Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial cystitis
|
|
|
- Warren Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), doi: /iju Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial cystitis Yukio Homma Department of Urology, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyoku, Tokyo, Japan Abbreviations & Acronyms BPS = bladder pain IC = interstitial cystitis ICS = International Continence Society HSB = hypersensitive bladder OAB = overactive bladder PBS = painful bladder Correspondence: Yukio Homma M.D., Ph.D., Department of Urology, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Hongo 7-3-1, Bunkyoku, Tokyo , Japan. homma-uro@umin.ac.jp Received 9 August 2013; accepted 4 September Abstract: Taxonomy or nomenclature concerning interstitial cystitis and its related symptom s is in a state of confusion. After analyzing the reasons for confusion in regard to three components (disease name, symptoms, Hunner s lesion), I would like to propose a new term, hypersensitive bladder, taking after overactive bladder, as a solution. Hypersensitive bladder symptoms are defined as increased bladder sensation, usually associated with urinary frequency and nocturia, with or without bladder pain. The proposal of hypersensitive bladder is based on: (i) it does not appear a symptom, but a disease by ending with an organ name, bladder ; (ii) it does not contain confusable symptom terms (pain and urgency), but indicates irritative symptoms including pain and urgency; and (iii) it suggests pathophysiological hyperactivity of sensory nerves. Interstitial cystitis is defined by three requirements: (i) hypersensitive bladder symptoms; (ii) bladder pathology; and (iii) no other diseases, where bladder pathology should be clearly stated either as Hunner s lesion or glomerulations after hydrodistention. Hypersensitive bladder can be used for the condition with hypersensitive bladder symptoms, but no obvious disease explaining hypersensitive bladder symptoms identified. Interstitial cystitis is a representative disease causing hypersensitive bladder symptoms, most typically with pain, but might be painless and indistinguishable from overactive bladder. Introducing hypersensitive bladder as a counter concept of overactive bladder into bladder dysfunction taxonomy will facilitate clinical practice and research progress, and attract considerable attention from the medical world. Key words: Introduction hypersensitivity, interstitial cystitis, pain, urgency, urinary bladder. Taxonomy or nomenclature concerning IC and its related symptom s is in a state of confusion. 1 Ambiguous definitions and inaccurate use of terminology generate confusion in practice and research, hindering the progress of research and/or leading to ignorance of IC by the medical world. In this presentation, I analyze the backgrounds and reasons for the confusion in regard to three components (disease name, symptoms, Hunner s lesion), and would like to suggest a solution. Disease name In the literature, we encounter IC, PBS, BPS, and chimeric terms combining IC and s (IC/PBS and IC/BPS or PBS/IC and BPS/IC). Chronic pelvic pain is also used as an umbrella term including IC, as patients with IC often perceive pain in the lower abdomen or external genitalia. PBS is defined by the ICS as suprapubic pain related to bladder filling, accompanied by other symptoms such as increased daytime and night-time frequency, in the absence of proven urinary infection or other obvious pathology. 2 According to ICS, PBS is a preferable term to IC, and IC is a specific diagnosis and requires confirmation by typical cystoscopic and histological features, although typical cystoscopic and histological features are not clearly mentioned. Definitions by The Panel of the American Urological Association Guideline and by the Society for Urodynamics and Female Urology are identical: an unpleasant sensation (pain, pressure, discomfort) perceived to be related to the urinary bladder, associated with lower urinary tract symptoms of more than 6 weeks duration, in the absence of infection or other identifiable causes. 3 BPS is defined by the European Society for the Study of Interstitial Cystitis as chronic pelvic pain, pressure, or discomfort perceived to be related to the urinary bladder accompanied by at least one other urinary symptom such as persistent urge to void or urinary frequency. Confusable diseases as the cause of symptoms must be excluded The Japanese Urological Association 43
2 Y HOMMA The definitions of these symptom s all share two requirements: unpleasant symptoms and lack of identifiable diseases explaining those symptoms. In other words, the symptom s do not imply symptoms alone or a specific disease. They are a tentative naming for convenience to describe a condition accompanying obvious symptoms without identifiable diseases. Chimeric terms combining IC and s, IC/PBS or IC/BPS, are even more complicated; they would indicate conditions presenting the symptoms in the absence of obvious diseases with possible presence of IC. 5 However, these terms are not used distinctly, but rather, interchangeably. User-friendly and clearly understandable terminology is required for efficient and accurate communications. Symptoms PBS and BPS contain the words painful and pain, which leads to a misunderstanding that the patients have to complain of pain. In reality, a proportion of patients do not. 6,7 Complaints heard might not be directly linked to pain; that is, the incessant need to void because of discomfort, loss of normal urinary sensation and an irritable sensation with only a little urine in the bladder. These unpleasant or discomfort sensations might be a kind of pain by scientific definition; pain is defined as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. 8 However, it is unrealistic for common physicians and patients to use pain to describe pressure or discomfort in their own words. Pain is commonly understood as the feeling you have when part of your body hurts or highly unpleasant physical sensation caused by illness or injury. The criteria for clinical trials of IC by the National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases require symptoms of either pain associated with bladder OR urinary urgency. 9 In other words, National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases criteria, which are allegedly too restrictive for clinical diagnosis, do not require pain as the symptom. Mentioned in the proposal paper for BPS is that many patients report a sensation of pressure or discomfort in the bladder/ pelvic area and do not report this sensation as pain but rather as urgency. 4 The discrepancy between the academic definition of pain and common usage of this word can lead to confusion. It might result in untoward consequences to patients benefit by excluding painless patients from the scope of PBS or BPS. It might create a belief that there is injury in the bladder. Furthermore, pain might be too strong a word both for patients and physicians. As far as the s contain pain, patients are never free of a fear of experiencing pain. Physicians might prefer to steer clear of the case, taking the approach that pain is the toughest symptom to control and should be managed by a pain specialist. Urgency is another symptom issue. It is the key symptom of OAB, and defined as sudden compelling desire to void, which is difficult to defer. 2 Urgency is also regarded as one of the key symptoms associated with IC or IC-like conditions, 9,10 and urgency in this case might not be identical to OAB urgency. Urgency in OAB is characterized by sudden onset and/or fear of leakage, whereas urgency in IC is of a persistent nature, and is associated with the fear of pain. 11 However, a distinction between these two urgencies on the basis of symptoms is not simple; approximately 40% of women with OAB also reported urgency as a result of pain, pressure or discomfort, and 60% of women with IC indicated that the urgency occurred suddenly rather than gradually. 12 Anyway, we still have to use the same word, urgency, even though urgency is different in OAB and IC. This is an inevitable confusion. The ICS definition in 2002, which restricted urgency to the sudden strong desire to void (and excluded the non-sudden strong desire to void from urgency), is a source of confusion. The original urgency (1988 definition) allowed for two types of strong desire to void. Amending the definition of urgency to the original one to encompass the sensation of IC-related urgency is a straightforward solution, yet it might stir up even more confusion. Taken together, a word different from pain or urgency might be preferable for describing symptoms of IC. Hunner s lesion It has been postulated that IC can be categorized into two types, one with Hunner s lesion and one without. The former is known as classic type, ulcer type or ulcerative IC, although Hunner s lesion is not an ulcer in pathological meaning. Endoscopically, it is recognized as a well-demarcated reddish mucosal lesion lacking in the normal capillary structure. Classic IC is characterized by older age, being more symptomatic and more inflammatory reactions. By contrast, those without Hunner s lesion reported more often extra-bladder symptoms and other functional s, such as irritable bowel, fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue Extra-bladder symptoms might be secondary to bladder symptoms or of a primary nature, with the bladder being an innocent bystander. 16 Alternatively, there might be a common pathological pathway for bladder and extra-bladder symptoms. 17 These two types of IC show marked histopathological differences; denudation of epithelium and inflammatory reactions are evident only in IC with Hunner s lesion. 18 Recent studies further underscore inflammatory reactions in patients with classic IC; high levels of intravesical nitric oxide, 19 elevated pro-inflammatory gene expression in the bladder biopsy 20,21 or in urinary sediment. 22,23 Pronociceptive inflammatory reactions mediating TRP channels and/or ASIC channel are found to be upregulated. 24 Clinically, this rationalizes the use of corticosteroid or surgery to resect the inflamed tissue of the classic IC bladder. 25,26 It is conceivable that Hunner s lesion, an obvious inflammatory lesion, causes pain or other symptoms. Why do patients without Hunner s lesion show such symptoms? Recent basic research has revealed that the urothelium is not a simple barrier to urine, but rather with sensory nerve properties. 27 The sensory nerve has a double function: an afferent function informing the central nervous system of physical or chemical stimuli; and an efferent function releasing mediators, such as substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and tachykinins, in response to sensory activity. The latter function triggers smooth muscle contraction, immune cell migration and mast cell degranulation. Thus, overactivity of sensory nerves induces chronic The Japanese Urological Association
3 Hypersensitive bladder is a solution inflammatory reactions, which might result in hypersensitivity of C-fiber nociceptors, forming a vicious cycle leading to allodynia or hyperalgesia of the bladder. 28,29 Central pain amplification might exaggerate hypersensitivity to visceral stimuli. 30 For example, sciatic nerve injury, an insult outside the bladder, can cause bladder hypersensitivity by upregulation of chemokine signaling in the bladder sensory neurons. 31 Upregulation of NGF expression in IC patients without Hunner s lesion suggests sensory overactivity in this specific type of IC. 24,32 Despite such a pronounced symptomatic, histological and pathophysiological distinction, it is not common practice to carry out cystoscopy to detect Hunner s lesion. In addition, Hunner s lesion is easily overlooked without intentional search. Surprisingly, many clinical studies lack information on the presence or absence of Hunner s lesion for the study population. Clinical practice and research combining these two into a single group of a vaguely-defined word (PBS, BPS, PSB/IC or BPS/IC) lead to further confusion in diagnosis, management and investigation of IC. Historical considerations IC was originally described as a distinct bladder disease with ulcerative lesion on cystoscopy. 33 However, bladder pathology is not always identifiable in patients with symptoms suggestive of IC. 34 A substantial portion of patients suspected as having IC had no evidence of bladder pathology, yet complained of debilitating symptoms including pain. Regarding the necessity for a diagnostic name for such patients, two approaches could be feasible. One is expanding the scope of IC; those complaining of IC-like symptoms with no obvious other diseases are included in IC irrespective of the presence or absence of bladder pathology or without exploration of bladder pathology. The other approach is using a symptom as a proxy for a disease name, such as PBS. As the expanded IC and symptom-based diagnosis (i.e. PBS) refer to a similar condition, these two terms were naturally combined (i.e. IC/PBS). Thus IC, PBS, IC/PBS or whatever like these, all terms were used interchangeably to indicate the IC-like condition ranging from the bladder with definite Hunner s lesion to a persistent complaint of unpleasant bladder sensation resistant to antibiotics. To create order in the midst of this confusion, BPS has been introduced, with IC abolished from medical terminology. 4 In reality, however, BPS is regarded as an alternative to PBS, and a chimeric word such as BPS/IC is still alive. Hence, IC or IC-like patients are left mixed up or unclassified, showing diversity in symptoms (with or without pain), cystoscopic findings (with or without Hunner s lesion) and histology (with or without inflammation). 35 Origin of confusion Why such a confusion? I believe it is because we have adopted symptom s to describe this condition. Symptom s refer to a set of symptoms without identifiable diseases. They do not imply symptoms alone or a specific disease. They do not define the extent of clinical tests to find the identifiable disease. It is a tentative naming for the sake of convenience with vague definition, which allows arbitrary interpretations by Symptoms No proven diseases Bladder pathology symptom disease Fig. 1 Distinction between symptom, symptom and disease. A cohort of symptomatic patients might present with symptoms such as pain and discomfort (symptom). If they have no obvious diseases, they are called by a symptom for convenience, such as PBS (). When detailed examinations have shown bladder pathology, the condition should be called by a disease name, such as IC (disease). In reality, these three are used interchangeably, causing confusion among patients, physicians and researchers. users. PBS, BPS, PBS/IC, PB/IC, and IC are used without strict discrimination for the difference among, symptom and disease (Fig. 1). The most well-known symptom of lower urinary tract dysfunction could be OAB. Its definition is, urinary urgency, usually associated with urinary frequency, with or without urgency incontinence. 2 Although originally developed as a symptom, it is actually functioning as a disease. The abbreviation is not OABS (overactive bladder ), but simply OAB. It ends with an organ name, bladder, sounding as if it referred to a disease of the urinary bladder associated with bladder overactivity. OAB is a successful naming in that it has been accepted widely, leading to public awareness of urinary problems in general and input from pharmaceutical companies to develop new medicines for lower urinary tract symptoms. We should take advantage of the popularity and naming of OAB in resolving confusion surrounding IC and its related symptom s. Hypersensitive bladder as an proposal Under these considerations, I would like to propose a new term hypersensitive bladder (HSB). 36 HSB was once used as a term for idiopathic sensory urgency and early IC. 37 Some editorials or papers used sensory disorder or hypersensitivity to describe the pathophysiology of IC. 38,39 The proposal of HSB is based on: (i) it does not appear a symptom, but a disease ending with bladder ; (ii) it does not contain pain or urgency, but indicates irritative symptoms including pain and urgency; and (iii) it suggests pathophysiological hyperactivity of sensory nerves. HSB symptoms are defined as increased bladder sensation, usually associated with urinary frequency and nocturia, with or without bladder pain. It looks like OAB symptoms: urinary urgency, usually associated with urinary frequency and nocturia, with or without urgency incontinence The Japanese Urological Association 45
4 Y HOMMA OAB HSB OAB with leakage HSB with pain Symptom of IC Fig. 2 Relationship between HSB and its related terms. Symptoms of OAB (urinary urgency, usually associated with urinary frequency and nocturia, with or without urgency incontinence) and HSB (increased bladder sensation, usually associated with urinary frequency and nocturia, with or without bladder pain) are overlapping, although OAB with leakage and HSB with pain are readily separated. Symptoms of IC usually present HSB symptoms, often accompanying pain, but occasionally mimicking OAB symptoms. Hypersensi ve Bladder Symptoms No Obvious Disease? Yes Hypersensi ve Bladder Disease Diagnosed No Bladder Pathology? Inters al Cys s (with or without Hunner lesion) Yes Fig. 3 Algorithm for hypersensitive bladder symptoms. HSB symptoms should be investigated for the causes. When there is no obvious disease, the condition is called as HSB. When bladder pathology is identified in HSB, the diagnosis of IC is made. When there is no such bladder abnormality, the condition remains as HSB. The presence or absence of Hunner lesion should be recorded for IC cases. In contrast, IC should be defined by three conditions: HSB symptoms, bladder pathology, and no other diseases explaining the symptoms. Bladder pathology shows Hunner s lesion or glomerulations after hydrodistention, if following NIDDK criteria. 9 However, the specificity of glomerulations is challenged and needs further investigation. Tentatively, by allowing both findings for bladder pathology, we should describe the presence of absence of Hunner s lesion for each patient for the future analysis. HSB can be used as a diagnostic name for the condition that is suspected of IC, but has not fulfilled the requirements for IC diagnosis. HSB symptoms might occur with or without evidence for bladder pathology. It could accompany chronic pelvic pain or functional disorders. By analogy, OAB can be used as a diagnostic name for the condition that is suspected of detrusor overactivity, but has not fulfilled the requirements for DO diagnosis. OAB symptoms might occur with or without evidence for detrusor overactivity. It could accompany benign prostatic enlargement or stress urinary incontinence. The relationship between HSB and related terms, IC and OAB, is shown in Fig. 2. Symptomatically, HSB and OAB are substantially overlapping. Detailed voiding recording with reference to bladder sensation indicated increased urinary sensation at a given bladder volume in OAB. 40,41 Urodynamically, those diagnosed as OAB have shown more detrusor overactivity and lower bladder volume at urinary sensation and increased sensitivity to electrostimulation. 42 These observations suggest OAB symptoms also reflect hypersensitivity of the bladder. IC is a representative disease causing HSB symptoms, most typically with pain, but might be painless and indistinguishable from OAB. An algorithm for hypersensitive bladder symptoms is shown in Fig. 3. When there is no obvious disease explaining HSB symptoms, the condition is called HSB. When bladder pathology is identified in HSB, the diagnosis of IC is made. When there is no such bladder abnormality, the condition remains as HSB. Bladder pathology is either Hunner s lesion or glomerulations after hydrodistention, although the latter is to be The Japanese Urological Association
5 Hypersensitive bladder is a solution challenged for specificity. The presence or absence of Hunner s lesion should be recorded to characterize IC cases. With these definitions, the following makes sense: (i) a woman complaining of HSB symptoms proved to have carcinoma in situ of the bladder; (ii) a woman with HSB symptoms was diagnosed with HSB because no obvious diseases were apparent, but now she is diagnosed with IC based on cystoscopic abnormality; and (iii) a man with HSB showed no abnormal findings at hydrodistention, so he remained as HSB. Introducing HSB, the counter concept of OAB, into bladder dysfunction taxonomy will clarify current confusion surrounding IC, and importantly lessen the ignorance of IC by the medical society. Conflict of interest None declared. References 1 Homma Y. Lower urinary tract symptomatology: its definition and confusion. Int. J. Urol. 2008; 15: Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2002; 21: Hanno P, Dmochowski R. Status of international consensus on interstitial cystitis/bladder pain /painful bladder : 2008 snapshot. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2009; 28: van de Merwe JP, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder /interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008; 53: Warren JW, Meyer WA, Greenberg P et al. Using the International Continence Society s definition of painful bladder. Urology 2006; 67: discussion Irwin P, Samsudin A. Reinvestigation of patients with a diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: common things are sometimes common. J. Urol. 2005; 174: discussion Ito T, Ueda T, Honma Y et al. Recent trends in patient characteristics and therapeutic choices for interstitial cystitis: analysis of 282 Japanese patients. Int. J. Urol. 2007; 14: Merskey H. The taxonomy of pain. Med. Clin. North Am. 2007; 91: 13 20, vii. 9 Gillenwater JY, Wein AJ. Summary of the National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases Workshop on Interstitial Cystitis, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, August 28 29, J. Urol. 1988; 140: O Leary MP, Sant GR, Fowler FJ Jr et al. The interstitial cystitis symptom index and problem index. Urology 1997; 49: Diggs C, Meyer WA, Langenberg P et al. Assessing urgency in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder. Urology 2007; 69: Clemens JQ, Bogart LM, Liu K et al. Perceptions of urgency in women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain or overactive bladder. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011; 30: Erickson DR, Morgan KC, Ordille S et al. Nonbladder related symptoms in patients with interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2001; 166: discussion Nickel JC, Tripp DA, Pontari M et al. Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder and associated medical conditions with an emphasis on irritable bowel, fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue. J. Urol. 2010; 184: Peters KM, Killinger KA, Mounayer MH et al. Are ulcerative and nonulcerative interstitial cystitis/painful bladder 2 distinct diseases? A study of coexisting conditions. Urology 2011; 78: Peters KM. Interstitial cystitis-is it time to look beyond the bladder? J. Urol. 2012; 187: Warren JW, Wesselmann U, Morozov V et al. Numbers and types of nonbladder s as risk factors for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder. Urology 2011; 77: Fall M, Johansson SL, Aldenborg F. Chronic interstitial cystitis: a heterogeneous. J. Urol. 1987; 137: Logadottir YR, Ehren I, Fall M et al. Intravesical nitric oxide production discriminates between classic and nonulcer interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2004; 171: discussion Gamper M, Viereck V, Geissbuhler V et al. Gene expression profile of bladder tissue of patients with ulcerative interstitial cystitis. BMC Genomics 2009; 10: Ogawa T, Homma T, Igawa Y et al. CXCR3 binding chemokine and TNFSF14 over expression in bladder urothelium of patients with ulcerative interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2010; 183: Tyagi P, Killinger K, Tyagi V et al. Urinary chemokines as noninvasive predictors of ulcerative interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2012; 187: Blalock EM, Korrect GS, Stromberg AJ et al. Gene expression analysis of urine sediment: evaluation for potential noninvasive markers of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain. J. Urol. 2012; 187: Homma Y, Nomiya A, Tagaya M et al. Increased mrna expression of genes involved in pronociceptive inflammatory reactions in bladder tissue of interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2013; 190: Soucy F, Gregoire M. Efficacy of prednisone for severe refractory ulcerative interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2005; 173: discussion Rossberger J, Fall M, Jonsson O et al. Long-term results of reconstructive surgery in patients with bladder pain /interstitial cystitis: subtyping is imperative. Urology 2007; 70: Birder LA, de Groat WC. Mechanisms of disease: involvement of the urothelium in bladder dysfunction. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2007; 4: Geppetti P, Nassini R, Materazzi S et al. The concept of neurogenic inflammation. BJU Int. 2008; 101 (Suppl 3): Sculptoreanu A, de Groat WC, Buffington CA et al. Abnormal excitability in capsaicin-responsive DRG neurons from cats with feline interstitial cystitis. Exp. Neurol. 2005; 193: Twiss C, Kilpatrick L, Craske M et al. Increased startle responses in interstitial cystitis: evidence for central hyperresponsiveness to visceral related threat. J. Urol. 2009; 181: Foster R, Jung J, Farooq A et al. Sciatic nerve injury induces functional pro-nociceptive chemokine receptors in bladder-associated primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 2011; 183: Liu HT, Kuo HC. Intravesical botulinum toxin A injections plus hydrodistension can reduce nerve growth factor production and control bladder pain in interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007; 70: Hunner G. A rare type of bladder ulcer in women: report of cases. Boston Med. Surg. J. 1915; 172: Parsons JK, Parsons CL. The historical origins of interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2004; 171: Teichman JM, Parsons CL. Contemporary clinical presentation of interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007; 69: Homma Y. Hypersensitive bladder: towards clear taxonomy surrounding interstitial cystitis. Int. J. Urol. 2013; 20: Frazer MI, Haylen BT, Sissons M. Do women with idiopathic sensory urgency have early interstitial cystitis? Br. J. Urol. 1990; 66: Erickson DR. Identifying biomarkers for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain. J. Urol. 2012; 187: Lazzeri M, Montorsi F. The therapeutic challenge of chronic cystitis : search well, work together, and gain results. Eur. Urol. 2011; 60: Yamaguchi O, Honda K, Nomiya M et al. Defining overactive bladder as hypersensitivity. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2007; 26: Fujihara A, Ukimura O, Honjo H et al. Urge perception index of bladder hypersensitivity. J. Urol. 2013; 189: Lee SR, Kim HJ, Kim A et al. Overactive bladder is not only overactive but also hypersensitive. Urology 2010; 75: The Japanese Urological Association 47
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
 Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
 Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis Hong-Chen Qu 1, Wei Zhang 2, Shi Yan 3, Yi-Li Liu 1, Ping Wang 1 * 1 Department of Urological
Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis Hong-Chen Qu 1, Wei Zhang 2, Shi Yan 3, Yi-Li Liu 1, Ping Wang 1 * 1 Department of Urological
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis
 Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER!
 REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015
 International Journal of Urology (2016) 23, 542--549 doi: 10.1111/iju.13118 Guideline Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015 Yukio Homma, 1 Tomohiro Ueda,
International Journal of Urology (2016) 23, 542--549 doi: 10.1111/iju.13118 Guideline Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015 Yukio Homma, 1 Tomohiro Ueda,
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
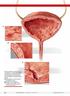 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails
 Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, FEBRUARY 2012
 REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB?
 What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB? K-E Andersson, MD, PhD Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Disclosures
What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB? K-E Andersson, MD, PhD Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Disclosures
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome and Male Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: How Are They Related?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice
 Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Naoki Wada, Seiji Matsumoto, Masafumi Kita, Kazumi Hashizume and Hidehiro Kakizaki
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (1) 1, 15 1 doi: 1.1111/iju.157 Original Article: Clinical Investigation Decreased urinary nerve growth factor reflects prostatic volume reduction and relief
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (1) 1, 15 1 doi: 1.1111/iju.157 Original Article: Clinical Investigation Decreased urinary nerve growth factor reflects prostatic volume reduction and relief
La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici
 La Prostata nel Mirino Napoli, 1 dicembre 2016 La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici Giorgio Annoni Cattedra e Scuola di Specializzazione in Geriatria Università degli Studi
La Prostata nel Mirino Napoli, 1 dicembre 2016 La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici Giorgio Annoni Cattedra e Scuola di Specializzazione in Geriatria Università degli Studi
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
ESSIC 2008 Annual Meeting Rome
 Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
Trigonal Injection of Botulinum Toxin A in Patients with Refractory Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 360 365 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Pelvic Pain Editorial by George A. Barbalias on pp. 366 368 of this issue
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 360 365 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Pelvic Pain Editorial by George A. Barbalias on pp. 366 368 of this issue
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 May 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Urol. 2014 May ; 191(5): 1294 1299. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.11.099. Segmental Hyperalgesia to Mechanical Stimulus in Interstitial
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Urol. 2014 May ; 191(5): 1294 1299. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.11.099. Segmental Hyperalgesia to Mechanical Stimulus in Interstitial
The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical Study
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E581-E587 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Evaluation The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E581-E587 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Evaluation The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical
3. Pathogenesis of IC/BPS
 Urological Science 26 (2015) 225e229 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Urological Science journal homepage: www.urol-sci.com Review article Biomarkers for patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder
Urological Science 26 (2015) 225e229 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Urological Science journal homepage: www.urol-sci.com Review article Biomarkers for patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder
CONCLUSIONS. At a median of nearly 3 years after onset, baseline mild IC/PBS was
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Prognostic factors for recent-onset interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome John W. Warren *, Daniel J. Clauw and Patricia Langenberg *Department of Medicine, Department of
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Prognostic factors for recent-onset interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome John W. Warren *, Daniel J. Clauw and Patricia Langenberg *Department of Medicine, Department of
Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome
 CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
THE ACONTRACTILE BLADDER - FACT OR FICTION?
 THE ACONTRACTILE BLADDER - FACT OR FICTION? Jacob Golomb Department of Urology Chaim Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer NEUROGENIC UNDERACTIVE DETRUSOR Central (complete/incomplete): Spinal cord injury-
THE ACONTRACTILE BLADDER - FACT OR FICTION? Jacob Golomb Department of Urology Chaim Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer NEUROGENIC UNDERACTIVE DETRUSOR Central (complete/incomplete): Spinal cord injury-
W11: Functional Pain Syndromes: Bidirectional Influences in Visceral Nociceptive Processing Aims of course/workshop
 W11: Functional Pain Syndromes: Bidirectional Influences in Visceral Nociceptive Processing Workshop Chair: Matthew Fraser, United States 27 August 2013 09:00-10:30 Start End Topic Speakers 09:00 09:25
W11: Functional Pain Syndromes: Bidirectional Influences in Visceral Nociceptive Processing Workshop Chair: Matthew Fraser, United States 27 August 2013 09:00-10:30 Start End Topic Speakers 09:00 09:25
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
Teng-Lung Lin 16:20 16:30 Discussion and close remark All
 W11: Holistic Approach by Bio-Psycho-Social model to Patients with Interstitial Cystitis / Bladder Pain Syndrome Workshop Chair: Ming-Huei Lee, Taiwan 13 September 2016 13:30-16:30 Start End Topic Speakers
W11: Holistic Approach by Bio-Psycho-Social model to Patients with Interstitial Cystitis / Bladder Pain Syndrome Workshop Chair: Ming-Huei Lee, Taiwan 13 September 2016 13:30-16:30 Start End Topic Speakers
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Dr. Krithika Doshi. Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical?
 Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Functional Bladder Problems
 european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder
 Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Urinary Biomarkers Under Investigation for Overactive Bladder Syndrome. IUPUI Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery
 Urinary Biomarkers Under Investigation for Overactive Bladder Syndrome Authors: Nayera Guirguis, M.D. * IUPUI Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery 1633 N Capitol Ave # 436, Indianapolis, IN
Urinary Biomarkers Under Investigation for Overactive Bladder Syndrome Authors: Nayera Guirguis, M.D. * IUPUI Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery 1633 N Capitol Ave # 436, Indianapolis, IN
Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive Bladder
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Overactive Bladder; OAB. Aδ silent C. Adenosine triphosphate; ATP SD g n Key words
 25-32 2009 SD 200-270g n 28 4 1 2 3 4 PE-50 4-5 0.25 60 C Key words acupuncture stimulation overactive bladder rat bladder irritation C C fiber Received November 17, 2008; Accepted January 9, 2009 I Overactive
25-32 2009 SD 200-270g n 28 4 1 2 3 4 PE-50 4-5 0.25 60 C Key words acupuncture stimulation overactive bladder rat bladder irritation C C fiber Received November 17, 2008; Accepted January 9, 2009 I Overactive
This Special Report supplement
 ...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU)
 SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
BJUI. Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive bladder
 ; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
CYSTISTAT. Hyaluronan Training
 CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
2/9/2008. Men Women. Prevalence of OAB. Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence (%) < Age (years)
 Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Since the 19th century, searches for the pathogenesis
 Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome and Nonbladder Syndromes: Facts and Hypotheses John W. Warren, Joop P. van de Merwe, and J. Curtis Nickel Commentary Since the 19th century, searches for the
Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome and Nonbladder Syndromes: Facts and Hypotheses John W. Warren, Joop P. van de Merwe, and J. Curtis Nickel Commentary Since the 19th century, searches for the
Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores
 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
Management of OAB. Lynsey McHugh. Consultant Urological Surgeon. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
3/20/10. Prevalence of OAB Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence of OAB with incontinence (OAB wet) Men: 2.6% Women: 9.3% Dry. Population (millions) Wet
 1 Prevalence of OAB Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336. Prevalence of OAB with incontinence (OAB wet) Men: 2.6% Women: 9.3% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336.
1 Prevalence of OAB Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336. Prevalence of OAB with incontinence (OAB wet) Men: 2.6% Women: 9.3% Stewart WF, et al. World J Urol. 2003;20:327-336.
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW?
 NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
Original Article. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men. Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center
 Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center Classification of LUTS Storage symptoms Voiding symptoms Post micturition
Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center Classification of LUTS Storage symptoms Voiding symptoms Post micturition
April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY
 April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY This month I am focusing on a topic that may seem a little boring. But I would like to look at it from a less common perspective.urinary Frequency and its relationship
April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY This month I am focusing on a topic that may seem a little boring. But I would like to look at it from a less common perspective.urinary Frequency and its relationship
Infection/Inflammation. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2017
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN
 Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN Diane K. Newman, DNP is a Biofeedback Certified Continence Specialist. With over 35-years experience, she is an expert in the assessment and management of pelvic-floor
Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN Diane K. Newman, DNP is a Biofeedback Certified Continence Specialist. With over 35-years experience, she is an expert in the assessment and management of pelvic-floor
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS)
 Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Compassionate and effective management
 IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
김준철 가톨릭대학교의과대학비뇨기과학교실
 비뇨기계자율신경병증의치료 김준철 가톨릭대학교의과대학비뇨기과학교실 Introduction Urologic complications have increasingly become a concern in those affected by DM Genitourinary problems are included among these complications, related
비뇨기계자율신경병증의치료 김준철 가톨릭대학교의과대학비뇨기과학교실 Introduction Urologic complications have increasingly become a concern in those affected by DM Genitourinary problems are included among these complications, related
O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA Injections for Refractory Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Toxins 2015, 7, 2860-2871; doi:10.3390/toxins7082860 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA
Toxins 2015, 7, 2860-2871; doi:10.3390/toxins7082860 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA
Voiding Dysfunction. Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan H. Kaufmann, David D. Chancellor, Michael B. Chancellor and Hann-Chorng Kuo,k
 Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Instillation of Liposome Encapsulated OnabotulinumtoxinA Improves Overactive Bladder Symptoms: A Prospective, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan
Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Instillation of Liposome Encapsulated OnabotulinumtoxinA Improves Overactive Bladder Symptoms: A Prospective, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines
 Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE
 GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE 9 J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, J-T. Andersen, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, M. Hohenfellner, T. Tammela, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE 9 J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, J-T. Andersen, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, M. Hohenfellner, T. Tammela, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
The new International Continence Society
 ROLE OF CYSTOMETRY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH OVERACTIVE BLADDER ADAM J. FLISSER AND JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Overactive bladder (OAB) can be caused by a variety of conditions. We believe that cystometrography
ROLE OF CYSTOMETRY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH OVERACTIVE BLADDER ADAM J. FLISSER AND JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Overactive bladder (OAB) can be caused by a variety of conditions. We believe that cystometrography
Prevalence of the Overactive Bladder Syndrome byapplying the International Continence Society Definition
 European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 622 627 Female Urology ^ Incontinence Prevalence of the Overactive Bladder Syndrome byapplying the International Continence Society Definition Christian Temml
European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 622 627 Female Urology ^ Incontinence Prevalence of the Overactive Bladder Syndrome byapplying the International Continence Society Definition Christian Temml
A review of the SENSORY BLADDER MEETING
 A review of the SENSORY BLADDER MEETING Les Pensières, Fondation Merieux, Veyrier du Lac, France 22-23 June 2012 Jane Meijlink Around 95 expert speakers and participants from 13 different countries gathered
A review of the SENSORY BLADDER MEETING Les Pensières, Fondation Merieux, Veyrier du Lac, France 22-23 June 2012 Jane Meijlink Around 95 expert speakers and participants from 13 different countries gathered
A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL
 A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, 10-12 MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL Jane Meijlink This year, the ESSIC Annual Meeting was held 10-12 May at the HF Ipanema Park Hotel in the beautiful old city of
A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, 10-12 MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL Jane Meijlink This year, the ESSIC Annual Meeting was held 10-12 May at the HF Ipanema Park Hotel in the beautiful old city of
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT
 Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
NEUROGENIC BLADDER. Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph
 NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
Summary. Neuro-urodynamics. The bladder cycle. and voiding. 14/12/2015. Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics
 Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
BJUI. Mini Reviews. Urological Oncology. Lower Urinary Tract. Sexual Medicine. Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology. Reconstructive and Paediatric Urology
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Mini Reviews Urological Oncology Sexual Medicine Lower Urinary Tract Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology Reconstructive and Paediatric Urology Investigative Urology 8 The Authors Original
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Mini Reviews Urological Oncology Sexual Medicine Lower Urinary Tract Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology Reconstructive and Paediatric Urology Investigative Urology 8 The Authors Original
Interstitial cystitis
 Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
REVIEW OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY 45 th ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 6-9 October 2015, Montreal, Canada
 REVIEW OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY 45 th ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 6-9 October 2015, Montreal, Canada Jane Meijlink In recent years, the International Continence Society (ICS) has increasingly
REVIEW OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY 45 th ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 6-9 October 2015, Montreal, Canada Jane Meijlink In recent years, the International Continence Society (ICS) has increasingly
Overactive Bladder (OAB) and Quality of Life
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) and Quality of Life Dr. Byron Wong MBBS (Sydney), FRCSEd, FRCSEd (Urol), FCSHK, FHKAM (Surgery) Specialist in Urology Central Urology Clinic Hong Kong Continence Society Annual
Overactive Bladder (OAB) and Quality of Life Dr. Byron Wong MBBS (Sydney), FRCSEd, FRCSEd (Urol), FCSHK, FHKAM (Surgery) Specialist in Urology Central Urology Clinic Hong Kong Continence Society Annual
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also
 Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder Case study: Mr. Lin I I have started to rush out of meetings to go to the toilet I I need to void every one hour I I used to be quite active. This is becoming
Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder Case study: Mr. Lin I I have started to rush out of meetings to go to the toilet I I need to void every one hour I I used to be quite active. This is becoming
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
CITATIONS FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS. Urine cytokines suggest an inflammatory response in the overactive bladder: a pilot study.
 CITATIONS FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS IntUrolNephrol. 2010 Sep;42(3):629-35. Epub 2009 Sep 26. Urine cytokines suggest an inflammatory response in the overactive bladder: a pilot study. Tyagi P, Barclay
CITATIONS FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS IntUrolNephrol. 2010 Sep;42(3):629-35. Epub 2009 Sep 26. Urine cytokines suggest an inflammatory response in the overactive bladder: a pilot study. Tyagi P, Barclay
A REVIEW OF THE ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS), AUGUST 2013, BARCELONA, SPAIN
 A REVIEW OF THE ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS), 26-30 AUGUST 2013, BARCELONA, SPAIN Jane Meijlink It was perhaps not so surprising to find that this year s ICS
A REVIEW OF THE ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS), 26-30 AUGUST 2013, BARCELONA, SPAIN Jane Meijlink It was perhaps not so surprising to find that this year s ICS
