Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy The Spectrum of Mitochondrial DNA Mutations in Chinese Patients
|
|
|
- Baldric Dixon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy The Spectrum of Mitochondrial DNA Mutations in Chinese Patients May-Yung Yen*, An-Guor Wang*, Wei-Ling Chang*, Wen-Ming Hsu*, Jorn-Hon Liu* and Yau-Huei Wei *Department of Ophthalmology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC; Department of Biochemistry and Center for Cellular and Molecular Biology, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan, ROC Purpose: To investigate the spectrum of mitochondrial DNA (mtdna) mutations in Chinese patients with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), optic atrophy of unknown etiology, and optic neuropathy of known etiology. Methods: Twenty-seven patients from 25 LHON pedigrees, 22 patients with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology, 21 patients with optic neuropathy of known etiology, and 25 normal healthy controls were included in this study. Twelve pairs of primers that covered the 21 reported mtdna mutations were utilized. Single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis and DNA sequencing were used to detect base substitutions in mtdna. Results: Twenty-three LHON pedigrees (92%) had the mtdna primary mutation. Two pedigrees (8%) had the mutation. No 3460 mutations were detected in this group. Thirteen other sequence changes were found in these patients, but only the 4216 mutation had been reported previously. Thirteen pedigrees had multi-mutation patterns consisting of one primary mutation together with other sequence changes. No primary mutations were found in patients with optic atrophy of unknown etiology or in patients with optic neuropathy of known etiology. Conclusions: High frequency of mtdna mutation was found in Chinese patients with LHON. No specific multi-mutation pattern such as the European mtdna haplogroup J was found. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2002;46: Japanese Ophthalmological Society Key Words: spectrum. Haplogroup, Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy, mitochondrial DNA, mutation Introduction Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is an inherited form of bilateral optic atrophy in which the primary etiologic factor is a mutation in the mitochondrial genome. It is characterized by acute bilateral blindness predominantly in healthy young men. In 1988, Wallace et al 1 first identified a point mutation of mitochondrial DNA (mtdna). They found that Leber s patients carried a G to A point mutation at nucleotide position that converts the highly conserved 340th amino acid from arginine to Received: April 2, 2001 Address correspondence and reprint requests to: May-Yung YEN, MD, Department of Ophthalmology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei 11217, Taiwan, ROC histidine in subunit 4 of Complex I of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Since the mutation was reported, more than 17 point mutations in mtdna have been described in LHON patients. 2 3 Based on genetic, clinical, and biochemical parameters, mutations at nucleotide positions (np) 3460, 11778, and are regarded as primary mutations in that each of these mutations alone can cause LHON. These primary mutations are not found in normal controls. These mutations result in amino acid substitutions in the ND1, ND4, and ND6 mitochondrial genes, respectively, which are three of the seven genes that encode subunits of Complex I of the respiratory chain. The other mutations are regarded as secondary mutations. The secondary mutations are found in normal controls, but Jpn J Ophthalmol 46, (2002) 2002 Japanese Ophthalmological Society /02/$ see front matter Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S (01)
2 46 Jpn J Ophthalmol Vol 46: 45 51, 2002 at a much lower frequency than in LHON patients. The pathogenic or etiological role of the secondary mutation has not yet been established. The three primary LHON mutations are estimated to account for 8 25%, 50 70%, and 10 15% of all Caucasian LHON patients described, respectively. 4 5 However, the np 3460 and np mutations have rarely been reported in Asian LHON patients. In Japan, the prevalence of the np mutation among families with LHON is significantly higher (91.7%) than in Europeans, 6 although a Japanese group of investigators found three patients with the np 3460 mutation (4%) and six patients with the np mutation (9%) among 68 LHON patients. 7 However, no mutation other than the mtdna mutation has ever been reported in Chinese LHON patients The aim of this study was to investigate the spectrum of mtdna mutations in Chinese patients with LHON using single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis 11 and direct DNA sequencing. In addition, screening was performed for Leber s mtdna mutations on patients with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology and patients with optic neuropathy of known etiology. Materials and Methods Methods, including proper consent and approval for this study from the National Science Council in Taiwan, were in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Subjects Twenty-five Chinese LHON pedigrees, including 27 patients and 16 maternally unaffected relatives were studied as group 1. Of the LHON patients, 26 were men and one was a woman. The age of onset ranged between 10 and 40 years with a mean age of onset of 22 years. All had acute or subacute bilateral sequential visual loss. Their visual acuity ranged from only light perception to 6/20. All patients had optic neuropathy only, and no associated neurological or cardiac abnormalities. Eleven pedigrees had familial optic atrophy and 14 were singleton cases. They had tested positive for mtdna or mutation. Four patients were not clinically typical for LHON. The diagnosis was made after molecular testing. All of the unaffected maternal relatives (3 men and 13 women) were visually normal, being able to see 6/6, read 15 out of 15 Ishihara color plates, and had normal fundi without microangiopathy. The clinical symptoms and signs of LHON can vary greatly To assure that no case of LHON was included as optic atrophy of unknown etiology, 22 cases of the latter were included as group 2. Eighteen patients were men and four were women. The age of onset ranged between 7 and 52 years with a mean age of onset of 31 years. All had subacute or chronic progressive visual loss in one or both eyes. Optic neuropathy was the only clinical deficit. Vision ranged from 1/60 to 6/10. Their fundi did not show telangiectatic microangiopathy. They had no maternal relatives within three generations with visual problems. Clinically, they did not fit the diagnosis of LHON, although LHON should be suspected. They subsequently tested negative for mtdna 3460, 11778, or mutations. Twenty-one patients with optic neuropathy of known etiology were included as group 3. Sixteen had acute optic neuritis, 1 had anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, 4 had dominant optic atrophy. Four of the 16 patients with acute optic neuritis were diag- Table 1. Primers and Sizes of Polymerase Chain Reaction Products Used in This Study Number Gene 5 Primer 3 Primer Size (bp) Previously Reported Mutations That Are Covered in This Study 1 ND , ND , 4160, ND ND COI COIII COIII ND , ND , ND , 14482, 14484, 14498, Cyt b Cyt b
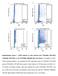
3 M.-Y. YEN ET AL. 47 mtdna MUTATIONS IN CHINESE LHON Figure 1. (A) N, O, K, and Q are pedigrees of Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) subjects from group 1. : unaffected male, : unaffected female, : affected male, affected female. Numbers 4, 6, 10, and 12 are probands of LHON. Subjects with numbered symbols had clinical and molecular examinations. (B) Single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of polymerase chain reaction products amplified with primer pair 1. Electrophoretic condition: 500 V, 5 C, 2 hours. Analysis showed band shift in lanes 5, 6, 11, and 12. N: normal control. Figure 2. (A) A, B, C, and D are pedigrees of the Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) subjects from group 1. *One pedigree of optic neuropathy of known etiology from group 3. Number 9 is a case of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. : unaffected male, : unaffected female, : affected male, affected female. Numbers 1, 6, 12, and 14 are probands of LHON. (B) Single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of polymerase chain reaction products amplified with primer pair 8. Electrophoretic conditions: 500 V, 5 C, 3 hours. N: normal control. All lanes show band shift compared to normal control. nosed with multiple sclerosis. The age of patients with optic neuritis ranged from 8 to 69 years with a mean age of 34. Twenty-five normal healthy people were recruited as group 4, a control group. Nineteen were men and six were women. Their ages ranged from 2 to 86 years with a mean age of 44. Blood Sampling With informed consent, blood samples were obtained from LHON patients, their unaffected maternal relatives, patients with optic atrophy of unknown cause, patients with optic neuropathy of known cause, and healthy controls. Five milliliters of whole blood was withdrawn and collected in a glass tube containing EDTA. DNA Isolation and PCR-RFLP Analysis Total DNA was extracted from the blood cells and purified using a DNA purification kit (Puregene; Gentra Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). Twelve pairs of primers (Table 1) covering the 21 reported mtdna mutations were prepared with a DNA synthesizer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The primers were used to amplify DNA segments ranging from 171 base pairs (bp) to 265 bp in length with the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique using a DNA thermal cycler (Perkin- Elmer/Cetus, Norwalk, CT, USA). In total, 2236 base pairs of mtdna were screened. The thermal profile consisted of 30 cycles of denaturation for 20 seconds at 94 C, annealing for 30 seconds at 56 C, and extension for 30 seconds at 72 C. Single-Strand Conformation Polymorphism Analysis Five milliliters of the PCR product plus 5 L of the denaturing dye (25 ml containing ml of 99% formamide, 1.25 ml of 1% xylene cyanol, and 10 mg of bromophenol blue) were denatured by heating at 95 C for 5 minutes. The samples were electrophoresed using a GenePhor Electrophoresis unit (Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden) at 5 C, 500 V for 3 hours. The gel was stained with a DNA silver staining kit using an automatic gel stainer (Pharmacia Biotech). DNA Sequencing The bands with a shift on SSCP analysis were chosen for DNA sequencing. The fragments were purified with a purification kit (Boehringer Mannheim, Mannheim, FRG), mixed with a dye terminator cycle sequencing kit (Perkin-Elmer), and sequenced using an autosequencer (Model 310, Perkin-Elmer).
4 48 Jpn J Ophthalmol Vol 46: 45 51, 2002 Table 2. Mutations of Mitochondrial DNA Found in Each Group Mutation Gene Amino Acid Change LHON* (n 25) OAUE (n 22) ONKE (n 21) Normal (n 25) G3460A ND1 A52T G11778A ND4 R340H T14484C ND6 M64V T3394C ND1 Y30H A3434G ND1 Y43C C3497T ND1 A64V T3548C ND1 I81T C3571T ND1 L89F T4115C ND1 F270S A4129G ND1 T275A T4216C ND1 Y304H A4833G ND2 T122A G4924T ND2 S152I G4959A ND2 A164T A5301G ND2 I278V C5363T ND2 A298V C13702G ND5 R456G C13712T ND5 A459V A13748G ND5 N471S C13754G ND5 S473C G13759A ND5 A475T A15236G Cyt b I164V C15324G Cyt b A193G A15326G Cyt b T195A G15884A Cyt b A480T *LHON: Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. OAUE: optic neuropathy of unknown etiology. ONKE: optic neuropathy of known etiology. Previous analyses have shown that mutations at np and are Cambridge Reference Sequence errors or rare polymorphisms. Results Figure 1 shows the SSCP analysis of PCR products amplified with primer pair 1. Band shift is shown in lanes 5, 6, 11, and 12. DNA fluorescent autosequencing revealed an np 3394 T to C point mutation. Figure 2 shows the SSCP analysis of PCR products amplified with primer pair 8. All lanes show band shift when compared to the control. DNA fluorescent autosequencing of lanes 1 8 and lanes all revealed an np A to G mutation. Patient 9 was a 70-yearold female patient with ischemic optic neuropathy in whom Sfa NI analysis gave a positive result for mtdna mutation. SSCP analysis showed band shift. However, DNA fluorescent autosequencing revealed np C to T silent mutation. After excluding the silent mutations, the spectrum and the frequency of mutations of the four groups are listed in Table 2. In the LHON group, 23 pedigrees (92%) had the np and 2 pedigrees (8%) had the np primary mutation. No np 3460 primary mutation of mtdna was found. In addition to the primary mutations, 13 mutations were found in this group. Six occurred in the ND1 gene, and 10 involved the mitochondrial encoded Complex I subunits. Two of the 13 were also found in controls. These mutations comprised 13 different mutation patterns (Table 3). A single-mutation pattern consisting of the primary mutation was found in 11 pedigrees. Fourteen pedigrees had multi-mutation patterns consisting of one primary mutation together with one or more secondary mutations. Although three pedigrees had mutation, the mutation occurred at a high frequency in the other optic neuropathy and control groups. Other patterns of multi-mutation occurred individually in only one pedigree each (Table 3). No np 3460, np 11778, or np primary mutations were found in the group of patients with optic atrophy of unknown etiology. However, four mutations, 3434, 5301, 13754, and 15884, were each found in one patient in this group. They involved the ND1, ND2, ND5, and CYTB genes, respectively. They
5 M.-Y. YEN ET AL. 49 mtdna MUTATIONS IN CHINESE LHON Table 3. Frequency of Mitochondrial DNA Mutations Associated with Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Primary Mutations Secondary Mutations Number of Pedigrees control 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 0/25 12/25 were not found in LHON, or optic neuropathy of known etiology patients, or controls. No primary mutation was found in patients with optic neuropathy of known etiology or in controls. Discussion Our results showed a false-positive Sfa NI analysis (patient 9 in Figure 2). The most common pathogenic mutation of mtdna for LHON is at np and is usually detected by loss of an Sfa NI restriction site. The Sfa NI restriction site includes five base pairs 5 -GCATC-3. Substitution of any of the nucleotides from np to will cause the loss of the Sfa NI cutting site. The false-positive rate of Sfa NI analysis was found to be % It requires double confirmation either by Mae III restriction 19 or by SSCP and direct sequencing. Multiple mtdna mutations have been reported in LHON patients. 20 The significance of secondary mutations is unclear. The accumulation of mtdna mutations was thought to have a synergistic effect on the clinical expression of LHON. Howell et al 21 described a large Queensland family with the np 4160 mutation that presented with neurological abnormalities and infantile encephalopathy in addition to characteristic ophthalmological changes. One branch of this family carried both the np 4136 and np 4160 mutations. The affected members in this branch had only ophthalmological abnormalities. The np 4136 mutation was thought to be an intragenic suppressor mutation, that may ameliorate the biochemical defect of Complex I and the neurological abnormalities. However, no other report supported this synergism. Haplotype analysis of mtdna found that 70% of positive Caucasian LHON patients or Caucasian patients from North America had significant clustering and positive patients had moderate clustering on Caucasian mtdna haplogroup J. 22,23 Haplogroup J is one of the European-specific mtdna haplogroups that is characterized by two secondary mutations at np 4216 and It was found that this combination in haplogroup J increased both the penetrance of the two primary mutations and 14484, and the risk of disease expression. However, in vivo study did not support synergism of the 4216 and secondary mutations with the primary mutation in determining the deficit of energy metabolism in LHON. 24 In this study, neither pedigree showed the mutation pattern of European-specific haplogroup J and no specific multi-mutation pattern was found because every pattern occurred in only one pedigree. Patients who had simultaneous multiple mutations were not clinically different from those with a single mutation. The three primary mtdna mutations account for 95% of the LHON pedigrees of northern European descent. 5 The frequency of the np mtdna mutation is about 50% in Caucasians The frequency of the np mutation reported by Mackey et al 5 included 75% (12/16) of Australian/ New Zealand patients, 72% (48/67) of United Kingdom/Northern Ireland patients, 60% (25/42) of Dutch patients, 86% (19/22) of Danish patients, and 50% (6/12) of Finnish patients. The np mutation is significantly more prevalent in Japanese LHON patients. About 87% of Japanese LHON pedigrees possess this mutation. 6,7,30 Mutations at np
6 50 Jpn J Ophthalmol Vol 46: 45 51, and np were found in 4% and 9%, respectively, of Japanese LHON pedigrees. 7 In this study, mutation at np and np were found in 92% and 8% of pedigrees, respectively. No np 3460 mtdna mutation was found. The np mutation is also significantly more prevalent in Chinese LHON patients. No primary mutations at np 3460, np 11778, or np were found in the group of patients with optic atrophy of unknown etiology. However, four mutations, 3434, 5301, 13754, and 15884, were each found in 1 patient in this group. They involved the ND1, ND2, ND5, and Cyt. b genes, respectively. The mutations were not found in the LHON, optic neuropathy of known etiology, and control groups, and have not been described previously. The pathological roles of these mtdna mutations warrant further investigation. In conclusion, the np mutation is significantly more prevalent in Chinese LHON patients. Although no 3460 mutations were found, we cannot exclude its existence in Chinese patients with LHON. Fourteen pedigrees had multi-mutation patterns consisting of one primary mutation together with other sequence changes. No specific multi-mutation pattern was found, and none was associated with the European-specific haplogroup J. This work was supported by research grants from the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC B ) and from Taipei Veterans General Hospital (VGH ). References 1. Wallace DC, Singh G, Lott MT, et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Science 1988;242: Brown MD, Wallace DC. Spectrum of mitochondrial DNA mutations in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Clin Neurosci 1994;2: Howell N, Bogolin C, Jamieson R, Marenda DR, Mackey DA. MtDNA mutations that cause optic neuropathy: how do we know? Am J Hum Genet 1998;62: Newman NJ. Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. New genetic consideration. Arch Neurol 1993;50: Mackey DA, Oostra R-J, Rosenberg T, et al. Primary pathogenic mtdna mutations in multigeneration pedigrees with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 59: Nakamura M, Ara F, Yamada M, et al. High frequency of mitochondrial ND4 gene mutation in Japanese pedigrees with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol 1992;36: Mashima Y, Yamada K, Wakakura M, et al. Spectrum of pathogenic mitochondrial DNA mutations and clinical features in Japanese families with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Curr Eye Res 1998;17: Yen MY, Yen TC, Pang CY, Liu JH, Wei YH. Mitochondrial DNA mutation in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992;33: Zhang LS, Huang Y, Li FY. Mitochondrial DNA mutation in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy in China. Chung Hua I Hsueh Tsa Chih 1994;74: Sudoyo H, Sitepu M, Malik S, Poesponegoro HD, Marzuki S. Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy in Indonesia: two families with mtdna 11778G A and 14484T C mutations. Hum Mutat 1998(Suppl 1):S Orita M, Suzuki Y, Sekiya T, Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 1989;5: Borruat FX, Green WT, Graham EM, Borruat FX, Green WT, Graham EM, Sweeney MG, Morgan-Hughes JA, Sanders MD. Late onset Leber s optic neuropathy: a case confused with ischemic optic neuropathy. Br J Ophthalmol 1992;76: Weiner NC, Newman NJ, Lessell S, Johns DR, Lott MT, Wallace DC. Atypical Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy with molecular confirmation. Arch Neurol 1993;50: Cullom ME, Heher KL, Miller NR, Savino PJ, Johns DR. Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy masquerading as tobacco-alcohol amblyopia. Arch Ophthalmol 1993;111: Dotti MT, Plewnia K, Cardaioli E, Manneschi L, Rufa A, Alema G. A case of ethambutol-induced optic neuropathy harbouring the primary mitochondrial LHON mutation at nt J Neurol 1998;245: Jacobson DM, Stone EM. Difficulty differentiating Leber s from dominant optic neuropathy in a patient with remote visual loss. J Neuro-ophthalmol 1991;11: Johns DR, Neufeld MJ. Pitfalls in the molecular genetic diagnosis of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON). Am J Hum Genet 1993;53: Mashima Y, Hiida Y, Saga M, Oguchi Y, Kudoh J. Risk of false-positive molecular genetic diagnosis of Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1995;119: Stone EM, Coppinger JM, Kardon RH, Donelson J. Mae III positively detects the mitochondrial mutation associated with type I Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Arch Ophthalmol 1990;108: Johns DR, Berman J. Alternative, simultaneous complex I mitochondrial DNA mutations in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1991;174: Howell N, Kubacka M, Xu M, McCullough DA. Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: involvement of the mitochondrial ND1 gene and evidence for an intragenic suppressor mutation. Am J Hum Genet 1991;48: Torroni A, Petrozzi M, D Urbano L, et al. Haplotype and phylogenetic analyses suggest that one European-specific mtdna background plays a role in the expression of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy by increasing the penetrance of the primary mutations and Am J Hum Genet 1997;60: Brown MD, Sun F, Wallace DC. Clustering of Caucasian Leber hereditary optic neuropathy patients containing the or mutations on an mtdna lineage. Am J Hum Genet 1997;60: Lodi P, Montagna P, Cortelli P, et al. Secondary 4216/ND1 and 13708/ND5 Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy mitochondrial DNA mutations do not further impair in vivo mitochondrial oxidative metabolism when associated with the 11778/ND4 mitochondrial DNA mutation. Brain 2000;123;
7 M.-Y. YEN ET AL. 51 mtdna MUTATIONS IN CHINESE LHON 25. Vilkki J, Savontaus ML, Nikoskelainen EK. Genetic heterogeneity in Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy revealed by mitochodrial DNA polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 1989; 45: Holt IJ, Miller DH, Harding AE. Genetic heterogenity and mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. J Med Genet 1989;26: Poulton J, Deadman ME, Brownte-Stewart J, Foulds WS, Gardiner RM. Analysis of mitochondrial DNA in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. J Med Genet 1991;28: Bolhuis PA, Bleeker-Wagemakers EM, Ponne NJ, et al. Rapid shift in genotype of human mitochondrial DNA in a family with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990;170: Kormann BA, Schuster H, Berninger TA, Leo-Kottler B. Detection of the G to A mitochondrial DNA mutation at position in German families with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Hum Genet 1991;88: Mashima Y, Hiida Y, Oguchi Y, Kudoh J, Schimizu N. High frequency of mutations at position in mitochondrial ND4 gene in Japanese families with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy. Hum Genet 1993;92: Howell N, McCullough DA, Kubacka I, Halvorson S, Mackey DA. The sequence of human mtdna: the question of errors versus polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 1992; 50:
Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy A B Figure 1. Fundus photographs of the right (A) and left (B) eyes showing bilateral optic disc hyperemia and mar
 LEBER S HEREDITARY OPTIC NEUROPATHY: A CASE REPORT Chi-Wu Chang, Chi-Huang Chang, and Mei-Lin Peng Department of Ophthalmology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan. Leber s hereditary optic
LEBER S HEREDITARY OPTIC NEUROPATHY: A CASE REPORT Chi-Wu Chang, Chi-Huang Chang, and Mei-Lin Peng Department of Ophthalmology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan. Leber s hereditary optic
A pedigree of Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy with visual loss in childhood, primarily in girls
 Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1999) 237:714 719 Springer-Verlag 1999 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Hagen Thieme Bernd Wissinger Claudia Jandeck Margot Christ-Adler Hannelore Kraus Ulrich Kellner Michael
Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1999) 237:714 719 Springer-Verlag 1999 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Hagen Thieme Bernd Wissinger Claudia Jandeck Margot Christ-Adler Hannelore Kraus Ulrich Kellner Michael
Review article. relevance of different mitochondrial DNA mutations. Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: the clinical
 JMed Genet 1995;32:81-87 Review article 81 Department of Neuro-Ophthalmology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square, London WCIN 3BG, UK P Riordan-Eva University Department of
JMed Genet 1995;32:81-87 Review article 81 Department of Neuro-Ophthalmology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square, London WCIN 3BG, UK P Riordan-Eva University Department of
1220 Letters to the Editor
 1220 Letters to the Editor lationship between paternal age, sex ratios, and aneuploidy frequencies in human sperm, as assessed by multicolor FISH. Am J Hum Genet 57:1395 1399 Neu RL, Kouseff BG, Madan
1220 Letters to the Editor lationship between paternal age, sex ratios, and aneuploidy frequencies in human sperm, as assessed by multicolor FISH. Am J Hum Genet 57:1395 1399 Neu RL, Kouseff BG, Madan
Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy - case report
 Journal of Health Sciences www.jhsci.ba Volume 2, Number 2, September 2012 - case report Mirjana A. Janicijevic-Petrovic 1 *, Tatjana Sarenac Vulovic 1, Nenad Petrovic 1, Suncica Sreckovic 1, Svetlana
Journal of Health Sciences www.jhsci.ba Volume 2, Number 2, September 2012 - case report Mirjana A. Janicijevic-Petrovic 1 *, Tatjana Sarenac Vulovic 1, Nenad Petrovic 1, Suncica Sreckovic 1, Svetlana
Yukihiko Mashima 1,2*, Kazuteru Kigasawa 1,2, Kei Shinoda 1,3, Masato Wakakura 4 and Yoshihisa Oguchi 1
 Mashima et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:192 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0583-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Visual prognosis better in eyes with less severe reduction of visual acuity one year after onset of Leber hereditary
Mashima et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:192 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0583-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Visual prognosis better in eyes with less severe reduction of visual acuity one year after onset of Leber hereditary
A case-control study of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy
 Brain (996), 9, 4-46 A case-control study of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy R. M. Chalmers and A. E. Harding^ University Department of Clinical Neurology (Neurogenetics Section), Institute of Neurology,
Brain (996), 9, 4-46 A case-control study of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy R. M. Chalmers and A. E. Harding^ University Department of Clinical Neurology (Neurogenetics Section), Institute of Neurology,
Identification of an X-Chromosomal Locus and Haplotype Modulating the Phenotype of a Mitochondrial DNA Disorder
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 77:1086 1091, 2005 Report Identification of an X-Chromosomal Locus and Haplotype Modulating the Phenotype of a Mitochondrial DNA Disorder Gavin Hudson, 1 Sharon Keers, 1 Patrick Yu Wai
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 77:1086 1091, 2005 Report Identification of an X-Chromosomal Locus and Haplotype Modulating the Phenotype of a Mitochondrial DNA Disorder Gavin Hudson, 1 Sharon Keers, 1 Patrick Yu Wai
modified dye uptake assay including formazan test EC 90 not tested plaque reduction assay
 Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
The phenotype of Arg555Trp mutation in a large Turkish family with corneal granular dystrophy
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 11 no. 4, 2001 / pp. 333-337 The phenotype of Arg555Trp mutation in a large Turkish family with corneal granular dystrophy H. KIRATLI 1, M. İRKEÇ 1, K. ÖZGÜL 2,
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 11 no. 4, 2001 / pp. 333-337 The phenotype of Arg555Trp mutation in a large Turkish family with corneal granular dystrophy H. KIRATLI 1, M. İRKEÇ 1, K. ÖZGÜL 2,
Investigation of auditory dysfunction in Leber Hereditary
 The definitive version of this article is published and available online as: Yu-Wai-Man, P; Elliott, C; Griffiths, PG; Johnson, IJ; Chinnery, PF, Investigation of auditory dysfunction in Leber hereditary
The definitive version of this article is published and available online as: Yu-Wai-Man, P; Elliott, C; Griffiths, PG; Johnson, IJ; Chinnery, PF, Investigation of auditory dysfunction in Leber hereditary
Characterization of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness changes associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy by optical coherence tomography
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 483-487, 2014 Characterization of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness changes associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy by optical coherence tomography
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 483-487, 2014 Characterization of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness changes associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy by optical coherence tomography
Frequency and Spectrum of Mitochondrial ND6 Mutations in 1218 Han Chinese Subjects With Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
 Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Frequency and Spectrum of Mitochondrial ND6 Mutations in 1218 Han Chinese Subjects With Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Min Liang, 1,2 Pingping Jiang, 1 Feng Li,
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Frequency and Spectrum of Mitochondrial ND6 Mutations in 1218 Han Chinese Subjects With Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Min Liang, 1,2 Pingping Jiang, 1 Feng Li,
TD* (n=46) Supplementary Table 2 Clinical characteristics of CHARGE participants with autism and typical development. Samples for mtdna deletions
 1 Supplementary Material Supplementary Table1 Demographic characteristics of CHARGE participants with autism and typical development Samples for mtdna deletions Samples for mtdna sequencing (n=67) (n=46)
1 Supplementary Material Supplementary Table1 Demographic characteristics of CHARGE participants with autism and typical development Samples for mtdna deletions Samples for mtdna sequencing (n=67) (n=46)
Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a maternally
 Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Affects Only Female Matrilineal Relatives in Two Chinese Families Jia Qu,*,1,2,3,4 Ying Wang, 5 Yi Tong, 1,5,6 Xiangtian Zhou, 1 Fuxin
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Affects Only Female Matrilineal Relatives in Two Chinese Families Jia Qu,*,1,2,3,4 Ying Wang, 5 Yi Tong, 1,5,6 Xiangtian Zhou, 1 Fuxin
Clinical prospective study of visual function in patients with acute optic neuritis
 Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2013) 112, 87e92 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical prospective study of visual function
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2013) 112, 87e92 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical prospective study of visual function
A study of 133 Chinese children with mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I deficiency
 Clin Genet 2015: 87: 179 184 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLNCAL GENETCS doi: 10.1111/cge.12356 A study of 133 Chinese
Clin Genet 2015: 87: 179 184 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLNCAL GENETCS doi: 10.1111/cge.12356 A study of 133 Chinese
Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in a Japanese Family with Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa
 Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in a Japanese Family with Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa Budu,* Masayuki Matsumoto, Seiji Hayasaka, Tetsuya Yamada and Yoriko Hayasaka Department
Rhodopsin Gene Codon 106 Mutation (Gly-to-Arg) in a Japanese Family with Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa Budu,* Masayuki Matsumoto, Seiji Hayasaka, Tetsuya Yamada and Yoriko Hayasaka Department
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0579 TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yuichiro Tanaka, Ph.D. Rajvir Dahiya, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0579 TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yuichiro Tanaka, Ph.D. Rajvir Dahiya, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
CYP19 gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility to breast cancer in Xinjiang Uigur women
 CYP19 gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility to breast cancer in Xinjiang Uigur women L. Yang, X.Y. Wang, Y.T. Li, H.L. Wang, T. Wu, B. Wang, Q. Zhao, D. Jinsihan and L.P. Zhu The Department of Mammary
CYP19 gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility to breast cancer in Xinjiang Uigur women L. Yang, X.Y. Wang, Y.T. Li, H.L. Wang, T. Wu, B. Wang, Q. Zhao, D. Jinsihan and L.P. Zhu The Department of Mammary
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information HBV maintains electrostatic homeostasis by modulating negative charges from phosphoserine and encapsidated nucleic acids Authors: Pei-Yi Su 1,2,3, Ching-Jen Yang 2, Tien-Hua Chu
Supplementary Information HBV maintains electrostatic homeostasis by modulating negative charges from phosphoserine and encapsidated nucleic acids Authors: Pei-Yi Su 1,2,3, Ching-Jen Yang 2, Tien-Hua Chu
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Non-Mendelian inheritance
 Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Hepatitis B Virus Genemer
 Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Clinical differences between young and older patients with optic neuritis
 Original Article Page 1 of 5 Clinical differences between young and older patients with optic neuritis Wenjing Luo 1 *, Qiu-Shui Huang 2 *, Jian-Feng He 2, Min Han 1, Bo Liu 1, Yi Du 2 1 The Cadre Ward
Original Article Page 1 of 5 Clinical differences between young and older patients with optic neuritis Wenjing Luo 1 *, Qiu-Shui Huang 2 *, Jian-Feng He 2, Min Han 1, Bo Liu 1, Yi Du 2 1 The Cadre Ward
Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy with late disease onset: clinical and molecular characteristics of 20 patients
 Dimitriadis et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2014, 9:158 RESEARCH Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy with late disease onset: clinical and molecular characteristics of 20 patients Open Access
Dimitriadis et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2014, 9:158 RESEARCH Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy with late disease onset: clinical and molecular characteristics of 20 patients Open Access
A retrospective analysis of characteristics of visual field damage in patients with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-2540-7 RESEARCH Open Access A retrospective analysis of characteristics of visual field damage in patients with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy Ruijin Ran 1,2, Shuo Yang 1, Heng
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-2540-7 RESEARCH Open Access A retrospective analysis of characteristics of visual field damage in patients with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy Ruijin Ran 1,2, Shuo Yang 1, Heng
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Genotype Detection in Fingernails among Non-alcoholic Northeastern Thai Population and Derived Gene Frequency
 ScienceAsia 28 (2002) : 99-103 Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Genotype Detection in Fingernails among Non-alcoholic Northeastern Thai Population and Derived Gene Frequency Paiboon Mongconthawornchai a, *, Somsong
ScienceAsia 28 (2002) : 99-103 Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Genotype Detection in Fingernails among Non-alcoholic Northeastern Thai Population and Derived Gene Frequency Paiboon Mongconthawornchai a, *, Somsong
Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS
 Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS A. STOCK SOLUTIONS FOR DNA ISOLATION 0.5M Ethylene-diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) (ph=8.0) 1M Tris-Cl (ph=8.0) 5M NaCl solution Red cell lysis buffer (10X) White cell
Annexure III SOLUTIONS AND REAGENTS A. STOCK SOLUTIONS FOR DNA ISOLATION 0.5M Ethylene-diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) (ph=8.0) 1M Tris-Cl (ph=8.0) 5M NaCl solution Red cell lysis buffer (10X) White cell
Prevalence and mode of inheritance of major genetic eye diseases in China
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 584-588 Prevalence and mode of inheritance of major genetic eye diseases in China DAN-NING HU From the Zhabei Eye Institute, Shanghai, and Section of Ophthalmic Genetics,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 584-588 Prevalence and mode of inheritance of major genetic eye diseases in China DAN-NING HU From the Zhabei Eye Institute, Shanghai, and Section of Ophthalmic Genetics,
The Organism as a system
 The Organism as a system PATIENT 1: Seven-year old female with a history of normal development until age two. At this point she developed episodic vomiting, acidosis, epilepsy, general weakness, ataxia
The Organism as a system PATIENT 1: Seven-year old female with a history of normal development until age two. At this point she developed episodic vomiting, acidosis, epilepsy, general weakness, ataxia
Relative activity (%) SC35M
 a 125 Bat (H17N) b 125 A/WSN (H1N1) Relative activity (%) 0 75 50 25 Relative activity (%) 0 75 50 25 0 Pos. Neg. PA PB1 Pos. Neg. NP PA PB1 PB2 0 Pos. Neg. NP PA PB1 PB2 SC35M Bat Supplementary Figure
a 125 Bat (H17N) b 125 A/WSN (H1N1) Relative activity (%) 0 75 50 25 Relative activity (%) 0 75 50 25 0 Pos. Neg. PA PB1 Pos. Neg. NP PA PB1 PB2 0 Pos. Neg. NP PA PB1 PB2 SC35M Bat Supplementary Figure
Multi-clonal origin of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates. determined by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
Research Article Analysis of Genetic Mutations in a Cohort of Hereditary Optic Neuropathy in Shanghai, China
 Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 6186052, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6186052 Research Article Analysis of Genetic Mutations in a Cohort of Hereditary Optic Neuropathy in Shanghai, China Dekang
Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 6186052, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6186052 Research Article Analysis of Genetic Mutations in a Cohort of Hereditary Optic Neuropathy in Shanghai, China Dekang
An Introduction to mitochondrial disease.
 9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer. Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment
 Product Manual Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2002-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in
Product Manual Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2002-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population
 Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
Mitochondrial DNA (T/C) Polymorphism, Variants and Heteroplasmy among Filipinos with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Mitochondrial DNA (T/C) 16189 Polymorphism, Variants and Heteroplasmy among Filipinos with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Elizabeth Paz-Pacheco 1, Eva Maria Cutiongco-Dela Paz 2, Cynthia Halili-Manabat 3, Mary
Mitochondrial DNA (T/C) 16189 Polymorphism, Variants and Heteroplasmy among Filipinos with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Elizabeth Paz-Pacheco 1, Eva Maria Cutiongco-Dela Paz 2, Cynthia Halili-Manabat 3, Mary
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Optic neuritis in Singapore
 667 Original Article Optic neuritis in Singapore Lim S A, Goh K Y, Tow S, Fu E, Wong T Y, Seah A, Tan C, Cullen J F ABSTRACT Introduction: Optic neuritis (ON) is the commonest optic neuropathy encountered
667 Original Article Optic neuritis in Singapore Lim S A, Goh K Y, Tow S, Fu E, Wong T Y, Seah A, Tan C, Cullen J F ABSTRACT Introduction: Optic neuritis (ON) is the commonest optic neuropathy encountered
Genetic Diseases. SCPA202: Basic Pathology
 Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Genetic Diseases SCPA202: Basic Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Genetic disease An illness caused by abnormalities
Cancer Investigators: Medical Diagnostics in Your Classroom
 Cancer Investigators: Medical Diagnostics in Your Classroom Thomas Cynkar Paul Miller Edvotek, Inc. www.edvotek.com Follow @Edvotek EDVOTEK Biotech The Biotechnology Education Company Celebrating 30 years
Cancer Investigators: Medical Diagnostics in Your Classroom Thomas Cynkar Paul Miller Edvotek, Inc. www.edvotek.com Follow @Edvotek EDVOTEK Biotech The Biotechnology Education Company Celebrating 30 years
HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis
 Product Manual HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures for clinical purposes Catalog
Product Manual HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures for clinical purposes Catalog
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
variant led to a premature stop codon p.k316* which resulted in nonsense-mediated mrna decay. Although the exact function of the C19L1 is still
 157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
Late-onset Leber hereditary optic neuropathy mimicking Susac s syndrome
 J Neurol (2010) 257:1999 2003 DOI 10.1007/s00415-010-5649-6 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Late-onset Leber hereditary optic neuropathy mimicking Susac s syndrome Stefano Zoccolella Vittoria Petruzzella Francesco
J Neurol (2010) 257:1999 2003 DOI 10.1007/s00415-010-5649-6 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Late-onset Leber hereditary optic neuropathy mimicking Susac s syndrome Stefano Zoccolella Vittoria Petruzzella Francesco
Association between MTHFR 677C/T and 1298A/C gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk
 Association between MTHFR 677C/T and 1298A/C gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk X.F. Zhang 1, T. Liu 2, Y. Li 1 and S. Li 2 1 Department of Breast, Liao Ning Cancer Hospital and Institute, Shenyang,
Association between MTHFR 677C/T and 1298A/C gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk X.F. Zhang 1, T. Liu 2, Y. Li 1 and S. Li 2 1 Department of Breast, Liao Ning Cancer Hospital and Institute, Shenyang,
ACUTE MANIFESTATION OF LHON AND COINCIDENTAL FINDING OF A PITUITARY ADENOMA: A CASE REPORT
 ACUTE MANIFESTATION OF LHON AND COINCIDENTAL FINDING OF A PITUITARY ADENOMA: A CASE REPORT MULLIEZ E.*, BLANCKAERT M.**, BLANCKAERT J.*, ** SUMMARY A patient with Leber Hereditary Opticus Neuropathy (LHON)
ACUTE MANIFESTATION OF LHON AND COINCIDENTAL FINDING OF A PITUITARY ADENOMA: A CASE REPORT MULLIEZ E.*, BLANCKAERT M.**, BLANCKAERT J.*, ** SUMMARY A patient with Leber Hereditary Opticus Neuropathy (LHON)
INVESTIGATION THE PREVALENCE OF MUTATIONS IVS 10 AND R158Q IN A NUMBER OF IRANIAN PATIENTS WITH PKU
 : 293-297 ISSN: 2277 4998 INVESTIGATION THE PREVALENCE OF MUTATIONS IVS 10 AND R158Q IN A NUMBER OF IRANIAN PATIENTS WITH PKU SHIRIN JAHANBAZI, FATEMEHKESHAVARZI* Department of Biology, Sanandaj Branch,
: 293-297 ISSN: 2277 4998 INVESTIGATION THE PREVALENCE OF MUTATIONS IVS 10 AND R158Q IN A NUMBER OF IRANIAN PATIENTS WITH PKU SHIRIN JAHANBAZI, FATEMEHKESHAVARZI* Department of Biology, Sanandaj Branch,
Lack of Association between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response Genes and Suicidal Victims
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 53, No. 4, pp. 151-155, 2007 Lack of Association between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response Genes and Suicidal Victims KAORU SAKURAI 1, NAOKI NISHIGUCHI 2, OSAMU SHIRAKAWA 2,
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 53, No. 4, pp. 151-155, 2007 Lack of Association between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response Genes and Suicidal Victims KAORU SAKURAI 1, NAOKI NISHIGUCHI 2, OSAMU SHIRAKAWA 2,
HEREDITARY HEMOCHROMATOSIS
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES For use with the UnitedHealthcare Laboratory Benefit Management Program, administered by BeaconLBS HEREDITARY HEMOCHROMATOSIS Policy Number: PDS - 020 Effective Date: January 1, 2015
CLINICAL GUIDELINES For use with the UnitedHealthcare Laboratory Benefit Management Program, administered by BeaconLBS HEREDITARY HEMOCHROMATOSIS Policy Number: PDS - 020 Effective Date: January 1, 2015
Chapter 1 : Genetics 101
 Chapter 1 : Genetics 101 Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role of genes, behavior, and the environment will be important to appropriately collecting and applying genetic
Chapter 1 : Genetics 101 Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role of genes, behavior, and the environment will be important to appropriately collecting and applying genetic
Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E,
 Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E, TY93/H5N1 GFP-627K, or the TY93/H5N1 PB2(588-759) virus library. To establish our GFP- FACS screening platform, we compared
Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E, TY93/H5N1 GFP-627K, or the TY93/H5N1 PB2(588-759) virus library. To establish our GFP- FACS screening platform, we compared
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma
 Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population
 Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3.
 Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome
 Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Identification of Somatic Mutations in the von Hippel Lindau (VHL) Gene in a Patient With Renal Cell Carcinoma
 CASE REPORT Identification of Somatic Mutations in the von Hippel Lindau (VHL) Gene in a Patient With Renal Cell Carcinoma Wen-Chung Wang, 1 Hui-Ju Chen, 2 Yu-Hua Tseng, 3 Yen-Chein Lai 2 * One of the
CASE REPORT Identification of Somatic Mutations in the von Hippel Lindau (VHL) Gene in a Patient With Renal Cell Carcinoma Wen-Chung Wang, 1 Hui-Ju Chen, 2 Yu-Hua Tseng, 3 Yen-Chein Lai 2 * One of the
doi: /brain/aws279 Brain 2013: 136; 1 5 e230 Persistence of the treatment effect of idebenone in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy
 doi:10.1093/brain/aws279 Brain 2013: 136; 1 5 e230 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY LETTER TO THE EDITOR Persistence of the treatment effect of idebenone in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy T. Klopstock,
doi:10.1093/brain/aws279 Brain 2013: 136; 1 5 e230 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY LETTER TO THE EDITOR Persistence of the treatment effect of idebenone in Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy T. Klopstock,
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING OPENS NEW VIEWS ON VIRUS EVOLUTION AND EPIDEMIOLOGY. 16th International WAVLD symposium, 10th OIE Seminar
 NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING OPENS NEW VIEWS ON VIRUS EVOLUTION AND EPIDEMIOLOGY S. Van Borm, I. Monne, D. King and T. Rosseel 16th International WAVLD symposium, 10th OIE Seminar 07.06.2013 Viral livestock
NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING OPENS NEW VIEWS ON VIRUS EVOLUTION AND EPIDEMIOLOGY S. Van Borm, I. Monne, D. King and T. Rosseel 16th International WAVLD symposium, 10th OIE Seminar 07.06.2013 Viral livestock
Identifying potential pitfalls in interpreting mitochondrial DNA mutations of male infertility cases
 Indian J Med Res 134, October 2011, pp 447-451 Identifying potential pitfalls in interpreting mitochondrial DNA mutations of male infertility cases Malliya Gounder Palanichamy * *, ** & Ya-Ping Zhang *
Indian J Med Res 134, October 2011, pp 447-451 Identifying potential pitfalls in interpreting mitochondrial DNA mutations of male infertility cases Malliya Gounder Palanichamy * *, ** & Ya-Ping Zhang *
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
Sequential non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Sequential non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 68 year old white woman had a new onset of floaters in her right eye and was found to have
Sequential non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 68 year old white woman had a new onset of floaters in her right eye and was found to have
Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells *
 Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Hiroki Fujita, Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, Soh Futagami and Takashi Tokoro Department of Visual Science, Tokyo Medical
Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Hiroki Fujita, Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, Soh Futagami and Takashi Tokoro Department of Visual Science, Tokyo Medical
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29;
 SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
 The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0579 TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yuichiro Tanaka, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Northern California
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0579 TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yuichiro Tanaka, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Northern California
Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is the most. Mitochondrial ND1 Variants in 1281 Chinese Subjects With Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
 Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Mitochondrial ND1 Variants in 1281 Chinese Subjects With Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Yanchun Ji, 1,2 Min Liang, 1,3 Juanjuan Zhang, 1,4 Ling Zhu, 1 Zengjun Zhang,
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Mitochondrial ND1 Variants in 1281 Chinese Subjects With Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Yanchun Ji, 1,2 Min Liang, 1,3 Juanjuan Zhang, 1,4 Ling Zhu, 1 Zengjun Zhang,
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Hepatitis B virus genotype, mutations, human leukocyte antigen polymorphisms and their interactions in hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-centre case-control study Juan Wen, Ci
Supplementary information Hepatitis B virus genotype, mutations, human leukocyte antigen polymorphisms and their interactions in hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-centre case-control study Juan Wen, Ci
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase
 6866 Med Genet 1991; 28: 686-690 Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene as an aid to the diagnosis of phenylketonuria L Kalaydjieva, B Dworniczak, C Aulehla-Scholz,M Devoto, G Romeo, M
6866 Med Genet 1991; 28: 686-690 Silent mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene as an aid to the diagnosis of phenylketonuria L Kalaydjieva, B Dworniczak, C Aulehla-Scholz,M Devoto, G Romeo, M
Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children
 Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children Andrew Morris Willink Unit, Manchester Mitochondrial function Carbohydrate Fat Respiratory chain Energy Mitochondria are the product
Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children Andrew Morris Willink Unit, Manchester Mitochondrial function Carbohydrate Fat Respiratory chain Energy Mitochondria are the product
Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 mutation as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study PKS Chan *, JSY Chor, AC Vlantis, TL
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study PKS Chan *, JSY Chor, AC Vlantis, TL
I have nothing to disclose but I
 OPTIC NEUROPATHIES Robert L. Tomsak MD PhD Professor of Ophthalmology and Neurology Wayne State t University it Sh School of Mdii Medicine I have nothing to disclose but I wish I did. dd Road map for this
OPTIC NEUROPATHIES Robert L. Tomsak MD PhD Professor of Ophthalmology and Neurology Wayne State t University it Sh School of Mdii Medicine I have nothing to disclose but I wish I did. dd Road map for this
Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
New: P077 BRCA2. This new probemix can be used to confirm results obtained with P045 BRCA2 probemix.
 SALSA MLPA KIT P045-B2 BRCA2/CHEK2 Lot 0410, 0609. As compared to version B1, four reference probes have been replaced and extra control fragments at 100 and 105 nt (X/Y specific) have been included. New:
SALSA MLPA KIT P045-B2 BRCA2/CHEK2 Lot 0410, 0609. As compared to version B1, four reference probes have been replaced and extra control fragments at 100 and 105 nt (X/Y specific) have been included. New:
A Gene for X-Linked Optic Atrophy Is Closely Linked to the Xp11.4-Xp11.2 Region of the X Chromosome
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 61:934 939, 1997 A Gene for X-Linked Optic Atrophy Is Closely Linked to the Xp11.4-Xp11.2 Region of the X Chromosome Jacqueline J. M. Assink, 1 Nel T. Tijmes, 1 Jacoline B. ten Brink,
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 61:934 939, 1997 A Gene for X-Linked Optic Atrophy Is Closely Linked to the Xp11.4-Xp11.2 Region of the X Chromosome Jacqueline J. M. Assink, 1 Nel T. Tijmes, 1 Jacoline B. ten Brink,
IVF Michigan, Rochester Hills, Michigan, and Reproductive Genetics Institute, Chicago, Illinois
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
Variants in mitochondrial DNA (mtdna) have been
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mitochondrial DNA Coding and Control Region Variants as Genetic Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Chia-Wei Liou, 1 Jin-Bor Chen, 2 Mao-Meng Tiao, 3 Shao-Wen Weng, 4 Tiao-Lai Huang,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mitochondrial DNA Coding and Control Region Variants as Genetic Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Chia-Wei Liou, 1 Jin-Bor Chen, 2 Mao-Meng Tiao, 3 Shao-Wen Weng, 4 Tiao-Lai Huang,
Association between the -77T>C polymorphism in the DNA repair gene XRCC1 and lung cancer risk
 Association between the -77T>C polymorphism in the DNA repair gene XRCC1 and lung cancer risk B.B. Sun, J.Z. Wu, Y.G. Li and L.J. Ma Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital Affiliated to
Association between the -77T>C polymorphism in the DNA repair gene XRCC1 and lung cancer risk B.B. Sun, J.Z. Wu, Y.G. Li and L.J. Ma Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital Affiliated to
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH
 SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
AZOOSPERMIA Chromosome Y
 AZOOSPERMIA Chromosome Y M i c r o d e l e t i o n Ref.: PI EDP003024-40 testspi EDP002024 1. INTRODUCTION In 1976, Tiepolo and Zuffardi reported de novo, microscopically detectable deletions of the distal
AZOOSPERMIA Chromosome Y M i c r o d e l e t i o n Ref.: PI EDP003024-40 testspi EDP002024 1. INTRODUCTION In 1976, Tiepolo and Zuffardi reported de novo, microscopically detectable deletions of the distal
L eber s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is one of the
 626 PAPER Progressive auditory neuropathy in patients with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy BĆeranić, L M Luxon... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Borka Ćeranić,
626 PAPER Progressive auditory neuropathy in patients with Leber s hereditary optic neuropathy BĆeranić, L M Luxon... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Borka Ćeranić,
CLINICAL CASE. Vision Recovery Despite Retinal Ganglion Cell Loss in Leber s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. Ann L. Webber*
 1040-5488/16/9312-0000/0 VOL. 93, NO. 12, PP. 00Y00 OPTOMETRY AND VISION SCIENCE Copyright * 2016 American Academy of Optometry CLINICAL CASE Vision Recovery Despite Retinal Ganglion Cell Loss in Leber
1040-5488/16/9312-0000/0 VOL. 93, NO. 12, PP. 00Y00 OPTOMETRY AND VISION SCIENCE Copyright * 2016 American Academy of Optometry CLINICAL CASE Vision Recovery Despite Retinal Ganglion Cell Loss in Leber
Evolution of Genetic Testing. Joan Pellegrino MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics SUNY Upstate Medical University
 Evolution of Genetic Testing Joan Pellegrino MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics SUNY Upstate Medical University Genetic Testing Chromosomal analysis Flourescent in situ hybridization (FISH) Chromosome
Evolution of Genetic Testing Joan Pellegrino MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics SUNY Upstate Medical University Genetic Testing Chromosomal analysis Flourescent in situ hybridization (FISH) Chromosome
The P48T germline mutation and polymorphism in the CDKN2A gene of patients with melanoma
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 237-241 The P48T mutation and polymorphisms in melanoma ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 237 The P48T germline mutation and polymorphism
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2006) 39: 237-241 The P48T mutation and polymorphisms in melanoma ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 237 The P48T germline mutation and polymorphism
SALSA MLPA KIT P060-B2 SMA
 SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
Diabetes and deafness; is it sufficient to screen for the mitochondrial 3243A>G mutation alone?
 Diabetes Care In Press, published online May 31, 2007 Diabetes and deafness; is it sufficient to screen for the mitochondrial 3243A>G mutation alone? Received for publication 8 March 2007 and accepted
Diabetes Care In Press, published online May 31, 2007 Diabetes and deafness; is it sufficient to screen for the mitochondrial 3243A>G mutation alone? Received for publication 8 March 2007 and accepted
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Detection and differential diagnosis of colon cancer by a cumulative analysis of promoter methylation Qiong Yang 1,3*, Ying Dong 2,3, Wei Wu 1, Chunlei Zhu 1, Hui Chong 1, Jiangyang
Supplementary Information Detection and differential diagnosis of colon cancer by a cumulative analysis of promoter methylation Qiong Yang 1,3*, Ying Dong 2,3, Wei Wu 1, Chunlei Zhu 1, Hui Chong 1, Jiangyang
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Ku CA, Hull S, Arno G, et al. Detailed clinical phenotype and molecular genetic findings in CLN3-associated isolated retinal degeneration. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online
Supplementary Online Content Ku CA, Hull S, Arno G, et al. Detailed clinical phenotype and molecular genetic findings in CLN3-associated isolated retinal degeneration. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online
Allelic and Haplotype Frequencies of the p53 Polymorphisms in Brain Tumor Patients
 Physiol. Res. 51: 59-64, 2002 Allelic and Haplotype Frequencies of the p53 Polymorphisms in Brain Tumor Patients E. BIROŠ, I. KALINA, A. KOHÚT 1, E. BOGYIOVÁ 2, J. ŠALAGOVIČ, I. ŠULLA 3 Department of Medical
Physiol. Res. 51: 59-64, 2002 Allelic and Haplotype Frequencies of the p53 Polymorphisms in Brain Tumor Patients E. BIROŠ, I. KALINA, A. KOHÚT 1, E. BOGYIOVÁ 2, J. ŠALAGOVIČ, I. ŠULLA 3 Department of Medical
This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository:
 This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/99560/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted
This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/99560/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in a Chinese population
 Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in a Chinese population R. Zhao and M.F. Ying Department of Pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University,
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in a Chinese population R. Zhao and M.F. Ying Department of Pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University,
