HIATUS HERNIA IN CHILDHOOD*
|
|
|
- Sharlene May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIATUS HERNIA IN CHILDHOOD* BY J. H. JOHNSTON From the Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool The first description of a hiatus hernia was probably that of Bright (1836), who recorded the autopsy of a girl aged 19 years in whom a large portion of the stomach was in the chest and the cardia was at the level of the fourth dorsal vertebra. In the early part of the present century the condition was thought to be rare; Eppinger's (1911) series of 650 diaphragmatic herniae contained only 11 cases of hiatus hernia and in Quenu's (1920) series of 112 cases of diaphragmatic hernia treated surgically there were only two cases of hiatus hernia. With the introduction and development of radiology it was recognized (Akerlund, 1926) that sliding hiatus hernia, in which the cardia and part of the stomach lie a varying distance above the diaphragm, is the most common form of diaphragmatic hernia and occurs frequently. The condition is found chiefly in the infant and in the middle-aged adult and it has generally been assumed that, in both age groups, similar factors are concerned in the aetiology and the mechanism of production of symptoms. There are, however, significant differences in the clinical features, the natural course of the disease and the response to treatment which suggest that, although the complications may be identical, hiatus hernia in the child is pathogenetically quite distinct from the majority of adult cases. There is little doubt that infantile hiatus hernia is either present at, or develops shortly after birth; symptoms usually date from the first few days of life and the condition has been demonstrated radiologically during the first week. It was considered by Findlay and Kelly (1931) that hiatus hernia in the child is a congenital, developmental anomaly in which the oesophagus fails to lengthen synchronously with the caudal migration of the septum transversum so that the diaphragmatic hiatus comes to surround the stomach instead of the oesophagus. Botha (1958) thought that a large proportion of hiatus herniae is due to such a developmental short oesophagus. The rapid elongation of the oesophagus in the normal embryo occurs during the * A paper read at a meeting of the British Association of Paediatric Surgeons held in Liverpool in June, sixth and seventh weeks (Keith, 1948) and a gross anomaly occurring at such an early period of development would be expected to be accompanied frequently by other major abnormalities as is oesophageal atresia which arises about this time. The evidence concerning associated malformations with hiatus hernia is somewhat conflicting, but the reports of multiple anomalies, which include hiatus hernia, have been mostly of isolated cases or of small series (Williams, 1945; Radloff and King, 1947; Barrett, 1950). In our own clinical series of 76 cases no child has a known major congenital abnormality and a low incidence of associated lesions was found by Thomsen (1955) and by Bonham Carter (1956), although mental deficiency was not uncommon in their series. The anatomical features of hiatus hernia in the child suggest that a developmental shortness of the oesophagus is an unlikely aetiological explanation. The almost invariable presence of a sliding peritoneal sac covering the anterior and left aspects of the intra-thoracic portion of the stomach, the fact that this part of the stomach derives its vascular supply from the coeliac axis and not from the thoracic aorta, and the operative finding that the vagi are not taut and, unless involved in peri-oesophageal fibrosis, do not interfere with reduction of the hernia appear to indicate that the cardia was originally in the abdomen and only later migrated into the chest. In the acquired hiatus hernia of the adult, in which the pathological anatomy is identical with that of the child, an important aetiological factor in most cases, and the primary one in many, is relaxation of the diaphragmatic hiatus due to degenerative changes in the musculature. Barrett (1954) and Forshall (1955) have therefore considered that the essential lesion in the infantile case is a congenital weakness or laxity of the hiatus which allows herniation of the cardia shortly after birth when a negative intra-thoracic pressure develops with the onset of respiration. An objection to this hypothesis is that hiatus hernia in the child can undergo gradual spontaneous reduction (Figs. 1 and 2) and eventual cure; spontaneous recovery of
2 62 ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD FIG. I.-Long, tubular hiatus hernia in child aged FIG. 2.-Same patient as in Fig. 1, aged 18 3 months. Cardia at level of sixth dorsal vertebra. months. Symptomless. Marked spontaneous reduction in size of hernia. Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 February Downloaded from FIG. 3.-Autopsy specimen of hiatus hernia in still-born anencephalic infant. Forceps in sliding peritoneal sac FIG. 4.-Same specimen as in Fig. 3. Stomach and cardia withdrawn from above diaphragm. demonstrating sliding sac. on 4 July 2018 by guest. Protected by
3 HIATUS HERNIA IN CHILDHOOD 63 a diaphragmatic weakness, if possible at all, would Some of the clinical features of infantile hiatus be unlikely to lead to the reduction of a large hernia. hernia, even when there is no associated hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, also suggest the presence The autopsy finding of a hiatus hernia in a still-born anencephalic infant indicates that a pressure difference between the abdomen and the thorax is not an the incompetent cardia, although responsible for of a gastric emptying disorder. That the hernia and the essential pathogenetic factor. The gross associated anomaly in this case at first suggested that the condition was a 'congenital short oesophagus' but dissection revealed the typical anatomical features of a sliding hernia (Figs. 3 and 4). As the child had never breathed, the cardia must have become displaced during pre-natal life. An important agent in the production and maintenance of some cases of adult hiatus hernia is pressure from below, displacing the cardia upwards through the hiatus; symptomatic and even radiological cure may follow reduction of intra-abdominal pressure by the elimination of obesity, the abandonment of corsets or the evacuation of a pregnant uterus (Dutton and Bland, 1953). There is no evidence of an unduly high intra-abdominal pressure in the infant with hiatus hernia but the not infrequent association with hypertrophic stenosis of the pylorus, the phreno-pyloric syndrome of Roviralta (1952), suggests that raised intra-gastric pressure or increased gastric peristalsis may similarly force the cardia into the chest. The coincidence of pyloric stenosis in our hiatus hernia series is 10 5%. In Bonham Carter's (1956) series of 136 cases of hiatus hernia five children had pyloric stenosis and he suggested that the vomiting caused by the latter leads to the development of the hernia when there is a congenital laxity of the oesophageal hiatus. In our eight patients with the double lesion, however, vomiting began shortly after birth and not, as occurs with pyloric obstruction alone, after the second week of life. The pathogenesis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis remains unknown. Thomson (1933) considered that the muscular hypertrophy of the pyloric canal occurs as a result of a preceding functional obstruction at the pyloric sphincter. Friesen, Boley and Miller (1956) claim to have demonstrated immaturity of ganglion cells in the pyloric tumour. As pyloric stenosis, unlike hiatus hernia, occurs predominantly in the male and has a high familial and hereditary incidence, there is obviously no all-embracing aetiological explanation for the two conditions but their frequent co-existence lends support to Thomson's theory of a prenatal functional pyloric obstruction; the increase in intragastric pressure so produced may then lead to prolapse of the cardia into the chest especially since, at this period of development, the gastro-oesophageal junction is probably not yet stabilized in its normal position. development of oesophagitis, are perhaps not the primary cause of the main symptom of vomiting is indicated by the fact that, in those children treated medically and in many of those treated surgically, the hernia and gastro-oesophageal reflux may still be demonstrable radiologically many months after vomiting has ceased. Interference with gastric emptying is suggested by the frequent clinical finding of visible gastric peristalsis and by the fact that the vomiting itself, unlike the passive postural reflux of a small quantity of gastric contents which occurs in the adult, is usually forcible or even projectile, of large volume and not immediately controlled by postural treatment. Medical management of hiatus hernia in infancy is often successful in relieving the symptoms and in allowing spontaneous cure of the hernia and the development of a competent gastro-oesophageal sphincter. The disadvantage of conservative management is that hospital treatment must often be prolonged, and it is difficult to decide when the patient may be considered free of the risk of complications developing. It is often considered that cure has been achieved when vomiting ceases and the child gains weight normally. The hernia and the incompetent cardia persist, however, for some considerable time after vomiting has stopped and the symptomless patient may still be exposed to the risks of oesophagitis and its sequelae. Severe complications, if they are going to occur, usually develop early but this is not invariably the case; in one of our patients an oesophageal stricture first appeared at the age of 10 years (Figs. 5 and 6). Chronic penetrating ulcer of the intra-thoracic portion of the stomach (Barrett's ulcer) may also develop in later childhood (Fig. 7). The conventional surgical procedure for hiatus hernia in the child, as in the adult, is transthoracic, transdiaphragmatic reduction of the hernia and repair of the enlarged oesophageal hiatus. In our experience of 40 cases this operation has not given satisfactory results; vomiting has persisted after operation in over 50% of patients and radiological examination, carried out one year or more after operation, has shown recurrence of the hernia or persistence of gastro-oesophageal reflux in over 70%. Unsatisfactory results of hiatal herniorrhaphy in childhood have also been recorded by Husfeldt (1953) and by Thomsen (1955). Although there is no radiological confirmation of
4 64 FIG. 5.-Hiatus hernia without stricture FIG. 6.-Same patient as in Fig. 5, aged 10 years. stricture. ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD n boy aged 6 years. Severe oesophageal a gastric emptying disorder in cases of infantile hiatus hernia, there would appear to be sufficient clinical evidence of its temporary presence, responsible at least in part for the development of the lesion and the production of the symptom of vomiting, to justify the therapeutic application of this hypothesis. The operation of pyloroplasty has therefore been applied to the treatment of hiatus hernia in childhood. The rationale of this procedure is that facilitation of gastric emptying will discourage FIG. 7.-Operation specimen. Chronic penetrating peptic ulcer (Barrett's ulcer) of intra-thoracic part of stomach in boy aged 9 years with recurrent haematemesis. vomiting and encourage spontaneous cure of the hernia and the development of a competent gastrooesophageal sphincter. Peptic oesophagitis is due to reflux of pepsin and acid from the stomach; the most severe effects are probably produced by reflux of unbuffered gastric juices when the stomach is empty of food. In order to inhibit this neurogenic peptic secretion and so render inert fluid regurgitating into the oesophagus, bilateral vagotomy has been performed in addition to pyloroplasty when endoscopy revealed the presence of oesophagitis. These procedures have so far been applied to only a small series of cases. The early response has been satisfactory but more prolonged study of the patients is required before full assessment of the results is possible. Summary The pathogenesis of infantile hiatus hernia is discussed. It is considered that an important factor in the causation of the hernia and in the production of vomiting is a disorder of gastric emptying. The operation of pyloroplasty and, in the presence of peptic oesophagitis, vagotomy has therefore been carried out in a small series of cases. I am grateful to my colleagues Miss Isabella Forshall and Mr. P. P. Rickham and to the paediatric physicians
5 HIATUS HERNIA IN CHILDHOOD 65 of the Liverpool Region who have permitted me to examine their patients. I am indebted to Dr. E. G. Hall for the use of autopsy material. REFERENCES Akerlund, A. (1926). Acta radiol., 6, 3. Barrett, N. R. (1950). Brit. J. Surg., 38, (1954). Ibid., 42, 231. Bonham Carter, R. E. (1956). Proc. roy. Soc. Med., 49, 543. Botha, G. S. M. (1958). Arch. Dis. Childh., 33, 78. Bright, R. (1836). Guy's Hosp. Rep., 1, 398. Dutton, W. A. W. and Bland, H. J. (1953). Brit. med. J.. 2, 864. Eppinger, H. (1911). In Nothnagel, H. Spezielle Pathologie und Therapie. Suppl. I: Allgemeine und Spezielle Pathologie des Zwerchfells. Holder, Vienna and Leipzig. Findlay, L. and Kelly, A. B. (1931). J. Laryng., 46, 797. Forshall, I. (1955). Arch. Dis. Childh., 30, 46. Friesen, S. R., Boley, J. O. and Miller, D. R. (1956). Surgery, 39, 21. Husfeldt, E. (1953). Gt Ormond Str. J., No. 6, p. 71. Keith, A. (1948). Human Embryology and Morphology, 6th ed. Arnold, London. Quenu, J. (1920). Les Hernies Diaphragmatiques. Etude clinique et optlratoire. (Thesis, Paris.) Arnette, Paris. Radloff, F. F. and King, R. L. (1947). Gastroenterology, 9, 249. Roviralta, E. (1952). Les Vomissements du Nourrisson. Flammarion, Paris. Thomsen, G. (1955). Acta radiol., Supplement 129. Thomson, J. (1933). The Clinical Study and Treatment of Sick Children, 5th ed., revised by L. Findlay. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh. Williams, E. R. (1945). Brit. J. Radiol., 18,
THE NATURAL EVOLUTION OF HIATAL HERNIAS
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 143. THE NATURAL EVOLUTION OF HIATAL HERNIAS BY EMILIO ROVIRALTA From Instituto Policlinico, Barcelona, Spain (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MAY 1, 1963) Observations made over
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 143. THE NATURAL EVOLUTION OF HIATAL HERNIAS BY EMILIO ROVIRALTA From Instituto Policlinico, Barcelona, Spain (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MAY 1, 1963) Observations made over
Symptomatic hiatus hernia:
 Thorax (1966), 21, 67. Symptomatic hiatus hernia: A study of the pyloro-duodenal region and the rationale of vagotomy in its treatment HAROLD W. BURGE, ALAN MORTON GILL, CHARLES D. T. MAcLEAN, AND RONALD
Thorax (1966), 21, 67. Symptomatic hiatus hernia: A study of the pyloro-duodenal region and the rationale of vagotomy in its treatment HAROLD W. BURGE, ALAN MORTON GILL, CHARLES D. T. MAcLEAN, AND RONALD
THE CARDIO-OESOPHAGEAL SYNDROME IN CHILDHOOD
 THE CARDIO-OESOPHAGEAL SYNDROME IN CHILDHOOD The term 'cardio-oesophageal syndrome' is used to cover all infants and children with incompetence of the cardia. Ninety-three instances of the syndrome have
THE CARDIO-OESOPHAGEAL SYNDROME IN CHILDHOOD The term 'cardio-oesophageal syndrome' is used to cover all infants and children with incompetence of the cardia. Ninety-three instances of the syndrome have
Reflux after cardiomyotomy
 Gut, 1965, 6, 80 FRANK ELLIS AND F. L. COLE From the Departments of Surgery and Radiology, Guy's Hospital, London EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS A series of 56 patients with achalasia of the cardia included 16 with
Gut, 1965, 6, 80 FRANK ELLIS AND F. L. COLE From the Departments of Surgery and Radiology, Guy's Hospital, London EDITORIAL SYNOPSIS A series of 56 patients with achalasia of the cardia included 16 with
LATE RESULTS IN TRANSTHORACIC
 Thorax (1951), 6, 316. LATE RESULTS IN TRANSTHORACIC HERNIOTOMIES BY TYGE CL. GERTZ, J. E. P. M. REGOUT, AND GREGERS THOMSEN From the Department of Thoracic Surgery and Radiology, the University Hospital,
Thorax (1951), 6, 316. LATE RESULTS IN TRANSTHORACIC HERNIOTOMIES BY TYGE CL. GERTZ, J. E. P. M. REGOUT, AND GREGERS THOMSEN From the Department of Thoracic Surgery and Radiology, the University Hospital,
Selective vagotomy of the canine oesophagusa
 Thorax (1976), 31, 185. Selective vagotomy of the canine oesophagusa model for the treatment of hiatal hernia Surgical Unit, M. H. EDWARDS University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff Edwards, M. H. (1976). Thorax,
Thorax (1976), 31, 185. Selective vagotomy of the canine oesophagusa model for the treatment of hiatal hernia Surgical Unit, M. H. EDWARDS University Hospital of Wales, Cardiff Edwards, M. H. (1976). Thorax,
Observations on oesophageal length
 Thorax (1976), 31, 284. Observations on oesophageal length G. J. KALLOOR, A. H. DESHPANDE, and J. LEIGH COLLIS The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Kalloor, G. J., Deshpande, A. H., and Leigh Colfis,
Thorax (1976), 31, 284. Observations on oesophageal length G. J. KALLOOR, A. H. DESHPANDE, and J. LEIGH COLLIS The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Kalloor, G. J., Deshpande, A. H., and Leigh Colfis,
Hiatus hernia and heartburn
 Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
Hiatus hernia and heartburn E. W. GILLISON,l W. M. CAPPER, G. R. AIRTH, M. J. GIBSON, AND I. BRADFORD From the Department of Gastroenterology, Southmead Hospital, Bristol Gut, 1969, 1, 69-613 SUMMARY The
RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH
 Thorax (1956), 11, 275. RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH BY From tile United Leeds Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1956) This is a preliminary report describing
Thorax (1956), 11, 275. RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CARDIA AND FUNDUS OF THE STOMACH BY From tile United Leeds Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION SEPTEMBER 15, 1956) This is a preliminary report describing
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
A review of the management of 100 cases of
 Thorax (1972), 27, 599. A review of the management of 100 cases of benign stricture of the oesophagus S. RAPTIS' and D. MEARNS MILNE Thoracic Unit, Frenchay Hospital One hundred cases of benign stricture
Thorax (1972), 27, 599. A review of the management of 100 cases of benign stricture of the oesophagus S. RAPTIS' and D. MEARNS MILNE Thoracic Unit, Frenchay Hospital One hundred cases of benign stricture
Paraoesophageal Hernia
 Paraoesophageal Hernia Grand Round Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar Paraoesophageal Hernia Type of hiatal hernia Transdiaphragmatic migration of abdominal content gastric fundus gastric body pylorus colon
Paraoesophageal Hernia Grand Round Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar Paraoesophageal Hernia Type of hiatal hernia Transdiaphragmatic migration of abdominal content gastric fundus gastric body pylorus colon
GIT RADIOLOGY. Water-soluble contrast media (e.g. gastrograffin) are the other available agents.which doesn t cause inflammatory peritonitis..
 GIT RADIOLOGY Imaging techniques-general principles: Contrast examinations: Barium sulphate is the best contrast for GIT (with good mucosal coating & excellent opacification & being inert); but is contraindicated
GIT RADIOLOGY Imaging techniques-general principles: Contrast examinations: Barium sulphate is the best contrast for GIT (with good mucosal coating & excellent opacification & being inert); but is contraindicated
ALLOPLASTIC CLOSURE OF DEFECTS IN GROWING ORGANISMS*
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39,161. ALLOPLASTIC CLOSURE OF DEFECTS IN GROWING ORGANISMS* BY R. M. KONRAD From the Chirurgischen Klinik der Medizinischen Akademie, Dusseldorf The importance of operative correction
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39,161. ALLOPLASTIC CLOSURE OF DEFECTS IN GROWING ORGANISMS* BY R. M. KONRAD From the Chirurgischen Klinik der Medizinischen Akademie, Dusseldorf The importance of operative correction
was a contributory factor. Agreeing with Harrington as to the site of the bleeding, small but repeated blood losses were said to occur by
 Anaemia and hiatus hernia: Thorax (1067), 2±,?3. experience in 450 patients COLIN W. 0. WINDSOR AND J. LEIGH COLLIS From the United Birmingham Hospitals Since a correlation between hiatus hernia and anaemia
Anaemia and hiatus hernia: Thorax (1067), 2±,?3. experience in 450 patients COLIN W. 0. WINDSOR AND J. LEIGH COLLIS From the United Birmingham Hospitals Since a correlation between hiatus hernia and anaemia
STOMACH (HIATUS HERNIA) IN CHILDREN*
 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF THE PARTIAL THORACIC STOMACH (HIATUS HERNIA) IN CHILDREN* BY I. J. CARRt From the Department of Child Health, Queen's University, Belfast (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICAnON FEBRUARY 9, 1959)
THE NATURAL HISTORY OF THE PARTIAL THORACIC STOMACH (HIATUS HERNIA) IN CHILDREN* BY I. J. CARRt From the Department of Child Health, Queen's University, Belfast (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICAnON FEBRUARY 9, 1959)
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus. Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery
 Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Innervation of the diaphragm and its practical aspects in surgery
 Innervation of the diaphragm and its practical aspects in surgery ROBERT SCOTT' From Stobhill General Hospital, Glasgow N.J Thorax (1965), 20, 357. Older French anatomists speak of the formation vena cava,
Innervation of the diaphragm and its practical aspects in surgery ROBERT SCOTT' From Stobhill General Hospital, Glasgow N.J Thorax (1965), 20, 357. Older French anatomists speak of the formation vena cava,
Hiatal hernias may be classified. hiatal hernia DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION. This article is the first in a twopart series about these somewhat
 paraesophagealh hiatal hernia Leslie K Browder, MD, and Alex G Little, MD DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION Hiatal hernias may be classified as four types. The most common, Type I, may present as gastroesophageal
paraesophagealh hiatal hernia Leslie K Browder, MD, and Alex G Little, MD DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION Hiatal hernias may be classified as four types. The most common, Type I, may present as gastroesophageal
Contribution of fibreoptic endoscopy to diagnosis and management of children with gastro-oesophageal reflux
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1976, 51, 60. Contribution of fibreoptic endoscopy to diagnosis and management of children with gastro-oesophageal reflux P. P. FORGET and M. MERADJI From the Departments
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1976, 51, 60. Contribution of fibreoptic endoscopy to diagnosis and management of children with gastro-oesophageal reflux P. P. FORGET and M. MERADJI From the Departments
Clinical Study Congenital Paraesophageal Hernia with Intrathoracic Gastric Volvolus in Two Sisters
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 856568, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/856568 Clinical Study Congenital Paraesophageal Hernia with Intrathoracic Gastric Volvolus
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Surgery Volume 2011, Article ID 856568, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/856568 Clinical Study Congenital Paraesophageal Hernia with Intrathoracic Gastric Volvolus
Simultaneous measurement of intraluminal pressure and ph in the stomach and oesophagus
 Thorax (1969), 24, 589. Simultaneous measurement of intraluminal pressure and ph in the stomach and oesophagus With special reference to the diagnosis of hiatal and hiatal incompetence KNUD LOCKWOOD AND
Thorax (1969), 24, 589. Simultaneous measurement of intraluminal pressure and ph in the stomach and oesophagus With special reference to the diagnosis of hiatal and hiatal incompetence KNUD LOCKWOOD AND
PALPABLE CONTRACTILE PYLORIC TUMOURS IN THE
 PALPABLE CONTRACTILE PYLORIC TUMOURS IN THE NEWLY BORN BY W. S. CRAIG From the Department ofpaediatrics and Child Health, the University ofleeds A palpable tumour which contracts and relaxes is generally
PALPABLE CONTRACTILE PYLORIC TUMOURS IN THE NEWLY BORN BY W. S. CRAIG From the Department ofpaediatrics and Child Health, the University ofleeds A palpable tumour which contracts and relaxes is generally
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
POSTURAL TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH A PARTIAL THORACIC STOMACH ('HIATUS HERNIA')
 POSTURAL TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH A PARTIAL THORACIC STOMACH ('HIATUS HERNIA') BY I. J. CARRJt* From the Department of Child Health and Paediatrics, University ofbirmingham and the Children's Hospital,
POSTURAL TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH A PARTIAL THORACIC STOMACH ('HIATUS HERNIA') BY I. J. CARRJt* From the Department of Child Health and Paediatrics, University ofbirmingham and the Children's Hospital,
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
THE LOWER END OF THE OESOPHAGUS
 Thorax (1961), 16, 36. THE LOWER END OF THE OESOPHAGUS BY JOHN HAYWARD From the Royal Melbourne Hospital, Australia The lower end of the oesophagus is a region where the pathology, the physiology, and
Thorax (1961), 16, 36. THE LOWER END OF THE OESOPHAGUS BY JOHN HAYWARD From the Royal Melbourne Hospital, Australia The lower end of the oesophagus is a region where the pathology, the physiology, and
THE COLUMNAR-LINED ESOPHAGUS (BARRETT ACQUIRED CONDITION?
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, No.5 Printed in U.S.A. THE COLUMNAR-LINED ESOPHAGUS (BARRETT ACQUIRED CONDITION? S Y N D R O M E ) ~ A N SANFORD M. MOSSBERG, M.D.
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 50, No.5 Printed in U.S.A. THE COLUMNAR-LINED ESOPHAGUS (BARRETT ACQUIRED CONDITION? S Y N D R O M E ) ~ A N SANFORD M. MOSSBERG, M.D.
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
CASE REPORTS. Giant Esophagus. An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy
 CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY
 THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia information for parents. David M Notrica MD FACS FAAP Pediatric Surgeons of Phoenix
 Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia information for parents David M Notrica MD FACS FAAP Pediatric Surgeons of Phoenix CDH Congenital absence of a portion of the diaphragm allowing abdominal contents to migrate
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia information for parents David M Notrica MD FACS FAAP Pediatric Surgeons of Phoenix CDH Congenital absence of a portion of the diaphragm allowing abdominal contents to migrate
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY
 GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
Diffuse oesophageal spasm
 Diffuse oesophageal spasm Thorax (1966), 21, 511. D. R. CRADDOCK, A. LOGAN, AND P. R. WALBAUM From the Incoordination of muscular contraction is sometimes seen in the apparently healthy oesophagus, but
Diffuse oesophageal spasm Thorax (1966), 21, 511. D. R. CRADDOCK, A. LOGAN, AND P. R. WALBAUM From the Incoordination of muscular contraction is sometimes seen in the apparently healthy oesophagus, but
approach suffer from mild dyspepsia and never seek treatment. The increasing frequency with which this
 Thorax (1966), 21, 295. Surgical treatment of hiatal hernia, with particular reference to the transthoracic subdiaphragmatic approach S. ZELLOS' From the Regional Cardiothoracic Unit, Newcastle UpOlt Tyne
Thorax (1966), 21, 295. Surgical treatment of hiatal hernia, with particular reference to the transthoracic subdiaphragmatic approach S. ZELLOS' From the Regional Cardiothoracic Unit, Newcastle UpOlt Tyne
Hiatus Hernia. Endoscopy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
HIATAL HERNIA, DIVERTICULITIS AND VARICOSE VEINS: Three Peas In A Pod By Evan Almeda READ ONLINE
 HIATAL HERNIA, DIVERTICULITIS AND VARICOSE VEINS: Three Peas In A Pod By Evan Almeda READ ONLINE What is a hiatal hernia? Unlike ventral hernias, which protrude through the abdominal wall, The good news
HIATAL HERNIA, DIVERTICULITIS AND VARICOSE VEINS: Three Peas In A Pod By Evan Almeda READ ONLINE What is a hiatal hernia? Unlike ventral hernias, which protrude through the abdominal wall, The good news
Chapter Outline. Structural defects. Obstructive disorders. Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 98. Cleft lip and cleft palate
 Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN*
 THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
THE DYSFUNCTIONAL 'LAZY' BLADDER SYNDROME IN CHILDREN* BY FRANK G. DELUCA, ORVAR SWENSONt, JOHN H. FISHER and ADEL H. LOUTFI From the Boston Floating Hospital for Infants and Children, Boston, Massachusetts
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes
 Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
Gastrointestinal problems in individuals with CdLS. Peter Gillett Consultant Gastroenterologist RHSC Edinburgh UK Cork 2011
 Gastrointestinal problems in individuals with CdLS Peter Gillett Consultant Gastroenterologist RHSC Edinburgh UK Cork 2011 Major problems Gastro-oesophageal reflux and GORD Swallowing problems and
Gastrointestinal problems in individuals with CdLS Peter Gillett Consultant Gastroenterologist RHSC Edinburgh UK Cork 2011 Major problems Gastro-oesophageal reflux and GORD Swallowing problems and
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia. Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone. Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital
 THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery
 A Doubtful Cause of Symptoms Thomas P. Comer, M.D., Malvin Weinberger, M.D., and Howard D. Sirak, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with surgically treated aberrant right subclavian artery are reviewed. In half,
A Doubtful Cause of Symptoms Thomas P. Comer, M.D., Malvin Weinberger, M.D., and Howard D. Sirak, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with surgically treated aberrant right subclavian artery are reviewed. In half,
Compression of the oesophagus by the aorta1
 Thorax (1969), 24, 32. Compression of the oesophagus by the aorta1 I. K. R. McMILLAN AND I. HYDE From the Wessex Cardiac and Thoracic Centre, Southampton Chest Hospital Compression of the lower dorsal
Thorax (1969), 24, 32. Compression of the oesophagus by the aorta1 I. K. R. McMILLAN AND I. HYDE From the Wessex Cardiac and Thoracic Centre, Southampton Chest Hospital Compression of the lower dorsal
Lower oesophageal sphincter tone in patients with peptic stricture
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 574578 Lower oesophageal sphincter tone in patients with peptic stricture R LOBELLO,1 M STEKELMAN, AND D A W EDWARDS2 From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School,
Thorax, 1978, 33, 574578 Lower oesophageal sphincter tone in patients with peptic stricture R LOBELLO,1 M STEKELMAN, AND D A W EDWARDS2 From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School,
THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE
 Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
Brit. Heart J., 25, 1963, 748. THE SOUNDS AND MURMURS IN TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS BY BERTRAND WELLS From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W. C.J Received April 18,
James Paget University Hospitals. NHS Foundation Trust. Hiatus hernia. Patient Information
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
ISUOG Basic Training. Examining Fetal Anatomy from Longitudinal Sections Titia Cohen-Overbeek, The Netherlands
 ISUOG Basic Training Examining Fetal Anatomy from Longitudinal Sections Titia Cohen-Overbeek, The Netherlands Learning objectives 2 & 3 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to obtain
ISUOG Basic Training Examining Fetal Anatomy from Longitudinal Sections Titia Cohen-Overbeek, The Netherlands Learning objectives 2 & 3 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to obtain
A REVIEW OF SURGICAL RESULTS IN HIATUS HERNIA
 Thorax (1961), 16, 114. A REVIEW OF SURGICAL RESULTS IN HIATUS HERNIA BY J. LEIGH COLLIS From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In 1954 a paper was published (Collis, Kelly, and Wiley) which described
Thorax (1961), 16, 114. A REVIEW OF SURGICAL RESULTS IN HIATUS HERNIA BY J. LEIGH COLLIS From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In 1954 a paper was published (Collis, Kelly, and Wiley) which described
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
Calvin 9 year old NM DLH. Dr. Norman Ackerman Memorial Radiography Case Challenge
 September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
VOMITING. Tan Lay Zye
 VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION. DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon
 SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon CASE PRESENTATION :- New born baby, boy, referred to the paediatric surgical team at the age of 14 hours. Birth History
SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon CASE PRESENTATION :- New born baby, boy, referred to the paediatric surgical team at the age of 14 hours. Birth History
The forgotten Upper gastrointestinal series. When and how I do it?
 The forgotten Upper gastrointestinal series. When and how I do it? Poster No.: C-0617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, K. Bouslama, M. Maatouk, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
The forgotten Upper gastrointestinal series. When and how I do it? Poster No.: C-0617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Mnari, K. Bouslama, M. Maatouk, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, R. Salem,
INCARCERATED AND OBSTRUCTED DIAPHRAGMATIC
 Thorax (1960), 15, 59. INCARCERATED AND OBSTRUCTED DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA BY J. HORTON AND J. D. S. HAMMOND From the University Department of Medicine, Royal Hospital, Sheffield Diaphragmatic hernia is now
Thorax (1960), 15, 59. INCARCERATED AND OBSTRUCTED DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA BY J. HORTON AND J. D. S. HAMMOND From the University Department of Medicine, Royal Hospital, Sheffield Diaphragmatic hernia is now
Inguinal Hernia. Hernia Awareness Month. What is a Hernia? Common Hernia Types
 Hernia Awareness Month What is a Hernia? A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened
Hernia Awareness Month What is a Hernia? A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened
AND TECHNIC. GEORGE CRILE, Jr., M.D. Division of Surgery
 SUBDIAPHRAGMATIC VAGOTOMY; AND TECHNIC INDICATIONS GEORGE CRILE, Jr., M.D. Division of Surgery The principle of vagotomy as described by Dragstedt 1 has been widely accepted in the treatment of peptic
SUBDIAPHRAGMATIC VAGOTOMY; AND TECHNIC INDICATIONS GEORGE CRILE, Jr., M.D. Division of Surgery The principle of vagotomy as described by Dragstedt 1 has been widely accepted in the treatment of peptic
CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST
 CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST IDENTIFICATION DATA ผ ป วยเด กชายไทย อาย 13 ว น เช อชาต ไทย ส ญชาต ไทย ภ ม ล าเนา จ งหว ด อ ท ยธาน เข าร บการร กษาท รพ.มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวรว
CASE CONFERENCE GASTRIC VOLVULUS PIKOM, MD NONGLUK, MD; RADIOLOGIST IDENTIFICATION DATA ผ ป วยเด กชายไทย อาย 13 ว น เช อชาต ไทย ส ญชาต ไทย ภ ม ล าเนา จ งหว ด อ ท ยธาน เข าร บการร กษาท รพ.มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวรว
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
Metoclopramide in gastrooesophageal reflux
 Metoclopramide in gastrooesophageal reflux C. STANCIU AND JOHN R. BENNETT From the Gastrointestinal Unit, Hull Royal Infirmary Gut, 1973, 14, 275-279 SUMMARY In 3 patients with gastrooesophageal reflux,
Metoclopramide in gastrooesophageal reflux C. STANCIU AND JOHN R. BENNETT From the Gastrointestinal Unit, Hull Royal Infirmary Gut, 1973, 14, 275-279 SUMMARY In 3 patients with gastrooesophageal reflux,
Response of the gullet to gastric reflux in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophagitis
 Thorax (1970), 5, 459. Response of the gullet to gastric reflux in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophagitis D. A. K. WOODWARD1 Oesophageal Laboratory, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham 15 The variability
Thorax (1970), 5, 459. Response of the gullet to gastric reflux in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophagitis D. A. K. WOODWARD1 Oesophageal Laboratory, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham 15 The variability
The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE*
 RESULTS WITH ABDOMINAL RESECTION IN HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE* BY F. REHBEIN and H. VON ZIMMERMANN From the Surgical Department of the Children's Hospital, Bremen For six years we have been practising abdominal
RESULTS WITH ABDOMINAL RESECTION IN HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE* BY F. REHBEIN and H. VON ZIMMERMANN From the Surgical Department of the Children's Hospital, Bremen For six years we have been practising abdominal
Lectures of Human Embryology
 Lectures of Human Embryology "Body Cavities & GIT" By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Embryology "Body Cavities & GIT" By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
The anti-reflux mechanism after cardiomyotomy'
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 569-573 The anti-reflux mechanism after cardiomyotomy' R LOBELLO,2 D A W EDWARDS,3 J W P GUMMER, AND M STEKELMAN From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, the
Thorax, 1978, 33, 569-573 The anti-reflux mechanism after cardiomyotomy' R LOBELLO,2 D A W EDWARDS,3 J W P GUMMER, AND M STEKELMAN From the Surgical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, the
The Foregut. At first the esophagus is short. but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly
 GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 605. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge This study is based on observations made on boys at birth, during infancy, and throughout
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 605. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge This study is based on observations made on boys at birth, during infancy, and throughout
On the relationship between gastric ph and pressure
 Gut, 1979, 20, 59-63 On the relationship between gastric ph and pressure in the normal human lower oesophageal sphincter M. D. KAYE1 From the Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Medicine, University of
Gut, 1979, 20, 59-63 On the relationship between gastric ph and pressure in the normal human lower oesophageal sphincter M. D. KAYE1 From the Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Medicine, University of
Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
 A Sonographic walk-through: Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Tara K. Cielma, RDMS, RDCS, RVT, RT(S) Anjum N. Bandarkar, MD, Adebunmi O. Adeyiga, MD, Diagnostic Imaging and Radiology, Children s
A Sonographic walk-through: Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Tara K. Cielma, RDMS, RDCS, RVT, RT(S) Anjum N. Bandarkar, MD, Adebunmi O. Adeyiga, MD, Diagnostic Imaging and Radiology, Children s
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS
 Thorax (1955), 10, 137. THE LATE RESULTS OF THE CONSERVATION OF THE APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS BY E. HOFFMAN From the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge
Thorax (1955), 10, 137. THE LATE RESULTS OF THE CONSERVATION OF THE APICAL SEGMENT OF THE LOWER LOBE IN RESECTIONS FOR BRONCHIECTASIS BY E. HOFFMAN From the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge
Hernia. emoryhealthcare.org
 Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
SURGERY LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
LAPAROSCOPIC ANTI-REFLUX (GORD) If you suffer from heartburn, your surgeon may have recommended Laparoscopic Anti-reflux Surgery to treat this condition, technically referred to as Gastro-oesophageal Reflux
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
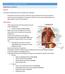 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
Intrathoracic fundoplication for reflux stricture
 Thorax 1983;38:36-40 Intrathoracic fundoplication for reflux stricture associated with short oesophagus K MOGHISSI From the Humberside Cardiothoracic Surgical Centre, Castle Hill Hospital, Cottingham,
Thorax 1983;38:36-40 Intrathoracic fundoplication for reflux stricture associated with short oesophagus K MOGHISSI From the Humberside Cardiothoracic Surgical Centre, Castle Hill Hospital, Cottingham,
Clinical Payment and Coding Policy Committee Approval Date: 02/23/2018
 In the event of a conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
In the event of a conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
Clinical Payment and Coding Policy Committee Approval Date: 02/23/2018
 In the event of conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
In the event of conflict between a Clinical Payment and Coding Policy and any plan document under which a member is entitled to Covered Services, the plan document will govern. Plan documents include,
The diaphragm as an anti-reflux barrier
 Thorax (1972), 27, 692. The diaphragm as an anti-reflux barrier A manometric, oesophagoscopic, and transmucosal potential study K. S. HABIBULLA Oesophageal Laboratory, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham
Thorax (1972), 27, 692. The diaphragm as an anti-reflux barrier A manometric, oesophagoscopic, and transmucosal potential study K. S. HABIBULLA Oesophageal Laboratory, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham
Anatomy: From cricoid cartilage to diaphragm 25 Cms. 4 portions: Cervical 5 cms. Thoracic 25 cms. Abdominal 2 cms. Blood supply Lymphatic spread
 Esophagus Anatomy: From cricoid cartilage to diaphragm 25 Cms. 4 portions: Cervical 5 cms. Thoracic 25 cms. Abdominal 2 cms. Blood supply Lymphatic spread Upper 2/3 Cephalad Lower 1/3 Caudad Physiology:
Esophagus Anatomy: From cricoid cartilage to diaphragm 25 Cms. 4 portions: Cervical 5 cms. Thoracic 25 cms. Abdominal 2 cms. Blood supply Lymphatic spread Upper 2/3 Cephalad Lower 1/3 Caudad Physiology:
Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article
 Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article Authors: Dr Vaibhav Pandey 1*, Dr. Pranay Panigrahi 2 Srivastav 4 & Dr Rakesh Kumar
Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article Authors: Dr Vaibhav Pandey 1*, Dr. Pranay Panigrahi 2 Srivastav 4 & Dr Rakesh Kumar
RENAL SIZE IN NORMAL CHILDREN
 RENAL SIZE IN NORMAL CHILDREN A RADIOGRAPHIC STUDY DURING LIFE BY Simultaneously with the collection and publication (Karn, 1962) of a large series of kidney measure- 616 C. J. HODSON, J. A. DREWF, M.
RENAL SIZE IN NORMAL CHILDREN A RADIOGRAPHIC STUDY DURING LIFE BY Simultaneously with the collection and publication (Karn, 1962) of a large series of kidney measure- 616 C. J. HODSON, J. A. DREWF, M.
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Post-Prandial Trouble! KPA 2017 Nutrition pre-congress case Presentation Dr. Esther Kimani. Facilitator- Dr. A. Laving. 25/04/2017
 Post-Prandial Trouble! KPA 2017 Nutrition pre-congress case Presentation Dr. Esther Kimani. Facilitator- Dr. A. Laving. 25/04/2017 Biodata. Name- I.M.M. Age-6 years Gender- female Referred to the Paediatric
Post-Prandial Trouble! KPA 2017 Nutrition pre-congress case Presentation Dr. Esther Kimani. Facilitator- Dr. A. Laving. 25/04/2017 Biodata. Name- I.M.M. Age-6 years Gender- female Referred to the Paediatric
Three Decades of Managing Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
 Three Decades of Managing Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Desmond Bohn The Department of Critical Care Medicine The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto Robert E Gross Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia 1960-80
Three Decades of Managing Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Desmond Bohn The Department of Critical Care Medicine The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto Robert E Gross Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia 1960-80
High peptic stricture of the oesophagus
 High peptic stricture of the oesophagus JAMES S. DAVIDSON Bradford Royal Infirmary Thorax (1976), 31, 1. Davidson, J. S. (1976). Thorax, 31, 1-14. High peptic sticture of the oesophagus. Fifty-seven patients
High peptic stricture of the oesophagus JAMES S. DAVIDSON Bradford Royal Infirmary Thorax (1976), 31, 1. Davidson, J. S. (1976). Thorax, 31, 1-14. High peptic sticture of the oesophagus. Fifty-seven patients
Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus*
 Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIAS
 MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIAS Theresa W. Fossum DVM, MS, PhD, Diplomate ACVS Professor of Veterinary Surgery; Vice President for Research and Strategic Initiatives, Midwestern University, Glendale,
MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIAS Theresa W. Fossum DVM, MS, PhD, Diplomate ACVS Professor of Veterinary Surgery; Vice President for Research and Strategic Initiatives, Midwestern University, Glendale,
