Algorithm for managing severe ulcerative colitis
|
|
|
- Myron Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tropical Gastroenterology 2014;Suppl:S40 44 Algorithm for managing severe ulcerative colitis Vineet Ahuja 1, Ajay Kumar 2, Rakesh Kochhar 3 ABSTRACT Dept of Gastroenterology, 1 All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi 2 Apollo Indraprastha Hospitals, New Delhi, 3 Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh India Corresponding author: Vineet Ahuja vins_ahuja@hotmail.com Acute severe ulcerative colitis as defined by Truelove Witt s criteria is a medical emergency which requires hospitalization. Patient requires close clinical monitoring with assessment of daily vital parameters, stool frequency, serum electrolytes and daily abdominal examination. Intravenous corticosteroids are the mainstay of therapy. Approximately two thirds of patients will respond to steroids. Response to steroids should be assessed at day 3 of admission and partial/ non-responders should be considered for alternative medical therapy/ surgery. Medical rescue therapies include intravenous cyclosporin and infliximab.this article provides an time bound step up algorithm for management of acute severe ulcerative colitis. Keywords: Acute severe colitis, Ulcerative colitis, management, algorithm Acute severe ulcerative colitis is a medical emergency and carries a mortality rate of 1-2.9%. Effective treatment relies on two management principles: a) Multidisciplinary management including a gastroenterologist as well as a colorectal surgeon b) Time Framed Step Up strategy as prolonged steroid therapy or delay in surgical therapy can be life threatening. This article presents a time bound framework, which looks at stepwise management of acute severe ulcerative colitis. Literature details have been spared as they have already been described in reviews within this supplement. Step 1: Categorizing a patient as having Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis (ASUC) In a diagnosed case of ulcerative colitis, Truelove and Witts classification still remains most appropriate to diagnose acute severe ulcerative colitis Parameter Severe Colitis Number of bloody stools per day (n) >6 and at least one of the following : Temperature ( C) >37.8 Heart rate (beats per minute) >90 Haemoglobin (g/dl) <10.5 Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (mm/h) >30 Tropical Gastroenterology 2014 Step 2: Does every patient of acute severe ulcerative colitis require hospitalization? i) All patients with ASUC requiring intravenous steroids should be hospitalized. The term fulminant colitis is no longer used routinely. Fulminant colitis denotes a very severe form of disease as evidenced by 10 or more bloody stools with systemic features of activity and colonic dilatation on plain abdominal Xray. A patient with fulminant colitis should be immediately hospitalized. i ASUC patients presenting with toxic megacolon or features of peritonism should be immediately hospitalized. iv) However if a patient has not been on oral steroids and has Step 3: progressed from a mild or moderate to severe disease then a trial of oral steroids may be given without immediate hospitalization. Day 1 Management i) Haemogram including ESR, CRP, serum electrolytes, blood sugar, serum albumin, liver function tests and renal function tests Viral markers: HbsAg, IgG anti HBc, anti HCV and HIV
2 Algorithm for managing severe ulcerative colitis S41 i Stool tests: a) Stool assay for Clostridium difficile cytotoxin (both A and B) b) Stool culture for bacterial pathogens c) Stool examination for parasitic infestations iv) Baseline abdominal radiographs v) Flexible unprepared sigmoidoscopy with minimal air insufflation to confirm disease, assess endoscopic severity and rectal biopsies for CMV colitis. CMV testing may be done at tertiary care centers only as facilities may not be available at all centers. vi) Investigations best avoided: a) Barium enema b) Full length colonoscopy c) Colon biopsy from a site more than 10 cms from anal verge Therapy Patients with ASUC should be treated in hospital jointly by a gastroenterologist and a colorectal surgeon. i Intravenous quinolone and metronidazole combination is the preferred choice. Adjunct Therapy: i) Intravenous fluid and electrolyte replacement to correct and prevent dehydration or electrolyte imbalance. Prophylaxis for thromboembolic complications i Blood transfusion to maintain a haemoglobin of 10 g/dl Role of 5-aminosalicylates: iv) Topical therapy in form of 5ASA/steroids enemas or suppositories is advisable, although no trials are available which have evaluated the role of topical therapy in ASUC. v) Physician experience suggests that oral 5ASA may be discontinued temporarily as it may not provide any additional anti- inflammatory benefit over intravenous steroids. Nutrition: Definitive Therapy Steroid therapy: i) First-line medical therapy for patients should be intravenous corticosteroids hydrocortisone 100 mg four times or methylprednisolone 60 mg daily. Divided dose injection is as effective as continuous infusion i Treatment is usually given for about 5 days, since extending therapy beyond 7 to 10 days carries no benefit. iv) In patients with severe osteoporosis, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus or history of steroid psychosis or intolerant of intravenous steroids, monotherapy with intravenous cyclosporin (to achieve a minimum therapeutic concentration) is an option. Antibiotics: i) Routine use of antibiotics is not recommended. Antibiotics are given in following situations :i) if infection is considered (such as in an acute first attack of short duration, or after recent admission to hospital or presence of leucocytosis), severe toxaemia i features of toxic megacolon are present. i) Patients should be offered a normal diet or enteral nutrition unless such a diet is not tolerated. TPN is not effective as primary therapy. TPN should be considered only in malnourished patients who cannot tolerate oral intake or enteral nutrition. Drugs which should not be given: i) Drugs which may slow down intestinal transit and precipitate colonic dilation should be avoided. These include: anticholinergics, antidiarrhoeal agents, NSAIDs and opiates. Monitoring: i) Bedside stool monitoring chart to be maintained. Surgical consultation should be obtained for all patients with systemic toxicity or megacolon. Patient Counselling: Often neglected but a key factor for effective management is making the patient and family aware of the possible course of disease and therapeutic options including surgery. An informed
3 S42 Tropical Gastroenterology 2014;Suppl:S40 44 patient will help the treating physician in making choice for further management. Step 4 Day 2 Management: Daily Monitoring: i) Physical examination daily to evaluate abdominal tenderness, presence of rebound tenderness and bowel sounds. Recording of vital signs four times daily and noted in monitoring chart. i Stool chart (to record number, consistency i.e. liquid versus solid stool, presence or absence of blood and nocturnal frequency of bowel movements) and family the options of surgery or medical rescue therapy with cyclosporin or infliximab and guide the patient to participate in an informed decision making process. If a patient is planned for cyclosporin then investigations to be done include: serum magnesium, serum cholesterol and serum creatinine i If a patient is planned for biological therapy then the following investigations should be done: High resolution contrast tomography of chest to exclude active TB infection, Monteux test or Interferon gamma release assay should be done. iv) If a patient is planned for biological therapy or surgery and serum albumin is low then in both instances intravenous albumin should be supplemented so as to build up albumin levels. i) Haemogram, ESR, CRP, serum electrolytes, serum albumin, and glucose every 24 hours. If there are signs of colonic distension and/or there is significant deterioration in clinical condition or blood parameters then abdominal X ray should be done Day 3-5 Management: Joint medical and surgical management is appropriate. Monitoring and investigations as planned for Day 2 are to be similarly carried out on day 3, 4 and 5. In addition, monitoring after 72 hours of intravenous steroid institution includes: a) Decision Making Tool: Evaluating for Oxford (Travis) Index Non Responders: A stool frequency >4 and CRP >45 mg/l on day 3; or a stool frequency > 8 /24 hours. Responders: A stool frequency of less than 3 at Day 3. b) Chances of colectomy are much higher in non/ incomplete responders Non or Incomplete Responders: In non responders or incomplete responders, following measures should be planned: i) Patient Education and Counselling: Explaining the patient Step 5: Day 5 and beyond Time Bound Decisions: i) A decision regarding surgical or medical rescue therapy (Infliximab or cyclosporin) should be made within 5 7 days after initiation of intravenous steroids. Response to infliximab or cyclosporin should also be made within 5-7 days after initiation i Either intravenous cyclosporin or infliximab is an appropriate choice for selected patients who have failed intravenous corticosteroid therapy. iv) Factors which may dictate choice of either agent include: For infliximab, major impediment is affordability; For cyclosporin, major impediments are lack of physician experience in its usage and if the patient is already on azathioprine. Cyclosporin may be more beneficial in azathioprine naïve ASUC patients. iv) It is best for centers with inadequate experience to refer patients at this stage to centers which have appropriate experience and support in use of cyclosporin and infliximab. Cyclosporin use: i) Cyclosporin should not be used if cholesterol <115 mg/dl or magnesium<1.4 meq/l. It should also be avoided in presence of hypertension, renal impairment, epilepsy, sepsis, age >80 years. Magnesium, cholesterol, and creatinine should be measured at baseline and within 48 hours of starting cyclosporin. Cyclosporin should be administered in a dose of 2 mg/kg/
4 Algorithm for managing severe ulcerative colitis S43 day intravenously aiming for trough levels ng/mL. i Blood pressure and renal function should be monitored and cyclosporin should be stopped if serum creatinine rises >25%. iv) Cyclosporin should be stopped if there is no improvement in 7 days v) In responders, intravenous cyclosporin should be switched to oral cyclosporine 4 mg/kg/day twice daily. Monitoring of trough levels ( ng/ml) should be regularly done. Azathioprine, which should be started along with oral cyclosporin. Cyclosporin should be stopped after 3 months. Infliximab Therapy: i) Patients who respond to a single infusion of infliximab 5 mg/kg IV should be given two additional induction doses at 2 and 6 weeks, followed by maintenance infliximab therapy. If patients are not on azathioprine, it can be started by day 5 after the initiation of infliximab injection in ASUC Sequential rescue therapy in patients with cyclosporin non responders with infliximaband vice versa should be avoided. Tacrolimus (FK506): Tacrolimus is a calcineurin inhibitor, which can be an alternative agent. Tacrolimus (0.1 mg/kg body weight per day) may be administered orally and initially intravenously (0.01 mg/kg body weight per day), aiming for serum trough levels of 4-8 ng/ml. Surgery: i) Patients who fail to respond to infliximab or cyclosporin within 5 7 days have a poor outcome and surgery is advisable. When surgery is required, total or subtotal colectomy with end ileostomy is the procedure of choice. i Pouchitis frequency is much less when done by an experienced colorectal surgeon who does at least 10 pouch surgeries every year. The described algorithm lays down the flow of investigations and therapeutic strategies in a timed format (Figure 1 and 2). Acute severe ulcerative colitis: IV hydrocortisone 100 mg every 6 hourly or iv methylprednisolone 60 mg/day Assess response at day 3 Complete responders Stool frequency <3/day Incomplete responders Stool frequency 3 8/day and CRP <45 mg/l Non responders Stool frequency >8/day or 3 8/day and CRP > 45 mg/l Oral steroids, Add AZA subsequently if pancolitis/ left colitis with previous one steroid course Medical rescue therapy or colectomy Figure 1: Algorithm for treatment decisions for patients with acute severe UC on intensive steroid therapy
5 S44 Tropical Gastroenterology 2014;Suppl:S40 44 Cyclosporin (In AZA naive patients) Single dose Infliximab infusion at 5 mg/kg Assess response at day 4 7 Assess response at day 4 7 Adequate response: Switch to oral CsA, add AZA at day 7 Inadequate response Adequate response: Infliximab dose at 2 and 6 weeks, AZA to be continued Colectomy Figure 2: Algorithm for medical rescue therapy after failure of response to intravenous steroids Suggested reading: 1. Dignass A, Van Assche G, Lindsay JO, Lemann M, Soderholm J, ColombelJF,et al. The second European evidence-based Consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn s disease: Current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2010;4: Turner D, Travis SP, Griffiths AM, Ruemmele FM, Levine A, Benchimol EI, et al. European Crohn s and Colitis Organization; Porto IBD Working Group, European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. Consensus for managing acute severe ulcerative colitis in children: a systematic review and joint statement from ECCO, ESPGHAN, and the Porto IBD Working Group of ESPGHAN. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106: Van Assche G, Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P. Management of acute severe ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2011;60:130 3.
Protocol for the management of acute severe ulcerative colitis in children
 Protocol for the management of acute severe ulcerative colitis in children Introduction: Paediatric UC is severe and more extensive than adult onset UC with 6-8% presenting as pancolitis (1,2) Within five
Protocol for the management of acute severe ulcerative colitis in children Introduction: Paediatric UC is severe and more extensive than adult onset UC with 6-8% presenting as pancolitis (1,2) Within five
Anti-TNF and cyclosporine are identical choices for severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy CON Peter Laszlo LAKATOS Semmelweis
 Anti-TNF and cyclosporine are identical choices for severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy CON Peter Laszlo LAKATOS Semmelweis University, 1st Department of Medicine Budapest June 13-15,
Anti-TNF and cyclosporine are identical choices for severe ulcerative colitis refractory to steroid therapy CON Peter Laszlo LAKATOS Semmelweis University, 1st Department of Medicine Budapest June 13-15,
Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis
 Adalimumab in the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis: ULTRA 2 Trial Results Sandborn WJ, van Assche G, Reinisch W, et al. Adalimumab induces and maintains clinical remission in patients
Adalimumab in the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis: ULTRA 2 Trial Results Sandborn WJ, van Assche G, Reinisch W, et al. Adalimumab induces and maintains clinical remission in patients
Achieving Success in Ulcerative Colitis: the Role of Infliximab
 Achieving Success in Ulcerative Colitis: the Role of Infliximab Dr Gill Watermeyer IBD clinic Groote Schuur Hospital 17 th August 2012 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis
Achieving Success in Ulcerative Colitis: the Role of Infliximab Dr Gill Watermeyer IBD clinic Groote Schuur Hospital 17 th August 2012 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis
Response to First Intravenous Steroid Therapy Determines the Subsequent Risk of Colectomy in Ulcerative Colitis Patients
 Response to First Intravenous Steroid Therapy Determines the Subsequent Risk of Colectomy in Ulcerative Colitis Patients Tamás Molnár 1, Klaudia Farkas 1, Tibor Nyári 2, Zoltán Szepes 1, Ferenc Nagy 1,
Response to First Intravenous Steroid Therapy Determines the Subsequent Risk of Colectomy in Ulcerative Colitis Patients Tamás Molnár 1, Klaudia Farkas 1, Tibor Nyári 2, Zoltán Szepes 1, Ferenc Nagy 1,
-2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine. -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency
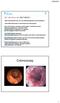 SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
Diarrhoea for the Acute Physician
 Diarrhoea for the Acute Physician STEPHEN INNS GASTROENTEROLOGIST AND PHYSICIAN HUTT VALLEY DHB August 2013 Outline Case History 1 Initial assessment of acute diarrhoea Management of fulminant UC Management
Diarrhoea for the Acute Physician STEPHEN INNS GASTROENTEROLOGIST AND PHYSICIAN HUTT VALLEY DHB August 2013 Outline Case History 1 Initial assessment of acute diarrhoea Management of fulminant UC Management
Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis Part 2: Current management
 Journal of Crohn's and Colitis (2012) 6, 991 1030 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com SPECIAL ARTICLE Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis (2012) 6, 991 1030 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com SPECIAL ARTICLE Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis
Trust Guideline. for Ciclosporin Treatment & Monitoring for Adult* Patients with Acute, Severe Ulcerative Colitis. (*ie aged 16 years and over)
 Trust Guideline for Ciclosporin Treatment & Monitoring for Adult* Patients with Acute, Severe Ulcerative Colitis (*ie aged 16 years and over) abc A guideline recommended for use In: Gastroenterology/Medical
Trust Guideline for Ciclosporin Treatment & Monitoring for Adult* Patients with Acute, Severe Ulcerative Colitis (*ie aged 16 years and over) abc A guideline recommended for use In: Gastroenterology/Medical
Definitions. Clinical remission: Resolution of symptoms (stool frequency 3/day, no bleeding and no urgency)
 CROHN S DISEASE Definitions Clinical remission: Resolution of symptoms (stool frequency 3/day, no bleeding and no urgency) Recurrence: The reappearance of lesions after surgical resection Endoscopic remission:
CROHN S DISEASE Definitions Clinical remission: Resolution of symptoms (stool frequency 3/day, no bleeding and no urgency) Recurrence: The reappearance of lesions after surgical resection Endoscopic remission:
Incidence of Colectomy During Long-term Follow-up After Cyclosporine-Induced Remission of Severe Ulcerative Colitis
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:760 765 Incidence of Colectomy During Long-term Follow-up After Cyclosporine-Induced Remission of Severe Ulcerative Colitis DAVID N. MOSKOVITZ, GERT VAN
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:760 765 Incidence of Colectomy During Long-term Follow-up After Cyclosporine-Induced Remission of Severe Ulcerative Colitis DAVID N. MOSKOVITZ, GERT VAN
TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS Target Audience: Physicians, Physician Assistants, Nurse Practitioners and Nurses impacted by the protocol. Scope/Patient Population: All adult
TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS Target Audience: Physicians, Physician Assistants, Nurse Practitioners and Nurses impacted by the protocol. Scope/Patient Population: All adult
Predicting outcome in severe ulcerative colitis
 Gut 1996; 38: 95-91 Predicting outcome in severe ulcerative colitis 95 S P L Travis, J M Farrant, C Ricketts, D J Nolan, N M Mortensen, M G W Kettlewell, D P Jewell Gastroenterology Unit S P L Travis J
Gut 1996; 38: 95-91 Predicting outcome in severe ulcerative colitis 95 S P L Travis, J M Farrant, C Ricketts, D J Nolan, N M Mortensen, M G W Kettlewell, D P Jewell Gastroenterology Unit S P L Travis J
Indications for use of Infliximab
 Indications for use of Infliximab Moscow, June 10 th 2006 Prof. Dr. Dr. Gerhard Rogler Klinik und Poliklinik für Innere Medizin I Universität Regensburg Case report 1989: Diagnosis of Crohn s disease of
Indications for use of Infliximab Moscow, June 10 th 2006 Prof. Dr. Dr. Gerhard Rogler Klinik und Poliklinik für Innere Medizin I Universität Regensburg Case report 1989: Diagnosis of Crohn s disease of
TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS Target Audience: Physicians, Physician Assistants, Nurse Practitioners and Nurses impacted by the protocol. Scope/Patient Population: All adult
TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS Target Audience: Physicians, Physician Assistants, Nurse Practitioners and Nurses impacted by the protocol. Scope/Patient Population: All adult
Third European Evidence-based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 2: Current Management
 Journal of Crohn's and Colitis, 2017, 769 784 doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx009 Advance Access publication January 28, 2017 ECCO Guideline/Consensus Paper ECCO Guideline/Consensus Paper Third European Evidence-based
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis, 2017, 769 784 doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx009 Advance Access publication January 28, 2017 ECCO Guideline/Consensus Paper ECCO Guideline/Consensus Paper Third European Evidence-based
Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis
 Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS Acting Chief, Gastrointestinal Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Sequential Therapies
Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS Acting Chief, Gastrointestinal Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Sequential Therapies
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 1. Medical Condition INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) specifically includes Crohn s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) but also includes IBD unclassified (IBDu), seen in about 10% of cases. These
1. Medical Condition INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD) specifically includes Crohn s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) but also includes IBD unclassified (IBDu), seen in about 10% of cases. These
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical updates. Dr Jeff Chao Princess Alexandra Hospital
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical updates Dr Jeff Chao Princess Alexandra Hospital Inflammatory bowel disease 2017 Clinical updates and future directions Pathogenesis Treatment targets Therapeutic agents
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical updates Dr Jeff Chao Princess Alexandra Hospital Inflammatory bowel disease 2017 Clinical updates and future directions Pathogenesis Treatment targets Therapeutic agents
Biologics in IBD. Brian P. Bosworth, MD, NYSGEF Associate Professor of Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College
 Biologics in IBD Brian P. Bosworth, MD, NYSGEF Associate Professor of Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Case 30 year old man diagnosed with ulcerative proctitis diagnosed in 2003 Had been maintained
Biologics in IBD Brian P. Bosworth, MD, NYSGEF Associate Professor of Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Case 30 year old man diagnosed with ulcerative proctitis diagnosed in 2003 Had been maintained
Implementation of disease and safety predictors during disease management in UC
 Implementation of disease and safety predictors during disease management in UC DR ARIELLA SHITRIT DIGESTIVE DISEASES INSTITUTE SHAARE ZEDEK MEDICAL CENTER JERUSALEM Case presentation A 52 year old male
Implementation of disease and safety predictors during disease management in UC DR ARIELLA SHITRIT DIGESTIVE DISEASES INSTITUTE SHAARE ZEDEK MEDICAL CENTER JERUSALEM Case presentation A 52 year old male
ULCERATIVE COLITIS. Sean Lynch, MD and Richard Bloomfeld, MD Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC
 ULCERATIVE COLITIS Sean Lynch, MD and Richard Bloomfeld, MD Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC What is Ulcerative Colitis? Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a disease marked by inflammation
ULCERATIVE COLITIS Sean Lynch, MD and Richard Bloomfeld, MD Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC What is Ulcerative Colitis? Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a disease marked by inflammation
CCFA. Crohns Disease vs UC: What is the best treatment for me? November
 CCFA Crohns Disease vs UC: What is the best treatment for me? November 8 2009 Ellen J. Scherl,, MD, FACP,AGAF Roberts Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Weill Medical College Cornell University New York
CCFA Crohns Disease vs UC: What is the best treatment for me? November 8 2009 Ellen J. Scherl,, MD, FACP,AGAF Roberts Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Weill Medical College Cornell University New York
What is ulcerative colitis?
 What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is a disease that causes inflammation and sores, called ulcers, in the lining of the rectum and colon. Ulcers form where inflammation has killed the cells
What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative colitis is a disease that causes inflammation and sores, called ulcers, in the lining of the rectum and colon. Ulcers form where inflammation has killed the cells
Management of the Hospitalized IBD Patient. Drew DuPont MD
 Management of the Hospitalized IBD Patient Drew DuPont MD Ulcerative Colitis: Indications for Admission Severe ulcerative colitis Frequent loose bloody stools ( 6 per day) Severe cramps Systemic toxicity:
Management of the Hospitalized IBD Patient Drew DuPont MD Ulcerative Colitis: Indications for Admission Severe ulcerative colitis Frequent loose bloody stools ( 6 per day) Severe cramps Systemic toxicity:
CLINICAL TRIAL PROTOCOL
 CLINICAL TRIAL PROTOCOL Azathioprine maintenance therapy in steroid-refractory Ulcerative Colitis responsive to i.v. Cyclosporine A: Is a therapeutic bridge with oral Cyclosporine A necessary? Miquel A.
CLINICAL TRIAL PROTOCOL Azathioprine maintenance therapy in steroid-refractory Ulcerative Colitis responsive to i.v. Cyclosporine A: Is a therapeutic bridge with oral Cyclosporine A necessary? Miquel A.
WHAT IS ULCERATIVE COLITIS?
 235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Ulcerative Colitis WHAT IS ULCERATIVE COLITIS? Ulcerative colitis is
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Ulcerative Colitis WHAT IS ULCERATIVE COLITIS? Ulcerative colitis is
Ulcerative Colitis: State of the Art 2006
 Ulcerative Colitis: State of the Art David T. Rubin, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center University of Chicago Improving Management of Ulcerative Colitis (UC) Better classification/diagnostic
Ulcerative Colitis: State of the Art David T. Rubin, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center University of Chicago Improving Management of Ulcerative Colitis (UC) Better classification/diagnostic
Ileal Pouch Anal Anastomosis: The Preferred Method of Reconstruction after Proctocolectomy in Children
 Ileal Pouch Anal Anastomosis: The Preferred Method of Reconstruction after Proctocolectomy in Children Stephanie Jones, D.O. Surgical Fellow March 21, 2011 Ulcerative Colitis Spectrum of inflammatory bowel
Ileal Pouch Anal Anastomosis: The Preferred Method of Reconstruction after Proctocolectomy in Children Stephanie Jones, D.O. Surgical Fellow March 21, 2011 Ulcerative Colitis Spectrum of inflammatory bowel
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory. Therapeutic Options in Steroid-Refractory Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis.
 Therapeutic Options in Steroid-Refractory Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Wojciech Blonski, MD, PhD, Prashant R. Mudireddy, MD, Anna M. Buchner, MD, PhD, and Gary R. Lichtenstein, MD Abstract Objective:
Therapeutic Options in Steroid-Refractory Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Wojciech Blonski, MD, PhD, Prashant R. Mudireddy, MD, Anna M. Buchner, MD, PhD, and Gary R. Lichtenstein, MD Abstract Objective:
Update on Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis. Scott Plevy, MD University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC
 Update on Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Scott Plevy, MD University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC Objectives Discuss the latest advances in the pharmacologic management of ulcerative colitis Describe
Update on Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Scott Plevy, MD University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC Objectives Discuss the latest advances in the pharmacologic management of ulcerative colitis Describe
Guideline Ulcerative colitis: management
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline Ulcerative colitis: management Draft for consultation, December 0 This guideline covers the care and treatment of adults, children and young
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline Ulcerative colitis: management Draft for consultation, December 0 This guideline covers the care and treatment of adults, children and young
Inflammatory bowel disease. Kawa Obeid, PhD
 Inflammatory bowel disease Kawa Obeid, PhD 63 Introduction Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can be divided into two chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastro- intestinal tract, namely Crohn's disease
Inflammatory bowel disease Kawa Obeid, PhD 63 Introduction Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can be divided into two chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastro- intestinal tract, namely Crohn's disease
The Spectrum of IBD. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Symptoms. Epidemiology. Tests for IBD. CD or UC? Inflamatory Bowel Disease. Fernando Vega, M.D.
 The Spectrum of IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Fernando Vega, M.D. Epidemiology CD and UC together 1:400 UC Prevalence 1:500 UC Incidence 6-12K/annum CD Prevalence 1:1000 CD Incidence 3-6K/annum Symptoms
The Spectrum of IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease Fernando Vega, M.D. Epidemiology CD and UC together 1:400 UC Prevalence 1:500 UC Incidence 6-12K/annum CD Prevalence 1:1000 CD Incidence 3-6K/annum Symptoms
Doncaster & Bassetlaw Medicines Formulary
 Doncaster & Bassetlaw Medicines Formulary Section 1.5 Chronic Bowel Disorders (including IBD) Aminosalicylates: Mesalazine 400mg and 800mg MR Tablets (Octasa) Mesalazine 1.2g MR Tablets (Mezavant XL) Mesalazine
Doncaster & Bassetlaw Medicines Formulary Section 1.5 Chronic Bowel Disorders (including IBD) Aminosalicylates: Mesalazine 400mg and 800mg MR Tablets (Octasa) Mesalazine 1.2g MR Tablets (Mezavant XL) Mesalazine
Latest Treatment Updates for Ulcerative Colitis: Evolving Treatment Goals
 Latest Treatment Updates for Ulcerative Colitis: Evolving Treatment Goals Stephen Hanauer, MD Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Digestive Disease Center Northwestern Medicine Chicago, Illinois Speaker
Latest Treatment Updates for Ulcerative Colitis: Evolving Treatment Goals Stephen Hanauer, MD Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Digestive Disease Center Northwestern Medicine Chicago, Illinois Speaker
 Tacrolimus therapy as an alternativ Titlemaintaining remission in patients w colitis. Author(s) Yamamoto, Shuji; Nakase, Hiroshi; M Masuda, Satohiro; Inui, Ken-ichi; C Citation Journal of clinical gastroenterolog
Tacrolimus therapy as an alternativ Titlemaintaining remission in patients w colitis. Author(s) Yamamoto, Shuji; Nakase, Hiroshi; M Masuda, Satohiro; Inui, Ken-ichi; C Citation Journal of clinical gastroenterolog
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture,
 To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture, click Options in the Message Bar, and then click Enable
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture, click Options in the Message Bar, and then click Enable
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 3 October 2012
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 3 October 2012 REMICADE 100 mg, powder for concentrate for solution for infusion B/1 vial (CIP code: 562 070-1) Applicant:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 3 October 2012 REMICADE 100 mg, powder for concentrate for solution for infusion B/1 vial (CIP code: 562 070-1) Applicant:
What is Crohn's disease?
 What is Crohn's disease? Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any area of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most
What is Crohn's disease? Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any area of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most
Infliximab (Remicade) for paediatric ulcerative colitis - second line
 Infliximab (Remicade) for paediatric ulcerative colitis - second line September 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Infliximab (Remicade) for paediatric ulcerative colitis - second line September 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Dr David Rowbotham. The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS
 Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Useful Titbits from the World of Gastroenterology David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Useful Titbits from the World of Gastroenterology David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
Primary & Secondary Care Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathway February 2018
 South East London Area Prescribing Committee: Primary & Secondary Care Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathway February 2018 Developed by: South East London IBD Pathway Development Group Approved: February
South East London Area Prescribing Committee: Primary & Secondary Care Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathway February 2018 Developed by: South East London IBD Pathway Development Group Approved: February
IBD Case Studies. David Rowbotham. Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Auckland City Hospital
 IBD Case Studies David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Auckland City Hospital Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
IBD Case Studies David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Auckland City Hospital Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
Efficacy and Safety of Treatment for Pediatric IBD
 Efficacy and Safety of Treatment for Pediatric IBD Andrew B. Grossman MD Co-Director, Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Associate Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology,
Efficacy and Safety of Treatment for Pediatric IBD Andrew B. Grossman MD Co-Director, Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Associate Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology,
Mild-moderate Ulcerative Colitis Sequential & Combined treatments need to be tested. Philippe Marteau, Paris, France
 Mild-moderate Ulcerative Colitis Sequential & Combined treatments need to be tested Philippe Marteau, Paris, France Sequential vs combined treatments When should one switch? Sequential vs combined treatments
Mild-moderate Ulcerative Colitis Sequential & Combined treatments need to be tested Philippe Marteau, Paris, France Sequential vs combined treatments When should one switch? Sequential vs combined treatments
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
My Child Has Inflammatory Bowel Disease : Why? What now? What s next?
 My Child Has Inflammatory Bowel Disease : Why? What now? What s next? George M. Zacur, M.D., M.S. Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics and Communicable Diseases Division of Gastroenterology
My Child Has Inflammatory Bowel Disease : Why? What now? What s next? George M. Zacur, M.D., M.S. Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics and Communicable Diseases Division of Gastroenterology
I B D. etter than this. isease UNDERSTANDING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASES
 I B D m etter than this isease UNDERSTANDING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASES What types of people have learned how to manage their IBD? Athletes Musicians Firefighters DOCTORS HEROES Artists Presidents Actors
I B D m etter than this isease UNDERSTANDING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASES What types of people have learned how to manage their IBD? Athletes Musicians Firefighters DOCTORS HEROES Artists Presidents Actors
Summary of SAMEP review
 EVALUATION SUMMARY Infliximab for treatment of immunomodulator-naïve patients for treatment of acute and severe colitis refractory to intravenous corticosteroid therapy South Australian Medicines Evaluation
EVALUATION SUMMARY Infliximab for treatment of immunomodulator-naïve patients for treatment of acute and severe colitis refractory to intravenous corticosteroid therapy South Australian Medicines Evaluation
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Acute Colitis Protocol Dr Seamus J Murphy Gastroenterology Acute Date Uploaded: 01/06/18 Review Date June 2021 Clinical Guideline
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Acute Colitis Protocol Dr Seamus J Murphy Gastroenterology Acute Date Uploaded: 01/06/18 Review Date June 2021 Clinical Guideline
Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD):
 Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): What Every Patient Needs to Know William H Holderman, MD Digestive Health Specialists Tacoma, WA Today s Objectives Define IBD, its potential causes and
Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): What Every Patient Needs to Know William H Holderman, MD Digestive Health Specialists Tacoma, WA Today s Objectives Define IBD, its potential causes and
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
Efficacy and Safety of Treatment for Pediatric IBD
 Efficacy and Safety of Treatment for Pediatric IBD Andrew B. Grossman MD Co-Director, Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology,
Efficacy and Safety of Treatment for Pediatric IBD Andrew B. Grossman MD Co-Director, Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology,
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
Clinical Study Clinical Study of the Relation between Mucosal Healing and Long-Term Outcomes in Ulcerative Colitis
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 192794, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/192794 Clinical Study Clinical Study of the Relation between
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 192794, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/192794 Clinical Study Clinical Study of the Relation between
Diarrhoea on the AMU. Dr Chris Roseveare
 Diarrhoea on the AMU Dr Chris Roseveare The Society for Acute Medicine, Spring Meeting, Radisson Blu Hotel, Dublin 3-4 May 2012 Acute diarrhoea in developed countries adult populations Mainly a primary
Diarrhoea on the AMU Dr Chris Roseveare The Society for Acute Medicine, Spring Meeting, Radisson Blu Hotel, Dublin 3-4 May 2012 Acute diarrhoea in developed countries adult populations Mainly a primary
Disclosures. What Do I Do When Anti-TNF Therapy Is Not Working Anymore? Fadi Hamid, M.D. Saint Luke s GI Specialists
 What Do I Do When Anti-TNF Therapy Is Not Working Anymore? Fadi Hamid, M.D. Saint Luke s GI Specialists Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose. 1 Learning Objectives Case 24M with ileocolonic
What Do I Do When Anti-TNF Therapy Is Not Working Anymore? Fadi Hamid, M.D. Saint Luke s GI Specialists Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose. 1 Learning Objectives Case 24M with ileocolonic
Από τη θεωρία στη πράξη: Συζήτηση κλινικών περιστατικών. Κωνσταντίνος Κατσάνος Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Γαστρεντερολογίας Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων
 Από τη θεωρία στη πράξη: Συζήτηση κλινικών περιστατικών Κωνσταντίνος Κατσάνος Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Γαστρεντερολογίας Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων Conflict of interest By means of this, the speaker confirms that
Από τη θεωρία στη πράξη: Συζήτηση κλινικών περιστατικών Κωνσταντίνος Κατσάνος Επίκουρος Καθηγητής Γαστρεντερολογίας Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων Conflict of interest By means of this, the speaker confirms that
Clinical Course of Infliximab Treatment in Korean Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Patients: A Single Center Experience
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2014.17.1.31 Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition 2014 March 17(1):31-36 Original Article PGHN Clinical Course of Infliximab
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2014.17.1.31 Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition 2014 March 17(1):31-36 Original Article PGHN Clinical Course of Infliximab
Ulcerative Colitis. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse. What is ulcerative colitis (UC)?
 Ulcerative Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is ulcerative colitis (UC)? Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, or long-lasting, disease that causes inflammation and sores, called
Ulcerative Colitis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse What is ulcerative colitis (UC)? Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, or long-lasting, disease that causes inflammation and sores, called
Current management options and recent advances in IBD
 n DRUG REVIEW Current management options and recent advances in IBD Ben Warner BSc, MRCP and Peter Irving MA, MD, FRCP SPL The advent of biological therapies has revolutionised the management of inflammatory
n DRUG REVIEW Current management options and recent advances in IBD Ben Warner BSc, MRCP and Peter Irving MA, MD, FRCP SPL The advent of biological therapies has revolutionised the management of inflammatory
5-ASA Therapy, Steroids and Antibiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 5-ASA Therapy, Steroids and Antibiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease David T. Rubin, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Co-Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center University it of Chicago Medical
5-ASA Therapy, Steroids and Antibiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease David T. Rubin, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Co-Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center University it of Chicago Medical
Surgical Management of IBD. Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003
 Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
UNC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE DRUG PROTOCOL VEDOLIZUMAB (ENTYVIO)
 UNC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE DRUG PROTOCOL VEDOLIZUMAB (ENTYVIO) TREATMENT PROTOCOL: Vedolizumab is a humanized immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody that targets 41 integrin and blocks its interaction
UNC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE DRUG PROTOCOL VEDOLIZUMAB (ENTYVIO) TREATMENT PROTOCOL: Vedolizumab is a humanized immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody that targets 41 integrin and blocks its interaction
2.0 Synopsis. Adalimumab M Clinical Study Report Final R&D/15/1054. (For National Authority Use Only)
 2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Inc. Name of Study Drug: Adalimumab Name of Active Ingredient: Adalimumab Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National Authority Use Only) Title
2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Inc. Name of Study Drug: Adalimumab Name of Active Ingredient: Adalimumab Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National Authority Use Only) Title
An Update on the Biologic Treatment for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. David A. Schwartz, MD
 An Update on the Biologic Treatment for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease David A. Schwartz, MD Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Associate Professor of Medicine Vanderbilt University
An Update on the Biologic Treatment for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease David A. Schwartz, MD Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Associate Professor of Medicine Vanderbilt University
abstract STATE-OF-THE-ART REVIEW ARTICLE
 Management of Acute Severe Colitis in Children With Ulcerative Colitis in the Biologics Era Claudio Romano, MD, a Sana Syed, MD, b Simona Valenti, MD, a Subra Kugathasan, PhD b BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVE:
Management of Acute Severe Colitis in Children With Ulcerative Colitis in the Biologics Era Claudio Romano, MD, a Sana Syed, MD, b Simona Valenti, MD, a Subra Kugathasan, PhD b BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVE:
IBD 101. Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition
 IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
IBD 101 Ronen Stein, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Objectives Identify factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel
Optimizing the effectiveness of anti-tnf therapy in paediatric IBD
 Optimizing the effectiveness of anti-tnf therapy in paediatric IBD Anne Griffiths MD, FRCPC Co-Lead, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Northbridge Chair in IBD Hospital for Sick Children, Professor of
Optimizing the effectiveness of anti-tnf therapy in paediatric IBD Anne Griffiths MD, FRCPC Co-Lead, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Northbridge Chair in IBD Hospital for Sick Children, Professor of
Treatment Goals. Current Therapeutic Pyramids Crohn s Disease Ulcerative Colitis 11/14/10
 Current Management of IBD: From Conventional Agents to Biologics Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago Treatment Goals Induce and maintain response/ remission Prevent complications Improve quality
Current Management of IBD: From Conventional Agents to Biologics Stephen B. Hanauer, M.D. University of Chicago Treatment Goals Induce and maintain response/ remission Prevent complications Improve quality
Optimal care during pregnancy and delivery
 Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Optimal care during pregnancy and delivery Professor Catherine Nelson-Piercy, London, UK Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Therapeutic goals in
Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Optimal care during pregnancy and delivery Professor Catherine Nelson-Piercy, London, UK Oxford Inflammatory Bowel Disease MasterClass Therapeutic goals in
How do I choose amongst medicines for inflammatory bowel disease. Maria T. Abreu, MD
 How do I choose amongst medicines for inflammatory bowel disease Maria T. Abreu, MD Overview of IBD Pathogenesis Bacterial Products Moderately Acutely Inflamed Chronic Inflammation = IBD Normal Gut Mildly
How do I choose amongst medicines for inflammatory bowel disease Maria T. Abreu, MD Overview of IBD Pathogenesis Bacterial Products Moderately Acutely Inflamed Chronic Inflammation = IBD Normal Gut Mildly
Medical Therapy for Pediatric IBD: Efficacy and Safety
 Medical Therapy for Pediatric IBD: Efficacy and Safety Betsy Maxwell, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Pediatric IBD: Defining Remission
Medical Therapy for Pediatric IBD: Efficacy and Safety Betsy Maxwell, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Pediatric IBD: Defining Remission
Surgery in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Rajesh Gupta MS, MCh Surgical Gastroenterology Division Dept of General Surgery PGIMER, Chandigarh
 Surgery in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Rajesh Gupta MS, MCh Surgical Gastroenterology Division Dept of General Surgery PGIMER, Chandigarh 1 Ulcerative colitis (UC) Ulcerative colitis (UC) characterized
Surgery in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Rajesh Gupta MS, MCh Surgical Gastroenterology Division Dept of General Surgery PGIMER, Chandigarh 1 Ulcerative colitis (UC) Ulcerative colitis (UC) characterized
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Paediatric Gastroenterology Clinical Network. Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents in New Zealand
 Paediatric Gastroenterology Clinical Network Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents in New Zealand A Clinical Guideline Prepared by: Dr Andrew Day on behalf of the Paediatric
Paediatric Gastroenterology Clinical Network Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents in New Zealand A Clinical Guideline Prepared by: Dr Andrew Day on behalf of the Paediatric
P a g e 1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Guidelines
 P a g e 1 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Guidelines Introduction Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) system. It is comprised of two major
P a g e 1 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Guidelines Introduction Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) system. It is comprised of two major
CASE STUDY: ULCERATIVE COLITIS. Sammi Montag Dietetic Intern
 CASE STUDY: ULCERATIVE COLITIS Sammi Montag Dietetic Intern 2013-2014 PATIENT (CK) INTRODUCTION 26 year old female Chief complaint: bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain Admitting diagnosis: Ulcerative colitis
CASE STUDY: ULCERATIVE COLITIS Sammi Montag Dietetic Intern 2013-2014 PATIENT (CK) INTRODUCTION 26 year old female Chief complaint: bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain Admitting diagnosis: Ulcerative colitis
IBD Updates. Themes in IBD IBD management journey. New tools for therapeutic monitoring. First-line treatment in IBD
 IBD Updates Maria T. Abreu, MD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida Themes in IBD 213 First-line treatment in IBD New tools for therapeutic monitoring Biologic therapy for CD and
IBD Updates Maria T. Abreu, MD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida Themes in IBD 213 First-line treatment in IBD New tools for therapeutic monitoring Biologic therapy for CD and
CHRONIC DIARRHEA DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE THAN 4 WEEKS
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 CHRONIC DIARRHEA DEFINITION: *LOOSE, WATERY STOOLS *MORE THAN 3 TIMES A DAY *FOR MORE
Index. Surg Clin N Am 87 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Clin N Am 87 (2007) 787 796 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscesses in anorectal Crohn s disease, 622 intra-abdominal, in Crohn s disease, 590 591 perirectal,
Surg Clin N Am 87 (2007) 787 796 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscesses in anorectal Crohn s disease, 622 intra-abdominal, in Crohn s disease, 590 591 perirectal,
PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Alexis Rodriguez, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Advocate Children s Hospital Disclosers Abbott Nutrition - Speaker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Chronic inflammatory disease
PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Alexis Rodriguez, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Advocate Children s Hospital Disclosers Abbott Nutrition - Speaker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Chronic inflammatory disease
Management of Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis
 Management of Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis Neilanjan Nandi, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Associate Program Director Division of Gastroenterology Drexel University College of Medicine Hahnemann
Management of Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis Neilanjan Nandi, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Associate Program Director Division of Gastroenterology Drexel University College of Medicine Hahnemann
PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA 1 DEFINITION Prolongation of acute diarrhoea / dysentery for more than 14 days Generally associated with weight loss. 2 PROTRACTED DIARRHOEA Prolongation of acute diarrhoea or dysentery
PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA 1 DEFINITION Prolongation of acute diarrhoea / dysentery for more than 14 days Generally associated with weight loss. 2 PROTRACTED DIARRHOEA Prolongation of acute diarrhoea or dysentery
Slide 1 Medications in inflammatory bowel disease a primer for health care providers. Slide 2. Slide 3 Theory of pathogenesis. IBD - epidemiology
 Slide 1 Medications in inflammatory bowel disease a primer for health care providers Athos Bousvaros, MD Associate director Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Boston Children s Hospital 617 355 2962 Slide
Slide 1 Medications in inflammatory bowel disease a primer for health care providers Athos Bousvaros, MD Associate director Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Boston Children s Hospital 617 355 2962 Slide
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Michael Weiss MD, FACG
 Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
Refractory Ulcerative Colitis Treatment
 Refractory Ulcerative Colitis Treatment Richard P. MacDermott, MD, and Jesse A. Green, MD Dr. MacDermott is the Albert M. Yunich, MD, Professor of Medicine and Director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Refractory Ulcerative Colitis Treatment Richard P. MacDermott, MD, and Jesse A. Green, MD Dr. MacDermott is the Albert M. Yunich, MD, Professor of Medicine and Director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Case Report: Induction of Remission in Drug-Resistant Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Cannabinoid Therapy
 Case Report: Induction of Remission in Drug-Resistant Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Cannabinoid Therapy Natasha R. Ryz, PhD*, Caroline MacCallum, MD (FRCPC Internal Medicine)**, Robert T. Brooke*
Case Report: Induction of Remission in Drug-Resistant Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Cannabinoid Therapy Natasha R. Ryz, PhD*, Caroline MacCallum, MD (FRCPC Internal Medicine)**, Robert T. Brooke*
OUNCE OF PREVENTION WORTH A POUND OF CURE
 Healthcare maintenance in the patient with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. OUNCE OF PREVENTION WORTH A POUND OF CURE Your gastroenterologist is NOT your primary care physician Your gastroenterologist is NOT
Healthcare maintenance in the patient with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. OUNCE OF PREVENTION WORTH A POUND OF CURE Your gastroenterologist is NOT your primary care physician Your gastroenterologist is NOT
Crohn's Disease. The What, When, and Why of Treatment
 Crohn's Disease The What, When, and Why of Treatment Brian Feagan, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics Director, Robarts Clinical Trials Robarts Research Institute University
Crohn's Disease The What, When, and Why of Treatment Brian Feagan, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology and Biostatistics Director, Robarts Clinical Trials Robarts Research Institute University
Managing Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicities. Megan L. Menon, Pharm.D., BCOP Roswell Park Cancer Institute
 Managing Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicities Megan L. Menon, Pharm.D., BCOP Roswell Park Cancer Institute Approved Indications Ipilimumab Nivolumab Pembrolizumab* Atezolizumab Avelumab Durvalumab Ipi + Nivol
Managing Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicities Megan L. Menon, Pharm.D., BCOP Roswell Park Cancer Institute Approved Indications Ipilimumab Nivolumab Pembrolizumab* Atezolizumab Avelumab Durvalumab Ipi + Nivol
The use of a segmental endoscopic score may improve the prediction of clinical outcomes in acute severe ulcerative colitis
 1130-0108/2016/108/11/697-702 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2016. SEPD y ARÁN EDICIONES, S.L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2016, Vol. 108, N.º 11, pp. 697-702 ORIGINAL PAPERS The use of a
1130-0108/2016/108/11/697-702 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2016. SEPD y ARÁN EDICIONES, S.L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2016, Vol. 108, N.º 11, pp. 697-702 ORIGINAL PAPERS The use of a
This program is supported by an educational grant from Janssen Biotech Inc., Shire, Inc., and a sponsorship from Takeda
 This program is supported by an educational grant from Janssen Biotech Inc., Shire, Inc., and a sponsorship from Takeda Today s Presenter Adam S. Cheifetz, MD Director, Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
This program is supported by an educational grant from Janssen Biotech Inc., Shire, Inc., and a sponsorship from Takeda Today s Presenter Adam S. Cheifetz, MD Director, Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Ulcerative colitis: the management of ulcerative colitis Quality standard title: Ulcerative
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Ulcerative colitis: the management of ulcerative colitis Quality standard title: Ulcerative
SURGERY FOR COLITIS THE BOTTOM LINE
 SURGERY FOR COLITIS THE BOTTOM LINE Speaker Declarations This presenter has the following declarations of relationship with industry None [Nov 2017] Surgeons just like to cut.. ABSOLUTE INDICATIONS Toxic
SURGERY FOR COLITIS THE BOTTOM LINE Speaker Declarations This presenter has the following declarations of relationship with industry None [Nov 2017] Surgeons just like to cut.. ABSOLUTE INDICATIONS Toxic
10/23/2014. Program Goals
 Program Goals Help you understand ulcerative colitis and its effects Review current treatments, including medications, and surgery Provide tips for managing your disease through diet and complementary
Program Goals Help you understand ulcerative colitis and its effects Review current treatments, including medications, and surgery Provide tips for managing your disease through diet and complementary
Ali Keshavarzian MD Rush University Medical Center
 Treatment: Step Up or Top Down? Ali Keshavarzian MD Rush University Medical Center Questions What medication should IBD be treated with? Can we predict which patients with IBD are high risk? Is starting
Treatment: Step Up or Top Down? Ali Keshavarzian MD Rush University Medical Center Questions What medication should IBD be treated with? Can we predict which patients with IBD are high risk? Is starting
