PROPOSED CURRICULUM FOR THE DEPARTMENT OF DERMATOLOGY, VENEREOLOGY AND LEPROSY FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, UNIVERSITY OF DELHI,
|
|
|
- Owen Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROPOSED CURRICULUM FOR THE DEPARTMENT OF DERMATOLOGY, VENEREOLOGY AND LEPROSY FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, UNIVERSITY OF DELHI, YEAR 2008
2 CONTENTS TOPIC PAGE NO. Undergraduate dermatology curriculum (including STD & leprosy) 3-16 Postgraduate curriculum General dermatology Sexually transmitted diseases Leprosy Skills Teaching and learning methods Evaluation Recommended text
3 Dermatology Curriculum For undergraduates: Overall Aims To provide an integrated undergraduate course in clinical dermatology for medical students. Students completing the course should have attained a level of clinical competence sufficient to allow them to deal competently with dermatology cases presenting in the general practice. They should also have had sufficient exposure to dermatology to allow them to make an informed decision about dermatology as a possible career option. Course Objectives On completion of the course the student should know the following: 1. Basic structure, and function of the skin and its appendages, (including hair, nail, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands (eccrine and apocrine) and an understanding of the principles of the skin immune system. 2. Dermatological terminology of skin lesions (Primary and secondary). 3. Dermatological history taking and examination. 4. Demonstrate good knowledge of common skin diseases, clinical manifestations & bed side investigations. 5. Demonstrate adequate knowledge of various dermatological therapies with special emphasis on mode of topical therapy. 6. Should be able to recapitulate the mode of action of commonly used dermatological drugs including their indications, dose, toxicity, metabolism & drug interactions. On completion of the course the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the knowledge necessary to be able to diagnose and treat common skin conditions. 2. Utilize this knowledge to interpret evidence, formulate simple management plans and communicate effectively. 3. Recognize and be aware of the significance of less common but important skin problems including dermatological emergencies. 4. Perform/ observe skills utilized in the field of dermatology. 5. Be aware of the psychosocial impact of skin diseases. Recommended Texts:
4 'Dermatology, an illustrated colour text' Gawkrodgers 'Clinical Dermatology' Hunter/Savin/Dahl 'Textbook of Dermatology' Roxburg Clinical Content of Dermatology Course For UG s I. HISTORY AND EXAMINATION History 1) Presenting complaints and Duration 2) History Of Present Complaints 3) Relevant personal / past / family history 4) Relevant occupational exposure associated with presenting complaints / disease 5) Treatment history topical / systemic - Duration of use, method of application - Application of substances: mustard oil / soaps / cosmetics / neem / home remedies - History of drug intake-prescription drugs/self-medication 6) Sexual history marital status/ PMC / EMC / single / multiple / hetero / homo / protected / unprotected / nature of contact 7) Personal history of - Atopic diathesis - Change of climate or environment - Dietary history - H/O substance abuse/addictions 8) Systemic complaints: Respiratory TB / sarcoidosis / SS Cardiovascular SS / Lentiginosis GI DH, HS Purpura Neurological Leprosy Constitutional symptoms 9) Obstetric/Gynecologic History 10) Family History EXAMINATION A) Dermatologic 1) Identify all types of lesions primary / secondary
5 2) Distribution of lesion - Photoexposed - Exposed but photoprotected - Flexural - Acral - Site of contact of particular allergen 3) Pattern - Segmental - Zosteriform - Nevoid / Blaschkoid - Linear 4) Site 5) Number 6) For an individual lesion Type, number, colour, margins (definition, regularity), edge, surface, scaling, crusting, any discharge Signs of acute inflammation-redness, temperature, tenderness, swelling 7) Examination of hair Scalp, axillary, pubic Change in colour, texture, density, distribution of terminal hair Scaling/ crusting Alopecia - scarring / non-scarring 8) Nails Proximal and lateral nail folds Nail plate surface, colour Nail bed 9) Mucosa oral, ocular, nasal, anal, genital 10) Relevant systemic examination B)General physical examination Pallor, icterus, cyanosis Lymphadenopathy Facies Structure of skin and its appendages a) Skin as an organ system b) Development of skin and its structure
6 c) Functions of skin d) Layers of skin, different cell types and their functions e) Racial and regional variations f) Basis of keratinization g) Skin h) Epidermis i) Dermis- papillary and reticular Hair : Structure of hair follicle Distribution age, sex and racial variations Types of hair Hair cycle Rate of hair growth and Regulation of hair growth Nail: Structure and Growth rate Primary and Secondary skin lesions: definitions and examples: Primary Macule: Hyperpigmentation Hypopigmentation Vascular abnormalities Capillary dilatation-erythema Purpura Papules: Acuminate Dome shaped Flat-topped Scaly erythematous Yellowish Necrotic Waxy Succulent Plaques and Nodules Wheals Vesicles/bullae: Intraepidermal subcorneal suprabasal Subepidermal Pustules Petechiae Purpura Ecchymoses Telangiectasias Erythema Comedones Burrow Secondary Scale Crust Erosion Excoriation Ulcer Atrophy : Epidermal and Dermal
7 Scar- hypertrophic, keloid Fissure Lichenification hyperpigmentation, thickening, accentuated skin markings Sclerosis Fibrosis: formation of excessive fibrous tissue Callus Milium Sinus Cyst Fistula Poikiloderma II.Signs and Symptoms in Dermatology and Laboratory Methods / staining Symptoms a. Pruritus b. Burning sensation c. Pain d. Paresthesia e. Hypo/Anaesthesia For all S/S Onset, duration, site, diurnal variation, aggravating and relieving factors, grade Signs a. Grattage b. Auspitz c. Buschke Ollendroff s sign d. Tin tack e. Dariers f. Bulla spread g. Nikolsky s sign h. Koebner s phenomenon Laboratory Methods / staining 1) Potassium hydroxide - Skin - Hyphae - Hair - Pseudohyphae - Nail - P. versicolor, Spores 2) Giemsa stain: To demonstrate Giant cells, Acantholytic cells, Molluscum contagiosum bodies, LD bodies / donovan bodies
8 3) Gram s stain 4) AFB ZN staining 5) Methods of demonstration of mite / lice 6) Tissue smears / Crush smear 7) Dark ground microscopy Parasitic infections Scabies 1) Etiological agent and Structure of the mite male / female 2) Life cycle 3) Incubation period and Mode of transmission 4) Host / site specificity and Immunity 5) Clinical features lesion morphology and their distribution 6) Variants - Crusted / norwegian scabies - Scabies incognito - Infantile scabies and scabies in pregnancy / Scabies in the elderly 7) Diagnosis: a. demonstration of mites / eggs b. Epiluminescence microscopy 8) Management General measures Topical antiscabetics Systemic antiscabetics Community Treatment 12) Complications Pediculosis 1) Etiological agent 2) Different species morphology- structural differences of pediculosis humanus var. capitis and corporis and Pthirus pubis 3) Life cycle 4) Clinical features and Complications 5) Laboratory diagnosis 6) Management
9 Bacterial Infections 1) Normal skin flora a) Age / sex / racial variation b) Site variation flora of specialized areas c) Role of skin flora in skin in defense 2) Primary and secondary infections 3) Primary Gram positive bacteria a. Staphylococcus b. Streptococci Cutaneous infections: Impetigo, ecthyma, cellulitis, erysipelas, folliculitis, furuncle, carbuncle, SSSS Predisposing factors Treatment-general, topical, systemic c. Corynebacteria Cutaneous infections- Erythrasma, Trichomycoses axillaris, Pitted keratolysis. Salient features Causative organisms, predisposing factors, pathology, clinical features and variants, complications, lab diagnosis, treatment. Pigmentary disorders 1) Epidermal melanin unit 2) Normal skin colour and variation 3) Define hyper and hypo-pigmentation 4) Different types epidermal / dermal 5) Clinical patterns reticulate, acral, flexural, variegate, rippled 6) Melasma 7) Vitiligo 8) Role of woods lamp in diagnosis of pigmentary diseases Vitiligo (1) Definition (2) Pathogenesis and Pathology (3) Clinical features and variants-sign of trichome, Associations ( (4) Diagnosis and Management Melasma
10 (1) Definition (2) Etiology (3) Clinical types (4) Diagnosis and Management Papulosquamous Psoriasis, 1) Definition 2) Predisposing / provocating factors 3) Epidemiology and Pathogenesis 4) Clinical features and PASI 5) Clinical variants by Site, Distribution, Morphology 6) Koebner s phenomenon 7) Investigations: Histopathology 8) Complications: Pustular psoriasis, Psoriatic arthritis 9) Treatment Topical drugs- emollients, coal tar, salicylic acid, retinoids, topical steroids Systemic drugs- methotrexate, cyclosporine, PUVA, retinoids, 10) Natural history and prognosis Similar salient features for lichen planus, pityriasis rosea, seborrheic dermatitis Hair & nail Hair : Hypertrichosis, hirsutism, hypotrichosis, telogen effluvium Alopecia a) Androgenetic, areata b) Cicatricial, non-cicatricial Nail Clubbing, koilonychias, platyonychia, micro/macronychia, anonychia, onycholysis, onychomadesis, Beau s lines, pitting, leukonychia, Terry s nail, Whitlow s, paronychia Viral Infections 1) Definition of exanthems and enanthems 2) Different types of rash rosealar/ scarlantiform/ morbilliform 3) Individually in each virus group clinical S/S, diagnosis, investigations, vaccines, association with HIV, complications, variable presentations
11 structure, cellular characteristics, modes of transmission, epidemiology Management, prophylaxis, prognosis Different groups POX Molluscum contagiosum Herpes HSV, Varicella and Zoster HPV Measles Mycology 1) Definition of fungus, classification 2) Predisposing factors 3) Lab diagnosis a) Sampling techniques skin scraping, nail, hair in 10% KOH b) Wood s lamp c) Culture media, characteristics Disease caused by Yeast c) Pityriasis versicolor, other disorders associated with malassezia yeast d) Candida - Normal carriage - Pathogenesis and Predisposing factors - Candidiasis and HIV - Clinical presentation oral candidiasis (types), flexural candidiasis, Vulcovaginal, Balanoposthitis, perianal and scrotal, napkin candidiasis, paronychia, onychomycoses - Lab diagnosis-pseudohyphae, BYC, culture - Management-general measures, drugs e) Dermatophytosis Host specificity, pathogenesis, HPE - Clinical forms Tinea capitis, Tinea corporis, barbae, faciei, pedis, manuum, cruris, unguuim, incognito, id eruptions - Lab diagnosis - Management f) Subcutaneous and deep mycoses- just names and predisposing factors Eczemas and adverse drug reactions
12 ECZEMAS 1) Definition acute, subacute and chronic 2) Endogenous vs exogenous 3) Histopathology 4) Endogenous atopic, seborrheic dermatitis, discoid, pityriasis alba, hand eczema, gravitational eczema 5) Exogenous irritant, allergic, photoallergic, PMLE, infective, dermatophytid 6) Diagnosis 7) Treatment general measures, topical & systemic 8) Erythroderma Adverse drug reactions 1) Definition and Classification by mechanism 2) Association with HIV 3) Major reactions erythema multiforme, SJS syndrome, TEN 4) For each salient features including causative drugs, clinical features and variants, systemic involvement, lab diagnosis including HPE, scoring methods, treatment Tuberculosis a) Causative organism b) Classification of mycobacteria c) Immunity, natural history, pathogenesis, Tuberculin test d) Cutaneous TB classification e) Types: Lupus vulgaris, TBVC, TB chancre, miliary TB, scrofuloderma, orificial TB, gumma f) Tuberculids g) Atypical mycobacterial infections For all types - clinical features, HPE, Mantoux test, complications Vesicobullous disorders a) Classification infective, autoimmune, hereditary, drug induced b) BMZ structure and function c) Basic pathogenesis acantholysis and acantholytic cells d) Signs Nikolsky s and bulla spread
13 a) Intraepidermal pemphigus b) Sub-epidermal bullous pemphigoid, cicatricial pemphigoid, dermatitis herpetiformis c) For each salient features including clinical features & variants, pathogenesis, HPE, lab diagnosis, target antigen d) Management Investigations Tzanck smear Histopathology DIF & IIF Treatment General measures Topical therapy Systemic therapy-steroids (daily, pulse therapy), immunosuppressives Connective tissue disorders a. Lupus erythematosus b. Classification DLE, SCLE, SLE, RA c. Scleroderma / morphea d. Dermatomyositis For each salient features including - clinical features, systemic manifestations, diagnostic criteria, investigations and treatment Acne and acneiform disorders a) Definition b) Pathogenesis- 4 factors c) Clinical feature and Grading and clinical variants d) Differential Diagnosis e) Complications f) Systemic associations g) Management-general measures, topical and systemic drugs Topical / Systemic drugs in dermatology and OT procedures Principles of topical therapy a) Factors affecting percutaneous absorption b) Classification of topical preparations c) Ideal vehicle d) Uses of different preparations
14 Topical Emollients, soap substitutes, shampoos, antiseptics, antifungals, antibiotics, steroids, steroid antibiotic combinations, retinoids, keratolytics, dithranol, tar, calcipotriol, wet wraps, bandages and compression hosiery. Local anaesthetics Systemic drugs: Students should be aware of the indications for and side effects of dermatological treatments including: Systemic steroids Immunosuppressives, Methotrexate, azathioprine, cyclosporin, dapsone, Isotretinoin,, acitretin and systemic steroids. Antileprotics Antibiotcs, antifungals, antivirals Penicillamine, colchicine, sulfasalazine, chloroquin OT procedures in dermatology a) Sampling blood, pus, throat swab, nasal smear universal precautions b) Extirpation milia, molluscum c) Intralesional injections d) Cautery chemical (TCA, phenol), electrical, radiocautery e) Skin biopsy f) Cryotherapy Emergencies in dermatology: Recognition, Salient feature, and management a. Adverse drug eruptions b. EM, SJS,TEN c. Acute urticaria, angioedema and Anaphylaxis d. Pemphigus e. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome f. Erythroderma g. Acute generalised pustular psoriasis h. Acute skin loss syndrome Students should have witnessed and understand the indications for and side effects of the following procedures if available:
15 Examination under Woods light Patch testing UVB and PUVA therapy Ellipse biopsy and punch biopsy Curettage and cautery Cryotherapy Skills required At the end of the course students should be able to : Take an appropriate history from a patient presenting with dermatological symptoms. Perform an appropriate physical examination of the patient. Recognise normal cutaneous changes. Distinguish between dermal and epidermal changes. Describe a solitary skin lesion and a cutaneous eruption using dermatological terms correctly Carry out simple bedside investigations like Gram stain, Slit skin smear examination, KOH scraping for fungus and Tzanck smear examination. Sexually transmitted diseases a) History and examination pertaining to an STD patient b) Counselling c) Syndromic approach definition, advantages / disadvantages, flow charts d) Major STD pathogens e) Major & minor STDs f) Difference between STD and STI g) Bed side procedures- DGI, gram s stain, Tzanck smear h) Culture methods i) Lab diagnosis, serological tests j) Newer Techniques-CFT, ELISA, MIF, PCR k) For each disease salient features including causative organism, incubation period, risk factors, pathogenesis, immunity, natural history, clinical features and variants, lab diagnosis, complications, treatment and association with HIV
16 LEPROSY a) Etiological agent- name, characteristics and mode of transmission b) Epidemiology c) Immunity d) Cardinal signs & Classification-spectrum e) Clinical spectrum Facies, mucosal involvement and ocular involvement f) Patterns of nerve damage g) Diagnosis- BI, MI, nerve conduction studies, Lepromin test, histopathology h) Management: Anti-leprosy Drugs (First line, second line) i) Reactions- Type I, Type II, lazarine leprosy, Lucio Reaction and Management j) Types of deformities and WHO grading, Trophic ulcer k) Management l) Disabilities and Rehabilitation m) National Programmes Teaching Methods/Aids A variety of teaching methods and aids, as outlined below, are to be used during this course: 1. Lectures by dermatology specialists with AV aids. 2. Attendance at out patients where a group of students will be seeing and, where possible, examining a variety of cases under the guidance of dermatology specialists. 3. Students will also attend sessions of phototherapy, patch testing, and Will have the opportunity to observe biopsy and laser clinic sessions. Evaluation Dermatology has emerged as a rapidly evolving specialty with new developments every year. In this scenario, the students are made conversant with the latest developments. Dermatology contributes significant number of the general practitioners case load. In this situation it is only logical that the evaluation of the students be also conducted by a dermatologist and the marks allocated should be up to 20% of the total marks available in internal medicine. Therefore theory and clinical examination should be formulated and evaluated by Dermatological faculty members.
b) SKILLS The student should be able to
 1. GOAL The aim of teaching the undergraduate student in Dermatology, S.T.D. and Leprology is to impart such knowledge and skills that may enable him to diagnose and treat common ailments and to refer
1. GOAL The aim of teaching the undergraduate student in Dermatology, S.T.D. and Leprology is to impart such knowledge and skills that may enable him to diagnose and treat common ailments and to refer
Contents. QAaptm-2. CAaptei-3. CAaptm-4. Cftapte%-5. Qfiaptvt-6. QhapteK-7. Qkaptefc-8 Clinical Immunology and Allergy 71
 Contents Ckaptm-1 Aaatomy, Physiology, Embryology, Bacteriology and Pathology ~ 1 Anatomy 1 Physiology 10 Embryology 14 Pathology 19 Bacteriology 22 Laboratory and other aids in dermatological pratice
Contents Ckaptm-1 Aaatomy, Physiology, Embryology, Bacteriology and Pathology ~ 1 Anatomy 1 Physiology 10 Embryology 14 Pathology 19 Bacteriology 22 Laboratory and other aids in dermatological pratice
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
DESCRIPTIONS FOR MED 3 ROTATIONS Dermatology A3S
 Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN
 CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology. Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders. Acne. Acne Vulgaris. Pomade Acne. Steroid Acne
 Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Undergraduate Dermatology Curriculum July 2016
 Undergraduate Dermatology Curriculum July 2016 British Association of Dermatologists Introduction This document is the 2016 revised dermatology undergraduate curriculum (UK) from the British Association
Undergraduate Dermatology Curriculum July 2016 British Association of Dermatologists Introduction This document is the 2016 revised dermatology undergraduate curriculum (UK) from the British Association
page: 582 alphabetical Index by Causes picture cause basic lesion search contents print last screen viewed back next
 page: 582 Index by Causes basic lesion cause picture alphabetical Index by Causes page: 583 Mechanical factors Acquired digital fibrokeratoma,393 Angioma,418 Atopic dermatitis in the adult: xerosis, lichenification
page: 582 Index by Causes basic lesion cause picture alphabetical Index by Causes page: 583 Mechanical factors Acquired digital fibrokeratoma,393 Angioma,418 Atopic dermatitis in the adult: xerosis, lichenification
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY
 WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition
 National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some associated with systemic diseases Learn the causative
 General Dermatology Julia R. Nunley, MD, FAAD, FACP Professor Program Director Department of Dermatology General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some
General Dermatology Julia R. Nunley, MD, FAAD, FACP Professor Program Director Department of Dermatology General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham
 Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Dermatology Syllabus for 5th Year Med Students
 Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of medicine 2011-2012 Dermatology Syllabus for 5th Year Med Students Course Information: Course Title : Dermatology Credit Hours : Time Theoretical:
Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of medicine 2011-2012 Dermatology Syllabus for 5th Year Med Students Course Information: Course Title : Dermatology Credit Hours : Time Theoretical:
COURSE DESCRIPTION AND STUDY REGULATIONS
 COURSE DESCRIPTION AND STUDY REGULATIONS Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Course type: COMPULSORY ELECTIVE ECTS credits: 6 Nominated teacher(s): prof. dr. Tomaž Lunder, izr. prof. dr. Mateja Dolenc-Voljč
COURSE DESCRIPTION AND STUDY REGULATIONS Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Course type: COMPULSORY ELECTIVE ECTS credits: 6 Nominated teacher(s): prof. dr. Tomaž Lunder, izr. prof. dr. Mateja Dolenc-Voljč
Course Regime. Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES. Study Programme: Medicine. Year of the Course: 4 th study year.
 Komisija za študijske zadeve UL Medicinske fakultete Vrazov trg 2 SI-1000 Ljubljana E: ksz@mf.uni-lj.si T: +386 1 543 7700 Course Regime Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Study Programme: Medicine Year
Komisija za študijske zadeve UL Medicinske fakultete Vrazov trg 2 SI-1000 Ljubljana E: ksz@mf.uni-lj.si T: +386 1 543 7700 Course Regime Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Study Programme: Medicine Year
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
Site and distribution: symmetrical, asymmetrical. Surface characteristics: smooth, scaly, warty
 B I O T E R R O R I S M PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF DERMATOLOGY Dr Matthew Ng Joo Ming INTRODUCTION Medical schools and textbooks teach us dermatology by subjects such as eczema and psoriasis. This is useful
B I O T E R R O R I S M PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF DERMATOLOGY Dr Matthew Ng Joo Ming INTRODUCTION Medical schools and textbooks teach us dermatology by subjects such as eczema and psoriasis. This is useful
Dermatology GP Referral Guidelines
 Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
The side effects of prolonged used of systemic Corticosteroids
 The side effects of prolonged used of systemic Corticosteroids -Lowering the resistance to many infections. -Metabolic disturbance, particularly in regard to electrolytes and carbohydrates leading to fluid
The side effects of prolonged used of systemic Corticosteroids -Lowering the resistance to many infections. -Metabolic disturbance, particularly in regard to electrolytes and carbohydrates leading to fluid
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails. 2 Cultivating Your Senses
 1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
Skin lesions & Abrasions
 Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Some skin conditions
 Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
 DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
Issues in Dermatology. Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN
 Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Index. Angiosarcoma diagnosis, 47 lymphedema-related vs. non-lymphedemarelated, 48
 A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin. 1. ECZEMA Atopic Dermatitis- specific form of eczema starting in childhood
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
Chapter 29. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont d) 9/10/2012. Cutaneous Disorders
 Chapter 29 Cutaneous Disorders Learning Objectives Describe the three layers of skin, and their composition and functions Describe the morphology of primary skin lesions Describe the morphology of secondary
Chapter 29 Cutaneous Disorders Learning Objectives Describe the three layers of skin, and their composition and functions Describe the morphology of primary skin lesions Describe the morphology of secondary
Learning Objectives. History 8/1/2016. An Approach to Pediatric Rashes
 An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
Integumentary System. Anatomy of the Skin
 Integumentary System Chapter four Medical Terminology Hit # 141 Anatomy of the Skin Epidermis = outer layer of skin. Melanin = color or pigmentation of the skin. Dermis= inner layer of skin. Sweat glands
Integumentary System Chapter four Medical Terminology Hit # 141 Anatomy of the Skin Epidermis = outer layer of skin. Melanin = color or pigmentation of the skin. Dermis= inner layer of skin. Sweat glands
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES. Sharon Seguin MD FAAD
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesive tape impression 1 Diff Quik in EPD diagnosis, 583 Allergy(ies). See also Food allergy; specific types, e.g., Culicoides hypersensitivity
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesive tape impression 1 Diff Quik in EPD diagnosis, 583 Allergy(ies). See also Food allergy; specific types, e.g., Culicoides hypersensitivity
Conflicts. Objectives. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Pediatrics Grand Rounds 24 August Pediatric Dermatology 101
 Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY
 DECEMBER OI DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY Time : llhours Max. Marks : 00 Attempt all questions in order. Each question carries 0 marks. PAPER. I DVD/D/t06t. a. When calculating sample size in a clinical
DECEMBER OI DERMATOLOGY AND VENEREOLOGY Time : llhours Max. Marks : 00 Attempt all questions in order. Each question carries 0 marks. PAPER. I DVD/D/t06t. a. When calculating sample size in a clinical
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology. Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
 Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Study & Evaluation Scheme
 Study & Evaluation Scheme of M.D. (Dermatology) [Applicable for the Batch 2014-15 till revised] TEERTHANKER MAHAVEER UNIVERSITY Delhi Road, Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh-244001 Website: www.tmu.ac.in Annexure-1
Study & Evaluation Scheme of M.D. (Dermatology) [Applicable for the Batch 2014-15 till revised] TEERTHANKER MAHAVEER UNIVERSITY Delhi Road, Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh-244001 Website: www.tmu.ac.in Annexure-1
Undergraduate. Introduction:
 Undergraduate The main base of the chair is surgical units 2 clinics Regional SVD and Republics SVD. The clinical bases of the department completely fit the profile of training, are part of the dermatovenerologis
Undergraduate The main base of the chair is surgical units 2 clinics Regional SVD and Republics SVD. The clinical bases of the department completely fit the profile of training, are part of the dermatovenerologis
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES. DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE
 DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
0BCore Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Pimecrolimus Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% P-RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR: 06.06.2013 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to pimecrolimus,
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Pimecrolimus Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% P-RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR: 06.06.2013 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to pimecrolimus,
Emergency Dermatology. Emergency Dermatology
 Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Dutasteride female pattern hair loss management 49, 50 male baldness management 41, 42 Dyeing, see Hair care
 Subject Index Acne keloidalis nuchae, ethnic patients 146, 147 Actinic keratosis, ultraviolet radiation exposure 108 Aging hair effects 4, 5 melanocyte aging 130 132 molecular mechanisms 5 7 pigment loss,
Subject Index Acne keloidalis nuchae, ethnic patients 146, 147 Actinic keratosis, ultraviolet radiation exposure 108 Aging hair effects 4, 5 melanocyte aging 130 132 molecular mechanisms 5 7 pigment loss,
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Facial Rash. Facial Rash 10/14/2013. Ten Look Alike Rashes Michelle DiBaise, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA Associate Clinical Professor NAU PA Program
 Ten Look Alike Rashes Michelle DiBaise, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA Associate Clinical Professor NAU PA Program Facial Rash Facial Rash Case 1 28 year female Progressive development of erythematous facial lesions
Ten Look Alike Rashes Michelle DiBaise, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA Associate Clinical Professor NAU PA Program Facial Rash Facial Rash Case 1 28 year female Progressive development of erythematous facial lesions
Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3
 BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 7 Integumentary System Disorders 1 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, student should be
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 7 Integumentary System Disorders 1 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, student should be
Common Dermatological Conditions in Adults in Ghana. Margaret Lartey FWACP
 Common Dermatological Conditions in Adults in Ghana Margaret Lartey FWACP Outline Introduction Two Common disorders Discussion Case 1 34 yr old female C/o pruritus of 2 months duration First episode Seen
Common Dermatological Conditions in Adults in Ghana Margaret Lartey FWACP Outline Introduction Two Common disorders Discussion Case 1 34 yr old female C/o pruritus of 2 months duration First episode Seen
الاكزيماتيد= Eczematid
 1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Scrub In. What is a function of the skin: The innermost layer of the epidermis is constantly reproducing itself. This function enable the skin to:
 Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana)
 Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
A Clinical Study of Paediatric Dermatoses
 2018; 4(3): 477-481 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2018; 4(3): 477-481 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 5-01-2018 Accepted: 9-02-2018 Dr. M Subramanya Swamy MD,
2018; 4(3): 477-481 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2018; 4(3): 477-481 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 5-01-2018 Accepted: 9-02-2018 Dr. M Subramanya Swamy MD,
Dermatology Pearls. Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018
 Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies
 My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis
 Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
Diagnose dermatologic conditions based on physical examination (visual recognition). The majority of the items will come from Group 1.
 This document was developed by a committee of the American Board of Dermatology (ABD) for the purpose of preparing the BASIC Examination. The BASIC Exam is assessment of fundamental knowledge and skills.
This document was developed by a committee of the American Board of Dermatology (ABD) for the purpose of preparing the BASIC Examination. The BASIC Exam is assessment of fundamental knowledge and skills.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Primary and Secondary Skin Lesions. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Primary and Secondary Skin Lesions. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify different
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Primary and Secondary Skin Lesions. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify different
MUCOCUTANEOUS MANIFESTATIONS OF HIV/AIDS IN ADOLESCENTS
 MUCOCUTANEOUS MANIFESTATIONS OF HIV/AIDS IN ADOLESCENTS Dr. Y.S.MARFATIA Prof. and Head, Dept. Skin & V.D. Medical college, Vadodara LET US CREATE BRILLIANCE TOGETHER MEDICAL COLLEGE, VADODARA Editor in
MUCOCUTANEOUS MANIFESTATIONS OF HIV/AIDS IN ADOLESCENTS Dr. Y.S.MARFATIA Prof. and Head, Dept. Skin & V.D. Medical college, Vadodara LET US CREATE BRILLIANCE TOGETHER MEDICAL COLLEGE, VADODARA Editor in
Poonkiat Suchonwanit, MD Hair and Scalp Disorders Unit Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital
 Poonkiat Suchonwanit, MD Hair and Scalp Disorders Unit Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Hair loss Excessive hair growth Hair haft abnormalities Hair color Anagen Catagen
Poonkiat Suchonwanit, MD Hair and Scalp Disorders Unit Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Hair loss Excessive hair growth Hair haft abnormalities Hair color Anagen Catagen
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system?
 Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
B. Autoimmune blistering diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Common Superficial Fungal Infections
 How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
Sick Call Screener Course. Integumentary System
 Sick Call Screener Course Integumentary System (2.10) 2.10.2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.52 Utilize the knowledge of integumentary system anatomy while assessing a patient with a integumentary complaint 1.53
Sick Call Screener Course Integumentary System (2.10) 2.10.2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.52 Utilize the knowledge of integumentary system anatomy while assessing a patient with a integumentary complaint 1.53
DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
 UNC DIVISION OF PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE A. Anatomy/Physiology/Embryology Goal: The resident will have knowledge
UNC DIVISION OF PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE A. Anatomy/Physiology/Embryology Goal: The resident will have knowledge
My Algorithm. Questions to ask. Do you or your family have a history of?... Allergic rhinitis, Sensitive skin, Asthma Skin Cancer
 Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Contents. Part I Genodermatoses
 Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
be the presenting symptom of HIV-related illness. 4 CD4 cell count and CD4 cell percentage are key markers for determining disease progress and the ri
 Cutaneous Maniestations In HIV Positive Paediatric Patients Kondreddy B 1, Kuruvila M 2, Ullal KR 3, Bhat K 4 1 Resident, 2 Professor, 3 Senior Resident, Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy,
Cutaneous Maniestations In HIV Positive Paediatric Patients Kondreddy B 1, Kuruvila M 2, Ullal KR 3, Bhat K 4 1 Resident, 2 Professor, 3 Senior Resident, Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy,
Oral Medicine. Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN
 Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
Rehabilitation Skin Conditions Medical Terminology
 Proficiencies Each of the items outlined below is a technique/term that we commonly use in the New Trier athletic training room. As student athletic training aides, you will be given the opportunity to
Proficiencies Each of the items outlined below is a technique/term that we commonly use in the New Trier athletic training room. As student athletic training aides, you will be given the opportunity to
Chapter 6 The Integumentary System
 Chapter 6 The Integumentary System Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms apocrine epidermis melanin alopecia erythema melanocyte arrector pili exfoliation
Chapter 6 The Integumentary System Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms apocrine epidermis melanin alopecia erythema melanocyte arrector pili exfoliation
KEY MESSAGES. Psoriasis patients are more prone to cardiovascular diseases, stroke, lymphoma and non-melanoma skin cancers, and increased mortality.
 KEY MESSAGES Psoriasis is a genetically determined, systemic immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that affects primarily the skin and joints. Psoriasis Vulgaris is characterised by well-demarcated
KEY MESSAGES Psoriasis is a genetically determined, systemic immune-mediated chronic inflammatory disease that affects primarily the skin and joints. Psoriasis Vulgaris is characterised by well-demarcated
Objectives. Terminology. Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions. Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease
 Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Psoriasis management. A/Prof Amanda Oakley Dermatologist, Waikato
 Psoriasis management A/Prof Amanda Oakley Dermatologist, Waikato AbbVie Breakfast Session, 14 June 2014 Disclosure This breakfast session is sponsored by Abbvie Autoimmune skin disorders Psoriasis Eczema
Psoriasis management A/Prof Amanda Oakley Dermatologist, Waikato AbbVie Breakfast Session, 14 June 2014 Disclosure This breakfast session is sponsored by Abbvie Autoimmune skin disorders Psoriasis Eczema
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care
 Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE. Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio
 COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio DISCLOSURE The Speaker and members of the planning committee do not have a conflict of interest
COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio DISCLOSURE The Speaker and members of the planning committee do not have a conflict of interest
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
My ear won t stop hurting!
 This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
 Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Why Should I Care? 53% of all skin related visits are to non
Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Why Should I Care? 53% of all skin related visits are to non
Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
 Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
DERMCASE. Doc, my baby s all spotty! Case 1
 Test Your Knowledge With Multiple-Choice Cases This month 5 cases: Case 1 1. Doc, my baby s all spotty! 2. A Mediterranean Matter 3. Mommy, what s wrong with my head? 4. Armed with Lesions 5. It s spreading!
Test Your Knowledge With Multiple-Choice Cases This month 5 cases: Case 1 1. Doc, my baby s all spotty! 2. A Mediterranean Matter 3. Mommy, what s wrong with my head? 4. Armed with Lesions 5. It s spreading!
29a Pathology - Integumentary System
 29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases
 Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases Attitude is more important than the past, than education, than money, than circumstances, than what people do or say. It is more important than appearance, giftedness,
Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases Attitude is more important than the past, than education, than money, than circumstances, than what people do or say. It is more important than appearance, giftedness,
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014
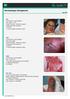 Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
Types of Skin Infections
 Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
MERCY RETREAT Dermatology
 MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
Psoriasis. What is Psoriasis? What causes psoriasis? Medical Topics Psoriasis
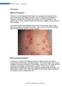 1 Psoriasis What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a long standing inflammatory non-contagious skin disease which waxes and wanes with triggering factors. There is a genetic predisposition in psoriasis. Internationally,
1 Psoriasis What is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is a long standing inflammatory non-contagious skin disease which waxes and wanes with triggering factors. There is a genetic predisposition in psoriasis. Internationally,
The Integumentary System. Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases
 The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Original Article. Abstract. Introduction
 Original Article The prevalence of skin diseases among the geriatric patients in Eastern Turkey Serap Gunes Bilgili, 1 Ayse Serap Karadag, 2 Hatice Uce Ozkol, 3 Omer Calka, 4 Necmettin Akdeniz 5 Department
Original Article The prevalence of skin diseases among the geriatric patients in Eastern Turkey Serap Gunes Bilgili, 1 Ayse Serap Karadag, 2 Hatice Uce Ozkol, 3 Omer Calka, 4 Necmettin Akdeniz 5 Department
Primary Care Dermatology Update
 Primary Care Dermatology Update 15.50 Lorraine Wooster Skin lesions what to refer where 16.10 Liz Riches Treating Actinic Keratosis in Primary care 16.25 Lucy Scriven Update on Primary Care Dermatology
Primary Care Dermatology Update 15.50 Lorraine Wooster Skin lesions what to refer where 16.10 Liz Riches Treating Actinic Keratosis in Primary care 16.25 Lucy Scriven Update on Primary Care Dermatology
