MDCT of Abdominal Wall Hernias: Is There a Role for Valsalva s Maneuver?
|
|
|
- Melina Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 bdominal Imaging Jaffe et al. s Maneuver in MDCT of Hernia Tracy. Jaffe 1 Martin J. O Connell John P. Harris Erik K. Paulson David M. DeLong Received May 10, 2004; accepted after revision July 23, ll authors: Department of Radiology, Duke University Medical Center, ox 3808, Durham, NC ddress correspondence to T.. Jaffe (jaffe002@mc.duke.edu). JR 2005;184: X/05/ merican Roentgen Ray Society MDCT of bdominal Wall Hernias: Is There a Role for s Maneuver? OJECTIVE. Our objective was to evaluate the role of s maneuver during MDCT for the diagnosis and characterization of abdominal wall hernias. SUJECTS ND METHODS. From September 2002 to May 2003, 100 consecutive patients (37 men and 63 women; mean age, 53 years) with suspected anterior abdominal wall hernias underwent 4-, 8-, or 16-MDCT with and without s maneuver. Patients received both oral and IV contrast material. On a workstation, three independent reviewers evaluated each scan obtained during rest and during s maneuver for the following parameters: anteroposterior (P) diameter of the abdomen; presence, location, and contents of the hernia; and transverse diameter of the fascial defect. The scans were compared to assess for changes in hernia size and contents and to determine whether the hernia would have been overlooked without s maneuver. Fisher s exact test, the McNemar test, and Cohen s kappa coefficient were used to assess for significant differences. RESULTS. The three reviewers identified a mean of 72 abdominal wall hernias (72%). The reviewers agreed (κ = 0.723) with respect to the presence of a hernia. P diameters increased an average of 1.33 cm during s maneuver (p < 0.001). The transverse diameter of the fascial defect increased an average of 0.66 cm and the P diameter of the hernia sac increased an average of 0.79 cm during s maneuver (p < 0.001). Fifty percent of the hernias became more apparent with s maneuver. Ten percent of the hernias could be detected only on the scan obtained during s maneuver. Conversely, in no patients was the hernia detected only on the rest scan. CONCLUSION. s opposed to scans obtained at rest, scans obtained during s maneuver aid in the detection and characterization of suspected abdominal wall hernias. single scan obtained during s maneuver is sufficient to detect 100% of anterior abdominal wall hernias identified on CT. he repair of abdominal wall hernias has become a growth area for T many surgical practices [1, 2]. Implicit in the workup of these hernias is the ability to diagnose and characterize the size and specific location of the anatomic defect and the contents of the hernia sac. The diagnosis of abdominal wall hernias is based primarily on physical examination, which includes s maneuver. s maneuver is used to make the hernia more apparent clinically, because the increase in intraabdominal pressure causes the hernia sac to enlarge and protrude through the anatomic defect [3]. The physical examination is made more difficult in obese or postoperative patients, in whom it is difficult to distinguish a hernia from a postoperative complication such as a hematoma, abscess, or seroma [4 19]. Patients are often referred for imaging studies to confirm a suspected hernia. These studies include radiography, sonography, barium studies, and herniography. CT is being used increasingly to show the specific anatomy of the hernia sac and distinguish a hernia from its mimics. lthough s maneuver is often used in barium studies or sonography of the abdominal wall, we found no research that evaluated the role of s maneuver in MDCT diagnosis of abdominal wall hernias [1, 2]. With MDCT, the short acquisition time allows imaging of the entire abdomen and pelvis within a single breath-hold including s maneuver. The aim of our study was to determine the effect and benefit of s maneuver in the MDCT diagnosis of abdominal wall hernias. JR:184, March
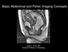
2 Jaffe et al. Subjects and Methods This study was approved by the institutional review board. From September 2002 to May 2003, 100 consecutive patients with suspected abdominal wall hernias underwent MDCT (37 men and 63 women; age range, years; mean, 53 years). Scanning was performed from the dome of the diaphragm to the inferior margin of the pubic symphysis with a 4-, 8-, or 16-MDCT scanner. Patients ingested 450 ml of a 2% barium sulfate suspension (Readi-Cat Z, E-Z-EM) or dilute meglumine diatrizoate (Gastrografin, ristol-myers Squibb) 1 2 hr before imaging. The initial rest acquisition was performed at end-inspiration during a single breath-hold. For this acquisition, 150 ml of iopamidol (Isovue 300, ristol-myers Squib) was injected at a rate of 3 ml per second, unless contraindicated. Seventy-three of the 100 patients received IV contrast material. Scans were acquired during the portal venous phase of enhancement, with a delay determined by bolus tracking and automated triggering technology. Protocols varied depending on whether a 4-, 8-, or 16-MDCT scanner was used. Pitch ranged from 1.5 to 1.75, and table speed ranged from 15 mm per rotation to 17.5 mm per rotation. ll scanners had a 0.5-sec tube rotation. Slice reconstruction thickness was 5 mm for all patients. cquisition duration ranged from 12 to 20 sec. Immediately after the initial scanning, at end-inspiration, the patient was instructed to bear down or strain and a second acquisition was completed during s maneuver. No additional IV or oral contrast material was administered for the second acquisition. The technical parameters for the scan obtained during s maneuver were identical to those of the scan obtained at end-inspiration. Three experienced radiologists with subspecialty training in abdominal imaging reviewed, on a workstation (Centricity 1.0, GE Healthcare), each scan obtained at rest and during s maneuver. The reviewers were unaware of patient identifiers and interpreted each scan independently. Clinical information was not provided to the reviewers. Most notably, reviewers were unaware of the patients prior surgical histories. Each scan was evaluated for multiple parameters including presence, location, and contents of the hernia; anteroposterior (P) diameter of the abdomen; and transverse diameter of the fascial defect. The P diameter of the abdomen was determined by measuring the distance from the anterior aspect of the L5 vertebral body to the anterior skin surface. This distance was measured on both scans. For the purposes of this study, a hernia was defined as a protrusion of abdominal contents through a defect in the normally restraining muscles of the abdomen and pelvis. The location of the hernia was designated as ventral, inguinal, or other. Contents were designated mesenteric or omental fat, colon, small bowel, stomach, bladder, or other. The transverse diameter of the hernia sac aperture and the P diameter of the hernia sac were measured on both scans. The scans obtained at rest and during s maneuver were compared to assess changes in hernia size and contents and to determine whether the hernia was more conspicuous after s maneuver. The reviewers determined whether the hernia would have been overlooked without s maneuver. In addition, they assessed whether evidence of a prior hernia repair was present or whether postoperative complications were present. In the patient with multiple hernias, the reviewers were instructed to characterize the largest defect. The data were collected and entered into a database by the principal investigator. No clinical information was included in this study. The department statistician analyzed the data using version 8.2 of the SS software system (SS Institute). The statistical reliability of a given difference in response rates between respondent subgroups for specific questions was analyzed with Fisher s exact test, the McNemar test, and Cohen s kappa coefficient. p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. kappa value of greater than 0.5 supported agreement between reviewers. Results The three reviewers, designated as R1, R2, and R3, identified an abdominal wall hernia in 69, 74, and 72, respectively, of the 100 patients (mean, 72 hernias). The reviewers agreed with respect to the presence of a hernia (κ = 0.72). Most hernias were ventral (Fig. 1) (R1, 63 [91%]; R2, 66 [89%]; R3, 67 [93%]); Fig year-old man with suspected ventral hernia after abdominal surgery., CT scan obtained with IV and oral contrast material at rest shows defect in anterior abdominal wall (arrows). No intraperitoneal contents herniate through defect. Second defect in muscular anterior abdominal wall is seen (arrowheads) just craniad to ileostomy. t rest, no intraperitoneal contents protrude through this defect., CT scan obtained during s maneuver shows protrusion of colon through midline defect (arrows). In addition, small bowel protrudes (arrowheads) at peristomal defect. 848 JR:184, March 2005
3 s Maneuver in MDCT of Hernia the inguinal hernias were fewer (R1, 5 [7%]; R2, 7 [9%]; R3, 4 [5%]). One hernia was posterior intercostal. The reviewers did not differ in the identification of hernias between men and women. s maneuver was associated with an increase in P diameter in 82 patients (82%) (Fig. 2), a decrease in 14 patients (14%), and no change in four patients (4%). The mean increase in diameter was 1.40 cm, as detailed in Table 1. The change in mean P diameter was statistically significant for all three reviewers (p < 0.001). The P diameter of the hernia sac increased by an average of 0.8 cm with s maneuver (p < 0.001). With s maneuver, the transverse diameter of the hernia sac increased in 51 patients (72%) (Fig. 2), decreased in 11 patients (15%), and did not change in 10 patients (14%). For all three reviewers, the mean change in transverse diameter was 1.40 cm, which was statistically significant (p < 0.001). Hernias became more conspicuous after s maneuver (Table 2). Reviewers noted that the appearance of 56 77% (mean, 70%) of the hernias changed with s maneuver, and 32 72% (mean, 36%) of the hernias became more apparent with s maneuver. The contents of the hernia sac changed with s maneuver, as the maneuver caused small bowel, colon, liver, or fat to protrude into the hernia (Fig. 3). Most important, R1, R2, and R3 found that the hernias in 10, seven, and four patients, respectively, (mean, 7) would have been overlooked if s maneuver had not been not performed (Fig. 4). Conversely, in no patient was a hernia detected only on a rest scan. R1, R2, and R3 identified 32 of 68, 37 of 74, and 46 of 72 hernias, respectively, as craniad to the umbilicus. The remaining hernias were caudad to the umbilicus. For each reviewer, the effect of s maneuver, change in P diameter, change in transverse measurement of the fascial defect, and conspicuity were similar regardless of whether TLE 1 Reviewer Fig year-old man with suspected abdominal wall hernia., CT scan obtained with IV and oral contrast material at rest shows deficiency of anterior abdominal wall (arrows) with protrusion of small bowel and omental fat. Horizontal line denotes transverse diameter of hernia aperture. Short vertical line denotes anteroposterior (P) measurement of hernia sac; long vertical line denotes P measurement of abdomen., CT scan obtained during s maneuver shows protrusion of mesenteric fat and additional small bowel into hernia sac (arrows). In addition, transverse diameter of hernia aperture is wider (horizontal line). Note increase in P measurement of hernia sac (short vertical line) and P diameter of abdomen (long vertical line) with s maneuver. the hernia was craniad or caudad to the umbilicus (p > 0.2 in all cases). Similarly, whether the hernia was craniad or caudad to the umbilicus had no bearing on the likelihood that a hernia would be missed without the s maneuver scan (p > 0.4). In 24% of the patients scanned, prior hernia repair was evident through the presence of mesh or coils on CT. The reviewers identified 14 postoperative complications, including seroma, hematoma, and abscess. Discussion The identification and repair of abdominal wall hernias have become an area of great interest and growth in surgical programs Effect of s Maneuver on bdominal Diameter and Transverse Diameter of Hernia Sac efore P Diameter fter Change p efore Transverse Diameter fter Change R < < R < < R < Mean N N Note. Values are in centimeters. N = not applicable. p JR:184, March
4 Jaffe et al. Fig year-old man with suspected ventral hernia., CT scan obtained at rest with IV and oral contrast material shows defect (arrows) in upper abdominal wall. Portion of colon protrudes through defect, CT scan obtained during s maneuver shows no change in appearance of hernia (arrows). throughout the world [1, 2, 4 17]. Most abdominal wall hernias are obvious clinically. However, the physical examination may be unreliable in obese patients and patients who have had a prior herniorraphy. Studies have found cross-sectional imaging to be sensitive and specific for the evaluation and characterization of hernias, especially in obese or postoperative patients, in whom the clinical diagnosis of recurrence may be difficult [4 19]. MDCT acquisition times have decreased to such a degree that it is possible to scan the entire abdomen and pelvis during a single s maneuver. lthough the addition of s maneuver during CT has been suggested, to our knowledge, no study has documented the efficacy of this maneuver in the diagnosis of abdominal wall hernia. ll our patients received oral and IV contrast material unless clinically contraindicated. Oral contrast material helps distend bowel loops and enhances the differentiation of small bowel from colon. We used IV contrast material to help distinguish between the presence of Fig year-old woman after mesh placement for hernia repair., CT scan obtained at rest with IV and oral contrast material shows mesh (arrows) in anterior abdominal wall. No recurrent hernia is evident at rest., CT scan obtained during s maneuver shows herniation of portion of gas-filled small bowel (arrowheads) at left aspect of mesh (arrow). In this patient, recurrent hernia would have been overlooked unless s maneuver scan had been obtained. 850 JR:184, March 2005
5 s Maneuver in MDCT of Hernia a hernia and its mimics, to assess for inflammation, and to increase the sensitivity for incidental abnormality in the solid organs [11, 16]. s maneuver was originally described in 1704 by ntonio Maria, an Italian anatomist who developed this method for inflating the middle ear. y creating force against a closed glottis, this exercise increases pressure within the thoracic and abdominal cavity. The proposed and desired effect of s maneuver in this study was to increase intraabdominal pressure and accentuate any herniation that may have been occult at rest [3]. Ventral hernias have been evaluated using both rest scans and s maneuver scans at our institution for a number of years. This study was designed to evaluate the role of a scan obtained during s maneuver. Our study showed that s maneuver has an effect on the abdomen and its contents that aids in the detection and characterization of anterior abdominal wall hernias. To our knowledge, no published norms exist on the expected change in intraabdominal morphology on CT after s maneuver. We hypothesized that measurement of P diameter changes would reflect an increase in intraabdominal pressure. In patients with or without identifiable hernias, P diameter increased during s maneuver, suggesting an increase in intraabdominal pressure and producing a satisfactory result from the s maneuver. This was a consistent observation and provided evidence that patients can be instructed in the performance of s maneuver and can maintain the maneuver throughout an MDCT scan. With s maneuver, the transverse measurement of the fascial defect increased. The change in size implies that the abdominal wall musculature changes with s maneuver. These changes accentuate the aperture of the hernia sac. In addition, the P diameter of the hernia sac changes with the addition of s maneuver, implying that the increase in intraabdominal pressure also is transmitted to the hernia sac and its contents. More important, a mean of 51% of hernias become more conspicuous with s maneuver because of protrusion of mesenteric or omental fat, bowel, or solid organs into the hernia sac. s maneuver simulates certain activities of daily living such as heavy lifting, making these findings more clinically relevant. Most important, there are hernias (10% in this series) that will not be diagnosed unless a scan is obtained with s maneuver. These defects are subtle. t rest, the hernia sac is confined within the abdominal wall and not TLE 2 Reviewer Effect of s Maneuver on Hernia Conspicuity Number of Hernias Change with s Maneuver detected. It is only with the increased pressure from s maneuver that these fascial defects and hernia sacs become identifiable. The identification of this subset of patients provides a strong argument that in patients referred with suspected hernia, it is imperative to obtain a scan during s maneuver. bsence of hernia on a scan obtained at rest cannot exclude the presence of a hernia. This study had some limitations. First, the s maneuver scan was obtained immediately after the rest scan. The scans were not identical because no additional IV contrast material was administered for the second scan. We do not think that this discrepancy in technique affected the final characterization of the anterior abdominal wall. Second, the rest scan and the s maneuver scan were interpreted at the same time. This design may have created a bias that would not be present if the studies were interpreted individually and randomly. Third, we reviewed only 100 patients, and only ventral hernias were well represented. Finally, we did not study the clinical impact of the noted increase in hernia conspicuity. In our series, no patient showed a hernia on the rest scan but no hernia on the s maneuver scan. This finding suggests that a single scan during s maneuver would identify most, if not all, anterior abdominal wall hernias. On the basis of our results, we have altered our practice: In patients referred for suspected hernia, we obtain a scan only during s maneuver, as opposed to both at rest and during s maneuver. This approach will reduce the radiation dose to the patient and lower the cost, scanner time, and archive memory. single scan obtained during s maneuver is sufficient to detect 100% of anterior abdominal wall hernias identified on CT. More Conspicuous with s Maneuver Identified Only with s Maneuver R (75) 49 (71) 10 (14) R (77) 37 (50) 7 (9) R (56) 23 (32) 4 (6) Mean (69) 36 (50) 7 (10) Note. Numbers in parentheses are percentages. References 1. Gore RM, Levine MS, eds. Textbook of gastrointestinal radiology, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, P: Saunders, 2000: Schwartz SI, Shires GT, eds. Principles of surgery, 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Inc., 1994: Light HG, Routeledge J. Intra-abdominal pressure factor in hernia disease. rch Surg 1965;90: Lee GHM, Cohen J. CT imaging of abdominal hernias. JR 1993;161: Toms P, Cash CCJ, Fernando, Freeman H. bdominal wall hernias: a cross-sectional pictoral review. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2002;23: Wechsler RJ, Kurtz, Needleman L, et al. Cross-sectional imaging of abdominal wall hernias. JR 1989;153: Hojer M, Rygaard H, Jess P. CT in the diagnosis of abdominal wall hernias: a preliminary study. Eur Radiol 1997;7: Stable Ianora, Midiri M, Vinci R, Rotondo, ngelelli G. bdominal wall hernias: imaging with spiral CT. Eur Radiol 2000;10: Rose M, Eliakim R, ar-ziv Y, Vromen, Rachmilewitz D. bdominal wall hernias: the value of computed tomography diagnosis in the obese patient. J Clin Gastroenterol 1994;19: Gutierrez del la Pena G, Vargas Romero J, Dieguez Garcia J. The value of CT diagnosis of hernia recurrence after prosthetic repair of ventral incisional hernias. Eur Radiol 2001;11: Lin HJ, Vargish T, Dachman H. CT findings after laparoscopic repair of ventral hernia. JR 1999;172: Emby DJ, oun G. CT technique for suspected anterior abdominal wall hernia. JR 2003;181: Toms P, Dixon K, Murphy JMP, Jamieson NV. Illustrated review of new imaging techniques in the diagnosis of abdominal wall hernias. r J Surg 1999;86: Harrison L, Keesling C, Martin NL, Lee KR, Wetzel LH. bdominal wall hernias: review of herniography and correlation with cross-sectional imaging. RadioGraphics 1995;15: Miller P, Mezwa DG, Feczko PJ, Jafri ZH, Madrazo L. Imaging of abdominal hernias. RadioGraphics 1995;15: Goodman P, alachandran S. CT evaluation of the abdominal wall. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 1995;33: Ghahremani GG, Jimenez M, Rosenfeld M, Rochester D. CT diagnosis of occult incisional hernias. JR 1987;148: Stamm ER, Pretorius DH, Olson LK. bdominal wall CT: a pictorial essay. Comput Radiol 1985;9: Zarvan NP, Lee FT, Yandow DR, Unger JS. bdominal hernias: CT findings. JR 1995;164: JR:184, March
MSCT in evalutation of hernial sac volume using Valsalva's maneuver in patients with ventral hernias
 MSCT in evalutation of hernial sac volume using Valsalva's maneuver in patients with ventral hernias Poster No.: C-0794 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Petrenko, O. P. Sharmazanova,
MSCT in evalutation of hernial sac volume using Valsalva's maneuver in patients with ventral hernias Poster No.: C-0794 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Petrenko, O. P. Sharmazanova,
Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction
 Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction Scott Lenobel 1*, Robert Lenobel 2, Joseph Yu 1 1. Department of Radiology, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center,
Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction Scott Lenobel 1*, Robert Lenobel 2, Joseph Yu 1 1. Department of Radiology, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center,
Pictorial Essay. Abdominal Wall Hernias: MDCT Findings. Diego A. Aguirre1, Giovanna Casola, Claude Sirlin
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.100 on 11/29/17 from IP address 37.44.192.100. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay bdominal Wall Hernias: MDCT Findings
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.100 on 11/29/17 from IP address 37.44.192.100. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay bdominal Wall Hernias: MDCT Findings
Differentiation of Femoral Versus Inguinal Hernia: CT Findings
 Suzuki et al. CT of Femoral and Inguinal Hernias Abdominal Imaging Original Research Shigeru Suzuki 1 Shigeru Furui 1 Kota Okinaga 2 Tsutomu Sakamoto 3 Jun Murata 4 Akira Furukawa 5 Yasuo Ohnaka 6 Suzuki
Suzuki et al. CT of Femoral and Inguinal Hernias Abdominal Imaging Original Research Shigeru Suzuki 1 Shigeru Furui 1 Kota Okinaga 2 Tsutomu Sakamoto 3 Jun Murata 4 Akira Furukawa 5 Yasuo Ohnaka 6 Suzuki
Original Report. Stercoral Colitis Leading to Fatal Peritonitis: CT Findings. Gastrointestinal Imaging Heffernan et al. CT of Stercoral Colitis
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Heffernan et al. CT of Stercoral Colitis Cathleen Heffernan 1 H. Leon Pachter 2 lec J. Megibow 1 Michael Macari 1 Hefferman C, Pachter HL, Megibow J, Macari M Received pril 21,
Gastrointestinal Imaging Heffernan et al. CT of Stercoral Colitis Cathleen Heffernan 1 H. Leon Pachter 2 lec J. Megibow 1 Michael Macari 1 Hefferman C, Pachter HL, Megibow J, Macari M Received pril 21,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Original Report. Duodenal Diverticula Mimicking Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas: CT and MR Imaging Findings in Seven. Patients
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.198.217 on 12/11/17 from IP address 46.3.198.217. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Michael Macari 1 Dawn Lazarus Gary Israel lec Megibow
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.198.217 on 12/11/17 from IP address 46.3.198.217. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Michael Macari 1 Dawn Lazarus Gary Israel lec Megibow
CT Findings in the Abdomen and Pelvis After Gastric Carcinoma Resection
 CT Findings in the Abdomen and Pelvis After Gastric Carcinoma Resection Kyeong Ah Kim 1, Cheol Min Park 1, Sang Woo Park 1, Sang Hoon Cha 1, Hae Young Seol 1, In Ho Cha 1, Ki Yeol Lee 2 G astric carcinoma
CT Findings in the Abdomen and Pelvis After Gastric Carcinoma Resection Kyeong Ah Kim 1, Cheol Min Park 1, Sang Woo Park 1, Sang Hoon Cha 1, Hae Young Seol 1, In Ho Cha 1, Ki Yeol Lee 2 G astric carcinoma
Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to:
 RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
Hernias Umbilical Hernia When to See a Surgeon? What Are Symptoms of an Umbilical Hernia? How is Repair Performed?
 Hernias Umbilical Hernia An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the intestine protrudes through the umbilical opening in the abdominal muscles. Umbilical hernias are common and typically harmless. They
Hernias Umbilical Hernia An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the intestine protrudes through the umbilical opening in the abdominal muscles. Umbilical hernias are common and typically harmless. They
Hernia. emoryhealthcare.org
 Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Abdominal Wall Hernias: Cross- Sectional Imaging Signs of Incarceration Determined with Sonography
 Thomas Rettenbacher 1 Alois Hollerweger 2 Peter Macheiner 2 Norbert Gritzmann 2 Thaddeus Gotwald 1 Robert Frass 3 Barbara Schneider 4 Received March 19, 2001; accepted after revision May 11, 2001. 1 Department
Thomas Rettenbacher 1 Alois Hollerweger 2 Peter Macheiner 2 Norbert Gritzmann 2 Thaddeus Gotwald 1 Robert Frass 3 Barbara Schneider 4 Received March 19, 2001; accepted after revision May 11, 2001. 1 Department
THE INS AND OUTS OF HERNIAS WHERE TO START? WHAT IS A HERNIA? CLINICAL INDICATIONS THE INGUINAL CANAL THE CLINICAL QUESTION 18/09/2018
 THE INS AND OUTS OF HERNIAS Cassandra Harrison BA/BSc, MMRU, AMS WHERE TO START? The Clinical Question Essential anatomy Inguinal hernia Scanning technique Variations WHAT IS A HERNIA? CLINICAL INDICATIONS
THE INS AND OUTS OF HERNIAS Cassandra Harrison BA/BSc, MMRU, AMS WHERE TO START? The Clinical Question Essential anatomy Inguinal hernia Scanning technique Variations WHAT IS A HERNIA? CLINICAL INDICATIONS
CT Findings of Rupture, Impending Rupture, and Contained Rupture of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Schwartz et al. CT of bdominal ortic neurysms bdominal Imaging Pictorial Essay W57.FM 12/7/06 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.182 on 01/02/18 from IP address 46.3.194.182. Copyright RRS.
Schwartz et al. CT of bdominal ortic neurysms bdominal Imaging Pictorial Essay W57.FM 12/7/06 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.182 on 01/02/18 from IP address 46.3.194.182. Copyright RRS.
MSCT in diagnostics of rectus abdominis diastasis
 MSCT in diagnostics of rectus abdominis diastasis Poster No.: C-0021 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit D. Petrenko, O. Sharmazanova, N. Bortnuy; Kharkiv/UA Abdomen, Anatomy,
MSCT in diagnostics of rectus abdominis diastasis Poster No.: C-0021 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit D. Petrenko, O. Sharmazanova, N. Bortnuy; Kharkiv/UA Abdomen, Anatomy,
Multitechnique Imaging Findings of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair
 Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Cronin et al. Imaging of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Carmel G. Cronin 1 Mukesh G. Harisinghani Onofrio Catalano Michael. lake
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Cronin et al. Imaging of Prolene Plug Hernia Repair Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Carmel G. Cronin 1 Mukesh G. Harisinghani Onofrio Catalano Michael. lake
Radiologic Anatomy of the Inguinofemoral Region: Insights from MDCT
 Inguinofemoral MDCT Abdominal Imaging Original Research P. T. Cherian 1 A. P. Parnell 2 Cherian PT, Parnell AP Keywords: CT, femoral hernia, inguinal hernia DOI:10.2214/AJR.07.2489 Received November 14,
Inguinofemoral MDCT Abdominal Imaging Original Research P. T. Cherian 1 A. P. Parnell 2 Cherian PT, Parnell AP Keywords: CT, femoral hernia, inguinal hernia DOI:10.2214/AJR.07.2489 Received November 14,
Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences
 C S E R E P O R T Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences Chih-Shun Wu*, Wei-Jen Yao 1, Yen-Hua Huang 2 Sonographic features used in the diagnosis
C S E R E P O R T Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences Chih-Shun Wu*, Wei-Jen Yao 1, Yen-Hua Huang 2 Sonographic features used in the diagnosis
CT Cystography with Multiplanar Reformation for Suspected Bladder Rupture: Experience in 234 Cases
 han et al. T ystography for Suspected ladder Rupture Genitourinary Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G David P. N. han 1 Hani H. bujudeh 2 George L. ushing, Jr. 2 Robert. Novelline
han et al. T ystography for Suspected ladder Rupture Genitourinary Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G David P. N. han 1 Hani H. bujudeh 2 George L. ushing, Jr. 2 Robert. Novelline
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous)
 CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis
 INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
Consecutive, Bilateral Obturator Hernia in a Single Case HO Aydın¹, EHA Soy¹, T Avcı¹, T Tezcaner¹, S Yıldırım ABSTRACT
 Consecutive, Bilateral Obturator Hernia in a Single Case HO Aydın¹, EHA Soy¹, T Avcı¹, T Tezcaner¹, S Yıldırım ABSTRACT Obturator hernia (OH) is a rare pelvic hernia. It is diffucult to make an early diagnosis
Consecutive, Bilateral Obturator Hernia in a Single Case HO Aydın¹, EHA Soy¹, T Avcı¹, T Tezcaner¹, S Yıldırım ABSTRACT Obturator hernia (OH) is a rare pelvic hernia. It is diffucult to make an early diagnosis
Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis
 Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis Poster No.: C-978 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Plata Ariza, E. MARTINEZ CHAMORRO, J.
Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis Poster No.: C-978 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Plata Ariza, E. MARTINEZ CHAMORRO, J.
Which Blunt Trauma Patients Should Be Studied by Abdominal CT?
 MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
CT of the Abdominal Wall
 1207 CT of the Abdominal Wall PhilipGoodma& 2 and Bharat Raval1 CT is an excellent method for evaluating the abdominal wall. Various abnormalities including hernia, hematoma, abscess, tumor, and neuromuscular
1207 CT of the Abdominal Wall PhilipGoodma& 2 and Bharat Raval1 CT is an excellent method for evaluating the abdominal wall. Various abnormalities including hernia, hematoma, abscess, tumor, and neuromuscular
CT staging in sigmoid diverticulitis
 CT staging in sigmoid diverticulitis Poster No.: C-1503 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Buchberger, B. von Rahden, J. Schmid, W. Kenn, C.-T. Germer, D. Hahn; Würzburg/DE Keywords:
CT staging in sigmoid diverticulitis Poster No.: C-1503 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Buchberger, B. von Rahden, J. Schmid, W. Kenn, C.-T. Germer, D. Hahn; Würzburg/DE Keywords:
Gastrectomy procedure and its complications: Findings at TC multi-detector 64 row.
 Gastrectomy procedure and its complications: Findings at TC multi-detector 64 row. Poster No.: C-2184 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. M. Mendigana Ramos, A. Burguete, A. Sáez de
Gastrectomy procedure and its complications: Findings at TC multi-detector 64 row. Poster No.: C-2184 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. M. Mendigana Ramos, A. Burguete, A. Sáez de
INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR PROCEDURE GUIDE
 ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
Characteristic Locations of Inguinal Region and Anterior Abdominal Wall Hernias: Sonographic Appearances and Identification of Clinical Pitfalls
 Sonography of Inguinal Region and bdominal Wall Hernias Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay David. Jamadar 1 Jon. Jacobson 1 Yoav Morag 1 Gandikota Girish 1 Qian Dong 1 Mahmoud l-hawary 1 Michael
Sonography of Inguinal Region and bdominal Wall Hernias Gastrointestinal Imaging Pictorial Essay David. Jamadar 1 Jon. Jacobson 1 Yoav Morag 1 Gandikota Girish 1 Qian Dong 1 Mahmoud l-hawary 1 Michael
Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol
 Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol Romolo Gaspari CHAPTER 3 GOAL OF THE FAST EXAM Demonstrate free fluid in abdomen, pleural space, or pericardial space. EMERGENCY ULTRASOUND
Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol Romolo Gaspari CHAPTER 3 GOAL OF THE FAST EXAM Demonstrate free fluid in abdomen, pleural space, or pericardial space. EMERGENCY ULTRASOUND
Missed And Delayed Diagnosis Of Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report
 Missed And Delayed Diagnosis Of Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report Mohammed Tafash Dagash M.B.Ch.B, FICMS Instructor Department of Surgery College of Medicine Anbar University Iraq- Al-Anbar-Fallujah
Missed And Delayed Diagnosis Of Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report Mohammed Tafash Dagash M.B.Ch.B, FICMS Instructor Department of Surgery College of Medicine Anbar University Iraq- Al-Anbar-Fallujah
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest
 (Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
Intestinal Ischemia Versus Intramural Hemorrhage: CT Evaluation
 Michael Macari 1 Hersch Chandarana Emil althazar James abb Received March 27, 2002; accepted after revision July 11, 2002. 1 ll authors: Department of Radiology, bdominal Imaging Section, Tisch Hospital,
Michael Macari 1 Hersch Chandarana Emil althazar James abb Received March 27, 2002; accepted after revision July 11, 2002. 1 ll authors: Department of Radiology, bdominal Imaging Section, Tisch Hospital,
C. CT scan shows ascites and thin enhancing parietal peritoneum
 291 A B Fig. 1. A 55-year-old gastric cancer patient with peritoneal carcinomatosis. At surgery, there was large amount of ascites in peritoneal cavity and there were multiple small metastatic nodules
291 A B Fig. 1. A 55-year-old gastric cancer patient with peritoneal carcinomatosis. At surgery, there was large amount of ascites in peritoneal cavity and there were multiple small metastatic nodules
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery doi: To be assigned Early view version published: November
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery doi: To be assigned Early view version published: November
A Study of the Clinical Manifestation of Subclinical Inguinal Hernias
 75 Original Article J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 8, pp. 75 81, 2017 A Study of the Clinical Manifestation of Subclinical Inguinal Hernias Keisuke Ida, Shinjiro Kobayashi, Takehito Otsubo, Natsuko Sasaki,
75 Original Article J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 8, pp. 75 81, 2017 A Study of the Clinical Manifestation of Subclinical Inguinal Hernias Keisuke Ida, Shinjiro Kobayashi, Takehito Otsubo, Natsuko Sasaki,
The Comparison Of Measurements On Chest X-Ray For Patients With Pectus Deformity. S Gurkok, O Genc, M Dakak, A Gozubuyuk, R Gorur, K Balkanli
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 The Comparison Of Measurements On Chest X-Ray For Patients With Pectus Deformity S Gurkok, O Genc, M Dakak, A Gozubuyuk,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 The Comparison Of Measurements On Chest X-Ray For Patients With Pectus Deformity S Gurkok, O Genc, M Dakak, A Gozubuyuk,
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial)
 CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
2015 General Surgery Survival Guide
 2015 General Surgery Survival Guide Chapter 10: Hernia Repair Know What to Look for When Coding Hernia Repair Reporting hernia repair can be tricky. But if you know what to look for then half the work
2015 General Surgery Survival Guide Chapter 10: Hernia Repair Know What to Look for When Coding Hernia Repair Reporting hernia repair can be tricky. But if you know what to look for then half the work
Cross-Sectional Imaging of Abnormalities of the Abdominal Wall in Pediatric Patients
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.207.198 on 02/06/18 from IP address 37.44.207.198. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved ross-sectional Imaging of bnormalities of the bdominal
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.207.198 on 02/06/18 from IP address 37.44.207.198. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved ross-sectional Imaging of bnormalities of the bdominal
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment
 1 I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment II. Author Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Indiana University Department of Radiology Riley Hospital for Children 702 Barnhill Rd., Rm 1053b
1 I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment II. Author Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Indiana University Department of Radiology Riley Hospital for Children 702 Barnhill Rd., Rm 1053b
Clinical Outcomes of Pediatric Patients With Acute Abdominal Pain and Incidental Findings of Free Intraperitoneal Fluid on Diagnostic Imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Clinical Outcomes of Pediatric Patients With Acute Abdominal Pain and Incidental Findings of Free Intraperitoneal Fluid on Diagnostic Imaging Samantha Matz, DO, Mary Connell, MD, Madhumita
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Clinical Outcomes of Pediatric Patients With Acute Abdominal Pain and Incidental Findings of Free Intraperitoneal Fluid on Diagnostic Imaging Samantha Matz, DO, Mary Connell, MD, Madhumita
Abdominalwall hernias
 Abdominalwall hernias Poster No.: C-1120 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Molinares, W. Quiceno, G. Vélez, L. Sanchez; CO Keywords: Abdomen, Abdominal wall, Anatomy, CT, Ultrasound,
Abdominalwall hernias Poster No.: C-1120 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Molinares, W. Quiceno, G. Vélez, L. Sanchez; CO Keywords: Abdomen, Abdominal wall, Anatomy, CT, Ultrasound,
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less)
 Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Pulmonary Nodule Volumetric Measurement Variability as a Function of CT Slice Thickness and Nodule Morphology
 CT of Pulmonary Nodules Chest Imaging Original Research Myria Petrou 1 Leslie E. Quint 1 in Nan 2 Laurence H. aker 3 Petrou M, Quint LE, Nan, aker LH Keywords: chest, lung disease, MDCT, oncologic imaging,
CT of Pulmonary Nodules Chest Imaging Original Research Myria Petrou 1 Leslie E. Quint 1 in Nan 2 Laurence H. aker 3 Petrou M, Quint LE, Nan, aker LH Keywords: chest, lung disease, MDCT, oncologic imaging,
Pictorial Essay. Imaging of Urinary Bladder Hernias. Genitourinary Imaging Bacigalupo et al. Urinary Bladder Hernias
 Genitourinary Imaging acigalupo et al. Urinary ladder Hernias Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 05/14/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
Genitourinary Imaging acigalupo et al. Urinary ladder Hernias Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 05/14/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
Emergency presentation of hernias of the torso: What your surgeon wants to know.
 Emergency presentation of hernias of the torso: What your surgeon wants to know. Ken F Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology UW Medicine Harborview Medical Center klinnau@uw.edu Nordic Forum 2017 Helsinki,
Emergency presentation of hernias of the torso: What your surgeon wants to know. Ken F Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology UW Medicine Harborview Medical Center klinnau@uw.edu Nordic Forum 2017 Helsinki,
2. Blunt abdominal Trauma
 Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Clinical Payment and Coding Policy Committee Approval Date: 02/23/2018
 In the event of a conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
In the event of a conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
Clinical Payment and Coding Policy Committee Approval Date: 02/23/2018
 In the event of conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
In the event of conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls
 MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls Poster No.: C-0987 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. V. Bhargavi, R. Avantsa, P. Kala; Bangalore/IN
MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls Poster No.: C-0987 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. V. Bhargavi, R. Avantsa, P. Kala; Bangalore/IN
Discussion of Complex Clinical Scenarios and Variable Review ACS NSQIP Clinical Support Team
 Discussion of Complex Clinical Scenarios and Variable Review CS NSQIP Clinical Support Team SCR Open Q& Calls The CS NSQIP Clinical Team is trialing Open format Q& calls for NSQIP SCRs Participation in
Discussion of Complex Clinical Scenarios and Variable Review CS NSQIP Clinical Support Team SCR Open Q& Calls The CS NSQIP Clinical Team is trialing Open format Q& calls for NSQIP SCRs Participation in
Communicating Vein between the Left Renal Vein and Left Ascending Lumber Vein: Incidence and Significance on Abdominal CT
 YAO ET AL ORIGINAL ARTICLE Radiation Medicine: Vol. 21 No. 6, 252 257 p.p., 2003 Communicating Vein between the Left Renal Vein and Left Ascending Lumber Vein: Incidence and Significance on Abdominal CT
YAO ET AL ORIGINAL ARTICLE Radiation Medicine: Vol. 21 No. 6, 252 257 p.p., 2003 Communicating Vein between the Left Renal Vein and Left Ascending Lumber Vein: Incidence and Significance on Abdominal CT
High-Dose IV Contrast in CT Scanning of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine
 703 High-Dose IV Contrast in CT Scanning of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine Peter J. Yang 1 Joachim F. Seeger1 Robert. Dzioba 2 Raymond F. Carmody 1 Todd. urt 1 Norman N. Komar 1 Janice R. Smith 1 Evaluation
703 High-Dose IV Contrast in CT Scanning of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine Peter J. Yang 1 Joachim F. Seeger1 Robert. Dzioba 2 Raymond F. Carmody 1 Todd. urt 1 Norman N. Komar 1 Janice R. Smith 1 Evaluation
Effect of Adjusted Positioning on Gastric Distention and Fluid Distribution During CT Gastrography
 CT Gastrograph y Gastrointestinal Imaging Technical Innovation Se Hyung Kim 1 Jeong Min Lee 1,2 Joon Koo Han 1,2 Jae Young Lee 1,2 Han Kwang Yang 3 Hyuk-Joon Lee 3 Kyung-Sook Shin 4 Byung Ihn Choi 1,2
CT Gastrograph y Gastrointestinal Imaging Technical Innovation Se Hyung Kim 1 Jeong Min Lee 1,2 Joon Koo Han 1,2 Jae Young Lee 1,2 Han Kwang Yang 3 Hyuk-Joon Lee 3 Kyung-Sook Shin 4 Byung Ihn Choi 1,2
Breathe In... Breathe Out... Stop Breathing: Does Phase of Respiration Affect the Haller Index in Patients With Pectus Excavatum?
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research irkemeier et al. Haller Index in Patients With Pectus Excavatum Pediatric Imaging Original Research Krista L. irkemeier 1 Daniel J. Podberesky 1 Shelia Salisbury 2 Suraj
Pediatric Imaging Original Research irkemeier et al. Haller Index in Patients With Pectus Excavatum Pediatric Imaging Original Research Krista L. irkemeier 1 Daniel J. Podberesky 1 Shelia Salisbury 2 Suraj
Inguinal Hernia. Hernia Awareness Month. What is a Hernia? Common Hernia Types
 Hernia Awareness Month What is a Hernia? A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened
Hernia Awareness Month What is a Hernia? A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
A Pleuroperitoneal Bleb Mimicking an Intrathoracic Mass in a Cirrhotic Patient: Three Case Reports 1
 Pleuroperitoneal leb Mimicking an Intrathoracic Mass in a irrhotic Patient: Three ase Reports 1 Jun Ho Kim, M.D., Kyung Hee Lee, M.D., Soon Gu ho, M.D., Yong Sun Jeon, M.D. In a cirrhotic patient, an increase
Pleuroperitoneal leb Mimicking an Intrathoracic Mass in a irrhotic Patient: Three ase Reports 1 Jun Ho Kim, M.D., Kyung Hee Lee, M.D., Soon Gu ho, M.D., Yong Sun Jeon, M.D. In a cirrhotic patient, an increase
Morgagni hernia repair in adult obese patient by hybrid robotic thoracic surgery
 Case Report Morgagni hernia repair in adult obese patient by hybrid robotic thoracic surgery Dario more, Carlo ergaminelli, Davide Di Natale, Dino Casazza, Roberto Scaramuzzi, Carlo Curcio Division of
Case Report Morgagni hernia repair in adult obese patient by hybrid robotic thoracic surgery Dario more, Carlo ergaminelli, Davide Di Natale, Dino Casazza, Roberto Scaramuzzi, Carlo Curcio Division of
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Sonography for diagnosing the presence and type of groin herniae
 Sonography for diagnosing the presence and type of groin herniae Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. H. Y. Leung, K. L. Lee, J. F. Griffith, A. W. H. Ng; Shatin/HK
Sonography for diagnosing the presence and type of groin herniae Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. H. Y. Leung, K. L. Lee, J. F. Griffith, A. W. H. Ng; Shatin/HK
The Questionable Utility of Oral Contrast for the Patient with Abdominal Pain in the Emergency Department
 The Questionable Utility of Oral Contrast for the Patient with Abdominal Pain in the Emergency Department Jonathan Rakofsky, MD PGY3 Henry Ford Hospital Emergency Medicine Program December 2014 All patients
The Questionable Utility of Oral Contrast for the Patient with Abdominal Pain in the Emergency Department Jonathan Rakofsky, MD PGY3 Henry Ford Hospital Emergency Medicine Program December 2014 All patients
Examination of the Extracranial Carotid Bifurcation by Thin-Section Dynamic CT: Direct Visualization
 xamination of the xtracranial Carotid Bifurcation by Thin-Section Dynamic CT: Direct Visualization of Intimal theroma in Man (Part 2) 361. R. Heinz1 J. Fuchs2 D.Osborne 1 B. Drayer1. Yeates 1 H. Fuchs
xamination of the xtracranial Carotid Bifurcation by Thin-Section Dynamic CT: Direct Visualization of Intimal theroma in Man (Part 2) 361. R. Heinz1 J. Fuchs2 D.Osborne 1 B. Drayer1. Yeates 1 H. Fuchs
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts. David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology
 Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Computer-Aided Detection in Screening CT for
 Yuan et al. Screening CT for Pulmonary Chest Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:1280 1287 0361 803X/06/1865 1280 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O Ren Yuan 1 Patrick
Yuan et al. Screening CT for Pulmonary Chest Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:1280 1287 0361 803X/06/1865 1280 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O Ren Yuan 1 Patrick
Elbow Effusions in Trauma in Adults and Children: Is There an Occult Fracture?
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.193.109 on 01/20/18 from IP address 46.3.193.109. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Nancy M. Major 1 Steven T. Crawford 1,2 Received July
Incarcerated obturator hernia: pitfalls in the application of ultrasound
 Crit Ultrasound J (2009) 1:59 63 DOI 10.1007/s13089-009-0017-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Incarcerated : pitfalls in the application of ultrasound Masaaki Ogata Published online: 18 November 2009 Springer-Verlag
Crit Ultrasound J (2009) 1:59 63 DOI 10.1007/s13089-009-0017-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Incarcerated : pitfalls in the application of ultrasound Masaaki Ogata Published online: 18 November 2009 Springer-Verlag
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V
 CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Reducing Radiation Dose in Body CT: A Practical Approach to Optimizing CT Protocols
 Medical Physics and Informatics Review Goldman and Maldjian Reducing Radiation Dose in ody CT Medical Physics and Informatics Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by lice Goldman on 03/26/13 from IP
Medical Physics and Informatics Review Goldman and Maldjian Reducing Radiation Dose in ody CT Medical Physics and Informatics Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by lice Goldman on 03/26/13 from IP
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D
 Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 4 2013 Article 6 Case report: Intussusception of the colon through a colostomy: A rare presentation of colonic intussusception. Dr. Nora Trabulsi Dr.
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 4 2013 Article 6 Case report: Intussusception of the colon through a colostomy: A rare presentation of colonic intussusception. Dr. Nora Trabulsi Dr.
The nontraumatic acute abdomen
 CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE. T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar
 ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
Diagnostic Imaging
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC
 INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
ISPUB.COM. Cardiac Dimensions Derived From Helical Ct: Correlation With Plain Film Radiography
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 1 Number 1 Cardiac Dimensions Derived From Helical Ct: Correlation With Plain Film Radiography J Miller, A Singer, C Hinrichs, S Contractor, S Doddakashi
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 1 Number 1 Cardiac Dimensions Derived From Helical Ct: Correlation With Plain Film Radiography J Miller, A Singer, C Hinrichs, S Contractor, S Doddakashi
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
with Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repair Positioning System SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Designed for Accurate Mesh Centering
 with Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repair Positioning System Designed for Accurate Mesh Centering SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. with A Consistent, Reproducible Technique
with Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repair Positioning System Designed for Accurate Mesh Centering SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. with A Consistent, Reproducible Technique
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research
 Contrast Enema for Detecting nastomotic Strictures Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research David Dolinsky 1 Marc S. Levine 1 Stephen E. Rubesin 1 Igor Laufer 1 John L. Rombeau 2 Dolinsky D, Levine MS,
Contrast Enema for Detecting nastomotic Strictures Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research David Dolinsky 1 Marc S. Levine 1 Stephen E. Rubesin 1 Igor Laufer 1 John L. Rombeau 2 Dolinsky D, Levine MS,
Ask EuroSafe Imaging. Tips & Tricks. CT Working Group. Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose
 Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nancy, FR) Mika Kortesniemi (HUS Medical Imaging
Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nancy, FR) Mika Kortesniemi (HUS Medical Imaging
Left diaphragmmatic eventration with gastric volvulus: Laparoscopic mesh repair of left diaphragmatic eventration
 JMSR Dr. Lakshmikanth T Case Report Left diaphragmmatic eventration with gastric volvulus: Laparoscopic mesh repair of left diaphragmatic eventration Lakshmikanth T 1 and Sanjeeva Rao K 1 1 Department
JMSR Dr. Lakshmikanth T Case Report Left diaphragmmatic eventration with gastric volvulus: Laparoscopic mesh repair of left diaphragmatic eventration Lakshmikanth T 1 and Sanjeeva Rao K 1 1 Department
MDCT of the Elbow in Pediatric Patients with Posttraumatic Elbow Effusions
 Chapman et al. MDCT of the Pediatric Elbow Pediatric Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:812 817 0361 803X/06/1873 812 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O Vernon Chapman
Chapman et al. MDCT of the Pediatric Elbow Pediatric Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:812 817 0361 803X/06/1873 812 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O Vernon Chapman
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V
 CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Evaluate inguinal hernia
 Evaluate inguinal hernia Search 3-3-2018 OBJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to investigate the CT findings of femoral hernias, focusing on their differentiation from inguinal hernias. 3-3-2018 OBJECTIVE.
Evaluate inguinal hernia Search 3-3-2018 OBJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to investigate the CT findings of femoral hernias, focusing on their differentiation from inguinal hernias. 3-3-2018 OBJECTIVE.
International Journal of Current Research and Academic Review ISSN: Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp
 International Journal of Current Research and Academic Review ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 348-354 www.ijcrar.com Study of Operative Procedures and their Indications in Management
International Journal of Current Research and Academic Review ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 348-354 www.ijcrar.com Study of Operative Procedures and their Indications in Management
The Physician as Medical Illustrator
 The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
Abdomen: Introduction. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
