5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
|
|
|
- Toby Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and attended by a total of 750 people. Aspects covered in this review: - Task of the 23 ICI Committees - Committee 19: Painful Bladder Syndrome - Poster abstract on IC from France - Successful IPBF info stand raises question: is sufficient attention being paid to this topic in medical education? Task of the 23 ICI Committees The purpose of this 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence (ICI), attended by medical professionals with a special interest in all aspects of incontinence including Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome, was to: Review the current state of knowledge on incontinence Propose a widely accepted strategy for the practical diagnostic and therapeutic management of incontinence following the Evidence-Based Medicine principles Propose validated standard international instruments (i.e. Symptom Scores) to evaluate incontinence in collaboration with the major associations involved in the field of incontinence Help standardize response criteria and recommendations for clinical research on incontinence. In addition to their presentation in Paris, each of the 23 committees dealing with a specific topic will contribute a chapter to a book to be published hopefully by the end of this year, or early Each committee was asked to assess: What we know What we think we know What we don t know What we need to know. The consultation s methodology follows Evidence Based Principles defined in collaboration with the Oxford and Cochrane groups. 1
2 Committee 19: Painful Bladder Syndrome A summary Since committee chairman Professor Philip Hanno from the USA was unable to attend the ICI meeting in Paris, the report on Painful Bladder Syndrome was instead presented by Professor Jørgen Nordling from Denmark. He opened with a brief history of the name and proposed changing the name to Bladder Pain Syndrome, in accordance with the name change proposal (2006) by the European Society for the Study of IC/PBS (ESSIC) of which he is chairman. This proved to be a controversial issue since it is only 4 years since the last ICI meeting in Monaco in 2004 when this committee proposed using the name Painful Bladder Syndrome including Interstitial Cystitis. Professor Nordling reviewed definitions and criteria used over the years, including the NIDDK criteria, the ICS definition and most recently the ESSIC definition, with an explanation of the ESSIC classification system based on findings at cystoscopy, hydrodistension and biopsy and whether or not these investigations have been performed. On the topic of IC epidemiology, he quoted from the 2004 Consultation with its description of epidemiology as being:.confounded by the lack of a uniform definition, lack of any readily available validated diagnostic marker than can be reproducibly utilized in the general population, and an unknown etiology and pathophysiology. Professor Nordling then added that today in 2008 there has been no significant improvement in those confounding factors. This committee emphasized that disorders associated with IC are being inadequately investigated. These associated disorders did not form part of the classic NIDDK diagnostic criteria and have not been considered to be part of the routine history or physical examination for IC. They have not been reported on in published clinical studies of IC and updated literature is not discussed in major urology textbooks. These associated disorders should be explored because: there is no agreed-upon pathognomonic bladder pathology to suggest that it is solely an end-organ disorder; the outcome of well-designed, multi-centre, placebo-controlled trials directed at the bladder have been disappointing; if asked, patients frequently complain of diverse concomitant symptoms which are also chronic and bothersome. While there has been increasing interest in IC and associated disorders, they have largely been investigated by specialists in the associated diseases. The committee concluded that when properly investigated, it can be demonstrated that there are many symptom-based chronic pain disorders significantly associated with IC. Professor Nordling also mentioned genetic links that have been studied. Professor Nordling presented a diagram with an etiological hypothesis: it may commence with a bladder insult which hypothetically could be caused by pelvic floor dysfunction, an autoimmune disorder, bacterial cystitis, primary neurogenic inflammation, bladder trauma or bladder overdistension, leading to damage to the bladder epithelium. The bladder then fails to repair the damage (possibly due to antiproliferative factor secreted by epithelial cells), causing leakage of toxic urine constituents (potassium) into the interstitium. This could result in a number of events 2
3 such as mast cell activation and histamine release, C-fiber activation, substance P release as well as immunogenic and allergic responses, leading to progressive bladder injury. Consequent chronic pain could perhaps lead to change in neurotransmission in the spinal cord or brain, with the possibility of causing persistent chronic neuropathic pain even when the original bladder insult has ceased. Moving on to diagnosis and evaluation, Professor Nordling emphasized that confusable diseases must be excluded as the cause of the symptoms. The long list of confusable diseases can be excluded in stages by a detailed medical history and focused physical examination, urinalysis and culture, flow, pressure-flow and ultrasound, cystoscopy and biopsy. On the subject of clinical symptom scores: no questionnaire has either the specificity or sensitivity to be used in clinical diagnosis. A variety of questionnaires can be used for following the course of the disease, assessing the severity of the disease or as primary endpoint in clinical treatment studies to measure overall improvement. Treatment: Grades of recommendation go from A (highest) to D (lowest), and levels of evidence from 1 (highest) to 4 (lowest). Please note that grading is based on evidence from published studies. This may differ from unpublished clinical practice. In the field of conservative treatment: behavioural modification (evidence level 3), physical therapy (level 2 evidence), stress reduction (level 4 evidence) and dietary manipulation (level 4 evidence) all received a grade C recommendation. Pharmacotherapy: Oral medications discussed were: Antidepressants Antihistamines Immunosuppressants Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Analgesics. Antidepressants: Amitriptyline: Level 2 evidence, grade B recommendation. There has been 1 randomized controlled trial and a number of non-controlled studies. The theoretical mechanisms of amitriptyline include: central and peripheral anticholinergic action, sedative action, blocking H1-histaminergic receptors, analgesic action (inhibiting re-uptake of serotonin and noradrenaline). Desipramine and doxepin received level 3 evidence and grade C recommendation. Antihistamines: Hydroxyzine: Level 1b evidence, grade D recommendation. Blocks neuronal activation of mast cells, is anticholinergic, angiolytic and analgesic. It has been shown to have good therapeutic effects by several non-controlled studies, but an NIDDK study in 2003 showed no significant benefit. Immunosuppressants: Cyclosporine: Level 3 evidence, grade C recommendation. 3 uncontrolled studies, 1 study comparing cyclosporine with PPS. Cyclosporine appears to improve pain and 3
4 frequency, but has potentially serious side effects and should only be considered in severe, intractable patients. IPD-1151T: Suppresses helper T-cells producing IL-4 and 5. There has only been one uncontrolled study reported, but a large-scale placebo-controlled study is underway. Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium (PPS): There have been 5 randomized controlled trials with mixed results. Unfavourable results came from Holm-Bentzen et al in 1997 and Sant et al (NIDDK study) in 2003; favourable results from Parsons & Mulholland (1987), Mulholland et al (1990), Parsons et al (1993). The committee awarded PPS level 1 evidence but grade D recommendation due to conflicting level 1 evidence. Intravesical treatment The committee s grading for intravesical treatment was as follows: DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide 2 B Heparin 3 C Hyaluronic acid 4 D Chrondroitin sulfate 4 D Pentosan polysulfate sodium 4 D Capsaicin, Resiniferatoxin 1 D Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) 1 D Oxybutynin 4 D Lidocaine 2 C Botulinum toxin 4 D Sacral Neuromodulation Sacral Neuromodulation for IC patients is still an investigational procedure. Its therapeutic effects have not yet been fully confirmed. The committee emphasized that strict patient selection and detailed discussion with the patient, including providing the patient with reported long-term results are all essential before embarking on this procedure. Bladder distension Bladder distension has been used for many years not only as a diagnostic tool but also for the treatment of IC patients. However most studies are retrospective and uncontrolled and evidence is conflicting. Level of evidence 3, grade C recommendation. Hunner s lesion (ulcer) Transurethral resection: results with this method of treatment were first reported in 1974 by Greenberg et al. Peeker et al reported in 2000 that 92 of 116 patients experienced an improvement in their symptoms. The average duration was 23 months, ranging from months. Up to 16 re-resections were performed. Laser fulgeration: in 1994 Malloy & Shanberg reported improvement but a need for further therapy in some patients. Small bowel perforation was seen in 2 patients by Shanberg & Malloy in
5 In 2001 Rofeim et al reported on Nd:YAG laser ablation in 24 IC patients with Hunner s lesion. Within days all experienced symptom improvement without complications. Pain, urgency, nocturia and frequency were improved after 23 months, but relapse in 11 patients necessitated up to four further treatments. Transurethral resection, coagulation or laser ablation of Hunner s lesion (ulcer) were given level 3 evidence and grade C recommendation. Cystoplasty According to the committee, there is some evidence that cystoplasty with supratrigonal resection may benefit selected patients with end stage classic IC (with Hunner s lesion). There is no evidence that subtrigonal cystectomy with cystoplasty has any outcome advantage over supratrigonal cystectomy but is associated with more complications and poorer functional bladder rehabilitation. Surgery The committee gave the following evidence levels and recommendation grades in the field of surgery: Hydrodistension 3 C Hunner s lesion resection/fulgeration 3 C Bladder augmentation/cystoplasty 3 C - end stage disease Diversion with or without cystectomy 3 C Principles of Management Recommendations by the committee included the following: treatment decisions should be based as far as possible on placebo-controlled RCTs; treatment should be guided by patient-driven outcomes; start with the least invasive treatments; approach surgical therapies with caution; add or subtract treatments on the basis of results in individual patients; consider more extensive evaluation and more invasive therapies in patients who have failed oral and intravesical treatments; unproven therapies should be given within the framework of clinical trials; irreversible surgery should be a last resort, with rare exceptions. The treatment algorithm presented by Professor Nordling and which will be published in the chapter included: Symptoms: in accordance with the Essic definition pain, pressure or discomfort perceived to be related to the bladder with at least one other urinary symptoms (eg frequency, nocturia, urgency); Basic assessment: history, frequency/volume chart, focused physical examination, urinalysis, culture, cytology; 1 st line treatment: conservative therapy, patient education, dietary modification, nonprescription analgesics, pelvic floor relaxation, address treatment of pain; 2 nd line treatment: consider: oral therapies, intravesical therapies, physical therapy, address treatment of pain; 3 rd line treatment: consider: cystoscopy under anaesthesia with bladder distension, fulgeration of Hunner s lesion, address treatment of pain; 5
6 4 th line treatment: consider in context of clinical trial: neuromodulation, botulinum toxin intramural, pharmacologic management, address treatment of pain. Consider: diversion with or without cystectomy, substitution cystoplasty. Future directions of research - Epidemiological study The committee suggested that a screening tool with adequate sensitivity and specificity should be developed and that epidemiological studies should be conducted in the population aimed at detecting incidence and prevalence and at identifying risk factors. A patient database should be established in different regions with long-term follow-up for the purpose of understanding the natural history of the disease and to examine differences in the natural history of the disease between regions. - Phenotyping/sub-grouping patients Patients who also have pain syndromes or autoimmune diseases may have different pathophysiology, natural history and treatment responses from patients who do not have associated disorders. Sub-grouping patients would allow better treatment strategies to be developed but may also answer the question as to whether this is an end-organ disease of the bladder or a systemic condition. A simple tool should be developed for non-specialists to pick out patients with concomitant disorders. Researchers should test the concept that categorizes all types of pelvic pain into one chronic urological pelvic pain syndrome, bearing in mind that some patients have symptoms involving multiple pelvic organs, concurrently or sequentially. - Development of a simple diagnostic test The committee is of the opinion that this is most likely to involve urinary markers. It may help to phenotype patients and may differentiate this condition from other conditions. - Development of a practical multi-disciplinary care model According to the committee, a practical, multi-disciplinary care model, which includes physicians in charge, dieticians, physiotherapists, pain specialists, psychologists, psychiatrists and patient support groups should be developed and evaluated in various settings. This is merely a brief summary of the committee s presentation. The chapter on Painful Bladder Syndrome that will ultimately be contributed to the Incontinence book by committee 19 will of course be much more detailed and include all references. The ICI 2008 committee 19 for Painful Bladder Syndrome comprised the following 6 members: Philip Hanno, MD (Chairman), Jorgen Nordling, MD, Arndt van Ophoven, MD, Alex Lin, MD, Tomohiro Ueda, MD, Leroy Nyberg, MD. 6
7 Poster Abstract on interstitial cystitis 114 abstracts covering a broad scope of topics in the field of incontinence were presented as posters during ICI in Paris. All the ICI poster abstracts can be read exclusively in the new online UroToday International Journal (UIJ): id,27/ There was one study on interstitial cystitis presented from France: Using the Interstitial Cystitis New Diagnostic Criteria in Daily Practice: About 156 Patients. Pascal Mouracade, Hervé Lang, Didier Jacqmin, Christian Saussine. UroToday International Journal 1 (June). doi: /uij The aim of this study was to describe the characteristics of patients with IC and to determine what percentage of a group of 156 patients diagnosed with IC met the ESSIC (European Society for the Study of IC/PBS) 2005 definition of IC and to see how those who met the definition differed from those who did not. The authors concluded that the ESSIC 2005 definition may not be sufficiently sensitive since it appears to exclude over 26% of patients diagnosed as having IC. Minor modifications in the definition (pain type and location) appeared to increase its sensitivity. Read the complete abstract online: methods_ techniques_diagnosis/using_the_intersitital_cystitis_new_diagnostic_criteria_in_daily _practice_about_156_patients.html Explanatory note: The definition referred to here is an International Continence Society (ICS) definition modified by ESSIC in 2005 and subsequently published in European Urology Today in March 2006 in an article entitled: Interstitial Cystitis: definitions and confusable diseases by Dr Joop P van de Merwe and Professor Jørgen Nordling. This definition was also cited by Professor Nordling in 2006 in his review article: J. Nordling. Sensory Bladder Disorders. Int J Clin Pract Suppl 2006 December;(151): 38 42: IC is a disease of unknown origin consisting of the complaint of suprapubic pain related to bladder filling, accompanied by other symptoms, such as increased daytime (1 8 ) and night-time (1 1 ) frequency, and with cystoscopic (glomerulations and/or Hunner s lesions) and/or histological features (mononuclear inflammatory cells including mast cell infiltration and granulation tissue) in the absence of infection or other pathology. This differs from the current ESSIC definition published in 2008 (Van de Merwe JP, Nordling J et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol Jan;53(1):60-7. Epub 2007 Sep 20) which is as follows: Chronic pelvic pain, pressure or discomfort perceived to be related to the urinary bladder accompanied by at least one other urinary symptom such as persistent urge to void or frequency. 7
8 Successful IPBF info stand raises question: is sufficient attention being paid to this topic in medical education? We would like to thank the ICI organizers for so kindly providing us with complimentary stand space in the most perfect location possible. We were overwhelmed by requests for information about IC! Clinicians are also increasingly seeking information about associated disorders. The upcoming NIH/NIDDK MAPP project has already triggered much interest in this aspect. There is still clearly a huge need for information on IC which seems to indicate that insufficient attention may be being paid to this topic in medical education and/or educational courses. It is indeed possible that the information being provided in education and courses is insufficiently practical for clinicians and particularly those working at grass roots level in countries where the treatment options are limited. With the name issue being an exceedingly controversial topic in Paris, we had every opportunity for feedback on our stand and it was becoming increasingly clear that doctors outside Europe (and indeed many IC experts in Europe) do not think that another change in nomenclature is advisable right now and that it should only be done on the basis of scientific evidence. A typical comment was that repeated name changes will result in the disease itself losing credibility in the eyes of both the doctors and the patients. This is a very worrying prospect. For the sake of the patients, internationally acceptable solutions need to be sought. Jane Meijlink 2008 International Painful Bladder Foundation 8
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial cystitis
 Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
LLLT FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS USING AN 830 NM GaAlAs DIODE LASER
 LLLT FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS USING AN 830 NM GaAlAs DIODE LASER *Katsumi Sasaki M.D. 1, Toshio Ohshiro M.D. Ph.D. 2, Takafumi Ohshiro M.D. 1, Shunji Fujii M.D. 1, Yuki Taniguchi M.D. 1, and Toshihide
LLLT FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS USING AN 830 NM GaAlAs DIODE LASER *Katsumi Sasaki M.D. 1, Toshio Ohshiro M.D. Ph.D. 2, Takafumi Ohshiro M.D. 1, Shunji Fujii M.D. 1, Yuki Taniguchi M.D. 1, and Toshihide
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, FEBRUARY 2012
 REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
4/30/2008. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS)
 Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Treatment effectiveness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines?
 original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond
 Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH
 TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores
 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
1 of 8 3/2/15 9:22 PM
 Close window Guideline Title Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Bibliographic Source(s) Hanno PM, Burks DA, Clemens JQ, Dmochowski RR, Erickson D, FitzGerald MP, Forrest
Close window Guideline Title Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Bibliographic Source(s) Hanno PM, Burks DA, Clemens JQ, Dmochowski RR, Erickson D, FitzGerald MP, Forrest
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline.
 Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU)
 SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION
 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier-Kastler, G. Kramer, A. Mattiasson, J-J. Wyndaele Introduction NLUTD (neurogenic lower urinary
GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier-Kastler, G. Kramer, A. Mattiasson, J-J. Wyndaele Introduction NLUTD (neurogenic lower urinary
Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review
 eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
Management of Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Management of ladder Pain Syndrome Green-top Guideline No. 70 RCOG/SUG Joint Guideline ecember 2016 Please cite this paper as: Tirlapur SA, irch JV, Carberry CL, Khan KS, Latthe PM, Jha S, Ward KL, Irving
Management of ladder Pain Syndrome Green-top Guideline No. 70 RCOG/SUG Joint Guideline ecember 2016 Please cite this paper as: Tirlapur SA, irch JV, Carberry CL, Khan KS, Latthe PM, Jha S, Ward KL, Irving
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, March 2008, Milan, Italy
 A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
Endoscopic ablation of Hunner s lesions in interstitial cystitis patients
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Endoscopic ablation of Hunner s lesions in interstitial cystitis patients Ryan A. Payne, MD; R. Corey O Connor, MD; Margarita Kressin, MD; Michael L. Guralnick, MD, FRCSC See related
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Endoscopic ablation of Hunner s lesions in interstitial cystitis patients Ryan A. Payne, MD; R. Corey O Connor, MD; Margarita Kressin, MD; Michael L. Guralnick, MD, FRCSC See related
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information
 Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Program and Abstracts
 Program and Abstracts summary INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR THE STUDY OF BPS ESSIC Annual Meeting Philadelphia (USA) 13-15 June 2014 Venue Geary Hall Hahnemann Hospital, Drexel University 230 North Broad Street
Program and Abstracts summary INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR THE STUDY OF BPS ESSIC Annual Meeting Philadelphia (USA) 13-15 June 2014 Venue Geary Hall Hahnemann Hospital, Drexel University 230 North Broad Street
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
ESSIC 2008 Annual Meeting Rome
 Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Functional Bladder Problems
 european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
Interstitial Cystitis
 J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE
 12 GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE (Text updated March 2005) J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, K.E. Andersson, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
12 GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE (Text updated March 2005) J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, K.E. Andersson, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
BJUI. Mini Reviews. Urological Oncology. Lower Urinary Tract. Sexual Medicine. Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology. Reconstructive and Paediatric Urology
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Mini Reviews Urological Oncology Sexual Medicine Lower Urinary Tract Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology Reconstructive and Paediatric Urology Investigative Urology 8 The Authors Original
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Mini Reviews Urological Oncology Sexual Medicine Lower Urinary Tract Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology Reconstructive and Paediatric Urology Investigative Urology 8 The Authors Original
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
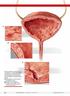 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006
 Annexe 4-1 Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006 (Version courte) 685 686 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E.
Annexe 4-1 Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006 (Version courte) 685 686 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E.
UroToday International Journal. Volume 2 - October 2009
 UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
 Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
 Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain
 Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults
 Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER!
 REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
REVIEW OF THE 42 nd ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS) 15-19 OCTOBER 2012, BEIJING, CHINA GREAT MEETING FOR CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN AND PAINFUL BLADDER! Jane Meijlink This
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA
 PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
s r e t n I sititsyc laititsret ystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis In itial Ctsretn IC I sititsyc laititsretni PRODUCT MONOGRAPH
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Intersti t i a l Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Inters IC CONTENTS Interstitial Cystitis: An Overview Introduction... Epidemiology of
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Intersti t i a l Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Inters IC CONTENTS Interstitial Cystitis: An Overview Introduction... Epidemiology of
Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial cystitis
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome
 CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC)
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Management of OAB. Lynsey McHugh. Consultant Urological Surgeon. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL
 A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, 10-12 MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL Jane Meijlink This year, the ESSIC Annual Meeting was held 10-12 May at the HF Ipanema Park Hotel in the beautiful old city of
A REVIEW OF THE ESSIC ANNUAL MEETING 2012, 10-12 MAY 2012, PORTO, PORTUGAL Jane Meijlink This year, the ESSIC Annual Meeting was held 10-12 May at the HF Ipanema Park Hotel in the beautiful old city of
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
 Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice
 Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
2/9/2008. Men Women. Prevalence of OAB. Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence (%) < Age (years)
 Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
 Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
International Painful Bladder Foundation
 International Painful Bladder Foundation The IPBF is a voluntary non-profit organization for interstitial cystitis/ painful bladder syndrome www.painful-bladder.org IPBF E-Newsletter, Issue 12, June 2008
International Painful Bladder Foundation The IPBF is a voluntary non-profit organization for interstitial cystitis/ painful bladder syndrome www.painful-bladder.org IPBF E-Newsletter, Issue 12, June 2008
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Incontinence; Lets talk about it. Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery
 Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
BSUG Annual scientific update 5/6 th Nov 2012
 BSUG Annual scientific update 5/6 th Nov 2012 Zainab Khan SWIG 4/12/2012 New developments in drug therapy B3 Agonists: Mirabegron - FDA approval - Mirabegron (50 &100mg) vs tolterodine 4mg- similar efficacy,
BSUG Annual scientific update 5/6 th Nov 2012 Zainab Khan SWIG 4/12/2012 New developments in drug therapy B3 Agonists: Mirabegron - FDA approval - Mirabegron (50 &100mg) vs tolterodine 4mg- similar efficacy,
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS
 NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS
 Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome
 page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Primary Care management of Overactive Bladder (OAB) Prescribing Tips All medicines for OAB have similar dose-related efficacy. More than one agent (up
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations
 EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 179 186 Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations Jørgen Nordling* Department of Urology, Herlev Hospital, University
EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 179 186 Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations Jørgen Nordling* Department of Urology, Herlev Hospital, University
Physicians are required to be scrupulously honest in their dealings with the College.
 CENSURE: IC1902 DR. AARON MATTIS MELLON On September 19, 2014, in accordance with Section 47(1)(c) of The Medical Act, the Investigation Committee censured Dr. Mellon as a record of its disapproval of
CENSURE: IC1902 DR. AARON MATTIS MELLON On September 19, 2014, in accordance with Section 47(1)(c) of The Medical Act, the Investigation Committee censured Dr. Mellon as a record of its disapproval of
Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines
 Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old. The International Continence Society has. In this article:
 Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
Diagnosis and classification of CPP
 GUIDELINEs ON Chronic Pelvic Pain (Text update March 2009) M. Fall (chairman), A.P. Baranowski, S. Elneil, D. Engeler, J. Hughes, E. J. Messelink, F. Oberpenning, A.C. de C. Williams 218 Chronic Pelvic
GUIDELINEs ON Chronic Pelvic Pain (Text update March 2009) M. Fall (chairman), A.P. Baranowski, S. Elneil, D. Engeler, J. Hughes, E. J. Messelink, F. Oberpenning, A.C. de C. Williams 218 Chronic Pelvic
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT
 Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
