Immediate implant placement is becoming increasingly
|
|
|
- Cameron Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 case report Immediate Implant Placement Ridge Augmentation Simultaneous With Immediate Implant Placement: The Subperiosteal Tunneling Technique Barry P. Levin, DMD; and Stephen J. Chu, DMD, MSD, CDT Abstract: The efficacy of immediate implant placement has made it an appealing treatment modality in dentistry. Over the past several decades various surgical techniques to minimize the ridge collapse and other adverse changes that occur after tooth extraction have been advocated. This case series proposes a method of soft-tissue augmentation when multiple implants are being immediately placed. The authors describe a subperiosteal tunneling technique that achieves the dual purpose of graft containment/guided bone regeneration and soft-tissue augmentation around maxillary anterior implants. Immediate implant placement is becoming increasingly common in current implant practice. The expediency and efficiency this treatment modality offers makes it attractive to both patients and clinicians. The early belief or philosophy that placement of an implant into a fresh extraction socket would preserve dentoalveolar contours 1,2 has been disproven, 3-5 as implants do not alter the wound healing process in the extraction socket after tooth removal. More currently, many authors have advocated various surgical techniques to minimize the ridge collapse and negative changes that occur after extraction. These techniques include implant placement without reflection of mucoperiosteal flaps 6,7 and with the use of bone augmentation, 8,9 soft-tissue grafting, 10 guided bone regeneration (GBR), or various combinations of these procedures. 11,12 When anterior single-tooth implants are placed, it is not uncommon for surgeons to use autogenous connective tissue grafts for soft-tissue augmentation. The size of these grafts is relatively small and the morbidity associated with their procurement is mild to moderate in most cases, though Chung et al reported on the possibility of graft failure. 13 When multiple immediate implants are placed, the relative size of these grafts can be significant, and the surgical time and morbidity are typically increased. Alternatives to this approach often include the use of allogeneic dermal grafts. A drawback to these materials, however, is their inert, avascular composition. 14 Though these grafts are capable of being incorporated into native tissues, 15 time is required for adequate revascularization; the exact amount of time needed for incorporation to occur is speculative, though clinically this usually takes place over several weeks. Therefore, these grafts must be covered with the overlying soft tissues to prevent premature exposure and consequent sloughing of the graft. In flapless immediate implant placement, soft tissues cannot be coronally advanced significantly, and, therefore, a resultant void usually exists between the implant and hard/soft-tissue socket walls. 16 This void can be obturated with particulate bone graft materials, collagen membranes, and/or soft-tissue grafts. It may also be sealed with provisional restorations 17,18 or anatomically shaped healing abutments. 19 The size of the gap is also important. 20 It has been demonstrated that sites with larger gaps, ie, greater than 1 mm, result in significantly greater osseous regeneration. 21 Recently, a technique to augment peri-implant soft tissues at the time of immediate implant placement and temporization was introduced for single-tooth replacement. 22 When multiple implants are being placed, another method of soft-tissue augmentation is proposed, as discussed herein. This case series describes a subperiosteal tunneling technique for the dual purpose of graft containment/gbr and soft-tissue augmentation around multiple maxillary anterior implants. Clinical Technique This procedure, illustrated in Figure 1 through Figure 5, is indicated for flapless immediate implant placement in maxillary anterior sites where implants are placed to the palatal aspect of the extraction sockets. Implant diameter is deliberately selected to preserve a gap between the inner aspect of the buccal wall of the socket and implant 2 compendium May 2018 Volume 39, Number 5
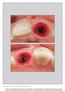
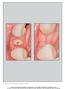
2 Fig 1. Fig 1. Implants are placed to the palatal aspect of extraction sockets. Fig 2. A gap is deliberately preserved between inner aspect of buccal wall of socket and implant surface. Fig 3. Gap is obturated with composite bone graft material consisting of mineralized FDBA and DBBM. Fig 4. Dermal allograft is trimmed to match subperiosteal zone and perforated according to position of abutments. Fig 5. Graft is advanced via suture under papillae. Additional sutures are used to secure allograft to the soft tissues facially and palatally and to compress detached soft tissue. Fig 2. Fig 3. Fig 4. Fig 5. surface. The gap is obturated with a composite bone graft material consisting of mineralized freeze-dried bone allograft (FDBA) and deproteinized bovine bone mineral (DBBM) in a ratio of 4:1. Implants are sealed with appropriately sized stock healing abutments. Subsequent to bone grafting, a subperiosteal dissection of the facial, palatal, and proximal soft tissues is performed. This is accomplished with periodontal knives and small periosteal elevators. Great care is necessary to avoid soft-tissue dehiscence and perforation. The procedure requires serial and circumferential elevation moving the elevator mesial-distally as well as coronal-apically beneath the papillae. Singular focus in one area can lead to unwanted soft-tissue tearing; patience is needed to widen the zone of subperiosteal elevation, slowly and gradually moving the reflection. Once a zone of at least 4 mm to 5 mm of facial and palatal elevation is confirmed, the dermal allograft is trimmed to match the subperiosteal zone created by elevation. A soft-tissue punch is used to perforate the dermal graft according to the position of the healing abutments. It is critical to orient the dermal allograft in a manner in which the connective tissue surface is facing up to be in direct contact with the periosteum of the overlying soft tissues. This is done to facilitate and ensure integration of the graft within the soft tissues. A monofilament, resorbable suture is passed through the distofacial aspect of the mucosa relative to one of the terminal implants. It is tucked under the detached papilla or papillae to engage the dermal allograft in both facial and palatal positions and passed back through the initial path. A C-3 needle is then passed through the distal-palatal mucosa. With careful manipulation, the graft is advanced via the suture under the papillae and adapted between the facial and palatal bone and periosteum, and the initial suture is tied on the palatal aspect of the ridge. Additional sutures are used to secure the allograft to the soft tissues facially and palatally. May 2018 compendium 3
3 Case Report IMMediate Implant Placement Figure 8 design sutures are used to compress the detached soft tissue to minimize clots between the periosteum and dermal allograft and dermal allograft and coronal/proximal bone. Fig 6. Fig 7. Fig 8. Fig 9. Fig 10. Fig 6. Clinical situation with mobile crowns on teeth Nos. 9 and 10. Fig 7. Immediate implants placed in the palatal aspect of both extraction sockets. Fig 8. Monofilament sutures used for dermal allograft stabilization and soft-tissue compression. Fig 9. At 2 months healing, preserved ridge dimensions and healthy peri-implant mucosa were demonstrated. Fig 10. Final cement-retained crowns on both implants (restorative therapy performed by Ralph C. Attanasi, DDS, MS, and Ethan A. Pansick, DDS, MS). Case Reports Case 1 Clinical case No. 1 involves an 89-year-old female patient with a history of implant therapy. She presented with mobile crowns on teeth Nos. 9 and 10, which were placed only 1 year prior (Figure 6). Both teeth had a history of endodontic and restorative therapy and demonstrated significant recurrent caries. After extractions were done without flap elevation, the sockets were debrided with ultrasonic (Piezotome, Acteon, acteongroup. com) and manual instrumentation. Implants were intentionally placed toward the palatal aspect of the extraction sockets with primary stability, confirmed with an insertion torque exceeding 25 Ncm (Figure 7). 23 The gaps between the implants and inner walls of the extraction sockets were obturated with a composite particulate bone graft composed of FDBA/DBBM in a 4:1 ratio. The dermal allograft (PerioDerm, Dentsply Sirona, dentsplysirona.com), with a thickness of 0.4 mm to 0.8 mm, was trimmed as described earlier and pierced with tissue punches to correspond with the positions of the healing abutments. It was then placed beneath the periosteal aspect of the elevated soft tissues. Extreme care was taken to avoid detachment of the interproximal papillae. Monofilament sutures (Monocryl 5-0, Ethicon, ethicon. com) were used to secure the allograft and gently compress the overlying soft tissues (Figure 8). After 8 weeks of healing, the site appeared healthy with preservation of the alveolar ridge in three dimensions (Figure 9). The patient was referred to the restorative dentist to begin esthetic treatment at approximately 10 weeks after surgery. Both implants were restored with custom CAD/CAM abutments and cementretained single crowns (Figure 10). Case 2 The second case demonstrates a 76-year-old female patient with a failing three-unit fixed dental prosthesis (FDP) from teeth Nos. 7 through 9 (Figure 11). After flapless extraction, immediate implant placement toward the palatal aspect of the sockets was performed. Healing abutments were placed, and the void between the implant surface and socket walls was filled with the same particulate bone graft as in the previous clinical situation (Figure 12). The overlying soft tissues, including the pontic space of tooth No. 8, was reflected and the same dermal allograft was carried via suture through the field and secured as previously described. This was meant to augment the coronal and buccal aspect of the future ovate pontic site, as well as the peri-implant mucosa (Figure 13). After 5 weeks, the site appeared healthy, and facial contours were improved compared to the presurgical situation. The concavity in the edentulous site of No. 8 was convex and peri-implant bone levels were unchanged. After another 4 weeks, radiographic bone levels remained unchanged (Figure 14 and Figure 15). The healing abutment on the implant in the No. 9 position was changed to a taller (4 mm height versus 3.5 mm height) but narrower (4 4 compendium May 2018 Volume 39, Number 5
4 mm diameter versus 5 mm diameter) abutment to facilitate easier restorative therapy and encourage coronal migration of soft tissue prior to provisional restoration (Figure 16). The final cementretained FPD from Nos. 7 through 9 is shown in Figure 17. Case 3 The third and final case involves treatment of a 60-year-old male patient, whose restorative dentist had deemed teeth Nos. 7 and 8 unrestorable (Figure 18). Both teeth were extracted without flap reflection and implants were placed palatally with primary stability confirmed by resonance frequency analysis (Osstell Mentor, Osstell, osstell.com). Bone grafting was performed as previously described. Prior to subperiosteal tunneling, an open-tray impression was taken, which facilitated indirect fabrication of splinted screw-retained temporary restorations that would be delivered the same day as surgery. Healing abutments were placed and tunneling as described earlier was performed. Again, caution was used to avoid separation or detachment of the interproximal papillae. A thin (0.4 mm to 0.8 mm) dermal allograft was advanced through the subperiosteal space and secured with 5-0 monofilament sutures. The patient presented immediately to the restorative dentist for delivery of the splinted screw-retained restorations (Figure 19). Care was taken to prevent any occlusal contact with these restorations, and the patient was advised to avoid mastication on the surgical site for about 6 weeks. After approximately 12 weeks of healing, definitive restorative therapy was performed, comprising custom abutment fabrication and two individual cement-retained crowns (Figure 20). Discussion When treating hopeless teeth in the maxillary anterior sextant, clinicians face unique challenges. Both hard and soft tissues are relatively thin. 24 These tissues are susceptible to atrophy after tooth extraction. When immediate implants are placed in the esthetic zone, the naturally occurring diminutive changes of the alveolar ridge Fig 11. Fig 12. Fig 13. Fig 16. Fig 14. Fig 15. Fig 11. Both teeth supporting a failing three-unit bridge from Nos. 7 through 9 were determined to be nonrestorable. Fig 12. Particulate bone graft material was placed to obturate the gap between the implants and socket walls. The graft was placed to a vertical level slightly coronal to the facial crest. Fig 13. After subperiosteal tunneling was done to completely connect the two implant sites beneath the pontic site (No. 8), the dermal allograft was advanced with a 5-0 monofilament suture through the tunnel and fixed. Fig 14 and Fig 15. Proximal bone levels remained unchanged and above the implant-healing abutment junction. Fig 16. At 9 weeks post-surgery, the abutment on the No. 9 implant was changed in favor of a taller but narrower abutment to facilitate coronal migration of the soft-tissue margin and easier access for provisionalization. Fig 17. Final cement-retained FPD from Nos. 7 through 9. Fig May 2018 compendium 5
5 Case Report IMMediate Implant Placement Fig 18. Fig 19. Fig 20. Fig 18. Pretreatment condition of teeth Nos. 7 and 8 with mobile crowns and recurrent caries. Fig 19. Screw-retained, immediate temporization of implants Nos. 7 and 8. These crowns were splinted and out of occlusal contact. Fig 20. Final single-unit, cement-retained crowns Nos. 7 and 8 (restorative therapy performed by Brian L. Wilk, DMD). can compromise esthetic outcomes. 25 Investigators have proposed augmenting soft tissues at the time of implant placement. 26,27 The subperiosteal tunneling technique is designed to accomplish several goals. First, it eliminates the need to procure relatively large, autogenous connective tissue grafts. This reduces treatment time and surgical morbidity. Second, it allows peri-implant soft tissues to be augmented while they also function as a collagen barrier (ie, GBR). Because the allograft is passed under the interproximal papillae, it has the potential to increase soft-tissue volume between adjacent implants and/or implants and pontics in the esthetic zone. In the maxillary anterior sextant, where hard and soft tissues are naturally thin, it is difficult or impossible to reflect partial-thickness mucosal tissues. It has been speculated that the retention of minimal connective tissue coverage may be of little benefit compared to subperiosteal reflection, which is easier to perform, in terms of limiting bone resorption. 28 Because the soft-tissue elevation is subperiosteal in nature, some of the benefits of a flapless procedure are compromised, however. Therefore, the zone of elevation is minimized to approximately 4 mm to 5 mm beyond the crestal osseous margins of the extraction sockets. A similar approach for mucogingival corrective surgery has been documented. 29 In that technique, a subperiosteal elevation is combined with insertion of a dermal allograft between the alveolar bone and periosteum, and the soft tissues are coronally advanced to achieve root coverage secondary to gingival recession. Also, because the proximal tissues are not incised, blood supply from the facial and palatal aspects of the mucosa is not severed. Pressure to minimize the size of the postoperative blood clots and use of compression sutures encourage rapid healing and prevent soft-tissue necrosis and hematoma formation. Increasing the thickness of peri-implant mucosa is a topic of great interest. Linkevicius et al demonstrated the benefit of augmenting naturally occurring thin mucosa, in terms of crestal bone preservation. 30,31 These authors have exhaustively researched the role of tissue thickness as it relates to crestal bone levels in edentulous sites. Any extrapolation of their findings as they relate to immediate implant placement must be done with caution. The present author (BPL) has published a case series utilizing the same dermal allograft in an open or flapped immediate implant placement scenario. 32 The dermis is used as both a GBR membrane and tissue-thickening agent. Because the procedure is demonstrated in a case series and not a controlled clinical trial, more research is required to confirm its efficacy. Conclusion The present case series described a subperiosteal tunneling technique for the dual purpose of graft containment/gbr and softtissue augmentation around multiple maxillary anterior implants. The procedure, featuring flapless immediate implant placement where implants are placed to the palatal aspect of the extraction sockets, was shown to achieve alveolar ridge preservation and improved facial contours while enabling esthetic restoration in a timely fashion. The tunneling procedure is also intended to augment soft tissue volume in proximal and pontic regions; however, controlled studies are necessary to confirm this clinical finding. ABOUT THE AUTHORS Barry P. Levin, DMD Clinical Associate Professor, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Diplomate, American Board of Periodontology; Private Practice, Jenkintown, Pennsylvania Stephen J. Chu, DMD, MSD, CDT Clinical Associate Professor, Ashman Department of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry, New York University College of Dentistry, New York, New York; Private Practice, New York, New York REFERENCES 1. Werbitt MJ, Goldberg PV. The immediate implant: bone preservation and bone regeneration. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1992;12(3): Denissen HW, Kalk W, Veldhuis HA, van Waas MA. Anatomic consideration for preventive implantation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993;8(2): Araújo MG, Lindhe J. Ridge alterations following tooth extraction with and without flap elevation: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(6): Araújo MG, Wennström JL, Lindhe J. Modeling of the buccal and lingual bone walls of fresh extraction sites following implant 6 compendium May 2018 Volume 39, Number 5
6 installation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(6): Botticelli D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites. J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31(10): Chen ST, Darby IB, Reynolds EC, Clement JG. Immediate implant placement postextraction without flap elevation. J Periodontol. 2009; 80(1): Lazic Z, Golubovic M, Markovic A, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of blood vessels in peri-implant mucosa: a comparison between mini-incision flapless and flap surgeries in domestic pigs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(7): Sanz M, Lindhe J, Alcaraz J, et al. The effect of placing a bone replacement graft in the gap at immediately placed implants: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(8): Tarnow DP, Chu SJ, Salama MA, et al. Flapless postextraction socket implant placement in the esthetic zone: Part 1. The effect of bone grafting and/or provisional restoration of facial-palatal ridge dimensional change a retrospective cohort study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2014;34(3): Grunder U. Crestal ridge width changes when placing implants at the time of tooth extraction with and without soft tissue augmentation after a healing period of 6 months: report of 24 consecutive cases. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2011;31(1): Cardaropoli D, Gaveglio L, Gherlone E, Cardaropoli G. Soft tissue contour changes at immediate implants: a randomized controlled clinical study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2014;34(5): Caneva M, Botticelli D, Morelli F, et al. Alveolar process preservation at implants installed immediately into extraction sockets using deproteinized bovine bone mineral an experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2102;23(7): Chung S, Rungcharassaeng K, Kan JY, et al. Immediate single tooth replacement with subepithelial connective tissue graft using platform switching implants: a case series. J Oral Implantol. 2011;37(5): Potter MJ, Linge C, Cussons P, et al. An investigation to optimize angiogenesis within potential dermal replacements. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(6): Cohen M, Joester D, Geiger B, Addadi L. Spatial and temporal sequence of events in cell adhesion: from molecular recognition to focal adhesion assembly. Chembiochem. 2004;5(10): Botticelli D, Persson LG, Lindhe J, Berglundh T. Bone tissue formation adjacent to implants placed in fresh extraction sockets. an experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(4): Degidi M, Daprile G, Nardi D, Piattelli A. Immediate provisionalization of implants placed in fresh extraction sockets using a definitive abutment: the chamber concept. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013;33(5): Chu SJ, Salama MA, Garber DA, et al. Flapless postextraction socket implant placement, Part 2: the effects of bone grafting and provisional restoration on peri-implant soft tissue height and thickness a retrospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2015;35(6): Becker W, Doerr J, Becker BE. A novel method for creating an optimal emergence profile adjacent to dental implants. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2012;24(6): Ferrus J, Cecchinato D, Pjetursson EB, et al. Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(1): Le BT, Borzabadi-Farahani A. Labial bone thickness in area of anterior maxillary implants associated with crestal labial soft tissue thickness. Implant Dent. 2012:21(5): Levin BP. The dermal apron technique for immediate implant socket management: a novel technique. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2016;28(1): Norton MR. The influence of insertion torque on the survival of immediately placed and restored single-tooth implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011;26(6): Younes F, Eghbali A, Raes M, et al. Relationship between buccal bone and gingival thickness revisited using non-invasive registration methods. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27(5): Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Lozada JL, Zimmerman G. Facial gingival tissue stability following immediate placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants: a 2- to 8-year follow-up. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011;26(1): Yoshino S, Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, et al. Effects of connective tissue grafting on the facial gingival level following single immediate implant placement and provisionalization in the esthetic zone: a 1-year randomized controlled prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(2): Migliorati M, Amorini L, Signori A, et al. Clinical and aesthetic outcome with post-extractive implants with or without soft tissue augmentation: a 2-year randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17(5): Wood DL, Hoag PM, Donnenfeld OW, Rosenfeld LD. Alveolar crest reduction following full and partial thickness flaps. J Periodontol. 1972; 43(3): Allen EP. Subpapillary continuous sling suturing method for soft tissue grafting with the tunneling technique. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2010;30(5): Linkevicius T, Puisys A, Linkeviciene L, et al. Crestal bone stability around implants with horizontally matching connection after soft tissue thickening: a prospective clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015;17(3): Linkevicius T, Puisys A, Steigmann M, et al. Influence of vertical soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants with platform switching: a comparative clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015; 17(6): Levin BP. The dual function of a dermal allograft in immediate implant therapy. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2015;35(4): May 2018 compendium 7
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
Partially edentulous patients seeking fixed restoration
 Clinical Technique Review Tissue Augmentation Framing the Restorative Result: How Tissue Augmentation and Preservation Maximizes Implant Therapy Outcomes Barry P. Levin, DMD Abstract: The role of hard-
Clinical Technique Review Tissue Augmentation Framing the Restorative Result: How Tissue Augmentation and Preservation Maximizes Implant Therapy Outcomes Barry P. Levin, DMD Abstract: The role of hard-
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 719 Changes in Peri-implant Soft Tissue Thickness with Bone Grafting and Dermis Allograft: A Case Series of 15 Consecutive Patients Barry
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 719 Changes in Peri-implant Soft Tissue Thickness with Bone Grafting and Dermis Allograft: A Case Series of 15 Consecutive Patients Barry
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
continuing education 1 Esthetic-Zone Implants
 continuing education 1 Esthetic-Zone Implants 10 Keys for Successful Esthetic-Zone Single Immediate Implants: Importance of Biotype Conversion for Lasting Success Robert A. Levine, DDS; Jeffrey Ganeles,
continuing education 1 Esthetic-Zone Implants 10 Keys for Successful Esthetic-Zone Single Immediate Implants: Importance of Biotype Conversion for Lasting Success Robert A. Levine, DDS; Jeffrey Ganeles,
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A Case Series
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Immediate implant placement in a single staged
 Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Nicholas Caplanis DMD MS 6/13/2012
 Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants
 r s Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants richard t. kao, dds, phd; mark c. fagan, ms, dds; and gregory j. conte, ms, dmd abstract During the treatment
r s Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants richard t. kao, dds, phd; mark c. fagan, ms, dds; and gregory j. conte, ms, dmd abstract During the treatment
Initial findings and treatment plan
 12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
Geistlich Fibro-Gide. The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft
 Geistlich Fibro-Gide The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft Geistlich Fibro-Gide shows comparable results to connective tissue grafts in terms of change in soft-tissue volume over time., This demonstrates that
Geistlich Fibro-Gide The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft Geistlich Fibro-Gide shows comparable results to connective tissue grafts in terms of change in soft-tissue volume over time., This demonstrates that
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
CASE REPORT MEGAGEN IMPLANT. AnyRidge. CLINICAL CASE REPORT Davide Farronato, DDs, PhD, PD, AP
 AnyRidge CLINICAL CASE REPORT Davide Farronato, DDs, PhD, PD, AP AnyRidge Clinical Case Ⅰ. Dr. Davide Farronato Baseline - fractured tooth Baseline - fractured tooth #25 Rx view Atraumatic avulsion technique
AnyRidge CLINICAL CASE REPORT Davide Farronato, DDs, PhD, PD, AP AnyRidge Clinical Case Ⅰ. Dr. Davide Farronato Baseline - fractured tooth Baseline - fractured tooth #25 Rx view Atraumatic avulsion technique
Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery
 CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
Prosthodonticstown. Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites. clinical. Table I
 Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Then and Now. Implant Therapy:
 Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study
 immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants
 Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants By Dr. Meir Mamraev DMD LLB W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y The following case study discusses the flapless implant surgery approach using the Cortex
Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants By Dr. Meir Mamraev DMD LLB W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y The following case study discusses the flapless implant surgery approach using the Cortex
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Revisions for CDT 2016
 Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Immediate Implants Tips for improving the outcome in the aesthetic zone
 Immediate Implants Tips for improving the outcome in the aesthetic zone Not long ago, I attended a scientific meeting here in Spain. One of the speakers was a prestigious and well-known researcher in the
Immediate Implants Tips for improving the outcome in the aesthetic zone Not long ago, I attended a scientific meeting here in Spain. One of the speakers was a prestigious and well-known researcher in the
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior
 Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 03 July 16
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging
 Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
 International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area
 CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS,
 Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Tooth out what's next?
 Tooth out what's next Content >> Treatment Options >> Clinical Cases >> Product Information >> Product related FAQs >> Why Ridge Preservation > Minimise invasion: Bone volume preservation > Minimise invasion:
Tooth out what's next Content >> Treatment Options >> Clinical Cases >> Product Information >> Product related FAQs >> Why Ridge Preservation > Minimise invasion: Bone volume preservation > Minimise invasion:
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
Socket Treatment. Procedure Guide
 Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
