The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
|
|
|
- Beatrice Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
2 729 Resective Treatment of Peri-implantitis: Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes After 2 Years Emmanuel Englezos, DDS, MSc 1 Jan Cosyn, DDS, PhD 2 Sebastiaan Koole, MSc, PhD 3 Wolfgang Jacquet, MSc, PhD 4 Hugo De Bruyn, DDS, PhD 5 A prospective case series was performed to examine the clinical and radiographic changes to peri-implant tissues 2 years after resective treatment of peri-implantitis, including an apically positioned flap, osteoplasty, and implantoplasty. In total, 25 patients with 40 titanium implants of multiple brands and advanced peri-implantitis were included in this study. After 2 years, all implants survived, mean probing pocket depth was reduced from 8.7 to 3.3 mm, and bone level remained stable in 92.5% of the implants. Findings suggest the approach of an apically positioned flap combined with osteoplasty and implantoplasty as an effective and reliable strategy against peri-implantitis, although increased gingival recessions may limit its application in esthetic areas. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2018;38: doi: /prd Researcher, Ghent University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dental School, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Ghent, Belgium; Private Practice Limited to Periodontology and Implant Dentistry, Haacht, Belgium. 2 Professor, Ghent University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dental School, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Ghent, Belgium; Visiting Professor, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Research Unit Oral Health, Brussels, Belgium. 3 Researcher, Ghent University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dental School, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Ghent, Belgium. 4 Researcher and Biostatistician, Ghent University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dental School, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Ghent, Belgium. 5 Professor, Ghent University, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Dental School, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Ghent, Belgium; Head of Department, Section Implantology and Periodontology, Department of Dentistry, Radboud UMC, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Correspondence to: Dr Emmanuel Englezos, Keerbergsesteenweg 20, 3150, Haacht, Belgium. emmanuelegglezos@yahoo.gr 2018 by Quintessence Publishing Co Inc. Peri-implantitis is defined as inflammatory lesions in the peri-implant tissues with loss of supporting bone and consequent deep pocketing. 1,2 The etiology of peri-implantitis is complex and multifactorial, including infection, occlusal overload, and compromised healing response. The most validated causal factor is the presence of a biofilm-triggered inflammatory host response. 3,4 The aim of peri-implantitis treatment is thus focused on reducing the total bacterial load, including improving oral hygiene, removal of bacterial deposits and cement rests from implant surfaces, allowing cleansability of the suprastructure, regular maintenance, and controlling factors that influence host response, such as smoking. Nonsurgical therapy of periimplantitis with or without adjunctive antibiotics is ineffective in completely controlling disease progression. The efficacy of submucosal scaling is compromised because of the difficulty of decontaminating implants due to surface roughness and the presence of implant threads. In addition, the form of the suprastructure can limit accessibility for cleaning. 5 Surgical therapy is considered the treatment of choice and consists of open flap debridement with removal of the inflammatory tissue and mechanical and chemical decontamination of the exposed Volume 38, Number 5, 2018
3 730 implant surface Open flap debridement combined with antibiotics in cases of a limited extent of peri-implantitis demonstrated high effectiveness. 11 Recontouring of the bony architecture without removing the supporting bone is defined as osteoplasty and is commonly applied in periodontal surgery. The approach of removing sharp bony edges and leveling angular defects and craters facilitates debridement, allows for apical positioning of the flap, and is efficient in reducing pockets. Similarly, this procedure is effective in treating peri-implantitis, though not in all cases 12,13 and depending on the initial depth of the defect. 12 The implant surface may influence the development of periimplantitis, as rough implants have a higher risk for peri-implantitis than do implants with machined surfaces. 2,14,15 A systematic review 16 indicated that moderately rough and rough implants lose more bone than minimally rough implants. It is therefore acceptable to assume that smoothing of the implant surface would provide a better environment and may improve infection control. It has been shown that polishing implants with diamond and carbide burs produces a smoother surface. This surface modification approach is referred to as implantoplasty. 17 Romeo et al 18,19 concluded that implant surface modification of rough implants is more effective in controlling peri-implantitis than resective flap surgery alone. However, at present there is no consensus on which surgical intervention is most predictive and reliable in controlling peri-implantitis. 20 The aim of the present prospective case series was to evaluate the 2-year outcome of resective surgery, defined as an apically positioned flap combined with osteoplasty and implantoplasty at advanced periimplantitis lesions around moderately rough implants. Materials and Methods Patients referred for treatment of peri-implantitis to a private periodontal clinic were asked to participate in the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 as revised in 2000, and the study protocol was approved by the Ghent University Hospital ethical committee. Initial treatment consisted of oral hygiene instructions, motivation, and supra- and submucosal implant surface instrumentation with ultrasonic and hand instruments. Suprastuctures were adapted when needed to facilitate plaque removal. Patients with persistent peri-implant pocket depth 6 mm were scheduled for apically positioned flap surgery with osteoplasty and implantoplasty. All patients had a clinical baseline examination prior to the surgery, assessing bleeding on probing (BoP), probing pocket depth (PD), and suppuration at four sites around every implant (mesial, distal, buccal, and lingual). A conventional periapical radiograph was taken of each implant using the long cone paralleling technique. An effort was made to attain clearly visible threads. The consecutive inclusion criteria to participate in this prospective case series were as follows: (1) BoP at the affected implant, (2) PD 6 mm, and (3) radiographic evidence of bone loss 3 mm below the expected boneimplant contact. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) implants with machined titanium surface; (2) implants with clinically visible mobility; and (3) severe systemic diseases, diseases affecting bone metabolism, hematologic disorders, psychiatric disorders, any form of malignant cancer, patients under high-dose bisphosphonate therapy, and all other medical contraindications for oral surgery. The implants included in the study were treated surgically, as described below (Figs 1 to 3) by the same clinician (E.E.). Screw-retained suprastructures were removed prior to surgery and were replaced after suturing. Cemented crowns and fixed or removable partial dentures were not removed. Full-thickness mucoperiosteal flaps were raised, and pocket epithelium and granulation tissue were removed. During this process, an attempt was made to preserve a band of keratinized tissue when present. Correction of the bony architecture and smoothing of angular defects and bony craters was performed with rotating diamond burs under copious irrigation (osteoplasty). The aim was to remove the angular component of the defect as much as possible. Afterward, the implant surfaces were debrided with carbon fiber hand curettes and with ultrasonic implant cleaning scalers (PI instrument, EMS). The implant surface was modified by removing the implant threads and surface coating by means of diamonds burs and Arkansas stones, followed by a The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
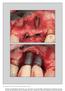
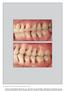
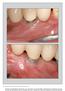
4 731 Fig 1 (a) Preoperative clinical photograph. (b) Baseline radiograph reveals angular bone loss and calcified deposits on the surface of the implant. a b Fig 2 (a) After removal of the screwretained partial denture, probing was possible. The preoperative pocket depth was 7 mm. (b) Elevation of a full-thickness mucoperiosteal flap provided access to the exposed implant surface and the bone margin. (c) A horizontal bone architecture was achieved with osteoplasty. Implantoplasty was used to polish the implant surface. (d) Apical repositioning of the flap was possible due to the removal of the angular component. Notice the preservation of a band of keratinized tissue around the implant. a b c d Fig3 (a) Clinical view at 2 years postoperative. There are no signs of inflammation. The apical positioning of the gingival margin led to marked recession and visible polished metal implant surface. The implant is easily accessible for interdental brushes. (b) Radiographic image shows no further bone loss and a stable bone margin. a b polish with brown and green polishing rubber flame-shaped burs under irrigation. This procedure is defined as implantoplasty. The implants were thoroughly cleaned afterward with gauze embedded in chlorhexidine and saline. The surgical site was further irrigated with saline to remove titanium particles from the surrounding tissues. Finally, the flaps were trimmed and positioned as apically as possible. Volume 38, Number 5, 2018
5 732 Table 1 Probing Pocket Depth (PPD) and Marginal Bone Level (BL) Prior to Treatment and at the 2-Year Follow-up Prior to treatment 2 y Treatment effect Parameter Mean SD Median tile range Mean SD Median tile range Mean SD Median tile range Interquar- P PD Mean value Deepest site BL Mean value Deepest site Statistical analysis of the treatment effect performed by means of Wilcoxon signed rank test with P <.05 as statistically significant. Following surgery, the patients were advised to take 3 g amoxicillin per day for 1 week and rinse with 0.12% chlorhexidine solution two times a day. Analgesics (ibuprofen or paracetamol) were prescribed. The sutures were removed after 2 weeks postoperatively. All the patients were recalled between 1 and 3 months after therapy. Afterward, the recall frequency varied from 2 to 4 times per year based on individual needs. At every recall appointment, the exposed implant surfaces were supra- and submucosally cleaned without anesthesia using carbon fiber curettes, ultrasonic implant cleaning scalers, rubber cups, and gauze with polishing paste. After 2 years, the same clinical and radiologic examinations as at baseline were performed. Outcome variables included BoP, suppuration, mean PD of four sites per implant, deepest PD value per implant, mean and the deepest radiographically visible bone loss mesial and distal at every implant, and gingival recession. Descriptive statistics on the outcome variables included frequency distributions and mean and median values, when applicable, with the implant as the experimental unit. Nonparametric statistics evaluated changes between baseline and 2-year follow-up using Wilcoxon signed rank test. All statistical analyses were executed using SPSS 22.0 (SPSS Statistics for Windows, IBM) with a preset significance level of P.05. Results A total of 25 patients with a mean age of 66.2 (SD 9.1) years, including 8 men (9 implants) and 17 women (31 implants), were treated. In total, 40 moderately rough surface implants were treated: 17 Nobel Biocare, 8 Straumann, 8 Ankylos, 1 Biomet3i, and 2 each of Astra, Zimmer, and IMZ. A total of six patients with 13 implants were smoking at the time of implant placement and continued to do so during the 2-year follow-up. One patient had Crohn s disease. All other patients were reported to be healthy. All patients but one had signs of a history of periodontal disease and radiographically visible bone loss. They had undergone previous periodontal therapy and periodontal maintenance. For edentulous patients, periodontal bone loss was diagnosed from previous dental records and radiographs. Of the affected implants, 8 supported a solitary crown and 13 supported fixed partial dentures, while 13 implants had implant-supported complete fixed dentures and 6 implants had overdentures. A total of 8 implants were located in the anterior maxilla and 14 in the posterior zone; 9 implants were in the anterior mandible and 9 implants in the posterior. No implants were lost, and no implants were surgically retreated during the 2-year follow-up. Plaque was present on 13 of 40 implants at the final assessment. The majority of patients (38 of 40) had plaque scores of < 10% at every control visit. Only two patients had scores > 40%. At the end of the examination period, 13 of 40 implants had PD 5 mm and 27 implants (67.5%) had PD 4 mm. The difference in PD before and after therapy was statistically significant (P.001). BoP was present on all implants at baseline The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
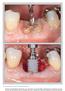
6 733 Fig 4 (a) Radiographic image of implant at baseline. (b) At 2 years after therapy, there was progression of bone loss despite therapy, possibly due to inadequate oral hygiene. The maxillary left first premolar was lost due to caries and replaced by an implant. The maxillary left second molar was lost due to endodontic reasons. a b as it was an inclusion criterion, but 2 years after therapy only 10 of 40 implants (25%) showed BoP. Suppuration was present at 28 of 40 implants (70%) at baseline, and only 1 implant (2.5%) remained with purulent exudate at 2 years post-therapy. The clinical parameters at implant level are summarized in Table 1. Therapy failed in only three implants in terms of further bone loss of 2 mm and a PD 6 mm at the 2-year evaluation. One of those demonstrated suppuration. These three failing implants belonged to two patients with plaque scores > 40% (Fig 4). Increase of gingival recession from baseline (after initial therapy) was observed at all implants and was expected due to the resective therapy. The mean increase was 2.5 (SD 0.85), and the median was 2 mm (range 2.00 to 3.00). Discussion The objective of the present study was to evaluate the 2-year outcome of resective surgery defined as an apically positioned flap combined with osteoplasty and implantoplasty for the treatment of peri-implantitis. Various treatments have been suggested for peri-implantitis, ranging from open flap debridement to complex soft and hard tissue grafting. Unfortunately, there is still conflicting evidence on which therapy offers the most predictable outcome. The patients in the present study were recruited from a private specialist and referral clinic and were treated consecutively. It has been emphasized that patients recruited from private or public dental clinics provide information on the effectiveness of the therapy, whereas patients treated in academic settings provide information on the efficacy of the treatment. 21 Peri-implantitis was clinically diagnosed by the referring dentist based on periimplant inflammation and unexpected bone loss. This clinical diagnosis, however, does not explain the etiologic factor inducing the disease. One may discuss whether all cases have a bacterial infection as primary cause and represent true disease or if bone loss was associated with factors such as incorrect implant positioning, traumatic surgical technique, failed bone augmentation, ill-fitting prosthesis, or cement rests. It was the choice of the clinician to treat all cases with the described technique in an effort to achieve the best possible clinical improvement. No cement rests were discovered, but visible calculus was present on the implant surface in almost all cases. This is related to ineffective oral hygiene and often associated with poor accessibility. 22 If necessary, the prosthetic construction was adjusted to facilitate plaque control. Osteoplasty and implantoplasty are technically demanding procedures. Complete removal of the angular component was not always achievable due to anatomical limitations including proximity of natural teeth, neurovascular bundles, or other vital structures. Flattening out of very deep defects would require removal of large amounts of sound bone. In such cases, a residual angular component remained after the therapy. In general, as predicted, small angular defects with a maximum depth of 3 mm were removed, whereas defects deeper than 5 mm were only reduced in depth. Additionally, it was not always possible to access all exposed implant surfaces with rotary instruments. In some cases, implantoplasty was incomplete at the depth of the defect, Volume 38, Number 5, 2018
7 734 especially at the lingual and palatal sides. The coronal portions of the implants were easily accessible and therefore could be adequately polished in all cases. Removal of implant threads should be done with the utmost care since overinstrumentation may weaken the implant and lead to future fractures. One pitfall of this technique is the time required for the implantoplasty and the concomitant removal of the scattered titanium particles. It is practically impossible to remove all of them from the hard and soft tissues of the surgical site, but the remaining particles do not seem to have a clinically important effect on healing. A recent report 23 suggested that antibiotics may be beneficial for implants with a modified surface. The authors argued that due to the aggressive nature of peri-implantitis and the proximity of the inflammatory lesions to the bone marrow, the use of systemic antibiotics and local antimicrobials could be effective. 24 There were no complications or adverse effects related to the therapy or the use of the prescribed medication. Ideally, the goal of periimplantitis treatment would be complete resolution of the disease and reestablishment and maintenance of healthy peri-implant tissues. That would be clinically reflected in a combined outcome of peri-implant PD of < 5 mm without bleeding on probing, no suppuration, and no ongoing bone loss. Since such data are rarely reported in the literature, criteria for successful treatment were proposed, including implant survival, mean PD < 5 mm, and no ongoing bone loss. 25 In the present study, all implants survived and 37 of the 40 implants (92.5%) reached the above-mentioned criteria. When absence of BoP is added to the criteria, the success rate of the treatment decreases to 75%. The observed reduction in PD was attributed to the increase in gingival recession and the increased tissue tonus. 26 In almost all cases, recession resulted in large open embrasure spaces with visible metal of the implant-abutment complex. It is important to inform patients prior to therapy about potential esthetic consequences. Patients with esthetic concerns should be offered alternative treatment options, including the use of bone grafts for filling in peri-implant defects or removal of implants. In cases of extremely advanced bone loss or challenging anatomical situations that limit access for cleaning and instrumentation, one can consider explantation of an alternative treatment. Each therapeutic modality should be evaluated in terms of predictability and economic aspects. A patientindividualized approach should be followed for every particular case. The results of the present study are slightly inferior to previously reported findings. 18,19 This may be attributed to the inadequate plaque control at three implants, deeper baseline PD, and deeper initial bone defects. The importance of strict plaque control and of regular supportive therapy is undoubted. 2,27,28 The authors observations further emphasize the importance of plaque control in the treatment of peri-implantitis. All the implants in patients with low plaque scores remained stable, and the two patients with high plaque scores suffered from progressive bone loss. In addition, the literature has identified smoking as an important influencing factor for the treatment outcome. 2,13,29 The present patient group included only six smokers. The authors did not observe any differences in healing response, but the small number of smokers prevents any strong conclusion. Furthermore, it needs to be emphasized that all smoking patients were very compliant with the supportive care program and performed meticulous individual plaque control. Conclusions The results of the study suggest that the applied surgical therapy, aimed at pocket elimination with an apically positioned flap, osteoplasty, and implant surface smoothing, is effective and predictable to arrest periimplantitis progression for a period of 2 years. However, compliance with meticulous daily plaque control is paramount. The esthetic outcome may limit applicability in the anterior maxilla. Acknowledgments Prof Cosyn has a collaboration agreement with Nobel Biocare (Gothenburg, Sweden). Prof De Bruyn has educational and research collaboration agreements with Dentsply Sirona (York, Pennsylvania, USA) and Southern Implants (Irene, South Africa). None of the authors reported any conflict of interest related to the study or products involved. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
8 735 References 1. Zitzmann NU, Berglundh T. Definition and prevalence of peri-implant diseases. J Clin Periodontol 2008;35(suppl): s286 s Heitz-Mayfield LJ. Peri-implant diseases: Diagnosis and risk indicators. J Clin Periodontol 2008;35(suppl):s292 s Renvert S, Quirynen M. Risk indicators for peri-implantitis. A narrative review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2015;26(suppl): s15 s Heitz-Mayfield LJ, Lang NP. Comparative biology of chronic and aggressive periodontitis vs. peri-implantitis. Periodontology ;53: Renvert S, Roos-Jansåker AM, Claffey N. Non-surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A literature review. J Clin Periodontol 2008;35 (suppl):s305 s Renvert S, Polyzois I, Claffey N. Surgical therapy for the control of periimplantitis. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012;23(suppl):s84 s Ntrouka VI, Slot DE, Louropoulou A, Van der Weijden F. The effect of chemotherapeutic agents on contaminated titanium surfaces: A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2011;22: Louropoulou A, Slot DE, Van der Weijden F. The effects of mechanical instruments on contaminated titanium dental implant surfaces: A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2014; 25: Leonhardt A, Dahlén G, Renvert S. Fiveyear clinical, microbiological, and radiological outcome following treatment of peri-implantitis in man. J Periodontol 2003;74: Máximo MB, de Mendonça AC, Renata Santos V, Figueiredo LC, Feres M, Duarte PM. Short-term clinical and microbiological evaluations of peri-implant diseases before and after mechanical anti-infective therapies. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20: Heitz-Mayfield LJ, Salvi GE, Mombelli A, Faddy M, Lang NP, Implant Complication Research Group. Anti-infective surgical therapy of peri-implantitis. A 12-month prospective clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012;23: Serino G, Turri A. Outcome of surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: Results from a 2-year prospective clinical study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 2011; 22: de Waal YC, Raghoebar GM, Meijer HJ, Winkel EG, van Winkelhoff AJ. Prognostic indicators for surgical peri-implantitis treatment. Clin Oral Implants Res 2016; 27: Rimondini L, Farè S, Brambilla E, et al. The effect of surface roughness on early in vivo plaque colonization on titanium. J Periodontol 1997;68: Bollen CM, Papaioanno W, Van Eldere J, Schepers E, Quirynen M, van Steenberghe D. The influence of abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and peri-implant mucositis. Clin Oral Implants Res 1996;7: Doornewaard R, Christiaens V, De Bruyn H, et al. Long-term effect of surface roughness and patients factors on crestal bone loss at dental implants. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2017;19: Rimondini L, Cicognani Simoncini F, Carrassi A. Micro-morphometric assessment of titanium plasma-sprayed coating removal using burs for the treatment of peri-implant disease. Clin Oral Implants Res 2000;11: Romeo E, Ghisolfi M, Murgolo N, Chiapasco M, Lops D, Vogel G. Therapy of peri-implantitis with resective surgery. A 3-year clinical trial on rough screwshaped oral implants. Part I: Clinical outcome. Clin Oral Implants Res 2005; 16: Romeo E, Lops D, Chiapasco M, Ghisolfi M, Vogel G. Therapy of peri-implantitis with resective surgery. A 3-year clinical trial on rough screw-shaped oral implants. Part II: Radiographic outcome. Clin Oral Implants Res 2007;18: Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Maghaireh H, Coulthard P, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Management of soft tissues for dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;(3):CD Lindhe J, Meyle J, Group D of European Workshop on Periodontology. Periimplant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35(suppl):s282 s Serino G, Ström C. Peri-implantitis in partially edentulous patients: Association with inadequate plaque control. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20: Carcuac O, Derks J, Charalampakis G, Abrahamsson I, Wennström J, Berglundh T. Adjunctive systemic and local antimicrobial therapy in the surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J Dent Res 2016; 95: Berglundh T, Zitzmann NU, Donati M. Are peri-implantitis lesions different from periodontitis lesions? J Clin Periodontol 2011;38(suppl):s188 s Heitz-Mayfield LJ, Mombelli A. The therapy of peri-implantitis: A systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2014;29(suppl):s325 s Mombelli A, Mühle T, Brägger U, Lang NP, Bürgin WB. Comparison of periodontal and peri-implant probing by depth-force pattern analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 1997;8: Roos-Jansåker AM, Lindahl C, Renvert H, Renvert S. Nine- to fourteen-year follow-up of implant treatment. Part I: Implant loss and associations to various factors. J Clin Periodontol 2006;33: Roos-Jansåker AM, Renvert H, Lindahl C, Renvert S. Nine- to fourteen-year followup of implant treatment. Part III: Factors associated with peri-implant lesions. J Clin Periodontol 2006;33: Aglietta M, Siciliano VI, Rasperini G, Cafiero C, Lang NP, Salvi GE. A 10- year retrospective analysis of marginal bone-level changes around implants in periodontally healthy and periodontally compromised tobacco smokers. Clin Oral Implants Res 2011;22: Volume 38, Number 5, 2018
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
Case Presentation. Overall Health. Oral Hygiene. Chief Complaint. I hate my upper denture. I can t taste food. I want an implant solution
 Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Straumann SmartOne. Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance. Step 2 Maintenance visit
 Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen
![Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen](/thumbs/82/86452679.jpg) University of Groningen Peri-implant infections de Waal, Yvonne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Peri-implant infections de Waal, Yvonne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Treatment Concepts for PERI-IMPLANTITIS
 Treatment Concepts for PERI-IMPLANTITIS CONTENT Definition, diagnosis and prevalence 3 Risk factors and preventive measures 5 Latest evidence on the treatment of peri-implantitis 6 Clinical Cases Regenerative
Treatment Concepts for PERI-IMPLANTITIS CONTENT Definition, diagnosis and prevalence 3 Risk factors and preventive measures 5 Latest evidence on the treatment of peri-implantitis 6 Clinical Cases Regenerative
Porous titanium granules in the treatment of peri-implant osseous defects a 7-year follow-up study
 Andersen et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:50 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0106-2 International Journal of Implant Dentistry SHORT REPORT Open Access Porous titanium granules in the
Andersen et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:50 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0106-2 International Journal of Implant Dentistry SHORT REPORT Open Access Porous titanium granules in the
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr.
 Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient. Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club
 Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Primary prevention of periimplantitis: peri-implant mucositis S152
 J Clin Periodontol 2015; 42 (Suppl. 16): S152 S157 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12369 Primary prevention of periimplantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis Jepsen S, Berglundh T, Genco R, Aass AM, Demirel K, Derks
J Clin Periodontol 2015; 42 (Suppl. 16): S152 S157 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12369 Primary prevention of periimplantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis Jepsen S, Berglundh T, Genco R, Aass AM, Demirel K, Derks
Case Report Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Peri-Implantitis: A Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 2491714, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2491714 Case Report Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Peri-Implantitis: A Report
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 2491714, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2491714 Case Report Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Peri-Implantitis: A Report
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1
 PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
What You Should Know About Dental Implants: The Process of Care Applies
 Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy
 Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Is peri-implant maintenance therapy (PIMT) important for preventing peri-implant disease?
 C L I N I C A L Is peri-implant maintenance therapy (PIMT) important for preventing peri-implant disease? Johan Hartshorne 1 A critical appraisal of a systematic review: A. Monje, L. Aranda, K.T. Diaz,
C L I N I C A L Is peri-implant maintenance therapy (PIMT) important for preventing peri-implant disease? Johan Hartshorne 1 A critical appraisal of a systematic review: A. Monje, L. Aranda, K.T. Diaz,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment
 The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology
 Article Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology LANG, Niklaus P, BERGLUNDH, Tord, MOMBELLI, Andrea Abstract Peri-implant diseases present in
Article Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology LANG, Niklaus P, BERGLUNDH, Tord, MOMBELLI, Andrea Abstract Peri-implant diseases present in
Periodontal Maintenance
 Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 485 Bacterial Biofilm Morphology on a Failing Implant with an Oxidized Surface: A Scanning Electron Microscope Study Massimo Simion, MD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 485 Bacterial Biofilm Morphology on a Failing Implant with an Oxidized Surface: A Scanning Electron Microscope Study Massimo Simion, MD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Periodontitis & Implants
 Objectives Periodontitis & Implants Dr Simon Hinckfuss D.C.D (Melb), Cert.Perio, MS (Minn, USA) Diplomat of the American Board of Periodontology Diagnose common types of periodontal disease Describe the
Objectives Periodontitis & Implants Dr Simon Hinckfuss D.C.D (Melb), Cert.Perio, MS (Minn, USA) Diplomat of the American Board of Periodontology Diagnose common types of periodontal disease Describe the
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera
 Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera Periodontal Clinic, Semmelweis University, Budapest 2017.02.14. Complex periodontal therapy Systemic phase
Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera Periodontal Clinic, Semmelweis University, Budapest 2017.02.14. Complex periodontal therapy Systemic phase
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Clinical outcomes following surgical treatment of peri-implantitis at grafted and non-grafted implant sites: a retrospective analysis
 Ramanauskaite et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2018) 4:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0135-5 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Clinical outcomes following surgical
Ramanauskaite et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2018) 4:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0135-5 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Clinical outcomes following surgical
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Retrospective analysis of periimplantitis therapy
 Retrospective analysis of periimplantitis therapy of 158 implants Abstract Objective Jörg-Ulf Wiegner, a Hermann Klinsmann a & Toralf Kömmling b a Private practice, Saalfeld, Germany b Private practice,
Retrospective analysis of periimplantitis therapy of 158 implants Abstract Objective Jörg-Ulf Wiegner, a Hermann Klinsmann a & Toralf Kömmling b a Private practice, Saalfeld, Germany b Private practice,
Full Arch Hygiene Protocol
 Full Arch Hygiene Protocol Patients should be evaluated and categorized into 3 different Recall Frequency Groups (RFG s). An evaluation of homecare should be made during the prosthetic phase of treatment
Full Arch Hygiene Protocol Patients should be evaluated and categorized into 3 different Recall Frequency Groups (RFG s). An evaluation of homecare should be made during the prosthetic phase of treatment
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93.
 Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic case report.
 European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT. Inside this issue: 2014 No. 3. Peri-implant disease Implant surface: An evolution Summaries of select scientific publications
 www.jird.com SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT Inside this issue: Peri-implant disease Implant surface: An evolution Summaries of select scientific publications Official Publication of The Institute for Implant and Reconstructive
www.jird.com SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT Inside this issue: Peri-implant disease Implant surface: An evolution Summaries of select scientific publications Official Publication of The Institute for Implant and Reconstructive
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Is Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy Cost Effective? Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information
Is Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy Cost Effective? Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information
Peri-implant marginal bone loss: What is the current concensus? an academic controversy or a clinical challenge?
 Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
As an increasing number of
 LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
2017 WORLD WORKSHOP. Received: 20 December 2017 Revised: 6 February 2018 Accepted: 1 March DOI: /jcpe.12957
 Received: 20 December 2017 Revised: 6 February 2018 Accepted: 1 March 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12957 2017 WORLD WORKSHOP Peri implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017
Received: 20 December 2017 Revised: 6 February 2018 Accepted: 1 March 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12957 2017 WORLD WORKSHOP Peri implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 91 Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Levels in Peri-implant Sulcus Fluid Adjacent to Titanium and Zirconium Nitride Surfaces Richard Meissen,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 91 Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Levels in Peri-implant Sulcus Fluid Adjacent to Titanium and Zirconium Nitride Surfaces Richard Meissen,
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Reclaiming the Lost Bastion for Successful Implant Therapy: A Case Series
 Rima Jaiswal et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1146 Reclaiming the Lost Bastion for Successful Implant Therapy: A Case Series 1 Rima Jaiswal, 2 S Mahantesha, 3 S Ashwini ABSTRACT Introduction:
Rima Jaiswal et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1146 Reclaiming the Lost Bastion for Successful Implant Therapy: A Case Series 1 Rima Jaiswal, 2 S Mahantesha, 3 S Ashwini ABSTRACT Introduction:
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review
 The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
PERIODONTAL ABSCESS TO PERIODONTAL PROSTHESIS: A MULTI-DISCIPLINARY JOURNEY
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report PERIODONTAL ABSCESS TO PERIODONTAL PROSTHESIS: A MULTI-DISCIPLINARY JOURNEY Renganath M. J. 1, Ramakrishnan T. 2, Anithadevi S. 1,
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report PERIODONTAL ABSCESS TO PERIODONTAL PROSTHESIS: A MULTI-DISCIPLINARY JOURNEY Renganath M. J. 1, Ramakrishnan T. 2, Anithadevi S. 1,
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery
 Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Optimal Peri- Implant Maintenance Science, Systems, and Success! Susan S. Wingrove RDH, BS RDH UnderOneRoof Chicago, IL 2014
 Optimal Peri- Implant Maintenance Science, Systems, and Success! Susan S. Wingrove RDH, BS RDH UnderOneRoof Chicago, IL 2014 Tooth Replacement treatment options and benefits Identify Existing Patients
Optimal Peri- Implant Maintenance Science, Systems, and Success! Susan S. Wingrove RDH, BS RDH UnderOneRoof Chicago, IL 2014 Tooth Replacement treatment options and benefits Identify Existing Patients
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental Toothbrushes in removing Dental Plaque
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental Toothbrushes 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1147 in removing Dental Plaque Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental
RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental Toothbrushes 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1147 in removing Dental Plaque Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation. Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman
 Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester
 Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester 1. Periodontal Assessment Signs of perio disease: - Gingivae become red/purple - Gingivae
Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester 1. Periodontal Assessment Signs of perio disease: - Gingivae become red/purple - Gingivae
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Implant decontamination during surgical peri-implantitis treatment de Waal, Yvonne; Raghoebar, Gerry; Slater, J.J.R.; Meijer, Hendrikus; Winkel, Edwin; van Winkelhoff, Arie Jan
University of Groningen Implant decontamination during surgical peri-implantitis treatment de Waal, Yvonne; Raghoebar, Gerry; Slater, J.J.R.; Meijer, Hendrikus; Winkel, Edwin; van Winkelhoff, Arie Jan
Initial Therapy. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS. Oral sulcular epithelium. Oral. epithelium. Junctional. epithelium. Connective tissue.
 Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Correlations between clinical parameters in implant maintenance patients: analysis among healthy and history-of-periodontitis groups
 Seki et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:45 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0108-0 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Correlations between clinical parameters in implant
Seki et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:45 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0108-0 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Correlations between clinical parameters in implant
I have always enjoyed Dr. Steigmann s lecture because it is practical, insightful and supported with sound rationale
 March 19-24, 2018 1 Introduction I have always enjoyed Dr. Steigmann s lecture because it is practical, insightful and supported with sound rationale Prof. Hom Lay Wang Dr. Marius Steigmann Dr. Steigmann
March 19-24, 2018 1 Introduction I have always enjoyed Dr. Steigmann s lecture because it is practical, insightful and supported with sound rationale Prof. Hom Lay Wang Dr. Marius Steigmann Dr. Steigmann
Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment
 SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang.
 Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang. NIWOP: The systematic and evidence-based workflow #niwop wh.com No Implantology without Periodontology NIWOP 1 Pretreatment Optimal periodontal
Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang. NIWOP: The systematic and evidence-based workflow #niwop wh.com No Implantology without Periodontology NIWOP 1 Pretreatment Optimal periodontal
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Astra Tech Implant System. Scientific Summary
 Astra Tech Implant System Scientific Summary Why we do what we do? Our vision of a world where everyone eats, speaks and smiles with confidence permeates and inspires everything we do. We believe in an
Astra Tech Implant System Scientific Summary Why we do what we do? Our vision of a world where everyone eats, speaks and smiles with confidence permeates and inspires everything we do. We believe in an
Frank Schwarz *, Andrea Schmucker and Jürgen Becker
 Schwarz et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:22 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0023-1 REVIEW Efficacy of alternative or adjunctive measures to conventional treatment of peri-implant mucositis
Schwarz et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:22 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0023-1 REVIEW Efficacy of alternative or adjunctive measures to conventional treatment of peri-implant mucositis
Newport News Public Schools Summary Schedule of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan
 Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Case Report Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report Po-Yu Lai, DDS, MS School of Dentistry, National Yang-Ming University Shing-Wai Yip, DDS, MS, DScD Prosthodontics
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report Po-Yu Lai, DDS, MS School of Dentistry, National Yang-Ming University Shing-Wai Yip, DDS, MS, DScD Prosthodontics
