Eugenol Inhibits ATP-induced P2X Currents in Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons
|
|
|
- Buddy Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Vol 12: , December, 2008 Eugenol Inhibits ATP-induced P2X Currents in Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons Hai Ying Li 1, Byung Ky Lee 1, Joong Soo Kim 1, Sung Jun Jung 2, and Seog Bae Oh 1 1 Department of Physiology, School of Dentistry and Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul , 2 Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chunchon , Korea Eugenol is widely used in dentistry to relieve pain. W e have recently demonstrated voltage-gated Na + and Ca 2+ channels as molecular targets for its analgesic effects, and hypothesized that eugenol acts on P2X 3, another pain receptor expressed in trigeminal ganglion (TG), and tested the effects of eugenol by whole-cell patch clamp and Ca 2+ imaging techniques. In the present study, we investigated whether eugenol would modulate 5 -triphosphate (ATP)-induced currents in rat TG neurons and P2X 3-expressing human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells. ATP-induced currents in TG neurons exhibited electrophysiological properties similar to those in HEK293 cells, and both ATP- and α,β -meatp-induced currents in TG neurons were effectively blocked by TNP-ATP, suggesting that P2X 3 mediates the majority of ATP-induced currents in TG neurons. Eugenol inhibited ATP-induced currents in both capsaicin-sensitive and capsaicin-insensitive TG neurons with similar extent, and most ATP-responsive neurons were IB4-positive. Eugenol inhibited not only Ca 2+ transients evoked by α,β -meatp, the selective P2X 3 agonist, in capsaicin-insensitive TG neurons, but also ATP-induced currents in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells without co-expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1). W e suggest, therefore, that eugenol inhibits P2X 3 currents in a TRPV1-independent manner, which contributes to its analgesic effect. Key Words: ATP, Eugenol, P2X receptor, Trigeminal ganglion neurons INTRODUCTION Eugenol has extensively been used in dentistry because of its ability to allay tooth pain, however, the molecular mechanisms of its action remain largely unexplained. We have recently demonstrated that inhibition of voltage-gated Na + and Ca 2+ channel currents by eugenol might contribute to its analgesic effects (Lee et al, 2005; Park et al, 2006; Chung et al, 2008). Furthermore, we showed that the activation of TRPV1 and inhibition of voltage-gated K + channel currents might be involved in its stimulatory effects (Yang et al, 2003; Li et al, 2007), and that the inhibitory effects of eugenol on voltage-gated ion channels result from TRPV1 independent mechanisms although eugenol per se activates TRPV1. Given the fact that wide ranges of ion channels are modulated by eugenol, there could be another molecular target for eugenol. P2X receptor is Ca 2+ -permeable cation channel which is activated by extracellular ATP which is released from damaged cells in the injured tissues. P2X receptors are involved in a variety of physiological responses in many different tissues and cell types, including trigeminal ganglion (TG) and dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons (Ralevic & Burnstock, 1998; Burnstock, 2007). Among seven different isoforms (P2X 1 P2X 7), P2X 3 receptor is known to be predominantly expressed in subpopulations of nociceptive sensory neurons (Chen et al, 1995; Lewis et al, 1995; Xiang et al, 1998; Jiang & Gu, 2002). Immunohistochemical studies showed that the P2X 3 receptors are found largely in the population of nociceptive neurons which are labeled with isolectin B4 (IB4) (Eriksson et al, 1998). Indeed, P2X receptors, particularly the P2X 3 subtype, have attracted a great deal of interest as a potential target for the development of novel analgesics (Burnstock, 2006). P2X 3 is expressed in tooth pulp, thereby mediating the initiation of pain (Burnstock, 1996). P2X 3 and P2X 2/3 receptors on sensory afferents in tooth pulp appear to mediate nociception not only in rats but also in human (Cook & McCleskey, 1997; Cook et al, 1997; Alavi et al, 2001; Renton et al, 2003). P2X 3 was also found to be co-expressed with TRPV1 receptor in small to medium-sized rat TG neurons and tooth pulp (Ichikawa & Sugimoto, 2004). In this study, we hypothesized that P2X 3 receptor would be inhibited by eugenol. We, therefore, examined its mode of action in rat nociceptive TG neurons and P2X 3-expressing human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells by using whole-cell patch clamp and Ca 2+ imaging techniques. Corresponding to: Seog Bae Oh, Department of Physiology, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, 28-2 Yeongeon-dong, Chongno-gu, Seoul , Korea. (Tel) , (Fax) , ( ) odolbae@snu.ac.kr ABBREVIATIONS: ATP, Adenosine 5 -triphosphate; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293; IB4, isolectin B4; TG, trigeminal ganglion; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid
2 316 HY Li, et al METHODS All experimental procedures for animal use were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), School of Dentistry, Seoul National University. Preparation of TG neurons TG neurons from neonatal rats were prepared as previously described (Park et al, 2006). Briefly, trigeminal ganglion neurons were isolated from neonatal (4- to 7-day-old) Sprague-Dawley rats (Orient BIO, INC., Gapyeong-City, Korea). Dissected TG were incubated in 3 ml of HBSS (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) containing 0.25% trypsin (Invitrogen) at 37 o C for 30 min. Neurons were then dissociated by trituration with a series of sterile Pasteur pipettes, re-suspended in TG media containing apyrase (2 units/ml; type VII; Sigma), and then plated onto glass coverslips previously coated with a solution of 0.1 mg/ml poly-l-ornithine (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Neurons were maintained in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air/5% CO 2 at 37 o C and were used for patch clamp recording within 6 and 8 hrs after being plated. Transient transfection of HEK293 cells cdnas encoding the P2X 3 subunits were expressed alone or cotransfected with TRPV1 in HEK 293 cells. HEK293 cells were cultured in Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium (WelGene, Inc., Daegu-city, Korea), supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum containing penicillin and streptomycin (Invitrogen). Cells reaching 60 80% confluency were used for transient cdnas of P2X 3 transfections with the cationic liposome method with 1 μg of supercoiled plasmid cdna per cells mixed with 2.5 μl enhancer and 3 μl WelFect-EX TM (WelGene) in 0.5 ml of serum-free medium. Green fluorescence protein (GFP) (Clontech Laboratories, Inc., CA, USA) was co-transfected with P2X receptors as an expression marker. After 5 hrs at 37 o C, the medium was replaced with normal HEK293 medium, and cells were incubated for another hrs before electrophysiological experiments. Electrophysiological recordings Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings were performed for the measurement of ATP-induced currents with an Axopatch-1C amplifier (Axon Instruments, Union City, CA, USA). The patch electrodes and puffer pipettes were pulled from borosilicate capillaries (Chase Scientific Glass, Inc., Rockwood, TN, USA). When the pipettes were filled with the solution, their resistance was 2~4 MΩ. The kinetics of ATP-induced inward currents was determined with the decay time which was calculated as the time taken for current to fall from 90% to 10% of the peak (decay time 90 10%). The extracellular solution contained (mm): NaCl 147, KCl 3, MgCl 2 1, CaCl 2 2, glucose 13, HEPES 10, and ph adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH. The pipette solution contained (mm): NaCl 145, glucose 10, HEPES 10, and EGTA 10, ph adjusted to 7.3 with NaOH. The resting potential was held at 60 mv. All the experiments were performed at room temperature. At the end of each recording in TG neurons, 10 μg/ml IB4-FITC was applied to the bath chamber for 10 min, and then rinsed for 10 min in extracellular solution. IB4-FITC staining was visualized with standard FITC filters. Intracellular calcium imaging Intracellular calcium imaging was performed as described previously (Yang et al, 2003). Briefly, neurons were loaded with fura-2 AM (2 μm; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) for 45 min at 37 o C in serum free medium. The cells were plated onto poly-l-ornithine-coated coverslips, mounted onto the chamber, placed on an inverted microscope (Olympus IX70, Japan) and perfused continuously with extracellular solution at 3 ml/min. Cells were illuminated with a 175-watt xenon arc lamp, and excitation wavelengths (340/380 nm) were selected by a Lambda DG-4 monochromator wavelength changer (Shutter Instrument, Novato, CA). Intracellular free calcium concentration ([Ca 2+ ] i) was measured by digital video microfluorometry with an intensified CCD camera (CasCade, Roper Scientific, Trenton, NJ) coupled to a microscope and software (Metafluor, Universal Imaging Corp., Downingtown, PA) on a Pentium 4 computer. Drugs Apyrase, ATP, α,β-meatp, TNP-ATP, capsaicin, eugenol, and IB4-FITC were purchased from Sigma. ATP and α,β-meatp were applied via a glass puffer pipette (1 μm tip diameter, 5 psi) using a Picopump (Medical Systems Corporation, PLI-100, Greenvale, NY, USA). The tip of the puffer pipette was positioned down-stream from the cell with respect to the direction of flow of the superfusing solution, and temporarily repositioned to a point about 15 μm from the cell for the period of application only. ATP was applied for 1s three times with the interval of 90s. Eugenol and capsaicin were dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) to make a stock solution, diluted to their final concentration in the extracellular solution, and then applied by gravity through a bath perfusion system. The final concentration of DMSO was less than 0.1% (v/v), which did not affect membrane currents and [Ca 2+ ] i (Yang et al, 2003). Eugenol was applied after 10s of the first ATP application until the third ATP application, and the ATP-induced currents were compared with those observed in other cells without eugenol pretreatment. The sensitivity of eugenol-responsive cells to capsaicin was determined by the induction of inward currents by 1 μm capsaicin after the exposure of the cells to eugenol. The perfusion rate of bath solution was unchanged (4 ml/min) during the experiment. Statistical analyses Data are expressed as mean±sem. ANOVA and Student s t test were used to determine the differences using the software Origin 6.0 (Northampton, MA, USA). Differences were considered to be significant when p value was less than RESULTS P2X 3 mediates most of the ATP-induced currents in rat TG neurons Using rat small-sized (<25 μm) TG neurons, we first
3 Inhibition of P2X Currents by Eugenol 317 characterized ATP-induced currents by comparison of those measured in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells. In 72% (60/83) of neurons tested, application of 10 μm ATP induced inward currents at the holding potential of -60 mv, in which 93% of (n=56/60) neurons showed fast activation and inactivation with decay time 90-10% of 212 ms, comparable to the kinetic properties of ATP-induced currents in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells (decay time 90-10%=225 ms) (Fig. 1A). The rest of neurons tested (n=4/60) showed fast activation and slow inactivation with decay time 90-10%>500 ms (data not shown). In both TG neurons and P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells, recovery from desensitization was also extremely slow, so that the second application of ATP (C 2) after 90s interval produced significantly smaller currents compared to the first application (C 1) (Fig. 1Ba and Bb). The magnitude of the first 10 μm ATP-induced currents in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells (3.25±0.50 na, n=60) was much bigger than that of TG neurons (1.01±0.21 na, n=10) (P<0.05), however, the normalized amplitude ratio (C 2/C 1) was not significantly different from each other (28±9% versus 39±10%, p>0.05) (Fig. 1Bc). When small-sized TG neurons were exposed to 1 μm TNP-ATP, a selective antago- Fig. 1. Comparison of current profiles of 10 μm ATP-induced currents in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells and rat TG neurons. (A) Representative current traces activated by 10 μm ATP in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells (left, n=60) and rat TG neurons (right, n=56). (B) Records of 10 μm ATPinduced currents activated by twice applications of 10 μm ATP with the interval of 90s in a P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cell (a) and rat TG neuron (b). The normalized amplitude ratio (C 2/C 1) in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells and that in TG neurons (c). (C) Inhibition of 10 μm ATP (a)- and 100 μm α,β-meatp (b)-induced currents by 1 μm TNP-ATP in small TG neurons. The summary of the inhibition of TNP-ATP on ATP (n=5)- and α,β-meatp (n=5)-induced currents (mean±sem, p<0.05) (c). Black points indicate the time point of ATP or α,βmeatp application.
4 318 HY Li, et al nist of P2X 3, ATP-induced currents were blocked by 91±2% (n=5, p<0.05) (Fig. 1Ca and Fig. 1Cc). Moreover, α,β-meatp (100 μm), the selective agonist of P2X 3 receptors, induced inward currents with similar current profile and amplitude, which were abolished by 1 μm TNP-ATP (91±1%, n=5, p <0.05) (Fig. 1Cb and Fig. 1Cc). Eugenol inhibits ATP-induced P2X currents in both capsaicin-sensitive and capsaicin-insensitive TG neurons We then tested whether eugenol inhibited ATP-induced currents in rat TG neurons. Because ATP-induced currents exhibited profound desensitization (See Fig. 1) and had a tendency to show wide variation of responses by repetitive application of ATP even after the long-term washout (>10 min between applications), we employed the analytical method of Gerevich et al (2007) and compared the normalized amplitude ratio (C 2/C 1 and C 3/C 1) of ATP-induced currents with the values of the control and eugenol pretreatment. When 1 mm eugenol was applied for 90s, eugenol did not inhibit 10 μm ATP-induced P2X currents in both capsaicin-sensitive and capsaicin-insensitive TG neurons (versus the first application p>0.05) (Fig. 2A and 2B). However, 3 min application of 1 mm eugenol inhibited ATP-induced P2X currents in both capsaicin-sensitive (50±7% versus the first application, n=10) and capsaicin-insensitive (55±8% versus the first application, n=15) neurons (Fig. 2B, p<0.05). The magnitude of the inhibition of ATP-induced P2X currents by 1 mm eugenol was similar between capsaicin-insensitive and capsaicin-sensitive TG neurons (Fig. 2B, p>0.05). Eighty-four% (n=42/50) of ATP-responsive neurons, including both capsaicin-sensitive and capsaicin-insensitive neurons, were IB4-positive (data not shown). Fig. 2. Eugenol inhibited ATP-induced P2X currents in both capsaicininsensitive and capsaicin-sensitive rat TG neurons. (A) Representative current traces of 10 μm ATP-induced P2X currents under control (Aa and Ab, left), and eugenol (1 mm) (Aa and Ab, right) in both capsaicin-insensitive (Aa) and capsaicin-sensitive (Ab) rat TG neurons. (B) The summary of the inhibition of ATP-induced P2X currents in both capsaicin-insensitive (Ba) and capsaicin-sensitive (Bb) rat TG neurons. The amplitude of second (C 2) and third currents (C 3) was normalized compared to the first one (C 1). Eugenol-induced inhibition in capsaicin-insensitive neurons (n=15) was similar to that obtained in capsaicin-sensitive neurons (n=10) (mean±sem, p>0.05). Black points indicate the time point of ATP application.
5 Inhibition of P2X Currents by Eugenol 319 Fig. 3. Eugenol inhibited α,βmeatp-induced Ca 2+ transients in rat TG neurons. (A) α,β-meatp (100 μm) induced Ca 2+ transients in small-sized TG neurons. Eugenol (1 mm) abolished α,β-meatp-induced Ca 2+ transients in capsaicin (0.5 μm)-insensitive TG neurons. (B) The summary of the inhibition of α,β-meatp-induced Ca 2+ transients by eugenol in capsaicininsensitive TG neurons (mean±sem, n=9, p<0.05). The amplitude changes of Ca 2+ transients induced by second (combined application with eugenol) and third (3 rd ) α,β-meatp applications were normalized compared to the first one (1 st ). Fig. 4. Eugenol inhibited ATP-induced P2X 3 currents in both P2X 3-expressing and P2X 3/TRPV1-coexpressing HEK293 cells. (A) Representative current traces of 10 μm ATP-induced P2X 3 currents under control (Aa and Ab, left), and eugenol (1 mm) (Aa and Ab, right) in both P2X 3-expressing (Aa) and P2X 3/TRPV1-coexpressing (Ab) HEK293 cells. (B) The summary of the inhibition of ATP-induced P2X 3 currents in both P2X 3-expressing (Aa) and P2X 3/TRPV1-coexpressing (Ab) HEK293 cells. The amplitude of second (C 2) and third currents (C 3) was normalized compared to the first one (C 1). Eugenol-induced inhibition in P2X 3-expressing cells (n=13) was similar to that obtained in P2X 3/TRPV1- coexpressing cells (n=12) (mean±sem, p>0.05). Black points indicate the time point of ATP application.
6 320 HY Li, et al Eugenol inhibits α,β-meatp-induced Ca 2+ transients in rat TG neurons To determine specific inhibitory effects on P2X 3 receptors and involvement of TPRV1 in the actions of eugenol, we examined the effects of eugenol on α,β-meatp-induced Ca 2+ transients in capsaicin-insensitive TG neurons. One hundred μm α,β-meatp induced Ca 2+ transients only in small-sized TG neurons, which was abolished by eugenol (Fig. 3A and 3B, 27±5% versus the first Ca 2+ transient, n=9, p<0.05) in a reversible manner. Inhibition of ATP-induced currents by eugenol is TRPV1 independent We tested the effects of 1 mm eugenol on ATP-induced currents in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells (Fig. 4Aa). Consistent with the above TG results, the 90s application of 1 mm eugenol did not inhibit 10 μm ATP-induced currents, while 180s application of 1 mm eugenol inhibited 10 μm ATP-induced currents (51±7% versus the first application, n=13) (Fig. 4B left, p<0.05). Likewise, exposure to eugenol for 180s, but not for 90s, blocked ATP-induced currents in P2X3/TRPV1-coexpressing cells (47±6%, n=12) (Fig. 4B right), and the extent of the inhibition was comparable to that obtained in only P2X 3-expressing cells (p> 0.05). Capsaicin induced inward currents only in P2X 3/ TRPV1-coexpressing HEK293 cells tested (Fig. 4Ab), but did not in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells. DISCUSSION In the present study, we found that eugenol inhibited ATP-induced currents in nociceptive TG neurons, suggesting that P2X receptor could be an another molecular target for eugenol in addition to voltage-gated Ca 2+ and Na + channels which have previously been demonstrated (Lee et al, 2005; Park et al, 2006; Chung et al, 2008). In agreement with the actions of eugenol on voltage-sensitive Ca 2+ and Na + channels, modulation of P2X 3 receptor by eugenol was TRPV1-independent as well. All P2X subtypes, except P2X 7, are present in TG neurons (Xiang et al, 1998). We also found mrna expression of all P2X receptors in TG neurons (unpublished data). Among P2X receptors, however, P2X 3 which is localized predominantly on small nociceptive sensory neurons in TG and DRG (Chen et al, 1995; Lewis et al, 1995; Xiang et al, 1998) has been shown to be the main P2X subtype that plays an important role in peripheral pain mechanisms in sensory neurons (Burnstock, 1996; Burnstock & Wood, 1996). Thus, we focused on P2X 3 receptor, and our results provided strong evidences that P2X 3 receptor is the main P2X subtype in TG neurons, not only activated by ATP but also modulated by eugenol. First, ATP-induced currents were observed in small-sized TG neurons, and most of these ATP-sensitive TG neurons tested were IB4-positive, which was consistent with previous studies (Eriksson et al, 1998; Dunn et al, 2001). Second, ATP-induced currents exhibited typical elecrophysiological properties of P2X 3 channel. The current profile of ATP-induced currents in rat TG neurons was similar to that in P2X 3-expressing HEK293 cells, whereas very different from that in P2X 1, P2X 2, and P2X 4-expressing HEK293 cells (North, 2002; Li et al, 2008), Besides, ATP-induced currents were rapidly desensitized upon repetitive ATP applications. These characteristics are in good agreement with previous studies (Luo et al, 2006). Third, both ATP- and α,β-meatp-induced currents were effectively blocked by TNP-ATP. Lastly, α,β-meatp induced Ca 2+ transients in small-sized TG neurons. Taken together, these results suggest that P2X 3 is the major P2X receptors expressed in nociceptive TG neurons, and that eugenol might exert its inhibitory effects on P2X 3 recepors in rat TG neurons. Eugenol inhibited ATP-induced P2X currents in nociceptive TG neurons in a TRPV1 independent manner, which is consistent with eugenol action on voltage-sensitive channels (Lee et al, 2005; Park et al, 2006; Li et al, 2007; Chung et al, 2008). Inhibition of ATP-induced P2X currents by eugenol was observed in both capsaicin-sensitive and capsaicin-insensitive TG neurons. In addition, eugenol inhibited α,β-meatp-induced Ca 2+ transients in capsaicin-insensitive TG neurons. By using heterologous expression system, it was also found that TRPV1 involvement was not prerequisite for the effect of eugenol on P2X 3 receptors. All these results indicate TRPV1-independent actions of eugenol on P2X 3 receptor. Because of abolishment of ATP-induced hyperalgesia in mice lacking TRPV1 receptors, the interactions between P2 and TRPV1 have previously been suggested (Caterina et al, 2000). Indeed, TG and DRG neurons expressing TRPV1 receptors also express P2X 3 receptors (Guo et al, 1999; Ichikawa & Sugimoto, 2004). However, our results which were observed in both TG neurons and heterologous expression system argue against the involvement of TRPV1 in P2X 3 modulation by eugenol, and detailed mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In contrast to the action of eugenol to voltage-sensitive channels, it was of an interest to note that action of eugenol on P2X was somehow delayed in both TG and heterologous expression system, suggesting a possibility of indirect interaction between eugenol and P2X which may involve other molecules. P2X 3 has been shown to be expressed in tooth pulp (Burnstock, 1996; Cook et al, 1997). ATP, which might be released from mechanically-stimulated odontoblasts or damaged pulpal cells in the mild inflamed pulp, could initiate tooth pain. Thus, our finding that eugenol inhibited P2X 3 receptors provides a plausible explanation of why eugenol is therapeutically applicable in this clinical situation. Indeed, the range of eugenol concentration ( 10 4 to 10 3 M) used in the present study is within the range of eugenol concentration in the cavity preparation below ZOE (Craig & Powers, 2002). In summary, in addition to the inhibition of voltage-gated Na + and Ca 2+ channels, the inhibition of P2X 3 channels by eugenol, which is TRPV1-independent, could be an additional underlying mechanism of its analgesic effects. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT This research was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD) (KRF E00465). We thank Dr. North RA (Faculty of Life Sciences, The University of Manchester, UK) for the kind gift of plasmid cdnas of P2X 3.
7 Inhibition of P2X Currents by Eugenol 321 REFERENCES Alavi AM, Dubyak GR, Burnstock G. Immunohistochemical evidence for ATP receptors in human dental pulp. J Dent Res 80: , 2001 Bleehen T, Keele CA. Observations on the algogenic actions of adenosine compounds on the human blister base preparation. Pain 3: , 1977 Burnstock G. A unifying purinergic hypothesis for the initiation of pain. Lancet 347: , 1996 Burnstock G, Wood JN. Purinergic receptors: their role in nociception and primary afferent neurotransmission. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6: , 1996 Burnstock G. Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther 110: , 2006 Burnstock G. Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 64: , 2007 Caterina MJ, Leffler A, Malmberg AB, Martin WJ, Trafton J, Petersen-Zeitz KR, Koltzenburg M, Basbaum AI, Julius D. Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science 288: , 2000 Chen CC, Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Colquhoun D, Burnstock G, Wood JN. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature 377: , 1995 Chung G, Rhee JN, Jung SJ, Kim JS, Oh SB. Modulation of CaV2.3 calcium channel currents by eugenol. J Dent Res 87: , 2008 Cook SP, McCleskey EW. Desensitization, recovery and Ca(2+)- dependent modulation of ATP-gated P2X receptors in nociceptors. Neuropharmacology 36: , 1997 Cook SP, Vulchanova L, Hargreaves KM, Elde R, McCleskey EW. Distinct ATP receptors on pain-sensing and stretch-sensing neurons. Nature 387: , 1997 Cook SP, McCleskey EW. Cell damage excites nociceptors through release of cytosolic ATP. Pain 95: 41 47, 2002 Craig RG, Powers JM. Biocompatibility of dental materials. In: Restorative dental materials. St. Louis: Mosby, p , 2002 Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Burnstock G. P2X receptors in peripheral neurons. Prog Neurobiol 65: , 2001 Eriksson J, Bongenhielm U, Kidd E, Matthews B, Fried K. Distribution of P2X3 receptors in the rat trigeminal ganglion after inferior alveolar nerve injury. Neurosci Lett 254: 37 40, 1998 Gerevich Z, Zadori Z, Müller C, Wirkner K, Schröder W, Rubini P, Illes P. Metabotropic P2Y receptors inhibit P2X3 receptorchannels via G protein-dependent facilitation of their desensitization. Br J Pharmacol 151: , 2007 Guo A, Vulchanova L, Wang J, Li X, Elde R. Immunocytochemical localization of the vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1): relationship to neuropeptides, the P2X3 purinoceptor and IB4 binding sites. Eur J Neurosci 11: , 1999 Ichikawa H, Sugimoto T. The co-expression of P2X3 receptor with VR1 and VRL-1 in the rat trigeminal ganglia. Brain Res 998: , 2004 Jiang J, Gu J. Expression of adenosine triphosphate P2X3 receptors in rat molar pulp and trigeminal ganglia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 94: , 2002 Kollarik M, Dinh QT, Fischer A, Undem BJ. Capsaicin-sensitive and -insensitive vagal bronchopulmonary C-fibres in the mouse. J Physiol 551: , 2003 Lee MH, Yeon KY, Park CK, Li HY, Fang Z, Kim MS, Choi SY, Lee SJ, Lee S, Park K, Lee JH, Kim JS, Oh SB. Eugenol inhibits calcium currents in dental afferent neurons. J Dent Res 84: , 2005 Lewis C, Neidhart S, Holy C, North RA, Buell G, Surprenant A. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature 377: , 1995 Li HY, Oh SB, Kim JS. Pharmacological and electrophysiological characterization of rat P2X currents. IJOB 33: 1 5, 2008 Li HY, Park CK, Jung SJ, Choi SY, Lee SJ, Park K, Kim JS, Oh SB. Eugenol inhibits K+ currents in trigeminal ganglion neurons. J Dent Res 86: , 2007 Luo J, Yin GF, Gu YZ, Liu Y, Dai JP, Li C, Li ZW. Characterization of three types of ATP-activated current in relation to P2X subunits in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. Brain Res 1115: 9 15, 2006 North RA. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82: , 2002 North RA. The P2X3 subunit: a molecular target in pain therapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 4: , 2003 North RA. P2X3 receptors and peripheral pain mechanisms. J Physiol 554: , 2004 Park CK, Li HY, Yeon KY, Jung SJ, Choi SY, Lee SJ, Lee S, Park K, Kim JS, Oh SB. Eugenol inhibits sodium currents in dental afferent neurons. J Dent Res 85: , 2006 Ralevic V, Burnstock G. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50: , 1998 Renton T, Yiangou Y, Baecker PA, Ford AP, Anand P. Capsaicin receptor VR1 and ATP purinoceptor P2X3 in painful and nonpainful human tooth pulp. J Orofac Pain 17: , 2003 Sarrami N, Pemberton MN, Thornhill MH, Theaker ED. Adverse reactions associated with the use of eugenol in dentistry. Br Dent J 193: , 2002 Tsuda M, Ueno S, Inoue K. In vivo pathway of thermal hyperalgesia by intrathecal administration of alpha,beta-methylene ATP in mouse spinal cord: involvement of the glutamate-nmda receptor system. Br J Pharmacol 127: , 1999 Xiang Z, Bo X, Burnstock G. Localization of ATP-gated P2X receptor immunoreactivity in rat sensory and sympathetic ganglia. Neurosci Lett 256: , 1998 Yang BH, Piao ZG, Kim YB, Lee CH, Lee JK, Park K, Kim JS, Oh SB. Activation of vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1) by eugenol. J Dent Res 82: , 2003
Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
(Supplementary information) TRPV1 EXHIBITS DYNAMIC IONIC SELECTIVITY DURING AGONIST STIMULATION. Man-Kyo Chung, Ali D. Güler, and #Michael J.
 (Supplementary information) TRPV1 EXHIBITS DYNAMIC IONIC SELECTIVITY DURING AGONIST STIMULATION Man-Kyo Chung, Ali D. Güler, and #Michael J. Caterina Title Supplementary Figure 1. Capsaicin evokes changes
(Supplementary information) TRPV1 EXHIBITS DYNAMIC IONIC SELECTIVITY DURING AGONIST STIMULATION Man-Kyo Chung, Ali D. Güler, and #Michael J. Caterina Title Supplementary Figure 1. Capsaicin evokes changes
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
INTRODUCTION. Key Words: camp, G i-protein, Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel, I h, Neuropathic pain
 Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Vol 16: 237-241, August, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.4.237 A Novel Carbamoyloxy Arylalkanoyl Arylpiperazine Compound (SKL-NP) Inhibits Hyperpolarization-Activated
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Vol 16: 237-241, August, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.4.237 A Novel Carbamoyloxy Arylalkanoyl Arylpiperazine Compound (SKL-NP) Inhibits Hyperpolarization-Activated
CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 THE PHARMACOLOGICAL DISTINCTION OF GABA A RECEPTOR
B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 THE PHARMACOLOGICAL DISTINCTION OF GABA A RECEPTOR
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel
 TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel Mechanical forces play numerous roles in physiology. When an object contacts our skin, it exerts a force that is encoded as touch or pain depending on its intensity.
TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel Mechanical forces play numerous roles in physiology. When an object contacts our skin, it exerts a force that is encoded as touch or pain depending on its intensity.
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Gerasimenko et al..73/pnas.39 SI Materials and Methods Reagents used in this study include Fluo-4/Fura- (Invitrogen), thapsigargin (albiochem), collagenase (Worthington), palmitoleic
Supporting Information Gerasimenko et al..73/pnas.39 SI Materials and Methods Reagents used in this study include Fluo-4/Fura- (Invitrogen), thapsigargin (albiochem), collagenase (Worthington), palmitoleic
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
D. Nishizawa 1, N. Gajya 2 and K. Ikeda 1, * Global Research & Development, Nagoya Laboratories, Pfizer Japan Inc, Nagoya, Japan
 Current Neuropharmacology, 2011, 9, 113-117 113 Identification of Selective Agonists and Antagonists to G Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Candidate Medicines for Drug Dependence
Current Neuropharmacology, 2011, 9, 113-117 113 Identification of Selective Agonists and Antagonists to G Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Candidate Medicines for Drug Dependence
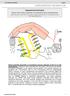
The Pain Pathway. dorsal root ganglion. primary afferent nociceptor. TRP: Transient Receptor Potential
 Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
Supplementary Figure 1 NMR spectra of hydroxy α and β-sanshool isomers. (Top) Hydroxy-α-sanshool (2E,6Z,8E,10E)-2'-
 Supplementary Figure 1 NMR spectra of hydroxy α and β-sanshool isomers. (Top) Hydroxy-α-sanshool (2E,6Z,8E,10E)-2'- hydroxyl-n-isobutyl-2,6,8,10-dodeca-tetraenamide) and (bottom) hydroxy-β-sanshool (2E,6E,8E,10E)-2'-hydroxyl-N-isobutyl-
Supplementary Figure 1 NMR spectra of hydroxy α and β-sanshool isomers. (Top) Hydroxy-α-sanshool (2E,6Z,8E,10E)-2'- hydroxyl-n-isobutyl-2,6,8,10-dodeca-tetraenamide) and (bottom) hydroxy-β-sanshool (2E,6E,8E,10E)-2'-hydroxyl-N-isobutyl-
Increased 5-HT 3 -mediated signalling in pelvic afferent neurons from mice deficient in P2X 2 and/or P2X 3 receptor subunits
 Purinergic Signalling (2006) 2:481 489 DOI 10.1007/s11302-006-9017-z Increased 5-HT 3 -mediated signalling in pelvic afferent neurons from mice deficient in P2X 2 and/or P2X 3 receptor subunits Bei Ma
Purinergic Signalling (2006) 2:481 489 DOI 10.1007/s11302-006-9017-z Increased 5-HT 3 -mediated signalling in pelvic afferent neurons from mice deficient in P2X 2 and/or P2X 3 receptor subunits Bei Ma
Inflammation-Induced Airway Hypersensitivity: From Ion Channels to Patients
 Inflammation-Induced Airway Hypersensitivity: From Ion Channels to Patients Lu-Yuan Lee, Ph.D. Airway Sensory Neurobiology Laboratory Department of Physiology University of Kentucky Medical Center BACKGROUND
Inflammation-Induced Airway Hypersensitivity: From Ion Channels to Patients Lu-Yuan Lee, Ph.D. Airway Sensory Neurobiology Laboratory Department of Physiology University of Kentucky Medical Center BACKGROUND
Introduction. Brief Communication
 6058 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 9, 2003 23(14):6058 6062 Brief Communication Possible Involvement of P2Y 2 Metabotropic Receptors in ATP-Induced Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Receptor 1-Mediated
6058 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 9, 2003 23(14):6058 6062 Brief Communication Possible Involvement of P2Y 2 Metabotropic Receptors in ATP-Induced Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Receptor 1-Mediated
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Suramin Affects Capsaicin Responses and Capsaicin-Noxious Heat Interactions in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurones
 Physiol. Res. 51: 193-198, 2002 Suramin Affects Capsaicin Responses and Capsaicin-Noxious Heat Interactions in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurones V. VLACHOVÁ, A. LYFENKO, L. VYKLICKÝ, R.K. ORKAND 1 Institute
Physiol. Res. 51: 193-198, 2002 Suramin Affects Capsaicin Responses and Capsaicin-Noxious Heat Interactions in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurones V. VLACHOVÁ, A. LYFENKO, L. VYKLICKÝ, R.K. ORKAND 1 Institute
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
TRPV1, ASICs and P2X2/3 expressed in bone cells simultaneously regulate bone metabolic markers in ovariectomized mice
 J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2016; 16(2):145-151 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article TRPV1, ASICs and P2X2/3 expressed in bone cells simultaneously regulate bone
J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2016; 16(2):145-151 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article TRPV1, ASICs and P2X2/3 expressed in bone cells simultaneously regulate bone
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 589.23 (2011) pp 5663 5676 5663 Selective silencing of Na V 1.7 decreases excitability and conduction in vagal sensory neurons Yukiko Muroi 1,FeiRu 1, Marian Kollarik 1, Brendan J. Canning 1,StephenA.Hughes
J Physiol 589.23 (2011) pp 5663 5676 5663 Selective silencing of Na V 1.7 decreases excitability and conduction in vagal sensory neurons Yukiko Muroi 1,FeiRu 1, Marian Kollarik 1, Brendan J. Canning 1,StephenA.Hughes
Functional Compartmentalization of Opioid Desensitization in Primary Sensory Neurons 1
 0022-3565/00/2942-0500$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/00/2942-0500$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
Synaptic Integration
 Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Effects of different dust particles on calcium current in the neurons of dorsal root ganglia of rats
 Effects of different dust particles on calcium current in the neurons of dorsal root ganglia of rats Yong Mei, Haibing Yang, Jingzhi Sun, Xiao Yin, Xiang Guo, Zhenglun Wang, Lei Yang * Department of Occupational
Effects of different dust particles on calcium current in the neurons of dorsal root ganglia of rats Yong Mei, Haibing Yang, Jingzhi Sun, Xiao Yin, Xiang Guo, Zhenglun Wang, Lei Yang * Department of Occupational
Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016
 Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016 1. The figure above was obtained from a paper on calcium channels expressed by dentate granule cells. The whole-cell Ca 2+ currents in (A) were measured
Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016 1. The figure above was obtained from a paper on calcium channels expressed by dentate granule cells. The whole-cell Ca 2+ currents in (A) were measured
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 16, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat. Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
Cardiac sensory neurons (afferents) continuously sense
 ASIC2a and ASIC3 Heteromultimerize to Form ph-sensitive Channels in Mouse Cardiac Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Tomonori Hattori, Jie Chen, Anne Marie S. Harding, Margaret P. Price, Yongjun Lu, Francois
ASIC2a and ASIC3 Heteromultimerize to Form ph-sensitive Channels in Mouse Cardiac Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Tomonori Hattori, Jie Chen, Anne Marie S. Harding, Margaret P. Price, Yongjun Lu, Francois
Selective Modulation of Ligand-Gated P2X Purinoceptor Channels by Acute Hypoxia Is Mediated by Reactive Oxygen Species
 0026-895X/04/6606-1525 1535$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 6 Copyright 2004 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 851/1182235 Mol Pharmacol 66:1525 1535, 2004 Printed
0026-895X/04/6606-1525 1535$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 6 Copyright 2004 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 851/1182235 Mol Pharmacol 66:1525 1535, 2004 Printed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
John C. Lopshire 1 and Grant D. Nicol 2
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 1998, 18(16):6081 6092 The camp Transduction Cascade Mediates the Prostaglandin E 2 Enhancement of the Capsaicin-Elicited Current in Rat Sensory Neurons: Whole-Cell
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 1998, 18(16):6081 6092 The camp Transduction Cascade Mediates the Prostaglandin E 2 Enhancement of the Capsaicin-Elicited Current in Rat Sensory Neurons: Whole-Cell
Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
Chronic exposure of sensory neurones to increased levels of nerve growth factor modulates CB 1 /TRPV1 receptor crosstalk
 British Journal of Pharmacology (27) 152, 44 413 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Chronic exposure of sensory neurones to increased levels
British Journal of Pharmacology (27) 152, 44 413 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Chronic exposure of sensory neurones to increased levels
Ghrelin Stimulates Porcine Somatotropes
 Animal Industry Report AS 650 ASL R1957 2004 Ghrelin Stimulates Porcine Somatotropes Aleksandra Glavaski-Joksimovic Ksenija Jeftinija Colin G. Scanes Lloyd L. Anderson Srdija Jeftinija Recommended Citation
Animal Industry Report AS 650 ASL R1957 2004 Ghrelin Stimulates Porcine Somatotropes Aleksandra Glavaski-Joksimovic Ksenija Jeftinija Colin G. Scanes Lloyd L. Anderson Srdija Jeftinija Recommended Citation
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013
 NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
Lidocaine Suppresses Subthreshold Oscillations by Inhibiting Persistent Na + Current in Injured Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
 Physiol. Res. 57: 639-645, 2008 Lidocaine Suppresses Subthreshold Oscillations by Inhibiting Persistent Na + Current in Injured Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons H. DONG 1, Y.-H. FAN 2, Y.-Y. WANG 1, W.-T.
Physiol. Res. 57: 639-645, 2008 Lidocaine Suppresses Subthreshold Oscillations by Inhibiting Persistent Na + Current in Injured Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons H. DONG 1, Y.-H. FAN 2, Y.-Y. WANG 1, W.-T.
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
Dependence of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Recovery from Desensitization on the Duration of Agonist Exposure 1
 0022-3565/99/2892-0656$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 289, No. 2 Copyright 1999 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/99/2892-0656$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 289, No. 2 Copyright 1999 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris
 ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Adenosine 5 0 -triphosphate and its relationship with other mediators that activate pelvic nerve afferent neurons in the rat colorectum
 Purinergic Signalling (2006) 2: 517 526 DOI: 10.1007/s11302-005-5305-2 # Springer 2006 Adenosine 5 0 -triphosphate and its relationship with other mediators that activate pelvic nerve afferent neurons
Purinergic Signalling (2006) 2: 517 526 DOI: 10.1007/s11302-005-5305-2 # Springer 2006 Adenosine 5 0 -triphosphate and its relationship with other mediators that activate pelvic nerve afferent neurons
axion Application Note Modeling Pain with Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons on MEAs BioSystems
 axion BioSystems Application Note Modeling Pain with Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons on MEAs Trademarks Axion BioSystems, Inc. and the logo are trademarks of Axion BioSystems, and may not be used without
axion BioSystems Application Note Modeling Pain with Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons on MEAs Trademarks Axion BioSystems, Inc. and the logo are trademarks of Axion BioSystems, and may not be used without
Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 651-656 65! Short communication Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis M. HENČĽK, D. ZACHAROVÁ and J. ZACHAR
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 651-656 65! Short communication Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis M. HENČĽK, D. ZACHAROVÁ and J. ZACHAR
Neurochemical Properties of Dental Primary Afferent Neurons
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5607/en.2012.21.2.68 Exp Neurobiol. 2012 Jun;21(2):68-74. pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Original Article Neurochemical Properties of Dental Primary Afferent Neurons Hue Vang 1+,
http://dx.doi.org/10.5607/en.2012.21.2.68 Exp Neurobiol. 2012 Jun;21(2):68-74. pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Original Article Neurochemical Properties of Dental Primary Afferent Neurons Hue Vang 1+,
and 5 College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
 J Neurophysiol 1: 1184 121, 28. First published May 28, 28; doi:1.1152/jn.1344.27. Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Innervating Skeletal Muscle Respond to Physiological Combinations of Protons, ATP, and Mediated
J Neurophysiol 1: 1184 121, 28. First published May 28, 28; doi:1.1152/jn.1344.27. Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Innervating Skeletal Muscle Respond to Physiological Combinations of Protons, ATP, and Mediated
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
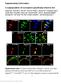 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Material and Methods
 Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Intracellular signalling cascades associated with TRP channels
 Gerald Thiel Intracellular signalling cascades associated with TRP channels Current state of investigations and potential applications Saarland University, Germany Campus Saarbrücken Department of Medical
Gerald Thiel Intracellular signalling cascades associated with TRP channels Current state of investigations and potential applications Saarland University, Germany Campus Saarbrücken Department of Medical
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Differential expression of P2X receptors on neurons from different parasympathetic ganglia
 Neuropharmacology 48 (2005) 766e777 www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropharm Differential expression of P2X receptors on neurons from different parasympathetic ganglia Bei Ma, Huai-Zhen Ruan, Geoffrey Burnstock,
Neuropharmacology 48 (2005) 766e777 www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropharm Differential expression of P2X receptors on neurons from different parasympathetic ganglia Bei Ma, Huai-Zhen Ruan, Geoffrey Burnstock,
A TRPA1-dependent mechanism for the pungent sensation of weak acids
 A r t i c l e A TRPA1-dependent mechanism for the pungent sensation of weak acids Yuanyuan Y. Wang, 1,2 Rui B. Chang, 1,2 Sallie D. Allgood, 3 Wayne L. Silver, 3 and Emily R. Liman 1,2 1 Department of
A r t i c l e A TRPA1-dependent mechanism for the pungent sensation of weak acids Yuanyuan Y. Wang, 1,2 Rui B. Chang, 1,2 Sallie D. Allgood, 3 Wayne L. Silver, 3 and Emily R. Liman 1,2 1 Department of
Parvalbumin and TRPV1 Receptor Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons after Acute Peripheral Inflammation
 Physiol. Res. 58: 305-309, 2009 RAPID COMMUNICATION Parvalbumin and TRPV1 Receptor Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons after Acute Peripheral Inflammation G. ZACHAŘOVÁ, J. PALEČEK Department of
Physiol. Res. 58: 305-309, 2009 RAPID COMMUNICATION Parvalbumin and TRPV1 Receptor Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons after Acute Peripheral Inflammation G. ZACHAŘOVÁ, J. PALEČEK Department of
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
de Montpellier, Montpellier, France and Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes Sorbonne, Paris, France.
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Analysis of Ca 2+ Signaling Mechanisms Our Experience on the Intercellular Communication in Muscle Remodeling S. Filip 1, J. Mokrý 2, O. Forostyak 3, G. Dayanithi 4,5 1 Charles University,
SHORT COMMUNICATION Analysis of Ca 2+ Signaling Mechanisms Our Experience on the Intercellular Communication in Muscle Remodeling S. Filip 1, J. Mokrý 2, O. Forostyak 3, G. Dayanithi 4,5 1 Charles University,
Competitive Antagonism of Recombinant P2X 2/3 Receptors by 2,3 -O-(2,4,6-Trinitrophenyl) Adenosine 5 -Triphosphate (TNP-ATP)
 0026-895X/00/061502-09$3.00/0 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 58, No. 6 Copyright 2000 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 398/868462 Mol Pharmacol 58:1502 1510, 2000 Printed
0026-895X/00/061502-09$3.00/0 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 58, No. 6 Copyright 2000 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 398/868462 Mol Pharmacol 58:1502 1510, 2000 Printed
Electrophysiological Evidence for Functional Astrocytic P2X 3 Receptors in the Mouse Trigeminal Caudal Nucleus
 https://doi.org/1.567/en.218.27.2.88 Exp Neurobiol. 218 Apr;27(2):88-93. pissn 1226-256 eissn 293-8144 Short Communication Electrophysiological Evidence for Functional Astrocytic P2X 3 Receptors in the
https://doi.org/1.567/en.218.27.2.88 Exp Neurobiol. 218 Apr;27(2):88-93. pissn 1226-256 eissn 293-8144 Short Communication Electrophysiological Evidence for Functional Astrocytic P2X 3 Receptors in the
Anesthesiology, V 107, No 2, Aug
 Anesthesiology 2007; 107:322 32 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Local Inflammation in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Alters Excitability and
Anesthesiology 2007; 107:322 32 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Local Inflammation in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Alters Excitability and
Supporting Information. A Two-In-One Fluorescent Sensor With Dual Channels to. Discriminate Zn 2+ and Cd 2+
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RS Advances Supporting Information A Two-In-One Fluorescent Sensor With Dual hannels to Discriminate Zn 2 and d 2 Li-Kun Zhang, a Guang-Fu Wu, a Ying Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RS Advances Supporting Information A Two-In-One Fluorescent Sensor With Dual hannels to Discriminate Zn 2 and d 2 Li-Kun Zhang, a Guang-Fu Wu, a Ying Zhang,
Acid-sensing ion channels ASIC2 and ASIC3 do not contribute to mechanically activated currents in mammalian sensory neurones
 J Physiol 556.3 (2004) pp 691 710 691 Acid-sensing ion channels ASIC2 and ASIC3 do not contribute to mechanically activated currents in mammalian sensory neurones Liam J. Drew 1, Daniel K. Rohrer 2, Margaret
J Physiol 556.3 (2004) pp 691 710 691 Acid-sensing ion channels ASIC2 and ASIC3 do not contribute to mechanically activated currents in mammalian sensory neurones Liam J. Drew 1, Daniel K. Rohrer 2, Margaret
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Methods. the ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex (VLO) and basolateral amygdala (BLA). AAV8-CaMKII-HAhM
 Supplementary Materials, Zimmermann et al. Supplementary Methods Surgery. AAV5-CaMKII-HA-hM 4 D(Gi)-IRES-mCitrine or AAV5-CaMKII-GFP was infused into the ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex (VLO) and basolateral
Supplementary Materials, Zimmermann et al. Supplementary Methods Surgery. AAV5-CaMKII-HA-hM 4 D(Gi)-IRES-mCitrine or AAV5-CaMKII-GFP was infused into the ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex (VLO) and basolateral
16. Excitability o f Squid Giant Axons in Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions
 68 Proc. Japan Acad., 51 (1975) [Vol. 51, 16. Excitability o f Squid Giant Axons in Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions By Fumio KUKITA*> and Shunichi YAMAGISHI**) (Comm. by Yasuj i KATSUKI, M. J. A., Jan.
68 Proc. Japan Acad., 51 (1975) [Vol. 51, 16. Excitability o f Squid Giant Axons in Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions By Fumio KUKITA*> and Shunichi YAMAGISHI**) (Comm. by Yasuj i KATSUKI, M. J. A., Jan.
Heat transduction in rat sensory neurons by calcium-dependent activation of a cation channel
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 7006 7011, June 1997 Neurobiology Heat transduction in rat sensory neurons by calcium-dependent activation of a cation channel (somatosensory transduction primary
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 7006 7011, June 1997 Neurobiology Heat transduction in rat sensory neurons by calcium-dependent activation of a cation channel (somatosensory transduction primary
Product Datasheet. Vanilloid R1/TRPV1 Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.05 ml. Aliquot and store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
 Product Datasheet Vanilloid R1/TRPV1 Antibody NB100-1617 Unit Size: 0.05 ml Aliquot and store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 15 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews,
Product Datasheet Vanilloid R1/TRPV1 Antibody NB100-1617 Unit Size: 0.05 ml Aliquot and store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 15 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews,
Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human
 July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
The plant alkaloid harmaline blocks the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na v 1.7 expressed in CHO cells: a study using automated patch clamp
 Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald Institute of Pathophysiology The plant alkaloid harmaline blocks the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na v 1.7 expressed in CHO cells: a study using automated
Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald Institute of Pathophysiology The plant alkaloid harmaline blocks the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na v 1.7 expressed in CHO cells: a study using automated
Acta Physiologica Sinica
 , 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
, 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Measuring Cardiac Activity:
 icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Measuring Cardiac Activity: Intracellular Calcium Flux Detection on the FLIPR Tetra System Introduction icell Cardiomyocytes are human cardiomyocytes that recapitulate
icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Measuring Cardiac Activity: Intracellular Calcium Flux Detection on the FLIPR Tetra System Introduction icell Cardiomyocytes are human cardiomyocytes that recapitulate
Single patch chip for planar lipid bilayer assays: Ion channels characterization and screening
 RTN Mid-Term Activity Molecular basis of antibiotic translocation Single patch chip for planar lipid bilayer assays: Ion channels characterization and screening Mohamed Kreir April 2008 Overview Planar
RTN Mid-Term Activity Molecular basis of antibiotic translocation Single patch chip for planar lipid bilayer assays: Ion channels characterization and screening Mohamed Kreir April 2008 Overview Planar
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD
 Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Pain and impulse conduction
 1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
CYCLIC AMP-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE-INDEPENDENT ANGIOTENSIN II-INDUCED INHIBITION OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN HAMSTER SUBMANDIBULAR GANGLION NEURONS
 Bull. Tokyo dent. Coll., Vol. 43, No. 2, pp.95 99, May, 2002 95 Short Communication CYCLIC AMP-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE-INDEPENDENT ANGIOTENSIN II-INDUCED INHIBITION OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN HAMSTER SUBMANDIBULAR
Bull. Tokyo dent. Coll., Vol. 43, No. 2, pp.95 99, May, 2002 95 Short Communication CYCLIC AMP-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE-INDEPENDENT ANGIOTENSIN II-INDUCED INHIBITION OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN HAMSTER SUBMANDIBULAR
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 15, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
HEK293 cells transfected with human MATE1, MATE2-K, or vector control were established by
 SUPPLEMENTAL DIGITAL CONTENT METHODS In Vitro Metformin Transport Studies Effect of Dolutegravir on Metformin Transport by MATE1 and MATE2-K HEK293 cells transfected with human MATE1, MATE2-K, or vector
SUPPLEMENTAL DIGITAL CONTENT METHODS In Vitro Metformin Transport Studies Effect of Dolutegravir on Metformin Transport by MATE1 and MATE2-K HEK293 cells transfected with human MATE1, MATE2-K, or vector
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
Mutual occlusion of P2X ATP receptors and nicotinic receptors on sympathetic neurons of the guinea-pig
 Keywords: Sympathetic neurone, Purinoceptor, Acetylcholine receptor 7609 Journal of Physiology (1998), 510.3, pp. 783 791 783 Mutual occlusion of P2X ATP receptors and nicotinic receptors on sympathetic
Keywords: Sympathetic neurone, Purinoceptor, Acetylcholine receptor 7609 Journal of Physiology (1998), 510.3, pp. 783 791 783 Mutual occlusion of P2X ATP receptors and nicotinic receptors on sympathetic
Chapter Nervous Systems
 The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
doi: /brain/awr345 Brain 2012: 135;
 doi:10.1093/brain/awr345 Brain 2012: 135; 359 375 359 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Reduced conduction failure of the main axon of polymodal nociceptive C-fibres contributes to painful diabetic neuropathy
doi:10.1093/brain/awr345 Brain 2012: 135; 359 375 359 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Reduced conduction failure of the main axon of polymodal nociceptive C-fibres contributes to painful diabetic neuropathy
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
The HCN channel, a novel target for the treatment of pain. Ernest A Jennings
 The HCN channel, a novel target for the treatment of pain. Ernest A Jennings Abstract: One of the key initiating factors in long-lasting pain is peripheral sensitization. Peripheral sensitization results
The HCN channel, a novel target for the treatment of pain. Ernest A Jennings Abstract: One of the key initiating factors in long-lasting pain is peripheral sensitization. Peripheral sensitization results
BLADDER AND CUTANEOUS SENSORY NEURONS OF THE RAT EXPRESS DIFFERENT FUNCTIONAL P2X RECEPTORS
 Neuroscience 120 (2003) 667 675 BLADDER AND CUTANEOUS SENSORY NEURONS OF THE RAT EXPRESS DIFFERENT FUNCTIONAL P2X RECEPTORS Y. ZHONG, a * 1 A. S. BANNING, a D. A. COCKAYNE, b A. P. D. W. FORD, b G. BURNSTOCK
Neuroscience 120 (2003) 667 675 BLADDER AND CUTANEOUS SENSORY NEURONS OF THE RAT EXPRESS DIFFERENT FUNCTIONAL P2X RECEPTORS Y. ZHONG, a * 1 A. S. BANNING, a D. A. COCKAYNE, b A. P. D. W. FORD, b G. BURNSTOCK
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers
 Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Comparative effects of heterologous TRPV1 and TRPM8 expression in rat hippocampal neurons
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 Comparative effects of heterologous TRPV1 and TRPM8 expression in rat hippocampal neurons Devon C. Crawford
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 Comparative effects of heterologous TRPV1 and TRPM8 expression in rat hippocampal neurons Devon C. Crawford
Neurokinin-1 Receptor Enhances TRPV1 Activity in Primary Sensory Neurons via PKC : A Novel Pathway for Heat Hyperalgesia
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 31, 2007 27(44):12067 12077 12067 Cellular/Molecular Neurokinin-1 Receptor Enhances TRPV1 Activity in Primary Sensory Neurons via PKC : A Novel Pathway for Heat Hyperalgesia
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 31, 2007 27(44):12067 12077 12067 Cellular/Molecular Neurokinin-1 Receptor Enhances TRPV1 Activity in Primary Sensory Neurons via PKC : A Novel Pathway for Heat Hyperalgesia
