NEOMYCIN INDUCES APOPTOSIS IN THE INNER EAR NEOMICINA INDUCE APOPTOZA ÎN URECHEA INTERNĂ
|
|
|
- Duane Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 42 (1) (2009), Timişoara NEOMYCIN INDUCES APOPTOSIS IN THE INNER EAR NEOMICINA INDUCE APOPTOZA ÎN URECHEA INTERNĂ ROXANA D. VINTILA 1, STAN COTULBEA 1, KARINA GÜLTIG 2, ANDREA MÜLLER 2, CORNELIA VINTILA 3, BERNHARDT HIRT 2, HUBERT LÖWENHEIM 2, H. P. ZENNER 1 Department of ENT, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara, Romania 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University of Tübingen, E. Aulhornstr. 5, Germany (Tübingen Hearing Research Center), Marie Curie Program 3 Banat University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine Timisoara Objectives: to study the apoptotic response of auditory hair cells in the organ of Corti after exposure to neomycin within the first 6 hours. Materials and methods: auditory hair cells harvested on the postnatal day 7 from the cochleae of C57BL6 wild type mice were cultured in vitro in the presence (neomycin group, n= 59 cochleas) or absence of neomycin (control group, n= 31 cochleas). Apoptotic cells were evaluated within 6 hours of incubation for the expression of active caspases (8, 9 or 3) in the cytoplasm and counterstained using propidium iodide to highlight apoptotic nuclei. Cells were statistically quantified using average and standard deviation. The differences between the averages were tested with the help of Student T test (threshold p< 0,05). Results: The statistic comparison between the different caspase types (caspase 3, 8 and 9), the average and dispersion inside the cell groups, permitted us to detect the first step of apoptosis taking place in the cytoplasm. The comparison of the cell group where propidium iodide was accumulated in the nucleus with the cell group where both the caspase and propidium iodide appeared, permitted us to detect the initiation and development of the second step of apoptosis, the one where the nucleus has already been affected. Conclusions: Neomycin is initiating, right after 6 hours of incubation, the process of apoptosis in auditory hair cells, determining the activation of cytoplasm caspases. Keywords: Apoptosis, auditory hair cells, neomycin Introduction Many in vivo and in vitro studies have suggested that aminoglycosides determine hair cell death in the organ of Corti. Morphological evidence suggest that hair cells loss in response to amynoglycoside treatment occurs via apoptosis [5;8]. At least two types of cellular degeneration are 104
2 recognized in tissues, necrosis and apoptosis. The cytologic features of these are quite distinct [6]. In recent years, specific intracellular proteases belonging to the caspase family have surfaced as crucial effectors of apoptosis [1,4]. Caspases are expressed as proenzymes and are activated by upstream stimuli, determining the beginning of the apoptotic process. There are data that indicate that undamaged mouse vestibular hair cells express pro- caspases 3, 7, 8 and 9, and that activation of caspase 9 may be crucial for neomycin- induced apoptosis [2,3]. Laura Zöllner, H. Löwenheim, 2005 [7], Tubingen Hearing Research center, have registered the apoptotic changes that occur in the Organ of Corti under neomycin influence after 24 and 12 hours of incubating the inner ears in bioreactors, in a culture medium with neomycine. We had the mission to establish the cytotoxic effect of neomycin upon auditory hair cells after 6 hours of in vitro contact of the cochleas with the antibiotic. Objectives Our research had the following purpose: 1) To establish if after a 6 hour contact of the cochleas with 1 mm neomycin we can find death between sensory hair cells in the organ of Corti 2) To establish if cell death is realized through necrosis or apoptosis 3) To know if cells in the three cochlear segments (, and ) are equally sensitive to the cytotoxic effect of neomycin In order to obtain correct responses to these questions, we organized a number of experiments on cochleas cultivated in vitro under same conditions, having as variable factor the presence or absence of neomycin from the culture medium. In the following chapter we will describe in detail the working tehniques. Materials and Methods Our study took place in Tuebingen Hearing Research Center, Marie Curie training site, Germany, during 1 year, in the departement of Molecular Otology, leaded by Dr. H. Löwenheim. Our work is included in a research program which has the purpose to understand the modifications which are produced in the structure of the hearing cells under the influence of ototoxic aminoglycosides treatment. Organisation of experiments In order to answer the question, if neomycin can induce hair cell death in the organ of Corti, we harvested cochleas (n= 90) from 7 days old mice, which we splitted in two groups. One group of cochleae was named neomycin group and was cultivated for 6 hours in a microgravity rotator bioreactor in the presence of 1 mm neomycin. In order 105
3 to analyze caspase 3 we treated 21 cochleas with neomycin. For highlighting caspase 8, 16 cochleas were treated with neomycin. For caspase 9, 22 cochleas were treated with neomycin. Another group of cochleae was cultivated under the same conditions but in the absence of neomycin (caspase 3 with 10 control cochleas; caspase 8 with 7 control cochleas and caspase 9 with 14 control cochleas ). In order to obtain a good response to the question if hair cell death due to neomycin is realized by necrosis or apoptosis, the two cochlear groups were sacrificed, fixed and specifically stained, after 6 hours of cultivation in bioreactors. We performed specific staining in order to evidence active caspases in hair cells (3, 8 and 9) as well as to evidence the level of nuclear degeneration by propidium iodide staining. Both the presence of active caspases in cellular cytoplasm as well as the appearance of propidium iodide in the nucleus, assures us that cell death occurs through apoptosis and not necrosis. The quantification of hair cell death due to both apoptosis and necrosis was evidenced with help of phalloidin staining, a specific marker for F- actin in the stereocillia. Cochlear culture preparation The study was performed in the Tubingen Hearing Research Center (Marie Curie Program). We obtained organotopypic cultures of the organ of Corti (n= 45) from postnatal day seven (p7) C57BL6 mouse pups. The mice were sacrificed by decapitation. Organ explantation was approved by the Committee for Animal Experiments of the Regional Council (Regierungsprasidium Tubingen). The temporal bones were dissected in HEPES- buffered saline with Hank s salts (HHBSS) at ph 7,3 under sterile conditions. The dissection period of one ear lasted around 5 minutes. In order to allow diffusion of cell culture medium to the sensory epithelium, the bony labyrinths are widely opened to allow fluid exchange to the perilymphatic space. The extension of the opening of the scala tympani perilymphatic space beginning at the round window and prepared along the turn in direction. The thin bony shell covering the scala tympani perilymphatic space is further removed along 270 of the turn. The next step was to open the scala vestibuli perilymphatic space achieved by removing the bony cap covering the turn of the cochlea. Care was taken not to injure the endolymphatic space in all preparations. The Corti organs were incubated in rotatory cell culture microgravity systems with or without 1 mm neomycin (RCCS TM, Synthecon Inc. Houston) for six hours at 37 C and 5 % CO27/ 95% air, in 55 ml culture medium. The rotation speed was set to 30 rotations/ minute and the the position of the roation vessels was vertically. Cultivation was carried forward under continuous rotation. The culture medium consisted of Neuro TM A medium (Gibco) supplemented with B27 supplement (Gibco), 1M Hepes buffer (Gibco), 0,5 mm L- glutamine (Gibco) and 15 units/ml of penicillin. The ears were splitted into control and neomycin probes. In order to destroy the hair cells we added 1 mm neomycin (SIGMA). 106
4 Treatment of cultures and micro dissection After the initial culture period of 6 hours, the cochleas were removed from the rotation vessels, and incubated for 40 minutes at 37 C in 48- wellplates (Corning Incorporated, NY) in the caspase inhibitor solution, depending on the caspase we wanted to check: caspase 8, 9 or 3. In order to visualize the localization of the caspases, we used cell permeable fluorochrominhibitors (FLICA) from CHEMICON caspase kits, for each caspase: caspase 3: FAM-DEVD-FMK (APT 403); caspase 8: FAM-LETD-FMK(APT 428)and for caspase 9: FAM-LEHD-FMK (APT 429), Chemicon. The lyophilized FLICA reagent was mixed with 50 ul DMSO (SIGMA) and then, immediately before use, 1:5 diluted in PBS (ph= 7,4) in order to obtain a 30X solution. All the procedures were done under light protection. After that, the cochleae were washed 3 times for 10 minutes in wash buffer (diluted 1:10 in distilled water). The next step was to stain the apoptotic nuclei with propidium iodid (CHEMICON)(4,5 ul) for 4 minutes on ice. The cochleae were then fixed with 50 µl fixing solution (CHEMICON) for 2 hours on ice. After that we washed the cochleae 2 times in PBS and maintained them overnight in 1 % PFA at 4ºC. The next day, the cochleas were mycrodissected in PBS under a ZEISS microscope by entirely removing the bony labyrinth and the modiolus. The membranous cochlea was split in three parts: a, medial and part. From each segment we removed the Reissner and tectorial membrane. The cochlea parts were then placed on Superfrost thin glass in Vectashield (Vector laboratories). Fluorescence microscopy Once the caspase inhibitors have entered the cell, they bind covalent on the active center of the caspase and the prosthetic chromophore group permits a green fluorescent light emission of 520 nm. Propidium iodid can be excited with a 488 line of an argonion laser and its absorption maximum is 535 nm. The organs were analyzed under a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (LSM) Pascal system (ZEISS) with a Neon- Helium- Laser (543 nm, Lasos) and an Argon- Laser (488 nm, Lasos). We used an LSM software (EMBL, Heidelberg) and a AxioCam MR c5 camera. The photos were taken with the 25- th objective under immersion oil. We measured the length of the entire Corti tunnel, the length of the caspase staining, the one of the propidium iodide (PI) staining and the length of Caspase- PI staining. After that, we counted each stained hair cell (inner hair cells and the three rows of outer hair cells) for caspase (green), PI (red) and caspase- PI (yellow). Each curve needed a number of shots: the part 8 photos, the medial part 5-8 and the part 3-5. Statistic analysis The analysis of the data was made with the help of an Excel program (Windows 2000). For the statistical analysis we used Student t- test and standard deviation in order to 107
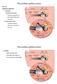
5 obtain a significance level. For T- test, we took as significant the values p< 0,05 ( * ), p< 0,01 (**), p< 0,005 (***). In general we performed 3-4 experiments x Corti organs per each caspase. For caspase 9 we used 36 cochleae from which 22 cochleas were treated with neomycin and 14 were controls. For caspase 8 we used 16 neomycin treated cochleas and 7 controls. Caspase 3 experiments included 20 neomycin treated cochleae and 10 controls. We analyzed the caspase expression pro mm Corti organ (controls, neomycin), caspase expression depending on the segment (controls and neomycin) and caspase expression depending on the cell type (controls, neomycin). Results and Discussion 1. Regarding the cytotoxic effect of neomycin upon sensorial hair cells in the organ of Corti Cell death occurs by two ways. One is necrosis and the other one is apoptosis. Apoptosis can be detected by the presence of active caspases and propidium iodide in the cells. Hair cell death in the organ of Corti, not depending on the cause, can be evidenced by the presence or absence of stereocillia with the help of phalloidin, a marker for F- actin in hair cell stereocillia. A- 6 ore bazal medial Cont rol Neo micin OHC Figure 1. Neomycin induced sensorial cell degeneration and cellular death after 6 hours. Phalloidin staining characteristic to F-actin in the stereocillia. After neomycin treatment we can observe the disappearance of stereocillia and the appearance of the characteristic scar. Evidencing hair cell death due to both apoptosis and necrosis In figure 1 we expose the obtained results from our experiments regarding auditory cell death in general in cochleae treated and not treated with neomycin. IHC 108
6 In figure 1 we can observe that after 6 hours of cochlear contact with neomycin, cellular death occurs only in the and cochlear segment. Cells which have lost their stereocillia and which present instead the specific scar, are more frequent in cochleae treated with neomycin than in the control group. In the organs exposed above we can observe a structural degradation of external auditory hair cells compared to internal auditory hair cells. In order to sustain this idea, we expose in the figure below (figure 2), the proportion of dead hair cells by apoptosis and necrosis in the three cochlear segments belonging to the control and neomycin group. % sensorial cell death in the control and neomycin treated cochleae after 6 hours of culture (phalloidin staining) % cell death % Corti organ destruction due to neomycin % Destroyed Corti organ in the controls Figure 2. Neomycin induces cell death Data exposed in figure 2 suggest that neomycin induces stereocilliar loss first in the segment of the cochlea, followed by the one and finally by the one. Hair cell death after 6 hours from the beginning of the treatment reaches in the segment more than 60% of the cochlear length, followed by 52% in the segment and 40% in the one. It is interesting to observe that a certain amount of hair cells lose their stereocillia even outside neomycin treatment. This phenomenon seems to appear mostly in the segment and less in the one. 2. Regrading apoptotic neomycin induced hair cell death Phalloidin staining is a marker for stereocilliar F-actin. Hair cell death due to neomycin can be seen clearly with the help of this method, by observing the disappearance of the stereocillia and the appearance of the characteristic scar. In order to estimate the number of hair cells which have died only because of apoptosis and not necrosis, we have stained the cochleae in order to evidence active 3, 8 and 9 cytoplasm caspases and nuclear propidium iodide. Obtained results are shown in figure
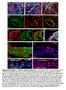
7 Because apoptotic hair cell death due to neomycin was similar in all analyzed slides marked for caspase 3, 8 and 9, we will present only the results for caspase 8 and counterstained with propidium iodide. A B B C D E F Figure 3. Activation of caspase 8 (green) and PI nuclear staining (red). Nuclei of apoptotic cells appear bright red and round and the cytoplasm stained green. We can remark also the presence of apoptotic bodies stained yellow. IHC: outer hair cells; IHC: inner hair cells Left (A,C,E)- controls without neomycin; right (B,D,F)- after 6 hours neomycin treatment. After segments: (A,B), medial (C,D) and B (E,F). Scale bar: 20 µm Figure 3 reveals the frequency of cells stained for caspase 3, 8 and 9 (green color of the cytoplasm) as well as with propidium iodide (red color of nuclei), from the in vitro cultivated cochleae, in the presence or absence of neomycin. From microscopic analyzing of the two groups of cochleae we can observe that the frequency of cells stained green, with red nuclei, or green cytoplasm with red nuclei, present in the neomycin treated group, is superior to the one in the control group. The fact that the amplitude of caspase and propidium iodide stained cell frequency in cochleae treated with neomycin is similar to the amplitude of cell death evidenced with phalloidin (fig. 110
8 2), suggests that hair cell death in the organ of Corti is realized mostly by apoptosis and less by necrosis. The fact that in the and segments of the cochleae belonging to the neomycin group we can observe a larger number of cells stained for the three active caspases (3, 8 and 9) in the cytoplasm, compared to control cochleae, is an argument which sustains the idea that neomycin induces apoptosis in auditory hair cells. 3. Regarding neomycin induced apoptotic hair cell death quantification In order to establish if qualitative observations specified above are real, we tried to statistically quantify the apoptotic process. On this purpose we counted all cells with green cytoplasm, marking the presence of active cytoplasmic caspases 3, 8 and 9 in all cochleae belonging to the two groups (control and neomycin). Obtained data were then statistically calculated obtaining the media and standard deviation for each group and segment of cultivated cochlea. Results are exposed in figure 4. Number of stained hair cells per mm Corti organ Active Caspase 8, 9 and 3 expression depending on the cohlear segment Control caspase 8 caspase 9 caspase 3 *** *** Neomycin *** *** ** *** Figure 4. The average number of hair cells in the segments of the Corti organ marked for caspase 3, 8 and 9 after 6 hours of neomycin contact, compared to the stained cells in the control group. In figure 4 we showed as columns the average number of stained cells for each of the three active caspases (8, 9 and 3). The vertical line stays for average standard deviation. The significance of the differences between the average of apoptotic cells in the three cochlear segments from the neomycin treated group compared to the control 111
9 one is symbolized with (p<0,05) or (p<0,005). The data exposed in figure 4 suggest that under 6 hours of neomycin influence, many phenomenon take place. These are the following: 1. The average value of hair cells where we identified the three types of active caspases being significantly bigger in the cochleae cultivated in the presence of neomycin compared to the control cochleae, lets us conclude that neomycin induces and sustains the apoptotic process of self distruction in auditory hair cells. The process starts to manifest itself after 6 hours of neomycin contact. 2. Simultaneous active caspase 8, 9 and 3 presence in cell cytoplasm (around 20/ 60 cells per mm Corti organ) shows that they participate together in this process and in a certain way in inducing and realizing the apoptotic process in the organ of Corti 3. Neomycin ototoxic activity followed by apoptotic unleash at 6 hours from neomycin contact of the cochleae, are manifested only in the and segments of the Corti organ. Cells in the area of the Corti organ are almost not affected by the ototoxic neomycin effect. 4. High standard deviation values in all neomycin treated cochlear groups suggest that the sensitivity of hearing cells in the organ of Corti towards neomycin is very variable and different from one individual to another. 5. The fact that the average number of cells marked for active caspases is the biggest in the group marked for caspase 8 followed in a decreasing order by other caspases, suggests that there is a hierarchy in the participation of the three caspases in initiating and sustaining the apoptotic process. Control Number of stained hair cells per mm Corti organ Propidium iodid expression depending on the cochlear segment PI (caspase 8) PI(caspase 9) * * Neomycin *** ** *** medial apikal medial Figure 5. The average number of cells where apoptosis has involved also their nuclei in cochleae stained for caspase 3, 8 and 9, in the presence or absence of neomycin. Apoptotic process phases in auditory hair cells, after 6 hours of neomycin treatment 112
10 While the apoptotic process can be identified at the beginning by evidencing cytoplasmic caspase 3, 8 and 9, the advancement of the process towards the nucleus, can be identified by propidium iodide nuclear incorporation and the red colour of the nucleus. In order to know if after 6 hours of neomycin treatment, apoptosis is at its debut or if the process has started much earlier, we have counted all red coloured, round nuclei within the 3 experiments concerning caspase 3, 8 and 9 and processed them statistically. Results are shown in figure 5. The average number of cells which have incorporated propidium iodide in their nuclei and their standard deviations, in the three cochlear groups stained for active caspases, shown in the figure above, suggests that in auditory hair cells, at 6 hours from the contact with neomycin, following processes take place: 1. The fact that auditory hair cell number where propidium iodide has accumulated is significantly higher within the experiments concerning activated caspase 3, 8 and 9 compared to the control group, suggests that the apoptotic process doesn t start only at 6 hours after neomycin treatment, but probably much earlier. 2. The fact that the average number of cells which have incorporated propidium iodid in their nuclei (red nuclei) is significantly high (p<0,005), in cochleae treated with neomycin compared to the control group, is a solid argument which sustains the idea that neomycin initiates the process of apoptosis by activating the three procaspases. On their turn, these are sustaining further the process of nuclear destruction (propidium iodide penetrates the nucleus only if its membrane is affected). 3. Apoptosis is present also in hair cell nuclei, especially in the and cochlear segment and is almost absent in the segment. 4. Although the cell number where apoptosis has reached the nucleus is higher in cochleae stained for caspase 9 compared to other experiments, the differences are not significant because of high standard deviation. 5. High deviation standard values suggest that hair cell sensitivity towards cytotoxic action of neomycin is very different from one individual to another because of genetic differences between each individual. Conclusions Experiments done on mice cochleae cultivated for 6 hours in the presence or absence of neomycin and specifically stained for apoptosis by cytoplasm presence of active caspase 8, 9 and 3 and nuclear propidium iodide presence let us conclude the following: 1. Neomycin induces massive hair cell death in the organ of Corti after 6 hours of neomycin contact with the antibiotic 113
11 2. Hair cell death in the organ of Corti is produced especially by apoptosis and less by necrosis (in dead cells active caspase 3, 8 and 9 are present in the cytoplasm and propidium iodide in the nucleus). 3. Initiation and finalizing of hair cell apoptosis due to neomycin, takes place only in the and segment of the Corti organ. Hair cells in the segment are almost not affected by ototoxic effect of neomycin. 4. Auditory cell sensitivity towards neomycin is very different from one individual to another. References 1. Adams JM, Cory S., 1998, The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science, 281(5381), Cheng AG, Cunningham LL, Rubel EW., 2003, Hair cell death in the avian basilar papilla: characterization of the in vitro model and caspase activation. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol., 4(1), Cunningham LL, Cheng AG, Rubel EW. 2002, Caspase activation in hair cells of the mouse utricle exposed to neomycin. J Neurosci., 22(19): Devarajan P, Savoca M, Castaneda MP, et al., 2002, Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in auditory cells: role of death receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Hear Res.; 174(1-2), Forge A, Li L., 2000, Apoptotic death of hair cells in mammalian vestibular sensory epithelia. Hear Res. 139(1-2), Lang H, Liu C., 1997, Apoptosis and hair cell degeneration in the vestibular sensory epithelia of the guinea pig following a gentamicin insult. Hear Res. 111(1-2), Löwenheim H, Kil J, Gultig K., Zenner HP, 1999, Determination of hair cell degeneration and hair cell death in neomycin treated cultures of neonatal rat cochlea Hearing Research 128, Matsui JI, Gale JE, Warchol ME., 2004, Critical signaling events during the aminoglycoside-induced death of sensory hair cells in vitro. J Neurobiol., 61(2),
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism
 Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
NERVE ENDINGS OF THE ORGAN OF CORTI AUTHORS: DOMINGGUS MANGAPE DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
 Ear Res Jpn 13 NERVE ENDINGS OF THE ORGAN OF CORTI AUTHORS: DOMINGGUS MANGAPE YASUO HARADA NOBUHARU TAGASHIRA DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. Nerve endings of the
Ear Res Jpn 13 NERVE ENDINGS OF THE ORGAN OF CORTI AUTHORS: DOMINGGUS MANGAPE YASUO HARADA NOBUHARU TAGASHIRA DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. Nerve endings of the
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
to vibrate the fluid. The ossicles amplify the pressure. The surface area of the oval window is
 Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Vancomycin Enhances the Ototoxic Properties of the Aminoglycoside Antibiotic Gentamicin
 Vancomycin Enhances the Ototoxic Properties of the Aminoglycoside Antibiotic Gentamicin Paul Sooby Supervised by Prof. Guy Richardson and Dr. Richard Goodyear Background Sensori-neural hearing loss and
Vancomycin Enhances the Ototoxic Properties of the Aminoglycoside Antibiotic Gentamicin Paul Sooby Supervised by Prof. Guy Richardson and Dr. Richard Goodyear Background Sensori-neural hearing loss and
Apoptosis Progression in the Hair Cells in the Organ of Corti of GJB2 Conditional Knockout Mice
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 5, No. 3: 132-138, September 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.132 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Apoptosis Progression in
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 5, No. 3: 132-138, September 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.132 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Apoptosis Progression in
Ear. Utricle & saccule in the vestibule Connected to each other and to the endolymphatic sac by a utriculosaccular duct
 Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(1):159 164 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Protective effect of L-N-acetylcysteine against gentamycin ototoxicity in
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(1):159 164 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Protective effect of L-N-acetylcysteine against gentamycin ototoxicity in
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! Chapter 17 Part 2 Special Senses! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Author: Christine Thuyvan Dinh, M.D. Mentors: Thomas Van De Water, Ph.D., Fred Telischi, M.D., Simon Angeli, M.D.
 Title: Effects of Dexamethasone on Cisplatin Ototoxicity In Vitro Author: Christine Thuyvan Dinh, M.D. Mentors: Thomas Van De Water, Ph.D., Fred Telischi, M.D., Simon Angeli, M.D. Acknowledgement: This
Title: Effects of Dexamethasone on Cisplatin Ototoxicity In Vitro Author: Christine Thuyvan Dinh, M.D. Mentors: Thomas Van De Water, Ph.D., Fred Telischi, M.D., Simon Angeli, M.D. Acknowledgement: This
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples.
 ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
AUDITORY APPARATUS. Mr. P Mazengenya. Tel 72204
 AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
Auditory System Feedback
 Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves
 The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology III. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology III Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of this lecture Focus (3) on the cochlear lateral wall and Reissner s membrane:
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology III Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of this lecture Focus (3) on the cochlear lateral wall and Reissner s membrane:
Experimental Study on Cochlear Damage Induced by an Endotoxin-like Substance
 Otol Jpn 1 (1): 22-27, 1991 Experimental Study on Cochlear Damage Induced by an Endotoxin-like Substance Takehiko Harada, Tatsuya Yamasoba, Masashi Sugasawa Department Otolaryngology, University Tokyo
Otol Jpn 1 (1): 22-27, 1991 Experimental Study on Cochlear Damage Induced by an Endotoxin-like Substance Takehiko Harada, Tatsuya Yamasoba, Masashi Sugasawa Department Otolaryngology, University Tokyo
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology II. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology II Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of this lecture Focus (2) on the biophysics of the cochlea, the dual roles
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology II Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of this lecture Focus (2) on the biophysics of the cochlea, the dual roles
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit
 Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Neurologische Klinik und Poliklinik Prof. Dr. M. Dieterich Animal models of meningitis-associated hearing loss M Klein, Siena 5/2012 Hearing Loss is common in survivors of Pneumococcal Meningitis oedema
Neurologische Klinik und Poliklinik Prof. Dr. M. Dieterich Animal models of meningitis-associated hearing loss M Klein, Siena 5/2012 Hearing Loss is common in survivors of Pneumococcal Meningitis oedema
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). View kit datasheet: www.abcam.com/ab14085
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). View kit datasheet: www.abcam.com/ab14085
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Round window gentamicin application: an inner ear hair cell damage protocol for the mouse
 Hearing Research 192 (2004) 65 74 www.elsevier.com/locate/heares Round window gentamicin application: an inner ear hair cell damage protocol for the mouse Jennifer L. Heydt, Lisa L. Cunningham, Edwin W.
Hearing Research 192 (2004) 65 74 www.elsevier.com/locate/heares Round window gentamicin application: an inner ear hair cell damage protocol for the mouse Jennifer L. Heydt, Lisa L. Cunningham, Edwin W.
The cochlea: auditory sense. The cochlea: auditory sense
 Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
ab Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit
 ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 (Cat#: 68FT-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 (Cat#: 68FT-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
SOLUTIONS Homework #3. Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03
 SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
A&P 1. Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab. Basic Concepts. These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab
 A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE:
A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE:
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D.
 Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Fluorescence Microscopy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Dako IT S ABOUT TIME. Interpretation Guide. Agilent Pathology Solutions. ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis)
 INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Biological Bases of Age- Related Hearing Loss
 Biological Bases of Age- Related Hearing Loss Robert D. Frisina,, PhD Professor and Assoc. Chair Otolaryngology Department University of Rochester Medical School, International Center for Hearing & Speech
Biological Bases of Age- Related Hearing Loss Robert D. Frisina,, PhD Professor and Assoc. Chair Otolaryngology Department University of Rochester Medical School, International Center for Hearing & Speech
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
Mechanisms of hair cell death and protection Alan G. Cheng a, Lisa L. Cunningham b and Edwin W Rubel a
 SPECIAL COMMENTARY Mechanisms of hair cell death and protection Alan G. Cheng a, Lisa L. Cunningham b and Edwin W Rubel a Purpose of review Sensory hair cells are mechanotransducers of the inner ear that
SPECIAL COMMENTARY Mechanisms of hair cell death and protection Alan G. Cheng a, Lisa L. Cunningham b and Edwin W Rubel a Purpose of review Sensory hair cells are mechanotransducers of the inner ear that
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH).
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Difficult Cases: Controversies in Cochlear Implantation
 Difficult Cases: Controversies in Cochlear Implantation David S Haynes, MD FACS Fred F Telischi, MD MEE FACS Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Robert F Labadie, PhD MD Nikolas H Blevins, MD Matthew L. Carlson, MD
Difficult Cases: Controversies in Cochlear Implantation David S Haynes, MD FACS Fred F Telischi, MD MEE FACS Lawrence R. Lustig, MD Robert F Labadie, PhD MD Nikolas H Blevins, MD Matthew L. Carlson, MD
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Supporting Information For
 Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
What is the effect on the hair cell if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium?
 CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Cochlear hair cell densities in the rabbit
 Anatomical Science International https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-018-0461-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cochlear hair cell densities in the rabbit Fang Yuan 1 Dalian Ding 2 Yitan Cao 1 Weidong Qi 1 Received: 6 June
Anatomical Science International https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-018-0461-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cochlear hair cell densities in the rabbit Fang Yuan 1 Dalian Ding 2 Yitan Cao 1 Weidong Qi 1 Received: 6 June
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of ephrin-b2 H2BGFP persists in the post-hearingonset organ of Corti and is specifically restricted to supporting cells. Sox2 immunolabeling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of ephrin-b2 H2BGFP persists in the post-hearingonset organ of Corti and is specifically restricted to supporting cells. Sox2 immunolabeling
ab65311 Cytochrome c Releasing Apoptosis Assay Kit
 ab65311 Cytochrome c Releasing Apoptosis Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate detection of Cytochrome c translocation from Mitochondria into Cytosol during Apoptosis in
ab65311 Cytochrome c Releasing Apoptosis Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate detection of Cytochrome c translocation from Mitochondria into Cytosol during Apoptosis in
Vestibular/Auditory Systems
 Vestibular/Auditory Systems Jay Zenner on February 3, 2012 Dental Neuroanatomy Scott Rogers Office: SOM 2C132 Boney Labyrinth Vestibular Apparatus Two Major Divisions Cochlea (anterior) VIII VII Semicircular
Vestibular/Auditory Systems Jay Zenner on February 3, 2012 Dental Neuroanatomy Scott Rogers Office: SOM 2C132 Boney Labyrinth Vestibular Apparatus Two Major Divisions Cochlea (anterior) VIII VII Semicircular
CytoPainter LysoGreen Indicator Reagent
 ab176826 CytoPainter LysoGreen Indicator Reagent Instructions for Use For staining lysosomes in live cells with our proprietary Green probe. This product is for research use only and is not intended for
ab176826 CytoPainter LysoGreen Indicator Reagent Instructions for Use For staining lysosomes in live cells with our proprietary Green probe. This product is for research use only and is not intended for
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016)
 International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM
 SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol
 Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit
 Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit Catalog Number KA3808 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit Catalog Number KA3808 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Caspase-3 Assay Cat. No. 8228, 100 tests. Introduction
 Introduction Caspase-3 Assay Cat. No. 8228, 100 tests Caspase-3 is a member of caspases that plays a key role in mediating apoptosis, or programmed cell death. Upon activation, it cleaves a variety of
Introduction Caspase-3 Assay Cat. No. 8228, 100 tests Caspase-3 is a member of caspases that plays a key role in mediating apoptosis, or programmed cell death. Upon activation, it cleaves a variety of
Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease
 Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura President The Society for Promotion of International Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Tokyo, Japan
Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura President The Society for Promotion of International Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Tokyo, Japan
Inhibition of the c-jun N-Terminal Kinase-Mediated Mitochondrial Cell Death Pathway Restores Auditory Function in Sound-Exposed Animals
 0026-895X/07/7103-654 666$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 71, No. 3 Copyright 2007 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 28936/3175789 Mol Pharmacol 71:654 666, 2007 Printed
0026-895X/07/7103-654 666$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 71, No. 3 Copyright 2007 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 28936/3175789 Mol Pharmacol 71:654 666, 2007 Printed
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology. Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment
 Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment Three main types of hearing impairment Conductive Sound is not properly transmitted from the outer to the inner ear Sensorineural
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment Three main types of hearing impairment Conductive Sound is not properly transmitted from the outer to the inner ear Sensorineural
Primary Cilia are Expressed on a Small Fraction of Cells in Trabecular Bone and Marrow
 Primary Cilia are Expressed on a Small Fraction of Cells in Trabecular Bone and Marrow Thomas R. Coughlin 1, Muriel Voisin, Ph.D. 2, Glen L. Niebur, PhD 1, Laoise M. McNamara 2. 1 University of Notre Dame,
Primary Cilia are Expressed on a Small Fraction of Cells in Trabecular Bone and Marrow Thomas R. Coughlin 1, Muriel Voisin, Ph.D. 2, Glen L. Niebur, PhD 1, Laoise M. McNamara 2. 1 University of Notre Dame,
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit
 Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Physiology of human perception
 Physiology of human perception Vision Hearing Thermal and tactile sensations Basic introduction and the list and description of the tasks to be carried out Visible light: 400-700 nm. Vision or sight Anatomy
Physiology of human perception Vision Hearing Thermal and tactile sensations Basic introduction and the list and description of the tasks to be carried out Visible light: 400-700 nm. Vision or sight Anatomy
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent
 ab14143 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not
ab14143 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not
N acetyl cysteine prevents age related hearing loss and the progressive loss of inner hair cells in γ glutamyl transferase 1 deficient mice
 www.impactaging.com AGING, April 2016, Vol 8 No 4 Research Paper N acetyl cysteine prevents age related hearing loss and the progressive loss of inner hair cells in γ glutamyl transferase 1 deficient mice
www.impactaging.com AGING, April 2016, Vol 8 No 4 Research Paper N acetyl cysteine prevents age related hearing loss and the progressive loss of inner hair cells in γ glutamyl transferase 1 deficient mice
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury
 Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit
 7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1293 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
7-AAD/CFSE Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1293 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Dexamethasone uptake in the murine organ of Corti with transtympanic versus systemic administration
 Grewal et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2013, 42:19 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dexamethasone uptake in the murine organ of Corti with transtympanic versus systemic administration
Grewal et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2013, 42:19 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dexamethasone uptake in the murine organ of Corti with transtympanic versus systemic administration
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium
 Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1. Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA. Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA (10 um) upon addition of GSH in HEPES (10 mm, ph = 7.4) containing 10% DMSO. Each spectrum was recorded
Supplementary Figure 1 Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA. Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA (10 um) upon addition of GSH in HEPES (10 mm, ph = 7.4) containing 10% DMSO. Each spectrum was recorded
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
In situ imaging of the mouse cochlea using two-photon microscopy
 In situ imaging of the mouse cochlea using two-photon microscopy Xin Yang 1, Ye Pu 1, Demetri Psaltis 1 and Konstantina M. Stankovic 2 1 Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
In situ imaging of the mouse cochlea using two-photon microscopy Xin Yang 1, Ye Pu 1, Demetri Psaltis 1 and Konstantina M. Stankovic 2 1 Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
For this lab you will use parts of Exercise #18 in your Wise lab manual. Please be sure to read those sections before coming to lab
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
 Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, Auditory system. http:
 Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
ab Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells
 ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery. against melanoma
 Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab
 Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Anatomy of the Ear Region. External ear Middle ear Internal ear
 Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Instructions. Fuse-It-Color. Overview. Specifications
 Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
