Technical Note: Compatibility of Microtomographic Imaging Systems for Dental Measurements
|
|
|
- Posy Fowler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 134: (2007) Technical Note: Compatibility of Microtomographic Imaging Systems for Dental Measurements Anthony J. Olejniczak, 1 * Paul Tafforeau, 2,3 Tanya M. Smith, 1 Heiko Temming, 1 and Jean-Jacques Hublin 1 1 Department of Human Evolution, Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Deutscher Platz 6, D Leipzig, Germany 2 Laboratoire de Géobiologie, Biochronologie et Paléontologie Humaine, UMR CNRS 6046, 40 avenue du Recteur Pineau, F Poitiers cedex, France 3 European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, 6 rue Jules Horowitz, BP 220, Grenoble Cedex, France KEY WORDS Microtomographic imaging; enamel thickness; dental ; synchrotron radiation; conventional X-ray source ABSTRACT Modern micro-computed tomography techniques allow the accurate visualization of internal dental structures, and are becoming widely used within (paleo-) anthropological dental studies. There exist several types and name brands of microtomographic systems, however, which have been demonstrated to produce images that vary in resolution and signal-to-noise ratio. As a growing body of dental research using disparate microtomographic techniques is likely to continue accumulating, it is imperative that different systems are compared to ensure that results are comparable and not machine-dependent. In the present study, we compare volume, surface area, and linear recorded on a sample of modern and fossil teeth using four microtomographic systems (three laboratory scanners, and the ID19 beamline of the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility). Results indicate that are comparable between systems (within 3%), but that synchrotron radiation is superior to the other systems because its monochromatic X-rays prevent beam hardening and its parallel beam prevents geometric artifacts in the resultant images, making it easier to record and see fine details at the enamel cervix or dentine horn tips. Although the synchrotron produces higher resolution images with less artifacts, results indicate that for gross morphological (e.g., enamel cap volume, intercuspal distances), each of the scanners produces approximately the same. Combining of teeth from multiple microct systems presupposes that from each system are comparable; the research presented here indicates that this is the case when teeth are not severely diagenetically remineralized. Am J Phys Anthropol 134: , VC 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Modern laboratory micro-computed tomography (microct) and third generation synchrotron microct facilitate the accurate imaging and measurement of internal dental structures, provided teeth have not undergone severe diagenetic remineralization (Chaimanee et al., 2003; Tafforeau, 2004; Olejniczak and Grine, 2006; Tafforeau et al., 2006). Dental studies based on microct imaging are becoming commonplace in anthropological literature, and several types of microct systems are utilized in the measurement of recent and fossil primate teeth. Conventional laboratory microct has been employed to measure enamel thickness and volume, for instance by Kono (2004; Suwa and Kono, 2005), Olejniczak and Grine (2005, 2006; Olejniczak, 2006), Avishai et al. (2004), and Smith et al. (in press). Synchrotron microct has been used for of enamel thickness and volume by Tafforeau and colleagues (Chaimanee et al., 2003, 2006; Tafforeau, 2004; Macchiarelli et al., 2006; Tafforeau et al., 2006; Smith et al., in press). The accuracy of both laboratory microct (Olejniczak and Grine, 2006) and synchrotron microct (Tafforeau, 2004) were established independently by examining physically produced sections and digital microct sections from the same specimens. Nonetheless, fundamental differences between techniques lead to differences in image quality (Tafforeau, 2004; Tafforeau et al., 2006), which may result in different. As non-destructive microct imaging of teeth becomes widespread, it is essential that taken on images produced by different systems are compared to determine whether combining from multiple microct systems in analyses is justified in light of potential inter-system variance, or perhaps whether system-specific differences are great enough to preclude comparing. Five teeth representing primate and reptilian taxa with varying degrees of diagenetic re-mineralization and enamel thickness (Table 1) were scanned using four different microct systems: a Scanco lct 40 (Department of Biomedical Engineering, Stony Brook University), a SkyScan 1172 system and a BIR Actis 300/225 FP system (both housed at the Department of Human Evolu- Grant sponsors: Max Planck Society, the CNRS, the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, the European Virtual Anthropology Network; Grant sponsor: \EVAN" Marie Curie Research Training Network; Grant number: MRTN-CT *Correspondence to: Anthony J. Olejniczak, Department of Human Evolution, Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Deutscher Platz 6, D Leipzig, Germany. olejniczak@eva.mpg.de Received 20 October 2006; accepted 19 February 2007 DOI /ajpa Published online 14 May 2007 in Wiley InterScience ( VC 2007 WILEY-LISS, INC.
2 MICROTOMOGRAPHIC IMAGING SYSTEM COMPATIBILITY 131 TABLE 1. Specimens scanned by multiple mct systems Taxon Tooth type Notes Pongo pygmaeus Maxillary Molar ca. 130 Kya Homo sapiens Mandibular Molar Recent Alligator mississippiensis Caniniform Tooth Recent Diademodon tetragonus Molariform Tooth ca. 180 Mya Gavial sp. Caniniform Tooth ca. 17 Mya tion, Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology), and the ID19 beamline (European Synchrotron Radiation Facility). The emphasis of this research is not on statistical comparisons between systems, rather the goal was to evaluate the quality of images produced by each system and the percentage difference in of the same objects between systems. As such, a small and diachronically diverse sample is adequate for Fig. 1. Comparison of synchrotron microct (right) and laboratory microct (left) volume models and cross-sections. The synchrotron model has fewer occlusal artifacts and presents finer details, and in cross-section the synchrotron images appear sharper, of similar quality to a physical section. The laboratory microct section appears noisier and with less distinct features. For the same voxel size, the synchrotron exhibits a higher resolution than the laboratory microct.
3 132 A.J. OLEJNICZAK ET AL. TABLE 2. Linear recorded for each tooth Measurement Definition Alligator Length of the entire tooth Distance between apical-most points at the tooth base Width at mid-point of pulp chamber Homo Length Breadth Buccal enamel cusp tip distance Gavial Circumference at 1 mm apical to cusp tip Circumference at 2 mm apical to cusp tip Circumference at 3 mm apical to cusp tip Diademodon a Length Breadth at 1/3 length apical to cusp tip Breadth at 2/3 length apical to cusp tip Pongo Length Breadth Distance between two buccal cusp tips a These are of root dentine, not enamel. evaluation; a larger sample would facilitate testing for statistical differences. The Scanco and SkyScan machines are both cone beam systems, and are generally similar in design and function with the exception of higher source voltage in the SkyScan machine (*100 kv versus *70 kv). All scans on the SkyScan machine were performed with an aluminum-copper filter at 100 kv and 100 la. The BIR machine is capable of higher source voltage than the other laboratory machines (maximum 225 kv), and it also accommodates larger specimens. All specimens scanned on the BIR scanner were performed at 130 kv, 100 la, and with a brass filter. Unlike conventional X-ray micro-tomography, a third generation synchrotron light source necessitates that specimens are brought to the radiation facility for analysis (whereas some conventional systems are transportable). We employ synchrotron radiation in this study as a \golden standard" against which to assess the accuracy of the other systems. The third generation synchrotron light source we used to perform experiments here has several fundamental differences from the other systems we employed, which are thoroughly recounted by Tafforeau et al. (2006), and only briefly summarized here. Experiments were performed using a beam monochromatized using a double silicon crystal monochromator with an energy bandwidth of Dk/k ¼ mm of diamond and 2 mm of aluminum were put in the beam before the monochromator to limit the heat load (these filters have no effect on the monochromaticity of the beam after the silicon crystals). X-ray energy was set to 60 kev depending on the sample size and mineralization. Isotropic voxels were produced for all specimens. A third generation synchrotron source can produce extremely intense nearly parallel X-ray beams that can be monochromatized, leading to high quality absorption scans without beam hardening effects or geometric artifacts (which are due, respectively, to the polychromatic spectrum and the cone beam geometry used in most laboratory microtomographic systems). Third generation synchrotron sources also have fast scan acquisition times (e.g., the same tooth scanned on the SkyScan and Synchrotron systems took 3.75 and 0.75 h, respectively). Figure 1 illustrates image quality differences between laboratory and synchrotron microct scans of the Pongo molar, recorded with approximately equivalent scan parameters (same voxel size and angular step during the TABLE 3. Average percent differences between scanners Specimen Linear Surface area Volume Alligator Diademodon Gavial Homo Pongo Mean % Difference scan). Three-dimensional rendering was performed using VG Studio Max software (Volume Graphics, Heidelberg, Germany). A tooth-specific set of linear was recorded on each of the image stacks from the different microct systems (Table 2). Additional included the volume of enamel and the surface area of enamel. In the case of the Diademodon tooth, root dentine was measured in lieu of enamel. All were collected by a single observer (AJO) in order to eliminate interobserver error. All were collected using OsiriX (Rosset et al., 2004), VoxBlast (Vaytek, Inc.), and 3D Slicer (Gering et al., 1999) software. Tissue segmentation protocols differed between specimens, as fossils evince variable levels of diagenetic remineralization, which impacts gray-scale values (Chaimanee et al., 2006; Olejniczak and Grine, 2006; Tafforeau et al., 2006). In all cases, segmentation consisted of one or both of the following filters: the median filter (with a kernel size of three pixels) and the anisotropic diffusion filter. An identical filtering protocol for each tooth was employed, for all scans of that tooth (regardless of which system produced the scans); in this way, the impact of variable filtering protocols on is eliminated. These filters have been demonstrated to greatly enhance tissue boundaries and tissue pixel value homogeneity in dental specimens (Olejniczak, 2006). The pixel value histogram of each image stack was also recorded to compare the locations of peaks and troughs representing enamel, dentine, mineral matrix (on the Pongo tooth), and background noise. Histograms were recorded before any filtering algorithms were applied to the image stacks. Pixel value histograms allow comparisons of the relative ease of tissue segmentation (separating enamel, dentine, and air in digital images produced by scanning, for the purpose of measuring each tissue). Voxel dimensions were kept as close to equal as possible between systems in order to isolate measurement variation due to machine differences rather than voxel size. The average percent differences for recorded in this study are reported by measurement type in Table 3. Results indicate that taken on all four systems appear to be comparable (less than 3.0% different between machines on average). Volumes are the most stable, with the lowest average percentage difference among systems. Linear and surface areas both show measurement differences of *2%. Despite the relative similarity of across systems, there is a notably sharper quality of images produced by synchrotron scanning, whereby images are produced with fewer artifacts and with more distinct tissues (e.g., Fig. 1; see also Tafforeau, 2004 and Tafforeau
4 MICROTOMOGRAPHIC IMAGING SYSTEM COMPATIBILITY 133 Fig. 2. Pixel value histograms of the Pongo specimen from each of the microct systems on which it was scanned. Only the pixel value range containing the object of interest has been shown in each case. The Scanco system histogram does not show any discrimination between tissues, as is the case in the histograms produced by the BIR system and the SkyScan system (without post-hoc beam-hardening correction filters). The synchrotron shows a separate peak for enamel, as well as two distinct peaks separating dentine from the surrounding matrix. Because of the discrepancy in underlying pixel values, the synchrotron image stack is easier to segment into unique tissues for the purpose of recording. When a beam hardening filter was applied to the SkyScan system s image stack, the histogram improved; this suggests that software solutions to beam hardening may partially improve the relative quality of laboratory microct scans. et al., 2006). Voxel value histograms (histograms showing the gray-scale value of all the pixels in a digital image; black is zero and white is 255) demonstrate that the synchrotron produces more distinguishable and homogenous tissue groups than the other scanners. Figure 2 depicts three-dimensional pixel value histograms for the same specimen (the fossil Pongo molar) produced by all four microct scanners. The Scanco, BIR, and SkyScan systems histograms show a single, smooth distribution of pixels, indicating that enamel, dentine, and the surrounding matrix have substantially overlapping pixel values. The synchrotron light source, however, produced an image stack with a separate peak of enamel pixels, and even shows a slight difference (in the form of two distinct peaks) between dentine and the surrounding matrix. The relative lack of tissue separation in the non-synchrotron microct systems examined here is probably partially due to beam hardening, which is effectively eliminated by the monochromatic beam of the synchrotron. It may also be explained by the synchrotron s higher resolution and signal-to-noise ratio, which result in tissue interfaces (e.g., the enamel-dentine junction) that are not blurred as much as laboratory microct scans, and less random noise in homogenous areas. To evaluate the beam hardening effect on the resulting histograms, we used a software-based linear gain correction filter (i.e., beam-hardening artifact reduction filter) and reconstructed the fossil Pongo molar image stack produced by the SkyScan system a second time. The resultant pixel value histogram demonstrates an improvement in the separation of tissues (see Fig. 2), although the synchrotron light source still produces the greatest tissue distinctions. Moreover, while software solutions to reduce image artifacts may be effective, it is always preferable to record the original scans using optimal parameters as image filters may introduce error, for instance by incorrectly locating the edge of a tissue boundary. That is to say, producing cleaner images by means of equipment modification is always preferable to post-hoc software solutions. Nonetheless, as monochromatic X-ray sources are not commonplace, it is important to note that polychromatic X-ray microct images may be enhanced to approach the condition produced by the synchrotron light source in terms of pixel value separation of whole teeth. Clearly separated tissues based on the pixel values in digital images expedite the tedious process of image segmentation, in which unique tissues in each image stack are rendered homogenous in order to facilitate accurate measurement. The synchrotron produces the cleanest images prior to segmentation, making this method of scanning superior to the laboratory scanners in terms of the efficiency of. Nonetheless, the accuracy of tooth crown taken on scans from each of the systems appears to be similar, such that area, linear, and volume of tooth crowns from different scanners may be combined in future analyses. Where fine structures are concerned (e.g., dentine horn tips and cervical enamel), the resolution of the third generation synchrotron would provide a more accurate representation of the true morphology than laboratory scanners. It must be noted, however, that the accessibility of synchrotron scanning is limited; synchrotron radiation facilities are rare, and fossils must be brought to the radiation source. Some conventional microct scanners are transportable, making it possible to bring the scanner to the specimen. As the use of microct in dental research becomes increasingly prevalent, future studies (especially metaanalyses, wherein multiple data-sets are combined) will likely contain data produced by multiple microct systems. Combining of teeth from multiple
5 134 A.J. OLEJNICZAK ET AL. microct systems presupposes that from each system are comparable; the research presented here indicates that this is the case (within 3%) when gross morphological are taken (e.g., enamel volume and intercuspal distances), and when teeth are not severely diagenetically remineralized. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS For access to specimens we thank R. Ciochon and F. Grine. Scanning assistance in Stony Brook was provided by F. Grine, S. Judex, and S. Xu. M. Skinner and R. Feeney graciously provided critical feedback on the original manuscript. LITERATURE CITED Avishai G, Müller R, Gabet Y, Bab I, Zilberman U, Smith P New approach to quantifying developmental variation in the dentition using serial microtomographic imaging. Microsc Res Tech 65: Chaimanee Y, Jolly D, Benammi M, Tafforeau P, Duzer D, Moussa I, Jaeger JJ A Middle Miocene hominoid from Thailand and orangutan origins. Nature 422: Chaimanee Y, Yamee C, Tian P, Khaowiset K, Marandat B, Tafforeau P, Nemoz C, Jaeger J-J Khoratpithecus piriyai, a late Miocene hominoid of Thailand. Am J Phys Anthropol 131: Gering D, Nabavi A, Kikinis R, Eric W, Grimson L, Hata N, Everett P, Jolesz F, and Wells III W An integrated visualization system for surgical planning and guidance using image fusion and interventional imaging. In: Proceeding of Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Cambridge: England, p Kono R Molar enamel thickness and distribution patterns in extant great apes and humans: new insights based on a 3- dimensional whole crown perspective. Anthropol Sci 112: Macchiarelli R, Bondioli L, Debénath A, Mazurier A, Tournepiche J-F, Birch W, Dean C How Neanderthal molar teeth grew. Nature 444: Olejniczak AJ Micro-computed tomography of the postcanine dentition. Ph.D. dissertation, Stony Brook University. Olejniczak AJ, Grine FE High-resolution measurement of Neanderthal tooth enamel thickness by micro-focal computed tomography. S Afr J Sci 101: Olejniczak AJ, Grine FE Assessment of the accuracy of dental enamel thickness using microfocal X-ray computed tomography. Anat Rec A 288: Rosset A, Spadola L, Ratib O OsiriX: an open-source software for navigating in multidimensional DICOM images. J Digit Imaging 17: Suwa G, Kono R A micro-ct based study of linear enamel thickness in the mesial cusp section of human molars: reevaluation of methodology and assessment of within-tooth, serial, and individual variation. Anthropol Sci 113: Smith TM, Olejniczak AJ, Tafforeau P, Reid DJ, Grine FG, and Hublin J-J. Molar crown thickness, volume, and development in South African Middle Stone Age humans. S Afr J Sci, in press. Tafforeau P Phylogenetic and functional aspects of tooth enamel microstucture and three-dimensional structure of modern and fossil primate molars. Ph.D. dissertation, Université de Montpellier II. Tafforeau P, Boistel R, Boller E, Bravin A, Brunet M, Chaimanee Y, Cloetens P, Feist M, Hoszowska J, Jaeger J-J, Kay RF, Lazzari V, Marivaux L, Nel A, Nemoz C, Thibault X, Vignaud P, Zabler S Applications of X-ray synchrotron microtomography for non-destructive 3D studies of paleontological specimens. Appl Phys A 83:
Enamel thickness in Asian human canines and premolars
 ANTHROPOLOGICAL SCIENCE Vol. 118(3), 191 198, 2010 Brief Communication Enamel thickness in Asian human canines and premolars Robin N.M. FEENEY 1, John P. ZERMENO 2, Donald J. REID 3, Syozi NAKASHIMA 4,
ANTHROPOLOGICAL SCIENCE Vol. 118(3), 191 198, 2010 Brief Communication Enamel thickness in Asian human canines and premolars Robin N.M. FEENEY 1, John P. ZERMENO 2, Donald J. REID 3, Syozi NAKASHIMA 4,
Variation in hominoid molar enamel thickness
 Journal of Human Evolution 48 (2005) 575e592 Variation in hominoid molar enamel thickness Tanya M. Smith a, *, Anthony J. Olejniczak a, Lawrence B. Martin b, Donald J. Reid c a Interdepartmental Doctoral
Journal of Human Evolution 48 (2005) 575e592 Variation in hominoid molar enamel thickness Tanya M. Smith a, *, Anthony J. Olejniczak a, Lawrence B. Martin b, Donald J. Reid c a Interdepartmental Doctoral
Brief Communication: Enamel Thickness Trends in the Dental Arcade of Humans and Chimpanzees
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 136:237 241 (2008) Brief Communication: Enamel Thickness Trends in the Dental Arcade of Humans and Chimpanzees Tanya M. Smith, 1 * Anthony J. Olejniczak, 1 Stefan
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 136:237 241 (2008) Brief Communication: Enamel Thickness Trends in the Dental Arcade of Humans and Chimpanzees Tanya M. Smith, 1 * Anthony J. Olejniczak, 1 Stefan
Modern human molar enamel thickness and enamel dentine junction shape
 Archives of Oral Biology (2006) 51, 974 995 www.intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/arob Modern human molar enamel thickness and enamel dentine junction shape T.M. Smith a, *, A.J. Olejniczak a,b, D.J. Reid
Archives of Oral Biology (2006) 51, 974 995 www.intl.elsevierhealth.com/journals/arob Modern human molar enamel thickness and enamel dentine junction shape T.M. Smith a, *, A.J. Olejniczak a,b, D.J. Reid
Molar Enamel Thickness and Dentine Horn Height in Gigantopithecus blacki
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 135:85 91 (2008) Molar Enamel Thickness and Dentine Horn Height in Gigantopithecus blacki A.J. Olejniczak, 1 * T.M. Smith, 1 W. Wang, 2,3 R. Potts, 4 R. Ciochon,
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 135:85 91 (2008) Molar Enamel Thickness and Dentine Horn Height in Gigantopithecus blacki A.J. Olejniczak, 1 * T.M. Smith, 1 W. Wang, 2,3 R. Potts, 4 R. Ciochon,
Brief Communication: Dental Development and Enamel Thickness in the Lakonis Neanderthal Molar
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 138:112 118 (2009) Brief Communication: Dental Development and Enamel Thickness in the Lakonis Neanderthal Molar T.M. Smith, 1 * K. Harvati, 1 A.J. Olejniczak,
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 138:112 118 (2009) Brief Communication: Dental Development and Enamel Thickness in the Lakonis Neanderthal Molar T.M. Smith, 1 * K. Harvati, 1 A.J. Olejniczak,
Taxonomic Assessment of the Trinil Molars Using Non-Destructive 3D Structural and Development Analysis
 Taxonomic Assessment of the Trinil Molars Using Non-Destructive 3D Structural and Development Analysis tanya m. smi th Department of Human Evolution, Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology,
Taxonomic Assessment of the Trinil Molars Using Non-Destructive 3D Structural and Development Analysis tanya m. smi th Department of Human Evolution, Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology,
Chapter Introduction Dental microstructure and age at death estimation
 Chapter 8 7 Tanya M. Smith, Donald J. Reid, Anthony J. Olejniczak, Paul T. Tafforeau, Jean-Jacques Hublin & Michel Toussaint Dental development in and age at death of the Scladina I-4A juvenile Neandertal
Chapter 8 7 Tanya M. Smith, Donald J. Reid, Anthony J. Olejniczak, Paul T. Tafforeau, Jean-Jacques Hublin & Michel Toussaint Dental development in and age at death of the Scladina I-4A juvenile Neandertal
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Materials. The deciduous (S14-5) and permanent (BD-J4-C9) Neanderthal molars used in this study are isolated specimens from La Chaise-de-Vouthon, Charente, France. The site (0
Supplementary Information Materials. The deciduous (S14-5) and permanent (BD-J4-C9) Neanderthal molars used in this study are isolated specimens from La Chaise-de-Vouthon, Charente, France. The site (0
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars
 Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images
 Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images A. Garay 1, J.H. Legarreta 1, I. Macía 1, R. C. Aza 2 1 Vicomtech-ik4, Mikeletegi Pasealekua, 57 Teknologi Parkea 20009 Donostia, Spain
Human tooth root canal geometry assessment through micro-ct images A. Garay 1, J.H. Legarreta 1, I. Macía 1, R. C. Aza 2 1 Vicomtech-ik4, Mikeletegi Pasealekua, 57 Teknologi Parkea 20009 Donostia, Spain
Chapter 13 Dental Development and Age at Death of a Middle Paleolithic Juvenile Hominin from Obi-Rakhmat Grotto, Uzbekistan
 Chapter 13 Dental Development and Age at Death of a Middle Paleolithic Juvenile Hominin from Obi-Rakhmat Grotto, Uzbekistan Tanya M. Smith, Donald J. Reid, Anthony J. Olejniczak, Shara Bailey, Mica Glantz,
Chapter 13 Dental Development and Age at Death of a Middle Paleolithic Juvenile Hominin from Obi-Rakhmat Grotto, Uzbekistan Tanya M. Smith, Donald J. Reid, Anthony J. Olejniczak, Shara Bailey, Mica Glantz,
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
The accuracy of histological assessments of dental
 J. Anat. (2006) 208, pp125 138 The accuracy of histological assessments of dental Blackwell Publishing Ltd development and age at death T. M. Smith, 1 D. J. Reid 2 and J. E. Sirianni 3 1 Department of
J. Anat. (2006) 208, pp125 138 The accuracy of histological assessments of dental Blackwell Publishing Ltd development and age at death T. M. Smith, 1 D. J. Reid 2 and J. E. Sirianni 3 1 Department of
High-resolution micro-ct scanning as an innovative tool for evaluating dental hard tissue development
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4, 2014 High-resolution micro-ct scanning as an innovative tool for evaluating dental hard tissue development Guangyan Dong, 1 Qianqian Dong,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4, 2014 High-resolution micro-ct scanning as an innovative tool for evaluating dental hard tissue development Guangyan Dong, 1 Qianqian Dong,
PAN CEPH 3D CONE BEAM
 PAN CEPH 3D CONE BEAM 2D - 3D panoramic units PANORAMIC CEPHALOMETRIC 3D CONE BEAM IMAGING I-MAX TOUCH Tactile & naturally intuitive panoramic imaging Discover the simplicity and efficiency this unit can
PAN CEPH 3D CONE BEAM 2D - 3D panoramic units PANORAMIC CEPHALOMETRIC 3D CONE BEAM IMAGING I-MAX TOUCH Tactile & naturally intuitive panoramic imaging Discover the simplicity and efficiency this unit can
3D visualization and quantification of bone and teeth mineralization for the study of osteo/dentinogenesis in mice models
 3D visualization and quantification of bone and teeth mineralization for the study of osteo/dentinogenesis in mice models Arnaud Marchadier, Catherine Vidal, Sylvain Ordureau, Roger Lédée, Christophe Léger,
3D visualization and quantification of bone and teeth mineralization for the study of osteo/dentinogenesis in mice models Arnaud Marchadier, Catherine Vidal, Sylvain Ordureau, Roger Lédée, Christophe Léger,
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT
 Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Chapter 2. Material and methods
 Chapter 2 Material and methods Material and methods Summary This chapter describes the subjects and methods being used in this study. Between 1986 and 1997 9 expeditions were undertaken in remote areas
Chapter 2 Material and methods Material and methods Summary This chapter describes the subjects and methods being used in this study. Between 1986 and 1997 9 expeditions were undertaken in remote areas
PERSPECTIVES OF THE TOOTH RESTORATION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON THE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY DATA
 PERSPECTIVES OF THE TOOTH RESTORATION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON THE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY DATA Maxim Putrik *, Vladimir Ivanov, Igor Antsygin Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education
PERSPECTIVES OF THE TOOTH RESTORATION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON THE COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY DATA Maxim Putrik *, Vladimir Ivanov, Igor Antsygin Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education
3D Accuitomo XYZ Slice View Tomograph. Super High-Resolution Images of Region of Interest
 3D Accuitomo XYZ Slice View Tomograph. Super High-Resolution Images of Region of Interest Thinking ahead. Focused on life. 2 Cone Beam X-Ray CT Imaging X-Ray Tube Imaging Intensifier Imaging Volume Voxel
3D Accuitomo XYZ Slice View Tomograph. Super High-Resolution Images of Region of Interest Thinking ahead. Focused on life. 2 Cone Beam X-Ray CT Imaging X-Ray Tube Imaging Intensifier Imaging Volume Voxel
BIOBank Innovation: The Customized Bone Graft
 Preserved and regenerated human bone Innovation: The Customized Bone Graft Concept A Customized Graft for bone apposition BENEFITS FOR SURGEONS: Easier planning of the surgery: properties and positioning
Preserved and regenerated human bone Innovation: The Customized Bone Graft Concept A Customized Graft for bone apposition BENEFITS FOR SURGEONS: Easier planning of the surgery: properties and positioning
Beyond Gorilla and Pongo: Alternative Models for Evaluating Variation and Sexual Dimorphism in Fossil Hominoid Samples
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 140:253 264 (2009) Beyond Gorilla and Pongo: Alternative Models for Evaluating Variation and Sexual Dimorphism in Fossil Hominoid Samples Jeremiah E. Scott, 1
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 140:253 264 (2009) Beyond Gorilla and Pongo: Alternative Models for Evaluating Variation and Sexual Dimorphism in Fossil Hominoid Samples Jeremiah E. Scott, 1
RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY. L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
 IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
English. Perfect Vision
 English Perfect Vision Everything becomes clearer and simpler with a big F.O.V. The complete dentomaxillofacial volume ready for your diagnosis One scan provides you with an incredible amount of information
English Perfect Vision Everything becomes clearer and simpler with a big F.O.V. The complete dentomaxillofacial volume ready for your diagnosis One scan provides you with an incredible amount of information
Incremental dental development: Methods and applications in hominoid evolutionary studies
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Human Evolution 54 (2008) 205e224 Incremental dental development: Methods and applications in hominoid evolutionary studies Tanya M. Smith* Department
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Human Evolution 54 (2008) 205e224 Incremental dental development: Methods and applications in hominoid evolutionary studies Tanya M. Smith* Department
I AM DEMANDING Type CMOS Flat Panel CMOS CMOS ø 40 x 40 mm, ø 60 x 60 mm, ø 80 x 80 mm, ø 110 x 80 mm
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS 1168 1501 1978 1237 1551-2351 Ø 1090 PANORAMIC CBCT CEPHALOMETRIC X-RAY SOURCE Tube type High frequency DC generator 2.8 mmal / 85 kv 7.0 mmal / 90 kv 2.8 mmal / 85 kv Operation
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS 1168 1501 1978 1237 1551-2351 Ø 1090 PANORAMIC CBCT CEPHALOMETRIC X-RAY SOURCE Tube type High frequency DC generator 2.8 mmal / 85 kv 7.0 mmal / 90 kv 2.8 mmal / 85 kv Operation
AGENTS WITHIN A DEVELOPMENTAL COMPLEX ADAPTIVE SYSTEM: INTRAUTERINE MALE HORMONES INFLUENCE HUMAN TOOTH SIZE AND SHAPE
 F. Lam, et al., Int. J. of Design & Nature and Ecodynamics. Vol. 11, No. 4 (2016) 696 702 AGENTS WITHIN A DEVELOPMENTAL COMPLEX ADAPTIVE SYSTEM: INTRAUTERINE MALE HORMONES INFLUENCE HUMAN TOOTH SIZE AND
F. Lam, et al., Int. J. of Design & Nature and Ecodynamics. Vol. 11, No. 4 (2016) 696 702 AGENTS WITHIN A DEVELOPMENTAL COMPLEX ADAPTIVE SYSTEM: INTRAUTERINE MALE HORMONES INFLUENCE HUMAN TOOTH SIZE AND
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes. **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures**
 Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown. By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi
 Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Head to new heights with your imaging SCANORA 3D
 SCANORA 3D Head to new heights with your imaging Benefits at a glance The solution for dentomaxillofacial and ENT imaging Easy Patient seated for added stability during exposure. Clear, self-explinatory
SCANORA 3D Head to new heights with your imaging Benefits at a glance The solution for dentomaxillofacial and ENT imaging Easy Patient seated for added stability during exposure. Clear, self-explinatory
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
The morphological studies of root r maxillary primary canines and their Title the position of successive permanen Micro-CT
 The morphological studies of root r maxillary primary canines and their Title the position of successive permanen Micro-CT Author(s) Saka, H; Koyama, T; Tamatsu, Y; Usa Alternative Journal Pediatric dental
The morphological studies of root r maxillary primary canines and their Title the position of successive permanen Micro-CT Author(s) Saka, H; Koyama, T; Tamatsu, Y; Usa Alternative Journal Pediatric dental
Profound understanding of anatomy
 ENGLISH Profound understanding of anatomy Planmeca ProMax 3D, the intelligent and multipurpose X-ray unit, is designed to obtain complete information on patient anatomy in the minutest detail. The unit
ENGLISH Profound understanding of anatomy Planmeca ProMax 3D, the intelligent and multipurpose X-ray unit, is designed to obtain complete information on patient anatomy in the minutest detail. The unit
The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from Dr. Eric Herbranson, Dr. Charles Goodacre, and Dr. Robert Hasel.
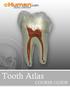 The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from Dr. Eric Herbranson, Dr. Charles Goodacre, and Dr. Robert Hasel. 2013 ehuman, Inc. 47865 Fremont Blvd. Fremont, CA 94538 Produced
The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from Dr. Eric Herbranson, Dr. Charles Goodacre, and Dr. Robert Hasel. 2013 ehuman, Inc. 47865 Fremont Blvd. Fremont, CA 94538 Produced
Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)
 Journal section: Clinical and Experimental Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using
Journal section: Clinical and Experimental Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
EXTRACT THE BREAST CANCER IN MAMMOGRAM IMAGES
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation
 Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
THE WAIT IS OVER CS D. 3D imaging is now available for everyone
 THE WAIT IS OVER CS 8100 3D 3D imaging is now available for everyone COMPLEXITY IS NO LONGER THE STANDARD NOW THERE ARE MANY REASONS TO MOVE TO 2D/3D IMAGING Now it s possible to experience nothing but
THE WAIT IS OVER CS 8100 3D 3D imaging is now available for everyone COMPLEXITY IS NO LONGER THE STANDARD NOW THERE ARE MANY REASONS TO MOVE TO 2D/3D IMAGING Now it s possible to experience nothing but
VistaVox S 3D from Dürr Dental
 VistaVox S 3D from Dürr Dental 3D and 2D X-ray images with exceptional image quality COMPRESSED AIR SUCTION IMAGING DENTAL CARE HYGIENE Taking diagnostics to the next level VistaVox S combines diagnostic
VistaVox S 3D from Dürr Dental 3D and 2D X-ray images with exceptional image quality COMPRESSED AIR SUCTION IMAGING DENTAL CARE HYGIENE Taking diagnostics to the next level VistaVox S combines diagnostic
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions
 CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Wisdom Can Be Painful: Third Molar Impaction In Human Populations and Its Evolutionary Significance
 Wisdom Can Be Painful: Third Molar Impaction In Human Populations and Its Evolutionary Significance Since Charles Darwin published the Origin of Species in 1859, evolution and the mechanisms underlying
Wisdom Can Be Painful: Third Molar Impaction In Human Populations and Its Evolutionary Significance Since Charles Darwin published the Origin of Species in 1859, evolution and the mechanisms underlying
Low Dose Excellent Image Quality Rapid Reconstruction
 Low Dose Excellent Image Quality Rapid Reconstruction Efficient 3 in 1 Dental X-ray System CBCT > Precise 3-D Anatomical structures - Accurate diagnosis for doctors - Safe implant for patients > Significant
Low Dose Excellent Image Quality Rapid Reconstruction Efficient 3 in 1 Dental X-ray System CBCT > Precise 3-D Anatomical structures - Accurate diagnosis for doctors - Safe implant for patients > Significant
Dental tissue proportions in fossil orangutans from mainland Asia and Indonesia
 Dental tissue proportions in fossil orangutans from mainland Asia and Indonesia The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Dental tissue proportions in fossil orangutans from mainland Asia and Indonesia The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
AN ALGORITHM FOR EARLY BREAST CANCER DETECTION IN MAMMOGRAMS
 AN ALGORITHM FOR EARLY BREAST CANCER DETECTION IN MAMMOGRAMS Isaac N. Bankman', William A. Christens-Barryl, Irving N. Weinberg2, Dong W. Kim3, Ralph D. Semmell, and William R. Brody2 The Johns Hopkins
AN ALGORITHM FOR EARLY BREAST CANCER DETECTION IN MAMMOGRAMS Isaac N. Bankman', William A. Christens-Barryl, Irving N. Weinberg2, Dong W. Kim3, Ralph D. Semmell, and William R. Brody2 The Johns Hopkins
Development of a Goniometer with Nanoradian Accuracy
 Development of a Goniometer with Nanoradian Accuracy Basil Blank, Thomas Kupp, Eric Johnson, Alex Deyhim, Chi-Chang Kao*, Wolfgang Caliebe*, Gary Navrotski** Abstract Advanced Design Consulting, Inc. 126
Development of a Goniometer with Nanoradian Accuracy Basil Blank, Thomas Kupp, Eric Johnson, Alex Deyhim, Chi-Chang Kao*, Wolfgang Caliebe*, Gary Navrotski** Abstract Advanced Design Consulting, Inc. 126
Dimensional stability in composite cone beam computed tomography
 (2010) 39, 512 516 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org TECHNICAL REPORT Dimensional stability in composite cone beam computed tomography S Kopp* and P Ottl Department of
(2010) 39, 512 516 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org TECHNICAL REPORT Dimensional stability in composite cone beam computed tomography S Kopp* and P Ottl Department of
Ontogeny of Canine Dimorphism in Extant Hominoids
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 115:269 283 (2001) Ontogeny of Canine Dimorphism in Extant Hominoids Gary T. Schwartz 1,2 * and Christopher Dean 3 1 Department of Anthropology, The George Washington
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 115:269 283 (2001) Ontogeny of Canine Dimorphism in Extant Hominoids Gary T. Schwartz 1,2 * and Christopher Dean 3 1 Department of Anthropology, The George Washington
Michael W. Kenyhercz, 1 * Alexandra R. Klales, 2,3 and William E. Kenyhercz 4. dental anthropology; ancestry; geometric morphometrics discriminant
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 153:269 279 (2014) Molar Size and Shape in the Estimation of Biological Ancestry: A Comparison of Relative Cusp Location Using Geometric Morphometrics and Interlandmark
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 153:269 279 (2014) Molar Size and Shape in the Estimation of Biological Ancestry: A Comparison of Relative Cusp Location Using Geometric Morphometrics and Interlandmark
BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging. Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes
 BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes 1 Outline Introduction K-Edge Imaging Patient imaging at the European synchrotron Medical Phase Contrast
BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes 1 Outline Introduction K-Edge Imaging Patient imaging at the European synchrotron Medical Phase Contrast
Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
 CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
Lecture. Permanent maxillary premolars
 Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
X X X. GXS-700 Direct USB Digital Intraoral Sensors. Buy a Sensor Combo and a Digital Pan Unit, Receive $600 Off! GO.BENCO benco.
 8 0 0. G O. B E N C O b e n c o. c o m GS-700 Direct USB Digital Intraoral Sensors Designed to make migrating from film, or upgrading an existing digital system, easier than ever High quality image capture
8 0 0. G O. B E N C O b e n c o. c o m GS-700 Direct USB Digital Intraoral Sensors Designed to make migrating from film, or upgrading an existing digital system, easier than ever High quality image capture
CBCT Assessment of Dental and Skeletal Changes Using the Damon versus Conventional (MBT) System
 Askari et al., 2015, 5:10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2161-1122.1000336 ISSN: 2161-1122 Research Articles CBCT Assessment of Dental and Skeletal Changes Using the Damon versus Conventional (MBT) System Marjan
Askari et al., 2015, 5:10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2161-1122.1000336 ISSN: 2161-1122 Research Articles CBCT Assessment of Dental and Skeletal Changes Using the Damon versus Conventional (MBT) System Marjan
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Analysis of Root Resorption in Dentistry using Collaborative Tools & Strategies
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 2, Issue 12 (August 2012), PP. 37-42 Analysis of Root Resorption in Dentistry using
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 2, Issue 12 (August 2012), PP. 37-42 Analysis of Root Resorption in Dentistry using
Profound understanding of anatomy
 ENGLISH Profound understanding of anatomy The unique Planmeca ProMax 3D product family offers equipment for all maxillofacial imaging. All volumes sizes from the smallest special cases to whole head images
ENGLISH Profound understanding of anatomy The unique Planmeca ProMax 3D product family offers equipment for all maxillofacial imaging. All volumes sizes from the smallest special cases to whole head images
Digital Imaging from a new perspective
 TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC SIRONA CREATING AND MAINTAINING VALUE. You are right to expect a great
TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC SIRONA CREATING AND MAINTAINING VALUE. You are right to expect a great
Profound understanding of anatomy
 ENGLISH Profound understanding of anatomy The unique Planmeca ProMax 3D product family offers equipment for all maxillofacial imaging. All volume sizes from the smallest special cases to whole head images
ENGLISH Profound understanding of anatomy The unique Planmeca ProMax 3D product family offers equipment for all maxillofacial imaging. All volume sizes from the smallest special cases to whole head images
Dental evidence for ontogenetic differences between modern humans and Neanderthals
 Dental evidence for ontogenetic differences between modern humans and Neanderthals Tanya M. Smith a,b,1, Paul Tafforeau c,1, Donald J. Reid d, Joane Pouech b,c, Vincent Lazzari b,c,e, John P. Zermeno a,
Dental evidence for ontogenetic differences between modern humans and Neanderthals Tanya M. Smith a,b,1, Paul Tafforeau c,1, Donald J. Reid d, Joane Pouech b,c, Vincent Lazzari b,c,e, John P. Zermeno a,
Current Positions. Education. Awards and Grants. Full Length (Peer-Reviewed) Publications
 Tanya M. Smith Department of Anthropology Peabody Museum 47 11 Divinity Avenue Cambridge, MA 02138 USA Phone: +1 617 496 8259 E-mail: tsmith@fas.harvard.edu Current Positions * Assistant Professor, Department
Tanya M. Smith Department of Anthropology Peabody Museum 47 11 Divinity Avenue Cambridge, MA 02138 USA Phone: +1 617 496 8259 E-mail: tsmith@fas.harvard.edu Current Positions * Assistant Professor, Department
Using MicroCT Scanning Techniques to Assess the Performance of Dental Students Tooth Cavity Preparation Skills
 Using MicroCT Scanning Techniques to Assess the Performance of Dental Students Tooth Cavity Preparation Skills Barry F. Quinn 1, Phil Salmon 2 and Margaret J. Cox 1 1 King's College London Dental Institute,
Using MicroCT Scanning Techniques to Assess the Performance of Dental Students Tooth Cavity Preparation Skills Barry F. Quinn 1, Phil Salmon 2 and Margaret J. Cox 1 1 King's College London Dental Institute,
Three-dimensional analysis of pulp Title maxillary second deciduous molars. Journal Journal of dentistry, 34(7):
 Three-dimensional analysis of pulp Title maxillary second deciduous molars Author(s) Amano, M; Agematsu, H; Abe, Alternative S; Suto, K; Ide, Y S; Usam Journal Journal of dentistry, 34(7): 503-50 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/53
Three-dimensional analysis of pulp Title maxillary second deciduous molars Author(s) Amano, M; Agematsu, H; Abe, Alternative S; Suto, K; Ide, Y S; Usam Journal Journal of dentistry, 34(7): 503-50 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/53
Prospective in (Primate) Dental Analysis through Tooth 3D Topographical Quantification
 Prospective in (Primate) Dental Analysis through Tooth 3D Topographical Quantification Franck Guy*, Florent Gouvard, Renaud Boistel, Adelaïde Euriat, Vincent Lazzari Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique,
Prospective in (Primate) Dental Analysis through Tooth 3D Topographical Quantification Franck Guy*, Florent Gouvard, Renaud Boistel, Adelaïde Euriat, Vincent Lazzari Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique,
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
Concepts of occlusion Balanced occlusion. Monoplane occlusion. Lingualized occlusion. Figure (10-1)
 Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Flaw Assessment Using Shear wave Phased array Ultrasonic Transducer
 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Flaw Assessment Using Shear wave Phased array Ultrasonic Transducer Byungsik YOON AUTHOR 1, Hee-Jong LEE CO-AUTHOR
18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa Flaw Assessment Using Shear wave Phased array Ultrasonic Transducer Byungsik YOON AUTHOR 1, Hee-Jong LEE CO-AUTHOR
1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
 1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
Cone Beam 3D Imaging
 Cone Beam 3D Imaging NewTom Sets the Standard in 3D Maxillofacial Imaging Cone Beam 3D Imaging The Global Market Leader The Inventors n of Cone Beam 3D In 1996, QR srl developed the first generation of
Cone Beam 3D Imaging NewTom Sets the Standard in 3D Maxillofacial Imaging Cone Beam 3D Imaging The Global Market Leader The Inventors n of Cone Beam 3D In 1996, QR srl developed the first generation of
The Optimum Choice for Implantologist
 The Optimum Choice for Implantologist What is essential for your practice? What s the best way to choose a 3D X-ray machine for implant treatment planning? 02 Doctor says.. There are diagnostic limitations
The Optimum Choice for Implantologist What is essential for your practice? What s the best way to choose a 3D X-ray machine for implant treatment planning? 02 Doctor says.. There are diagnostic limitations
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Diagnosis of Liver Tumor Using 3D Segmentation Method for Selective Internal Radiation Therapy
 Diagnosis of Liver Tumor Using 3D Segmentation Method for Selective Internal Radiation Therapy K. Geetha & S. Poonguzhali Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Campus of CEG Anna University,
Diagnosis of Liver Tumor Using 3D Segmentation Method for Selective Internal Radiation Therapy K. Geetha & S. Poonguzhali Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Campus of CEG Anna University,
Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Unusual root canal anatomy in a maxillary second molar Toshiko Inoue, Makoto Saito, Fumio Nishimura, Takashi Miyazaki ABSTRACT Abstract
Radiographic anatomy of pulpal chambers of primary molars
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright(cj 1983 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/Vot. 5, No. 1 Radiographic anatomy of pulpal chambers of primary molars Paninee Puddhikarant, DOS, MDS Robert Rapp, DOS, MS,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright(cj 1983 by The American Academy of Pedodontics/Vot. 5, No. 1 Radiographic anatomy of pulpal chambers of primary molars Paninee Puddhikarant, DOS, MDS Robert Rapp, DOS, MS,
1B Getting Ready for Instrumentation: Mathematical Principles and Anatomic Descriptors
 MODULE 1B Getting Ready for Instrumentation: Mathematical Principles and Anatomic Descriptors Module Overview This module contains a review of the mathematical principles and anatomic descriptors used
MODULE 1B Getting Ready for Instrumentation: Mathematical Principles and Anatomic Descriptors Module Overview This module contains a review of the mathematical principles and anatomic descriptors used
Manual Ultrasonic Inspection of Thin Metal Welds
 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic Manual Ultrasonic Inspection of Thin Metal Welds More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16364
11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), October 6-10, 2014, Prague, Czech Republic Manual Ultrasonic Inspection of Thin Metal Welds More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=16364
Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs
 2012 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology IPCBEE vol. 34 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs Rashmi Uddanwadiker
2012 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology IPCBEE vol. 34 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs Rashmi Uddanwadiker
The Evolution and Benefits of Phased Array Technology for the Every Day Inspector
 ECNDT 2006 - Poster 198 The Evolution and Benefits of Phased Array Technology for the Every Day Inspector Dan KASS, Tom NELLIGAN, and Erich HENJES Olympus NDT, Waltham, USA Abstract. Phased arrays were
ECNDT 2006 - Poster 198 The Evolution and Benefits of Phased Array Technology for the Every Day Inspector Dan KASS, Tom NELLIGAN, and Erich HENJES Olympus NDT, Waltham, USA Abstract. Phased arrays were
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals. Massimo Marenzana
 CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
NON-DESTRUCTIVE 3D STRUCTURAL STUDIES BY X-RAY MICROTOMOGRAPHY
 Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 485 NON-DESTRUCTIVE 3D STRUCTURAL STUDIES BY X-RAY MICROTOMOGRAPHY GR Davis 1, SEP Dowker 1, JC
Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 485 NON-DESTRUCTIVE 3D STRUCTURAL STUDIES BY X-RAY MICROTOMOGRAPHY GR Davis 1, SEP Dowker 1, JC
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT
 Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Morphologic classification of root incidence of accessory canals in ma Title molar palatal roots: Three-dimensio and measurement using Micro-CT Author(s) 下尾, 嘉昭 Journal, (): - URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/3605
Local Image Structures and Optic Flow Estimation
 Local Image Structures and Optic Flow Estimation Sinan KALKAN 1, Dirk Calow 2, Florentin Wörgötter 1, Markus Lappe 2 and Norbert Krüger 3 1 Computational Neuroscience, Uni. of Stirling, Scotland; {sinan,worgott}@cn.stir.ac.uk
Local Image Structures and Optic Flow Estimation Sinan KALKAN 1, Dirk Calow 2, Florentin Wörgötter 1, Markus Lappe 2 and Norbert Krüger 3 1 Computational Neuroscience, Uni. of Stirling, Scotland; {sinan,worgott}@cn.stir.ac.uk
#45 Ortho-Tain, Inc PREVENTIVE ERUPTION GUIDANCE -- PREVENTIVE OCCLUSAL DEVELOPMENT
 #45 Ortho-Tain, Inc. 1-800-541-6612 PREVENTIVE ERUPTION GUIDANCE -- PREVENTIVE OCCLUSAL DEVELOPMENT Analysis and Diagnosis of Occlusion: The ideal child of 5 y ears of age that probably has the best chance
#45 Ortho-Tain, Inc. 1-800-541-6612 PREVENTIVE ERUPTION GUIDANCE -- PREVENTIVE OCCLUSAL DEVELOPMENT Analysis and Diagnosis of Occlusion: The ideal child of 5 y ears of age that probably has the best chance
ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES
 ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES P.V.Rohini 1, Dr.M.Pushparani 2 1 M.Phil Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Mother Teresa women s university, (India) 2 Professor
ANALYSIS AND DETECTION OF BRAIN TUMOUR USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES P.V.Rohini 1, Dr.M.Pushparani 2 1 M.Phil Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Mother Teresa women s university, (India) 2 Professor
Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(1): 9 18 Original Article doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0500 Alveolar Growth in Japanese Infants: A Comparison between Now and 40 Years ago Hiroki Imai 1), Tetsuhide Makiguchi
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
LUNG NODULE DETECTION SYSTEM
 LUNG NODULE DETECTION SYSTEM Kalim Bhandare and Rupali Nikhare Department of Computer Engineering Pillai Institute of Technology, New Panvel, Navi Mumbai, India ABSTRACT: The Existing approach consist
LUNG NODULE DETECTION SYSTEM Kalim Bhandare and Rupali Nikhare Department of Computer Engineering Pillai Institute of Technology, New Panvel, Navi Mumbai, India ABSTRACT: The Existing approach consist
Available online at ScienceDirect
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 1251 1257 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Comparative Study
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 1251 1257 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Comparative Study
Enamel Thickness in Bornean and Sumatran Orangutan Dentitions
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 147:417 426 (2012) Enamel Thickness in Bornean and Sumatran Orangutan Dentitions Tanya M. Smith, 1,2 * Kornelius Kupczik, 2,3 Zarin Machanda, 1 Matthew M. Skinner,
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 147:417 426 (2012) Enamel Thickness in Bornean and Sumatran Orangutan Dentitions Tanya M. Smith, 1,2 * Kornelius Kupczik, 2,3 Zarin Machanda, 1 Matthew M. Skinner,
Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel
 Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel J. M. POWERS, R. G. CRAIG, and K. C. LUDEMA School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48104, USA, and College of Engineering,
Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel J. M. POWERS, R. G. CRAIG, and K. C. LUDEMA School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48104, USA, and College of Engineering,
Molar crown formation in the Late Miocene Asian hominoids, Sivapithecus parvada and Sivapithecus indicus
 Journal of Human Evolution 53 (2007) 61e68 Molar crown formation in the Late Miocene Asian hominoids, Sivapithecus parvada and Sivapithecus indicus Patrick Mahoney a, *, Tanya M. Smith b, Gary T. Schwartz
Journal of Human Evolution 53 (2007) 61e68 Molar crown formation in the Late Miocene Asian hominoids, Sivapithecus parvada and Sivapithecus indicus Patrick Mahoney a, *, Tanya M. Smith b, Gary T. Schwartz
Simulation of spiculated breast lesions
 Simulation of spiculated breast lesions Premkumar Elangovan* a, Faisal Alrehily b, R Ferrari Pinto a, Alaleh Rashidnasab a,c, David R Dance b,d, Kenneth C Young b,d, Kevin Wells a a Centre for Vision,
Simulation of spiculated breast lesions Premkumar Elangovan* a, Faisal Alrehily b, R Ferrari Pinto a, Alaleh Rashidnasab a,c, David R Dance b,d, Kenneth C Young b,d, Kevin Wells a a Centre for Vision,
THE TUFFEST STUFF CT REGISTRY REVIEW Live Lecture Seminar SATURDAY CURRICULUM
 1. The CT Imaging Chain-10 major components & their functions a. The x-ray tube b. Generator c. Filter d. Pre-patient collimator e. Pre-detector collimator f. Detector system g. Analog to digital converter
1. The CT Imaging Chain-10 major components & their functions a. The x-ray tube b. Generator c. Filter d. Pre-patient collimator e. Pre-detector collimator f. Detector system g. Analog to digital converter
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
European Veterinary Dental College
 European Veterinary Dental College EVDC Training Support Document Preparation of Radiograph Sets (Cat and Dog) Document version : evdc-tsd-radiograph_positioning_(dog_and_cat)-20120121.docx page 1 of 13
European Veterinary Dental College EVDC Training Support Document Preparation of Radiograph Sets (Cat and Dog) Document version : evdc-tsd-radiograph_positioning_(dog_and_cat)-20120121.docx page 1 of 13
