The Effects of Disinfectants on Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Quality of Impression Materials and Gypsum Casts
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article The Effects of Disinfectants on Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Quality of Impression Materials and Gypsum Casts Wala M. Amin a, g, Muna H. Al-Ali b, Sandra K. Al Tarawneh c, Sahar Th. Taha d, Mohamed W. Saleh e, Nadia Ereifij f Abstract Background: The study aimed to evaluating the effect of disinfecting impression materials on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the resulting casts. Methods: Impressions of a steel die constructed according to ANSI/ADA specification No.18 were made with each of alginate, addition cured silicone, condensation cured silicone and zinc oxide eugenol paste, and disinfected consequently by each of 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate, 1% sodium hypochlorite, 2% gluteraldehyde for 5 minutes, and 0.5% sodium hypochlorite for 10 minutes. Dimensions of the disinfected impressions and their resultant casts were measured using a computerized digital caliper, and the dimensional changes were calculated. Reproduction of detail and surface quality of the resultant casts were assessed by grading casts surfaces according to a specific scoring system. Manuscript accepted for publication April 24, a Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Jordan, P.O. Box 13455, Amman 11942, Jordan b Faculty of Dentistry, University of Melbourne, Australia c Faculty of Dentistry, University of North Carolina, USA d Faculty of Dentistry, University of Michigan, USA e Research fellow and Clinical Dental Practitioner, Private practice, Amman, Jordan f Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Jordan, Jordan g Corresponding author: profwala@gmail.com doi: /jocmr Results: The 0.5% sodium hypochlorite was found to produce the least dimensional changes in all the impression materials. Corsodyl produced the maximum changes in both alginate and zinc-oxide eugenol while addition-cured silicon was most affected by Gluteraldehyde and condensation-cured silicon was most affected by Hexana. The dimensional changes, however, were minimal and clinically insignificant. Addition-cured silicon showed the best surface quality and dimensional stability followed by condensation-cured silicon. Alginate and zinc-oxide eugenol had poorer surface quality and were affected to a higher extent by the disinfection procedures. Conclusions: The results were comparable with the standard specifications for dimensional stability. Recommendations were made for the use of 10 minutes immersion in 0.5% sodium hypochlorite as the most appropriate disinfection protocol to the investigated impression materials. Keywords: Disinfectants; Gypsum casts; Impressions; Alginate; Addition-cured silicone; Sodium hypochlorite Introduction Contamination of dental impressions with saliva and blood from the oral cavity occurs readily in dental clinics. Direct interaction between dental clinics and dental laboratories makes contaminated dental impressions difficult items to deal with from the cross infection point of view. Previous reports indicated that contaminated impressions can crossinfect gypsum casts that were poured against them [1]. Until 1991, rinsing impressions under running water was the recommended practice [2]. Guidelines for infection control in dental health care suggested that all dental prostheses and prosthodontic items should be cleaned, disinfected, and rinsed before they are handled in the laboratory using an active hospital disinfectant [3, 4]. Many studies have evaluated the effect of various disinfectants and methods of disinfecting impression materials, but the results of those studies varied widely. The role of a disinfectant should, ideally, be of a dual purpose, it must be an effective antimicrobial agent, yet cause no adverse response to the dimensional accuracy and surface features of the impression material and the resultant gypsum cast [5]. The dimensional stability of disinfected impressions had been a subject of investigation by many researchers who used a variety of approaches. Some studies used full arch casts [6-8] while others studied the effects on a die [8]. The measuring technique used in determining dimensional changes after disinfection also varied from using a Boley 81
2 Amin et al gauge [6], to the use of measuring microscope [9]. Therefore, the aim of the present investigation was to examine the effect of several disinfecting solutions on four commonly used impression materials. The objectives to achieve this aim were: (1) To assess the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the impressions and the resultant gypsum casts using a purpose-made computerized digital caliper of high sensitivity (accurate to mm); (2) To compare the results with the standard specifications; (3) To recommend, accordingly, a disinfection protocol for the corresponding impression materials. The null hypothesis tested was that the different types of disinfectants used would produce similar effects on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the various impression materials evaluated and the resultant casts. Materials and Methods The impression materials and disinfectants employed in this study were chosen to represent the most commonly used by dentists in Jordan (Tables 1 and 2). A stainless steel test die, an impression mould, a riser, and a gypsum mould were constructed according to ANSI/ ADA specification No.18 [10] and BSI 12:1999 [11]. These are shown in Figure 1. Impression materials were mixed according to manufacturers instructions, the impression mould was placed on the die and a freshly mixed homogenous impression material was placed in the center of the die and spread to fill the mould. A flat plastic plate was placed over the mould and pressed the impression material firmly against the die assuring a positive metal to metal contact between the mould and the die. A metal flat weight of 1 Kg simulating the operator s finger pressure on a tray was placed over the plastic plate and the whole assembly was transferred into a water bath which was kept at 35º C ± 1 simulating the mouth temperature [12]. Figure 1. The parts 1, 2, 3 of the assembly constructed according to the ADA specification number 18 for testing dimensional stability and reproduction of details of impression materials. The diagram 4 representing the surface of the die showing the three vertical lines. After the impression material had set, the assembly was removed from the water bath and the impression with the mould separated from the die. The test die and the mould were cleaned, dried and made ready for the next impression. After separation of the impression/mould assembly from the die, a riser was used to push the impression up to the same level of the surface of the mould. Each impression surface was scanned prior to its disinfection using a two-dimensional computer scanner (BenQ scanner 2005) at a resolution of 500 Pixels/inch. The impression was then immersed in the disinfecting solution for the recommended time followed by rinsing in tap water at room Table 1. Impression materials and their recommended setting times Impression material Brand name/supplier Batch Number Recommended setting time Alginate Alginoplast fast set/heraeus Kulzer/Holland min Add. Silicone Elite H-D + /Zhermack Badia Polesine (Rovigo) Italy C min Cond. Silicone Bonasil light DMP LTD, E.U min Zinc Oxide-Eugenol SS White Group/England min 82
3 Disinfectants on Impressions and Casts Table 2. The employed disinfectants and their recommended immersion times Disinfectant Brand name/supplier Conc. Batch Number Recommended immersion time Chlorhexidine Gluconate Hexana/ M.H. Sider Health Care Prep./Jordan 0.2% H min Chlorhexidine Gluconate Corsodyl/Glaxo Smith Kline/UK 0.2% 335E 5 min Sodium Hypochlorite Hypex/Jordan Chemical Industries Co. Ltd/Jordan 1.0% 5 min Sodium Hypochlorite Gluteraldehyde Hypex/Jordan Chemical Industries Co.Ltd/Jordan Eimaldehyde solution Al-Eiman for cosmetics/jordan 0.5% 10 min 2.2% min temperature for 10s. Twenty five impressions were made with each impression material, five impressions of each material for each of the five disinfectants. Additional five impressions of each material were immersed in sterile water for five minutes and used as control. Each impression was dried after rinsing with water and scanned in the same manner. All impressions were poured within 1h after disinfection (the alginate impressions were kept in a sealed bag at 100% humidity) using dental stone (Elite Dental Stone / Zhermack, type IV framework dental stone) which was first wetted manually and then mixed on a vibrator for 30 s. Two hours after pouring the impressions, they were separated, and the resultant casts were coded and scanned at a resolution of 500 Pixel/inch. Dimensional Stability Measurements were made by one operator using a computerized digital calipers (C.D.C) tool that measured the distance between any two given points on a scanned image of an impression or a cast by counting the pixels between the two points on the scanned image of the impression/cast, and Table 3. The mean dimensional change for each impression material/disinfectant combination illustrating the dimensional change between the stone cast and the original die Disinfectant Alginate (mm) 10-3 Addition Silicone (mm) 10-3 Condensation Silicone (mm) 10-3 Zinc Oxide Eugenol (mm) 10-3 Hexana Corsodyl Sterile water % Na-Hypochlorite % Na-Hypochlorite Gluteraldehyde
4 Amin et al Figure 2. Dimensional changes for casts made from alginate impression material after disinfection. calculated the distance in millimeters [13]. Measurements were made between the cross lines, shown in Figure 1. Three readings were made for each stone cast: the first reading was for line A, the second for line B and the third for line C. The mean of the readings was taken for each cast and the dimensional change was calculated by using the following formula: (L - L / L) X 100, where L represents the dimensions of the die, and L represents the mean dimension of the experimental cast (control or after disinfection). Data sets were treated statistically using analysis of variance (ANOVA) at 95% level of confidence and Fisher s Least Significant Difference for multiple comparisons. Surface quality Detail reproduction of impressions Impression were inspected visually without magnification and the accepted impressions were those that passed the ANSI/ADA specification for detail production which reproduced the full length of the 50μm-wide line for the alginate,and the full length of the 25μm-wide line for the Zinc Oxide Eugenol and both the addition and condensation cured silicone impression materials. Detail reproduction of stone casts For assessment of detail reproduction of stone casts, the scanned images of the casts were inspected at X10 magnification and the following scoring system [12] with rating values from one to four was used as following: Rating 1: Well-defined, sharp detail and continuous line; Rating 2: Continuous line but with some loss of sharpness; Rating 3: Poor detail or loss of continuity of line; Rating 4: Marginally or completely not discernible line. According to ANSI/ADA specification No.18 [10] dental stone casts made from alginate specimens have to reproduce the 75μm-wide line, and to satisfy specification No.19 [14] casts poured against silicone rubber must reproduce the 25μm-wide line. For grading purposes both the 75μm and 50μm-wide lines were assessed for alginate [9] and only the 25μm-wide line was evaluated for Zinc Oxide Eugenol and the two silicone materials. Assessment of surface quality and evaluation of the detail reproduction of stone cast were carried out by one operator. The results were subjected to statistical analysed using Kruskal-Wallis test. Results Dimensional stability The mean value of the 15 measurements made on the casts, which resulted from pouring disinfected impressions, compared with corresponding measurements made on the steel die and controls are presented in Table 3. Dimensional changes of the casts made by pouring impressions of each material, namely, alginate, addition-cured silicone, condensation-cured silicone and zinc oxide-eugenol are presented graphically in Figures 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively. The disinfectant that showed the least detrimental effect on the alginate impression material was 0.5% sodium hypochlorite which demonstrated as little dimensional change as % and resulted in a cast with significantly improved dimensions (p < 0.05) compared to that of the water control (the cast which resulted by pouring an alginate impression after 10 min immersion in distilled water). Corsodyl, on 84
5 Disinfectants on Impressions and Casts Figure 3. Dimensional changes for casts made from addition silicone impression material after disinfection. Figure 4. Dimensional changes for casts made from condensation silicone impression material after disinfection. the other hand, was the disinfectant that caused the largest dimensional changes in alginate and incurred 0.108% swelling of the alginate impression. Similar to its effect on alginate, sodium hypochlorite 0.5% disinfectant caused the smallest dimensional change (0.0024%) in the addition-cured silicone impression material and showed some improvement, although not significant, in the dimensions of the resultant casts compared to that of the water control. On the other hand, Gluteraldehyde caused the biggest change (0.008%) in the material s dimensions. The condensation-cured silicone impression material demonstrated the least dimensional change (0.0006%) when disinfected by 0.5% sodium hypochlorite that showed a significant improvement (p < 0.05) in cast dimensions over the cast of the water control, whereas, Hexana disinfectant caused the largest dimensional change (0.0012%) in this impression material. The zinc oxide-eugenol impression material showed a 85
6 Amin et al Figure 5. Dimensional changes for casts made from Zinc Oxide Eugenol impression materials after disinfection. minimum dimensional change (0.0011%) following disinfection by 1% sodium hypochlorite and a maximum change in dimension (0.005%) after disinfection by Corsodyl. Surface quality The results of evaluating the effect of the disinfectants on the surface integrity of the stone casts revealed that 70% of the casts were grade 1; 19.2% grade 2 and 10.8% demonstrated grade 3 surface quality. None of the examined casts showed grade 4 surface. These results are illustrated in Figure 6. The majority of the casts that showed grade 1 surface were those made from pouring addition-cured silicone impression material (36.5%), followed by those resulted from pouring condensation-cured silicone impressions (32.4%); and those resulted from pouring alginate impressions (23%), whereas only 8.1% of grade 1 surface quality impressions were demonstrated by casts made from pouring disinfected zinc oxide-eugenol impressions. Grade 2 quality surfaces were mostly of casts that resulted from pouring disinfected alginate and zinc oxideeugenol impressions (34.8% each) and partly of casts resulted from pouring condensation-cured silicone impressions (17.4%) and addition-cured silicone impressions (13%). The casts that showed grade 3 surface quality were mostly those poured from zinc oxide-eugenol impressions (46.2%) followed by those made by pouring alginate impressions (38.4%). The condensation-cured silicone impressions produced casts that formed 15.4% of grade 3 surface quality casts; whereas none of the casts that resulted from pouring the addition-cured silicone impression were rated as grade 3 quality surfaces. Discussion Dimensional changes of the stone casts None of the disinfectants had a discernable adverse effect on the accuracy of the resultant casts. In fact, some disinfectants such as 0.5% sodium hypochlorite significantly improved the dimensions of the resultant casts. This has confirmed the findings of some of the previous studies [5, 9, 15], while it contrasted with other studies that demonstrated adverse effects of elastomer immersion in disinfecting solutions [16]. Stone casts resulted from pouring decontaminated alginate impressions using the employed disinfectants showed slight dimensional shrinkage. This may be attributed to the processes of syneresis and imbibitions to which alginate was subjected. Alginate impressions were kept in a humid atmosphere for 1h prior to pouring the stone casts, during which the material might have been subjected to syneresis which caused shrinkage of the impression, but upon pouring the impressions with stone, the alginate imbibed the moisture of the stone mix which caused swelling of the impression and partly compensated for the syneresis shrinkage. Of all the disinfectants employed for decontaminating alginate impressions, sodium hypochlorite 0.5% affected the least changes in the dimensions of the resultant casts. This disinfectant, in fact, improved cast dimensions compared to those of the wa- 86
7 Disinfectants on Impressions and Casts Figure 6. The distribution of impression materials according to their surface quality grades scored after disinfection. ter control. These findings were consistent with the previous studies which reported that no significant distortion of alginate impressions could result from decontaminating these impressions by a variety of disinfectants [7, 17]. Stone casts that resulted by pouring disinfected addition-cured silicone impressions demonstrated a minimal reduction in dimensions caused by a marginal swelling of the impressions. Compared to the other impression materials investigated in this study, addition-cured silicone demonstrated superior dimensional stability. The changes in the dimensions of the resultant casts produced by pouring disinfected addition-cured silicone impressions were extremely minimal, clinically insignificant and within the range of changes that is acceptable by the standard specifications [14]. Once again, sodium hypochlorite 0.5% disinfectant affected some improvement in the dimensions of the casts that resulted by pouring addition-cured silicone impressions compared to the casts of the water control. The stone casts poured from condensation-cured silicone impressions that were disinfected by each of: sodium hypochlorite 0.5%, gluteraldehyde, Corsodyl and Hexana demonstrated slight expansion as a result of shrinkage that took place in the condensation-cured silicone impression material upon disinfection. Whereas, casts produced by pouring the condensation-cured silicone impressions following disinfection by 1% sodium hypochlorite displayed a marginal reduction in dimensions as a result of swelling of the impression material upon exposure to 1% sodium hypochlorite. These differences may be attributed to the nature of the setting reaction of the condensation-cure silicone rather than to the disinfectant itself. This is consistent with previous studies [18-21] which pointed that care should be taken when working with condensation-cured silicone impression which may uncontrollably contract due to the loss of byproducts. Similar to the other investigated impression materials, the condensation-cured silicone produced stone casts that exhibited minimal dimensional changes when the impressions were disinfected by 0.5% sodium hypochlorite. These casts were closer in dimensions to the steel die than were the water control casts. Casts produced by pouring disinfected zinc oxide-eugenol impressions demonstrated slight reduction in dimensions caused by marginal swelling of zinc oxide-eugenol impression upon exposure to the disinfectants except to 1% sodium hypochlorite which affected a minimal and clinically insignificant expansion of the resultant casts. To this end, the observed differences in the behavior of the impression materials when exposed to disinfectants which affected some changes in the dimensions of the resultant casts may be attributed partly to the different characteristics of the impression materials themselves, and partly to the different disinfection regimens used. 87
8 Amin et al Figure 7. Surface quality and detail reproduction (X10 magnification): 1- sharp detail, continuous line; 2- continuous lines but with some loss of sharpness; 3- rough appearance with loss of continuity of the line. In the light of the findings of the present investigation, the following conclusions can be obtained: (1) The five disinfectants employed in the present study affected all four impression materials very marginally and the stone casts obtained from disinfected impressions showed minimal dimensional changes that can be considered clinically insignificant. (2) Silicone impression materials of the two types, addition-cured and condensation-cured types, displayed superior qualities in terms of dimensional stability and surface integrity over alginate and zinc oxide-eugenol impression materials. The latter two materials, although showed minimal changes in dimensions, but were less stable compared to the silicones. (3) Stone casts obtained from alginate and zinc oxide-eugenol impression materials were of comparable dimensional stability and surface quality following each of the disinfection procedures. (4) Decontaminated addition-cured silicone impressions using all the employed disinfectants produced stone casts with dimensions very closely comparable to those of the standard metal die. (5) Of all the disinfectants employed in the present investigation, 0.5% sodium hypochlorite affected the least changes in the dimensions of the four impression materials and had a negligible effect on the quality of the materials surface. The use of 0.5% sodium hypochlorite can, therefore, be recommended for disinfection by 10-minutes immersion of alginate; zinc oxide-eugenol; addition-cured silicone and condensation-cured silicone impressions prior to transporting these impressions to the laboratory. Acknowledgements Surface quality The effect of disinfectants on the surface quality of impressions indicated that the silicones, both addition and condensation-cured types, were superior in terms of surface integrity to the other impression materials. This is due to the hydrophobic nature of silicones which made the surface of these impressions highly resistant to the attack by the aqueous disinfectants regardless of their types or the length of exposure period. On the other hand, alginate impression material imbibed the disinfectants which, in turn, inflicted a discernable damage to the alginate impression surface. Similar surface effects were displayed by zinc oxideeugenol impressions which in spite of the oily nature of its surface, the tested disinfectants seemed to have attacked the impression surface chemically and inflicted a noticeable damage. The extent of this damage was proportionally related to the concentration of the disinfectant and the length of exposure of the impression to the disinfectant. Summary The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this article. References 1. Leung RL, Schonfeld SE. Gypsum casts as a potential source of microbial cross-contamination. J Prosthet Dent 1983;49: Fabiani L, Mosca G, Giuliani AR. Hygiene in dental practices. Eur J Paediatr Dent 2006;7: Infection control recommendations for the dental office and the dental laboratory. ADA Council on Scientific Affairs and ADA Council on Dental Practice. J Am Dent Assoc 1996;127: Kohn WG, Collins AS, Cleveland JL, Harte JA, Eklund KJ, Malvitz DM. Guidelines for infection control in dental health-care settings MMWR Recomm Rep 2003;52: Taylor RL, Wright PS, Maryan C. Disinfection procedures: their effect on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of irreversible hydrocolloid impression materials and gypsum casts. Dent Mater 2002;18: Merchant VA, McNeight MK, Ciborowski CJ, Molinari JA. Preliminary investigation of a method for disinfection of dental impressions. J Prosthet Dent 1984;52: Herrera SP, Merchant VA. Dimensional stability of dental impressions after immersion disinfection. J Am Dent Assoc 1986;113:
9 Disinfectants on Impressions and Casts 8. Palenik CJ, Miller CH. Treating highly infectious patients in the dental office. J Indiana Dent Assoc 1985;64: al-omari WM, Jones JC, Wood DJ. The effect of disinfecting alginate and addition cured silicone rubber impression materials on the physical properties of impressions and resultant casts. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent 1998;6: Council adopts American Dental Association Specification no. 18 (alginate impression material). Council on Dental Materials and Devices. J Am Dent Assoc 1968;77: Revised American Dental Association Specification no. 19 for Non-aqueous, Elastomeric Dental Impression Materials. J Am Dent Assoc 1977;94: Morrow RM, Brown CE, Jr., Stansbury BE, DeLorimier JA, Powell JM, Rudd KD. Compatibility of alginate impression materials and dental stones. J Prosthet Dent 1971;25: Amin WM, Taha ST, Al-Tarawneh SK, Saleh MW, Ghzawi A. The relationships of the maxillary central incisors and canines to the incisive papilla in Jordanians. J Contemp Dent Pract 2008;9: Millman K. Disinfection of impressions. Br Dent J 1995;179: Matyas J, Dao N, Caputo AA, Lucatorto FM. Effects of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy of impression materials. J Prosthet Dent 1990;64: Thouati A, Deveaux E, Iost A, Behin P. Dimensional stability of seven elastomeric impression materials immersed in disinfectants. J Prosthet Dent 1996;76: Durr DP, Novak EV. Dimensional stability of alginate impressions immersed in disinfecting solutions. ASDC J Dent Child 1987;54: Lepe X, Johnson GH, Berg JC. Surface characteristics of polyether and addition silicone impression materials after long-term disinfection. J Prosthet Dent 1995;74: Davis BA, Powers JM. Effect of immersion disinfection on properties of impression materials. J Prosthodont 1994;3: Adabo GL, Zanarotti E, Fonseca RG, Cruz CA. Effect of disinfectant agents on dimensional stability of elastomeric impression materials. J Prosthet Dent 1999;81: Johansen RE, Stackhouse JA, Jr. Dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization. J Prosthet Dent 1987;57:
The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials
 441 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 50, No. 4, 441-446, 2008 Original The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials Dario Melilli, Antonio
441 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 50, No. 4, 441-446, 2008 Original The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials Dario Melilli, Antonio
An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization
 Original Article An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization Poonam K. Khinnavar, B. H. Dhanya Kumar, D. B. Nandeeshwar Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization Poonam K. Khinnavar, B. H. Dhanya Kumar, D. B. Nandeeshwar Department of Prosthodontics,
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and Dimensional Stability of Self-disinfecting Irreversible Hydrocolloid: An in vitro Study
 JCDP Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and Dimensional Stability of Self-disinfecting 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2144 Irreversible Hydrocolloid ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and
JCDP Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and Dimensional Stability of Self-disinfecting 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2144 Irreversible Hydrocolloid ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and
IMPRESSION MATERIALS
 IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
Professor Dept. of Prosthodontics, Crown and Bridge, Sri Aurobindo College of Dentistry, Indore M.P.
 A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF POLYVINYL SILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIAL FOLLOWINGDISINFECTION WITH 2% GLUTARALDEHYDE AND U.V. RAYS USING THREE DIMENSIONAL OPTICAL DIGITIZATION. 1 Kavita
A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF POLYVINYL SILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIAL FOLLOWINGDISINFECTION WITH 2% GLUTARALDEHYDE AND U.V. RAYS USING THREE DIMENSIONAL OPTICAL DIGITIZATION. 1 Kavita
Effects of disinfection procedures on surface quality of compound impressions and the resultant gypsum casts
 Dental Journal Effects of disinfection procedures on surface quality of compound impressions and the resultant gypsum casts Potchaman Sinavarat 1, Saysana Visayrath 2 1 D.D.S., M.Sc. (Prosthetic Dentistry)
Dental Journal Effects of disinfection procedures on surface quality of compound impressions and the resultant gypsum casts Potchaman Sinavarat 1, Saysana Visayrath 2 1 D.D.S., M.Sc. (Prosthetic Dentistry)
Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes on the Dimensional Stability of poly (Vinyl Siloxane) Impression Material.
 IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
The Puzzle of OSHA Compliance and Infection Control in the Dental Laboratory. The Puzzle of OSHA Compliance in the Dental Laboratory
 The Puzzle of OSHA Compliance and Infection Control in the Dental Laboratory The Puzzle of OSHA Compliance in the Dental Laboratory The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard: 29 CFR 1910.1030 1991/2001 The Hazard
The Puzzle of OSHA Compliance and Infection Control in the Dental Laboratory The Puzzle of OSHA Compliance in the Dental Laboratory The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard: 29 CFR 1910.1030 1991/2001 The Hazard
Abdulsalam A. Zwiad. Associ.. Prof. in Prosthodontics
 Abdulsalam A. Zwiad Associ.. Prof. in Prosthodontics Faculty of Medical Sciences Qeen Arwa University Former Assist. Prof. College of dentistry- Baghdad University COMMON ERRORS DURING MANIPULATION ALGINATE
Abdulsalam A. Zwiad Associ.. Prof. in Prosthodontics Faculty of Medical Sciences Qeen Arwa University Former Assist. Prof. College of dentistry- Baghdad University COMMON ERRORS DURING MANIPULATION ALGINATE
Hardness and Surface Detail Reproduction of Gypsum Casts Retrieved from Addition Silicone Impressions Disinfected for Different Time Points
 Original Article Hardness and Surface Detail Reproduction of Gypsum Casts Retrieved from Addition Silicone Impressions Disinfected for Different Time Points S. Koosha 1, Sh. Pourhaghani 2, K. Attar 1.
Original Article Hardness and Surface Detail Reproduction of Gypsum Casts Retrieved from Addition Silicone Impressions Disinfected for Different Time Points S. Koosha 1, Sh. Pourhaghani 2, K. Attar 1.
Acknowledgments Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal
 Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1383 Yamini Nandini et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1383 Yamini Nandini et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study
Efficacy of Various Disinfectants on Dental Impression Materials. U Sukhija, M Rathee, N Kukreja, S Khindria, V Singh, J Palaskar
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 9 Number 1 Efficacy of Various Disinfectants on Dental Impression Materials U Sukhija, M Rathee, N Kukreja, S Khindria, V Singh, J Palaskar Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 9 Number 1 Efficacy of Various Disinfectants on Dental Impression Materials U Sukhija, M Rathee, N Kukreja, S Khindria, V Singh, J Palaskar Citation
Reference to primary publication Properties of alginates in ZWP 4/2014 Xantalgin Crono - Introduction
 Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 21(1), 2009 The effect of using different..
 The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
The effect of using different impression techniques and materials on vertical tissue displacement in free end extension ridges. (Dental survey and clinical study) Rawia. N. AL- Dafaii, B.D.S., MSc. (1)
Lecture:6 dental material dr. Aseel Mohammed
 4. Zinc oxide eugenol impression material: It's described as a rigid, mucostatic, irreversible (set by chemical reaction) and hydrophobic impression material. We have 2 types of zinc oxide eugenol impression
4. Zinc oxide eugenol impression material: It's described as a rigid, mucostatic, irreversible (set by chemical reaction) and hydrophobic impression material. We have 2 types of zinc oxide eugenol impression
Al-Qarni AA. Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from
 IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Disinfection Of Gypsum Casts: Comparing Microwave Irradiation And Chemical Disinfection-An In Vivo Study
 IJCMR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Disinfection Of Gypsum Casts: Comparing Microwave Irradiation And Chemical Disinfection-An In Vivo Study Sohil Rajkumar Daswani 1, Ragya Bharadwaj 2, Meena A. Aras 3, Vidya Chitre
IJCMR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Disinfection Of Gypsum Casts: Comparing Microwave Irradiation And Chemical Disinfection-An In Vivo Study Sohil Rajkumar Daswani 1, Ragya Bharadwaj 2, Meena A. Aras 3, Vidya Chitre
International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research
 International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Original Research Article Addition of mouth washes as a disinfectants for irreversible hydrocolloid impression material Ibrahim M. Hamouda
International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Original Research Article Addition of mouth washes as a disinfectants for irreversible hydrocolloid impression material Ibrahim M. Hamouda
Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Dimensional stability of compression and injection molding denture bases in long and short curing procedures Noppavan Nagaviroj, Krantarat Wanitchanont,
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Dimensional stability of compression and injection molding denture bases in long and short curing procedures Noppavan Nagaviroj, Krantarat Wanitchanont,
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Dentistry Reversible-irreversible hydrocolloid impression material systems
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13716 First edition 1999-05-01 Dentistry Reversible-irreversible hydrocolloid impression material systems Art dentaire Systèmes de produits pour empreintes à base d'hydrocolloïdes
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 13716 First edition 1999-05-01 Dentistry Reversible-irreversible hydrocolloid impression material systems Art dentaire Systèmes de produits pour empreintes à base d'hydrocolloïdes
Rahul Nagrath Manesh Lahori Manjari Agrawal
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Evaluation of Contamination Reduction on Gypsum Casts from Alginate Impressions Disinfected with Four Different Materials
 Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 8, No. 12; 2016 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Evaluation of Contamination Reduction on Gypsum Casts from Alginate
Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 8, No. 12; 2016 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Evaluation of Contamination Reduction on Gypsum Casts from Alginate
Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals
 Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(4) Original Article Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals Aalaei Sh a, Rezaei Adli A a, Mansoorali MR b,
Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(4) Original Article Dimensional Stability of Two Polyvinyl Siloxane Impression Materials in Different Time Intervals Aalaei Sh a, Rezaei Adli A a, Mansoorali MR b,
Impression for crown and bridge work
 Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
IMPRESSION TRAYS. Stainless Steel Edentulous Impression Trays. 73
 IMPRESSION TRAYS Standard Stainless Steel Trays Perforated stainless steel impression trays - the most popular type. Retention is assured by holes over the whole surface of the tray. A rim on the back
IMPRESSION TRAYS Standard Stainless Steel Trays Perforated stainless steel impression trays - the most popular type. Retention is assured by holes over the whole surface of the tray. A rim on the back
Facts About. Express. Penta Putty/ Ultra-Light Body. Vinyl Polysiloxane Precision Impression Materials
 Facts About Express Penta Putty/ Vinyl Polysiloxane Precision Impression Materials European Field Evaluation Results May August 2004 Ultra Light Body Contents 1 Innovative VPS Impression Materials....................
Facts About Express Penta Putty/ Vinyl Polysiloxane Precision Impression Materials European Field Evaluation Results May August 2004 Ultra Light Body Contents 1 Innovative VPS Impression Materials....................
Clinical. Alginates. Algipedia
 Clinical Alginates Algipedia Zhermack Alginates, the most complete range from the number 1 manufacturer in the world The purpose of this guide is to highlight the applications and advantages of each type
Clinical Alginates Algipedia Zhermack Alginates, the most complete range from the number 1 manufacturer in the world The purpose of this guide is to highlight the applications and advantages of each type
Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed using various impression materials and gypsum products
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2013) xx, 1e6 + MODEL Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed
Journal of Dental Sciences (2013) xx, 1e6 + MODEL Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the surface roughness of gypsum models constructed
The Application of the HIP-Analyzer for the Evaluation of the Maxillary Occlusal Plane Topography
 The Application of the HIP-Analyzer for the Evaluation of the Maxillary Occlusal Plane Topography Sergey Shestopalov, PhD, DO, Konstantin Ronkin, DMD, MICCMO The orientation of the upper occlusal plane
The Application of the HIP-Analyzer for the Evaluation of the Maxillary Occlusal Plane Topography Sergey Shestopalov, PhD, DO, Konstantin Ronkin, DMD, MICCMO The orientation of the upper occlusal plane
Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy
 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1033 Fabiana Santos Gonçalves et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy Fabiana Santos Gonçalves, Wallace de Freitas Oliveira,
10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1033 Fabiana Santos Gonçalves et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impression Materials and Storage Time Influence on Cast Models Accuracy Fabiana Santos Gonçalves, Wallace de Freitas Oliveira,
IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL
 IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL 01 01 A.B. DENTAL A.B. Dental is proud to present this impression taking procedure protocol. This manual explains, step by step, the procedure while using A.B. Dental
IMPRESSION PROCEDURES TRAINING MANUAL 01 01 A.B. DENTAL A.B. Dental is proud to present this impression taking procedure protocol. This manual explains, step by step, the procedure while using A.B. Dental
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture Using Modified Impression Technique: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
Effect of Incorporation of Disinfectant Solutions on Setting Time, Linear Dimensional Stability, and Detail Reproduction in Dental Stone Casts
 Effect of Incorporation of Disinfectant Solutions on Setting Time, Linear Dimensional Stability, and Detail Reproduction in Dental Stone Casts Matheus Guilherme Lucas, DDS, MSc, 1 João Neudenir rioli-filho,
Effect of Incorporation of Disinfectant Solutions on Setting Time, Linear Dimensional Stability, and Detail Reproduction in Dental Stone Casts Matheus Guilherme Lucas, DDS, MSc, 1 João Neudenir rioli-filho,
Impression for complete dentures is a negative replica of the edentulous ridges and the adjacent supporting structures.
 Available Online through ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article www.ijptonline.com SURVEY OF IMPRESSION PROCEDURES FOR COMPLETE DENTURES AMONG DENTAL PRACTITIONERS IN CHENNAI Preethi Mariona.R,
Available Online through ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article www.ijptonline.com SURVEY OF IMPRESSION PROCEDURES FOR COMPLETE DENTURES AMONG DENTAL PRACTITIONERS IN CHENNAI Preethi Mariona.R,
Research Article Effect of Different Denture Base Materials and Changed Mouth Temperature on Dimensional Stability of Complete Dentures
 International Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 7085063, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7085063 Research Article Effect of Different Denture Base Materials and Changed Mouth Temperature on Dimensional
International Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 7085063, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7085063 Research Article Effect of Different Denture Base Materials and Changed Mouth Temperature on Dimensional
Using technology to create the perfect impression
 The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
hydrorise implant SIMPLY ACCURATE High-rigidity addition silicone
 hydrorise implant SIMPLY ACCURATE High-rigidity addition silicone 2 Hydrorise Implant, simply accurate Dental implants represent a solid solution in prosthetic dentistry and are considered the privileged
hydrorise implant SIMPLY ACCURATE High-rigidity addition silicone 2 Hydrorise Implant, simply accurate Dental implants represent a solid solution in prosthetic dentistry and are considered the privileged
Dimensional Accuracy of 2 Irreversible Hydrocolloid Alternative Impression Materials with Immediate and Delayed Pouring
 ca Applied Research Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2010;76:aXXX 2012;78:c2 Dimensional Accuracy of 2 Irreversible Hydrocolloid Alternative Impression Materials with Immediate and Delayed Pouring
ca Applied Research Cite this article as: J Can Dent Assoc 2010;76:aXXX 2012;78:c2 Dimensional Accuracy of 2 Irreversible Hydrocolloid Alternative Impression Materials with Immediate and Delayed Pouring
Straight Octagon Abutment for Tissue Level Implant
 Cover screw in place The presentation that follows lists only one combination of parts. Obviously the clinical situation may call for substitution of another part on this slide Prosthetic instruments needed
Cover screw in place The presentation that follows lists only one combination of parts. Obviously the clinical situation may call for substitution of another part on this slide Prosthetic instruments needed
Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 7, July 2015 1 Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 7, July 2015 1 Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
POS Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement Documentation Coversheet
 POS Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement Documentation Coversheet Student Name: Secondary School Name: Secondary School Address: CTE Program of Study: CIP # CIP Program Name Grade 9 1. CAREER AND TECHNICAL
POS Perkins Statewide Articulation Agreement Documentation Coversheet Student Name: Secondary School Name: Secondary School Address: CTE Program of Study: CIP # CIP Program Name Grade 9 1. CAREER AND TECHNICAL
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
SOLUBILITY OF DIFFERENT SOFT LINING MATERIALS IN DISTILLED WATER, ARTIFICIAL SALIVA AND DENTURE DISINFECTANT SOLUTION
 Original Article Received : 27 09 14 Review completed : 11 11 14 Accepted : 29 11 14 SOLUBILITY OF DIFFERENT SOFT LINING MATERIALS IN DISTILLED WATER, ARTIFICIAL SALIVA AND DENTURE DISINFECTANT SOLUTION
Original Article Received : 27 09 14 Review completed : 11 11 14 Accepted : 29 11 14 SOLUBILITY OF DIFFERENT SOFT LINING MATERIALS IN DISTILLED WATER, ARTIFICIAL SALIVA AND DENTURE DISINFECTANT SOLUTION
The Sheffield Fit Test - Revisited. Academic Unit of Restorative Dentistry, School of Clinical Dentistry, University of
 The Sheffield Fit Test - Revisited Dr A. Johnson 1 MMedSci; PhD; LCGI; MCGI; FHEA, Dr C.A. Miller 2 BEng (hons), PhD. Dr G.E. White 1 MMedSci; PhD; CGIA. 1 Academic Unit of Restorative Dentistry, School
The Sheffield Fit Test - Revisited Dr A. Johnson 1 MMedSci; PhD; LCGI; MCGI; FHEA, Dr C.A. Miller 2 BEng (hons), PhD. Dr G.E. White 1 MMedSci; PhD; CGIA. 1 Academic Unit of Restorative Dentistry, School
Incisal Edge Abrasion Caused By An Unusual Eating Habit
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 6 Number 1 W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim Citation W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim.. The Internet Journal of Dental Science. 2007 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 6 Number 1 W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim Citation W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim.. The Internet Journal of Dental Science. 2007 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY. Lab. Manual. Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics. 3 rd year
 ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
Precision. Hydrophilicity. V-Posil. Dimensional stability. Intraoral setting time. Working time. Precision impression material, A-silicone-based
 Dimensional stability Precision Working time Toughness Intraoral setting time Hydrophilicity Precision impression material, A-silicone-based Addition silicone impression material impressively precise Models
Dimensional stability Precision Working time Toughness Intraoral setting time Hydrophilicity Precision impression material, A-silicone-based Addition silicone impression material impressively precise Models
Accuracy 9 articles 4 Posters Shade measurement 1 article. Technology comparison 1 article
 Accuracy 9 articles 4 Posters Shade measurement 1 article Technology comparison 1 article 3Shape TRIOS Color had the best agreement of all included methods for the color chroma and hue... whereas the
Accuracy 9 articles 4 Posters Shade measurement 1 article Technology comparison 1 article 3Shape TRIOS Color had the best agreement of all included methods for the color chroma and hue... whereas the
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path
 Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Horizontal jaw relations: The relationship of mandible to maxilla in a
 Horizontal relations Horizontal jaw relations: The relationship of mandible to maxilla in a horizontal plane (in anteroposterior and side to side direction). a- Protruded or forward relation. b-lateral
Horizontal relations Horizontal jaw relations: The relationship of mandible to maxilla in a horizontal plane (in anteroposterior and side to side direction). a- Protruded or forward relation. b-lateral
An evaluation of the hardness of flexible Denture Base Resins
 ORIGINAL STUDY An evaluation of the hardness of flexible Denture Base SHEEBA GLADSTONE, SUDEEP S, ARUN KUMAR G Department of Prosthodontics, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Golden Hills, Vattappara,
ORIGINAL STUDY An evaluation of the hardness of flexible Denture Base SHEEBA GLADSTONE, SUDEEP S, ARUN KUMAR G Department of Prosthodontics, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Golden Hills, Vattappara,
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report
 Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 04, Issue: 01, October 2015, Pages 17-25
 Original article: A Comparative evaluation of shear bond strengths of denture base to cross linked acrylic resin maxillary anterior teeth with and without retentive grooves - An invitro study Dr.D.Sudha
Original article: A Comparative evaluation of shear bond strengths of denture base to cross linked acrylic resin maxillary anterior teeth with and without retentive grooves - An invitro study Dr.D.Sudha
Horizontal Jaw Relation
 Horizontal Jaw Relation Horizontal Jaw Relation It is the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla in a horizontal plane. It can also be described as the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla
Horizontal Jaw Relation Horizontal Jaw Relation It is the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla in a horizontal plane. It can also be described as the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla
Preparation Instructions for the CAMLOG /CONELOG Implant System
 J8000.0032 Rev.6 EN 06/2015 Preparation Instructions for the CAMLOG /CONELOG Implant System ENGLISH The following descriptions contain detailed instructions on cleaning, disinfection and sterilization
J8000.0032 Rev.6 EN 06/2015 Preparation Instructions for the CAMLOG /CONELOG Implant System ENGLISH The following descriptions contain detailed instructions on cleaning, disinfection and sterilization
Prof. Dr. Hikmat J. Al-Judy B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D in Prosthodontic, College of Dentistry/ Baghdad University/ Baghdad, Iraq.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2015), PP 35-40 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of the effect of sectional
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2015), PP 35-40 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of the effect of sectional
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 10 Page October 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.57 The Effect of Different Techniques of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.57 The Effect of Different Techniques of
Complete denture impressions
 Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Original Research. Absorption of soft lining materials Kumar SK et al
 Absorption of soft lining materials Kumar SK et al Journal of International Oral Health 2015; 7(11):47-52 Received: 07 th June 2015 Accepted: 13 th September 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of
Absorption of soft lining materials Kumar SK et al Journal of International Oral Health 2015; 7(11):47-52 Received: 07 th June 2015 Accepted: 13 th September 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of
Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy and Dimensional Stability of Three Interocclusal Recording Materials- An In Vitro Study
 Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy and Dimensional Stability of Three Interocclusal Recording Materials- An In Vitro Study Running title-study on accuracy of inter arch record material. DR. ARYA. S
Comparative Evaluation of the Accuracy and Dimensional Stability of Three Interocclusal Recording Materials- An In Vitro Study Running title-study on accuracy of inter arch record material. DR. ARYA. S
Establishing a High Quality Infection Control and Safety Program
 Establishing a High Quality Infection Control and Safety Program ü 12- Planning Guide to Establish a High Quality Infection Control and Safety Program This planning guide is designed to assist the infection
Establishing a High Quality Infection Control and Safety Program ü 12- Planning Guide to Establish a High Quality Infection Control and Safety Program This planning guide is designed to assist the infection
ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY
 ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated
 Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated with Three Retraction Cord Medicaments : An In Vitro Study Pravin Raipure
Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated with Three Retraction Cord Medicaments : An In Vitro Study Pravin Raipure
Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 341546, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/341546 Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dentistry Volume 2011, Article ID 341546, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2011/341546 Research Article Accuracy of Single-Step versus 2-Step Double-Mix Impression Technique
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE
 DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
CASE REPORT ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES Aims
 An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy of Master Cast Fabricated by Three Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1143 Transfer Techniques for Single Tooth CASE REPORT An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy
An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy of Master Cast Fabricated by Three Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1143 Transfer Techniques for Single Tooth CASE REPORT An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy
Study on antimicrobial effect of disinfecting solutions on alginate impression materials
 Updat Dent. Coll.j 2013; 3(1):18-23 Original Article Study on antimicrobial effect of disinfecting solutions on alginate impression materials *Mohamad Rafiul Ahsan a, Kazi Ziaul Islam b, Jebunnesa begum
Updat Dent. Coll.j 2013; 3(1):18-23 Original Article Study on antimicrobial effect of disinfecting solutions on alginate impression materials *Mohamad Rafiul Ahsan a, Kazi Ziaul Islam b, Jebunnesa begum
Original article DOI: Journal of International Medicine and Dentistry 2016; 3(3):
 Original article DOI: https://doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201603.03151 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Comparison of various
Original article DOI: https://doi.org/10.18320/jimd/201603.03151 JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share p-issn: 2454-8847 e-issn: 2350-045X Comparison of various
Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty-wash Impression Technique
 Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
DETERMINING THE POSITION OF ARTIFICIAL TOOTH IN RELATION TO THE BASE OF THE PALATAL RUGAE: A PILOT STUDY
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 05 DETERMINING THE POSITION OF ARTIFICIAL TOOTH IN RELATION TO THE BASE OF THE PALATAL RUGAE: A PILOT STUDY Aruna J.
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 05 DETERMINING THE POSITION OF ARTIFICIAL TOOTH IN RELATION TO THE BASE OF THE PALATAL RUGAE: A PILOT STUDY Aruna J.
International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 04, Issue: 03, April 2016, 83-92
 Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials
 Prosthodontics Prosthodontics Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials Jefferson Ricardo Pereira (a) Karina Yumi Murata (b) Accácio Lins do Valle (c) Janaina
Prosthodontics Prosthodontics Linear dimensional changes in plaster die models using different elastomeric materials Jefferson Ricardo Pereira (a) Karina Yumi Murata (b) Accácio Lins do Valle (c) Janaina
When faced with an element which is the
 USE OF DENTAL IMPRESSION MATERIALS IN THE ANALYSIS OF TOOL MARKS TO IDENTIFY CAUSAL ELEMENTS National Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences, Special Edition SUMMARY When faced with an element
USE OF DENTAL IMPRESSION MATERIALS IN THE ANALYSIS OF TOOL MARKS TO IDENTIFY CAUSAL ELEMENTS National Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences, Special Edition SUMMARY When faced with an element
IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES)
 IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES) DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS 17.06.2007 Impressions An impression
IMPRESSION MAKING (IN COMPLETE DENTURES) DR ZURYATI AB GHANI BDS (WALES), Grad Dip Clin Dent (Adelaide), Doctor in Clinical Dentistry (prosthodontics), Adelaide, FRACDS 17.06.2007 Impressions An impression
MODIFIED FUNCTIONAL IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE FOR RESORBED MANDIBULAR RIDGE: TWO CASE STUDIES
 Prosthetic dentistry MODIFIED FUNCTIONAL IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE FOR RESORBED MANDIBULAR RIDGE: TWO CASE STUDIES Divia CHUGH 1, Siddharth PHULL 2, Arpan RANA 1, Yashendra SAINI 1 1 Resident (Prosthodontics)
Prosthetic dentistry MODIFIED FUNCTIONAL IMPRESSION TECHNIQUE FOR RESORBED MANDIBULAR RIDGE: TWO CASE STUDIES Divia CHUGH 1, Siddharth PHULL 2, Arpan RANA 1, Yashendra SAINI 1 1 Resident (Prosthodontics)
History and innovation
 LEADERSHIP History and innovation Since KROMOPAN was created it has been an incredible break through in dentistry. Thanks to a careful selection of raw materials and well-advanced manufacturing processes
LEADERSHIP History and innovation Since KROMOPAN was created it has been an incredible break through in dentistry. Thanks to a careful selection of raw materials and well-advanced manufacturing processes
Comparative evaluation of sodium hypochlorite and microwave disinfection on dimensional stability of denture bases
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.24 Comparative evaluation of sodium hypochlorite and microwave disinfection on dimensional stability of denture bases Rutuja Madhukarrao Nirale*,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.24 Comparative evaluation of sodium hypochlorite and microwave disinfection on dimensional stability of denture bases Rutuja Madhukarrao Nirale*,
Technical. Dental Stones
 Technical Dental Stones Elite Master Type 4 extra hard resin reinforced dental die stone for fixed prosthesis and implantology Elite Stone Type 4 dental die stone for models in removable prosthesis Elite
Technical Dental Stones Elite Master Type 4 extra hard resin reinforced dental die stone for fixed prosthesis and implantology Elite Stone Type 4 dental die stone for models in removable prosthesis Elite
DENTAL INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL MANUAL
 DENTAL INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL MANUAL www.infectioncontroldental.com.au Infection Prevention and Control Manual Copyright 2016: Infection Control Dental Pty Ltd All Rights Reserved. Without limiting
DENTAL INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL MANUAL www.infectioncontroldental.com.au Infection Prevention and Control Manual Copyright 2016: Infection Control Dental Pty Ltd All Rights Reserved. Without limiting
FLEXCEED EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS
 EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS 1 because FIRST IMPRESSION lasts GC introduces FLEXCEED, a new vinyl polysiloxane impression material that is affordable yet accurately replicates the highest level of detail
EXCEEDS YOUR EXPECTATIONS 1 because FIRST IMPRESSION lasts GC introduces FLEXCEED, a new vinyl polysiloxane impression material that is affordable yet accurately replicates the highest level of detail
The Effect of Addition of Calcium Hypochlorite Disinfectant on Setting Expansion and Surface Hardness of Dental Stone
 Original Article The Effect of Addition of Calcium Hypochlorite Disinfectant on Setting Expansion and Surface Hardness of Dental Stone M. Sabouhi 1, N. Khodaeian 2, E. Ataei 3, F. Kiani 4. 1 Member of
Original Article The Effect of Addition of Calcium Hypochlorite Disinfectant on Setting Expansion and Surface Hardness of Dental Stone M. Sabouhi 1, N. Khodaeian 2, E. Ataei 3, F. Kiani 4. 1 Member of
The Effect of Using Modified Flask on the Porosity of Processed Heat- Cure Acrylic Resin
 International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 37-4531 http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied The Effect of Using Modified Flask on the Porosity of Processed
International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 37-4531 http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied The Effect of Using Modified Flask on the Porosity of Processed
Manufacturer s information
 WARNINGS: Observe the standard German accident prevention regulations (UVV) We are not aware of any warnings if the instructions for the devices and disinfection and cleaning agents to be used are followed.
WARNINGS: Observe the standard German accident prevention regulations (UVV) We are not aware of any warnings if the instructions for the devices and disinfection and cleaning agents to be used are followed.
Student Course Document. CONTACT INFORMATION:
 Dental Hygiene Department Student Course Document COURSE CODE & TITLE: DEN 2318 / DEN 2318L Dental Materials / Dental Materials Laboratory TERM: Fall 2016 INSTRUCTORS: Dr. L. Friedman / Prof. A. Lam /
Dental Hygiene Department Student Course Document COURSE CODE & TITLE: DEN 2318 / DEN 2318L Dental Materials / Dental Materials Laboratory TERM: Fall 2016 INSTRUCTORS: Dr. L. Friedman / Prof. A. Lam /
Articulators. 5- Wax up and refining the occlusion for dental restorations.
 Articulators It is a mechanical device represents the TMJ, maxillary and mandibular arches. It can be used to hold the upper and lower casts according to their relationships to facilitate the purposes
Articulators It is a mechanical device represents the TMJ, maxillary and mandibular arches. It can be used to hold the upper and lower casts according to their relationships to facilitate the purposes
IJOCR ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Original article Analysis of Bacterial Colonization 10.5005/jp-journals-10051-0148 due to Salivary Contamination Analysis of Bacterial Colonization due to Salivary Contamination on Gypsum Casts and Effect
Original article Analysis of Bacterial Colonization 10.5005/jp-journals-10051-0148 due to Salivary Contamination Analysis of Bacterial Colonization due to Salivary Contamination on Gypsum Casts and Effect
CURRICULUM VITAE. Nesreen.A. Salim (BDS, MSc, PhD)
 CURRICULUM VITAE Nesreen.A. Salim (BDS, MSc, PhD) PERSONAL DETAILS NAME: Nesreen. A. Salim ADDRESS: Al-Jandweel, Amman, Jordan MOBILE: 00962-798020722 EMAIL: n.salim@ju.edu.jo nisreen_salim1@yahoo.com
CURRICULUM VITAE Nesreen.A. Salim (BDS, MSc, PhD) PERSONAL DETAILS NAME: Nesreen. A. Salim ADDRESS: Al-Jandweel, Amman, Jordan MOBILE: 00962-798020722 EMAIL: n.salim@ju.edu.jo nisreen_salim1@yahoo.com
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET (MSDS) Information about stainless steel for Surgical/Dental/Orthodontic Instruments.
 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET (MSDS) THE INFORMATION BELOW IS BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE AND REPRESENTS THE BEST INFORMATION CURRENTYLY AVAILABLE TO US. HOWEVER, WE MAKE NO WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR ANY
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET (MSDS) THE INFORMATION BELOW IS BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE AND REPRESENTS THE BEST INFORMATION CURRENTYLY AVAILABLE TO US. HOWEVER, WE MAKE NO WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR ANY
3000 Series Articulator System
 3000 Series Articulator System Models 3040 and 3140 Instruction Manual Whip Mix Corporation 361 Farmington Ave. P.O. Box 17183 Louisville, KY 40217-0183 USA 502-637-1451 800-626-5651 Fax 502-634-4512 www.whipmix.com
3000 Series Articulator System Models 3040 and 3140 Instruction Manual Whip Mix Corporation 361 Farmington Ave. P.O. Box 17183 Louisville, KY 40217-0183 USA 502-637-1451 800-626-5651 Fax 502-634-4512 www.whipmix.com
A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding Kheur M 1, Jambhekar S 2, Sethi T 3, Kheur S 4 1Professor, 3 PG student, Dept. of Prosthodontics,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding Kheur M 1, Jambhekar S 2, Sethi T 3, Kheur S 4 1Professor, 3 PG student, Dept. of Prosthodontics,
The Convergence Angle of Full-coverage Crown Preparations Made by Dental Students
 Original Article The Convergence Angle of Full-coverage Crown Preparations Made by Dental Students H. Dorriz 1, 2, S. Nokar 3, 4, R. Baghai Naini 3, 4, A. Madadi 5 1 Associate Professor, Department of
Original Article The Convergence Angle of Full-coverage Crown Preparations Made by Dental Students H. Dorriz 1, 2, S. Nokar 3, 4, R. Baghai Naini 3, 4, A. Madadi 5 1 Associate Professor, Department of
Wear Rates of Resin Composites
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-2, 226-233 Wear Rates of Resin Composites WW Barkmeier RL Erickson MA Latta TM Wilwerding Clinical Relevance Laboratory wear testing of resin composites provides valuable
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2013, 38-2, 226-233 Wear Rates of Resin Composites WW Barkmeier RL Erickson MA Latta TM Wilwerding Clinical Relevance Laboratory wear testing of resin composites provides valuable
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx
 Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
Psychological Impact of Communication
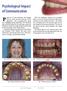 Psychological Impact of Communication Patient is a 47 year old female was unhappy with her smile and self conscience of her appearance. She is missing teeth, which was impinging during mastication. The
Psychological Impact of Communication Patient is a 47 year old female was unhappy with her smile and self conscience of her appearance. She is missing teeth, which was impinging during mastication. The
A conservative restorative smile makeover
 C L I N I C A L A conservative restorative smile makeover Aneta Grzesinska 1 Introduction The patient was a 37-year-old female who presented to the practice requesting six porcelain veneers for her upper
C L I N I C A L A conservative restorative smile makeover Aneta Grzesinska 1 Introduction The patient was a 37-year-old female who presented to the practice requesting six porcelain veneers for her upper
Impression techniques for removable partial dentures: A review
 Review Article DOI: 10.18231/2455-8486.2017.0012 Impression techniques for removable partial dentures: A review Reeta Jain 1,*, Supriya 2, Shweta 3, Kimmi 4 1 Professor & HOD, 2,3,4 PG Student, Dept. of
Review Article DOI: 10.18231/2455-8486.2017.0012 Impression techniques for removable partial dentures: A review Reeta Jain 1,*, Supriya 2, Shweta 3, Kimmi 4 1 Professor & HOD, 2,3,4 PG Student, Dept. of
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Symposium on Occlusal Articulation. Mandibular Movement Recordings and Articulator Adjustments Simplified. Harry C. Lundeen, D.D.S.
 Symposium on Occlusal Articulation Mandibular Movement Recordings and Articulator Adjustments Simplified Harry C. Lundeen, D.D.S. Judging from the volume of writing that has appeared in the dental literature
Symposium on Occlusal Articulation Mandibular Movement Recordings and Articulator Adjustments Simplified Harry C. Lundeen, D.D.S. Judging from the volume of writing that has appeared in the dental literature
