IDIOPATHIC BRACHIAL NEURITIS
|
|
|
- Aldous Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IDIOPATHIC BRACHIAL NEURITIS Pedro Gonzalez-Alegre, MD; Ana Recober, MD and Praful Kelkar, MD ABSTRACT Idiopathic brachial neuritis is a well defined clinical condition that most commonly affects young adults, seen usually by primary care physicians, neurologists or orthopaedic surgeons. Its onset is characterized by acute, aching shoulder pain lasting a few days to weeks, followed by progressive shoulder girdle and upper extremity weakness and atrophy, with a slow but progressive recovery of motor function over 6 to 18 months. Its early recognition can help avoid unnecessary and potentially harmful diagnostic and therapeutic interventions, and avoid delays in prescribing appropriate therapies that may be helpful only early in the course of the disease. We present a case of idiopathic brachial neuritis and discuss important aspects of the disease and difficulties in reaching the correct diagnosis. INTRODUCTION Idiopathic brachial neuritis (IBN), also known as neuralgic amyotrophy, acute shoulder neuritis, acute brachial neuritis, idiopathic brachial plexus neuropathy or Parsonage-Turner syndrome is a disorder of unknown etiology with asymmetric involvement of the brachial plexus. 13 It usually affects young adults and presents with acute severe shoulder pain lasting days to weeks followed by painless paresis of the upper extremity with slow but gradual recovery. 11 Although in typical cases clinical diagnosis is easy to establish, in atypical presentations or situations where the treating physician is not familiar with this condition, misdiagnosis leading to multiple unnecessary diagnostic and therapeutic interventions can occur. Diagnostic tests such as electromyography and nerve conduction studies (EMG/NCS), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the Department of Neurology. University of Iowa College of Medicine. Correspondence to: Praful Kelkar, MD. Director, Division of Neuromuscular Disorders. Department of Neurology. University of Iowa College of Medicine. 200 Hawkins Drive. Iowa City, IA kelkarp@mail.medicine.uiowa.edu shoulder, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination are not required, but can support the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. Good clinical history and examination are key to a correct diagnosis. 9 We present a complex case of IBN and discuss the more important aspects of the disease. CASE HISTORY A 47-year-old right-handed man presented with acute onset left shoulder pain following physical activity related to his job in the construction field. He was evaluated locally and diagnosed with left rotator cuff disease. EMG/NCS were obtained and reportedly showed mild bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. He underwent surgery for left rotator cuff and left carpal tunnel release. As pain improved, weakness developed in the following weeks, and a repeat EMG/NCS reportedly showed left suprascapular neuropathy, which led to a release procedure on that nerve. In the immediate postoperative period, the pain and weakness worsened, and he also developed numbness in the lateral aspect of the left forearm and hand. The pain was treated with non-steroidal antiinflammatory agents, and an MRI of the cervical spine was obtained which was unremarkable. The pain slowly improved, but the weakness continued to worsen within the following 2-3 weeks. A repeat EMG/NCS was interpreted as probable lateral cord brachial plexopathy, left suprascapular neuropathy, ulnar neuropathy at the elbow and carpal tunnel syndrome. MRI of the left brachial plexus showed nonspecific signal abnormality with T2 hyperintensity interpreted as soft tissue edema from surgery. His past, family and social history were otherwise unremarkable. He was sent to our hospital for second opinion. On examination by us he was found to have a flaccid, areflexic paresis involving all muscle groups of the left upper extremity, more pronounced in the supra- and infraspinatus, deltoid and biceps, with mild muscle atrophy. Sensory exam showed mild hypesthesia throughout the left upper extremity. The rest of the physical examination was within normal limits. A clinical diagnosis of IBN was established. Over the next year he underwent physical therapy and the paresis has been slowly improving, although it has not completely resolved. Volume 22 81
2 P. Gonzalez-Alegre, A. Recober, P. Kelkar TABLE 1 Preceding Events in IBN - Infection - Vaccination - Pregnancy and parturition - Trauma at a remote site - Surgery - Radiation - Intravenous heroin use - Treatment with interferon ETIOLOGY AND EPIDEMIOLOGY The etiology of this condition remains unclear, but an immune attack on the brachial plexus or its branches within the limb triggered by various preceding events (Table 1) has been suggested as a cause, 16 although pathological evidence is scant. 7 There is one report of brachial plexus biopsy in patients with IBN showing mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates. 17 Although the great majority of cases of brachial neuritis are sporadic, there is also an autosomal dominant hereditary form, known as hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy (HNA), with some distinct features as discussed below. This disorder has been linked to chromosome 17q24. Patients with HNA suffer recurrent attacks precipitated by the same preceding events as the idiopathic form. 4 Epidemiologically, IBN presents more commonly in the fourth decade, although it is also seen in children and elderly, and in most series it is more common in men in a proportion of 2:1. 8 The estimated incidence has been reported to be 1.64/100,000 persons per year, but this figure is probably low due to misdiagnosis and underrecognition of this clinical entity. 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION Antecedent events days or weeks prior to onset are reported in 28-83% of cases in different series (Table 1). 7,18 The typical clinical course starts with acute, severe, aching, unilateral shoulder and proximal arm pain lasting from days to a few weeks. When the pain abates, painless shoulder girdle and arm weakness develops, more prominent in the upper plexus muscles including deltoid, supra and infraspinatus, serratus anterior and biceps. Forearm and hand muscles are less frequently involved. Marked atrophy of the involved muscles usually develops, but subsequently there is a slow but steady recovery of motor function over the following 6 to 18 months. 11 Usually a longer duration of pain will translate into a longer delay in the recovery phase. The sequence of events described are the classical presentation of IBN, and a good clinical and chronological history should be enough to suspect the diagnosis in the TABLE 2 Dysmorphic Features in HNA - Hypotelorism - Epicanthal folds - Cleft palate - Syndactily or webbing of toes - Primitive pinna with folded helix - Long narrow face - Facial asymmetry absence of atypical features. A detailed neuromuscular examination will show involvement of two or more nerves, confirming a disorder of the brachial plexus. One highly characteristic feature is differential involvement of different muscles innervated by a single peripheral nerve, a pattern seldom seen with other neuropathic disorders. 7 The presence of less common clinical features can make the diagnosis difficult. Up to 15 % of patients have been reported to lack the initial painful stage, the symptom that most commonly suggests the diagnosis. 8 Some patients may have sensory involvement in the form of localized areas of hypoesthesia. Bilateral involvement can be seen in up to 1/3 of patients, although when present is strikingly asymmetric (sometimes one of the involved extremities is asymptomatic, only detected by electrophysiological studies). Single nerve involvement is occasionally seen as the manifestation of IBN, presenting clinically as axillary, suprascapular or long thoracic nerve mononeuropathies, among others. Even less commonly, isolated branches of peripheral nerves can be the only symptom, affecting only individual muscles such as supraspinatus, infraspinatus or flexor pollicis longus. 5,19 Caudal cranial nerves and phrenic nerves may also be affected. 12,14 Very rarely this syndrome can occur in the lumbar area. 15 Pediatric and familial cases differ in some aspects from the more frequent adult-sporadic forms. Children are more likely to have a painless course, have a less favorable recovery, but when they fully recover they do so in a shorter period of time. 21 Familial cases are more easily identifiable if there is a family history of the disease. It differs from the sporadic form in that there are no gender differences, recurrence is common, cranial nerves are more commonly affected and it may be associated with mild dysmorphic features (Table 2). 4 On initial examination, the pain is unaltered by neck or arm movements. Later on, signs of lower motor neuron involvement appear, more pronounced in the upper plexus distribution, with hypotonic, areflexic paresis, and finally signs of denervation such as fasciculations 82 The Iowa Orthopaedic Journal
3 Idiopathic Brachial Neuritis TABLE 3 Differential Diagnosis of IBN Disorder Idiopathic Brachial Cervical Spine Rotator Cuff Mononeuropathies Idiopathic Hypertrophic Symptom Neuritis* Disease Disease Brachial Neuropathy Pain: Characteristics Spontaneous. Mechanical, aggravated Mechanical, aggravated Usually painless. If Usually painless. When Burning/aching. with neck motion. with overhead use. present, pain at present, similar to IBN, Impingement signs. entrapment site or but milder. neuropathic pain in area innervated by it. Onset Acute. Usually insidious. Usually insidious, except postraumatic injuries. Location Shoulder. Neck, radiating to Lateral deltoid and deltoid shoulder and arm. tuberosity. Duration Few days to weeks. Chronic. Chronic. Chronology Precedes motor Simultaneous with motor Simultaneous with motor symptoms. symptoms. symptoms. Weakness Shoulder girdle and arm Follows root distribution Shoulder movement Muscles innervated by Spontaneous resolution (more prominent in Needs medical or surgical muscles. Needs medical single nerve. Resolution but relapses and upper plexus) Slow intervention for or surgical intervention and therapy depends on common residual spontaneous resolution. improvement. for improvement. etiology. weakness. *In hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy there are multiple recurrent episodes similar to IBN, commonly associated with dysmorphic features. and atrophy. The sensory exam is usually, but not always, intact. All these findings slowly improve during the recovery phase. 10 DIAGNOSIS The most important element for the correct diagnosis of IBN is clinical suspicion based on a detailed history and examination, with special emphasis in the chronological development of symptoms and signs. Electrophysiological studies are not needed in typical cases, and they usually show denervation of affected and some clinically unaffected muscles. 18 In the acute/ subacute stages, MRI of the shoulder shows denervation, best on T2-weighted fast spin-echo images with fat saturation. There is increased signal intensity related to neurogenic edema. During the chronic phase, changes are best seen on T1-weighted spin-echo images, which show loss of muscle bulk and diffuse areas of increased signal intensity within the muscle. 3,6 CSF exam is not routinely obtained and is usually normal, but occasionally shows nonspecific abnormalities, such as mildly elevated proteins and IgG. 8 When considering the differential diagnosis, four entities are occasionally mistaken for IBN: cervical spine disease, rotator cuff disease, entrapment neuropathies and idiopathic hypertrophic brachial neuritis (IHBN), although a good clinical history and exam should be enough to differentiate these conditions from typical cases of IBN (Table 3). Cervical radiculopathy (CR) can be also characterized by pain and weakness, but with a different pattern. In CR, the pain usually starts in the neck and radiates down the arm, is worsened by neck movements, sometimes begins after physical injury and pain and weakness occur simultaneously. On exam the weakness and hypesthesia follow a root distribution, and imaging studies of the cervical spine or EMG/NCS will show abnormalities in the affected roots. 10 In rotator cuff disease (RCD), more commonly seen with repetitive overhead or throwing movements, the pain has several characteristic differences, and is the main complaint during the full duration of the disease. The pain usually has an insidious onset, localizes to the lateral deltoid or deltoid tuberosity and worsens with motion such as overhead activities. It is also worse at night or even with palpation, does not resolve with the development of weakness and there is decreased range of motion. Signs of impingement are present and, very characteristic of RCD, they resolve after lidocaine injection in the subacromial space. Imaging studies help in the diagnosis of RCD. 20 On some occasions, IBN may present as an isolated peripheral nerve lesion, suggesting focal compression, when in fact the pathological process is affecting the brachial plexus and the treatment is non-surgical. Examples are cases of IBN presenting as anterior or posterior interosseous, long thoracic or median nerve syndromes, among others. 5 The presence of shoulder pain Volume 22 83
4 P. Gonzalez-Alegre, A. Recober, P. Kelkar followed by the motor deficits should raise the possibility of IBN, which could be then confirmed by electrodiagnostic studies. Idiopathic hypertrophic brachial neuritis (IHBN) is a rare, predominantly motor disorder affecting the brachial plexus and more distal upper limb nerve trunks, with progressive weakness in brachial muscles and hypertrophy of the components of the brachial plexus. Its main difference with IBN is its painless course, although some patients may have significant pain. In this disorder, EMG/NCS will show demyelinating features (not seen in IBN), as have been confirmed by histopathological studies, likely representing a localized form of other peripheral demyelinating disorders, such as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy or multifocal motor neuropathy. 7 Enlargement of the brachial plexus can be seen by MRI, although this is not needed for the diagnosis. TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS The treatment of IBN usually involves a combination of corticosteroids, analgesics, immobilization and physical therapy. The use of corticosteroids is controversial and there are no randomized-controlled trials. However, anecdotal evidence suggests that their use leads to a more rapid resolution of the painful phase of the illness, in particular when used early in its course, although it does not seem to influence the ultimate prognosis. It has been suggested by non-controlled clinical observations that very early treatment with corticosteroids in some cases has resulted in very prompt resolution of the pain, and weakness has not occurred or has been minimal. 7 We recommend prescribing oral prednisone (1mg/kg/day) for 2 weeks, tapering off over an additional 2 week period, if possible starting 24 to 48 hours after the onset of pain. The appropriate control of the initial pain is very important, as it can be quite severe and debilitating. Medications used for pain control are narcotics and nonsteroidals, in combinations as needed. Other agents used for control of neuropathic pain such as tricyclics or antiepileptics are not used because of slow onset of action, requiring a few weeks to reach effective pain control. This is an acute onset severe pain of relatively short duration requiring rapid onset-potent analgesics. In addition, immobilization of the extremity during the short painful stage is also recommended. Once the pain is resolved and the weakness is the prominent symptom, physical therapy is usually initiated with prescribed exercises to continue home rehabilitation. Despite the sometimes dramatic clinical presentation with very severe pain and weakness with denervation, the prognosis is usually good with complete recovery over months in the majority of patients. In a large series, 36% of patients recovered in 1 year, 75 % in two years and 89% in three years. 19 It is very important to inform and educate the patients about the natural history of the disease, and to assure them that, although slow, the recovery is usually very good. Occasionally, there may be residual weakness, or the recovery may be slower taking up to 24 or more months. There are very rare recurrences later in life, but IBN is usually a monophasic illness. 2 Recurrences are common in the inherited form. SUMMARY In summary, IBN is an uncommon condition of probable autoimmune etiology presenting with acute shoulder pain and with a well-defined clinical course. Its diagnosis is easy to establish if the physician is familiar with its clinical manifestations. Detailed history and physical examination may be supported by diagnostic tests as EMG/NCV or MRI of shoulder, which can be useful to exclude other conditions that present with similar symptoms and signs. Management includes a short course of corticosteroids and pain control in the initial stages of the disease, followed by physical therapy. The recovery is usually very good but slow. REFERENCES 1. Beghi E, Kurland LT, Mulder DW, Nicolosi A. Brachial plexus neuropathy in the population of Rochester, Minnesota, Ann Neurol 1985;18: Bradley WG, Madrid R, Thrush DC, et al. Recurrent brachial plexus neuropathy. Brain 1975 Sep;98(3): Bredella MA, Tirman PF, Fritz RC, et al. Denervation syndromes of the shoulder girdle: MR imaging with electrophysiologic correlation. Skeletal Radiol 1999 Oct;28(10): Chance PF, Windebank AJ. Hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy. Curr Opin Neurol 1996 Oct;9(5): England JD. The variations of neuralgic amyotrophy. Muscle Nerve 1999 Apr;22(4): Helms CA, Martinez S, Speer KP. Acute brachial neuritis (Parsonage-Turner syndrome): MR imaging appearance report of three cases. Radiology 1998 Apr;207(1): Kelkar P, Parr y GJ. Brachial plexus disorders. In Noseworthy JH (Editor). Neurologic Therapeutics: Principles and Practice. Martin Dunitz Publishers, London, (in press) 8. Martinez-Salio A, Porta-Etessam J, Berbel A, et al. Amyotrophic neuralgia: review of 37 cases. Rev Neurol 1998 Nov;27(159): McCarty EC, Tsairis P, Warren RF. Brachial neuritis. Clin Orthop 1999 Nov;(368): The Iowa Orthopaedic Journal
5 Idiopathic Brachial Neuritis 10. Miller JD, Pruitt S, McDonald TJ. Acute brachial plexus neuritis: an uncommon cause of shoulder pain. Am Fam Physician 2000 Nov 1;62(9): Misamore GW, Lehman DE. Parsonage-Turner syndrome (acute brachial neuritis). J Bone Joint Surg Am 1996 Sep;78(9): Nardone R, Bernhart H, Pozzera A, et al. Respiratory weakness in neuralgic amyotrophy: report of two cases with phrenic nerve involvement. Neurol Sci 2000 Jun;21(3): Parsonage MJ, Turner JWA. Neuralgic amyotrophy, the shoulder girdle syndrome. Lancet 1948;1: Pierre PA, Laterre CE, Van den Bergh PY. Neuralgic amyotrophy with involvement of cranial nerves IX, X, XI and XII. Muscle Nerve 1990 Aug;13(8): Refisch A, van Laack W. Neuralgic amyotrophy of the lumbar area. Case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1989;108(5): Sierra A, Prat J, Bas J, et al. Blood lymphocytes are sensitized to branchial plexus nerves in patients with neuralgic amyotrophy. Acta Neurol Scand 1991;83: Suarez GA, Giannini C, Bosch EP, et al. Immune brachial plexus neuropathy: suggestive evidence for an inflammatory-immune pathogenesis. Neurology 1996 Feb;46(2): Subramony SH. Neuralgic amyotrophy (acute brachial neuropathy). Muscle Nerve 1988 Jan;11(1): Tsairis P, Dyck PJ, Mulder DW. Natural history of brachial plexus neuropathy. Report on 99 patients. Arch Neurol 1972 Aug;27(2): Tytherleigh-Strong G, Hirahara A, Miniaci A. Rotator cuff disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2001 Mar;13(2): Van Alfen N, Schuuring J, van Engelen BG, et al. Idiopathic neuralgic amyotrosphy in children. A distinct phenotype compared to the adult form. Neuropediatrics 2000 Dec;31(6): Volume 22 85
Case 3. Your Diagnosis?
 Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Brachial Neuritis: An Uncommon Cause of Shoulder Pain
 Brachial Neuritis: An Uncommon Cause of Shoulder Pain ROBERT G. HOSEY, MD; RICHARD E. RODENBERG, MD Brachial neuritis, an uncommon idiopathic syndrome, should be considered in the differential diagnosis
Brachial Neuritis: An Uncommon Cause of Shoulder Pain ROBERT G. HOSEY, MD; RICHARD E. RODENBERG, MD Brachial neuritis, an uncommon idiopathic syndrome, should be considered in the differential diagnosis
Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of unsuspected cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome: two case reports
 Kumar et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:255 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of unsuspected cases of Parsonage-Turner
Kumar et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:255 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of unsuspected cases of Parsonage-Turner
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment
 Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
The clinical manifestations and outcomes of neuralgic amyotrophy
 Neurology Asia 2017; 22(1) : 9 13 The clinical manifestations and outcomes of neuralgic amyotrophy 1 Jung Soo Lee MD PhD, 2 Yoon Tae Kim MD PhD, 3 Joon Sung Kim MD PhD, 3 Bo Young Hong MD PhD, 3 Lee Chan
Neurology Asia 2017; 22(1) : 9 13 The clinical manifestations and outcomes of neuralgic amyotrophy 1 Jung Soo Lee MD PhD, 2 Yoon Tae Kim MD PhD, 3 Joon Sung Kim MD PhD, 3 Bo Young Hong MD PhD, 3 Lee Chan
Unusual presentation of neuralgic amyotrophy with impairment of cranial nerve XII
 Unusual presentation of neuralgic amyotrophy with impairment of cranial nerve XII Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch, Anne Kerbrat, Paul Sauleau To cite this version: Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch,
Unusual presentation of neuralgic amyotrophy with impairment of cranial nerve XII Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch, Anne Kerbrat, Paul Sauleau To cite this version: Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch,
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression. Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre
 Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
MRI Findings of 26 Patients with
 MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
Patients with cervical radiculopathy (CR) are frequently encountered
 Cervical Radiculopathy or Parsonage-Turner Syndrome: Differential Diagnosis of a Patient With Neck and Upper Extremity Symptoms Christopher J. Mamula, MPT, ATC 1 Richard E. Erhard, PT, DC 2 Sara R. Piva,
Cervical Radiculopathy or Parsonage-Turner Syndrome: Differential Diagnosis of a Patient With Neck and Upper Extremity Symptoms Christopher J. Mamula, MPT, ATC 1 Richard E. Erhard, PT, DC 2 Sara R. Piva,
Advances in Knowledge Of 30 shoulders examined with MR imaging in patients with Parsonage-Turner syndrome, 29 (97%) had involvement of the suprascapul
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Cree M. Gaskin, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Cree M. Gaskin, MD
Cervical Radiculopathy: My 32 Year-Old Cyclist is Nervous What do I do on the initial visit?
 Cervical Radiculopathy: My 32 Year-Old Cyclist is Nervous What do I do on the initial visit? Scott D Boden, MD The Emory Spine Center Atlanta, Georgia History of Trauma? 2 History of Trauma? 3 Sometimes
Cervical Radiculopathy: My 32 Year-Old Cyclist is Nervous What do I do on the initial visit? Scott D Boden, MD The Emory Spine Center Atlanta, Georgia History of Trauma? 2 History of Trauma? 3 Sometimes
Neurology Topics. Ian Rosemergy
 Neurology Topics Ian Rosemergy Plan An unusual presentation of a not so unusual problem Some seizure cases 49 year old female Patient 1 Hit on back and neck by swinging car door o Severe neck and shoulder
Neurology Topics Ian Rosemergy Plan An unusual presentation of a not so unusual problem Some seizure cases 49 year old female Patient 1 Hit on back and neck by swinging car door o Severe neck and shoulder
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME: A FREQUENT CAUSE OF NON-DISCOGENIC BRACHIALGIA
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME: A FREQUENT CAUSE OF NON-DISCOGENIC BRACHIALGIA Debora Garozzo Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Surgery Unit Neurospinal Hospital Dubai, United Arab Emirates THE THORACIC OUTLET
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME: A FREQUENT CAUSE OF NON-DISCOGENIC BRACHIALGIA Debora Garozzo Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Surgery Unit Neurospinal Hospital Dubai, United Arab Emirates THE THORACIC OUTLET
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain. Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic
 Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG
 Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG Limitations of other methods of investigations of the neuromuscular system - Dr Rob Henderson, Neurologist Assessment of Weakness Thanks Peter Silburn PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG Limitations of other methods of investigations of the neuromuscular system - Dr Rob Henderson, Neurologist Assessment of Weakness Thanks Peter Silburn PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities
 Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
Case Report Recurrent Vocal Fold Paralysis and Parsonage-Turner Syndrome
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 763201, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/763201 Case Report Recurrent Vocal Fold Paralysis and Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Marcus Vinicius Pinto,
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 763201, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/763201 Case Report Recurrent Vocal Fold Paralysis and Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Marcus Vinicius Pinto,
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG
 Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT:
 submitted by Keith M. Bartley, D.C. Jasper, IN 07/21/11 presented at Cox Seminar in Nashville, TN, on October 8 9, 2011 HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT: 01/21/11 55 year old male press operator for Jasper
submitted by Keith M. Bartley, D.C. Jasper, IN 07/21/11 presented at Cox Seminar in Nashville, TN, on October 8 9, 2011 HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT: 01/21/11 55 year old male press operator for Jasper
Diagnosis of Neck & Upper Extremity Pain
 Diagnosis of Neck & Upper Extremity Pain David B. Bumpass, MD Assistant Professor, Spine Surgery UAMS Depts. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Neurosurgery May 12, 2018 Disclosures Medtronic Spine speaking fees
Diagnosis of Neck & Upper Extremity Pain David B. Bumpass, MD Assistant Professor, Spine Surgery UAMS Depts. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Neurosurgery May 12, 2018 Disclosures Medtronic Spine speaking fees
Case Report An Unusual Case of Recurrent Guillain-Barre Syndrome of a Different Subtype Five Years after Initial Diagnosis
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 356157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/356157 Case Report An Unusual Case of Recurrent Guillain-Barre Syndrome of a Different Subtype
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 356157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/356157 Case Report An Unusual Case of Recurrent Guillain-Barre Syndrome of a Different Subtype
Lumbosacral plexus lesion Lumbosacral plexus disorders G54.1 Neuralgic amyotrophy Neuralgic amyotrophy G
 ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
Acute Orthopaedic Injuries Developing a Diagnostic Approach to the Shoulder
 Acute Orthopaedic Injuries Developing a Diagnostic Approach to the Shoulder WWW.FISIOKINESITERAPIA.BIZ Overview To be able to quickly categorize shoulder injuries To take appropriate history and conduct
Acute Orthopaedic Injuries Developing a Diagnostic Approach to the Shoulder WWW.FISIOKINESITERAPIA.BIZ Overview To be able to quickly categorize shoulder injuries To take appropriate history and conduct
Personal use only. MR Imaging Assessment of Rotator Cuff Muscle Quality
 MR Imaging Assessment of Rotator Cuff Muscle Quality Christian W. A. Pfirrmann Orthopedic University Hospital Balgrist University of Zurich Switzerland Atrophy of Infraspinatus Infraspinatus Atrophy: Diagnosis?
MR Imaging Assessment of Rotator Cuff Muscle Quality Christian W. A. Pfirrmann Orthopedic University Hospital Balgrist University of Zurich Switzerland Atrophy of Infraspinatus Infraspinatus Atrophy: Diagnosis?
The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging
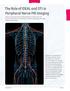 In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University
 Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax 2018 Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University Angela Scott, Association of Electromyography Technologists of
Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax 2018 Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University Angela Scott, Association of Electromyography Technologists of
Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Speaker Disclosure
 Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Eric C. McCarty, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Eric C. McCarty, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies
 Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
June 1996 EMG Case-of-the-Month
 June 1996 EMG Case-of-the-Month This case is no longer available for CME credit. Cases prepared by: Ian MacLean, MD; Daniel Dumitru, MD; Lawrence R. Robinson, MD HISTORY Six weeks ago a 28-year-old woman
June 1996 EMG Case-of-the-Month This case is no longer available for CME credit. Cases prepared by: Ian MacLean, MD; Daniel Dumitru, MD; Lawrence R. Robinson, MD HISTORY Six weeks ago a 28-year-old woman
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
 Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy
 Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Title. CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
A nt erior Int ero s s eou s N erv e Sy n drom e - Obs erv ation s f or T hree Surg ical Ca s e s -
 3 2 Vol. 3, No 2, November 1998. - 3 -, * * =A bs trac t = A nt erior Int ero s s eou s N erv e Sy n drom e - Obs erv ation s f or T hree Surg ical Ca s e s - Min Jong P ark, M.D., Jong Yoon Lee, M.D.,
3 2 Vol. 3, No 2, November 1998. - 3 -, * * =A bs trac t = A nt erior Int ero s s eou s N erv e Sy n drom e - Obs erv ation s f or T hree Surg ical Ca s e s - Min Jong P ark, M.D., Jong Yoon Lee, M.D.,
Case 1: History of J.H. Outside Evaluation. Outside Labs. Question #1
 Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Taxonomy of. Diabetic Lumbosacral Radiculoplexus Neuropathy and Diabetic Radiculoplexus Neuropathy. P. James B. Dyck, M.D.
 Taxonomy of Diabetic Lumbosacral Radiculoplexus Neuropathy and Diabetic Radiculoplexus Neuropathy P. James B. Dyck, M.D. December 12, 2017 CONCEPPT/IDNC Taxonomy Washington D.C. (author has nothing to
Taxonomy of Diabetic Lumbosacral Radiculoplexus Neuropathy and Diabetic Radiculoplexus Neuropathy P. James B. Dyck, M.D. December 12, 2017 CONCEPPT/IDNC Taxonomy Washington D.C. (author has nothing to
SHOULDER PAIN. A Real Pain in the Neck. Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017
 SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies
 18 Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies Juan A. Acosta and Elizabeth M. Raynor Summary Brachial and lumbosacral plexopathies represent a heterogeneous group of disorders including
18 Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies Juan A. Acosta and Elizabeth M. Raynor Summary Brachial and lumbosacral plexopathies represent a heterogeneous group of disorders including
D E L L O N I N S T I T U T E S F O R P E R I P H E R A L N E R V E S U R G E R Y
 Thoracic Outlet (TOS), Winged Scapula, Brachial Plexus Compression 12 D E L L O N I N S T I T U T E S F O R P E R I P H E R A L N E R V E S U R G E R Y 1122 KENILWORTH DRIVE, SUITE 18, TOWSON, MARYLAND
Thoracic Outlet (TOS), Winged Scapula, Brachial Plexus Compression 12 D E L L O N I N S T I T U T E S F O R P E R I P H E R A L N E R V E S U R G E R Y 1122 KENILWORTH DRIVE, SUITE 18, TOWSON, MARYLAND
High Yield Neurological Examination
 High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
There is substantial variation in
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1770 1774 / DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4183-3 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons Published online: 18 February
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1770 1774 / DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4183-3 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons Published online: 18 February
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb.
 Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Definitions Radiculopathy Process affecting the nerve root, most commonly by a herniated disc Weakness in muscles supplied by the
Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Limb www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Definitions Radiculopathy Process affecting the nerve root, most commonly by a herniated disc Weakness in muscles supplied by the
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease. Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine
 Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS AND PAIN
 Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder
 Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder Introduction What conditions causing shoulder pain commonly present in General Practice? Subacromial impingement Rotator cuff tears AC joint pathology
Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder Introduction What conditions causing shoulder pain commonly present in General Practice? Subacromial impingement Rotator cuff tears AC joint pathology
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Quadrilateral Space Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Quadrilateral Space Syndrome Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Quadrilateral Space Syndrome Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Work-related shoulder pain
 Work-related shoulder pain Stadler Kirsten M.B., Ch.B. (1987) (Pret), M. Med. (Orthop) (1998) (Stell.), Orthopaedic Surgeon, Room 333, Louis Leipoldt Medical Centre, Broadway Street, Bellville Cape Town
Work-related shoulder pain Stadler Kirsten M.B., Ch.B. (1987) (Pret), M. Med. (Orthop) (1998) (Stell.), Orthopaedic Surgeon, Room 333, Louis Leipoldt Medical Centre, Broadway Street, Bellville Cape Town
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries. First Global Conflict Medicine Congress
 Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF CERVICAL SPINE DISORDERS
 CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF CERVICAL SPINE DISORDERS Gregory M Yoshida MD Supports the skull Allows movement of the head Houses the spinal cord CERVICAL SPINE Unique anatomy Upper C spine
CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF CERVICAL SPINE DISORDERS Gregory M Yoshida MD Supports the skull Allows movement of the head Houses the spinal cord CERVICAL SPINE Unique anatomy Upper C spine
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
H ereditary brachial plexus neuropathy (HBPN) is an
 PAPER Inflammation and neuropathic attacks in hereditary brachial plexus neuropathy C J Klein, PJBDyck, S M Friedenberg, T M Burns, A J Windebank, P J Dyck... See end of article for authors affiliations...
PAPER Inflammation and neuropathic attacks in hereditary brachial plexus neuropathy C J Klein, PJBDyck, S M Friedenberg, T M Burns, A J Windebank, P J Dyck... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Brachial Plexopathy in a Division I Football Player
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Brachial Plexopathy in a Division I Football Player Brachial Plexus Injuries in Sport Typically a transient neurapraxia - 70% of injured players said they did not always report
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Brachial Plexopathy in a Division I Football Player Brachial Plexus Injuries in Sport Typically a transient neurapraxia - 70% of injured players said they did not always report
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy
 MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy
 MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group
 Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
Immune Mediated Neuropathies
 Immune Mediated Neuropathies Hernan Gatuslao, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine AIDP and CIDP Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Immune Mediated Neuropathies Hernan Gatuslao, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine AIDP and CIDP Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
* WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 84/07
 * WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 84/07 BEFORE: A. Suissa: Vice-Chair HEARING: January 12, 2007 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 12, 2007 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2007
* WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 84/07 BEFORE: A. Suissa: Vice-Chair HEARING: January 12, 2007 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 12, 2007 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2007
EMG CASE No. 61, April 2003
 EMG CASE No. 61, April 2003 Presenting Symptom(s): Progressive left arm weakness, cramping, and muscle twitching. Case prepared by: Ann A. Little, M.D. James W. Teener, M.D. University of Michigan Department
EMG CASE No. 61, April 2003 Presenting Symptom(s): Progressive left arm weakness, cramping, and muscle twitching. Case prepared by: Ann A. Little, M.D. James W. Teener, M.D. University of Michigan Department
Differentialdianosis to CRPS Departmentdoctor Bo Biering-Sørensen, Pain Clinic, Neurological Department
 Differentialdianosis to CRPS Departmentdoctor Bo Biering-Sørensen, Pain Clinic, Neurological Department Dato (Sidehoved/fod) Case 1 36 year old man other ethnically background than Danish 2006 Left foot
Differentialdianosis to CRPS Departmentdoctor Bo Biering-Sørensen, Pain Clinic, Neurological Department Dato (Sidehoved/fod) Case 1 36 year old man other ethnically background than Danish 2006 Left foot
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE
 MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam
 A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease. Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013
 Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift
 Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Clinical Anatomy 31:616 621 (2018) EDITORIAL From Targeted Fascicular Biopsy of Major Nerve to Targeted Cutaneous Nerve Biopsy: Implementing Clinical Anatomy Can Catalyze a Paradigm Shift TOMAS MAREK,
Official Definition. Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
 Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
November 16-18, 2017 Hotel Monteleone New Orleans, LA. Provided by
 November 16-18, 2017 Hotel Monteleone New Orleans, LA Provided by Diabetic Neuropathy: A Global and Growing Problem John D. England, MD Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine
November 16-18, 2017 Hotel Monteleone New Orleans, LA Provided by Diabetic Neuropathy: A Global and Growing Problem John D. England, MD Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine
Shoulder examination. P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College
 Shoulder examination P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College Manipal University, Manipal Common symptoms Tingling Numbness Pain Loss of movements Weakness Approach
Shoulder examination P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College Manipal University, Manipal Common symptoms Tingling Numbness Pain Loss of movements Weakness Approach
Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy. Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction
 Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy Chris Edwards, MD Ochsner Neurology, Main Campus Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction A very common complaint in the clinic Presentation is variable Multiple
Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy Chris Edwards, MD Ochsner Neurology, Main Campus Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction A very common complaint in the clinic Presentation is variable Multiple
ARTHROSCOPIC SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE RELEASE
 ARTHROSCOPIC SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE RELEASE Laurent Lafosse & Robert Fullick Alps Surgery Institute Annecy France DISCLOSURE Royalties Depuy Consultant Depuy Stock options ITS Stock options Orthospace 1 Background
ARTHROSCOPIC SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE RELEASE Laurent Lafosse & Robert Fullick Alps Surgery Institute Annecy France DISCLOSURE Royalties Depuy Consultant Depuy Stock options ITS Stock options Orthospace 1 Background
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of
 Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Spine Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Spine Neurosurgery Spine neurosurgeons treat
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Spine Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Spine Neurosurgery Spine neurosurgeons treat
Electromyography in Shoulder Disorders
 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 13: 29 34, 2000 2000 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal Electromyography in Shoulder Disorders SAMI L. KHELLA, M.D. Introduction This
The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 13: 29 34, 2000 2000 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal Electromyography in Shoulder Disorders SAMI L. KHELLA, M.D. Introduction This
FILED: RICHMOND COUNTY CLERK 01/17/ :45 PM INDEX NO /2015 NYSCEF DOC. NO. 65 RECEIVED NYSCEF: 01/17/2019
 BROOKLYN, N.Y. 11234 Kalant & Roytblat, PLLC January 3, 2019 9131 Queens Blyd., Ste. 313 Elmhurst, NY 11373 Attention: Alexander Roytblat, Esq. Re: Eran Taussi Date of Accident: January 30, 2014 Dear Mr.
BROOKLYN, N.Y. 11234 Kalant & Roytblat, PLLC January 3, 2019 9131 Queens Blyd., Ste. 313 Elmhurst, NY 11373 Attention: Alexander Roytblat, Esq. Re: Eran Taussi Date of Accident: January 30, 2014 Dear Mr.
2015 OPSC Annual Convention. syllabus. February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California
 2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
Proper Performance and Interpretation of Electrodiagnostic Studies
 Proper Performance and Interpretation of Electrodiagnostic Studies Introduction The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) has developed the following position statement
Proper Performance and Interpretation of Electrodiagnostic Studies Introduction The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) has developed the following position statement
Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging
 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy 85 Chapter 5 Radiation-induced Brachial Plexopathy: MR Imaging Neurological symptoms and signs of brachial plexopathy may develop in patients who have had radiation
A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital
 A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital Nerve Conduction Studies Test to evaluate the function of motor / sensory nerves Evaluate Paraesthesia (numbness, tingling, burning) Weakness of arms and legs
A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital Nerve Conduction Studies Test to evaluate the function of motor / sensory nerves Evaluate Paraesthesia (numbness, tingling, burning) Weakness of arms and legs
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
CNS & PNS Entrapment. Disclosure - Nothing
 Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
Chief Complaint. History. History of Similar Episodes. A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache
 A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache Chief Complaint Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 10 year-old boy presented with his fifth lifetime bout of left-sided head pain followed by diplopia. Amy A. Gelfand, MD
A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache Chief Complaint Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 10 year-old boy presented with his fifth lifetime bout of left-sided head pain followed by diplopia. Amy A. Gelfand, MD
Objectives. Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies. Abnormal Muscle Signal Intensity. Inflammatory Myositis. Polymyostis / Dermatomyositis.
 Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
Pain Assessment Patient Interview (location/nature of symptoms), Body Diagram. Observation and Examination: Tests and Measures
 Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES
 Neurology DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-382 LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES ANA MARIA GALAMB, IOAN DAN MINEA Department of Medical and Surgical Specialities, Faculty of Medicine,
Neurology DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-382 LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES ANA MARIA GALAMB, IOAN DAN MINEA Department of Medical and Surgical Specialities, Faculty of Medicine,
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
