Bradykinin potentiates 5-HT 3 receptor-mediated current in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons
|
|
|
- Wesley French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2005 Apr; 26 (4): Full-length article Bradykinin potentiates 5-HT 3 receptor-mediated current in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons Wang-ping HU 1,2, Xue-mei LI 2, Ji-liang WU 3, Min ZHENG 3, Zhi-wang LI 4 2 Department of Physiology, 3 Department of Pharmacology, Xianning College, Xianning , China; 4 Department of Neurobiology, Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan , China Key words bradykinin; 5-HT3 serotonin receptor; regulation; patch-clamp techniques; trigeminal ganglion 1 Correspondence to Prof Wang-ping HU. Phn huwangping@21cn.com Received Accepted doi: /j x Abstract Aim: To explore the modulatory effect of bradykinin (BK) on 5-HT 3 receptormediated current in trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons in rats. Methods: The wholecell patch-clamp technique was used to record 5-HT-activated currents (I 5-HT ) in neurons freshly dissociated from rat TG. Drugs were applied by rapid solution exchange. Results: The majority of the neurons examined responded to 5-HT applied externally with an inward current (76.3%, 74/97) that could be blocked by the 5-HT 3 receptor antagonist, ICS-205,930 ( mol/l). In 66 of the 74 cells sensitive to 5-HT (89.2%), pretreatment for 30 s with BK ( mol/l) could potentiate I 5-HT with the maximal modulatory effect occurring at 10-7 mol/l BK (71.6%±4.9%). BK shifted the 5-HT concentration-response curve upwards with an increase of 68.9%±7.2% in the maximal current response, but with no significant change in the EC 50 value (19.1±3.2 µmol/l vs 20.9±3.5 µmol/l; t-test, P>0.05; n=8). BK potentiated I 5-HT in a holding potential-independent manner and did not alter the reverse potential of I 5-HT. This BK-induced potentiation of I 5-HT was almost completely blocked by Hoe 140 ( mol/l), a selective B 2 BK receptor antagonist, and was removed after intracellular dialysis of GF X (2 µmol/l), a selective protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, with the re-patch clamp. Conclusion: Pre-application of BK exerts an enhancing effect on I 5-HT via a PKCdependent pathway in rat TG neurons, which may explain the peripheral mechanism of pain and hyperalgesia caused by, for example, tissue damage and inflammation. Introduction Serotonin (5-HT), a major component of the inflammatory chemical milieu, is released from platelets, mast cells, or basophils that infiltrate an area of tissue damage [1]. Once released, 5-HT is free to interact with a number of molecularly distinct receptor subtypes, including the 5-HT 3 receptor expressed in primary afferent nociceptors [2,3], and is capable of evoking pain and hyperalgesia [4]. To date, receptors for 5-HT can be classified into seven types and can be further distinguished into at least 13 subtypes. Unlike all other known 5-HT receptor subtypes, which are G-protein coupled, the 5-HT 3 receptor is a member of the excitatory ligand-gated ion channel (LGIC) superfamily [5,6]. Researchers believe that 5-HT 3 receptors located on sensory nerve terminals are mainly responsible for 5-HT-induced pain and hyperalgesia, although other subtypes of 5-HT receptors are also involved [4,7 10]. Recently we have demonstrated the potentiation of 5-HT 3 receptor function by substance P and α-methyl-5-ht, an agonist of 5-HT 2 receptor, through a protein kinase C (PKC)-dependentpathway in primary sensory neurons [11,12]. Bradykinin (BK) is an inflammatory mediator that plays a pivotal role in pain and hyperalgesia by exciting nociceptors and sensitizing them through activation of PKC [13]. BK responses are mediated by BK receptors. There are two main types of BK receptors, B 1 and B 2. B 2 BK receptors are constitutively and abundantly expressed in primary sensory neu CPS and SIMM
2 Hu WP et al rons [14]. The B 2 BK receptor has been implicated in BKinduced nociceptor activities and nociceptive behaviors [15 17], and animals deficient in B 2 BK receptors show hypoalgesia and reduced inflammatory responses [18,19]. The cdna of the B 2 BK receptor has already been cloned [20] and evidence for the contribution of the PKC pathway to the B 2 BK receptormediated algesic action ofbk has accumulated [17,21]. Thus, it is highly possible that 5-HT 3 receptor function is also enhanced by BK through a PKC-dependent pathway. The present study aimed to explore whether the modulation of BK in 5-HT 3 receptor-mediated current could occur in trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons. Materials and methods Isolation of TG neurons Spraque-Dawley rats, 2 3 weeks old, were anesthetized with ether and decapitated. The TG were removed and transferred immediately into Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium (DMEM, Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA) at ph 7.4. After removal of the surrounding connective tissues the TG were minced with fine spring scissors and the ganglion fragments were placed in a flask containing 5 ml DMEM in which trypsin (type II-S, Sigma) 0.5 g/l, collagenase (type I-A, Sigma) 1.0 g/l, and DNase (type IV, Sigma) 0.1 g/l had been dissolved, and incubated at 35 C in a shaking water bath for min. Soybean trypsin inhibitor (type II-S, Sigma) 1.25 g/l was added to stop trypsin digestion. Dissociated neurons were placed into a 35 mm Petri dish and kept for at least another 30 min before electrophysiological recording. The neurons selected for the patch-clamp experiment measured µm in diameter. Electrophysiological recordings Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were carried out at room temperature (22 24 ºC) using a whole-cell patch-clamp amplifier (CEZ-2400, Nihon Kohden, Tokyo, Japan). Pipettes were filled with internal solution containing (in mmol/l): KCl 140, CaCl 2 1, MgCl 2 2.5, HEPES 10, egtazic acid 11, and ATP 5; the ph was adjusted to 7.2 with KOH and the osmolarity was adjusted to 310 mosm/l with sucrose. Cells were bathed in an external solution containing (in mmol/l): NaCl 150, KCl 5, CaCl 2 2.5, MgCl 2 2, HEPES 10, and D-glucose 10; the osmolarity was adjusted to 340 mosm/l with sucrose and the ph was adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH. The resistance of the recording pipette was in the range of 2 5 MΩ. A small patch of membrane underneath the tip of the pipette was aspirated to form a gigaseal and then more negative pressure was applied to rupture it, thus establishing a whole-cell configuration. The adjustment of capacitance compensation and series resistance compensation was done before recording the membrane currents. The holding potential was set at -60 mv, unless otherwise indicated. Membrane currents were filtered at 10 khz (-3 db), and the data were stored and analyzed in a computer with data acquisition software and hardware systems (Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China) and recorded using a pen recorder (Nihon Kohden). Drug application Drugs used in the experiments included: serotonin hydrochloride (5-HT, Sigma), bradykinin (BK, Sigma), 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine maleate (Research Biochemicals Incorporated, Natick, MA, USA), ICS -205,930 (Research Biochemicals Incorporated), Hoe 140 (Sigma), and GF X (Research Biochemicals Incorporated). All drugs except GF X were dissolved in the external solution just prior to use and held in a linear array of fused silica tubes (od/id=500/200 µm) connected to a series of independent reservoirs. The distance from the tube mouth to the cell examined was approximately 100 µm. The application of each drug was driven by gravity and controlled by the corresponding valve, and rapid solution exchange could be achieved by shifting the tubes horizontally with a micromanipulator. Cells were constantly bathed in normal external solution flowing from one tube connected to a larger reservoir between drug applications. In a number of the experiments GF X needed to be applied intracellularly and was dissolved in the internal solution. Data analysis Data were statistically analyzed using Student s t-test or analysis of variance (ANOVA). Statistical analysis of the concentration-response data was carried out using the non-linear, curve-fitting program ALLFIT. Current values were expressed as mean±sem. Results Current mediated by the 5-HT 3 receptor in rat TG neurons In our experiments neurons freshly isolated from rat TG were round or elliptic in shape under light microscopy. The majority of the cells examined responded to 5-HT applied externally with a concentration ( mol/l)- dependent inward current (76.3%, 74/97). This 5-HT-activated current (I 5-HT, mol/l) could be mimicked by 2- methyl-5-ht ( mol/l), a specific 5-HT 3 receptor agonist, and could be blocked by ICS-205,930 ( mol/l), a selective antagonist of 5-HT 3 receptor, indicating that this current was mediated by the 5-HT 3 receptor (Figure 1A). When 5-HT was applied regularly for 3-s durations with 3-min intervals, the I 5-HT was repeated stably within at least 90 min, and the change in amplitude was within 8% (data not shown). Thus, we used this pattern of 5-HT applications in the following experiments. Potentiation of I 5-HT by pre-application of BK BK applied for 30 s prior to the application of 5-HT ( mol/l) 429
3 Hu WP et al Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ISSN Figure 1. Potentiation of I 5-HT by BK. (A) The current traces show that 5-HT ( mol/l) activated an inward current in TG neurons, which could be mimicked by the application of 2-methyl-5-HT ( mol/l), and blocked by ICS-205,930 ( mol/l) (n=7). All current traces were recorded from the same neuron. (B) BK potentiated I 5-HT in a concentration-dependent manner. The duration of BK preapplication lasted for 30 s. Each point represents the mean±sem of 7 9 neurons. The current traces in the inset show that BK ( mol/l) potentiated I 5-HT. (C) The enhancing effect of BK ( mol/l) on I 5-HT ( mol/l) increased with increments in BK preapplication duration from 0 to 120 s (n=6 9). potentiated I 5-HT reversibly in the majority of the neurons examined (66/74, 89.2%). In 18 of the 74 (24.3%) cells sensitive to 5-HT there was also a response to BK with a very small inward or outward current (<150 pa), which showed slow desensitization (data not shown). The BK potentiation of I 5-HT was observed irrespective of whether BK evoked an inward or outward current, or no response. The I 5-HT was potentiated by the pre-application of BK ( mol/l) in a concentration-dependent manner. Figure 1B shows that with an increase in BK concentration from to mol/l, the amplitude of I 5-HT ( mol/l) increased stepwise until it reached its maximum at a concentration of mol/l BK (71.6±4.9%). Thereafter this potentiating effect did not increase further, but rather decayed with further increases in BK concentration until 10-6 mol/l (Figure 1B). Effect of the duration of BK pre-application on I 5-HT To explore the relationship between the effect of BK on I 5-HT and the duration of the pre-application of BK, different BK preapplication durations ranging from 15 to 120 s were tested. Figure 1C illustrates that the amplitude of I 5-HT ( mol/l) increased with increasing BK ( mol/l) pre-application durations. With the duration of BK pre-application at 120 s, the amplitude of I 5-HT increased (1.97±0.13)-fold compared with that of the control. However, there was no enhancing effect observed when 5-HT and BK were co-applied for 3 s (n=7; data not shown). Effect of the B 2 BK receptor antagonist Hoe 140 on BK potentiation of I 5-HT To verify whether the BK potentiation of I 5-HT was mediated by the receptor for BK, we examined the effect of the pre-application of both BK and Hoe 140, a selective B 2 BK receptor antagonist, on I 5-HT. The pre-application of both BK and Hoe 140 abolished BK-induced potentiation of I 5-HT significantly (Figure 2A,B, paired t-test, P<0.01, n=7). Concentration-response relationship for 5-HT with and without BK pre-application Figure 3A demonstrates the concentration-response curves for 5-HT with or without the pre-application of BK ( mol/l). The threshold concentrations of 5-HT in the two concentration-response curves for 5-HT with or without BK pre-application were similar at approximately mol/l; and the EC 50 values were also very similar (19.1±3.2 µmol/l and 20.9±3.5 µmol/l; t-test; P>0.05; n=8); whereas the maximal response induced by 5-HT with BK pre-application increased by 68.9%±7.2% of that without BK pre-application. The present results reveal that the concentration-response curve for 5-HT pretreated with BK shifts upwards compared with the curve for 5-HT alone. Current-voltage (I-V) relationship for I 5-HT with or without BK pre-application I 5-HT ( mol/l) with or without the pre-application of BK ( mol/l) was recorded at different holding potentials. All current values from the same cell were normalized to the current response induced by 430
4 Hu WP et al Figure 2. Blockade of BK-induced potentiation of I 5-HT by the B 2 BK receptor antagonist Hoe 140. The current traces in (A) and the bar graph in (B) show that the potentiation of I 5-HT by BK pre-applied alone was abolished by the co-application of BK and Hoe 140, a selective B 2 BK receptor antagonist (paired t-test, c P<0.01 vs BK+5-HT). 5-HT alone at a holding potential of -60 mv when I-V curves were drawn (Figure 3B). The reverse potential values for the two curves were essentially the same at 0 mv. The amplitude of I 5-HT with BK pre-application was greater than that without BK pre-application at all holding potentials from -80 to +40 mv, and the BK-induced alteration of I 5-HT did not correlate with the change in holding potential (ANOVA; P>0.05, n=8), which suggests that the potentiation of I 5-HT by BK occurs in a voltage-independent manner and the reverse potential of I 5-HT is unchanged by BK. Intracellular signal transduction mechanism underlying BK potentiation of I 5-HT To explore whether this enhancing effect is mediated through BK-receptor-induced intracellular signal transduction, for example, activating PKC, GF X, a selective PKC inhibitor [22], was included in the recording pipette for intracellular dialysis using the re-patch technique. In the control experiment with the pipette filled with normal internal solution, the BK-induced potentiation of I 5-HT was 72.2%±5.2%. In contrast, when using a pipette filled with GF X (2 µmol/l) containing internal solution the BK-induced potentiation of I 5-HT was 13.5%±4.3%. It is evident that GF X applied intracellularly removes the enhancing effect of BK on I 5-HT (Figure 4). Discussion The 5-HT-activated current we recorded from TG neu- Figure 3. Concentration-response and current-voltage relationships for 5-HT with or without the pre-application of BK. (A) The concentration-response curves for 5-HT with or without BK ( mol/l) pre-application, each point represents the mean±sem of 7 11 neurons. All 5-HT-induced currents were normalized to the response induced by 10-4 mol/l 5-HT applied alone (marked with asterisk). The holding potential was set at -60 mv. The data for 5-HT alone is a good fit to the logistic equation I=I max /[1+(EC 50 /C) n ], where C is the concentration of 5-HT, I is the normalized I 5-HT value, and EC 50 is the concentration of 5-HT for half maximal current response. The Hill coefficients (n) for the cases with and without BK pre-application were 0.98 and 0.96, respectively. It is evident that the curve for 5-HT with BK pre-application shifts upwards compared with the curve for 5-HT applied alone. (B) The I-V curves for 5-HT ( mol/l)-activated current with or without BK ( mol/l) pre-application. BK did not alter the reverse potential of I 5-HT (0 mv in both cases). All current values from the same cell were normalized to the current response induced by 5-HT ( mol/l) alone at the holding potential of -60 mv (marked with asterisk). BK pre-application potentiated I 5-HT at all holding potentials from -80 to +40 mv. Each point represents the mean±sem of 7 9 neurons. This experiment was carried out using recording pipettes filled with CsCl containing internal solution. 431
5 Hu WP et al Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ISSN Figure 4. Reversal of the BK potentiation of I 5-HT by intracellular dialysis of GF X. The diagram in the upper row in (A) schematically shows the experiment of intracellular dialysis of GF X, a selective PKC inhibitor, on an individual cell. The current traces in the lower row in (A) demonstrate that intracellular dialysis of GF X (2 µmol/l) markedly reversed the potentiating effect of BK on I 5-HT. The bar graph in (B) shows the percentage increases in the I 5-HT induced by BK pre-application with recording pipettes filled with the normal internal solution or with GF X containing internal solution. n=7. Mean±SEM. (paired t-test, c P<0.01 vs normal). rons was mediated by the 5-HT 3 receptor, the sole ligandgated ion channel (LGIC) in the family of 5-HT receptors, because it was blocked by ICS-205,930, a selective antagonist of the 5-HT 3 receptor (Figure 1A). There was evidence to indicate that 5-HT 3 receptors were present in rat TG neurons [23]. Similarly, B 2 BK receptors were also expressed in TG neurons [14]. In the present study we recorded both B 2 BK receptors and 5-HT 3 receptors in TG neurons, and in the majority of these neurons (89.2%, 66/74) the pre-application of BK ( mol/l) potentiated I 5-HT ( mol/l). This potentiation was mediated by B 2 BK receptors because the selective B 2 BK receptor antagonist Hoe 140 blocked this potentiating effect, obviously and reversibly (Figure 2). However, a previous study has reported that the inflammatory mediators BK, 5-HT, and prostaglandin E 2 do not cooperate to elevate intracellular calcium concentration when applied simultaneously for 10 s in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons [24]. The distinction possibly results from different observation indices and specimens, or may be caused by the different treatment of BK. In the present experiment, there was also no enhancing effect observed when 5-HT and BK were co-applied for 3 s, whereas I 5-HT was potentiated by the pre-application of BK for more than 15 s (Figure 1C). It is evident from Figure 1B that the enhancement of amplitude of I 5-HT increased gradually with incremental increases in the concentration of BK from to 10-7 mol/l. However, when the concentration of BK increased to 10-6 mol/l the modulatory effect of BK on I 5-HT did not increase further. The decrease in potentiation of I 5-HT by BK (10-6 mol/l) might be a non-specific action of the agonist that emerges at high concentrations because very high concentrations of drug or ligand may block the channel and/or shelter the binding site of the receptor [25]. From the comparison between the concentration-response curves for 5-HT with and without the pre-application of BK (Figure 3A) it is clear that: (i) pre-application of BK shifted the curve upwards; (ii) the maximal response induced by 5-HT with BK pre-application increased by 68.9%, whereas the threshold concentrations of 5-HT in both cases were similar; and (iii) the EC 50 values of the two curves were very close (19.1±3.2 µmol/l vs 20.9±3.5 µmol/l). This implies that the intrinsic efficacy of the 5-HT 3 receptor increases after pretreatment with BK; however, its affinity does not change. From the I-V curves for I 5-HT with and without BK pretreatment, it can be seen that the reverse potentials were the same (0 mv), indicating that there was no change in the ionic components mediating this current. This enhancement was not caused by the release of the channel blocker, as is the case in the voltage-dependent Mg 2+ block of NMDA-gated ion channel, because the BK-induced alteration of I 5-HT was not correlated with the change in holding potential (Figure 3B). This implies that the potentiation of I 5-HT by BK occurs in a voltage-independent manner. The potentiation of I 5-HT by BK may involve intracellular signal transduction because there was no enhancing effect observed when 5-HT and BK were co-applied; nevertheless, BK applied prior to 5-HT application induced the enhancement of I 5-HT and this effect was positively related to the duration of BK pretreatment, implying that this enhancement is a time-consuming process. Furthermore, this potentiation was blocked by Hoe 140, a selective B 2 BK receptor antagonist. B 2 BK receptors belong to the superfamily of G- protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) [20]. When activated by BK, the B 2 BK receptor is coupled to PLC β1 via G q/11 protein; which in turn catalyzes PIP 2 into secondary messengers, IP 3 and DAG. The latter activates PKC. Reports have shown 432
6 Hu WP et al that 5-HT 3 receptor function is enhanced by the activation of PKC [26,27]. In the present experiment, the enhancing effect of BK on I 5-HT was evidently blocked by intracellular dialysis of GF X, a selective PKC inhibitor [22], indicating that potentiation occurs via a PKC-dependent pathway. How does PKC affect the function of 5-HT 3 receptors? Recently, a novel mechanism for 5-HT 3 receptor modulation by the activation of PKC was demonstrated [28] ; that is, the PKCinduced potentiation of 5-HT 3 receptor mediated current in Xenopus oocytes and mouse NIE-115 neuroblastoma cells resulted from the enhancement of F-actin-dependent trafficking of 5-HT 3 receptors instead of direct phosphorylation of the 5-HT 3A receptor protein. What is the physiological significance of this BK modulation on I 5-HT or 5-HT 3 receptor function? In this work we used the cell body of TG neurons as a simple and accessible model to examine the characteristics of the membrane of peripheral terminals. The nerve endings of the peripheral axon of primary sensory neurons, including TG neurons, are sensitive to many inflammatory chemical mediators, of which BK and 5-HT are two potent stimulating mediators. In the case of inflammation and/or tissue damage these two substances are released. On the one hand, they exert a stimulating effect on the nerve endings and initiate nociceptive information through their corresponding receptors located on the membranes of separate nerve endings. On the other hand, in the present study we found that in the case of coexistence of B 2 BK receptors and 5-HT 3 receptors in TG neurons the inward current mediated by the 5-HT 3 receptor could be strengthened by pretreatment with BK, indicating that B 2 BK receptors and 5-HT 3 receptors may cross-talk in producing algesic information at nociceptors. Behavioral experiments have also demonstrated that 5-HT causes marked potentiation of BK-induced pain responses through 5-HT 3 receptors [29]. The present study may provide a hint for explaining the peripheral mechanism of pain and hyperalgesia caused by, for example, tissue damage and inflammation. References 1 Dray A. Inflammatory mediators of pain. Br J Anaesth 1995; 75: Martin GR, Eglen RM, Hamblin MW, Hoyer D, Yocca F. The structure and signaling properties of 5-HT receptors: an endless diversity? Trends Pharmacol Sci 1998; 19: Hamon M, Bourgoin S. Serotonin and its receptors in pain control. In: Sawynok J, Cowan A, editors. Novel aspects of pain management: opioids and beyond. New York: Wiley; p Dock GJ, Sawynok J. Formalin-induced nociceptive behavior and edema: involvement of multiple peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes. Neuroscience 1997; 80: Maricq AV, Peterson AS, Brake AJ, Myers RM, Julius D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5-HT 3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science 1991; 254: Davies PA, Pistis M, Harma MC, Peters JA, Lambert JJ, Hales TG, et al. The 5-HT 3 B subunit is a major determinant of serotonin receptor function. Nature 1999; 397: Orwin JM, Fozard JR. Blockade of the flare response to intradermal 5-hydroxytryptamine in man by MDL72222, a selective antagonist at neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1986; 30: Eschalier A, Kayser V, Guilbaud G. Influence of a specific 5-HT 3 antagonist on carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia in rats. Pain 1989; 36: Giordano J, Rogers LV. Perpherally administered serotonin 5- HT 3 receptor antagonists reduce inflammatory pain in the rats. Eur J Pharmacol 1989; 170: Zeitz KP, Guy N, Malmberg AB, Dirajlal S, Martin WJ, Sun L, et al. The 5-HT 3 subtype of serotonin receptor contributes to nociceptive processing via a novel subset of myelinated and unmyelinated nociceptors. J Neurosci 2002; 22: Hu WP, You XH, Guan BC, Ru LQ, Chen JG, Li ZW. Substance P potentiates 5-HT 3 receptor mediated current in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. Neurosci Lett 2004; 365: Hu WP, Guan BC, Ru LQ, Chen JG, Li ZW. Potentiation of 5- HT 3 receptor function by the activation of coexistent 5-HT 2 receptor in trigeminal ganglion neurons of rats. Neuropharmacology 2004; 47: Sugiura T, Tominaga M, Katsuya H, Mizumura K. Bradykinin lowers the threshold temperature for heat activation of vanilloid receptor 1. J Neurophysiol 2002; 88: Steranka LR, Manning DC, DeHaas CJ, Ferkany JW, Borosky SA, Connor JR, et al. Bradykinin as a pain mediator: receptors are localized to sensory neurons, and antagonists have analgesic actions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988; 85: Ferreira J, da Silva GL, Calixto JB. Contribution of vanilloid receptor to the overt nociception induced by B 2 kinin receptor activation in mice. Br J Pharmacol 2004; 141: Dray A, Perkins M. Bradykinin and inflammatory pain. Trends Neurosci 1993; 16: Mizumura K. Natural history of nociceptor sensitization: the search for a peripheral mechanism of hyperalgesia. Pain Rev 1998; 5: Boyce S, Rupniak NM, Carlson EJ, Webb J, Borkowski JA, Hess JF, et al. Nociception and inflammatory hyperalgesia in B 2 bradykinin receptor knockout mice. Immunopharmacology 1996; 33: Seabrook GR, Bowery BJ, Heavens R, Brown N, Ford H, Sirinathsinghi DJ, et al. Expression of B 1 and B 2 bradykinin receptor mrna and their functional roles in sympathetic ganglia and sensory dorsal root ganglia neurons from wild-type and B 2 receptor knockout mice. Neuropharmacology 1997; 36: Ma JX, Wang DZ, Chao L, Chao J. Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of the gene encoding the mouse bradykinin B 2 receptor. Gene 1994; 149: Cesare P, Dekker LV, Sardini A, Parker PJ, McNaughton PA. Specific involvement of PKC-epsilon in sensitization of the neuronal response to painful heat. Neuron 1999; 23:
7 Hu WP et al Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ISSN Toullec D, Pianetti P, Coste H, Bellevergue P, Grand-Perret T, Ajakane M, et al. The bisindolylmaleimide GF X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: Zhu M, Wu SX, Wang W, Li YQ. Expression of 5-HT receptor subtype mrnas in the rat trigeminal and spinal dorsal root ganglia: a polymerase chain reaction study. Chin J Neuroanat 2000; 16: Linhart O, Obreja O, Kress M. The inflammatory mediators serotonin, prostaglandin E2 and bradykinin evoke calcium influx in rat sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2003; 118: Arias HR. Binding sites for exogenous and endogenous noncompetitive inhibitors of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998; 1376: Coultrap SJ, Machu TK. Enhancement of 5-hydroxytryptamine 3A receptor function by phorbol 12-myristate, 13-acetate is mediated by protein kinase C and tyrosine kinase activity. Receptor Channels 2002; 8: Zhang L, Oz M, Weight FF. Potentiation of 5-HT 3 receptormediated responses by protein kinase C activation. Neuroreport 1995; 6: Sun H, Hu XQ, Moradel EM, Weight FF, Zhang L. Modulation of 5-HT 3 receptor-mediated response and trafficking by activation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: Richardson BP, Engel G, Donatsch P, Stadler PA. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature 1985; 316:
nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
D. Nishizawa 1, N. Gajya 2 and K. Ikeda 1, * Global Research & Development, Nagoya Laboratories, Pfizer Japan Inc, Nagoya, Japan
 Current Neuropharmacology, 2011, 9, 113-117 113 Identification of Selective Agonists and Antagonists to G Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Candidate Medicines for Drug Dependence
Current Neuropharmacology, 2011, 9, 113-117 113 Identification of Selective Agonists and Antagonists to G Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Candidate Medicines for Drug Dependence
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
Effects of different dust particles on calcium current in the neurons of dorsal root ganglia of rats
 Effects of different dust particles on calcium current in the neurons of dorsal root ganglia of rats Yong Mei, Haibing Yang, Jingzhi Sun, Xiao Yin, Xiang Guo, Zhenglun Wang, Lei Yang * Department of Occupational
Effects of different dust particles on calcium current in the neurons of dorsal root ganglia of rats Yong Mei, Haibing Yang, Jingzhi Sun, Xiao Yin, Xiang Guo, Zhenglun Wang, Lei Yang * Department of Occupational
CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 THE PHARMACOLOGICAL DISTINCTION OF GABA A RECEPTOR
B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 THE PHARMACOLOGICAL DISTINCTION OF GABA A RECEPTOR
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics
 Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Acta Physiologica Sinica
 , 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
, 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
The Pain Pathway. dorsal root ganglion. primary afferent nociceptor. TRP: Transient Receptor Potential
 Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
Presented by Issel Anne L. Lim 1 st Year PhD Candidate Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 580.427/580.633 Ca Signals in Biological Systems Outline The Pain Pathway TRP: Transient Receptor
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Gerasimenko et al..73/pnas.39 SI Materials and Methods Reagents used in this study include Fluo-4/Fura- (Invitrogen), thapsigargin (albiochem), collagenase (Worthington), palmitoleic
Supporting Information Gerasimenko et al..73/pnas.39 SI Materials and Methods Reagents used in this study include Fluo-4/Fura- (Invitrogen), thapsigargin (albiochem), collagenase (Worthington), palmitoleic
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Receptors Families. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Quantal Analysis Problems
 Quantal Analysis Problems 1. Imagine you had performed an experiment on a muscle preparation from a Drosophila larva. In this experiment, intracellular recordings were made from an identified muscle fibre,
Quantal Analysis Problems 1. Imagine you had performed an experiment on a muscle preparation from a Drosophila larva. In this experiment, intracellular recordings were made from an identified muscle fibre,
7.06 Spring of PROBLEM SET #6
 7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
MCB MIDTERM EXAM #1 MONDAY MARCH 3, 2008 ANSWER KEY
 MCB 160 - MIDTERM EXAM #1 MONDAY MARCH 3, 2008 ANSWER KEY Name ID# Instructions: -Only tests written in pen will be regarded -Please submit a written request indicating where and why you deserve more points
MCB 160 - MIDTERM EXAM #1 MONDAY MARCH 3, 2008 ANSWER KEY Name ID# Instructions: -Only tests written in pen will be regarded -Please submit a written request indicating where and why you deserve more points
(Supplementary information) TRPV1 EXHIBITS DYNAMIC IONIC SELECTIVITY DURING AGONIST STIMULATION. Man-Kyo Chung, Ali D. Güler, and #Michael J.
 (Supplementary information) TRPV1 EXHIBITS DYNAMIC IONIC SELECTIVITY DURING AGONIST STIMULATION Man-Kyo Chung, Ali D. Güler, and #Michael J. Caterina Title Supplementary Figure 1. Capsaicin evokes changes
(Supplementary information) TRPV1 EXHIBITS DYNAMIC IONIC SELECTIVITY DURING AGONIST STIMULATION Man-Kyo Chung, Ali D. Güler, and #Michael J. Caterina Title Supplementary Figure 1. Capsaicin evokes changes
Supplementary Figure 1 NMR spectra of hydroxy α and β-sanshool isomers. (Top) Hydroxy-α-sanshool (2E,6Z,8E,10E)-2'-
 Supplementary Figure 1 NMR spectra of hydroxy α and β-sanshool isomers. (Top) Hydroxy-α-sanshool (2E,6Z,8E,10E)-2'- hydroxyl-n-isobutyl-2,6,8,10-dodeca-tetraenamide) and (bottom) hydroxy-β-sanshool (2E,6E,8E,10E)-2'-hydroxyl-N-isobutyl-
Supplementary Figure 1 NMR spectra of hydroxy α and β-sanshool isomers. (Top) Hydroxy-α-sanshool (2E,6Z,8E,10E)-2'- hydroxyl-n-isobutyl-2,6,8,10-dodeca-tetraenamide) and (bottom) hydroxy-β-sanshool (2E,6E,8E,10E)-2'-hydroxyl-N-isobutyl-
Effect of hydrogen peroxide on persistent sodium current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes 1
 Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2005 Jul; 26 (7): 828 834 Full-length article Effect of hydrogen peroxide on persistent sodium current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes 1 Ji-hua MA 2, An-tao LUO, Pei-hua ZHANG
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2005 Jul; 26 (7): 828 834 Full-length article Effect of hydrogen peroxide on persistent sodium current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes 1 Ji-hua MA 2, An-tao LUO, Pei-hua ZHANG
HEK293-GRIK2. Glutamate receptor GluR6. Application Report:
 Application Report: HEK293-GRIK2 Glutamate receptor GluR6 This report presents QPatch studies based on whole-cell current recordings from the ligand-gated ion channel GRIK2 receptors (Glu6R), expressed
Application Report: HEK293-GRIK2 Glutamate receptor GluR6 This report presents QPatch studies based on whole-cell current recordings from the ligand-gated ion channel GRIK2 receptors (Glu6R), expressed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
John C. Lopshire 1 and Grant D. Nicol 2
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 1998, 18(16):6081 6092 The camp Transduction Cascade Mediates the Prostaglandin E 2 Enhancement of the Capsaicin-Elicited Current in Rat Sensory Neurons: Whole-Cell
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 1998, 18(16):6081 6092 The camp Transduction Cascade Mediates the Prostaglandin E 2 Enhancement of the Capsaicin-Elicited Current in Rat Sensory Neurons: Whole-Cell
Pharmacodynamics. OUTLINE Definition. Mechanisms of drug action. Receptors. Agonists. Types. Types Locations Effects. Definition
 Pharmacodynamics OUTLINE Definition. Mechanisms of drug action. Receptors Types Locations Effects Agonists Definition Types Outlines of Pharmacodynamics Antagonists Definition Types Therapeutic Index Definition
Pharmacodynamics OUTLINE Definition. Mechanisms of drug action. Receptors Types Locations Effects Agonists Definition Types Outlines of Pharmacodynamics Antagonists Definition Types Therapeutic Index Definition
Inflammation-Induced Airway Hypersensitivity: From Ion Channels to Patients
 Inflammation-Induced Airway Hypersensitivity: From Ion Channels to Patients Lu-Yuan Lee, Ph.D. Airway Sensory Neurobiology Laboratory Department of Physiology University of Kentucky Medical Center BACKGROUND
Inflammation-Induced Airway Hypersensitivity: From Ion Channels to Patients Lu-Yuan Lee, Ph.D. Airway Sensory Neurobiology Laboratory Department of Physiology University of Kentucky Medical Center BACKGROUND
Agmatine blocked voltage-gated calcium channel in cultured rat hippocampal neurons
 746 2002, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ISSN 1671-4083 Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Agmatine blocked voltage-gated calcium channel in cultured
746 2002, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ISSN 1671-4083 Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Agmatine blocked voltage-gated calcium channel in cultured
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD
 Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Suramin Affects Capsaicin Responses and Capsaicin-Noxious Heat Interactions in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurones
 Physiol. Res. 51: 193-198, 2002 Suramin Affects Capsaicin Responses and Capsaicin-Noxious Heat Interactions in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurones V. VLACHOVÁ, A. LYFENKO, L. VYKLICKÝ, R.K. ORKAND 1 Institute
Physiol. Res. 51: 193-198, 2002 Suramin Affects Capsaicin Responses and Capsaicin-Noxious Heat Interactions in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurones V. VLACHOVÁ, A. LYFENKO, L. VYKLICKÝ, R.K. ORKAND 1 Institute
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Functional Compartmentalization of Opioid Desensitization in Primary Sensory Neurons 1
 0022-3565/00/2942-0500$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/00/2942-0500$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
photometry on the extruded cytoplasm.
 Answers To Midterm 2011 Question 1. a) Isoproterenol. Used to dissect presynaptic and postsynaptic components of sympathetic modulation of neuromuscular junction (Orbelli effect). Specifically activates
Answers To Midterm 2011 Question 1. a) Isoproterenol. Used to dissect presynaptic and postsynaptic components of sympathetic modulation of neuromuscular junction (Orbelli effect). Specifically activates
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013
 NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Phys 173 / BGGN 266. LPA Induced Cl - Oscillations in Xenopus Oocytes. Nini Huynh David Marciano Chisa Suzuki
 Phys 173 / BGGN 266 LPA Induced Cl - Oscillations in Xenopus Oocytes Nini Huynh David Marciano Chisa Suzuki If only we hadn t poked these oocytes, how cute would it be! INTRODUCTION Electrophysiology in
Phys 173 / BGGN 266 LPA Induced Cl - Oscillations in Xenopus Oocytes Nini Huynh David Marciano Chisa Suzuki If only we hadn t poked these oocytes, how cute would it be! INTRODUCTION Electrophysiology in
Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris
 ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 16, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 18, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 18, 2016 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
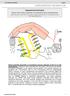
Pain Mechanisms. Prof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong. The Somatosensory System
 ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 15, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 15, 2018 -- PAGE 1 of 8 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
EDUCATION M.D., Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 1999 B.S., Beijing University, College of Life Science, Beijing, China, 1994
 CHAO MA, M.D. Yale University School of Medicine, Department of Anesthesiology, 333 Cedar Street, TMP3, New Haven, CT 06510, USA. Phone: 203-785-3522 (O), 203-606-7959 (C), Fax: 203-737-1528, Email: chao.ma@yale.edu
CHAO MA, M.D. Yale University School of Medicine, Department of Anesthesiology, 333 Cedar Street, TMP3, New Haven, CT 06510, USA. Phone: 203-785-3522 (O), 203-606-7959 (C), Fax: 203-737-1528, Email: chao.ma@yale.edu
Receptors and Drug Action. Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil
 Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 12 Signal Transduction
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
INTRODUCTION. The 5-HT 2C receptor is a seven transmembrane spanning protein coupled to G proteins.
 Multifactorial Analysis of the Dose Dependency of Desensitization of the 5-HT 2C Receptor in Oocytes of the African clawed frog, Xenopus laevis Andonian, A., Gee, M. & Regan, E. Department of Neurobiology,
Multifactorial Analysis of the Dose Dependency of Desensitization of the 5-HT 2C Receptor in Oocytes of the African clawed frog, Xenopus laevis Andonian, A., Gee, M. & Regan, E. Department of Neurobiology,
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
CYCLIC AMP-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE-INDEPENDENT ANGIOTENSIN II-INDUCED INHIBITION OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN HAMSTER SUBMANDIBULAR GANGLION NEURONS
 Bull. Tokyo dent. Coll., Vol. 43, No. 2, pp.95 99, May, 2002 95 Short Communication CYCLIC AMP-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE-INDEPENDENT ANGIOTENSIN II-INDUCED INHIBITION OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN HAMSTER SUBMANDIBULAR
Bull. Tokyo dent. Coll., Vol. 43, No. 2, pp.95 99, May, 2002 95 Short Communication CYCLIC AMP-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE-INDEPENDENT ANGIOTENSIN II-INDUCED INHIBITION OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN HAMSTER SUBMANDIBULAR
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Extracellular Proton-Modulated Pore-Blocking Effect of the Anticonvulsant Felbamate on NMDA Channels
 Biophysical Journal Volume 93 September 2007 1981 1992 1981 Extracellular Proton-Modulated Pore-Blocking Effect of the Anticonvulsant Felbamate on NMDA Channels Huai-Ren Chang* and Chung-Chin Kuo* y *Department
Biophysical Journal Volume 93 September 2007 1981 1992 1981 Extracellular Proton-Modulated Pore-Blocking Effect of the Anticonvulsant Felbamate on NMDA Channels Huai-Ren Chang* and Chung-Chin Kuo* y *Department
Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 651-656 65! Short communication Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis M. HENČĽK, D. ZACHAROVÁ and J. ZACHAR
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 651-656 65! Short communication Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis M. HENČĽK, D. ZACHAROVÁ and J. ZACHAR
EXAM II Animal Physiology ZOO 428 Fall 2006
 V Eq EXAM II Animal Physiology ZOO 428 Fall 2006 = RT X o. ln( [ zf [ X ) RT p K[K o pna[na o pcl[cl i V = m ln i F pk[k i pna[na i pcl[cl o I = g(v m V eq. ) Q = C m V m Q Driving Force = V m V eq. 10
V Eq EXAM II Animal Physiology ZOO 428 Fall 2006 = RT X o. ln( [ zf [ X ) RT p K[K o pna[na o pcl[cl i V = m ln i F pk[k i pna[na i pcl[cl o I = g(v m V eq. ) Q = C m V m Q Driving Force = V m V eq. 10
VaTx1 VaTx2 VaTx3. VaTx min Retention Time (min) Retention Time (min)
 a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel
 TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel Mechanical forces play numerous roles in physiology. When an object contacts our skin, it exerts a force that is encoded as touch or pain depending on its intensity.
TMC9 as a novel mechanosensitive ion channel Mechanical forces play numerous roles in physiology. When an object contacts our skin, it exerts a force that is encoded as touch or pain depending on its intensity.
Potentiation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission by protein kinase C-mediated sensitization of TRPV1 at the first sensory synapse
 J Physiol 581.2 (2007) pp 631 647 631 Potentiation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission by protein kinase C-mediated sensitization of TRPV1 at the first sensory synapse Parul Sikand and Louis S. Premkumar
J Physiol 581.2 (2007) pp 631 647 631 Potentiation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission by protein kinase C-mediated sensitization of TRPV1 at the first sensory synapse Parul Sikand and Louis S. Premkumar
THREE TYPES OF VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT CALCIUM CURRENTS DEVELOPING IN CULTURED HUMAN NEUROBLASTOMA CELLS
 ORIGINAL PAPER Nagoya 1. Med. Sci. 62. 39-45, 1999 THREE TYPES OF VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT CALCIUM CURRENTS DEVELOPING IN CULTURED HUMAN NEUROBLASTOMA CELLS MASAO KITO [, MITSUO MAEHARA 2 and KAZUYOSHI WATANABE
ORIGINAL PAPER Nagoya 1. Med. Sci. 62. 39-45, 1999 THREE TYPES OF VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT CALCIUM CURRENTS DEVELOPING IN CULTURED HUMAN NEUROBLASTOMA CELLS MASAO KITO [, MITSUO MAEHARA 2 and KAZUYOSHI WATANABE
Fundamentals of Pharmacology
 Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
Fundamentals of Pharmacology Topic Page Receptors 2 Ion channels / GABA 4 GPCR s 6 TK receptors 8 Basics of PK 11 ADR s / Clinical study design 13 Introduction to the ANS 16 Cholinergic Pharmacology 20
Isoprenaline and aminophylline relax bronchial smooth muscle by camp-induced stimulation of large-conductance Ca 2+ -activated K + channels 1
 408 2003, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Isoprenaline and aminophylline relax bronchial
408 2003, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica Chinese Pharmacological Society Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com Isoprenaline and aminophylline relax bronchial
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Receptors. Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel
 Receptors Types and Theories Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel Some terms in receptor-drug interactions Agonists: drugs that mimic the natural messengers and activate receptors. Antagonist: drugs that block receptors.
Receptors Types and Theories Dr. Sanaa Bardaweel Some terms in receptor-drug interactions Agonists: drugs that mimic the natural messengers and activate receptors. Antagonist: drugs that block receptors.
Lidocaine alters the input resistance and evokes neural activity in crayfish sensory neurons
 20 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (2007), 26, 20 26 Lidocaine alters the input resistance and evokes neural activity in crayfish sensory neurons M. B. Keceli and N. Purali Hacettepe University, Medical Faculty,
20 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (2007), 26, 20 26 Lidocaine alters the input resistance and evokes neural activity in crayfish sensory neurons M. B. Keceli and N. Purali Hacettepe University, Medical Faculty,
Heat transduction in rat sensory neurons by calcium-dependent activation of a cation channel
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 7006 7011, June 1997 Neurobiology Heat transduction in rat sensory neurons by calcium-dependent activation of a cation channel (somatosensory transduction primary
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 7006 7011, June 1997 Neurobiology Heat transduction in rat sensory neurons by calcium-dependent activation of a cation channel (somatosensory transduction primary
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2 Spring, 2006 Name
 Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2 Spring, 2006 Name Multiple Choice: 1. are responsible for phosphorylation of receptor proteins, whereas are responsible for dephosphorylation of receptor proteins. a) Kinases; phosphatases*
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2 Spring, 2006 Name Multiple Choice: 1. are responsible for phosphorylation of receptor proteins, whereas are responsible for dephosphorylation of receptor proteins. a) Kinases; phosphatases*
Name Biology 125 Midterm #2 ( ) Total Pages: 9
 Name - 1 - Biology 125 Midterm #2 (11-15-07) Part 1: (30 pts) Part 2: (40 pts) Part 3: (6 pts) Part 4: (12 pts) Part 5: (12 pts) Total Pages: 9 Total Score: (100 pts) 1 Name - 2 - Part 1: True or False.
Name - 1 - Biology 125 Midterm #2 (11-15-07) Part 1: (30 pts) Part 2: (40 pts) Part 3: (6 pts) Part 4: (12 pts) Part 5: (12 pts) Total Pages: 9 Total Score: (100 pts) 1 Name - 2 - Part 1: True or False.
Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human
 July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
PHRM20001 NOTES PART 1 Lecture 1 History of Pharmacology- Key Principles
 PHRM20001 NOTES PART 1 Lecture 1 History of Pharmacology- Key Principles Hippocrates (5 th century BCE):... benefit my patients according to my greatest ability and judgment, and I will do no harm or injustice
PHRM20001 NOTES PART 1 Lecture 1 History of Pharmacology- Key Principles Hippocrates (5 th century BCE):... benefit my patients according to my greatest ability and judgment, and I will do no harm or injustice
Physiology Unit 1 CELL SIGNALING: CHEMICAL MESSENGERS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS
 Physiology Unit 1 CELL SIGNALING: CHEMICAL MESSENGERS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS In Physiology Today Cell Communication Homeostatic mechanisms maintain a normal balance of the body s internal environment
Physiology Unit 1 CELL SIGNALING: CHEMICAL MESSENGERS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS In Physiology Today Cell Communication Homeostatic mechanisms maintain a normal balance of the body s internal environment
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches
 Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
11/8/16. Cell Signaling Mechanisms. Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016. Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer
 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat. Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
Mechanism of Pain Production
 Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
FIG. 1. Phase-contrast photomicrograph of a typical acutely. dissociated striatal neuron. (Bar = 10 Itm.)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 85, pp. 3618-3622, May 1988 Neurobiology Single K+ channels activated by D2 dopamine receptors in acutely dissociated neurons from rat corpus striatum (patch-clamp/caudate/putamen/quinpirole/antipsychotic)
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 85, pp. 3618-3622, May 1988 Neurobiology Single K+ channels activated by D2 dopamine receptors in acutely dissociated neurons from rat corpus striatum (patch-clamp/caudate/putamen/quinpirole/antipsychotic)
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
Synaptic Integration
 Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Drugs, Drug Targets and You: Patch Clamping
 Drugs, Drug Targets and You: Patch Clamping Introduction To elucidate how an ion channel operates, one needs to examine the factors that influence its opening and closing as well as measure the resulting
Drugs, Drug Targets and You: Patch Clamping Introduction To elucidate how an ion channel operates, one needs to examine the factors that influence its opening and closing as well as measure the resulting
BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11
 BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11 External signal is received and converted to another form to elicit a response 1 Lecture Outline 1. Types of intercellular
BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11 External signal is received and converted to another form to elicit a response 1 Lecture Outline 1. Types of intercellular
Objectives. Functions of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle. Smooth Muscle Contraction: Mechanism. Latch state. Smooth muscle contraction
 Objectives Functions of smooth muscle Sompol Tapechum,, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj hospital อธ บายล กษณะการหดต วของกล ามเน อเร ยบได อธ บายกลไกและป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการหดต
Objectives Functions of smooth muscle Sompol Tapechum,, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj hospital อธ บายล กษณะการหดต วของกล ามเน อเร ยบได อธ บายกลไกและป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการหดต
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic
 Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras
 Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Questions. Question 1!
 Questions Question 1 In a laboratory, scientists often study neurons in isolation, outside of a living creature, in a dish. In this setting, one can have a good deal of control over the local ionic environment
Questions Question 1 In a laboratory, scientists often study neurons in isolation, outside of a living creature, in a dish. In this setting, one can have a good deal of control over the local ionic environment
Development of Screening Tools to Identify Nicotinic Subtype-Selective Compounds
 Development of Screening Tools to Identify Nicotinic Subtype-Selective Compounds Glenn Kirsch, PhD Discovery Services Charles River Cleveland, Ohio USA Aurora Ion Channel Retreat July 7-9, 2015 Tobacco
Development of Screening Tools to Identify Nicotinic Subtype-Selective Compounds Glenn Kirsch, PhD Discovery Services Charles River Cleveland, Ohio USA Aurora Ion Channel Retreat July 7-9, 2015 Tobacco
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
abolished, the transient outward chloride current normally activated by membrane
 J. Physiol. (1984), 357, pp. 173-183 173 With 7 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain CHLORIDE CURRENT INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CLCIUM INTO XENOPUS OOCYTES BY R. MILEDI ND I. PRKER From the Department of
J. Physiol. (1984), 357, pp. 173-183 173 With 7 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain CHLORIDE CURRENT INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CLCIUM INTO XENOPUS OOCYTES BY R. MILEDI ND I. PRKER From the Department of
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
 Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus. Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity. Outline. Synaptic plasticity hypothesis
 Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016
 Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016 1. The figure above was obtained from a paper on calcium channels expressed by dentate granule cells. The whole-cell Ca 2+ currents in (A) were measured
Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016 1. The figure above was obtained from a paper on calcium channels expressed by dentate granule cells. The whole-cell Ca 2+ currents in (A) were measured
