Surgical and biological considerations of extensive Maxillary fibrous dysplasia
|
|
|
- Alban Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Science International 3(2): 65-70, 2014 ISSN: Surgical and biological considerations of extensive Maxillary fibrous dysplasia 1 Mohamed Foda and 2 Ibrahim Abde-Albare 1 Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Assiut Branch, Egypt. 2 Health Director Of Tanta Cancer Center And Head Of Surgical Oncology Department, Egypt. ABSTRACT Objective:Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a skeletal disorder including the maxilla and the mandible; nevertheless, its effects on dental tissues and the implications for dental care remain unclear. The aim of this study was to characterize the dental features associated with FD and the reaction of affected bones to routine dental therapy additionally the relation with endocrine disturbances Study design:thirty-two patients with FD underwent endocrine testing as part of the diagnosis of FD/McCune-Albright syndrome, maxillofacial evaluation and surgical shaving was performed. Any dental anomalies were recorded, and the associations between endocrinopathies and dental anomalies were analyzed statistically by means of the paired t test. Results:Eighty-four percent had FD in the maxilla and/or mandible; endocrine dysfunction; and/or renal phosphate wasting. The Malocclusion (81%) and other prevalent dental anomalies (41%) included tooth rotation, oligodontia, and taurodontism. The expansion of the maxilla or mandible by FD did not distort the dental arch curvature, and routine dental therapies such as extractions, restorations, and orthodontic treatment did not exacerbate FD lesions. Conclusion: Maxillomandibular FD was associated with higher rates of malocclusion than were present in healthy patients. Furthermore, patients with FD did not require special dental management and were able to undergo routine dental care without an exacerbation of FD lesions, Key words: Surgical,biological, maxillary and fibrous dysplasia Introduction Fibrous dysplasia (FD) of bone is characterized by the replacement of normal bone and marrow by fibrous tissue, within which irregular trabeculae of woven bone are haphazardly distributed, FD may affect a single bone (called monostotic MFD) or multiple bones (called polyostotic FD [PFD] and may be associated with endocrinopathy (Shenker et al., 2013) FD can occur as part of McCune-Albright syndrome (MAS), a rare multisystem disease that was first described as the triad of PFD, skin hyperpigmentation (cafe -au-lait), and precocious puberty (Moran et al., 2012). MAS is also associated with other endocrine disorders of the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands, (Smith, 2011; Ladenson, 1992; AKoutras,1997and Grant,1999). Hypophosphatemia and renal phosphate wasting are commonly observed in patients with FD/MAS, (Kushner et al., 2001). Two separate literature reviews of the years 1926 through 1995 revealed only 158 published cases.( MLevine, 1999 and Schwindinger and Levine,1996) FD in association with cafe -au-lait skin hyperpigmentation but no endocrinopathyis known as Jaffe-Lichtenstein syndrome.( Damm et al., 2002) FD is considered a disease of cells of the mesenchymal stem cell/ osteoblastic lineage in which excess cyclic adenosine mono phosphate impairs the ability of the stem ce1lto differentiate into a mature functioning osteoblastic. (Gejman et al., 1991) However, it is not known how or even whether excess cyclic adenosine monophosphate affects the developing tooth, either directly or indirectly. Craniofacial bones, including the maxilla and the mandible, are commonly affected by FD, often causing disfigurement. However, despite the frequency of craniofacial involvement, the dental features of FD have been poorly characterized, mainly in isolated case reports with sparse information about the effects of FD on dental tissues. (DeSanctis et al., 1999; Shenker et al., 2011 and Olander and Hammarstrom, 1985) 12,13,14) The development, eruption, and shedding of primary teeth followed by the development and eruption of permanent teeth are sequential events that may be altered by metabolic dysfunction with in dental tissues or the presence of bony pathosis within the jaws (Gejman et al., 1991). It remains unclear whether the presence of FD in the jaws has any effect on tooth development and function. The typical appearance of patients with FD of the Maxillomandibular bones is that of facial asymmetry, often associated with palatal asymmetry. FD is often associated with characteristic cafe -au-lait skin A pigmentation and rarely with cafe -au-lait pigmentation of the oral mucosa. Panoramic radiographic imaging of the jaws and computed tomography have revealed aground-glass trabeculation that may progress to mixed radiolucent/radiopaque lesions and thinning of the cortical margin. (Shenker et al., 2011) Craniofacial FD may present with a variety of manifestations depending on the area of bony involvement. Lesions may involve the maxilla, mandible, zygoma, calvarium, sphenoid, temporal or orbital bones. Corresponding Address: DR. Mohamed Foda, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Assiut Branch, Egypt. fodamohamed@hotmail.com
2 66 Symptoms develop secondary to slowly progressive bony expansion. Craniofacial bone involvement may produce asymmetry and cosmetic deformity. Massive cranial bone involvement has resulted in lion-like faces termed "leontiasis ossea," or maxillary involvement termed "cherubism." FD of the maxilla may also result in nasal obstruction, epiphora, and malocclusion. Visual disturbance can occur secondary to proptosis, extraocular muscle dysfunction, optic nerve or chiasm compression when FD affects the bony orbit. (DeSanctis et al., 1997) Fibrous dysplasia has often been confused with osseous lesions of hyperparathyroidism (Damm et al., 2002) indicating similar histopathologic features (DeSanctis et al., 1997). parathyroid hormone (PTH) is a peptide hormone produced in the parathyroid gland which acts directly on bone to increase bone resorption and mobilize calcium to control the concentration of calcium in the extracellular fluid; this function is effected through activation of a mechanism that transfers calcium from bone and from glomerular filtrate to the extracellular fluid compartment (AKoutras,1997). Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) was originally identified in tumors associated with hormonal hypocalcaemia of malignancy (Grant, 1999). Calcitonin (CT) could be classically considered to be a physiologic antagonist of PTH and PTHrP; it lowers the plasma calcium concentration by inhibiting bone resorption, with a stimulation of the renal calcium excretion (Grant, 1999). Although the ideal technique for the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of the maxilla is still an issue of controversy, The current work attempted to study the surgical intervention,dental feature and endocrine disturbances as an approach the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of the maxilla, as well as to find out suitability of this approach for treatment of this cases. The present study, have hypotheses that the surgical intervention could be of value as a suitable technique for treatment of fibrous dysplasia of the maxilla Aim of the work: The aim of this study was to characterize the dental features associated with FD and the reaction of affected bones to routine dental therapy additionally relation with endocrine disturbances Material And Methods Thirty-six patients diagnosed with FD/MAS gave written informed consent and were subsequently enrolled in this study. FD was diagnosed by a combination of the results from clinical history, physical examination, radiographic analyses, and lesion bone biopsy. Testing of the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, gonadal, adrenal functions was performed. The maxillofacial evaluation included extra oral and intraoral examinations, panoramic,ct (as showing in fig 1), intraoral radiographs, and the preparation of maxilla mandible study casts to assess the therapy-related bony changes such as the growth/enlargement of FD lesions or the development of malocclusion in the maxilla or mandible to assess the therapy-related bony changes such as the growth/enlargement of FD lesions or the development of malocclusion in the maxilla or mandible. Fig. 1: lateral,intraoral and frontal photograph preoperatively showing the clinical extent of the lesion with obliteration of nasolabial fold,(a, b,c, and d).coronal and axial section of Computed tomography of the maxillary fibrous dysplasia prior to the first operation showing peau d orange (orange peel) appearance was noted in the maxilla and mandible also th bilateral maxillary sinus was mostly replaced with the lesion.(e and f)
3 67 The CT scan can also evaluate the optic canal, superior and inferior orbital fissure, internal auditory canal, or skull base foramina for evidence of compression.technetium-99m radionuclide bone scan will demonstrate increased uptake in other sites of skeletal involvement and can be used to determine when the quiescent phase has been reached. As the priority was to relieve the obstructive symptoms, a conservative bone shaving surgery was performed through intraoral or a modified Weber Ferguson approach as showing in (fig 2) The patients was regularly followed up once in every 3 months till 1 year and every 6 months since then, and a secondary surgical procedure to further enhance the cosmetic appearance and improve the facial symmetry was refuted by the patient Fig. 2: Intraoperative photograph showing the incision,shaving the lesion, approximation of the flaps and finally orientation of lesion for pathologist as tags,(a, b, c, and d).immediate postoperative photograph showing closure of the mucoperiosteal flap (e and f) Conservative surgical treatment as in fig 2,is regarded by many as the treatment of choice. This involve decompression of cranial nerves at their respective foramina, contouring of bone to restore symmetry of facial skeleton, canaloplasty to relieve external audit auditory canal stenosis and minimal resection to relieve anosmia, and nasal and sinus ostia obstruction. When the extent of the lesion is such that total excision would result in greater deformity and functional loss than the disease itself. Endocrinology data and therapeutic consequence of calcitonin administration in association with surgical interventions. Surgical intervention performed after the local bone calcification by a calcitonin treatment, because of alleviation of vigorous hemorrhage by the bone remodeling..surgical therapy considered based on the residual cosmetic and functional problems. Some patients with minimal deformity may not require surgical intervention. In addition, if surgical therapy is postponed until after complications arise (visual or hearing impairment, cranial nerve dysfunction), the deficit maybe permanent and irreversible or make the surgery more technically difficult When optic canal compression occurs and visual acuity is compromised, the risk of damage to the optic nerve during decompression becomes more likely and visual acuity may not return to normal Statistical analysis: We analyzed associations between degree of endocrine disturbance and criteria of clinical examination using the paired t test, the results of which were calculated with the SAS statistical software package
4 68 Results: After undergoing full radiographic testing and technetium (99T) full-body bone scanning, 4 of the36 original patients evaluated (11%) were excluded because they did not have an FD lesion in any craniofacial bone. The 32 remaining patients with craniofacial FD are the focus of this report. There were 11 males and 21 females, ranging from 4 to 50 years of age (mean, 21.1 years old). Twenty-three patients had PFD, and 19 of these 23 were diagnosed with MAS on the basis of PFD in association with cafe -au-lait skin pigmentation and endocrinopathy or renal phosphate wasting, or both; 14 of these had a combination of 2 or more endocrinopathy and renal phosphate wasting. Fig. 3: 1 month postoperatively showing no swelling, a. 6 month postoperatively showing improving the nasolabial fold,b, 12 month postoperatively showing improving the nasolabial angle Precocious puberty, followed by hyperthyroidism and renal phosphate wasting,were the most common abnormalities. FD was present in the maxilla, mandible, or both in 27 patients (84%) and was frequently associated with malocclusion and palatal, maxillary, or mandibles asymmetry, ranging from mild to severe,severely affected mandibles; nevertheless, the vast majority of these patients did not report any paresthesia or dysesthesia. Two patients reported unilateral jaw paresthesia. However, both patients had a history of the surgical removal of FD from the associated nerve sites, so the paresthesia was judged to be a result of postoperative changes Another patient reported temporomandibular joint pain and clicking, but there were no degenerative or bony changes in the condylar head or glenoid fossa and the temporomandibular range of motion was within normal limits. The cosmetic of patents was improved as showing in (Fig 3). Interestingly, there were no changes in maxillary or mandible, FD after dental restorations (20 cases), tooth extractions (6 cases, the removal of odontoma (1 case), the removal of a maxillary cyst (1 case) Furthermore, there were no observed incidents or reports of prolonged bleeding, pain, or swelling; occlusal changes; or infection after these procedures. The dental anomalies included rotation, oligodontia, displacement, enamel hypoplasia and hypomineralization, taurodontism, retained deciduous teeth, and attrition.malocclusion was the most common abnormality, but it did not correlate with the concomitant presence of a tooth anomaly and an FD lesion, observed in the jaws of 9 patients (28%) as showing in table 1 There was no statistically significant correlation between any specific endocrine dysfunction or renal phosphate wasting and the DFT scores or tooth anomaly; nor was there a statistically significant relationship between renal phosphate wasting and enamel hypoplasia, hypomineralization, or between such wasting and attrition. In addition, the 15 impacted third molars that were extracted were normal radio graphically; the first 4 were decalcified and, when examined histological, were found to be normal. The remaining 11 were not examined histological. However, the prevalence of oligodontia and retained deciduous teeth suggest that mutation may
5 69 have prevented the formation of permanent successors.because of the gross radiopacity and sclerotic nature of gnathic FD, it was difficult to delineate the outline of the mandible canal in panoramic radiographs of severely Table I: Demographics of clinical findings in patients with fibrous dysplasia: Variables Age groups (years) Totals Precocious puberty Hyperthyroidism Phosphaturia GH excess FD in maxilla or mandible (no. (%) FD in maxilla and mandible (%) Malocclusion )%) Discussion This work represents the largest group of FD/MAS patients to date in whom the resultant dental characteristics have been described, allowing us to make a number of important observations. First, in patients with craniofacial FD, the maxilla or mandible or both is involved 84% of the time. Clinical clues to the presence of FD in the mandible or maxilla are facial or palatal asymmetry, typical cafe - au-lait spots, and a history of endocrine disorders associated with MAS, especially precocious puberty. Conversely, if FD is noted in the maxilla or mandible, associated endocrine disease should be suspected and the appropriate referrals should be made. We were also able to show that FD is frequently associated with dental anomalies, including rotation, oligodontia, displacement, enamel hypoplasia and hypomineralization, taurodontism, and others. The etiology of these anomalies is not known, but it is possible that they are the result of activating mutations in tooth development either directly (enamel hypomineralization and hypoplasia, oligodontia, attrition), or indirectly because of the proximity of abnormal bone (malocclusion, rotation, displacement, retention of deciduous teeth). Taurodontism, a condition visible radio graphically in ultirooted teeth and characterized by enlargement of the pulp chamber caused by apical displacement of the bifurcation or trifurcation of the roots, has been described in many syndromes, including patients with growth hormone excess,21-26 but never in FD/MAS. The incidence of taurodontism observed in this cohort was 9% (3/32) (data not shown). An earlier study associated taurodontism with multiple missing teeth and reported a 34.8% prevalence of taurodontism in subjects with oligodontia compared with 7.5% in a control group.27 We did not observe an association between oligodontia and taurodontism in our patients. However, the patients with taurodontism were also diagnosed with 1 or more endocrinopathies, including growth hormone excess, precocious puberty, secondary hyperparathyroidism and hyperthyroidism, or renal phosphate wasting. It is possible that associated abnormalities may account for this (especially the propensity for renal phosphate wasting to cause enamel hypoplasia or hypomineralization), but there was no statistically significant relationship between any given endocrinopathy and renal phosphate wasting or between a specific anomaly and an increased caries index score. This may be because of the small number of patients that could be classified into each endocrinopathy or renal phosphate wasting subgroup. Despite the prevalence of malocclusion, 28% of patients had tooth anomaly in the FD bone. The malpositioned teeth were rotated within the socket or inclined in the mesiodistal direction however, no buccolingual displacement or mobility was observed. In essence, the curvilinear pattern of the dental arch was preserved.of particular importance to the clinician is the lack of complications associated with the routine dental care of patients with FD. We noted no abnormal response or complications in association with dental restorations or extractions. Conclusions: Maxillomandibular FD was associated with higher rates of malocclusion than were present in healthy patients. Furthermore, patients with FD did not require special dental management and were able to undergo routine dental care without an exacerbation of FD lesions, References AKoutras, D.A.,1997. Hyperthyroidismin McCune-Albright syndrome with a review of thyroid abnormalities. Thyroid, 7:
6 70 Damm, D.D., C.M. Allen, J.E. Bouquot editors, Oraland maxillofacial pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders. DeSanctis, C., et al., A novel GNAS1 mutation, R201G, in McCune- Albright syndrome. J Bone Miner Res., 14: Gejman, P.V., M.J. Merino, A.M. Friedman Spiegel, Activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein. N Engl J Med., 325: Grant, D.B., Cushing ssyndrome. J Pediatr, 134: Kushner, H., M. Consugar, P. Rinaldo, et al., Renal phosphate wasting in fibrous dysplasia of bone J Bone Miner Res., 16: Ladenson, P.W., Octreotide therapy of growth hormoneexcess in the McCune-Albright syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest, 15: MLevine, M.A., Clinical implications of genetic defects for the McCune-Albright syndrome. Arch Med Res., 30: Moran, A., O.H. Pescovitz, N.J. Charest, C.M. Boney, et al., McCune-Albright syndrome. J Pediatr, 123: Olander, K.J., L. Hammarstrom, Fibrous dysplasia of bone Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol., 59: Schwindinger, W.F., M.A. Levine, Clinical implicationsof genetic defects in G proteins..medicine, 75: Shenker, A., A.M. Spiegel, P. Bianco, P. Gehron Robey, Fibrous dysplasia of bone in the McCune- Am JPathol, 151: Shenker, A., A.M. Spiegel, P.G. Robey, The histopathology of fibrous dysplasia of bone. J Pathol, 187: Smith, P., Syndrome characterizedby osteitis fibrosa disseminata,. N Engl J Med, 216:
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children. Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK
 Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 5-24-2012 Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia J S. Lee E J. FitzGibbon
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 5-24-2012 Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia J S. Lee E J. FitzGibbon
Management of Pediatric Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome
 Management of Pediatric Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome Alison Boyce, MD 3 rd Meeting of the FD/MAS International Consortium Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands Fibrous
Management of Pediatric Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome Alison Boyce, MD 3 rd Meeting of the FD/MAS International Consortium Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands Fibrous
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia A Case Report and Review of Literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IV (November. 2016), PP 110-114 www.iosrjournals.org Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IV (November. 2016), PP 110-114 www.iosrjournals.org Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO SELECTION EXAMINATION IN MD (ORAL SURGERY) OCTOBER 2009 PAPER 1.1. Part A (General Anatomy)
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO SELECTION EXAMINATION IN MD (ORAL SURGERY) OCTOBER 2009 Date : 5 th October 2009 Time : 2.00 p.m. 5.00p.m. PAPER 1.1 Answer three (03) questions
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO SELECTION EXAMINATION IN MD (ORAL SURGERY) OCTOBER 2009 Date : 5 th October 2009 Time : 2.00 p.m. 5.00p.m. PAPER 1.1 Answer three (03) questions
Case McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
 Case 14477 McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Lukasz Augsburg 1, Filip M. Vanhoenacker 1, 2, 3, Jan Gielen1 1. University Hospital Antwerp, Department of Radiology, University
Case 14477 McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Lukasz Augsburg 1, Filip M. Vanhoenacker 1, 2, 3, Jan Gielen1 1. University Hospital Antwerp, Department of Radiology, University
Case Report Fibrous Dysplasia versus Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Dilemma
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 6439026, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6439026 Case Report Fibrous Dysplasia versus Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Dilemma Sreelakshmi N. Nair,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 6439026, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6439026 Case Report Fibrous Dysplasia versus Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma: A Dilemma Sreelakshmi N. Nair,
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN Supplement 2011
 ISSN 2250-0359 Supplement 2011 Fibrous dysplasia of Faciomaxillary region case reports and review of literature Dr T Balasubramanian Abstract: This article discusses the author's experience in managing
ISSN 2250-0359 Supplement 2011 Fibrous dysplasia of Faciomaxillary region case reports and review of literature Dr T Balasubramanian Abstract: This article discusses the author's experience in managing
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
4/23/2015. Insights into McCune Albright Syndrome: A Complex, Rare Disease with Individual Presentations. Conflict of Interest Disclosure
 Insights into McCune Albright Syndrome: A Complex, Rare Disease with Individual Presentations Lori Guthrie RN C, BSN, CCRC Beth Brillante RN, BSN, MBA PENS 2015 National Conference Conflict of Interest
Insights into McCune Albright Syndrome: A Complex, Rare Disease with Individual Presentations Lori Guthrie RN C, BSN, CCRC Beth Brillante RN, BSN, MBA PENS 2015 National Conference Conflict of Interest
2018 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/ /31/2018
 D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
2018 Dental Code Set
 D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
Mousa Al-Abadi. Abd. Kharabsheh. Rand Abu Anzeh
 7 Mousa Al-Abadi Abd. Kharabsheh Rand Abu Anzeh 1 Recap The histological appearance of Giant cell tumor of bone shows only multi-nucleated giant cells. The histological appearance of Aneurysmal bone cyst
7 Mousa Al-Abadi Abd. Kharabsheh Rand Abu Anzeh 1 Recap The histological appearance of Giant cell tumor of bone shows only multi-nucleated giant cells. The histological appearance of Aneurysmal bone cyst
Testicular Microlithiasis related to McCune-Albright Syndrome Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Testicular Microlithiasis related to McCune-Albright Syndrome Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 04/25/2010 History 12 year old with McCune-Albright syndrome. Diagnosis Testicular Microlithiasis related to Mcune-Albright
Testicular Microlithiasis related to McCune-Albright Syndrome Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 04/25/2010 History 12 year old with McCune-Albright syndrome. Diagnosis Testicular Microlithiasis related to Mcune-Albright
The disease process may be localized to: A single bone (monostotic fibrous dysplasia) Multiple bones (polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) [4]
![The disease process may be localized to: A single bone (monostotic fibrous dysplasia) Multiple bones (polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) [4] The disease process may be localized to: A single bone (monostotic fibrous dysplasia) Multiple bones (polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) [4]](/thumbs/95/124167277.jpg) Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2017; 5(11E):4651-4655 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2017; 5(11E):4651-4655 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Dental Perspectives in Fibrous Dysplasia and McCune-Albright Syndrome
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 9-1-2014 Dental Perspectives in Fibrous Dysplasia and McCune-Albright Syndrome Sunday O. Akintoye University
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 9-1-2014 Dental Perspectives in Fibrous Dysplasia and McCune-Albright Syndrome Sunday O. Akintoye University
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report
 Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL
 What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
Dr Robert Drummond. BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho. Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015
 Dr Robert Drummond BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015 Severely compromised FPM with poor prognosis Children often present with a developing dentition affected
Dr Robert Drummond BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015 Severely compromised FPM with poor prognosis Children often present with a developing dentition affected
Endocrine Features of Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome
 Endocrine Features of Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome Alison Boyce, MD Sec@on on Skeletal Disorders and Mineral Homeostasis, NIDCR, NIH FD Founda@on Pa@ent and Family Conference 2017 Fibrous
Endocrine Features of Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome Alison Boyce, MD Sec@on on Skeletal Disorders and Mineral Homeostasis, NIDCR, NIH FD Founda@on Pa@ent and Family Conference 2017 Fibrous
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
London Intermediate Minor Oral Surgery Referral Form PATIENT DETAILS
 London Intermediate Minor Oral Surgery Referral Form 22.06.18 PATIENT DETAILS Patient s Title and Name: Gender: Date of Birth: Patient s Address: Postcode Patient s email address: Contact Number: (mobile
London Intermediate Minor Oral Surgery Referral Form 22.06.18 PATIENT DETAILS Patient s Title and Name: Gender: Date of Birth: Patient s Address: Postcode Patient s email address: Contact Number: (mobile
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 432676, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/432676 Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor F. Mantar, 1 S. Gunduz,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 432676, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/432676 Case Report A Reference Finding Rarely Seen in Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Brown Tumor F. Mantar, 1 S. Gunduz,
Cephalometric Analysis
 Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
General Dentist Fee Schedule
 General Dentist Fee Schedule ADA Diagnostic D0120 Periodic oral evaluation $0 $72 $72 D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused $77 $107 $30 D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation new or established patient
General Dentist Fee Schedule ADA Diagnostic D0120 Periodic oral evaluation $0 $72 $72 D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused $77 $107 $30 D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation new or established patient
General Dentist Fee Schedule
 General Dentist Fee Schedule Diagnostic D0120 Periodic oral evaluation $0 $59 $59 D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused $71 $88 $17 D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation new or established patient
General Dentist Fee Schedule Diagnostic D0120 Periodic oral evaluation $0 $59 $59 D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused $71 $88 $17 D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation new or established patient
Human, Child (7 years +/- 2 years)
 Human, Child (7 years +/- 2 years) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-276 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations:
Human, Child (7 years +/- 2 years) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-276 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations:
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
RETIREE DENTAL PLAN. RETIREE DENTAL PLAN FEE SCHEDULE Page 1 of 8
 D0120 periodic oral evaluation $ 30.50 D0140 limited oral evaluation problem focused $ 30.50 D0150 comprehensive oral evaluation - new or established patient $ 30.50 D0160 detailed and extensive oral evaluation
D0120 periodic oral evaluation $ 30.50 D0140 limited oral evaluation problem focused $ 30.50 D0150 comprehensive oral evaluation - new or established patient $ 30.50 D0160 detailed and extensive oral evaluation
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Saudi Dental Licensure Examination Content Outline
 Saudi Dental Licensure Examination Content Outline This outline provides a common organization of SDLE content. SDLE central committee continually reviews the outline to ensure content is relevant to the
Saudi Dental Licensure Examination Content Outline This outline provides a common organization of SDLE content. SDLE central committee continually reviews the outline to ensure content is relevant to the
Code Description Cap Freq D5660 ADD CLASP TO EXISTING PARTIAL DENTURE - PER TOOTH 4 1
 Code Description Cap Freq D5660 ADD CLASP TO EXISTING PARTIAL DENTURE - PER TOOTH D5650 ADD TOOTH TO EXISTING PARTIAL DENTURE D5411 ADJUST COMPLETE DENTURE - MANDIBULAR D5410 ADJUST COMPLETE DENTURE -
Code Description Cap Freq D5660 ADD CLASP TO EXISTING PARTIAL DENTURE - PER TOOTH D5650 ADD TOOTH TO EXISTING PARTIAL DENTURE D5411 ADJUST COMPLETE DENTURE - MANDIBULAR D5410 ADJUST COMPLETE DENTURE -
Human, Child (10 years +/- 2.5 years)
 Human, Child (10 years +/- 2.5 years) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-277 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General
Human, Child (10 years +/- 2.5 years) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-277 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General
Dental Health Considerations & Solutions in Patients with Turner Syndrome
 Dental Health Considerations & Solutions in Patients with Turner Syndrome Robert Korwin, D.M.D. Post Graduate Certificate in General Practice Master, Academy of General Dentistry Master, International
Dental Health Considerations & Solutions in Patients with Turner Syndrome Robert Korwin, D.M.D. Post Graduate Certificate in General Practice Master, Academy of General Dentistry Master, International
Case Report Percutaneous kyphoplasty for vertebral fracture second to polyostotic fibrous dysplasia: a case report and review of the literature
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1358-1362 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0040142 Case Report Percutaneous kyphoplasty for vertebral fracture second to polyostotic fibrous dysplasia: a case report and
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(1):1358-1362 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0040142 Case Report Percutaneous kyphoplasty for vertebral fracture second to polyostotic fibrous dysplasia: a case report and
Juvenile Angiofibroma
 Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Newport News Public Schools Summary Schedule of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan
 Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 650428, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/650428 Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease Varant Labajian,
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 650428, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/650428 Case Report An Uncommon Osseous Frontal Sinus Tumor: Monostotic Paget s Disease Varant Labajian,
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
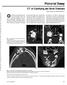 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
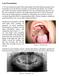 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
2016 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/16-12/31/16
 HCPCS DESCRIPTIONS D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0260 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0470 D0502 D1110 D1206 D1208 D1352 D2140 D2150 D2160 D2161
HCPCS DESCRIPTIONS D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0260 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0470 D0502 D1110 D1206 D1208 D1352 D2140 D2150 D2160 D2161
The ASE Example Case Report 2010
 The ASE Example Case Report 2010 The Requirements for Case Presentation in The Angle Society of Europe are specified in the Appendix I to the Bylaws. This example case report exemplifies how these requirements
The ASE Example Case Report 2010 The Requirements for Case Presentation in The Angle Society of Europe are specified in the Appendix I to the Bylaws. This example case report exemplifies how these requirements
Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries
 Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to: Identify the key anatomical structures of the face and eye and the impact of force on
Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to: Identify the key anatomical structures of the face and eye and the impact of force on
NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2017
 NC Dental Reimbursement s Refer to the NC and Health Choice Clinical Coverage Policies on the DMA website. D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 24.51 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 34.94 D0145
NC Dental Reimbursement s Refer to the NC and Health Choice Clinical Coverage Policies on the DMA website. D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 24.51 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 34.94 D0145
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
A Case of Atypical McCune-Albright Syndrome with Vaginal Bleeding
 Case Report Iran J Pediatr Sep 2011; Vol 21 (No 3), Pp: 399-403 A Case of Atypical McCune-Albright Syndrome with Vaginal Bleeding Noushin Rostampour 1, MD; Mahin Hashemipour* 1,2, MD; Roya Kelishadi 1,2,
Case Report Iran J Pediatr Sep 2011; Vol 21 (No 3), Pp: 399-403 A Case of Atypical McCune-Albright Syndrome with Vaginal Bleeding Noushin Rostampour 1, MD; Mahin Hashemipour* 1,2, MD; Roya Kelishadi 1,2,
T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N
 T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from: Cara Miyasaki, RDHEF, MS, Foothill College Kay Murphy,
T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from: Cara Miyasaki, RDHEF, MS, Foothill College Kay Murphy,
A rare case of solitary toxic nodule in a 3yr old female child a case report
 Volume 3 Issue 1 2013 ISSN: 2250-0359 A rare case of solitary toxic nodule in a 3yr old female child a case report *Chandrasekaran Maharajan * Poongkodi Karunakaran *Madras Medical College ABSTRACT A three
Volume 3 Issue 1 2013 ISSN: 2250-0359 A rare case of solitary toxic nodule in a 3yr old female child a case report *Chandrasekaran Maharajan * Poongkodi Karunakaran *Madras Medical College ABSTRACT A three
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RÉSUMÉ
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RÉSUMÉ
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation
 Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 ORAL SURGERY TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
DELTA DENTAL PPO EPO PLAN DESIGN CP070
 DELTA DENTAL PPO EPO PLAN DESIGN CP070 SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS AND The benefits shown below are performed as deemed appropriate by the attending Dentist subject to the limitations and exclusions of the program.
DELTA DENTAL PPO EPO PLAN DESIGN CP070 SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS AND The benefits shown below are performed as deemed appropriate by the attending Dentist subject to the limitations and exclusions of the program.
The New England Journal of Medicine NORMAL VISION DESPITE NARROWING OF THE OPTIC CANAL IN FIBROUS DYSPLASIA
 NORMAL VISION DESPITE NARROWING OF THE OPTIC CANAL IN FIBROUS DYSPLASIA JANICE S. LEE, D.D.S., M.D., EDMOND FITZGIBBON, M.D., JOHN A. BUTMAN, M.D., PH.D., CRAIG R. DUFRESNE, M.D., HARVEY KUSHNER, PH.D.,
NORMAL VISION DESPITE NARROWING OF THE OPTIC CANAL IN FIBROUS DYSPLASIA JANICE S. LEE, D.D.S., M.D., EDMOND FITZGIBBON, M.D., JOHN A. BUTMAN, M.D., PH.D., CRAIG R. DUFRESNE, M.D., HARVEY KUSHNER, PH.D.,
ORTHODONTICS Treatment of malocclusion Assist.Lec.Kasem A.Abeas University of Babylon Faculty of Dentistry 5 th stage
 Lec: Treatment of class I malocclusion Class I occlusion can be defined by Angles, classification as the mesiobuccal cusp of the upper 1 st permanent molar occlude with the developmental groove of the
Lec: Treatment of class I malocclusion Class I occlusion can be defined by Angles, classification as the mesiobuccal cusp of the upper 1 st permanent molar occlude with the developmental groove of the
Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction
 Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
IJCMR 292. CASE REPORT Craniomaxillofacial Fibrous Dysplasia: Conservative Treatment or Radical Surgery? Report of Two Cases
 IJCMR 292 CASE REPORT Craniomaxillofacial Fibrous Dysplasia: Conservative Treatment or Radical Surgery? Report of Two Cases Gayathri Goudar 1, Manjunath.G.A 2, Subramanya.G 3, Ashoka.k 4,Shwetha Kardalkar
IJCMR 292 CASE REPORT Craniomaxillofacial Fibrous Dysplasia: Conservative Treatment or Radical Surgery? Report of Two Cases Gayathri Goudar 1, Manjunath.G.A 2, Subramanya.G 3, Ashoka.k 4,Shwetha Kardalkar
Surgical Uprighting Is a Successful Procedure for Management of Impacted Mandibular Second Molars
 DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY Surgical Uprighting Is a Successful Procedure for Management of Impacted Mandibular Second Molars Bonnie L. Padwa, DMD, MD,* Rushil R. Dang, BDS, DMD,y and Cory M. Resnick, DMD, MDz
DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY Surgical Uprighting Is a Successful Procedure for Management of Impacted Mandibular Second Molars Bonnie L. Padwa, DMD, MD,* Rushil R. Dang, BDS, DMD,y and Cory M. Resnick, DMD, MDz
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS
 SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS COST-SHARING PEDIATRIC DENTAL CARE ESSENTIAL HEALTH BENEFIT Deductible One (1) Member under age 19 Two (2) or more Members
SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS COST-SHARING PEDIATRIC DENTAL CARE ESSENTIAL HEALTH BENEFIT Deductible One (1) Member under age 19 Two (2) or more Members
Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
Staywell FL Child Medicaid Plan Benefits
 The following is a complete list of dental procedures for which benefits are payable under this Plan. For beneficiaries under age 21, additional coverage may be available with documentation of medical
The following is a complete list of dental procedures for which benefits are payable under this Plan. For beneficiaries under age 21, additional coverage may be available with documentation of medical
AIJCR CASE REPORT ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. CASE REPORTS Case 1
 CASE REPORT Extensive Craniofacial 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1297 Fibrous Dysplasia: An Overview ABSTRACT Introduction: Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a common benign osseous tumor that may affect the craniofacial
CASE REPORT Extensive Craniofacial 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1297 Fibrous Dysplasia: An Overview ABSTRACT Introduction: Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a common benign osseous tumor that may affect the craniofacial
Case Report Monostotic fibrous dysplasia involved in cervical vertebrae
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3577-3581 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0043508 Case Report Monostotic fibrous dysplasia involved in cervical vertebrae Yi Yang *, Litai Ma *, Lingli Li, Hao Liu Department
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3577-3581 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0043508 Case Report Monostotic fibrous dysplasia involved in cervical vertebrae Yi Yang *, Litai Ma *, Lingli Li, Hao Liu Department
HSCSN Table Top Reference Guide
 Age Limitation Covered One per 6 months per dentist or dental group. Only one exam (D0120) every 6 months per dentist or dental D0120 iodic oral evaluation 0-20 No group. D0140 Limited oral evaluation
Age Limitation Covered One per 6 months per dentist or dental group. Only one exam (D0120) every 6 months per dentist or dental D0120 iodic oral evaluation 0-20 No group. D0140 Limited oral evaluation
Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19535-19539 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014642 Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19535-19539 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014642 Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Original Article. Spectrum of Fibro Osseous Lesions: A Retrospective Study
 Original Article Spectrum of Fibro Osseous Lesions: A Retrospective Study Sajitha K*, Kishan Prasad H L, Netra Sajjan and Jayaprakash Shetty K Dept of Pathology, K S Hegde Medical Academy, Mangalore, India
Original Article Spectrum of Fibro Osseous Lesions: A Retrospective Study Sajitha K*, Kishan Prasad H L, Netra Sajjan and Jayaprakash Shetty K Dept of Pathology, K S Hegde Medical Academy, Mangalore, India
SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental Schedule of Benefits
 COST-SHARING SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental Schedule of Benefits Members can search for a Network Provider at www.solsticecare.com/provider-search.aspx Member Services:
COST-SHARING SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental Schedule of Benefits Members can search for a Network Provider at www.solsticecare.com/provider-search.aspx Member Services:
Title. Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu. CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5. Issue Date
 Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Privileges REAPPOINTMENT Effective from July 1, 2015 to June 30, 2016
 Initial privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of privileges (reappointment) All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the Health Authority or Hospital, effective: 11/Dec/2014.
Initial privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of privileges (reappointment) All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the Health Authority or Hospital, effective: 11/Dec/2014.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 6(2) : 157-161, 2015 Case Report ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT a 1b c d NAVDHA CHAUDHARY, BABITA AHLAWAT,
Indian J.Sci.Res. 6(2) : 157-161, 2015 Case Report ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF A COMPLEX ODONTOMA - A CASE REPORT a 1b c d NAVDHA CHAUDHARY, BABITA AHLAWAT,
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
Triad of Bilateral Duplicated Permanent Teeth, Persistent Open Apex, and Tooth Malformation: A Case Report
 Triad of Bilateral Duplicated Permanent Teeth, Persistent Open Apex, and Tooth Malformation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this article is to report a case of bilateral multiple impacted supernumerary
Triad of Bilateral Duplicated Permanent Teeth, Persistent Open Apex, and Tooth Malformation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this article is to report a case of bilateral multiple impacted supernumerary
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2014
 NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2014 The inclusion of a rate on this table does not guarantee
NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2014 The inclusion of a rate on this table does not guarantee
Human, Child (2.5 years +/- 6 months)
 Human, Child (2.5 years +/- 6 months) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-275 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General
Human, Child (2.5 years +/- 6 months) Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-275 Natural bone specimen One panoramic radiograph (Panorex) 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
ATTACHMENT AA DentaQuest of Illinois, LLC
 DentaQuest of Illinois, LLC 112 ATTACHMENT AA DentaQuest of Illinois, LLC HFS Dental Program Fee Schedule for and Adult Beneficiaries Rates Effective July 1, 2009 Please note: have limited dental coverage.
DentaQuest of Illinois, LLC 112 ATTACHMENT AA DentaQuest of Illinois, LLC HFS Dental Program Fee Schedule for and Adult Beneficiaries Rates Effective July 1, 2009 Please note: have limited dental coverage.
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
DENTAL RATE FEE SCHEDULE rates effective 5/1/15 through 6/30/15
 Procedure Code D0120 Description April 2014 Fee Rate cute 16.75% Amount of Reduction May/June 2015 Fee $28.00 $28.00 Periodic Oral Exam Ages 0 thru 18 D0120 Periodic Oral Exam Ages 19 thru 20 and Pregnant
Procedure Code D0120 Description April 2014 Fee Rate cute 16.75% Amount of Reduction May/June 2015 Fee $28.00 $28.00 Periodic Oral Exam Ages 0 thru 18 D0120 Periodic Oral Exam Ages 19 thru 20 and Pregnant
Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report
 Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours)
 PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic Features and Osseous-Dental Treatments
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8795765, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8795765 Case Report Case Report of Nonfamilial Cherubism in a Toddler: Description of Clinic-Radiographic
Fibrous dysplasia: a case series of five cases
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Jagdale A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Nov;3(4):1068-1073 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20163751
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Jagdale A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Nov;3(4):1068-1073 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20163751
Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines
 Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
