Lectures of Human Embryology
|
|
|
- Leon Gaines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lectures of Human Embryology "Body Cavities & GIT" By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology" 1999 Associate Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University (Egypt) & College of Medicine, Majmaah University (Saudi Arabia)
2 Development of Body Cavities - A single U-shaped cavity called intraembryonic coelom develops in the lateral plate mesoderm and infront of the prochordal plate. - It divides the mesoderm into 2 layers: 1. Dorsal layer called somatic (parietal) layer. It gives rise to the parietal layer of the serous membranes (pleura, pericrdium and peritoneum). 2. Ventral layer called splanchnic (visceral) layer. It gives rise to the visceral layer of the serous membranes (pleura, pericrdium and peritoneum). - Fate of IEC: During the 2 nd month the IEC is divided as follows: 1. The cranial transverse part (infront of prochordal plate) gives rise to the pericardium. 2. The cranial parts of the 2 lonitudinal limbs gives rise to pleura on each side. 3. The caudal parts of the 2 lonitudinal limbs gives rise to peritonium. Intra-embryonic coelom
3 Development of Peritoneum 1. The peritoneum develops from the caudal parts of the 2 vertical limbs. 2. As a result of folding of the embryo, the caudal parts of the 2 vertical limbs become close together, surrounding the gut. 3. Therefore, the gut becomes connected to the ventral wall of the embryo by ventral mesentery and to the dorsal wall by dorsal mesentery. 4. Most of the ventral mesentery degenerates and disappears to from a single "peritoneal" cavity, except a small cranial part persists forming ventral mesogastrium. 5. On the other hand, most of the dorsal mesentery persists, except that of duodenum, ascending colon and descending colon. The dorsal mesentery forms mesogastrium of stomach, mesentery proper of small intestine and dorsal mesocolon (at both transverse and sigmoid colons). Lateral Folding and Development of peritoneal cavity Separation of the pericardium from the pleural cavities: 1. Separation begins through appearance of a membrane, called pleura-pericardial membrane that arises one on each side from mesenchyme of body wall and extends inwards. 2. At the same time, the developing lung bud on each side invaginate the medial wall of primitive pleural cavity.
4 3. As the lungs grow, the membrane extend ventrally around the heart through splitting the mesenchyme of body wall. Thus, it separates the pleura from the pericardium. Then, the membrane forms the fibrous pericardium. 4. The pleural sacs approach each other and fuse with root of lungs. Separation of the pericardium from the pleural cavities Separation of the peritonium from the pleural cavities "Development of Diaphragm": 1. Separation begins through appearance of a crescent-shaped fold, called pleuroperitonial membrane that arises dorso-laterally from the body wall, one on each side at the caudal ends of pleural cavities. 2. The membrane extends ventro-medially to join the septum transversum and dorsal mesentery of oesophagus, separating the peritoneum from the 2 pleural sacs. 3. The peripheral muscular rim of the diaphragm, supplied by intercostals nerves is derived by extension of body wall mesoderm. Development of Diaphragm
5 N.B.: The septum transversum is formed in the neck region by fusion of the cervical myotomes (3 rd, 4 th and 5 th ). Then as a result of cranial folding of the embryo, it descends cranially, pulling its nerve supply from phrenic nerve (C3,4,5). GIT Development Introduction - As a result of folding of the embryo during the 4 th week, the secondary yolk sac is divided into 2 parts; 1. Part enclosed inside the body of embryo, called primitive gut, that is lined by endoderm. 2. Part lying outside the body of embryo, called definitive yolk sac. The 2 parts are temporally connected together by a duct, called vitelline duct, passing through the primitive umbilical ring. N.B.: As the primitive umbilical ring becomes narrower, the vitelline duct becomes constricted to form the yolk stalk by the 5 th week. Then, it becomes divided to separate the gut from the definitive yolk sac. - The primitive gut forms 3 parts: 1. Middle portion, connected by vitelline duct to definitive yolk sac is called midgut. 2. Cranial portion, cranial to midgut is called foregut. 3. Caudal portion, caudal to midgut is called hindgut. Folding of embryo at the Cranial and Caudal Ends
6 - Cranially, the foregut (lined by endoderm) is separated from the stomatodeum (lined by ectoderm) by oral (buccopharyngeal) membrane. - Caudally, the hindgut (lined by endoderm) is separated from the proctodeum (lined by ectoderm) by cloacal membrane. - Later on, these membranes rupture leading to communication of the gut with the exterior at its 2 ends; cranial end forming mouth and caudal end forming the anus. Derivatives of the Gut The primitive gut extends from the oral membrane to the cloacal membrane. Parts: I. Foregut: It extends from the oral membrane to the origin of the hepatic diverticulum. It is divided by the respiratory diverticulum into: 1. Cranial portion; gives rise to: - Part of the mouth, - Pharynx and pharyngeal arches and its derivatives e.g. auditory tube, middle ear, tonsils). - Trachea and Bronchial tree. + - Teeth, - Tongue, -Thyroid gland, - Salivary glands. 2. Caudal portion, caudal to repiratory diverticulum. It gives rise to: - Esophagus, - Stomach, - Upper part of duodenum, + - Liver, gall bladder and biliary passages, - Pancreas.
7 II. Midgut: It begins from the hepatic diverticulum to the junction between the right two-thirds and the left one third of the transverse colon. It gives rise to: *Parts of small intestine; - Duodenum (lower part), - Jejunum, - Ileum. *Parts of large intestine; - Caecum and appendix, - Ascending colon, - Transverse colon (right two-thirds). III. Hindgut: It begins from the junction between the right two-thirds and the left one third of the transverse colon to the cloacal membrane. It is divided by the allantois into: 1. Cranial portion; gives rise to: - Transverse colon (left one-third), - Descending colon, - Sigmoid colon. II. Caudal portion; gives rise to: - Rectum, -Upper part of anal canal, + Some uro-genital organs. Gut development
8 Derivatives of the 3 parts of the gut Development of Mouth - It arises from 2 sources, separated by oral membrane: 1. Ectodermal-lined part is derived from the stomatodeum (a depression lying between the forebrain bulge and cardiac bulge). 2. Endodermal-lined part is derived from the cranial part of the foregut. - The oral membrane ruptures at the 4 th week, so that the mouth is continuous with the pharynx. Development of Esophagus - It arises from foregut, caudal to the respiratory bud. - At first, it is short, but its length increases as the heart descends. - Its musculature arises from the surrounding mesoderm.
9 Development of Stomach - It arises from foregut, caudal to the respiratory bud. - At first, it appears as a fusiform dilatation in the foregut. It is attached to the ventral body wall by ventral mesogastrium and to the dorsal body wall by dorsal mesogastrium. - Unequal growth of borders occurs, resulting in the following: 1. The dorsal border elongates more than the ventral border, forming the greater curvature of stomach, while the ventral border forms the lesser curvature of stomach. 2. The cranial part of greater curvature bulges upwards to form the fundus. - Stage of rotation: The stomach rotates to the right side for 90º, resulting in: 1. The left surface becomes anterior and the left vagus becomes anterior gastric nerve. At same time, the right surface becomes posterior and its right vagus becomes posterior gastric nerve. 2. The dorsal mesogastium is pulled to the left, creating a pouch behind the stomach, called omental bursa (or lesser peritoneal sac). Stomach development Development of the Intestine (Gut) - It passes into 4 stages, as follows: 1. Pre-herniation: The intestine is derived from the following parts: Caudal part of foregut, Mid-gut, Hindgut.
10 At this stage, the midgut elongates to form a U-shaped loop, convex ventrally. Its summit is connected at its summit to definitive yolk sac by the vitelline duct 2. Herniation: The developing intestine herniates outside the body cavity through the extra-embryonic coelom (EEC) "into the umbilical cord". This occurs at the 6 th week, as a result of faster development of the intestine more than the abdominal cavity. While in EEC, the intestinal loop undergoes rotation for 90º to the right side, so that its cranial limb becomes right in position and the caudal limb becomes left. The cranial (right) limb grows more rapid than the caudal limb forming series of convolutions, occupying mainly the right side. At the same time, the caudal limb shows a conical swelling near its apex, forming the coecum (and the appendix). N.B.: This conical part differentiates between the small and large intestine i.e. the part proximal to it forms the small intestine, while the other part forms the large intestine. 3. Reduction of Herniation: The intestinal loop returned again to the abdominal cavity. This occurs by about the 10 th week of fetal life, as a result of increase size of the abdominal cavity. The original cranial limb (forming the small intestine) returns before the other limb so that it occupies the dorsal and lower part of abdominal cavity and the caudal limb occupies the ventral and upper part of the cavity. N.B.: The conical swelling of coecum impeding this return may be the cause for lateness of return the caudal limb. As it returns, it undergoes another 180º rotation (to complete 270º) so that the coecum (with appendix) comes lie close to the liver in the upper right quadrant of abdomen. Also the caudal limb (forming the transverse colon) passes in-front of the duodenum. Then, the coecum descends to lie in the right iliac fossa, forming the ascending colon.
11 4. Fixation The dorsal mesentery of some parts of the GIT disappears, fixing these parts to the posterior abdominal wall. These parts are duodenum, ascending colon and descending colon. N.B.: The dorsal mesentery persists in the following parts: - Jejunum and ileum forming mesentery proper. - Transverse colon forming transverse mesocolon. - Sigmoid colon forming sigmoid mesocolon. Development of Intestine Clinical Application Congenital Esophageal Anomalies 1. Esophageal atresia Cause: Posterior deviation of the trachea-esophageal septum. Manifestations: Failure of normal swallowing of amniotic fluid by the embryo. This results in a condition called polyhydramnios (accumulation of excess amniotic fluid). 2. Esophageal stenosis It usually occur in the lower third of esophagus and results in difficulty in swallowing. Cause: It may result from incomplete recanalization or vascular abnormalies that affect the bloodflow. 3. Trachea-esophageal fistula Cause: Failure of complete separation between the esophagus and trachea. 4. Congenital Hiatal Hernia Cause: Failure of descent of esophagus, resulting in a short esophagus that leads to upward traction of stomach to be herniated through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm.
12 Clinical manifestations: This leads to regurgitation of the acidic juice of the stomach into the oesophagus, leading to heartburn and then irritation and ulceration of the oesophagus. Persistent reflux leads to fibrosis and stricture of the oesophagus. Figure showing: Hiatal Hernia Congenital Stomach Anomalies 1. Pyloric stenosis Cause: Congenital hypertrophy of the circular and lo a lesser extent the longitudinal muscles of the pylorus. Clinical manifestations: Obstruction of the passage of food. This results in severe vomiting. 2. Hour-glass stomach: The stomach shows a congenital constriction separating it into 2 dilated portions. 3. Transposition of stomach: It may be a part of situs inversus. Congenital Intestine Anomalies I. Abnormalities of mesenteries 1. Mobile coecum: Cause: It may result from failure of degeneration of a portion of ascending mesocolon. 2. Abnormal long mesentery: Cause: It may result from failure of fusion of the mesentery with the posterior abdominal wall. Clinical manifestations: Abnormal movements of gut or even volvulus (twisting of the intestine). 3. Retro-colic hernia: Entrapment of portion of small intestine behind the mesocolon.
13 Cause: It may result from failure of fusion of the mesentery with the posterior abdominal wall. This leads to creation of retro-colic pockets especially behind the ascending colon. II. Abnormalities of vitelline duct 1. Meckel's diverticulum: Cause: Failure of obliteration of the proximal portion of vitelline duct. This case is characterized by: - Incidence: about 2% of population. - Site: about 2 feet from the ileo-coecal junction. - Length: about 2 inches. - Manifestations: The case is usually asymptomatic. However, its inflammation may present with the clinical picture of acute appendicitis. N.B.: To remind it, remember number "2" 2. Vitelline sinus: Cause: Failure of obliteration of the distal "outer" portion of vitelline duct. It may lead to discharge of mucous. 3. Vitelline cyst: Cause: Failure of obliteration of a middle portion of vitelline duct. It may lead to intestinal strangulation and volvulus. 4. Vitelline fistula: Cause: Failure of obliteration of the vitelline duct. It may lead to discharge of faeces at the umbilicus. 5. Vitelline band: Cause: The duct is obliterated but fails to disappear and it persists as a fibrous band, connecting the umbilicus with intestine. It may lead to intestinal strangulation and volvulus. Anomalies of vitelline duct
14 III. Abnormalities due to imperfect reduction and rotation 1. Congenital umbilical hernia (Omphalocele): Cause: Failure of reduction of the intestinal loop after its physiological herniation during the 6 th to the 10 th. Congenital umbilical hernia (Omphalocele) 2. Congenital volvulus: Cause: Rotation occurs more than 270º. It is a condition in which the intestine twists on itself, causing intestinal obstruction, manifested by abdominal pain, distension and vomiting. 3. Left sided caecum and appendix: Cause: Rotation occurs less than 270º (for only 90º). 4. Posterior transverse colon, passing behind the duodenum: Cause: Rotation occurs in a reversed direction. IV. Other Abnormalities 1. Undescended caecum and appendix They lie below the liver. Undescended caecum and appendix 2. Atresia of the gut: The lumen is occluded due to failure of recanalization. 3. Stenosis of the gut: The lumen is narrowed due to incomplete recanalization.
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
The Foregut. At first the esophagus is short. but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly
 GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut
 Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2
 Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2 Last time we talked about embryology of the GIT. We said that the development of the stomach is accompanied with the development of the duodenum and the pancreas. Also we talked
Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2 Last time we talked about embryology of the GIT. We said that the development of the stomach is accompanied with the development of the duodenum and the pancreas. Also we talked
2/2/2011. Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Development of Gastrointestinal Tract
 11 Development of Gastrointestinal Tract Learning Objectives At the end of this chapter, students would be able to define and understand the following: Development of the esophagus and stomach Rotation
11 Development of Gastrointestinal Tract Learning Objectives At the end of this chapter, students would be able to define and understand the following: Development of the esophagus and stomach Rotation
Embryology of the Heart
 *Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
*Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
Pharyngeal apparatus. - At the third week, it is a 3 layered structure: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. This is called trilaminar disc
 Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
Chapter 7 The digestive system
 41 Chapter 7 The digestive system Primitive gut tube 41 Foregut 42 Other foregut derivatives 44 Midgut 45 Hindgut 47 4 Fig. 7.1 The gut tube in a 4-week embryo. Pharynx Foregut Respiratory diverticulum
41 Chapter 7 The digestive system Primitive gut tube 41 Foregut 42 Other foregut derivatives 44 Midgut 45 Hindgut 47 4 Fig. 7.1 The gut tube in a 4-week embryo. Pharynx Foregut Respiratory diverticulum
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
8. Development of digestive system II. Rotation if intestine. Liver, pancreas, spleen. Development of respiratory passages and lung.
 8. Development of digestive system II. Rotation if intestine. Liver, pancreas, spleen. Development of respiratory passages and lung. Duodenum originates partially from the terminal part of the foregut,
8. Development of digestive system II. Rotation if intestine. Liver, pancreas, spleen. Development of respiratory passages and lung. Duodenum originates partially from the terminal part of the foregut,
The peritoneum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website:
 The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
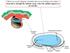 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
Anatomy (embryo 2) Aseel Al- khader 29/11/2015. Mohammad al Haidari. 1 P a g e
 14 Anatomy (embryo 2) Aseel Al- khader 29/11/2015 Mohammad al Haidari 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم *I advice you to watch this video ( from omar outom s post ) before studying this lecture for better
14 Anatomy (embryo 2) Aseel Al- khader 29/11/2015 Mohammad al Haidari 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم *I advice you to watch this video ( from omar outom s post ) before studying this lecture for better
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
CEA (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN)
 (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
(CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
ABDOMEN - GI. Duodenum
 TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Embryo#1. Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد. 0 P a g e
 Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
Embryo#1 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb باشق جهاد 0 P a g e Before you start, it is important to link what you learn in gross anatomy with developmental stages discussed in embryology. Cells that form organs
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER
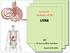 Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Embryology: Development of digestive system
 Embryology: Development of digestive system Embryo folding incorporation of endoderm to form primitive gut. Outside of embryo yolk sac and allantois. Vitelline duct Stomodeum (primitive mouth) the oral
Embryology: Development of digestive system Embryo folding incorporation of endoderm to form primitive gut. Outside of embryo yolk sac and allantois. Vitelline duct Stomodeum (primitive mouth) the oral
Development of the nasal cavity :
 Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL
 Lecture 2 ESS_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER - is the largest gland of
Lecture 2 ESS_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER - is the largest gland of
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe
 Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
In the name ofgod. Abdomen 3. Dr. Zahiri
 In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
Date Lab Pd. Lecture Notes (57)
 Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human;
 Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Mousa Salah. Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib. 1 P a g e
 8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Cardiovascular System Anatomy & Embryology
 بسم رلاهللا Cardiovascular System Anatomy & Embryology Portal circulation: Portal vessel: a vessel or a vein running between two sets of capillaries, the portal vein of the liver starts from a set of capillaries
بسم رلاهللا Cardiovascular System Anatomy & Embryology Portal circulation: Portal vessel: a vessel or a vein running between two sets of capillaries, the portal vein of the liver starts from a set of capillaries
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
The PHARYNX. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D
 The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
FORMS OF EMBRYONIC PRIMORDIA
 FORMS OF EMBRYONIC PRIMORDIA BY PROF. ANTHONY OBIOMA NWAOPARA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ONDO CITY, ONDO STATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES To recognise the different forms of embryonic primordia. To recognise
FORMS OF EMBRYONIC PRIMORDIA BY PROF. ANTHONY OBIOMA NWAOPARA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ONDO CITY, ONDO STATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES To recognise the different forms of embryonic primordia. To recognise
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green
 Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE
 SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
Name: Fetal Pig Dissection Internal Anatomy
 In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
Digestive system (Systema digestorium/ alimentarium) Lecture #1
 Digestive system (Systema digestorium/ alimentarium) Lecture #1 Internal organs are grouped into 1. System - Have the same functions and development Digestive system Respiratory system 2. Apparatus - Have
Digestive system (Systema digestorium/ alimentarium) Lecture #1 Internal organs are grouped into 1. System - Have the same functions and development Digestive system Respiratory system 2. Apparatus - Have
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM I. Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen A. Surface landmarks 1. Xiphoid process 2. Costal margin 3. Iliac crest 4. ASIS 5. Pubic symphysis 6. Inguinal groove B. Anterior abdominal
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM I. Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen A. Surface landmarks 1. Xiphoid process 2. Costal margin 3. Iliac crest 4. ASIS 5. Pubic symphysis 6. Inguinal groove B. Anterior abdominal
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal. - Dana AF
 - 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
- 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
Development of the Urinary System
 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
Embryology of the Gut and Mesenteries, slide 7 This is very similar to a cross-section we looked at when were talking about formation of the diaphragm
 Embryology of the Gut and Mesenteries, slide 2 This is a median sagittal section of a four week embryo, most of you can probably draw it in your sleep. I made a few modifications from some of the earlier
Embryology of the Gut and Mesenteries, slide 2 This is a median sagittal section of a four week embryo, most of you can probably draw it in your sleep. I made a few modifications from some of the earlier
