Patient Self-reported Satisfaction with Maxillary Anterior Dental Implant Treatment
|
|
|
- Rafe Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient Self-reported Satisfaction with Maxillary Anterior Dental Implant Treatment Anna Levi, DDS, MDSc 1 /Walter J. Psoter, DDS, PhD 2 /John R. Agar, DDS, MA 3 / Susan T. Reisine, PhD 4 /Thomas D. Taylor, DDS, MS 5 Purpose: Dental implants are accepted as a successful alternative to conventional fixed and removable prostheses for the treatment of partial or complete edentulism. However, there have been few studies of the success of implants from the patients perspective. The purpose of this study was to assess patient overall satisfaction with the outcome of treatment with maxillary anterior implants. Materials and Methods: A self-administered mailed questionnaire, which was developed for this project, and a data abstraction form, which was designed based on information available from the corresponding dental records of 123 eligible subjects, were utilized to survey implant patients. Results: Seventy-eight of 123 eligible subjects responded to the mailed, self-administered, structured questionnaire. Twelve of the 24 questionnaire variables demonstrated statistically significant bivariate associations with the dependent variable overall patient satisfaction. Five variables implant position, definitive restoration shape, appearance, effect on speech, and chewing capacity were strongly associated with overall satisfaction. No demographic or treatment-related, dental record abstracted variable, of the 25 that were examined, was statistically significant. Discussion: The practitioner who provides implant restorations should be aware of the multidimensional aspects of patient satisfaction with implant treatment. This study suggests that patient satisfaction with key elements influences the overall acceptance of maxillary anterior implant prostheses, which are esthetically critical. Communication between dentist and patient is important to achieve optimal results that will be satisfactory to both. Discussion of treatment limitations may also help patients to develop realistic expectations of the final result. Conclusions: In this limited investigation, patient satisfaction with implant position, restoration shape, overall appearance, effect on speech, and chewing capacity were critical for patient overall acceptance of the dental implant treatment. (Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18: ) Key words: dental esthetics, dental implants, patient satisfaction, questionnaires Dental implants are accepted as a successful alternative to conventional fixed and removable prostheses and have been demonstrated to be 1 Teaching Assistant, Department of Prosthodontics, University of Athens Dental School, Athens, Greece. 2 Assistant Professor, New York University College of Dentistry, Department of Epidemiology and Health Promotion, New York, New York; School of Dentistry, University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus, San Juan, Puerto Rico. 3 Associate Professor, Program Director of Graduate Prosthodontics, Department of Prosthodontics and Operative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, University of Connecticut, Farmington, Connecticut. 4 Professor, Department of Behavioral Sciences and Community Medicine, School of Dentistry, University of Connecticut, Farmington, Connecticut. 5 Professor and Chief, Department of Prosthodontics and Operative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, University of Connecticut, Farmington, Connecticut. Reprint requests: Dr Anna Levi, 38th, Zalokosta St, 15232, Halandri, Athens, Greece. Fax: levi@lar.forthnet.gr predictable and moderately trouble-free for the treatment of partial and complete edentulism, as judged by clinicians from a biologic standpoint. 1 9 The impact of dental implant treatment on patient quality of life (QOL) has been discussed in the literature It has been stated that it is important to use QOL measures, particularly when the conditions that are being studied are not life threatening and the treatment options may vary. 10 A report regarding the proceedings of the Toronto Symposium (1998) concluded that patient satisfaction outcome measures should be included in future implant success criteria, 9 highlighting the importance of the patient s perspective in clinical practice. Patient-based assessments of treatment outcomes have been reported for complete dentures Examples include the evaluation of patient satisfaction with complete dentures and masticatory performance and patient assessment of the perceived benefit from using dental implants to improve support and retention of complete dentures The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 113
2 Few surveys have been conducted regarding patient satisfaction with dental implant treatment in reference to maxillary fixed restorations Carlson and Carlsson 29 reported findings from a survey conducted during clinical recalls, indicating that 17% of those patients were dissatisfied with their implant prostheses and that one third of this dissatisfaction was attributed to esthetic problems. Only 1 study 30 (n = 39 patients) has investigated patient satisfaction specifically related to maxillary anterior teeth; this study compared patients and specialists opinions regarding esthetic results and reported that patients and prosthodontists disagree as to what each group considers important in achieving optimal esthetic results. Satisfaction with the esthetic result is an important determinant of patient overall satisfaction with dental implant treatment. 11,29 The most obvious area by which to judge esthetics is the maxillary anterior region, because it is particularly visible to the patient and others. Since the criteria for assessing the quality of the esthetic result are subjective, it is imperative to inquire about the patients opinion, which may differ from that of the clinician, so as to ensure patient satisfaction 31 with the final outcome. The purpose of this study was to examine whether there is an association between overall satisfaction with dental implant treatment and: (1) patient perceptions of selected technical aspects of treatment outcome, (2) patient perceptions of treatment experience, (3) clinical variables related to dental implant treatment, and (4) patient demographic characteristics. MATERIALS AND METHODS Study Design This cross-sectional study examined the association between overall satisfaction of patients treated with dental implants for the replacement of maxillary anterior teeth and treatment- and patient-related factors. An instrument was developed in this project to survey patients who had been treated with dental implants. This survey instrument (self-administered, structured, mailed questionnaire) and data abstracted from the corresponding patients dental records were utilized to assess patients overall satisfaction with maxillary dental implant treatment. The self-administered mailed questionnaire and dental record data abstraction form consisted of 24 and 25 items, respectively. Bivariate analysis was utilized to assess the association between the subjects overall satisfaction with the dental implant treatment questionnaire and dental record abstracted variables. The research protocol was reviewed and approved by the University of Connecticut Health Center (UCHC) Institutional Review Board. Sample Selection The study population consisted of all patients who had been treated with at least 1 dental implant in the area of teeth 4 to 13 (maxillary incisors, canines, and premolars), by the UCHC Prosthodontic and Advanced Education in General Dentistry residents and prosthodontic faculty, during the period January 1988 to July Those patients whose definitive restoration was completed and functional at the time of subject recruitment (May to August 2000) were included in this study. Patients treated by the investigators of this study were excluded from the study. Eligible patients were identified from the UCHC dental finance computerized records by corresponding procedure codes associated with implant surgical and prosthodontic treatment and then verified by dental record documentation as to meeting the inclusion criteria. Questionnaire and Record Abstraction A 24-item, self-administered, structured multipleresponse questionnaire was developed to serve as the instrument for this survey. The questionnaire covered the subjects overall satisfaction with their dental implant treatment, their perception of various technical aspects of their implant restoration, and specific aspects of treatment and the definitive prosthesis. Examples of survey questions included such items as: were cost and time until completion of treatment reasonable; did the patient like the treating doctor; did the patient think they experienced complications; and inquiries about selected demographic information. The subjects rated their satisfaction on a 4-point Likert scale for each item (1 = Highly Dissatisfied to 4 = Highly Satisfied or 1 = Strongly Disagree to 4 = Strongly Agree ). All subjects were given specific instructions to evaluate and answer the survey relative to only 1 implant restoration in their mouth ie, the implant that had the most anterior (mesial) position, regardless of other existing implant restorations. Eligible patients (n = 123) were subsequently mailed: (1) an introductory letter from the Director of the Graduate Prosthodontic Program; and (2) a package, which included a cover letter, the questionnaire itself, and a return-addressed, stamped envelope. A second survey package was sent to the initial non-respondents (cover letter, questionnaire, and return-addressed, stamped envelope). Dental Record Data Abstraction Data abstraction from dental records (25 items) of all eligible patients (n = 123) was conducted blind to 114 Volume 18, Number 1, 2003
3 the questionnaire data by one of the investigators. The abstraction included information regarding the patients dental and medical history, demographic data, and details about the dental implant treatment itself (eg, type of implant placed and whether a grafting procedure was performed). Statistical Analyses The dental record and the questionnaire data were double-entered in Epi Info version 6.04 (US Center for Disease Control and Prevention). Statistical analyses utilized SPSS version 10.1 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL). Overall patient satisfaction was considered the dependent variable, and the independent variables were the dental record abstracted data (25 variables) and the questionnaire responses on specific questions, other than overall satisfaction (23 variables). 1. Descriptive statistics of demographic data were tested for a statistical difference between subjects and nonparticipants. 2. Frequencies were obtained to describe the response distribution of questionnaire and the dental record abstracted items. 3. Most variables were dichotomized, and the Fisher exact test for categorical variables or t test for continuous variables was used to test bivariate associations with the overall satisfaction variable. Bivariate odds ratios (ORs) and confidence intervals (CIs) were produced by logistic regression for the variables shown to be statistically significant at a level of P.05. RESULTS The first questionnaire mailing produced a 50% response (n = 62), with the second mailing bringing the response to 63% (n = 78); however, 2 subjects failed to complete all questions. Sixty-seven (88.2%) of the subjects answered the overall satisfaction question with the highest possible response ( highly satisfied ), 8 (10.5%) were somewhat satisfied, and 1 (1.3%) was somewhat dissatisfied. The subjects mean age was 56 years old, ranging from 18 to 80 years. Fifty-two percent of the subjects were women and 47% were men. Forty-five (58%) of the sample were married and 32 (42%) were not currently married. This sample was highly educated; 78% of the subjects had at least some college education. Thirty subjects (45%) had an annual income above $50,000 (Table 1). Eighty-eight percent of the subjects answered the overall satisfaction question with the highest Table 1 Demographic Characteristics of Implant Satisfaction Survey Subjects (n = 78) Variable Frequency (%) Age (n = 78) 35 and under 8 (10.2) (16.6) (16.6) (25.6) Over (30.7) Gender (n = 78) Male 37 (47.4) Female 41 (52.5) Marital status (n = 77) Single 19 (24.7) Divorced 9 (11.7) Widowed 4 (5.2) Married 45 (58.4) Education level (n = 76) Eighth grade or less 3 (3.9) Some high school 1 (1.3) Graduated high school 12 (15.8) Some college 21 (27.6) Graduated college 20 (26.3) More than college 19 (25.0) Annual income (n = 65) Less than $10,000 5 (7.5) $10,000 25, (16.4) $25,000 50, (28.4) $50, , (28.4) $100,000 or more 11 (16.4) possible favorable response. Given this response distribution, it was decided to dichotomize the dependent variable into 2 groups, highly and less than highly satisfied, by aggregating the 3 less than highly satisfied potential responses. The questionnaire and dental record abstracted variables likewise had a generally skewed distribution, with the highest frequencies in the more favorable categories, and they also were dichotomized on their highest and less than highest levels. Table 2 presents data abstracted from dental records, comparing study subjects to questionnaire nonrespondents for selected variables. Relation of treatment to chief complaint approached statistical significance (P =.06). No other variable was statistically significant at the.05 level. The chief complaint of each patient was recorded from an existing form, which had been completed prior to the beginning of the treatment, and the judgment was made blind to participation status (by AL) as to whether the dental implant treatment was related to the chief complaint. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 115
4 Table 2 Comparison of Eligible Nonparticipants and Subjects of Implant Satisfaction Survey Variable Nonparticipants Subjects P value Mean age * Gender.710** Male Female Complications 1.000** No Yes 9 13 Previous implant failure.758** No Yes 1 1 Relation of treatment to chief complaint.06** No Yes Mean length of * treatment (days) * test; **Fisher exact test. As reported in progress notes (examples include abutment or occlusal screw loosening or fracture, anesthesia or paresthesia, and infection). The chief complaint of the patients was recorded from an existing form, which had been completed prior to the beginning of the treatment, and the judgment was made (by AL) as to whether it was relevant to the dental implant treatment. Table 3 Bivariate Odds Ratios (ORs) and Confidence Intervals (CIs) of Questionnaire Variables That Were Related to Patient Overall Satisfaction* Variable OR 95% CI P value Shape Position Appearance when smiling Comparison with natural teeth Speech Chewing capacity Comfort Complications Information prior to treatment Would redo treatment Would recommend treatment Satisfaction with doctor *As determined initially by Fisher exact test at a statistically significant level (P.05). Fisher exact test and t test analyses were utilized to examine the relationships between dichotomized overall satisfaction and questionnaire and data abstraction variables. Neither the demographic (age, gender, marital status, educational level, income) nor any other variables abstracted from the dental records (type, length, or diameter of implant; smoking habits; history of psychologic disorder; complications) were statistically significant, although the type of provisional restoration tested at P =.074. For the questionnaire variables, implant restoration color was the only esthetic variable specific to the implant restoration that was not related bivariately to overall satisfaction (P = 1.000). The questionnaire variables describing satisfaction with the appearance of the soft tissues around the dental implant, oral health, cost, and time until completion of treatment and factors such as who influenced your decision to select dental implant treatment were not significantly related to overall satisfaction. Cost approached statistical significance (P =.056). Twelve questionnaire variables demonstrated bivariate associations at a significant level of P.05. The significant variables were: (1) satisfaction with appearance (4 variables), (2) function (3 variables), (3) satisfaction with the treating doctor, (4) information about the procedure and outcome prior to treatment, (5) presence of complications, and (6) willingness to redo or recommend the procedure (2 variables). Logistic regression was conducted to assess the strength of association for these variables. The bivariate ORs and CIs of those variables are presented in Table 3. These point estimates ranged from ORs of 5.8 to 113.7, all with wide confidence intervals, which reflected the small sample size. The variables (1) position of the implant restoration, (2) shape of the implant restoration, (3) appearance when smiling, (4) speech, and (5) chewing capacity demonstrated strong associations with the patients self-reported overall satisfaction. It is important to note the instability of the point estimates, which is clearly demonstrated by the wide confidence intervals. However, the lower 95% confidence bound for each of these is greater than 3, which indicates a strong association. These results suggest that patients who were highly satisfied with the position of their implantsupported restoration were 113 times more likely to be highly satisfied with their overall treatment (OR = 113), compared to patients who were less than highly satisfied with their implant position. Similarly, patients who were highly satisfied with their chewing capacity were 20 times more likely to be highly satisfied with their overall treatment (OR = 20), compared to patients who were less than highly satisfied with this variable. The reliability of the questionnaire was assessed using the Cronbach alpha coefficient, 32,33 which was 116 Volume 18, Number 1, 2003
5 Table 4 2 By 2 Table of Variables Having a Large Proportion of Less Than Highly Satisfied Responses Overall satisfaction Less than Highly Highly P Variable Response Satisfied Satisfied value* Questionnaire variable Cost reasonable Strongly Agree 20 0 Less than Strongly Agree Time until completion Strongly Agree 20 1 of treatment reasonable Less than Strongly Agree Dental record abstracted variable Type of provisional Partial denture 30 1 restoration Other *As determined initially by Fisher exact test This estimate reflects a highly acceptable level of internal consistency. The variables included in this reliability analysis were the questionnaire variables (21), which required responses ranging from 1 through 4. DISCUSSION Dental implants have demonstrated high success rates, as judged by clinicians, based on biologic and esthetic criteria. However, the importance of evaluating the implant treatment from the patients standpoint 9 so as to assess their acceptance of the treatment outcome has not been adequately recognized in the literature, even though it has been suggested that implant success criteria should include the level of patient acceptance of the implant treatment. 9 The purpose of this study was to determine whether there is an association between patient overall satisfaction with defined aspects of dental implant treatment. Eighty-eight percent of the subjects of this study were highly satisfied with their implant restoration; this result is in agreement with previous studies. 29,30,34 No demographic variables were related to the overall satisfaction at a statistically significant level. These results are in agreement with those of Kiyak and coworkers 28 and those of Chang and associates 30 in terms of age and gender, but not with those of other studies, 31,35,36 which have reported that appearance was more important to women and younger patients than to men and older patients. Questionnaire variables concerning the appearance of the soft tissues around the implant were not significantly related to overall satisfaction, although 50% of the respondents reported dissatisfaction with the soft tissue related variables. It is possible that these patients were informed of the potential soft tissue problems and accepted the limitations of the treatment. Color was the characteristic that best predicted the subjective perception of dental attractiveness of a smile, as reported in a survey (n = 297) conducted by Dunn and coworkers. 37 The authors were unable to demonstrate a statistically significant association, even at the bivariate level, for the independent variable color in this investigation. The reason for this discrepancy of the results concerning the variable color, compared with those of previous studies, may have been that the treating doctors in this study were possibly aware of the importance of this factor in patients satisfaction and achieved the patients optimum color preference or ensured the patients acceptance of technical limitations. The subjects of this study appeared dissatisfied with both the cost and the time it took to complete their treatment. However, time was not significant, while cost approached significance (P =.056) (Table 4). These findings may suggest that patients do not find dental implant treatment inexpensive, but patients who proceed with this procedure are more often those who can afford it, making other personal considerations more important in their overall treatment satisfaction. The type of provisional restoration used by 51% of the subjects before placement of the definitive restoration was an interim-treatment partial denture (Table 4). Subjects who had an interim partial denture tended to be more highly satisfied with their implant restoration, although this was not statistically significant (P =.074). This finding may suggest that when patients have had previous removable prosthesis experience to compare their definitive The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 117
6 implant restoration with, the definitive implant restoration may be accepted more favorably. There is an increasing awareness of the importance of patient-doctor communication in achieving the desired health outcome The difference in proportion of treatment which addressed the chief complaint over chief complaint unrelated to the dental implant treatment between subjects who answered the survey and nonparticipants (21/21 versus 29/50) had a statistical significance level of.06. This finding may suggest that the nonparticipants may have been encouraged by the treating dentist to receive dental implant treatment, which may not have addressed the patients primary concern. This possible management failure may have led to some dissatisfaction and subsequent study participation refusal. This finding suggests that it is vital that patient-doctor communication take cognizance of patients concerns and perceptions, an insight that has also been recognized in the complete denture literature. 16,41,42 Communication between dentist and patient is important to achieve optimal esthetic results that will be satisfactory to both, since their perceptions of esthetics do not necessarily coincide. 30,43 The variable information received prior to treatment was related to patient overall satisfaction (P =.003), suggesting the importance of discussing treatment limitations that may apply, so that patients can have realistic expectations of each treatment phase. Consideration of patients concerns and perceptions and obtaining patient approval of the final result, by means of a diagnostic waxup during the initial treatment planning phase, as well as maintenance of communication throughout treatment, may increase the likelihood of successful outcomes. Two thirds of the subjects of this study strongly agreed with the statement that they would be willing to undergo the same treatment and would highly recommend it to a friend. These results seem to be in conflict with the responses regarding the overall satisfaction (89%). It would be interesting to further investigate the underlying reason why 89% of the subjects report highly favorable responses on their overall satisfaction, but only 67% would be willing to repeat the treatment. These results were slightly lower than those of a previous study, 34 which reported that 77% would redo and 85% would recommend to others their dental implant treatment. The 5 variables that were of primary importance in the patients ultimate satisfaction with the overall dental implant treatment were (1) implant position, (2) restoration shape, (3) appearance when smiling, (4) effect on speech, and (5) chewing capacity (Table 3), as suggested by the magnitude of their ORs. The first 3 variables represent overall appearance, and the last 2 reflect upon function. Hawkins and associates 44 found patients satisfaction with maxillary anterior fixed restorations to be higher in patients with class I than class II or III ridges, according to the classification of Siebert. 45 They concluded that ridge augmentation should be considered prior to the fabrication of maxillary anterior fixed prostheses, particularly when class II or III defects are present. The presence of adequate ridge height and width is essential for placement of implants to obtain proper position and contour (shape) of the definitive implant restoration. The direction and extent of resorption in the maxilla often result in situations where it is necessary to utilize augmentation procedures to correct implant site ridge defects. Restorative dentists have recognized the importance of properly positioned dental implants and the necessity for using a surgical guide to ensure appropriate surgical placement. In contemporary implant dentistry, the position of the bone should not dictate implant placement, as it may have previously. Several surgical techniques are available to augment the implant site when ridge height or width is inadequate. Attention to this aspect of rehabilitation may positively influence patient overall acceptance of the dental implant treatment. The self-administered, mailed questionnaire of this study did not include questions that addressed QOL issues. However, patients attention to the restoration of function namely, speech and chewing capacity of the definitive implant restoration indicates that future dental implant research should be designed toward refining the study instrument to consider the effect of dental implant treatment on patient QOL. There are several limitations to this study. The sample size was small (n = 78), the selected patients were all treated at the UCHC, and the distribution of subject responses was limited. Variables that were not shown to be statistically significant may have demonstrated significance with a larger sample size. Only 11.8% of the respondents reported negative outcomes (less than Highly Satisfied ), which limited the ability to detect any significant difference. Some questions were retrospective and relied on subjects memory and may have introduced an associated recall bias. Data collected through the self-administered questionnaire were subject to possible misinterpretations of the questions by the subjects; and finally, income categories in the questionnaire overlapped by double-listing of income transitions. 118 Volume 18, Number 1, 2003
7 CONCLUSION This study is in general agreement with previous reports on patient satisfaction with dental implant treatment. The results of this study suggest that patient satisfaction with implant position, restoration shape, and overall appearance, as well as effect on speech and chewing capacity, is critical for patient overall acceptance of the treatment. Practitioners who provide implant restorations should be aware of the multidimensional aspects of patients satisfaction with their implant treatment, giving particular attention to patient acceptance of dental implant ability to restore esthetics (position, shape, overall appearance) and function (effect on speech and chewing capacity). Two-way patient-doctor communication prior to and throughout treatment affects patient perception of success of the implant outcome. Future studies of different populations with larger sample sizes are necessary to support the conclusions and generalize the results of this study. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The corresponding author wishes to acknowledge the contribution of Dr Ralph V. Katz, New York University College of Dentistry, in developing the questionnaire used in this research project, as well as the assistance of Mr Richard Feinn, University of Connecticut Health Center, with the statistical analysis, and Dr Augusto R. Elias-Boneta, University of Puerto Rico School of Dentistry, for his encouragement and his efforts with future research on this project. REFERENCES 1. Taylor TD. Prosthodontic problems and limitations associated with osseointegration. J Prosthet Dent 1998;79: Albrektsson T, Dahl E, Enbom L, et al. Osseointegrated oral implants. A Swedish multicenter study of 8139 consecutively inserted Nobelpharma implants. J Periodontol 1988;59(5): Tolman DE, Laney WR. Tissue-integrated prosthesis complications. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1992;7(4): Jemt T. Failures and complications in 391 consecutively inserted fixed prostheses supported by Brånemark implants in edentulous jaws: A study of treatment from the time of prosthesis placement to the first annual checkup. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1991;6(3): Worthington P, Bolender CL, Taylor TD. The Swedish system of osseointegrated implants: Problems and complications encountered during a 4-year trial period. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1987;2(2): Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Brånemark P-I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg 1981;10(6): Adell R. Clinical results of osseointegrated implants supporting fixed prostheses in edentulous jaws. J Prosthet Dent 1983;50(2): Cox JF, Zarb GA. The longitudinal clinical efficacy of osseointegrated dental implants: A 3-year report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1987;2(2): Zarb GA, Albrektsson T. Consensus report: Towards optimized treatment outcomes for dental implants [editorial]. Int J Prosthodont 1998;5: Locker D. Patient-based assessment of the outcomes of implant therapy: A review of the literature. Int J Prosthodont 1998;11(5): Carr AB, McGivney GP. Measurement in dentistry. J Prosthet Dent 2000;83 (3): Guckes AD, Scurria MS, Shugars DA. A conceptual framework for understanding outcomes of oral implant therapy [review]. J Prosthet Dent 1996;75(6): Carr AB. Successful long-term treatment outcomes in the field of osseointegrated implants: Prosthodontic determinants. Int J Prosthodont 1998;11(5): Garrett NR, Kapur KK, Perez P. Effects of improvements of poorly fitting dentures on patient satisfaction. J Prosthet Dent 1996;76: Garrett NR, Perez P, Elbert C, Kapur KK. Effects of poorly fitting dentures and new dentures on masticatory performance. J Prosthet Dent 1996;75: Nassif J. A self-administered questionnaire An aid in managing complete denture patients. J Prosthet Dent 1978;40 (4): Grogono AL, Lancaster DM, Finger IM. Dental implants: A survey of patients attitudes. J Prosthet Dent 1989;62(5): Boerrigter EM, Stegenga B, Raghoebar GM, Boering G. Patient satisfaction and chewing ability with implantretained mandibular overdentures: A comparison with new complete dentures with or without preprosthetic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1995;53(10): Haraldson T, Jemt T, Stalblad PA, Lekholm U. Oral function in subjects with overdentures supported by osseointegrated implants. Scand J Dent Res 1988;96(3): Humphris GM, Healey T, Howell RA, Cawood J. The psychological impact of implant-retained mandibular prostheses: A cross-sectional study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1995;10(4): Boerrigter EM, Geertman ME, Van Oort RP, et al. Patient satisfaction with implant-retained mandibular overdentures. A comparison with new complete dentures not retained by implants A multicenter randomized clinical trial. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1995;33(5): Rogers SN, McNally D, Mahmoud M, Chan MF, Humphris GM. Psychologic response of the edentulous patient after primary surgery for oral cancer: A cross-sectional study. J Prosthet Dent 1999;82(3): Kapur KK, Garrett NR, Hamada MO, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implantsupported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part I: Methodology and clinical outcomes. J Prosthet Dent 1998;79(5): Garrett NR, Kapur KK, Hamada MO, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implantsupported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part II. Comparisons of masticatory performance. J Prosthet Dent 1998;79(6): Harle TJ, Anderson JD. Patient satisfaction with implantsupported prostheses. Int J Prosthodont 1993;6: The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 119
8 26. Kapur KK, Garrett NR, Hamada MO, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implantsupported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part III: Comparisons of patient satisfaction. J Prosthet Dent 1999;82(4): Kaptein ML, Hoogstraten J, de Putter C, de Lange GL, Blijdorp PA. Dental implants in the atrophic maxilla: Measurements of patients satisfaction and treatment experience. Clin Oral Implants Res 1998;9(5): Kiyak HA, Beach BH, Worthington P, Taylor T, Bolender C, Evans J. Psychological impact of osseointegrated dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1990;5(1): Carlson B, Carlsson GE. Prosthodontic complications in osseointegrated dental implant treatment. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1994;9: Chang M, Ödman PA, Wennström JL, Bernt A. Esthetic outcome of implant-supported single tooth replacements assessed by the patient and by prosthodontists. Int J Prosthodont 1999;12: Neumann LM, Christensen C, Cavanaugh C. Dental esthetic satisfaction in adults. J Am Dent Assoc 1989;(118): Cronbach LJ. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951;16: Aday LA. Designing and Conducting Health Surveys: A Comprehensive Guide, ed 2. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1996: Avivi-Arber L, Zarb GA. Clinical effectiveness of implantsupported single tooth replacement: The Toronto study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1996;11: Vallittu PK, Vallittu ASJ, Lassila VP. Dental aesthetics A survey of attitudes in different groups of patients. J Dent 1996;(24): Klima RJ, Wittermann JK, McIver JE. Body image, selfconcept and the orthodontic patient. Am J Orthod 1979;75 (5): Dunn WJ, Murchinson DF, Broome JC. Esthetics: Patients perceptions of dental attractiveness. J Prosthodont 1996;5: Boon H, Stewart M. Patient-physician communication assessment instruments: 1986 to 1996 in review. Patient Educ Couns 1998;35: Jameson CH. Understanding the patient. Dent Clin North Am 1960; Grieder A. Psychologic aspects of prosthodontics. J Prosthet Dent 1973;30: Levin B, Landesman HM. A practical questionnaire for predicting denture success or failure. J Prosthet Dent 1976;35: Swoope CC. Predicting denture success. J Prosthet Dent 1973;30: Brisman AS. Esthetics: A comparison of dentists and patients concepts. J Am Dent Assoc 1980;100: Hawkins CH, Sterrett JD, Murphy HJ, Thomas JC. Ridge contour related to esthetics and function. J Prosthet Dent 1991;66(2): Siebert JS. Reconstruction of deformed, partially edentulous ridges, using full thickness onlay grafts. Part I. Technique and wound healing. Compend Contin Educ Dent 1983;4: Volume 18, Number 1, 2003
Patient Self-Reported Satisfaction with Maxillary Anterior Dental Implant Treatment.
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn SoDM Masters Theses School of Dental Medicine June 2001 Patient Self-Reported Satisfaction with Maxillary Anterior Dental Implant Treatment. Anna Levi Follow
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn SoDM Masters Theses School of Dental Medicine June 2001 Patient Self-Reported Satisfaction with Maxillary Anterior Dental Implant Treatment. Anna Levi Follow
A SURVEY TO ASSESS PATIENT SATISFACTION AFTER RECEIVING COMPLETE DENTURE PROSTHESES IN A.B. SHETTY MEMORIAL INSTITUTE OF DENTAL SCIENCES
 Short Communication A SURVEY TO ASSESS PATIENT SATISFACTION AFTER RECEIVING COMPLETE DENTURE PROSTHESES IN A.B. SHETTY MEMORIAL INSTITUTE OF DENTAL SCIENCES 2 Vinaya S. Bhat, Krishna Prasad D. & Prakyath
Short Communication A SURVEY TO ASSESS PATIENT SATISFACTION AFTER RECEIVING COMPLETE DENTURE PROSTHESES IN A.B. SHETTY MEMORIAL INSTITUTE OF DENTAL SCIENCES 2 Vinaya S. Bhat, Krishna Prasad D. & Prakyath
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report
 Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
Mandibular implant-supported hybrid prostheses
 Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.525/jkaoms.204.40.3.30 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients Young-Kyun Kim, Hyun-Suk Kim, Yang-Jin Yi 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.525/jkaoms.204.40.3.30 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients Young-Kyun Kim, Hyun-Suk Kim, Yang-Jin Yi 2,
Endosseous cylindric implants are well accepted
 Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Patient satisfaction with oral implant rehabilitation: evaluation of responses to a questionnaire
 Patient satisfaction with oral implant rehabilitation: evaluation of responses to a questionnaire Susanna Annibali, MD, DDS 1 Anna Rita Vestri, MD 2 Annalisa Pilotto, DDS 1 Gerardo La Monaca, DDS, PhD
Patient satisfaction with oral implant rehabilitation: evaluation of responses to a questionnaire Susanna Annibali, MD, DDS 1 Anna Rita Vestri, MD 2 Annalisa Pilotto, DDS 1 Gerardo La Monaca, DDS, PhD
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM
 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Since the early 1980s, when the concept of
 Retention of Teeth Versus Extraction and Implant Placement: Treatment Preferences of Dental Faculty and Dental Students Peter M. Di Fiore, D.D.S., M.S.; Lawrence Tam, D.D.S.; Ha T. Thai, D.D.S.; Eugene
Retention of Teeth Versus Extraction and Implant Placement: Treatment Preferences of Dental Faculty and Dental Students Peter M. Di Fiore, D.D.S., M.S.; Lawrence Tam, D.D.S.; Ha T. Thai, D.D.S.; Eugene
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report
 Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Complete Denture Satisfaction among Population in Bihar A Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Feb. 2015), PP 68-72 www.iosrjournals.org Complete Denture Satisfaction among
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Feb. 2015), PP 68-72 www.iosrjournals.org Complete Denture Satisfaction among
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Implant Prosthodontic Management of Anterior Partial Edentulism: Long-Term Follow-Up of a Prospective Study John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Implant Prosthodontic Management of Anterior Partial Edentulism: Long-Term Follow-Up of a Prospective Study John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
The restoration of partially and completely
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
d Clinical Associate Professor of Advanced Prosthodontics, Biomaterials g Staff Prosthodontist, Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center,
 Randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implantsupported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part III: Comparisons of patient satisfaction Krishan K. Kapur,
Randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implantsupported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part III: Comparisons of patient satisfaction Krishan K. Kapur,
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
 A randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implantsupported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part II. Comparisons of masticatory performance Neal R. Garrett,
A randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of mandibular implantsupported overdentures and conventional dentures in diabetic patients. Part II. Comparisons of masticatory performance Neal R. Garrett,
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
Brånemark System Facts & Figures
 Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate
 AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/24625
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/24625
Brånemark System Facts & Figures
 Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
The indication for implant treatment as the first
 RESEARCH Patients Expectation Before and Satisfaction After Full- Arch Fixed Implant-Prosthesis Rehabilitation Miriã Corália da Cunha, DDS 1 Jarbas Francisco Fernandes dos Santos, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Mateus
RESEARCH Patients Expectation Before and Satisfaction After Full- Arch Fixed Implant-Prosthesis Rehabilitation Miriã Corália da Cunha, DDS 1 Jarbas Francisco Fernandes dos Santos, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Mateus
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic
 Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic 1Dr. Vishrut Shah, 2 Dr. Sunil Dhaded, 3 Dr. Chandrashekar Sajjan 1Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics,
Case report: Lingualized occlusion -A better way for enhancing function & esthetic 1Dr. Vishrut Shah, 2 Dr. Sunil Dhaded, 3 Dr. Chandrashekar Sajjan 1Post graduate student, Department of Prosthodontics,
Evaluation of Post-Operative Complaints in Complete Denture and Removable Partial Denture Wearers: A Questionnaire Based Study.
 Nandhini G Ashok et al /J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. Vol. 9(9), 17, 1438-1443 Evaluation of Post-Operative Complaints in Complete Denture and Removable Partial Denture Wearers: A Questionnaire Based Study. Nandhini
Nandhini G Ashok et al /J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. Vol. 9(9), 17, 1438-1443 Evaluation of Post-Operative Complaints in Complete Denture and Removable Partial Denture Wearers: A Questionnaire Based Study. Nandhini
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Evaluation of Gradual Trend of Patients Satisfaction with Complete Dentures in the Department of Prosthodontics: A Cross-sectional Study
 ISSN: 2203-1413 Vol.04 No.02 Evaluation of Gradual Trend of Patients Satisfaction with Complete Dentures in the Department of Prosthodontics: A Cross-sectional Study Ramin Negahdari 1, Seyyed Mahdi Vahid
ISSN: 2203-1413 Vol.04 No.02 Evaluation of Gradual Trend of Patients Satisfaction with Complete Dentures in the Department of Prosthodontics: A Cross-sectional Study Ramin Negahdari 1, Seyyed Mahdi Vahid
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Case Report Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report Po-Yu Lai, DDS, MS School of Dentistry, National Yang-Ming University Shing-Wai Yip, DDS, MS, DScD Prosthodontics
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report Po-Yu Lai, DDS, MS School of Dentistry, National Yang-Ming University Shing-Wai Yip, DDS, MS, DScD Prosthodontics
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr. ISSN (Print) Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website:
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction with Hybrid Restorations
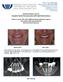 Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
Implants are a part of IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY CLINICAL
 CLINICAL IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Clifford B. Starr, DMD Mohamed A. Maksoud, DMD KEY WORDS Dental implants General dentistry Resident
CLINICAL IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Clifford B. Starr, DMD Mohamed A. Maksoud, DMD KEY WORDS Dental implants General dentistry Resident
Prosthodontic Needs in Patient after Tooth Extraction in South Indian Population
 Prosthodontic Needs in Patient after Tooth Extraction in South Indian Population Anas Bin Rosli BDS a, Ashish.R.Jain MDS, MD.ACU.VARMA a a Second Year, Department of Prosthodontics, Saveetha Dental College
Prosthodontic Needs in Patient after Tooth Extraction in South Indian Population Anas Bin Rosli BDS a, Ashish.R.Jain MDS, MD.ACU.VARMA a a Second Year, Department of Prosthodontics, Saveetha Dental College
Generation fifty plus: Restoring a natural smile
 Clinical Generation fifty plus: Restoring a natural smile Giovanni Molina Lugo, 1 Francisco Paul Curiel Aguilera, 2 Carlos A Ramirez Schleske 3 Today s quality conscious and vital seniors wish to retain
Clinical Generation fifty plus: Restoring a natural smile Giovanni Molina Lugo, 1 Francisco Paul Curiel Aguilera, 2 Carlos A Ramirez Schleske 3 Today s quality conscious and vital seniors wish to retain
Consequences of insufficient treatment planning for flapless implant surgery for a mandibular overdenture: A clinical report
 Consequences of insufficient treatment planning for flapless implant surgery for a mandibular overdenture: A clinical report Avinash S., BDS, MS a University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Conn.
Consequences of insufficient treatment planning for flapless implant surgery for a mandibular overdenture: A clinical report Avinash S., BDS, MS a University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Conn.
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported. in implant prosthodontics
 Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Many of the problems reported by conventional
 Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
The effect of attachment type and implant number on satisfaction and quality of life of mandibular implant-retained overdenture wearers
 Original Article The effect of attachment type and implant number on satisfaction and quality of life of mandibular implant-retained overdenture wearers Emre Mumcu, Hakan Bilhan and Onur Geckili Department
Original Article The effect of attachment type and implant number on satisfaction and quality of life of mandibular implant-retained overdenture wearers Emre Mumcu, Hakan Bilhan and Onur Geckili Department
Survival Analysis of Endosseous Implants in Grafted and Nongrafted Edentulous Maxillae
 Survival Analysis of Endosseous Implants in Grafted and Nongrafted Edentulous Maxillae Jonas P. Becktor, DDS 1 /Sten Isaksson, MD, DDS, PhD 2 /Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD 3 Purpose: The aim of this study was
Survival Analysis of Endosseous Implants in Grafted and Nongrafted Edentulous Maxillae Jonas P. Becktor, DDS 1 /Sten Isaksson, MD, DDS, PhD 2 /Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD 3 Purpose: The aim of this study was
During the last 30 years, endosseous oral
 Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
The influence of radiotherapy on osseointegration
 Experience with Osseointegrated Implants Placed in Irradiated Tissues in Japan and the United States Atsushi Niimi, DDS, DMSc*/Minoru Ueda, DDS, PhD**/ Eugene E. Keller, DDS, PhD***/Philip Worthington,
Experience with Osseointegrated Implants Placed in Irradiated Tissues in Japan and the United States Atsushi Niimi, DDS, DMSc*/Minoru Ueda, DDS, PhD**/ Eugene E. Keller, DDS, PhD***/Philip Worthington,
Oral health impact profile and prosthetic condition in edentulous patients rehabilitated with implant-supported overdentures and fixed prostheses
 535 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 4, 535-543, 2009 Original Oral health impact profile and prosthetic condition in edentulous patients rehabilitated with implant-supported overdentures and fixed
535 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 4, 535-543, 2009 Original Oral health impact profile and prosthetic condition in edentulous patients rehabilitated with implant-supported overdentures and fixed
Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence and Masticatory Function - A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
Low-Cost Implant Overdenture Option for Patients Treated in a Predoctoral Dental School Curriculum
 Milieu in Dental School and Practice Low-Cost Implant Overdenture Option for Patients Treated in a Predoctoral Dental School Curriculum Michael S. McCracken, D.D.S., Ph.D.; Ruth Aponte-Wesson, D.D.S.,
Milieu in Dental School and Practice Low-Cost Implant Overdenture Option for Patients Treated in a Predoctoral Dental School Curriculum Michael S. McCracken, D.D.S., Ph.D.; Ruth Aponte-Wesson, D.D.S.,
MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols
 Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
MDJ The effect of design on Removable Partial Dentures Vol.:11 No.:1 2014
 MDJ The effect of design on Removable Partial Dentures Dr. Najim O. Nasser, Institute of Technical Medicine, Baghdad Abstract The importance of properly designed removable partial denture cannot be overemphasized,
MDJ The effect of design on Removable Partial Dentures Dr. Najim O. Nasser, Institute of Technical Medicine, Baghdad Abstract The importance of properly designed removable partial denture cannot be overemphasized,
Much has been written about the success of various
 Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
CHAPTER 1. General Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 General Introduction Chapter 1 The loss of remaining natural teeth and provision of artificial removable dentition is a major and irreversible procedure for the patient. The main limitations
CHAPTER 1 General Introduction Chapter 1 The loss of remaining natural teeth and provision of artificial removable dentition is a major and irreversible procedure for the patient. The main limitations
A survey of dentists' attitudes toward denture adhesives
 VARIA A survey of dentists' attitudes toward denture adhesives Temel Koksal, DDS, PhD 1, Idil Dikbas, DDS, PhD 1, Zeynep Ozkurt, DDS 2, Burcu Bal, DDS 2, Ender Kazaoglu, DDS, PhD 3 Istanbul, Turkey Summary
VARIA A survey of dentists' attitudes toward denture adhesives Temel Koksal, DDS, PhD 1, Idil Dikbas, DDS, PhD 1, Zeynep Ozkurt, DDS 2, Burcu Bal, DDS 2, Ender Kazaoglu, DDS, PhD 3 Istanbul, Turkey Summary
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
Determination of the Rate of Need for Relining Complete Dentures in Patients Referring to a Department of Prosthodontics
 ISS: 2203-1413 Vol.04 o.02 Determination of the Rate of eed for Relining Complete Dentures in Patients Referring to a Department of Prosthodontics Ramin egahdari 1, Seyyed Mahdi Vahid Pakdel 2, Sepideh
ISS: 2203-1413 Vol.04 o.02 Determination of the Rate of eed for Relining Complete Dentures in Patients Referring to a Department of Prosthodontics Ramin egahdari 1, Seyyed Mahdi Vahid Pakdel 2, Sepideh
Patient s satisfaction following dental implant treatment among Sudanese patients
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Patient s satisfaction following dental
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 75-79 www.iosrjournals.org Patient s satisfaction following dental
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr ISSN (Print)
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr.2016.1.2.7 Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297
DOI:10.21276/sjodr.2016.1.2.7 Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options
 Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Simplified Method for fabrication of O- Ring Implant Supported Overdenture- Case Report
 CASE REPORT Simplified Method for fabrication of O- Ring Implant Supported Overdenture- Case Report Dr. Vikas Punia 1, Dr. Mohit Handa 2, Dr.Nikhil Verma 3, Dr.Virender Singh 4, Dr. Vivek Lath 5. M.D.S.,
CASE REPORT Simplified Method for fabrication of O- Ring Implant Supported Overdenture- Case Report Dr. Vikas Punia 1, Dr. Mohit Handa 2, Dr.Nikhil Verma 3, Dr.Virender Singh 4, Dr. Vivek Lath 5. M.D.S.,
A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible
 A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 /Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP 2 / Brett E. Stein 3 /Stephen F. Balshi, MBE 4 Purpose:
A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 /Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP 2 / Brett E. Stein 3 /Stephen F. Balshi, MBE 4 Purpose:
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Retrospective Cohort Study of the Clinical Performance of 1-Stage Dental Implants
 Retrospective Cohort Study of the Clinical Performance of 1-Stage Dental Implants Alan B. Carr, DMD, MS 1 /Yong-Geun Choi, DDS, MPH, MPH 2 / Steven E. Eckert, DDS, MS 1 /Ronald P. Desjardins, DMD, MS 3
Retrospective Cohort Study of the Clinical Performance of 1-Stage Dental Implants Alan B. Carr, DMD, MS 1 /Yong-Geun Choi, DDS, MPH, MPH 2 / Steven E. Eckert, DDS, MS 1 /Ronald P. Desjardins, DMD, MS 3
ISPUB.COM. Habitual Centric: A Case Report. Manisha, N Kathuria, A Gupta, N Gupta INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Geriatrics and Gerontology Volume 6 Number 2 Habitual Centric: A Case Report Manisha, N Kathuria, A Gupta, N Gupta Citation Manisha, N Kathuria, A Gupta, N Gupta. Habitual
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Geriatrics and Gerontology Volume 6 Number 2 Habitual Centric: A Case Report Manisha, N Kathuria, A Gupta, N Gupta Citation Manisha, N Kathuria, A Gupta, N Gupta. Habitual
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide
 Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Prosthetic RehabilitationofaPatientwithAlzheimersDiseaseusingaCombinedBallBarandClipRetainedImplantSupportedOverdentureA Case Report
 Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
EFFECT OF IMPLANTS ON MAXIMUM BITE FORCE
 CLINICAL EFFECT OF IMPLANTS ON MAXIMUM BITE FORCE IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS Mansour Rismanchian, DMD, MS; Farshad Bajoghli, DMD, MS; Zahra Mostajeran, DDS; Akbar Fazel, DMD, MS; P. sadr Eshkevari, DDS One
CLINICAL EFFECT OF IMPLANTS ON MAXIMUM BITE FORCE IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS Mansour Rismanchian, DMD, MS; Farshad Bajoghli, DMD, MS; Zahra Mostajeran, DDS; Akbar Fazel, DMD, MS; P. sadr Eshkevari, DDS One
Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete Denture and Mandibular Teeth supported Overdenture
 Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Cleft lip and palate; oronasal istula; prosthetic treatment; O ring attachment
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 4 (2018) Issue 6 ISSN 2379-1039 Prosthetic treatment of a unilateral left cleft lip and palate with anoronasal istula: A case report Yesiboli Yeerken,
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 4 (2018) Issue 6 ISSN 2379-1039 Prosthetic treatment of a unilateral left cleft lip and palate with anoronasal istula: A case report Yesiboli Yeerken,
4. What about age? There is no age limit. After puberty, anyone can get dental implants.
 Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1086 CASE REPORT Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible ABSTRACT This article aims to present a modified yet simple technique for the placement
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1086 CASE REPORT Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible ABSTRACT This article aims to present a modified yet simple technique for the placement
Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers
 Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Bernt Andersson, DDS, Odont Dr/PhD;* Sibel Bergenblock, DDS; Björn Fürst, DDS; Torsten Jemt, DDS, Odont Dr/PhD
 Long-Term Function of Single-Implant Restorations: A 17- to 19-Year Follow-Up Study on Implant Infraposition Related to the Shape of the Face and Patients Satisfactioncid_381 1..10 Bernt Andersson, DDS,
Long-Term Function of Single-Implant Restorations: A 17- to 19-Year Follow-Up Study on Implant Infraposition Related to the Shape of the Face and Patients Satisfactioncid_381 1..10 Bernt Andersson, DDS,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
The clinical use of endosseous implants has
 A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
Practice-Based Evidence from 29-Year Outcome Analysis of Management of the Edentulous Jaw Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants
 Practice-Based Evidence from 29-Year Outcome Analysis of Management of the Edentulous Jaw Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants Matilda Dhima, DMD, MS, 1 Vladimira Paulusova, MD, 2 Christine Lohse, MS,
Practice-Based Evidence from 29-Year Outcome Analysis of Management of the Edentulous Jaw Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants Matilda Dhima, DMD, MS, 1 Vladimira Paulusova, MD, 2 Christine Lohse, MS,
RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
oral implantology 52 Stoma.eduJ (2014) 1 (1) Abstract Introduction
 Cite this article: Kempler J. An implant supported maxillary fixed prosthesis with a substructure/suprastructure design: a clinical case. Stoma Edu J. 2014; 1(1);52-58. oral implantology An Implant Supported
Cite this article: Kempler J. An implant supported maxillary fixed prosthesis with a substructure/suprastructure design: a clinical case. Stoma Edu J. 2014; 1(1);52-58. oral implantology An Implant Supported
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Case Presentation Template for AO Master Certificate
 Case Presentation Template for AO Master Certificate You must have signed informed consent from patients (or relatives/guardians) before submitting an AO Case Presentation and ask them to sign the statement
Case Presentation Template for AO Master Certificate You must have signed informed consent from patients (or relatives/guardians) before submitting an AO Case Presentation and ask them to sign the statement
