Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective. Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist
|
|
|
- Lambert Blair
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist
2 Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology
3 Bacillus anthracis Bacteria implicated in 2001 biological attack Overall, 22 persons sickened 11 inhalation anthrax 11 cutaneous anthrax 5 deaths (23%) All inhalation About half of inhalation cases
4 Epi Curve of Anthrax Attacks Actual 2001 Anthrax Attack Epi Curve Note: arrows indicate inhalation anthrax, based on 5 letters sent
5 What is Anthrax? Bacteria Soil Usual route through infected animals Spore forming Types: Inhalation Cutaneous Gastrointestinal Incubation period 1-7 days (up to 60 has been shown; 43 days in USSR)
6 Inhalation Anthrax
7 Inhalation Anthrax: Pathway Deposition in alveolar space Macrophage ingestion Transport to mediastinal lymph nodes Germination Replication/Toxin Release = hemorrhage, edema and necrosis
8 Inhalation Anthrax: Clinical Progression Stage 1 Lasts hours to a few days non-specific symptoms including Fever Fatigue, malaise Cough Vomiting Sweating, chills Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
9 Inhalation Anthrax: Clinical Progression Stage 2 Develops abruptly Symptoms include Sudden fever Shortness of breath (dyspnea) Diaphoresis (excessive sweating) Shock Stridor (high pitched sound resulting from turbulent air flow in the upper airway) X-ray and chest computed tomographic (CT) abnormalities Mediastinal widening, infiltrates, pleural effusions
10 Chest X-Ray of 2001 Inhalation Anthrax Day 6 of clinical course Died
11 Inhalation Anthrax: Treatment Animal experiments suggest critical threshold for treatment In 2001, all four patients exhibiting signs of fulminant (sudden/severe) illness prior to antibiotics expired Treatment with ciprofloxacin or doxycycline
12 Cutaneous Anthrax
13 Cutaneous Anthrax: Transmission Contact with contaminated skins, wool or hides, or products made from these Contact with tissues of animals that are clinically ill or dead from anthrax Contact with soil contaminated with spores or contaminated bone meal used in gardening
14 Cutaneous Anthrax: Pathway Deposition on skin Germination Replication/Toxin Release = hemorrhage, edema and necrosis
15 Cutaneous Anthrax: Clinical Progression Local Edema Ulcer forms (Day 2) Small vesicles appear discharging clear or serosanguinous fluid - containing organism Black Eschar develops, dries up, and falls off within 1-2 weeks Systemic symptoms may occur
16 Cutaneous Anthrax: Treatment Antibiotic treatment is warranted Mortality rate 20% untreated Mortality rare among those treated Ciprofloxacin or Doxycycline
17 Gastrointestinal Anthrax
18 Gastrointestinal Anthrax: Pathway UPPER GI Deposition on oral cavity LOWER GI Deposition in terminal ileum or cecum Germination Germination Replication/Toxin Release = hemorrhage, edema and necrosis Replication/Toxin Release = hemorrhage, edema and necrosis
19 GI Anthrax: Clinical Progression UPPER GI Oral or Esophageal Ulcer Regional Lymphadenopathy Edema Sepsis LOWER GI Nausea Vomiting Malaise Bloody Diarrhea Acute Abdominal Pain Sepsis Day 9
20 Gastrointestinal Anthrax : Fewer studies Treatment Anticipated case fatality rate 4-12% Antibiotics recommended ciprofloxacin or doxycycline
21 Why Weaponize? Working Group on Civilian Biodefense ranked bacillius anthracis as one of the top organisms with the ability to cause disease and deaths in sufficient numbers or to gravely impact a city or region.
22 Optimal Characteristics Why Weaponize? Anthrax Living (can replicate) Bacterium High Stability Spores Highly Virulent LD 50 ~2,500-55,000 Quick Incubation 1-7 days Dissemination Efficient Aerosol (40-60%)
23 Weaponized Anthrax Powder High spore concentration Uniform particle size Low electrostatic charge Treated to reduce clumping
24 Epidemiology of Anthrax Overall, not common Animal vaccination programs available Spores remain prevalent in soil GI anthrax Reports mostly from Asia and Africa Mostly from undercooked food Cutaneous Most common out of three US cases = , one in 2000 Inhalation US cases = 18 from Most US cases involved with goat hair/wool/tannery; 2 lab workers
25 Anthrax & Bioterrorism One case of any type of anthrax is red flag and is immediately reportable to local or state health department Inhalation anthrax report of great concern Gastrointestinal and cutaneous anthrax necessitates immediate r/o of natural cause
26 Getting the Call Immediately reportable confirmed or suspected anthrax Clinical and Microbiological support Different species of bacillius Gram positive, non-motile, blood agar Investigation begins Most written recommendations are based on inhalation attack
27 Epidemiology Investigation Demographics Travel History during Incubation Period Food History for possible GI anthrax Any other known cases Links to residency, workplace, school, vacation, etc. Environmental Testing Determination of prophylaxis Prophylaxis is indicated for persons exposed to an airspace contaminated with B. anthracis. Ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, and penicillin G 60 days
28 Summary Inhalation anthrax most probable for attack Ability to spread easily High virulence Any report of anthrax requires investigation If treated early enough, antibiotics can help clinical course Prophylaxis is available for those in airspace - 60 days!
29 References Anonymous. Weapons of Mass Destruction. Last updated Sept Accessed November 8, Heath and Human Services. Update: Investigation of Bioterrorism-Related Anthrax and Interim Guidelines for Exposure Management and Antimicrobial Therapy, October MMWR Weekly; O (42); Inglesby, T.V., O Toole, T., Henderson, D.A., Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002: Updated Recommendations for Management. JAMA. 2002; 287(17): Jerningan, D.B. et al. Investigation of Bioterrorism-Related Anthrax, United States, 2001: Epidemiologic Findings. Emerg Infect Dis. Oct; 8(10): Sirisanthana, T. and Brown, A. Anthrax of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Emerg Infect Dis Jul;8(7):649-51
Anthrax. Department of Child Health Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara
 Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Anthrax. Surveillance Protocol. Provider Responsibilities. Laboratory Responsibilities. Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program
 January 2007 may result from a naturally occurring, unintentional exposure such as from infected animals or from an intentional exposure such as from a bioterrorism (BT) event. When necessary this protocol
January 2007 may result from a naturally occurring, unintentional exposure such as from infected animals or from an intentional exposure such as from a bioterrorism (BT) event. When necessary this protocol
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease)
 ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction
 Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine
 Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine Under Supervision of : Prof. Dr\ Ekram M. El-Shabrawy Team Work : Mostafa Emad Ahmed Mohammed Bahaa El-Din Mostafa Abd-Elsamee Ahmed Mohamed Taha Contents Causative Organism.
Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine Under Supervision of : Prof. Dr\ Ekram M. El-Shabrawy Team Work : Mostafa Emad Ahmed Mohammed Bahaa El-Din Mostafa Abd-Elsamee Ahmed Mohamed Taha Contents Causative Organism.
Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates.
 Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Should Anthrax Vaccine Be Tested in Children?
 21 November 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Should Anthrax Vaccine Be Tested in Children? Investigators outside the Dirksen Senate Office Building in Washington in October 2001 (You can download an MP3 of this
21 November 2011 voaspecialenglish.com Should Anthrax Vaccine Be Tested in Children? Investigators outside the Dirksen Senate Office Building in Washington in October 2001 (You can download an MP3 of this
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
Lecture (14) Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology
 AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
B-NICE Overview. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0. CDC & Prevention
 B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism
 Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Biological Hazards Module 3
 1 - Objectives - Describe salmonellosis and typhoid fever (salmonella) Recognize symptoms of exposure Describe treatments available Develop a response plan 2 - Salmonellosis Definition - Severe lower GI
1 - Objectives - Describe salmonellosis and typhoid fever (salmonella) Recognize symptoms of exposure Describe treatments available Develop a response plan 2 - Salmonellosis Definition - Severe lower GI
July 1, 2005 Page 1 of 5
 Abstract: Consensus Statement: Tularemia as a Biological Weapon: Medical and Public Health Abstracted from Dennis DT, Inglesby TV, Henderson DA, et al. Journal of the American Medical Association, June
Abstract: Consensus Statement: Tularemia as a Biological Weapon: Medical and Public Health Abstracted from Dennis DT, Inglesby TV, Henderson DA, et al. Journal of the American Medical Association, June
2. According to the information provided by the WHO, there is no justification at this stage for restrictions on travel or trade.
 Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal flora
 AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
Updated Recommendations for Management
 JAMA Vol. 287 No. 17, May 1, 2002 JAMA. 2002;287:2236-2252 Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Consensus Statement ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION CONSENSUS METHODS HISTORY
JAMA Vol. 287 No. 17, May 1, 2002 JAMA. 2002;287:2236-2252 Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Consensus Statement ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION CONSENSUS METHODS HISTORY
An Overview of Bioterrorism. SAEMS January 30, Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona
 An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Anthrax. Information for Health Care Providers. Physicians D Nurses D Laboratory Personnel D Infection Control Practitioners
 Anthrax Information for Health Care Providers Physicians D Nurses D Laboratory Personnel D Infection Control Practitioners Anthrax Caused by Bacillus anthracis, a large, encapsulated, gram-positive, aerobic,
Anthrax Information for Health Care Providers Physicians D Nurses D Laboratory Personnel D Infection Control Practitioners Anthrax Caused by Bacillus anthracis, a large, encapsulated, gram-positive, aerobic,
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner
 Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, Updated Recommendations for Management JAMA. 2002;287:
 CONSENSUS STATEMENT Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Thomas V. Inglesby, MD Tara O Toole, MD, MPH Donald A. Henderson, MD, MPH John G. Bartlett, MD Michael S.
CONSENSUS STATEMENT Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Thomas V. Inglesby, MD Tara O Toole, MD, MPH Donald A. Henderson, MD, MPH John G. Bartlett, MD Michael S.
Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives
 Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives Overview and Historical Perspective Marcelle Layton As weapons, biological agents have a number of advantages. There is the potential for wide dissemination
Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives Overview and Historical Perspective Marcelle Layton As weapons, biological agents have a number of advantages. There is the potential for wide dissemination
Characteristics and Management of Selected Bioterrorism Agents 1, 4
 Anthrax Bacillus anthracis 1-5 days possibly up to 60 days). Data from 21 patients infected in October 2001 indicate a 5-11 day (mean of 7 days) incubation period for inhalational anthrax and 1-10 day
Anthrax Bacillus anthracis 1-5 days possibly up to 60 days). Data from 21 patients infected in October 2001 indicate a 5-11 day (mean of 7 days) incubation period for inhalational anthrax and 1-10 day
and Fosfomycin Acta Medica et Biologica followed by massive bacteremia, and results in severe
 Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 49, No.3, 4, 95-99, 2001 In Vitro Susceptibility of Bacillus anthracis to Antimicrobial Agents Including Carbapenems and Fosfomycin Tatsuo YAMAMOTO, Ikue TANEIKE, Yukiko TAMURA
Acta Medica et Biologica Vol. 49, No.3, 4, 95-99, 2001 In Vitro Susceptibility of Bacillus anthracis to Antimicrobial Agents Including Carbapenems and Fosfomycin Tatsuo YAMAMOTO, Ikue TANEIKE, Yukiko TAMURA
Interim Guidelines for Action in the Event of a Deliberate Release: Anthrax ANTHRAX
 ANTHRAX INTERIM PHLS GUIDELINES FOR ACTION IN THE EVENT OF A DELIBERATE RELEASE Contents: page: 1 Background and Clinical Information 2 1.1 Introduction 2 1.2 Epidemiology 2 1.3 Clinical features 3 1.4
ANTHRAX INTERIM PHLS GUIDELINES FOR ACTION IN THE EVENT OF A DELIBERATE RELEASE Contents: page: 1 Background and Clinical Information 2 1.1 Introduction 2 1.2 Epidemiology 2 1.3 Clinical features 3 1.4
Anesthesiology Clin N Am 22 (2004) Anthrax. Alicia Gruber Kalamas, MD
 Anesthesiology Clin N Am 22 (2004) 533 540 Anthrax Alicia Gruber Kalamas, MD Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco General Hospital, Room
Anesthesiology Clin N Am 22 (2004) 533 540 Anthrax Alicia Gruber Kalamas, MD Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco General Hospital, Room
Answers to these questions are available on LF is a zinc-dependent protease EF is a calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase
 21 Bacillus Two hours after a dinner, a family of four developed acute abdominal cramps with nausea and vomiting. The illness lasted for less than a day. 1. Bacillus cereus is associated with two forms
21 Bacillus Two hours after a dinner, a family of four developed acute abdominal cramps with nausea and vomiting. The illness lasted for less than a day. 1. Bacillus cereus is associated with two forms
Shigella and salmonella
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Bacillus anthracis. Summary Data
 Bacillus anthracis Overview: Bacillus anthracis and Anthrax Bacillus anthracis is a rod shaped gram negative bacterium which is the causative of a multi-symptom disease anthrax. There are three main types
Bacillus anthracis Overview: Bacillus anthracis and Anthrax Bacillus anthracis is a rod shaped gram negative bacterium which is the causative of a multi-symptom disease anthrax. There are three main types
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4
 Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Bioterrorism. Eric S. Toner, MD. National Governors Association July 22, 2009
 Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
Effect of Host Species on the Dose Response of Inhaled Bacillus anthracis Spores
 Effect of Host Species on the Dose Response of Inhaled Bacillus anthracis Spores Mark H. Weir E.I.T. Dr. Charles N. Haas Drexel University Department of Civil Architectural and Environmental Engineering
Effect of Host Species on the Dose Response of Inhaled Bacillus anthracis Spores Mark H. Weir E.I.T. Dr. Charles N. Haas Drexel University Department of Civil Architectural and Environmental Engineering
Ch 15. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Ch 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Student Learning Outcomes Identify the principal portals of entry and exit. Using examples, explain how microbes adhere to host cells. Explain how capsules and
Ch 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Student Learning Outcomes Identify the principal portals of entry and exit. Using examples, explain how microbes adhere to host cells. Explain how capsules and
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Fourth Quarter / 2001 Volume 20 No. 4 Division of Surveillance West Virginia & Disease Control Statewide Disease Facts & Comparisons
 Bob Wise, Governor Paul L. Nusbaum, Secretary (DHHR) Fourth Quarter / 2001 Volume 20 No. 4 West Virginia EPI-LOG Division of Surveillance & Disease Control AIDS Surveillance (304) 558-2987 AIDS Prevention
Bob Wise, Governor Paul L. Nusbaum, Secretary (DHHR) Fourth Quarter / 2001 Volume 20 No. 4 West Virginia EPI-LOG Division of Surveillance & Disease Control AIDS Surveillance (304) 558-2987 AIDS Prevention
MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism
 MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism Questions for Today: (consider Med Micro course) 1. What is epidemiology? 2. How is epidemiology important to public health? 3. What pathogens are important
MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism Questions for Today: (consider Med Micro course) 1. What is epidemiology? 2. How is epidemiology important to public health? 3. What pathogens are important
Ebola Virus Patient Advisory
 22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
Infection Control Precautions during the Clinical Management of Injecting Drug Users with Possible, Probable or Confirmed Anthrax
 Infection Control Precautions during the Clinical Management of Injecting Drug Users with Possible, Probable or Confirmed Anthrax (Adapted from guidance developed by Health Protection Scotland and HPA
Infection Control Precautions during the Clinical Management of Injecting Drug Users with Possible, Probable or Confirmed Anthrax (Adapted from guidance developed by Health Protection Scotland and HPA
Biological Warfare Agents
 Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Epidemiology of Lassa Fever
 Epidemiology of Lassa Fever Njideka E. Kanu Department of Community Medicine, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo A lecture delivered at the Academic Seminar of University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, 14
Epidemiology of Lassa Fever Njideka E. Kanu Department of Community Medicine, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo A lecture delivered at the Academic Seminar of University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, 14
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest
 Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Anthrax. Dr.T.V.Rao MD. Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1
 Anthrax Dr.T.V.Rao MD Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1 General Characteristics of Bacillus ~ 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal
Anthrax Dr.T.V.Rao MD Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1 General Characteristics of Bacillus ~ 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal
What is Legionnaires' disease?
 Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Tuberculosis What you need to know. James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director
 Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Anthrax. Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases
 Anthrax Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases Overview History, etiology, pathogenesis Burden of natural disease Disease forms
Anthrax Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases Overview History, etiology, pathogenesis Burden of natural disease Disease forms
(Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand)
 MSD MANUAL Veterinary / Generalized Conditions / Anthrax Veterinary Manual Overview of Anthrax (Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand) By Martin E. Hugh Jones, VetMB, MPH, PhD, MRCVS, Professor
MSD MANUAL Veterinary / Generalized Conditions / Anthrax Veterinary Manual Overview of Anthrax (Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand) By Martin E. Hugh Jones, VetMB, MPH, PhD, MRCVS, Professor
Mike Rossman, MD; Daniel J. Schissel, MD
 Picture This. Mike Rossman, MD; Daniel J. Schissel, MD You are building relationships with a tribe that primarily inhabits the border region between Iraq and Syria when you are asked to examine a skin
Picture This. Mike Rossman, MD; Daniel J. Schissel, MD You are building relationships with a tribe that primarily inhabits the border region between Iraq and Syria when you are asked to examine a skin
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
Trichinellosis. By Michelle Randall
 Trichinellosis By Michelle Randall Disease Name: Trichinellosis Etiological Agent: Trichinella spiralis Transmission: People acquire Trichinellosis by consuming raw or undercooked meat infected with the
Trichinellosis By Michelle Randall Disease Name: Trichinellosis Etiological Agent: Trichinella spiralis Transmission: People acquire Trichinellosis by consuming raw or undercooked meat infected with the
Infection control in Aged Residential Care Facilities. Dr Sally Roberts Clinical Advisor for IP&C Service, ADHB
 Infection control in Aged Residential Care Facilities Dr Sally Roberts Clinical Advisor for IP&C Service, ADHB Background Endemic infections Epidemic infections Managing outbreaks Administrative measures
Infection control in Aged Residential Care Facilities Dr Sally Roberts Clinical Advisor for IP&C Service, ADHB Background Endemic infections Epidemic infections Managing outbreaks Administrative measures
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining
 Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Dr. May Book-Montellano, FPPS, FPIDSP, FPSMID President Pediatric Infectious Disease Society of the Philippines
 Dr. May Book-Montellano, FPPS, FPIDSP, FPSMID President Pediatric Infectious Disease Society of the Philippines CHRONOLOGY OF H1N1 PANDEMIC FLU 17 APRIL 2009 Two children in California became ill due
Dr. May Book-Montellano, FPPS, FPIDSP, FPSMID President Pediatric Infectious Disease Society of the Philippines CHRONOLOGY OF H1N1 PANDEMIC FLU 17 APRIL 2009 Two children in California became ill due
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES EMERGING NONE
 EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
ANTHRAX VACCINE ADSORBED (BIOTHRAX )
 ANTHRAX VACCINE ADSORBED (BIOTHRAX ) DESCRIPTION Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed, (BioThrax ) is a sterile, milky-white suspension (when mixed) made from cell-free filtrates of microaerophilic cultures of an
ANTHRAX VACCINE ADSORBED (BIOTHRAX ) DESCRIPTION Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed, (BioThrax ) is a sterile, milky-white suspension (when mixed) made from cell-free filtrates of microaerophilic cultures of an
SWABCHA Fact Sheet: Tuberculosis (TB)
 SWABCHA (TB) Text sourced from the SWABCHA Change Agent Training Guide - 2012 Introduction to TB Microscopic bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes TB Only TB of the lungs or throat may be infectious.
SWABCHA (TB) Text sourced from the SWABCHA Change Agent Training Guide - 2012 Introduction to TB Microscopic bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes TB Only TB of the lungs or throat may be infectious.
Q-FEVER Q FEVER. CPMP/4048/01, rev. 3 1/7 EMEA 2002
 Q FEVER CPMP/4048/01, rev. 3 1/7 General points on treatment Q fever is a zoonosis caused by Coxiella burnetii, an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium with high infectivity but with relatively
Q FEVER CPMP/4048/01, rev. 3 1/7 General points on treatment Q fever is a zoonosis caused by Coxiella burnetii, an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium with high infectivity but with relatively
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS
 VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis Public Health Immunization Program June 2018 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever,
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis Public Health Immunization Program June 2018 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever,
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS
 VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
BIOLOGICAL WARFARE AND TERRORISM
 BIOLOGICAL WARFARE AND TERRORISM Pierrette Melin Medical microbiology, University hospital of Liege, Belgium The dark side of microbiology 1 Definition Historical perspective How real is the threat Biological
BIOLOGICAL WARFARE AND TERRORISM Pierrette Melin Medical microbiology, University hospital of Liege, Belgium The dark side of microbiology 1 Definition Historical perspective How real is the threat Biological
Paragonimiasis added Jan 2016
 added Jan 2016 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Paragonimus species, a parasitic lung fluke (flat worm). More than 30 species of trematodes (flukes) of the genus Paragonimus have been reported which
added Jan 2016 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Paragonimus species, a parasitic lung fluke (flat worm). More than 30 species of trematodes (flukes) of the genus Paragonimus have been reported which
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals
 #61762 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals COURSE #61762 5 CE CREDITS Release Date: 09/01/17 Expiration Date: 08/31/20 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals HOW TO RECEIVE
#61762 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals COURSE #61762 5 CE CREDITS Release Date: 09/01/17 Expiration Date: 08/31/20 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals HOW TO RECEIVE
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard
 Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
RHODOCOCCUS EQUI. Post-mortem Environmental Persistence Specific Control Measures Release of Animals from Isolation
 RHODOCOCCUS EQUI Definition Clinical Signs Transmission Diagnostic Sampling, Testing and Handling Post-mortem Environmental Persistence Specific Control Measures Release of Animals from Isolation Biosecurity
RHODOCOCCUS EQUI Definition Clinical Signs Transmission Diagnostic Sampling, Testing and Handling Post-mortem Environmental Persistence Specific Control Measures Release of Animals from Isolation Biosecurity
Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A
 December 2011 Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Key Points Between 2000 and 2010, 209 cases of hepatitis A were reported in Hennepin County residents. This represents 30% of the cases reported
December 2011 Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Key Points Between 2000 and 2010, 209 cases of hepatitis A were reported in Hennepin County residents. This represents 30% of the cases reported
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
Chapter 4 Coxiella burnetii
 Chapter 4 Coxiella burnetii 4. General overview of Coxiella burnetii and Q fever Coxiella burnetii (C. burnetii), an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium, is the causative agent of Q fever. C.
Chapter 4 Coxiella burnetii 4. General overview of Coxiella burnetii and Q fever Coxiella burnetii (C. burnetii), an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacterium, is the causative agent of Q fever. C.
Legionnella. You can t t see it but you can catch it. Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit
 Legionnella You can t t see it but you can catch it Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit Legionella infections First documented outbreak name from 221 cases of pneumonia occurred
Legionnella You can t t see it but you can catch it Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit Legionella infections First documented outbreak name from 221 cases of pneumonia occurred
Community Acquired Pneumonia. Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP
 Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
NJSP HMRU June 10, 2004
 June 10, 2004 Chemical-Bio Agents Module 3 Overview 1 Objectives Student will: Demonstrate ability to recognize signs and symptoms of chemical agent exposure Describe how to protect oneself against chemical
June 10, 2004 Chemical-Bio Agents Module 3 Overview 1 Objectives Student will: Demonstrate ability to recognize signs and symptoms of chemical agent exposure Describe how to protect oneself against chemical
Anthrax: A Review For The Medical Officer
 J R Army Med Corps 2003; 149: 101-105 FOCUS ON Maj Guy Vautier BM BSc MRCP RAMC Consultant Physician Royal Hospital Haslar, Gosport, PO12 2AA. E-mail: guy.vaut@dsca.mod.uk Anthrax: A Review For The Medical
J R Army Med Corps 2003; 149: 101-105 FOCUS ON Maj Guy Vautier BM BSc MRCP RAMC Consultant Physician Royal Hospital Haslar, Gosport, PO12 2AA. E-mail: guy.vaut@dsca.mod.uk Anthrax: A Review For The Medical
Chapter 23 Lassa virus. Lassa virus is a RNA virus belonging to the family of Arenaviridae. As the causative agent of
 Chapter 23 Lassa virus 23.1 General overview of Lassa virus and hemorrhagic fever Lassa virus is a RNA virus belonging to the family of Arenaviridae. As the causative agent of hemorrhagic fever, Lassa
Chapter 23 Lassa virus 23.1 General overview of Lassa virus and hemorrhagic fever Lassa virus is a RNA virus belonging to the family of Arenaviridae. As the causative agent of hemorrhagic fever, Lassa
WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT. The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018.
 WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
WYANDOT COUNTY 2018 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT The communicable disease summary of reportable infectious diseases for January 2018 December 2018. TABLE OF CONTENTS Annual Communicable Diseases... 3 Communicable
New Jersey Department of Health Communicable Disease Service OUTBREAK REPORT FOR LONG TERM CARE AND OTHER INSTITUTIONS
 New Jersey Department of Health Communicable Disease Service OUTBREAK REPORT FOR LONG TERM CARE AND OTHER INSTITUTIONS Name of Lead Public Health Agency County E# Outbreak Reported to Local Health Department
New Jersey Department of Health Communicable Disease Service OUTBREAK REPORT FOR LONG TERM CARE AND OTHER INSTITUTIONS Name of Lead Public Health Agency County E# Outbreak Reported to Local Health Department
Biology. Magic Doctor. Magic Doctor. Topic Two: Immunity. 1) The first line of defense in our immune system is composed of what?
 Biology Topic Two: Immunity Magic Doctor 1) The first line of defense in our immune system is composed of what? Skin, nose, eye lashes, eyelids. 2) White blood cells and red blood cells are produced in
Biology Topic Two: Immunity Magic Doctor 1) The first line of defense in our immune system is composed of what? Skin, nose, eye lashes, eyelids. 2) White blood cells and red blood cells are produced in
The Threat of Domestic Bioterrorism: Fact or Fiction
 Volume 6 Number 5 Volume 6, No. 3, Fall 2013 Supplement: Ninth Annual IAFIE Conference: Expanding the Frontiers of Intelligence Education Journal of Strategic Security Article 22 The Threat of Domestic
Volume 6 Number 5 Volume 6, No. 3, Fall 2013 Supplement: Ninth Annual IAFIE Conference: Expanding the Frontiers of Intelligence Education Journal of Strategic Security Article 22 The Threat of Domestic
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment
 ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
Clinical Presentation of Inhalational Anthrax Following Bioterrorism Exposure JAMA. 2001;286:
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION JAMA-EXPRESS Clinical Presentation of Inhalational Anthrax Following Bioterrorism Exposure Report of 2 Surviving Patients Thom A. Mayer, MD Susan Bersoff-Matcha, MD Cecele Murphy,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION JAMA-EXPRESS Clinical Presentation of Inhalational Anthrax Following Bioterrorism Exposure Report of 2 Surviving Patients Thom A. Mayer, MD Susan Bersoff-Matcha, MD Cecele Murphy,
Bacillus anthracis meningitis during an outbreak of injectional anthrax in Scotland
 Bacillus anthracis meningitis during an outbreak of injectional anthrax in Scotland Dr Simon Dewar Microbiology Registrar and PhD Fellow University of Dundee SMA Free-paper session 31/10/15 Bacillis Anthraxis
Bacillus anthracis meningitis during an outbreak of injectional anthrax in Scotland Dr Simon Dewar Microbiology Registrar and PhD Fellow University of Dundee SMA Free-paper session 31/10/15 Bacillis Anthraxis
Viruses, bacteria, fungus, parasites (in rare cases) or other organisms can cause pneumonia.
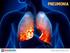 1 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection which inflames the air sacs either in one or both of the lungs. The air sacs are generally filled with fluid or pus, causing cough along with phlegm or pus, fever,
1 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection which inflames the air sacs either in one or both of the lungs. The air sacs are generally filled with fluid or pus, causing cough along with phlegm or pus, fever,
12 June The average EVD case fatality rate has been around 50 per cent.
 12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis?
 What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
TRAINER: Read this page ahead of time to prepare for teaching the module.
 Module 2 Overview: Employee Illness TRAINER: Read this page ahead of time to prepare for teaching the module. PARTICIPANTS WILL: 1. Describe FOODBORNE ILLNESS symptoms. 2. Explain the difference between
Module 2 Overview: Employee Illness TRAINER: Read this page ahead of time to prepare for teaching the module. PARTICIPANTS WILL: 1. Describe FOODBORNE ILLNESS symptoms. 2. Explain the difference between
Gastroenteritis Outbreaks Including Norovirus. Module 7
 Gastroenteritis Outbreaks Including Norovirus Module 7 Learner Outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: Outline the case definition for a gastroenteritis outbreak. Explain the difference
Gastroenteritis Outbreaks Including Norovirus Module 7 Learner Outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: Outline the case definition for a gastroenteritis outbreak. Explain the difference
Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009
 Vol. 59 / RR-6 Recommendations and Reports 1 Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009 Prepared by Jennifer Gordon Wright,
Vol. 59 / RR-6 Recommendations and Reports 1 Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009 Prepared by Jennifer Gordon Wright,
Table 2 1. Bacterial agents
 Agent/Disease Anthrax Brucellosis Likely Method 1. Spores in aerosol 1. Aerosol of 2. Sabotage (food) 2. Sabotage (food) No (except cutaneous) Person to Person Duration of Lethality Vaccine Efficacy Agent
Agent/Disease Anthrax Brucellosis Likely Method 1. Spores in aerosol 1. Aerosol of 2. Sabotage (food) 2. Sabotage (food) No (except cutaneous) Person to Person Duration of Lethality Vaccine Efficacy Agent
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about the
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about the
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about
Influenza Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals about
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Portals of Entry Mucous membranes Conjunctiva Respiratory tract: Droplet inhalation of moisture and dust particles. Most common portal of entry. GI tract: food, water,
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Portals of Entry Mucous membranes Conjunctiva Respiratory tract: Droplet inhalation of moisture and dust particles. Most common portal of entry. GI tract: food, water,
Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals
 #61761 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals COURSE #61761 5 CE CREDITS Release Date: 09/01/14 Expiration Date: 08/31/17 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals HOW TO RECEIVE
#61761 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals COURSE #61761 5 CE CREDITS Release Date: 09/01/14 Expiration Date: 08/31/17 Bioterrorism: An Update for Healthcare Professionals HOW TO RECEIVE
