with IC/CPP identified from the Patient Reported Outcomes of Complimentary, Alternative, and Integrative Medicine (PRO-CAIM) database. PRO-CAIM is a web-based database where patients reported their diagnoses and completed on-line validated questionnaires at enrolment and every 3 months for one year while undergoing International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
4 their treatments of choice. 223 patients from the USA were evaluated for degrees of mental distress, pain and physical impairment. The study team found that in this group of patients all measures of mental distress correlated significantly with the degree of physical impairment and pain. They concluded that mental distress is highly correlated with the degree of physical symptoms. Not surprisingly, pain severity is highly correlated with coping strategy. Physical impairment is highly correlated to somatisation and panic, but not catastrophizing. However, in this study - contrary to reports from similar studies - neither pain severity nor physical impairment correlated with depression in the regression model. Poster# 83 CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN PATIENTS WITH NEUROPATHIC SYMPTOMS DEMONSTRATE POORER MENTAL HEALTH STATUS Saluja SS, George A, Sadek M, Fariello J, Whitmore K, Wehbe S, Moldwin R. Based on the experience that visceral pelvic pain syndromes such as interstitial cystitis often present with neuropathic features, the aim of this study from two pelvic pain centres in the USA was to examine the physical and mental health scores of patients with both chronic pelvic pain (CPP) and coexisting neuropathic symptoms. As previous studies have indicated, this study team found that CPP is associated with diminished physical and mental health scores. The results from this study indicated that mental health scores are more profoundly affected in patients with neuropathic pain. The team recommends that future research on neuropathic pain should incorporate measures of quality of life, especially in CPP patients who already have poorer QOL outcomes. Poster# 84 LONG-TERM TOLERABILITY AND EFFICACY OF PENTOSAN POLYSULPHATE SODIUM IN THE TREATMENT OF PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME/INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (PBS/IC) Al-Zahrani A, Gajewski J. The purpose of this Canadian study with 271 PBS/IC patients (90% female) from a single hospital was to evaluate the long-term efficacy and tolerability of Pentosan Polysulphate Sodium (PPS) for treating PBS/IC ( ). Included in this study were all patients with bladder pain symptoms and either frequency, urgency or nocturia in the absence of urinary tract infection or any other pathology as per ICS definition. All patients had glomerulations revealed in cystoscopic hydrodistension under general anaesthesia. 93 patients decided to stop taking the medication for various reasons, the most common reason being poor response in 45 patients, drug side effects in 30 patients, resolution of the PBS/IC symptoms in 11 patients and financial reasons in 6 patients. The side effects included gastrointestinal disorders in 23 patients, headache in 6 patients, hair loss in 3 patients, hypersensitivity in 3 patients, and increase in liver enzyme in 2 patients. Patients who had a history of detrusor overactivity or a positive cough leak test during the urodynamic study showed poor results of the PPS for treatment of PBS/IC. This Canadian team concluded that PPS is an effective oral therapy to control symptoms of PBS/IC with long term efficacy and tolerability. More than 63% of these patients continued to take the PPS. Poster# 86 EARLY LIFETIME TRAUMA IMPACTS SYMPTOM SEVERITY OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS AND CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN Baxter C, Bolus R, Ackerman D, Mayer E, Rodriguez L. International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
5 This research team was looking at the possible impact of early lifetime trauma occurring < 18 years of age (general, sexual, emotional and total trauma exposure) on symptom severity and quality of life in 223 adults with interstitial cystitis and/or chronic pelvic pain, using the UC LA database of patient reported, validated questionnaires. Based on the results of this study, it was concluded that traumatic events early in life, particularly emotional trauma, significantly affect patient perception of disease and disease severity in IC and/or CPP patients. The researchers felt that identifying and addressing these trauma issues may have a significant effect on the outcome of treatment and that evaluating treatment outcomes could further clarify the impact of trauma in early life. Poster# 90 DO PATIENTS UNDERSTAND LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOM TERMINOLOGY? Cinman N, Herati A, Moldwin R. A fascinating study on whether patients and doctors understand each other correctly when discussing lower urinary tract symptoms. One of the reasons behind this was the term urgency which is a symptom associated with a variety of different voiding disorders. The aim of this study was to discover whether patients with a variety of voiding disorders understand terminology for urinary symptoms and to see whether various interpretations of urgency exist within these specific voiding disorders. The 66 patients (35 men, 31 women) who participated included groups with interstitial cystitis/pelvic floor dysfunction, overactive bladder, and benign prostatic hyperplasia. A group of urology patients without voiding disorders served as controls. The patients were invited to complete a questionnaire to assess whether they understood the meaning of a number of terms (frequency, hesitancy, nocturia, incontinence) and specifically to define the term urgency by choosing one of 5 definitions provided. Results for urgency: 20 of 66: defined urgency correctly (ICS definition) as the complaint of a sudden compelling desire to pass urine, which is difficult to defer. 21 of 66: defined urgency as compelling desire to pass urine. 12 of 66: defined urgency as the need to urinate due to increasing bladder pain/ discomfort/ pressure. 6 of 66: defined urgency as the desire to urinate often. 4 of 66: defined urgency as strong need to urinate for fear of urinary leakage. 3 of 66: defined urgency as persistent desire to pass urine. The authors concluded that the study showed that urology patients with various different voiding disorders that contain a feature of urgency feel unclear about LUTS terminology, and clearly interpret urgency quite differently. This is clinically important since communication between doctor and patient may consequently be confused and this could potentially lead to a wrong diagnosis. Poster# 91 INTRAVESICAL BUPIVACAINE FOR LIDOCAINE-REFRACTORY PATIENTS WITH PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME/INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
6 Quillin R, Hooper G, Erickson D. While a study from 2009 showed that intravesical lidocaine is better than placebo for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis (PBS/IC), some patients do not respond to lidocaine. Bupivacaine may be more effective because it is more lipophilic and more potent than lidocaine. Even though bupivacaine has been routinely used for some years either as the only anaesthetic or mixed with lidocaine, no study has so far been published comparing the two. In this study, Quillin and colleagues reviewed their experience with intravesical bupivacaine in PBS/IC patients who had previously failed to respond to intravesical lidocaine. The purpose of the study with 14 women and 1 man was to determine how many lidocaine non-responders would respond to bupivacaine, and to compare the clinical features of bupivacaine responders compared with nonresponders. On the basis of results in this study, it was concluded that bupivacaine should be tried before declaring a patient unresponsive to intravesical local anaesthetic. It was found that good response was more likely in patients without pelvic floor dysfunction. Poster# 92 THE EFFICACY OF VAGINAL DIAZEPAM USE FOR PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION PAIN, INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS, AND/OR VULVAR PAIN: PRELIMINARY DATA Carrico DJ, Burks F, Peters KM. Carrico and colleagues report that vaginal diazepam is currently being used off-label to help treat pain in pelvic floor dysfunction (PFD), interstitial cystitis (IC) and vulvar pain. They state that the usual dose being prescribed is 5 10 mg of diazepam tablets or compounded hypoallergenic suppositories or creams, used vaginally up to every 8 hours. Pain relief has been reported to be significant, without the side effects commonly found with oral diazepam. Since the authors believe that there have so far been no studies on the safety and efficacy of treatment with vaginal diazepam for the pain experienced in these disorders, the aim of this study with 11 female patients was to produce preliminary data on the efficacy and safety of vaginal diazepam in women with PFD, IC and/or vulvar pain. 64% (7/11) women reported no side effects while 36% reported mild drowsiness. It was significant to note that on the basis of the global response assessment (GRA), 7/11 women (64%) felt that they were moderately or markedly improved. 73% of women believed the vaginal diazepam was helping, while 4/11 women reported no change. None of the patients reported any worsening of pain. It was concluded that vaginal diazepam may be helpful in treating pelvic floor pain-related conditions. However, larger, randomized-controlled research trials are needed. Poster# 97 FUNCTIONAL BLADDER CAPACITY AS AN OBJECTIVE MEASURE OF RESPONSE TO INTRAVESICAL DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE FOR THE TREATMENT OF NEWLY DIAGNOSED INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Gafni-Kane A, Du H, Nguyen A, Vu M, Goldberg RP, Sand PK, Botros S. The effect of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) on the functional bladder capacity of female IC patients has until now been lacking in the literature. The purpose of this retrospective study with 15 newly diagnosed patients (with cystoscopy) was to determine whether initial treatment with weekly intravesical DMSO instillations for newly diagnosed IC patients results in a statistically significant increase in functional bladder capacity. Exclusions from this study International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
7 were patients with detrusor overactivity and patients taking other pain medication concomitantly and those who had had any prior therapy. It was concluded on the basis of the results that female patients with newly diagnosed IC showed a significant increase in functional bladder capacity following the second week of an initial series of intravesical DMSO treatment. According to the authors, future research will focus on correlating the objective findings from this study with subjective improvements in clinical symptoms reported by the patients. Podium #29 SURGICAL INTERVENTION FOLLOWING INTERSTIM SACRAL NEUROMODULATION IMPLANT FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS -14 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF ONE CENTER Al-Zahrani A, Jerzy Gajewski J. The authors note that the reoperation rate for sacral neuromodulation (SNM) remains a concern and that little has been published on this issue. This retrospective study was based on 14 years experience using SNM. Patient data between 1994 and 2008 was reviewed in order to assess the incidence and cause of reoperation following implantation of SNM. 96 SNM devices were implanted in 88 women and 8 men. Reasons for implantation were painful bladder syndrome/ interstitial cystitis (PBS/IC) (47.9%), urge urinary incontinence (UUI) (35.4%) and idiopathic urinary retention (IUR) (16.7%). The PBS/IC patients had the shortest time to explantation (average 15 months), the reasons being poor results in 12 patients (12.5%), painful stimulation in 6 patients (6.25%) and the stimulation radiating into the leg in 2 patients (2%).The long-term success rate was 87.5%, 84.8% and 73 % in the IUR, UUI and PBS/IC respectively. A total of 39% of the patients needed revision of their SNM implant, the revision rate being highest in IUR (56%), and lowest in UUI (32%). Loss of stimulation in 24 procedures (58.5%) formed the main reason for revision. Other reasons included pain from the pulse generator in 7 patients, painful stimulation in 5 patients and radiation of the stimulation into the leg in 5 patients. The battery had to be changed in 8 patients. The authors concluded that SNM is a minimally invasive procedure with good longterm outcome and observe that the rate of reoperation is improving with today s advances in surgical techniques and equipment. Podium #40 THE EFFECTS OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC STRESS ON BLADDER STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Smith A, Leung J, Harper S, Zang R, Raz S, Mayer E, Rodriguez L. Smith and colleagues note that stress appears to play a role in the exacerbation of urinary tract disorders including painful bladder syndrome (PBS) and overactive bladder (OAB). This study was performed in order to understand the mechanism behind this. Rats were exposed to water avoidance stress (WAS) a strong psychological stressor in order to characterize changes in voiding, anxiety behaviour and bladder pathology. They found that rats exposed to WAS developed a significant increase in voiding frequency and a reduction in latency to void and volume voided. It was concluded that psychological stress results in significant, lasting changes in voiding parameters and that this appears to be related to hypothalamicpituitary axis activation, expressed in end organ dysfunction and changes in tissue expression and angiogenesis. Similar effects previously reported on the gastrointestinal system together with these findings suggest that this response may be initiated centrally. This rat model may represent a valid tool for studying PBS and OAB. International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
8 The International Painful Bladder Foundation does not engage in the practice of medicine. It is not a medical authority nor does it claim to have medical knowledge. Information provided in IPBF s, newsletters and website is not medical advice. The IPBF recommends patients to consult their own physician before undergoing any course of treatment or medication. The IPBF endeavours to ensure that all information it provides is correct and accurate, but does not accept any liability for errors or inaccuracies. International Painful Bladder Foundation Review SUFU Winter Meeting
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2
 Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!!
 Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!! Dr. Hirachand S Mutagi. Senior Consultant Pain Physician. Head -Sakra World Hospital. Director ReLeaf Pain Services. Rapid advances in neurostimulation therapy
Sacral Neuromodulation Beyond Pelvic Pain!!! Dr. Hirachand S Mutagi. Senior Consultant Pain Physician. Head -Sakra World Hospital. Director ReLeaf Pain Services. Rapid advances in neurostimulation therapy
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information
 Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
03/13/18. A. Symptoms lasting for greater than or equal to 12 months that have resulted to significant impairment in activities of daily living; and
 Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Second-line Treatment for OAB
 Patient Information English 35 Second-line Treatment for OAB The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Sometimes the drugs your doctor prescribed do not improve your overactive symptoms (OAB). In
Patient Information English 35 Second-line Treatment for OAB The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Sometimes the drugs your doctor prescribed do not improve your overactive symptoms (OAB). In
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Management of OAB. Lynsey McHugh. Consultant Urological Surgeon. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain
 Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Tuesday 24 June Poster Session 1: Voiding Dysfunction Chairmen: C. Chapple and L. Stewart
 Tuesday 24 June 10.30 11.30 Poster Session 1: Voiding Dysfunction Chairmen: C. Chapple and L. Stewart P001 Can oral antibiotic prophylaxis reduce the rate of infection after conventional urodynamic studies?
Tuesday 24 June 10.30 11.30 Poster Session 1: Voiding Dysfunction Chairmen: C. Chapple and L. Stewart P001 Can oral antibiotic prophylaxis reduce the rate of infection after conventional urodynamic studies?
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve
 Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS
 NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Sacral neuromodulation (SNM), using permanent foramen S3 electrode, Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, March 2008, Milan, Italy
 A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
 Sacral Neuromodulation for Treatment of Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Alex Kavanagh, PGY3 Mar 30/2011 Goals 1. Define sacral neuromodulation (SNM) and review the clinical implementation 2. Provide
Sacral Neuromodulation for Treatment of Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Alex Kavanagh, PGY3 Mar 30/2011 Goals 1. Define sacral neuromodulation (SNM) and review the clinical implementation 2. Provide
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
Overactive bladder. Information for patients from Urogynaecology
 Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline.
 Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice
 Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Urogynecology Office. Can You Hold? An Update on the Treatment of OAB. Can You Hold? Urogynecology Office
 Urogynecology Office Urogynecology Office Can You Hold? An Update on the Treatment of OAB Can You Hold? Karen Noblett, MD Professor and Chair Department of OB/GYN University of California, Riverside Disclosures
Urogynecology Office Urogynecology Office Can You Hold? An Update on the Treatment of OAB Can You Hold? Karen Noblett, MD Professor and Chair Department of OB/GYN University of California, Riverside Disclosures
Intravesical Botox Injections
 Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
The cost of the Axonics sacral neuromodulation system is 475 for the trial phase, 9,210 for a
 pat hways Axonics sacral al neuromodulation system for overactive bladder and faecal incontinence Medtech innovation briefing Published: 10 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib164 Summary The technology
pat hways Axonics sacral al neuromodulation system for overactive bladder and faecal incontinence Medtech innovation briefing Published: 10 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib164 Summary The technology
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
2/9/2008. Men Women. Prevalence of OAB. Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence (%) < Age (years)
 Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
 Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 134 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: June 2018 Effective: July 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 134 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation/Stimulation for Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Next Review: December 2018 Last Review: June 2018 Effective: July 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Symptoms. Patient Information Leaflet
 Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Symptoms Patient Information Leaflet About this leaflet The information provided in this leaflet should be used as a guide. There may be some
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Overactive Bladder Symptoms Patient Information Leaflet About this leaflet The information provided in this leaflet should be used as a guide. There may be some
Interstitial cystitis
 Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract dysfunction
 World J Urol (2012) 30:445 450 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0780-2 TOPIC PAPER Sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract dysfunction Philip E. V. Van Kerrebroeck Tom A. T. Marcelissen Received: 22 August
World J Urol (2012) 30:445 450 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0780-2 TOPIC PAPER Sacral neuromodulation for lower urinary tract dysfunction Philip E. V. Van Kerrebroeck Tom A. T. Marcelissen Received: 22 August
Rezūm procedure for the Prostate
 Rezūm procedure for the Prostate Mr Jas Kalsi Consultant Urological Surgeon This booklet has been provided to help answer the questions you may have with regards to your enlarged prostate and the Rezūm
Rezūm procedure for the Prostate Mr Jas Kalsi Consultant Urological Surgeon This booklet has been provided to help answer the questions you may have with regards to your enlarged prostate and the Rezūm
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Page 1 of 23 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Professional Institutional
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Page 1 of 23 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Professional Institutional
Information about your operation: Sacral nerve stimulation (SNS)
 Information about your operation: Sacral nerve stimulation (SNS) Urogynaecology Unit Information for Patients i Important supplementary information What is an overactive bladder? Women with an overactive
Information about your operation: Sacral nerve stimulation (SNS) Urogynaecology Unit Information for Patients i Important supplementary information What is an overactive bladder? Women with an overactive
InterStim CONSULTATION INFORMATION.
 InterStim CONSULTATION INFORMATION www.urologyaustin.com The Urinary System Making An Informed Decision How Does The Urinary System Work? To understand how sacral nerve stimulation works, it is helpful
InterStim CONSULTATION INFORMATION www.urologyaustin.com The Urinary System Making An Informed Decision How Does The Urinary System Work? To understand how sacral nerve stimulation works, it is helpful
Patient Information. Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms. pubic bone. urethra. scrotum. bladder. vaginal canal
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation
 Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.69 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2001 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Sacral Nerve Neuromodulation / Stimulation Policy Number: 7.01.69 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2001 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
ESSIC 2008 Annual Meeting Rome
 Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT
 Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Enrico Finazzi-Agrò,*, Filomena Petta, Francesco Sciobica, Patrizio Pasqualetti, Stefania Musco and Pierluigi Bove
 Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation Effects on Detrusor Overactivity Incontinence are Not Due to a Placebo Effect: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial Enrico Finazzi-Agrò,*, Filomena
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation Effects on Detrusor Overactivity Incontinence are Not Due to a Placebo Effect: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial Enrico Finazzi-Agrò,*, Filomena
Bulkamid. Patient Information. Obstetrics & Gynaecology Department
 Bulkamid Patient Information Obstetrics & Gynaecology Department Author ID: JD Leaflet Number: Gyn 050 Version: 5 Name of Leaflet: Bulkamid Date Produced: November 2017 Review Date: November 2019 Bulkamid
Bulkamid Patient Information Obstetrics & Gynaecology Department Author ID: JD Leaflet Number: Gyn 050 Version: 5 Name of Leaflet: Bulkamid Date Produced: November 2017 Review Date: November 2019 Bulkamid
Urinary incontinence. Urology Department. Patient Information Leaflet
 Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Sacral Neuromodulation (SNM)
 47 Sacral Neuromodulation (SNM) for overactive bladder symptoms and for non-obstructive voiding dysfunction Patient Information Women and Children - Obstetrics and Gynaecology Sacro Neuromodulation Contents
47 Sacral Neuromodulation (SNM) for overactive bladder symptoms and for non-obstructive voiding dysfunction Patient Information Women and Children - Obstetrics and Gynaecology Sacro Neuromodulation Contents
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
 MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE?
 PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
Dr. Krithika Doshi. Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical?
 Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Updates in the nonpharmacological. treatment on overactive bladder
 Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Urinary Incontinence. Lora Keeling and Byron Neale
 Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS
 Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond
 Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER!
 REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
USE OF BOTOX IN BLADDER DISORDERS
 USE OF BOTOX IN BLADDER DISORDERS AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology January 2017 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Web site: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922 6696/6698
USE OF BOTOX IN BLADDER DISORDERS AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology January 2017 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Web site: w w w. s t o c k p o r t. n h s. u k Tameside: 0161 922 6696/6698
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients
 Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT!
 THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT! Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT! Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper
 NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper Great Lakes SUNA Inside Urology March 16, 2018 Michelle J. Lajiness FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner DMC Urology Incidence Really unknown Lack consensus
NON-Neurogenic Chronic Urinary Retention AUA White Paper Great Lakes SUNA Inside Urology March 16, 2018 Michelle J. Lajiness FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner DMC Urology Incidence Really unknown Lack consensus
Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
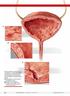 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial cystitis
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging
 Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY
 April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY This month I am focusing on a topic that may seem a little boring. But I would like to look at it from a less common perspective.urinary Frequency and its relationship
April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY This month I am focusing on a topic that may seem a little boring. But I would like to look at it from a less common perspective.urinary Frequency and its relationship
Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive Bladder
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
SACRAL NEUROMODULATION FOR PERSISTENT PAIN
 SACRAL NEUROMODULATION FOR PERSISTENT PAIN WHAT IS NEUROMODULATION? Also called neurostimulation, neuromodulation involves electrical stimulation of the nervous system for the purpose of modulating or
SACRAL NEUROMODULATION FOR PERSISTENT PAIN WHAT IS NEUROMODULATION? Also called neurostimulation, neuromodulation involves electrical stimulation of the nervous system for the purpose of modulating or
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy. Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester
 Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
Sacral nerve stimulation in patients with detrusor overactivity
 Peer review Sacral nerve stimulation in patients with detrusor overactivity Abstract Detrusor overactivity, particularly with symptoms of urge incontinence, can be a debilitating and embarrassing condition.
Peer review Sacral nerve stimulation in patients with detrusor overactivity Abstract Detrusor overactivity, particularly with symptoms of urge incontinence, can be a debilitating and embarrassing condition.
Continence Worksheet Name: Date: Name of Trainer: Name of Company: Clinical Update (NZ) Ltd
 Continence Worksheet Name: Date: Name of Trainer: Name of Company: Clinical Update (NZ) Ltd Segment 1 What is continence? Incontinence is not a but a sign of What organs are involved? and Urine incontinence
Continence Worksheet Name: Date: Name of Trainer: Name of Company: Clinical Update (NZ) Ltd Segment 1 What is continence? Incontinence is not a but a sign of What organs are involved? and Urine incontinence
Uroformation. Instillation of Botox. The Uroformation series is a co-operative venture in patient centered urological information.
 Uroformation Instillation of Botox The Uroformation series is a co-operative venture in patient centered urological information. June 2014 What is Botox? Botox or botulinum toxin, is a purified toxin
Uroformation Instillation of Botox The Uroformation series is a co-operative venture in patient centered urological information. June 2014 What is Botox? Botox or botulinum toxin, is a purified toxin
Urinary tract disorders
 Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
