ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Pectoralis Major Flap in Composite Lateral Skull Base Defect Reconstruction
|
|
|
- Myles Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pectoralis Major Flap in Composite Lateral Skull Base Defect Reconstruction Vicente A. Resto, MD, PhD; Michael J. McKenna, MD; Daniel G. Deschler, MD Objective: To report our experience with the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap (PMF) for the reconstruction of composite lateral temporal bone defects extending beyond the temporal line. Design: Retrospective review and illustration of specific technical modifications. Setting: Academic tertiary care center. Patients: Eight patients with composite lateral skull base defects that were reconstructed with the PMF between February 2001 and February Intervention: Reconstruction with the modified pedicled PMF. Main Outcome Measures: Reconstruction outcomes and complications. Results: Eight patients (median age, 80 years) underwent total or near-total auriculectomy, wide skin excision, and lateral temporal bone resection as part of the surgical ablation, thus requiring obliteration of the middle ear cavity as well as extensive replacement of skin cover. All patients received radiation therapy. The median postsurgical follow-up was 9 months. Complete healing of the reconstructed surgical defect with no flap loss was achieved in all cases. Conclusion: With specific technical modifications, the PMF can be reliably used for the reconstruction of composite lateral skull base defects extending up to and beyond the temporal line, making this flap an important alternative to free flap reconstruction in selected cases. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;133: Author Affiliations: Departments of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston (Dr Resto), and Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Boston (Drs McKenna and Deschler). THE RECONSTRUCTIVE MANagement of cases involving locally advanced lateral skull base tumors remains a challenge. Surgical treatment commonly requires wide resection of bony tissues, including the lateral temporal bone, mandibular condyle, and soft tissues such as skin, auricle, parotid gland, and infratemporal fossa contents as well as dura. The resulting complex composite defect frequently requires importation of tissue for wound closure. Axial flaps remain the reconstructive substrate of choice for the management of these complex defects because they provide dependable, large-volume tissue that allows successful, watertight wound closure. These features acquire increased importance as the majority of patients undergo radiation therapy as part of their treatment plan. A multitude of flaps have been described for the reconstruction of composite lateral skull base (CLSB) defects, including free tissue transfer from distant donor sites as well as regionally transferred pedicled flaps. The latter are often reserved for patients who are poor candidates for free flaps. Although the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap (PMF) has been a true workhorse in head and neck reconstruction for decades, its application to the reconstruction of CLSB defects has been restricted to defects below the external auditory canal because of the perceived difficulty in achieving sufficient flap length to ensure flap viability as well as a tension-free, watertight closure. 1,2 Specifically, concerns have been raised regarding the reach of the skin paddle, propensity for venous congestion when flap reach is maximized, and delayed wound dehiscence associated with flap bulk and weight. We present our experience using the PMF for the reconstruction of CLSB defects extending beyond the temporal line (supramastoid crest). 3 We also describe and illustrate specific technical modifications that allow the reliable use of this robust flap and review our experience using the PMF for the reconstruction of these defects. 490
2 METHODS The records of all lateral skull base cases reconstructed by the senior author (D.G.D.) using the described modified PMF between February 2001 and February 2006 were retrospectively reviewed. Cases were identified from a prospective database of reconstructive cases maintained by the senior author. Patient age, extent of surgical defect to be reconstructed, exposure to radiation, postoperative course, and complications were recorded and analyzed. Specific technical modifications important for the harvest and inset of the PMF when used for CLSB defect reconstruction are illustrated herein. The basic technique of PMF harvest is not presented, as it has been well described elsewhere in the literature. 4-7 The institutional review board of the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Boston, approved this study. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The PMF flap is based on the pectoralis major branch of the thoracoacromial artery. 8 This report focuses specifically on 5 relevant modifications that allow enhanced reach with reliable viability: (1) the skin paddle is designed over the entire length of muscle; (2) a 5-cm cuff of the superior rectus sheath is harvested in continuity with the distal pectoralis major muscle; (3) motor nerves around the proximal pedicle are identified and severed; (4) the flap is suspended by the harvested rectus sheath; and (5) the flap skin paddle inset is incorporated into the neck incision. Although, standard harvest of the PMF uses a curvilinear incision into the axila, thus preserving the deltopectoral fasciocutaneous flap, this modified technique for the reconstruction of CLSB defects requires the skin paddle of the flap to encompass the entire length of the muscle, with the skin ellipse extending distally over the harvested rectus sheath. The proximal aspect of the incision is then brought into continuity with the lower limb of a neck incision extended from the resultant CLSB defect. The latter incision transitions into the neck at the midpoint of the clavicle. Once the skin incisions are made, skin flap elevation is continued in the standard fashion using a suprafascial plane over the pectoralis major muscle. As the inferior aspect of the ellipse extends over the rectus muscle, the rectus fascia is exposed around and below this point, usually to the first inscription of the ipsilateral rectus abdominus muscle. Dissection in the suprafascial plane helps preserve continuity between the distal pectoralis major muscle and the proximal rectus sheath to be harvested. Once exposure is achieved, a rectangular cuff of rectus sheath measuring approximately 5 cm in length is outlined with cautery dissection through the anterior sheath, thus exposing the underlying rectus muscle fibers (Figure 1). A subfascial plane of dissection is then used to elevate the cuff of rectus sheath in continuity with the pectoralis major muscle. Care is taken to provide meticulous maintenance of the subfascial plane over the rectus abdominus muscle as the transition to the submuscular plane is made, allowing separation of the pectoralis muscle from its rib attachments. This step allows continuous elevation of the extended flap, without disinsertion of the proximal rectus muscle or violation of the rectus sheath to be harvested. Elevation of Anterior Fascia Lifted Figure 1. A cuff of the ipsilateral rectus sheath is harvested in continuity with the proximal pectoralis major muscle. the modified flap then continues from an inferior to superior dissection following standard technique. As the proximal aspect of the flap is elevated, the humeral head of the pectoralis major muscle is severed and the lateral and medial aspects of the clavicular head are isolated and severed. This maneuver requires division of the lateral thoracic pedicle to the pectoralis muscle. The pectoralis major vascular pedicle is directly visualized during this maneuver in order to avoid injury to the latter. A cuff of muscle measuring approximately 3 cm is maintained and inserted into the clavicle to protect the pedicle. Once this step is achieved, a blunt technique is used to dissect the pectoralis major vascular pedicle to its takeoff from the thoracoacromial artery, which marks the point of maximal elevation proximally. A nerve stimulator is then used to identify the motor nerve branches to the pectoralis major muscle around the vascular pedicle. The motor nerve branches are closely associated with the pedicle and usually require blunt dissection within the vascular bundle for complete identification. Once isolated, they are severed under direct vision (Figure 2). The fully elevated flap is then reflected over the clavicle. Next, flap inset geometry is assessed. By definition, the flap must be rotated 180 to position the skin paddle externally. The specific direction of rotation, clockwise vs counterclockwise, is chosen to allow maximal reach, while minimizing torsion on the pedicle (Figure 3). The harvested rectus sheath is then used to suspend the flap superiorly to available structures, usually residual temporalis fascia and muscle or pericranium (Figure 2). It provides the major tension-bearing point of inset, thus 491
3 Anterior Fascia Nerve Cut V A Skin Paddle Position Figure 2. Motor nerves traversing within and around the proximal pectoralis major vascular pedicle are identified and severed. This maneuver allows rotation of the flap, without concomitant vascular pedicle compression. V indicates vein; A, artery. Figure 3. Flap inset geometry is assessed. Asterisk indicates zygomatic arch; arrow, superior aspect of temporal craniotomy bone flap. sparing the skin paddle and its associated perforators from any shearing tension. The harvested muscle can be spread, draped into position, and affixed by sutures. The inset then continues by approximating the flap skin edges to the wound edges. The paddle can be conservatively trimmed as needed, with care being taken to retain a broad subcutaneous base connection to the muscle in order to maximize and protect perforators feeding the skin paddle. An inset of the flap skin island is carried into the neck incision (Figure 4). This step allows maximal distribution of the weight of the flap. The chest wound is closed primarily in layers. Standard wound drainage is used. RESULTS Between February 2001 and February 2006, 8 patients (median age, 80 years) with CLSB defects after surgical ablation for tumor underwent reconstruction with the PMF. All patients underwent total or near-total auriculectomy, wide skin excision, and lateral temporal bone Figure 4. The flap is suspended by the harvested cuff of rectus sheath. Tension is maximally distributed by insetting the skin island throughout the entire wound, including the neck. resection as part of the surgical ablation, thus requiring obliteration of the middle ear cavity as well as extensive replacement of skin cover. All patients received radiation therapy as part of their treatment plan. The median postsurgical follow-up was 9 months (mean, 17 months; range, 1-63 months). Complete healing of the reconstructed surgical defect with no flap loss (partial or total) was achieved in all 8 cases. Clavicle resection was not required in any case. There was 1 complication that consisted of a chest donor site hematoma on postoperative day 2. The hematoma was treated with operative drainage, without further setback. Two patients underwent secondary flap revision with the goals of reducing bulk and improving neck contour, without sequela (Figure 5). COMMENT As stated, repair of the CLSB defect presents specific challenges. A large dead space requires filling. Skin loss can be considerable, especially with auricular sacrifice. Dural exposure may require coverage. These issues are combined with a location more cephalad than that of other head and neck ablative defects, which are commonly repaired with pedicled flaps from the thorax. The use of free flaps for the reconstruction of CLSB defects has been well documented. Most commonly, myocutaneous or fasciocutaneous free flaps such as the rectus abdominus and the anterolateral thigh were used. 1,9-12 These flaps provide robust, high-volume tissue for closure with minimal donor site morbidity, provide long vascular pedicles, and easily allow 2-team harvesting. Such factors make them the preferred flaps for reconstruction of CLSB defects. However, free-tissue reconstruction requires longer operative times and carries the risk of multiple trips to the operating room if the flap requires reexploration dur- 492
4 A B Figure 5. Postoperative appearance after 4 months without revision (A) and after 2 years with revision (B). ing the immediate postoperative period. 13 Therefore, myocutaneous or fasciocutaneous free flaps may be inadequate for patients with significant comorbid conditions who would benefit from reduced operating time and exposure to anesthesia. Historically, regional pedicled axial flaps have been used successfully for CLSB defects. In recent years, with the advent of reliable free tissue transfer techniques, they are used less frequently but should still be considered in the setting of elderly or infirm patients who are poor candidates for free tissue transfer. Two in particular, the latissimus dorsi myocutanoeus flap and the lower island trapezius myocutaneous flaps, have been described for the reconstruction of CLSB defects. 2,14 Both provide large-bulk, wellvascularized tissue with sufficient length for the successful reconstruction of the lateral skull base. However, their use often results in poorer cosmetic results when compared with free flaps. They also require intraoperative repositioning of the patient for harvest, a maneuver that significantly lengthens the procedure. Furthermore, the use of these techniques can result in postoperative arm or shoulder dysfunction This is important in cases involving elderly, infirm patients who may suffer the greatest impediment from such functional loss. Despite these concerns, both the latissimus dorsi myocutanoeus flap and the lower island trapezius myocutaneous flap are excellent reconstructive options in select cases. The pectoralis major regional myocutaneous flap has found broad application for the reconstruction of head and neck defects. 5 Its use for reconstruction of defects of the lateral skull base, however, has been infrequent because of the notion that the flap length is insufficient to reach this area. 1,2 Modified harvest techniques for the pectoralis major flap have been reported. These techniques have included partially resecting the clavicle as well as tunneling the proximal end of the flap under the clavicle Despite these alterations, efforts to expand flap reach to the fullest extent have been complicated by pedicle compromise, with resultant partial or total flap loss, a complication that can have significant consequence for the debilitated patient. Herein, we present technical modifications that address the goals of (1) increased flap reach, (2) prevention of vascular pedicle compromise, and (3) tensionfree closure, thereby providing reliable application of the PMF for the reconstruction of CLSB defects. Increased flap reach is primarily accomplished by incorporating a portion of the proximal ipsilateral rectus sheath into the flap elevation. This maneuver results in a dependable, inferiorly expanded skin paddle design, with resultant increased flap length. Having a large skin ellipse extending up toward the clavicle allows the capture of more proximal perforators from the muscle, which, in turn, increases the viability of the random segment of skin over the rectus sheath. Extending flap reach requires rotating the thinned clavicular muscle insertion, with its associated pectoralis muscle pedicle, within a narrow axis. This maneuver may lead to pedicle compression by the closely associated motor nerves contained within the pedicle s sheath, which can create a strangulating effect, compressing the vessels, usually the vein. Blunt dissection within the pedicle s sheath permits identification and severing of these nerves, thus preventing this complication. Finally, suspending the muscle via the harvested cuff of rectus sheath reduces the potential shear effect on the perforators to the skin island as the pectoralis muscle retracts inferiorly as a result of muscle contraction and gravity. Also, by incorporating the extended skin island completely into the neck incision, an even distribution of flap weight is achieved, a maneuver that is critical for successful wound healing. Furthermore, incorporating the entire expanded skin paddle maximally captures perforators that are important for its support. The described technique has been successfully used for the reconstruction of CLSB defects in 8 cases. Selection of the PMF as the reconstruction modality, as opposed to free tissue transfer techniques, was based on the previous poor performance status of the treated patients. The average age of the patients in our study group was 80 years. Reconstruction was achieved expeditiously, without the need for patient repositioning, and with acceptable cosmetic and functional results. 493
5 The PMF is a robust myocutaneous flap that can be reliably used for the reconstruction of CLSB defects extending up to and beyond the temporal line (supramastoid crest). 3 Within our reconstructive algorithm for CLSB defects, we use the PMF as a second option for the reconstruction of these complex defects in male patients who are not suitable candidates for reconstruction with the anterolateral thigh myocutaneous free flap. Submitted for Publication: June 6, 2006; final revision received September 29, 2006; accepted October 23, Correspondence: Daniel G. Deschler, MD, Head and Neck Surgical Oncology, Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, 243 Charles St, Boston, MA (daniel _deschler@meei.harvard.edu). Author Contributions: Drs Resto, McKenna, and Deschler had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: Resto, McKenna, and Deschler. Acquisition of data: Resto. Analysis and interpretation of data: Resto and Deschler. Drafting of the manuscript: Resto and Deschler. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Resto, McKenna, and Deschler. Study supervision: McKenna and Deschler. Financial Disclosure: None reported. Previous Presentation: This study was presented as a poster at the American Head and Neck Society 2006 Annual Meeting and Research Workshop on the Biology, Prevention, and Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer; August 18, 2006; Chicago, Ill. REFERENCES 1. Schusterman MA, Kroll SS. Reconstruction strategy for temporal bone and lateral facial defects. Ann Plast Surg. 1991;26: Gal TJ, Kerschner JE, Futran ND, et al. Reconstruction after temporal bone resection. Laryngoscope. 1998;108: Turgut HB, Anil A, Peker T, Pelin C, Gulekon IN. Supraarticular, supramastoid and suprameatal crests on the outer surface of the temporal bone and the relation between them. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003;25: Baek SM, Biller HF, Krespi YP, Lawson W. The pectoralis major myocutaneous island flap for reconstruction of the head and neck. Head Neck Surg. 1979; 1: Koshy CE, Taams KO. Pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;104: Marx RE, Smith BR. An improved technique for development of the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990;48: Shank EC, Patow CA. The pectoralis major flap. Ear Nose Throat J. 1992;71: Wei WI, Lam KH, Wong J. The true pectoralis major myocutaneous island flap: an anatomical study. Br J Plast Surg. 1984;37: Amin A, Rifaat M, Civantos F, Weed D, Abu-Sedira M, Bassiouny M. Free anterolateral thigh flap for reconstruction of major craniofacial defects. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2006;22: Disa JJ, Rodriguez VM, Cordeiro PG. Reconstruction of lateral skull base oncological defects: the role of free tissue transfer. Ann Plast Surg. 1998;41: Teknos TN, Smith JC, Day TA, Netterville JL, Burkey BB. Microvascular free tissue transfer in reconstructing skull base defects: lessons learned. Laryngoscope. 2002;112: Wax MK, Burkey BB, Bascom D, Rosenthal EL. The role of free tissue transfer in the reconstruction of massive neglected skin cancers of the head and neck. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2003;5: Smeele LE, Goldstein D, Tsai V, et al. Morbidity and cost differences between free flap reconstruction and pedicled flap reconstruction in oral and oropharyngeal cancer: matched control study. J Otolaryngol. 2006;35: Cole I. The lower trapezius island myocutaneous flap for reconstruction of soft tissue of the lateral skullbase and neck. Aust NZJSurg. 1997;67: Lynch JR, Hansen JE, Chaffoo R, Seyfer AE. The lower trapezius musculocutaneous flap revisited: versatile coverage for complicated wounds to the posterior cervical and occipital regions based on the deep branch of the transverse cervical artery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109: Russell RC, Pribaz J, Zook EG, Leighton WD, Eriksson E, Smith CJ. Functional evaluation of latissimus dorsi donor site. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986;78: Lee KY, Lore JM Jr. Two modifications of pectoralis major myocutaneous flap (PMMF). Laryngoscope. 1986;96: Kerawala CJ, Sun J, Zhang ZY, Guoyu Z. The pectoralis major myocutaneous flap: is the subclavicular route safe? Head Neck. 2001;23: Freeman MS, Thomas JR, Zipper JA. Clavicular division technique: a new approach for lengthening the pectoralis flap. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989; 115: Fabian RL. Reconstruction of the laryngopharynx and cervical esophagus. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:
PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA
 PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA Pages with reference to book, From 72 To 76 Mohammad Arshad Cheema ( Department of Surgery,
PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA Pages with reference to book, From 72 To 76 Mohammad Arshad Cheema ( Department of Surgery,
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
T. Rapis, S.N. Zanakis, I.F. Letsa, A.P. Karamanos CLINICAL CASE. Summary. Introduction
 Journal of BUON 8: 397-401, 2003 2003 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece CLINICAL CASE Basal cell carcinoma of the posterior neck, reconstructed with lower trapezius island musculocutaneous
Journal of BUON 8: 397-401, 2003 2003 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece CLINICAL CASE Basal cell carcinoma of the posterior neck, reconstructed with lower trapezius island musculocutaneous
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Improved Skin Paddle Survival in Pectoralis Major Myocutaneous Flap Reconstruction of Head and Neck Defects
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Skin Paddle Survival in Pectoralis Major Myocutaneous Flap Reconstruction of Head and Neck Defects Vijay R. Ramakrishnan, MD; William Yao, BS; John P. Campana, MD Objective: To
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Skin Paddle Survival in Pectoralis Major Myocutaneous Flap Reconstruction of Head and Neck Defects Vijay R. Ramakrishnan, MD; William Yao, BS; John P. Campana, MD Objective: To
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
Stomal recurrence after total laryngectomy is 1
 CASE REPORT Eben L. Rosenthal, MD, Section Editor ANTEROLATERAL THIGH FREE FLAP FOR TRACHEAL RECONSTRUCTION AFTER PARASTOMAL RECURRENCE Umberto Caliceti, MD, 1 Ottavio Piccin, MD, 1 Ottavio Cavicchi, MD,
CASE REPORT Eben L. Rosenthal, MD, Section Editor ANTEROLATERAL THIGH FREE FLAP FOR TRACHEAL RECONSTRUCTION AFTER PARASTOMAL RECURRENCE Umberto Caliceti, MD, 1 Ottavio Piccin, MD, 1 Ottavio Cavicchi, MD,
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
ALTHOUGH FIRST described
 The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:1104-1108, 2000 Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS (C),* and Mark Burye, DDS Purpose: This article describes
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:1104-1108, 2000 Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS (C),* and Mark Burye, DDS Purpose: This article describes
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Chapter 117: Reconstruction of the Hypopharynx and Cervical Esophagus. Richard E. Hayden
 Chapter 117: Reconstruction of the Hypopharynx and Cervical Esophagus Richard E. Hayden In 1877 Czerny performed the first recorded pharyngoesophageal reconstruction, using local cervical skin flaps for
Chapter 117: Reconstruction of the Hypopharynx and Cervical Esophagus Richard E. Hayden In 1877 Czerny performed the first recorded pharyngoesophageal reconstruction, using local cervical skin flaps for
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
Disclosures. The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction. Overview. Things they are a Changing. Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp
 Disclosures Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Associate Professor Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF
Disclosures Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Associate Professor Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF
Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction J Mohammad Citation J Mohammad. Traumatic Hemi Facial
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 Traumatic Hemi Facial Soft Tissue Amputation. Immediate Surgical Flap Reconstruction J Mohammad Citation J Mohammad. Traumatic Hemi Facial
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY RECTUS ABDOMINIS FLAP FOR HEAD & NECK RECONSTRUCTION Patrik Pipkorn, Brian Nussenbaum The rectus abdominis flap is based on the deep inferior
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY RECTUS ABDOMINIS FLAP FOR HEAD & NECK RECONSTRUCTION Patrik Pipkorn, Brian Nussenbaum The rectus abdominis flap is based on the deep inferior
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer
 Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Thoracoacromial/Cephalic Vascular System for Microvascular Anastomoses in the Vessel-Depleted Neck
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Thoracoacromial/Cephalic Vascular System for Microvascular Anastomoses in the Vessel-Depleted Neck Jeffrey R. Harris, MD; E. Lueg, MD; E. Genden, MD; M. L. Urken, MD Objective: To
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Thoracoacromial/Cephalic Vascular System for Microvascular Anastomoses in the Vessel-Depleted Neck Jeffrey R. Harris, MD; E. Lueg, MD; E. Genden, MD; M. L. Urken, MD Objective: To
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 160 164 The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap Gang Zhou, Qi-Xu Zhang*, Guang-Yu Chen Scar Multiple Treatment Centre,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 160 164 The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap Gang Zhou, Qi-Xu Zhang*, Guang-Yu Chen Scar Multiple Treatment Centre,
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting
 Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
A review of the advantages of the anterolateral thigh flap in head and neck reconstruction
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 603 609 A review of the advantages of the anterolateral thigh flap in head and neck reconstruction Jagdeep S. Chana, Fu-chan Wei* Department of Plastic
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 603 609 A review of the advantages of the anterolateral thigh flap in head and neck reconstruction Jagdeep S. Chana, Fu-chan Wei* Department of Plastic
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps
 CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION
 THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION Emre Vural, MD, James Y. Suen, MD Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 West Markham,
THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION Emre Vural, MD, James Y. Suen, MD Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 West Markham,
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
SCOPE OF PRACTICE PGY-6 PGY-7 PGY-8
 PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
Medical Journal of the Volume 20 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 1385 November Original Articles
 Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck.
 Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Reconstruction of the Chest Wall
 HOW TO DO IT Reconstruction of the Chest Wall Reed 0. Dingman, M.D., and Louis C. Argenta, M.D. ABSTRACT Reconstruction of the chest wall can now be accomplished reliably and expeditiously. Past experience
HOW TO DO IT Reconstruction of the Chest Wall Reed 0. Dingman, M.D., and Louis C. Argenta, M.D. ABSTRACT Reconstruction of the chest wall can now be accomplished reliably and expeditiously. Past experience
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
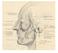 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the
 Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck
 Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck Robert J. Spence, MD, FACS Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD Correspondence: rspence@jhmi.edu
Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck Robert J. Spence, MD, FACS Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD Correspondence: rspence@jhmi.edu
THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction
 THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
Microvascular free tissue transfer is a standard
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERNAL MAMMARY ARTERY AND VEIN: RECIPIENT VESSELS FOR FREE TISSUE TRANSFER TO THE HEAD AND NECK IN THE VESSEL-DEPLETED NECK Mark L. Urken, MD, 1 Kevin M. Higgins, MD, 2 Bryant Lee, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERNAL MAMMARY ARTERY AND VEIN: RECIPIENT VESSELS FOR FREE TISSUE TRANSFER TO THE HEAD AND NECK IN THE VESSEL-DEPLETED NECK Mark L. Urken, MD, 1 Kevin M. Higgins, MD, 2 Bryant Lee, MD,
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery
 Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD
 Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts
 Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
Anatomical study. Clinical study. R. Ogawa, H. Hyakusoku, M. Murakami, R. Aoki, K. Tanuma* and D. G. Pennington?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H. Citation Journal of Clinical Urology, 7(5),
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage
 Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage Shareef Jandali, MD, and David W. Low, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia Correspondence:
Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage Shareef Jandali, MD, and David W. Low, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia Correspondence:
Vascularized Rib for Facial Reconstruction
 Vascularized Rib for Facial Reconstruction Steven P. Davison, M.D., D.D.S., James H. Boehmler, M.D., Jason C. Ganz, M.D., and Bruce Davidson, M.D. Washington, D.C. The reconstruction of maxillectomy defects
Vascularized Rib for Facial Reconstruction Steven P. Davison, M.D., D.D.S., James H. Boehmler, M.D., Jason C. Ganz, M.D., and Bruce Davidson, M.D. Washington, D.C. The reconstruction of maxillectomy defects
Sports Medicine Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Review Article Microsurgical Reconstruction of Large, Locally Advanced Cutaneous Malignancy of the Head and Neck
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 415219, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/415219 Review Article Microsurgical Reconstruction of Large, Locally Advanced
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 415219, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/415219 Review Article Microsurgical Reconstruction of Large, Locally Advanced
Interesting Case Series. Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Scalp
 Interesting Case Series Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Scalp Vasanth S. Kotamarti, BS, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Frank Ciminello, MD Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark Correspondence:
Interesting Case Series Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Scalp Vasanth S. Kotamarti, BS, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Frank Ciminello, MD Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark Correspondence:
Plate Exposure after Reconstruction by Plate and Anterolateral Thigh Flap in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with composite mandibular Defects
 Plate Exposure after Reconstruction by Plate and Anterolateral Thigh Flap in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with composite mandibular Defects Chia-Hsuan Tsai/ Huang-Kai Kao M. D. Introduction Malignant
Plate Exposure after Reconstruction by Plate and Anterolateral Thigh Flap in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with composite mandibular Defects Chia-Hsuan Tsai/ Huang-Kai Kao M. D. Introduction Malignant
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Flaps vs Grafts. Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC
 Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects
 Open Access Original Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2356 Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects Rhorie P. Kerr 1, Andrea Hanick 1, Michael A. Fritz 1 1. Head and Neck Institute,
Open Access Original Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2356 Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects Rhorie P. Kerr 1, Andrea Hanick 1, Michael A. Fritz 1 1. Head and Neck Institute,
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
17 FibulA FlAP Tor Chiu fibula flap 153
 17 Fibula Flap Tor Chiu Fibula Flap 153 Fibula Flap FLAP TERRITORY This flap includes a segment of the fibular bone with or without the overlying skin island on the peroneal/ lateral aspect of the calf.
17 Fibula Flap Tor Chiu Fibula Flap 153 Fibula Flap FLAP TERRITORY This flap includes a segment of the fibular bone with or without the overlying skin island on the peroneal/ lateral aspect of the calf.
BOAST 4 Algorithm. 6th September 2013
 BOAST 4 Algorithm 6th September 2013 Background The British Orthopaedic Association and the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons reviewed their 1997 guidance and published
BOAST 4 Algorithm 6th September 2013 Background The British Orthopaedic Association and the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons reviewed their 1997 guidance and published
Single-Stage Full-Thickness Scalp Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix and Skin Graft
 Single-Stage Full-Thickness Scalp Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix and Skin Graft Yoon S. Chun, MD, a and Kapil Verma, BA b a Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Single-Stage Full-Thickness Scalp Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix and Skin Graft Yoon S. Chun, MD, a and Kapil Verma, BA b a Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Surgery,
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects
 Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
Large full-thickness nasal tip defects after Mohs
 RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
Split Hemianterior Tibialis Turndown Muscle Flap for Coverage of Distal Leg Wounds With Preservation of Function
 Split Hemianterior Tibialis Turndown Muscle Flap for Coverage of Distal Leg Wounds With Preservation of Function Vinay Gundlapalli, MD, a John W. Gillespie III, MD, b and Chris D. Tzarnas, MD, FACS c a
Split Hemianterior Tibialis Turndown Muscle Flap for Coverage of Distal Leg Wounds With Preservation of Function Vinay Gundlapalli, MD, a John W. Gillespie III, MD, b and Chris D. Tzarnas, MD, FACS c a
Learning Objectives. Head and Neck Cancer: Post-Treatment Changes. Neck Dissection Classification * Radical neck dissection. Radical Neck Dissection
 Head and Neck Cancer: Post-Treatment Changes Daniel W. Williams III, MD Learning Objectives In patients treated for H/N Cancer: Describe the various types of neck dissections Explain reconstruction techniques
Head and Neck Cancer: Post-Treatment Changes Daniel W. Williams III, MD Learning Objectives In patients treated for H/N Cancer: Describe the various types of neck dissections Explain reconstruction techniques
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description)
 New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
Multi-dimensional analysis of oral cavity and oropharyngeal defects following cancer extirpation surgery, a cadaveric study
 Idris et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2018) 47:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-018-0276-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-dimensional analysis of oral cavity and
Idris et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2018) 47:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-018-0276-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-dimensional analysis of oral cavity and
Distal Femoral Resection
 Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects
 Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest
 Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest Jose L. Rios, M.D., Todd Pollock, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas The latissimus dorsi muscle
Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest Jose L. Rios, M.D., Todd Pollock, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas The latissimus dorsi muscle
-primarily by apposition of the anterior rectus
 2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL
 MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE - CONTAINS THE BLOOD VESSELS AND THE NERVES TO A MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE - LONGITUDINAL SECTION MUSCLE ATTACHMENTS: TENDONS
MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE - CONTAINS THE BLOOD VESSELS AND THE NERVES TO A MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE - LONGITUDINAL SECTION MUSCLE ATTACHMENTS: TENDONS
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
G24: Shoulder and Axilla
 G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
MEDIAL SURAL ARTERY PERFORATOR FLAP FOR TONGUE AND FLOOR OF MOUTH RECONSTRUCTION. Adequate speech and swallowing are dependent
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MEDIAL SURAL ARTERY PERFORATOR FLAP FOR TONGUE AND FLOOR OF MOUTH RECONSTRUCTION Shao-Liang Chen, MD, 1 Tim-Mo Chen, MD, 1 Niann-Tzyy Dai, MD, 1 Yi-Jan Hsia, DDS, MDSC, 2 Yaoh-Shiang Lin,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MEDIAL SURAL ARTERY PERFORATOR FLAP FOR TONGUE AND FLOOR OF MOUTH RECONSTRUCTION Shao-Liang Chen, MD, 1 Tim-Mo Chen, MD, 1 Niann-Tzyy Dai, MD, 1 Yi-Jan Hsia, DDS, MDSC, 2 Yaoh-Shiang Lin,
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
8 External Ear Canal Surgery
 30 Chapter 8 8 External Ear Canal Surgery Henning Hildmann, Holger Sudhoff Surgery in the external auditory canal without surgery in the middle ear may be necessary: 1. After surgery 2. After trauma 3.
30 Chapter 8 8 External Ear Canal Surgery Henning Hildmann, Holger Sudhoff Surgery in the external auditory canal without surgery in the middle ear may be necessary: 1. After surgery 2. After trauma 3.
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Reconstruction of axillary scar contractures retrospective study of 124 cases over 25 years
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
