Type I collagen glomerulopathy: postnatal collagen deposition follows glomerular maturation
|
|
|
- Posy West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 & 27 International Soiety of Nephrology original artile Type I ollagen glomerulopathy: postnatal ollagen deposition follows glomerular maturation AC Brodeur 1,2, DA Wirth 1, CL Franklin 3, LW Reneker 4, JH Miner 5 and CL Phillips 1,2 1 Department of Biohemistry, University of Missouri, Columbia, Missouri, USA; 2 Department of Child Health, University of Missouri, Columbia, Missouri, USA; 3 Department of Veterinary Pathobiology, University of Missouri, Columbia, Missouri, USA; 4 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Missouri, Columbia, Missouri, USA and 5 Renal Division, Washington University Shool of Mediine, St Louis, Missouri, USA In hroni renal disease, the progressive aumulation of ollagen and other extraellular matrix proteins in the mesangium results in fibrosis, glomeruloslerosis, and eventual renal failure. Mie defiient in proa2(i) ollagen are not only a model of osteogenesis imperfeta but also aumulate fibrillar homotrimeri type I ollagen in the mesangium. This aumulation spreads to the subendothelial spae in the peripheral apillary loops. Piosirius red staining of kidney setions demonstrates that in omparison to wild-type mie, Col1a2-defiient homozygous and heterozygous mie exhibit abnormal glomerular ollagen deposition in a gene dosage-dependent manner. The glomerulopathy initiates during the first postnatal week, appears progressive following the pattern of glomerular maturation and results in albuminuria in severely affeted animals. In situ hybridization revealed no gross differenes in steady-state proa1(i) and proa2(i) ollagen mrna levels among the three genotypes. Quantitative reverse transriptase-polymerase hain reation, however, using whole kidney setions showed a twofold inrease in steady-state proa1(i) ollagen mrna in 1-month homozygous Col1a2-defiient animals ompared with wild-type and heterozygous animals. We suggest that glomerular ollagen deposition seen in the osteogenesis imperfeta model mie is, in part, owing to pretranslational mehanisms and may represent an over ompensation of wound healing. Kidney International (27) 71, doi:1.138/sj.ki.52173; published online 14 Marh 27 KEYWORDS: glomeruloslerosis; podoyte; glomerular development; albuminuria; type I ollagen Correspondene: CL Phillips, Department of Biohemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia, M743 Medial Siene Building, Columbia, Missouri 65212, USA. phillipsl@missouri.edu Reeived 2 September 26; revised 18 Deember 26; aepted 17 January 27; published online 14 Marh 27 A novel type I ollagen glomerulopathy was identified in the Col1a2-defiient mouse model, haraterized by the deposition of homotrimeri type I ollagen in the renal mesangium. 1 Under normal physiologi onditions, very little type I ollagen is in the glomerulus. 2,3 In hroni renal disease, progressive aumulation of ollagen and other extraellular matrix (ECM) omponents in the mesangium results in fibrosis, glomeruloslerosis, and renal failure. 4 6 The primary event leading to development of the glomerulopathy in Col1a2-defiient mie appears to be deposition of homotrimeri type I ollagen in the mesangial matrix, similar to the progressive glomerular deline following injury and may represent overompensation of the glomerular wound healing response. 7 9 To haraterize further the type I ollagen glomerulopathy, we defined the pattern of disease initiation and progression, and began investigating the mehanisms responsible for glomerular ollagen deposition in Col1a2-defiient mie. The predominant isotype of type I ollagen is a heterotrimer omposed of two proa1(i) ollagen hains and one similar, but genetially distint, proa2(i) ollagen hain [a1(i) 2 a2(i)]. 1,11 The homotrimeri type I ollagen isotype ontaining three proa1(i) ollagen hains, [a1(i) 3 ] is a minor isotype, whose role is not well understood. 1,11 Homotrimer is found embryonially 2,12 in small amounts in skin, 13 in ertain tumors and ultured aner ell lines, 12,14,15 and also during wound healing. 7 Cultured mesangial ells produe homotrimeri type I ollagen, further suggesting that homotrimer plays a role in wound healing. 7,8 The Col1a2-defiient mouse model, otherwise known as the oim mouse (osteogenesis imperfeta model) is homozygous for a spontaneous nuleotide deletion in the Col1a2 gene, resulting in a frameshift altering the arboxy propeptide of the proa2(i) ollagen hain. Although the arboxy propeptide is not present in mature type I ollagen, it is responsible for assoiation of the a2(i) hain with the a1(i) hains during assembly of the triple helix The glomerulus, a network of apillaries, serves as the filtration unit of the kidney, with mesangial ells omposing 3 4% of the ell population, funtioning to reate and integrate a strutural saffold for the apillary network. 2,8 Kidney International (27) 71,
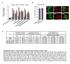
2 o r i g i n a l a r t i l e AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy Mesangial ells serete ECM proteins to provide a framework for the saffold. Glomeruli form in a entrifugal pattern around the renal medulla. At birth, mouse kidneys have numerous glomeruli, yet only a fration are funtional. Between birth and 21 days of age, glomeruli gain funtion regionally, 19 with initial funtioning glomeruli in the juxtamedullary region of the deep ortex. 2,21 As the mouse develops, there is stepwise indution of new nephrons and glomeruli gain funtional ativity, progressing until full maturation when glomeruli in the outer ortex assume the majority of glomerular funtion A similar progression of glomerular maturation ours in other mammalian speies, inluding humans. 21,23,24 Several studies using animal models demonstrate that glomerular ollagen deposition an result from either inreased pretranslational expression of type I ollagen (transriptional upregulation) or dereased matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) expression and/or ativity, or both In this study, we sought to determine whether the ollagen glomerulopathy in the Col1a2-defiient model was progressive with pre- or postnatal initiation and whether pretranslational upregulation of type I ollagen expression was involved in glomerular ollagen deposition. Through histologi examination, urine analyses, and quantitative reverse transriptase-polymerase hain reation (RT-PCR), we determined that the type I ollagen glomerulopathy in Col1a2-defiient mie initiates postnatally, progresses with age and glomerular maturation, is assoiated with a gene dose effet, impairs renal funtion, and is, in part, owing to inreased steady-state proa1(i) ollagen mrna levels. RESULTS Heterozygous mie demonstrate ollagen glomerulopathy Pirosirius red-stained setions of Col1a2-defiient, heterozygous, and wild-type mie were examined by light mirosopy to determine lesion sore. Heterozygous mie exhibited ollagen deposition in their glomeruli harateristi of the type I ollagen glomerulopathy identified in the Col1a2-defiient mie, though their lesions were less severe (Figure 1). Glomerulopathy initiation We determined the lesion sore of heterozygous and Col1a2- defiient mouse kidneys at 1 day, 1 week, 2 weeks, and 1 month of age to determine whether initiation of glomerular fibrillar ollagen deposition ourred postnatally. Figure 2 highlights the postnatal initiation of ollagen deposition within the renal glomeruli. Glomeruli of 1-day-old mie lak fibrillar ollagen deposition aross all genotypes. However, by 1 week of age, fibrillar ollagen deposition was present in Col1a2-defiient and heterozygous mie. By 1 month of age, Col1a2-defiient mie exhibited lesions that ranged from mild to severe, whereas heterozygous mie had mild to moderate lesions. Interestingly, the younger Col1a2-defiient mie had glomerular ollagen deposition in the juxtamedullary region in ontrast to older mie, where lesions were throughout the ortex. Morphometry To investigate further disease progression, we developed a morphometry-mapping system to examine severity and loalization of individual lesions. Morphometri analyses (Figure 3, Supplementary Material) onfirmed that the type I ollagen glomerulopathy is progressive and exhibits a gene dose effet. At 2 weeks of age, 55% of Col1a2-defiient glomeruli were affeted, whih inreased to 95% by 1 month of age. In omparison, only 8% of heterozygous glomeruli were affeted at 2 weeks of age inreasing to 53% by 1 month. Polynomial orthogonal ontrast analysis of the morphometri data onfirmed a linear gene dose response. Differenes also existed in lesion severity and perent of glomeruli affeted between the ortial and juxtamedullary regions within individual kidneys. The morphometry sore in the juxtamedullary region was signifiantly greater than the ortial region in Col1a2-defiient mie at 2 weeks and 1 month of age (Figure 4a). The mean juxtamedullary morphometry sore in 2-week Col1a2-defiient animals was.94, whereas the 1-month juxtamedullary morphometry sore was 2.1, demonstrating disease progression. Similar findings were true of perent glomeruli affeted (Figure 4b). At 2 weeks of age, 73% of juxtamedullary glomeruli were affeted as ompared with 36% of ortial glomeruli in Col1a2-defiient mie. In ontrast, by 1 month of age 97% of juxtamedullary and 93% of ortial glomeruli were affeted. A similar pattern exists in heterozygous mie, though the shift in affeted glomeruli from predominantly juxtamedullary to both juxtamedullary and ortial involvement was not as dramati. These data suggest a entrifugal pattern of a b Figure 1 Deposition of type I ollagen in heterozygous and Col1a2-defiient glomeruli. Pirosirius red-stained setions of (a) wild-type (lesion sore ), (b) heterozygous (lesion sore 1), and () Col1a2-defiient (lesion sore 4) kidneys from 1-month-old mie. Arrows indiate glomeruli. Asterisks denote affeted (Pirosirius red þ ) glomeruli. 986 Kidney International (27) 71,
3 AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy o r i g i n a l a r t i l e 1 day 2 weeks 1 month a b +/+ d e f +/ g h i / Figure 2 Initiation of type I ollagen deposition in glomeruli ours postnatally. Pirosirius red stain of (a, d, and g) 1-day-old, (b, e, and h) 2-week-old, and (, f, and i) 1-month-old mie. (a ) Wild-type ( þ / þ ) mie do not demonstrate ollagen deposition and have lesion sores of. (d f) Heterozygous ( þ / ) mie show evidene of disease at 2 weeks (inset: enlargement of indiated glomeruli (e)), demonstrating lesion sores of at 1 day, 1 at 2 weeks, and 1 at 1 month. (g i) Col1a2-defiient ( / ) mie also show evidene of deposition at 2 weeks with a lesion sore of at 1 day, 1 at 2 weeks, and 4 at 1 month. Arrows indiate glomeruli. Asterisks denote affeted (Pirosirius red þ ) glomeruli. % glomeruli affeted per field / +/ / +/ 2 weeks 1 month Figure 3 The type I ollagen glomerulopathy in heterozygous mie demonstrate a gene dose effet (Po.1) that is progressive with age (Po.1). The perent of affeted glomeruli per field is signifiantly greater in Col1a2-defiient ( / ) than heterozygous ( þ / ) kidneys at both 2 weeks and 1 month of age. Signifiant differenes in the perent of glomeruli affeted between kidneys examined at 2 weeks and 1 month of age is also shown irregardless of genotype. glomerular ollagen deposition as the animal ages, with disease initiation ourring primarily in the juxtamedullary region and progressing to involve both the juxtamedullary and ortial regions of the kidney. Lesion development oinides with glomerular maturation, whih progresses from the juxtamedullary region outward toward the ortex These data taken together onfirm that initiation of the type I ollagen glomerulopathy ours postnatally before 1 week of age and that initiation of disease oinides with the maturation of glomeruli into funtional filtration units. 22 Subendothelial type I ollagen aumulation Ultrastrutural examination of glomerular ollagen deposition in wild-type and severely affeted Col1a2-defiient (lesion sore G4) kidney setions revealed that the fibrillar ollagen was extraellular, aumulating in the mesangial matrix as well as between the fenestrated endothelial ells and the glomerular basement membrane within the glomeruli (Figure 5). In addition, there was podoyte foot proess effaement in areas demonstrating severe fibrillar ollagen deposition and marked separation of endothelial ells from the basement membrane. However, in all setions, the glomerular basement membrane remained intat. Albuminuria Analysis of albumin exretion in urine of wild-type and Col1a2-defiient mie demonstrated signifiant inreases in albumin exretion in Col1a2-defiient mie (Table 1). Col1a2-defiient mie had a mean albumin/reatinine ratio of mg albumin/mg reatinine, whereas wild-type had a mean ratio of.499 mg albumin/mg reatinine. Mie with higher lesion sores had greater albuminuria than those with less severe lesion sores. These data suggest that inreasing deposition of homotrimeri ollagen into the glomeruli results in impaired renal funtion. Kidney International (27) 71,
4 o r i g i n a l a r t i l e AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy Morphometry Sore b a % affeted per field weeks 1 month jm jm jm Heterozygous COL1A2 defiient Heterozygous 1 2 weeks 1 month % affeted per field Morphometry Sore jm COL1A2 defiient jm Heterozygous jm COL1A2 defiient jm jm Heterozygous COL1A2 defiient Figure 4 The type I ollagen glomerulopathy initiates postnatally and glomeruli sequentially beome affeted in a entrifugal pattern from the juxtamedullary (jm) to the ortial () region in a distribution onsistent with glomerular maturation and initiation of funtion. (a) Demonstrates that there is a signifiant differene between the morphometry sore in jm and glomeruli at 2 weeks and 1 month of age in Col1a2-defiient mie with more severely affeted glomeruli loated in the jm region where glomerular funtion initiates. (b) Demonstrates a signifiant differene between perent of glomeruli affeted per field between jm and glomeruli in Col1a2-defiient mie at 2 weeks of age whereas greater than 9% of jm and glomeruli per field are affeted by 1 month of age. Conversely, the heterozygous animals lak a signifiant differene at the earlier time point but demonstrate a signifiant differene in both lesion severity and perent glomeruli affeted per field between jm and glomeruli at 1 month of age. Further, the lesion severity and perent glomeruli affeted is signifiantly different between the 2 week and 1 month ages (y), onfirming the progressive nature of the glomerulopathy (Po.5, Po.5, Po.1). a p GBM b p m GBM p e m GBM Figure 5 (a) Eletron mirosopy of glomeruli from wild-type and (b and ) Col1a2-defiient mie (lesion sore 4) demonstrate that the Col1a2-defiient glomeruli exhibit deposition of extraellular fibrillar type I ollagen () into the subendothelial spae displaing the fenestrated endothelium (e) from the underlying glomerular basement membrane (b). Fibrils demonstrating ross striation of organized ollagen (b; inset) were also present. In areas of severe ollagen deposition and expansion of the subendothelial spae, podoyte (p) foot proess effaement is seen (). It is hypothesized that the type I ollagen is being produed by the mesangial (m) ell followed by deposition in the subendothelial spae. In all mie examined, the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) was intat. Wild-type provided for omparison (a). Steady-state proa1(i) and proa2(i) ollagen mrna In situ hybridization with Col1a1 and Col1a2 antisense probes to wild-type and Col1a2-defiient mouse kidneys demonstrated no differenes in temporal or spatial distribution of Col1a1 and Col1a2 mrnas (Supplementary Material). To assess quantitatively whether type I ollagen deposition in the glomerulus of Col1a2-defiient mie is assoiated with inreased steady-state proa1(i) and proa2(i) ollagen mrna levels, we evaluated Col1a2-defiient, heterozygous and wildtype mie at 1 week, 2 weeks, and 1 month of age by quantitative RT-PCR (Figure 6). A signifiant inrease in steady-state proa1(i) ollagen mrna levels was seen in 1-month old Col1a2-defiient mie as ompared with agemathed heterozygous and wild-type animals. In ontrast, a signifiant differene in steady-state proa2(i) ollagen mrna was not seen. Figure 6 also demonstrates a signifiant 988 Kidney International (27) 71,
5 AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy o r i g i n a l a r t i l e Table 1 Col1a2-defiient mie demonstrate albuminuria as ompared with wild-type animals Genotype n Albumin (lg)/reatinine (mg) (range) Wild-type ( ) Col1a2-defiient ( ) Lesion sore Po.1. Po.5. a RNA opy number b RNA opy number COL1A1 / +/ +/+ / +/ +/+ / +/ +/+ 1 week 2 weeks 1 month COL1A2 / +/ +/+ / +/ +/+ / +/ +/+ 1 week 2 weeks 1 month Figure 6 Quantitative RT-PCR demonstrates a signifiant inrease in (a) proa1(i) ollagen mrna expression in 1 month Col1a2-defiient ( / ) animals when ompared with age-mathed heterozygous ( þ / ) and wild-type ( þ / þ ) animals (Po.5). It also demonstrates a derease in proa(i) ollagen mrna expression with age independent of genotype (Po.1) and a signifiant differene in (b) proa2(i) ollagen mrna expression when omparing 1 month and 1 week animals for all three genotypes. derease in proa1(i) and proa2(i) ollagen mrna with inreasing age aross all three genotypes. DISCUSSION The original haraterization of the type I ollagen glomerulopathy in Col1a2-defiient mie demonstrated, by immunohistohemistry, that the fibrillar material deposited in the glomerulus was type I ollagen and suggested that heterozygous mie did not exhibit glomerular ollagen deposition. 1 However, revision of the lesion soring system to inlude the examination of kidney setions stained with Pirosirius red revealed that heterozygous mie indeed aumulate glomerular fibrillar ollagen, though to a lesser degree. Heterozygous mie, like Col1a2-defiient mie, exhibit a range of lesion sores, though the age-dependent inrease was less severe, suggesting that the loss of proa2(i) ollagen or the presene of homotrimeri type I ollagen has a gene dosage effet. It is not an unommon phenomenon for heterozygous animals to be less severely affeted than their homozygous ounterparts and has been shown to our in several disorders inluding ahondroplasia. 32,33 We also showed that the deposition of type I ollagen initiates postnatally, before 1 week of age, and that the progression follows a pattern similar to glomerular maturation. Initially, within 1 week of life, affeted glomeruli were onfined to the juxtamedullary region. However, by 1 month of age, affeted glomeruli were evident throughout the juxtamedullary and ortial regions in Col1a2-defiient mie, following the pattern for funtional maturation of glomeruli, whih is omplete by 21 days of age. 19 The glomerulopathy progressed in a entrifugal pattern, oiniding with initiation of glomerular funtion and maturation. 2,21 Further, as Col1a2-defiient mie age, inreasing amounts of fibrillar ollagen were deposited resulting in pathologial onsequenes; Col1a2-defiient mie exhibit miroalbuminuria and mie with greater lesion sores have a higher degree of miroalbuminuria. With age, Col1a2-defiient mie demonstrate inreasing severity in glomerular lesions and funtional impairment of their kidneys, onsistent with glomerular injury. Ultrastrutural analyses of Col1a2-defiient kidneys demonstrated fibrillar ollagen deposition in the subendothelial spae between the fenestrated endothelium and the basement membrane, though basement membrane appeared normal. Regions of severe deposition exhibited podoyte foot proess effaement. Podoytes funtion in ultrafiltration and establishment of the glomerular barrier to protein. Foot proess effaement and overall derease in podoyte number has been shown to result in inreased proteinuria, a hallmark of glomerular injury. 34,35 Similar findings were seen in a mouse model of glomeruloslerosis in whih the transforming growth fator (TGF)-b1 transgene under the ontrol of a murine albumin promoter expressed high plasma TGF-b1 levels as well as a subendothelial type I ollagen aumulation in the glomeruli and proteinuria in the severely affeted mie. 36,37 We hypothesize that the deposition of type I ollagen in the mesangial matrix and the subendothelial spae results in impaired podoyte/endothelial ell interations, podoyte foot proess effaement, inreased proteinuria, and is responsible for the progressive glomerular funtional deline. 38 In situ hybridization analyses of Col1a2-defiient, heterozygous, and wild-type kidneys demonstrated no temporal or Kidney International (27) 71,
6 o r i g i n a l a r t i l e AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy spatial differenes in proa1(i) and proa2(i) ollagen steadystate mrna levels. However, subsequent quantitative RT- PCR was performed due to insensitivity of in situ hybridization to quantitative hanges and demonstrated a signifiant inrease in proa1(i) ollagen mrna in 1-month Col1a2- defiient animals, as ompared with age-mathed heterozygous and wild-type animals. The presene of inreased steady-state proa1(i) and proa2(i) ollagen mrna levels normally at early ages may be due to developmental hanges and thus mask any differenes that might be ourring due to initiation of the glomerulopathy. Furthermore, the quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed on whole kidney setions, and to larify whether proa1(i) and proa2(i) ollagen steady-state mrna inreases our with initiation of disease, quantitative RT-PCR analyses needs to be performed on isolated glomeruli. Under normal physiologi onditions, a balane exists between synthesis and degradation of type I ollagen and other ECM omponents. To maintain homeostasis, synthesis and degradation must remain balaned. However, in disease states, the balane is often disrupted resulting in inreased synthesis and/or dereased degradation, and thus, aumulation of ECM omponents. 39 Steady-state levels of proa1(i) ollagen mrna were inreased by twofold in 1-month-old Col1a2-defiient animals relative to age-mathed heterozygous and wild-type animals, suggesting that the aberrant aumulation is due, at least in part, to a pretranslational inrease in type I ollagen gene expression. Type I ollagen degradation is regulated by MMPs and their assoiated tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). In a rat model of proliferative glomerulonephritis glomerular type I and IV ollagen deposition is assoiated with dereased MMP-9 steady-state mrna expression without differenes in expression of TIMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-13, MT1-MMP, type I ollagen, or type IV ollagen steady-state mrna. 3 This ontrasts the ICR-derived glomerulonephritis mie (ICGN) mouse model of idiopathi nephriti syndrome that demonstrates proteinuria, hypoproteinemia, and hyperlipidemia as well as type I ollagen deposition in their glomeruli. 28,29,31 ICGN mie have dereased MMP-1, 2, and 9 ativity 28 with a orresponding derease in MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 protein. 29 Subsequent studies of ICGN mie also demonstrate inreased steady-state proa1(i) ollagen and proa1(iii) ollagen mrna levels relative to ontrol animals. 31 Therefore, deposition of ECM omponents in the ICGN mouse result from inreased pretranslational synthesis as well as dereased degradative apaity of renal MMPs. The TGF-b transgeni mie also demonstrate glomerular type I ollagen deposition assoiated with inreased steady-state a1(i) mrna levels in young mie and inreased ativity of MMP-2 and TIMP-1 in severely affeted animals indiating that in the presene of elevated TGF-b, glomerular ollagen deposition is the result of an imbalane in pretranslational synthesis and degradative apaities mediated by MMP/TIMP interations. 25 Despite inreased proa1(i) ollagen mrna levels, we annot rule out that dereased MMP enzyme expression and/or ativity may ontribute to the glomerular type I ollagen aumulation in Col1a2-defiient animals. Partiularly, as 1-month heterozygous animals also demonstrate glomerular deposition without a signifiant inrease in ollagen gene expression as measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Our findings are also onsistent with the onept that the glomerular ollagen deposition seen in the Col1a2-defiient mie may represent overompensation of the glomerular wound healing response. Wild-type rat mesangial ells when subjeted to tissue ulture produe type I ollagen of whih more than 5% is homotrimeri. We postulate that the type I ollagen aumulation in Col1a2-defiient mie reflets an injury response to the initiation of inreased glomerular apillary pressures that ours with glomerular maturation (funtional ativation). Inreased glomerular apillary pressure is known to be tightly assoiated with inreased ECM prodution, mesangial expansion, and progression of glomeruloslerosis. 4,41 Moreover, we previously demonstrated that Col1a2-defiient mie have redued biomehanial integrity of the aorta. 42,43 If the glomerular apillaries have similar dereased vasular integrity then funtional ativation of the glomeruli may indue the wound response owing to altered mehanial strain on the apillaries. Though TGF-b, onnetive tissue growth fator, and the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/akt-signaling pathway are impliated in ellular sensing of mehanial strain in mesangial ells, whether these fators or even mehanial strain plays a role in homotrimeri type I ollagen deposition remains to be eluidated. 41,44 In summary, we demonstrated that the type I ollagen glomerulopathy affets heterozygous animals in a dose response manner, initiates postnatally following a pattern of glomerular maturation, and is progressive resulting in impaired renal funtion. We also suggest mehanistially that the glomerulopathy is due, in part, to pretranslational upregulation of proa1(i) ollagen mrna expression and suggests that further investigation is needed to determine in vivo expression and ativity of MMPs in Col1a2-defiient mie. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals Homozygous B6C3Fe a/a- Col1a2 oim/j (Col1a2-defiient, / ); heterozygous ( / þ ) and wild-type ( þ / þ ) mie were purhased from Jakson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). Animals were housed in an AAALAC aredited animal faility, provided with water and food (Purina 58 Formulab Diet; Purina Mills In., Rihmond, IN) ad libitum, and ared for in aordane with an approved University of Missouri Animal Care and Use protool. þ / þ, þ /, and / genotypes were determined by PCR-restrition fragment-length polymorphism analysis. 45 Animals were divided into four age groups, 1 month (n ¼ 52 mie), 2 weeks (n ¼ 56), 1 week (n ¼ 55), and 1 day (n ¼ 26) of age. Animals were killed and kidneys were harvested. The right kidney was snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at 81C. The left kidney was fixed in 1% neutral-buffered formalin for 48 h. 99 Kidney International (27) 71,
7 AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy o r i g i n a l a r t i l e Mirosopy Formalin-fixed kidneys embedded in paraffin were setioned longitudinally (5 mm) and stained with Pirosirius red stain. Glomeruli within individual setions were examined in a blinded fashion and a glomerular lesion sore for eah individual kidney was determined. Glomerular lesion sores were determined using the following sale: G1 mild lesions; p5% of glomeruli affeted; G2 moderate lesions; p5% of glomeruli affeted; G3 moderate lesions; X5% glomeruli affeted; G4 severe lesions; X5% of glomeruli affeted. A positive orrelation was demonstrated between the amount of ollagen deposited in the glomeruli and the lesion sore assigned to the mouse. 1 Morphometry mapping Pirosirius red-stained kidney setions from 1-month- (n ¼ 1 / (lesion sore G2 4), n ¼ 1 þ / þ (lesion sore G), and n ¼ 1 þ / (lesion sore G1 4)) and 2-week-(n ¼ 1 / (lesion sore G1 3), n ¼ 1 þ / þ (lesion sore G), and n ¼ 1 þ / (lesion sore G1)) old mie were examined in a blinded fashion to assess individual glomerulus morphometry lesion distribution and severity within longitudinal setions (see Supplementary Material). Longitudinal setions were assessed using four fields of original magnifiation 2 that braketed the renal ortex, from the juxtamedullary juntion to the renal apsule. Eah field was divided into juxtamedullary and ortial halves (zones). Within eah zone, we determined number of glomeruli, number of glomeruli without ollagen deposition (assigned a morphometry sore of M ¼ ), with o25% of glomerular area oupied by ollagen (sore M ¼ 1), with 25 5% of glomerular area oupied by ollagen (sore M ¼ 2), with 5 75% of glomerular area oupied by ollagen (sore M ¼ 3), and with 75 1% of glomerular area oupied by ollagen (sore M ¼ 4). A total sore for eah animal was then determined by multiplying the number of glomeruli in eah ategory by their respetive morphometry sore, adding the sores, and dividing by the total number of glomeruli. For example, if 4 glomeruli were found in the four ortial fields examined and 2 had no ollagen deposition, 1 had morphometry sores of 2, eight had morphometry sores of 3, and two had morphometry sores of 4, the total sore was ((2 ) þ (1 2) þ (8 3) þ (2 4))/4 ¼ 1.3. Mean juxtamedullary and ortial glomerular morphometry sores, mean juxtamedullary and ortial glomerular numbers, mean number of affeted glomeruli, and the perentage of affeted glomeruli were determined for eah genotype at 2 weeks and 1 month of age. Eletron mirosopy Kidneys were harvested and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, 4% glutaraldehyde, and.1 M aodylate buffer and tissue proessing arried out as desribed previously. 46 Thin setions were stained with lead itrate plus uranyl aetate for transmission eletron mirosopy. 47 Reagents were purhased from Polysienes In. (Warrington, PA). Albumin to reatinine ratio To determine whether Col1a2-defiient mie exhibit miroalbuminuria, urine was olleted before killing, stored at 21C and urine albumin onentration measured using the Albuwell M kit (Exoell, Philadelphia, PA) following a 1:13 dilution of the urine sample (Animal Models of Diabeti Compliations Consortium, September, 26). Creatinine onentration was analyzed using an automated Jaffe alkaline pirate assay on a urine sample diluted 1:2. Quantitative RT-PCR Snap-frozen kidneys from 1-month- (n ¼ 6 / (lesion sore G3 4), n ¼ 6 þ / þ (lesion sore G), and n ¼ 6 þ / (lesion sore G1 4)), 2-week- (n ¼ 7 / (lesion sore G1 4), n ¼ 6 þ / þ (lesion soreg),andn ¼ 6 þ / (lesion sore G1)), and 1-week- (n ¼ 6 / (lesion sore G1 2), n ¼ 6 þ / þ (lesion sore G), and n ¼ 7 þ / (lesion sore G1)) old mie were homogenized in TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen Corporation, Carlsbad, CA) using a TissueLyser homogenizer (QIAGEN, Valenia, CA), and total RNA isolated aording to manufaturer s protool (Invitrogen Corporation). Total RNA (5 mg) was reverse transribed with oligo(dt) primers aording to manufaturer s protool (Supersript, Invitrogen Corporation). PCR primer sequenes for Col1a1 and Col1a2 are found in Table 2. Primer sequenes for hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase have been previously reported. 48 Col1a1 and Col1a2 gene expression was quantified using real-time RT-PCR (LightCyler s ; Rohe Diagnosti Corporation, Basel, Switzerland) in a 2 ml PCR volume that ontained DNA (2 ng/ml),.5 mm of forward and reverse primers, 3 mm MgCl 2, SYBR & green, and QuantiTet TM SYBR & Green PCR Master Mix, whih ontains dntp mix, HotStart Taq DNA Polymerase, reation buffer I, and SYBR & green (QIAGEN). 49,5 Copy number of the desired genes was determined through generation of a standard urve using known onentrations, opies of the PCR-Blunt II-TOPO (Invitrogen Corporation) plasmid, whih ontains the amplion of interest that was previously loned. The PCR reations for Col1a1 and Col1a2 were inubated at 951C for 15 min to ativate the polymerase followed by 4 yles (15 s denaturation, 941C; 3 s annealing, 61C; 3 s extension, 721C). Fluoresene was monitored at the end of eah extension phase at 81C (5 s) and values were normalized to hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase levels. Table 2 Primer sequenes used for in situ hybridization and quantitative reverse transriptase-pcr analysis Primer GI number Sequene Nuleotide segment Amplion size ISH and RT-PCR COL1A1 forward AGC CTG AGT CAG CAG ATT GAG A bp COL1A1 reverse CTT GCA GTG ATA GGT GAT GTT CT ISH COL1A2 forward CTT CTT GGT GCT CCC GGT ATT CT bp COL1A2 reverse TTT TGG AGC AGC CAT CGA CTA RT-PCR COL1A2 forward TGA AGT GGG TCT TCC AGG TCT TTC bp COL1A2 reverse CAC CCT TGT TAC CGG ATT CTC CTT ISH, in situ hybridization; RT-PCR, reverse transriptase-polymerase hain reation. Kidney International (27) 71,
8 o r i g i n a l a r t i l e AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy Statistis Statistial analyses were performed using SAS (SAS Institute In., Cary, NC). Morphometry data were analyzed as a split plot in spae. The main plot ontains effets of gene, age, and the interations between genotype and age. The subplot ontains effets of side (ortial versus juxtamedullary) and all possible interations between side and the main plot effets. Polynomial orthogonal ontrasts were performed to test for linear and/or quadrati gene dose effet. Urine data was analyzed as a one-way ompletely randomized design analysis of variane. The RT-PCR data was analyzed as a ompletely randomized design in whih genotype and age were arranged as a 3/3 fatorial (three genotypes, three ages). Owing to heterogeneous varianes among albumin to reatinine ratios and among opy numbers, log transformations were used to stabilize the variation. Data presented are the atual mean and standard error but the differenes within genotype and lesion sore were analyzed using the transformed data sets. Mean differenes were asertained using Fisher s least signifiant differene. All results are presented as mean7s.e. Differenes were onsidered to be statistially signifiant at Po.5. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We are grateful to Stephanie Carleton, Brent Pfeiffer, and Anna Roberts-Pilgrim for assistane in speimen olletion, Allison Howard and Dr Matt Myles for assistane in the RT-PCR analyses, Jeanette Cunningham for assistane with eletron mirosopy, Howard Wilson and Elaine Brodeur for assistane in generating the digital and fine artwork depited, Dr Charles Wiedmeyer for urine analysis, and Dr Mark Ellersiek for the statistial analysis. This work was supported by Leda J Sears Trust Foundation Grant and NIH/NIDDK, R21DK SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary information is available on Kidney International website. REFERENCES 1. Phillips CL, Pfeiffer BJ, Luger AM et al. Novel ollagen glomerulopathy in a homotrimeri type I ollagen mouse (oim). Kidney Int 22; 62: Jimenez SA, Bashey RI, Benditt M et al. Identifiation of ollagen alpha1(i) trimer in embryoni hik tendons and alvaria. Biohem Biophys Res Commun 1977; 78: Yoshioka K, Tohda M, Takemura T et al. Distribution of type I ollagen in human kidney diseases in omparison with type III ollagen. J Pathol 199; 162: Couser WG, Johnson RJ. Mehanisms of progressive renal disease in glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 1994; 23: Glik AD, Jaobson HR, Haralson MA. Mesangial deposition of type I ollagen in human glomeruloslerosis. Hum Pathol 1992; 23: MLennan SV, Death AK, Fisher EJ et al. The role of the mesangial ell and its matrix in the pathogenesis of diabeti nephropathy. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1999; 45: Haralson MA, Jaobson HR, Hoover RL. Collagen polymorphism in ultured rat kidney mesangial ells. Lab Invest 1987; 57: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Yoshimura A et al. The ativated mesangial ell: a glomerular myofibroblast? J Am So Nephrol 1992; 2: S Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T et al. Robbins Pathologi Basis of Disease. 6th edn. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, Cohen IK, Diegelmann RF, Lindblad WJ. Wound Healing : Biohemial & Clinial Aspets. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co., Sriver CR. The Metaboli Basis of Inherited Disease. 6th edn, New York: MGraw-Hill, Rupard JH, Dimari SJ, Damjanov I et al. Synthesis of type I homotrimer ollagen moleules by ultured human lung adenoarinoma ells. Am J Pathol 1988; 133: Uitto J. Collagen polymorphism: isolation and partial haraterization of alpha 1(I)-trimer moleules in normal human skin. Arh Biohem Biophys 1979; 192: Ghersi G, La Fiura AM, Minafra S. Diret adhesion to type I and homotrimer ollagens by breast arinoma and embryoni epithelial ells in ulture: a omparative study. Eur J Cell Biol 1989; 5: Moro L, Smith BD. Identifiation of ollagen alpha1(i) trimer and normal type I ollagen in a polyoma virus-indued mouse tumor. Arh Biohem Biophys 1977; 182: Deak SB, Niholls A, Pope FM et al. The moleular defet in a nonlethal variant of osteogenesis imperfeta. Synthesis of pro-alpha 2(I) hains whih are not inorporated into trimers of type I proollagen. J Biol Chem 1983; 258: MBride DJ, Choe V, Shapiro JR et al. Altered ollagen struture in mouse tail tendon laking the alpha 2(I) hain. J Mol Biol 1997; 27: Chipman SD, Sweet HO, MBride DJ et al. Defetive pro alpha 2(I) ollagen synthesis in a reessive mutation in mie: a model of human osteogenesis imperfeta. Pro Natl Aad Si USA 1993; 9: Andrews KL, Betsuyaku T, Rogers S et al. Gelatinase B (MMP-9) is not essential in the normal kidney and does not influene progression of renal disease in a mouse model of Alport syndrome. Am J Pathol 2; 157: Spitzer A, Brandis M. Funtional and morphologi maturation of the superfiial nephrons. Relationship to total kidney funtion. J Clin Invest 1974; 53: Kleinman LI, Reuter JH. Maturation of glomerular blood flow distribution in the new-born dog. J Physiol 1973; 228: Bard J. Embryos: Color Atlas of Development. London Wolfe, Potter EL. Development of the human glomerulus. Arh Pathol 1965; 8: Aperia A, Herin P. Development of glomerular perfusion rate and nephron filtration rate in rats 17 6 days old. Am J Physiol 1975; 228: Mozes MM, Bottinger EP, Jaot TA et al. Renal expression of fibroti matrix proteins and of transforming growth fator-beta (TGF-beta) isoforms in TGF-beta transgeni mie. J Am So Nephrol 1999; 1: Franki A, Bradshaw AD, Bassuk JA et al. SPARC regulates the expression of ollagen type I and transforming growth fator-beta1 in mesangial ells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: Chatziantoniou C, Boffa JJ, Ardaillou R et al. Nitri oxide inhibition indues early ativation of type I ollagen gene in renal resistane vessels and glomeruli in transgeni mie. Role of endothelin. J Clin Invest 1998; 11: Uhio K, Manabe N, Tamura K et al. Dereased matrix metalloproteinase ativity in the kidneys of hereditary nephroti mie (ICGN strain). Nephron 2; 86: Uhio-Yamada K, Manabe N, Goto Y et al. Dereased expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase in the kidneys of hereditary nephroti (ICGN) mie. J Vet Med Si 25; 67: Tomita M, Koike H, Han GD et al. Dereased ollagen-degrading ativity ould be a marker of prolonged mesangial matrix expansion. Clin Exp Nephrol 24; 8: Uhio K, Manabe N, Yamaguhi-Yamada M et al. Changes in the loalization of type I, III and IV ollagen mrnas in the kidneys of hereditary nephriti (ICGN) mie with renal fibrosis. J Vet Med Si 24; 66: Zlotogora J. Dominane and homozygosity. Am J Med Genet 1997; 68: Rousseau F, Bonaventure J, Legeai-Mallet L et al. Mutations in the gene enoding fibroblast growth fator reeptor-3 in ahondroplasia. Nature 1994; 371: Pavenstadt H, Kriz W, Kretzler M. Cell biology of the glomerular podoyte. Physiol Rev 23; 83: Laurens W, Battaglia C, Foglieni C et al. Diret podoyte damage in the single nephron leads to albuminuria in vivo. Kidney Int 1995; 47: Sanderson N, Fator V, Nagy P et al. Hepati expression of mature transforming growth fator beta 1 in transgeni mie results in multiple tissue lesions. Pro Natl Aad Si USA 1995; 92: Kopp JB, Fator VM, Mozes M et al. Transgeni mie with inreased plasma levels of TGF-beta 1 develop progressive renal disease. Lab Invest 1996; 74: Kidney International (27) 71,
9 AC Brodeur et al.: Type I ollagen glomerulopathy o r i g i n a l a r t i l e 38. Remuzzi G, Bertani T. Pathophysiology of progressive nephropathies. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: Lenz O, Elliot SJ, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Matrix metalloproteinases in renal development and disease. J Am So Nephrol 2; 11: Hostetter TH, Olson JL, Rennke HG et al. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. J Am So Nephrol 21; 12: Cortes P, Riser BL, Yee J et al. Mehanial strain of glomerular mesangial ells in the pathogenesis of glomeruloslerosis: linial impliations. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1999; 14: Pfeiffer BJ, Franklin CL, Hsieh FH et al. Alpha 2(I) ollagen defiient oim mie have altered biomehanial integrity, ollagen ontent, and ollagen rosslinking of their thorai aorta. Matrix Biol 25; 24: Vouyouka AG, Pfeiffer BJ, Liem TK et al. The role of type I ollagen in aorti wall strength with a homotrimeri [a1(i)] 3 ollagen mouse model. J Vas Surg 21; 33: Krepinsky JC, Li Y, Chang Y et al. Akt mediates mehanial strain-indued ollagen prodution by mesangial ells. J Am So Nephrol 25; 16: Phillips CL, Bradley DA, Shlotzhauer CL et al. Oim mie exhibit altered femur and inisor mineral omposition and dereased bone mineral density. Bone 2; 27: Noakes PG, Miner JH, Gautam M et al. The renal glomerulus of mie laking s-laminin/laminin beta 2: nephrosis despite moleular ompensation by laminin beta 1. Nat Genet 1995; 1: Kikkawa Y, Virtanen I, Miner JH. Mesangial ells organize the glomerular apillaries by adhering to the G domain of laminin alpha5 in the glomerular basement membrane. J Cell Biol 23; 161: O Garra A, Chang R, Go N et al. Ly-1 B (B-1) ells are the main soure of B ell-derived interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol 1992; 22: Morrison TB, Weis JJ, Wittwer CT. Quantifiation of low-opy transripts by ontinuous SYBR Green I monitoring during amplifiation. Biotehniques 1998; 24: , 96, Bustin SA. Absolute quantifiation of mrna using real-time reverse transription polymerase hain reation assays. J Mol Endorinol 2; 25: Kidney International (27) 71,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
GLOMERULAR DEPOSITION OF HOMOTRIMERIC TYPE I COLLAGEN IN THE COL1A2 DEFICIENT MOUSE
 GLOMERULAR DEPOSITION OF HOMOTRIMERIC TYPE I COLLAGEN IN THE COL1A2 DEFICIENT MOUSE A Dissertation presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri-Columbia In Partial Fulfillment
GLOMERULAR DEPOSITION OF HOMOTRIMERIC TYPE I COLLAGEN IN THE COL1A2 DEFICIENT MOUSE A Dissertation presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School University of Missouri-Columbia In Partial Fulfillment
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 3. 3 UTR primer sequences. Primer sequences used to amplify and clone the 3 UTR of each indicated gene are listed.
 Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
describing DNA reassociation* (renaturation/nucleation inhibition/single strand ends)
 Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay. Nucleotide sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
c Tuj1(-) apoptotic live 1 DIV 2 DIV 1 DIV 2 DIV Tuj1(+) Tuj1/GFP/DAPI Tuj1 DAPI GFP
 Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER
 J. Cell Si. 30, 117-128 (1978) Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited igys THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER STUART HODSON
J. Cell Si. 30, 117-128 (1978) Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited igys THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER STUART HODSON
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
Sequence Analysis using Logic Regression
 Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
Systematic Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Mercury Concentrations
 Systemati Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Merury Conentrations Tom Grieb 1, Roxanne Karimi 2, Niholas Fisher 2, Leonard Levin 3 (1) Tetra Teh, In., Lafayette, CA, USA; (2) State University of New York,
Systemati Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Merury Conentrations Tom Grieb 1, Roxanne Karimi 2, Niholas Fisher 2, Leonard Levin 3 (1) Tetra Teh, In., Lafayette, CA, USA; (2) State University of New York,
CD31 5'-AGA GAC GGT CTT GTC GCA GT-3' 5 ' -TAC TGG GCT TCG AGA GCA GT-3'
 Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most
 Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Effect of Curing Conditions on Hydration Reaction and Compressive Strength Development of Fly Ash-Cement Pastes
 Effet of Curing Conditions on Hydration Reation and Development of Fly Ash-Cement Pastes Warangkana Saengsoy Candidate for the degree of Dotor of Philosophy Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Toyoharu Nawa Division
Effet of Curing Conditions on Hydration Reation and Development of Fly Ash-Cement Pastes Warangkana Saengsoy Candidate for the degree of Dotor of Philosophy Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Toyoharu Nawa Division
Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human embryoid body preparations contain non-cardiac structures. In early studies, infarcted hearts
 a Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human emryoid ody preparations ontain non-ardia strutures. In early studies, infarted hearts reeived ell preparations of low ardia purity (
a Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human emryoid ody preparations ontain non-ardia strutures. In early studies, infarted hearts reeived ell preparations of low ardia purity (
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards
 Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Learned spatiotemporal sequence recognition and prediction in primary visual cortex
 Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Information Computational Methods
 Supplementary Information Computational Methods Data preproessing In this setion we desribe the preproessing steps taken to establish the data matrix of hepatoyte single ell gene expression data (Table
Supplementary Information Computational Methods Data preproessing In this setion we desribe the preproessing steps taken to establish the data matrix of hepatoyte single ell gene expression data (Table
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and cdna sequences of the targeted regions in WT-KI and
 Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
phosphatidylcholine by high performance liquid chromatography: a partial resolution of molecular species
 A large-sale purifiation of phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylholine by high performane liquid hromatography: a partial resolution of moleular speies R. S. Fager,
A large-sale purifiation of phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylholine by high performane liquid hromatography: a partial resolution of moleular speies R. S. Fager,
Keywords: congested heart failure,cardiomyopathy-targeted areas, Beck Depression Inventory, psychological distress. INTRODUCTION:
 International Journal of Medial Siene and Eduation An offiial Publiation of Assoiation for Sientifi and Medial Eduation (ASME) Original Researh Artile ASSOCIATION BETWEEN QUALITY OF LIFE AND ANXIETY, DEPRESSION,
International Journal of Medial Siene and Eduation An offiial Publiation of Assoiation for Sientifi and Medial Eduation (ASME) Original Researh Artile ASSOCIATION BETWEEN QUALITY OF LIFE AND ANXIETY, DEPRESSION,
Impaired acetaldehyde oxidation in alcoholics*
 Impaired aetaldehyde oxidation in aloholis* K R PALMR and W J JNKINSt From the Aademi Department of Mediine, Royal Free Hospital, London Gut, 1982, 23, 729-733 SUMMARY High blood aetaldehyde levels in
Impaired aetaldehyde oxidation in aloholis* K R PALMR and W J JNKINSt From the Aademi Department of Mediine, Royal Free Hospital, London Gut, 1982, 23, 729-733 SUMMARY High blood aetaldehyde levels in
clinical conditions using a tape recorder system
 Thorax (1964), 19, 125 Objetive assessment of ough suppressants under linial onditions using a tape reorder system C. R. WOOLF AND A. ROSENBERG From the Respiratory Unit, Sunnybrook Hospital (Department
Thorax (1964), 19, 125 Objetive assessment of ough suppressants under linial onditions using a tape reorder system C. R. WOOLF AND A. ROSENBERG From the Respiratory Unit, Sunnybrook Hospital (Department
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res. 2010; 1(4): 144-148 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 4, Sep 2010 www.biomedsidiret.om ISSN: 0976:6685 BioMedSiDiret Publiations Contents lists available at BioMedSiDiret Publiations
Int J Biol Med Res. 2010; 1(4): 144-148 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 4, Sep 2010 www.biomedsidiret.om ISSN: 0976:6685 BioMedSiDiret Publiations Contents lists available at BioMedSiDiret Publiations
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependence of Radiation Induced Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1
 Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at
 Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Interrelationships of Chloride, Bicarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum
 Interrelationships of Chloride, Biarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum LEsLE A. TURNBERG, FREDERICK A. BIEBERDORF, STEPHEN G. MORAWSKI, and JOHN S. FORDTRAN From the Department of
Interrelationships of Chloride, Biarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum LEsLE A. TURNBERG, FREDERICK A. BIEBERDORF, STEPHEN G. MORAWSKI, and JOHN S. FORDTRAN From the Department of
Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc YFP N
 MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
Reversal of ammonia coma in rats by L-dopa: a peripheral effect
 Gut, 1979, 2, 28-32 Reversal of ammonia oma in rats by L-dopa: a peripheral effet L. ZV1, W. M. DOZAK, AND R. F. DRR From the Department of Mediine, Hennepin ounty Medial enter and Minneapolis Veterans
Gut, 1979, 2, 28-32 Reversal of ammonia oma in rats by L-dopa: a peripheral effet L. ZV1, W. M. DOZAK, AND R. F. DRR From the Department of Mediine, Hennepin ounty Medial enter and Minneapolis Veterans
Unit 02 - The Inside Story about Nutrition and Health. True / False
 True / False 1. Geneti traits exert the strongest overall influene on health and longevity. False 2. The bodies of modern humans adapted to exist on a diet of wild game, fish, fruits, nuts, seeds, roots,
True / False 1. Geneti traits exert the strongest overall influene on health and longevity. False 2. The bodies of modern humans adapted to exist on a diet of wild game, fish, fruits, nuts, seeds, roots,
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as a Biomarker in Children with Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder 1* 2 2 2
 JKIMSU, Vol. 4, No. 4, Ot-De 2015 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain-Derived Neurotrophi Fator as a Biomarker in Children with Attention Defiit-Hyperativity Disorder 1* 2 2 2 Farshid Saadat, Maryam
JKIMSU, Vol. 4, No. 4, Ot-De 2015 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain-Derived Neurotrophi Fator as a Biomarker in Children with Attention Defiit-Hyperativity Disorder 1* 2 2 2 Farshid Saadat, Maryam
The comparison of psychological evaluation between military aircraft noise and civil aircraft noise
 The omparison of psyhologial evaluation between military airraft noise and ivil airraft noise Makoto MORINAGA ; Ippei YAMAMOTO ; Hidebumi TSUKIOKA ; Koihi MAKINO 2, Sonoko KUWANO 3, Mitsuo MATSUMOTO 4
The omparison of psyhologial evaluation between military airraft noise and ivil airraft noise Makoto MORINAGA ; Ippei YAMAMOTO ; Hidebumi TSUKIOKA ; Koihi MAKINO 2, Sonoko KUWANO 3, Mitsuo MATSUMOTO 4
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
The effects of bilingualism on stuttering during late childhood
 Additional information is published online only at http:// ad.bmj.om/ontent/vol93/ issue11 1 Division of Psyhology and Language Sienes, University College London, London, UK; 2 Department of Language and
Additional information is published online only at http:// ad.bmj.om/ontent/vol93/ issue11 1 Division of Psyhology and Language Sienes, University College London, London, UK; 2 Department of Language and
Study of Necrosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mice
 THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 3, NO. 1, pp. 58 62, January, 2013 Study of Nerosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mie Ahmad Soni,
THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 3, NO. 1, pp. 58 62, January, 2013 Study of Nerosis in the Liver of Formaldehyde and Benzo(α)Pyrene Exposured-Mie Ahmad Soni,
Department of Virology, Wellcome Research Laboratories, Langley Court, Beckenham, Kent BR3 3BS, U.K. and heterologous virus challenge.
 Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Defective neutrophil function in low-birth-weight,
 J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:366-37 Defetive neutrophil funtion in low-birth-weight, premature infants H AL-HADITHY, IE ADDISON, AH GOLDSTONE, JC CAWLEY, AND JC SHAW From the Departments of Haematology and Paediatris,
J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:366-37 Defetive neutrophil funtion in low-birth-weight, premature infants H AL-HADITHY, IE ADDISON, AH GOLDSTONE, JC CAWLEY, AND JC SHAW From the Departments of Haematology and Paediatris,
Culture Density (OD600) 0.1. Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600)
 A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
A novel approach to regulate cell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH. formations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae induced by air cold plasma 1
 A novel approah to regulate ell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH formations in Saharomyes erevisiae indued by air old plasma 1 Xiaoyu DONG ( 董晓宇 ), Tingting LIU ( 刘婷婷 ), Yuqin XIONG ( 熊玉琴 ) Shool
A novel approah to regulate ell membrane permeability for ATP and NADH formations in Saharomyes erevisiae indued by air old plasma 1 Xiaoyu DONG ( 董晓宇 ), Tingting LIU ( 刘婷婷 ), Yuqin XIONG ( 熊玉琴 ) Shool
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT METHODS OF PRESERVATION ON THE QUALITY OF CATTLE AND GOAT MEAT. Abstract
 Bang. J. Anim. Si. 2009, 38(1&2) : 86 91 ISSN 0003-3588 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT METHODS OF PRESERVATION ON THE QUALITY OF CATTLE AND GOAT MEAT S. Bin. Faisal, S. Akhter 1 and M. M. Hossain Abstrat The study
Bang. J. Anim. Si. 2009, 38(1&2) : 86 91 ISSN 0003-3588 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT METHODS OF PRESERVATION ON THE QUALITY OF CATTLE AND GOAT MEAT S. Bin. Faisal, S. Akhter 1 and M. M. Hossain Abstrat The study
A 90-Day Chloroform Inhalation Study in F-344 Rats: Profile of Toxicity and Relevance to Cancer Studies
 FUNDAMENTAL AND APPLIED TOXICOLOGY 32, 109-125 (1996) ARTICLE NO. 0113 A 90-Day Chloroform Inhalation Study in F-344 Rats: Profile of Toxiity and Relevane to Caner Studies MICHAEL V. TEMPLIN, JEFFREY L.
FUNDAMENTAL AND APPLIED TOXICOLOGY 32, 109-125 (1996) ARTICLE NO. 0113 A 90-Day Chloroform Inhalation Study in F-344 Rats: Profile of Toxiity and Relevane to Caner Studies MICHAEL V. TEMPLIN, JEFFREY L.
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
KidneyParenchyma. Kidney (Renal Parenchyma)
 http://web2.fas.org/stage/kidneyparenhyma/shema.html for TNM 7 - Revised 01/21/2010 Kidney (Renal Parenhyma) C64.9 C64.9 Kidney, NOS (Renal parenhyma) Note: Laterality must be oded for this site. CS Tumor
http://web2.fas.org/stage/kidneyparenhyma/shema.html for TNM 7 - Revised 01/21/2010 Kidney (Renal Parenhyma) C64.9 C64.9 Kidney, NOS (Renal parenhyma) Note: Laterality must be oded for this site. CS Tumor
Increased Glomerular Thromboxane Synthesis as a Possible Cause of Proteinuria in Experimental Nephrosis
 nreased Glomerular Thromboxane Synthesis as a Possible Cause of Proteinuria in xperimental Nephrosis G. Remuzzi, L. mberti, M. Rossini, C. Morelli, C. Carminati, G. M. Cattaneo, and T. Bertani Mario Negri
nreased Glomerular Thromboxane Synthesis as a Possible Cause of Proteinuria in xperimental Nephrosis G. Remuzzi, L. mberti, M. Rossini, C. Morelli, C. Carminati, G. M. Cattaneo, and T. Bertani Mario Negri
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Cyclic Fluctuations of the Alveolar Carbon Dioxide Tension during the Normal Menstrual Cycle
 Cyli Flutuations of the Alveolar Carbon Dioxide Tension during the Normal Menstrual Cyle Ruth L. Goodland, M.S., and W. T. Pommerenke, Ph.D., M.D. THE SHORT spa~ of funtional life of the unfertilized human
Cyli Flutuations of the Alveolar Carbon Dioxide Tension during the Normal Menstrual Cyle Ruth L. Goodland, M.S., and W. T. Pommerenke, Ph.D., M.D. THE SHORT spa~ of funtional life of the unfertilized human
without LOI phenotype by breeding female wild-type C57BL/6J and male H19 +/.
 Sakatani et al. 1 Supporting Online Material Materials and methods Mice and genotyping: H19 mutant mice with C57BL/6J background carrying a deletion in the structural H19 gene (3 kb) and 10 kb of 5 flanking
Sakatani et al. 1 Supporting Online Material Materials and methods Mice and genotyping: H19 mutant mice with C57BL/6J background carrying a deletion in the structural H19 gene (3 kb) and 10 kb of 5 flanking
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustrating major conclusions of this study.
 ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
collagen-induced arthritis
 Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 92, pp. 517-521, January 1995 Medial Sienes Leukotriene B4 plays a ritial role in the progression of ollagen-indued arthritis R. J. GRIFFITHS*, E. R. PETrIPHER, K. KOCH, C.
Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 92, pp. 517-521, January 1995 Medial Sienes Leukotriene B4 plays a ritial role in the progression of ollagen-indued arthritis R. J. GRIFFITHS*, E. R. PETrIPHER, K. KOCH, C.
The effect of enalapril on the renal response to tilting in humans
 Br. J. lin. Pharma. (1989), 27, 191197 The effet of enalapril on the renal response to tilting in humans N. P. LWS & D. R. FRGUSON Department of Pharmaology, University of ambridge, Hills Road, ambridge
Br. J. lin. Pharma. (1989), 27, 191197 The effet of enalapril on the renal response to tilting in humans N. P. LWS & D. R. FRGUSON Department of Pharmaology, University of ambridge, Hills Road, ambridge
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
marker, followed by digital limits) 0.04% (0.02%)) but infiltration of macrophages was detected in minimal change nephropathy (0.29% (0.
 1181 Jlin Pathol 1997;:118-1 Papers Pathology, Leiester General Hospital, Gwendolen Road, Leiester LE 4PW P N Furness Nephrology K P G Harris Pathology, Leiester Royal nfirmary, PO Box 6, Leiester LE 7LX
1181 Jlin Pathol 1997;:118-1 Papers Pathology, Leiester General Hospital, Gwendolen Road, Leiester LE 4PW P N Furness Nephrology K P G Harris Pathology, Leiester Royal nfirmary, PO Box 6, Leiester LE 7LX
Urbanization and childhood leukaemia in Taiwan
 C International Epidemlologial Assoiation 1998 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 199827:587-591 Urbanization and hildhood leukaemia in Taiwan Chung-Yi Li, a Ruey S Iin b and
C International Epidemlologial Assoiation 1998 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 199827:587-591 Urbanization and hildhood leukaemia in Taiwan Chung-Yi Li, a Ruey S Iin b and
Sodium-Potassium-Activated Adenosine Triphosphatase
 Sodium-Potassium-Ativated Adenosine Triphosphatase of Brain Mirosomes: Modifiation of Sodium Inhibition by Diphenylhydantoins GORG J. SIGL and BVRLY B. GOODWIN From the Departments of Neurology and Physiology,
Sodium-Potassium-Ativated Adenosine Triphosphatase of Brain Mirosomes: Modifiation of Sodium Inhibition by Diphenylhydantoins GORG J. SIGL and BVRLY B. GOODWIN From the Departments of Neurology and Physiology,
Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mechanistic insight from a mathematical model of oscillating neuroendocrine dynamics
 Kim et al. RESEARCH arxiv:63.2773v [q-bio.nc] 9 Mar 26 Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mehanisti insight from a mathematial model of osillating neuroendorine dynamis Lae Kim, Maria
Kim et al. RESEARCH arxiv:63.2773v [q-bio.nc] 9 Mar 26 Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mehanisti insight from a mathematial model of osillating neuroendorine dynamis Lae Kim, Maria
% of Nestin-EGFP (+) cells
 8 7 6 3 Nestin CD % of Nestin-EGFP (+) ells 8 6 Nestin-EGFP Marge Nestin-EGFP Marge Expression levels of Expression levels of Tumorigeniity y stemness markers ifferentiation markers limiting ilution assay
8 7 6 3 Nestin CD % of Nestin-EGFP (+) ells 8 6 Nestin-EGFP Marge Nestin-EGFP Marge Expression levels of Expression levels of Tumorigeniity y stemness markers ifferentiation markers limiting ilution assay
between normal children and children with primary
 Arhives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 224-228 odium transport in erythroytes: differenes between normal hildren and hildren with primary and seondary hypertension M UCHIYAMA, V HAH, C E DAMAN WILLEM,
Arhives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 224-228 odium transport in erythroytes: differenes between normal hildren and hildren with primary and seondary hypertension M UCHIYAMA, V HAH, C E DAMAN WILLEM,
A smart acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive. live cell mrna imaging by the target-triggered intracellular self-assembly
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT. Keywords: Medical, Optimization, Modelling, Oscillation, Noise characteristics.
 PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Agonist-Induced Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation in Rat Thoracic Aorta May Be Mediated through cgmp
 352 Agonist-Indued Endothelium-Dependent in Rat Thorai Aorta May Be Mediated through Robert M. Rapoport and Ferid Murad From the Departments of Mediine and Pharmaology, Stanford University Shool of Mediine,
352 Agonist-Indued Endothelium-Dependent in Rat Thorai Aorta May Be Mediated through Robert M. Rapoport and Ferid Murad From the Departments of Mediine and Pharmaology, Stanford University Shool of Mediine,
Shift work is a risk factor for increased total cholesterol level: a 14-year prospective cohort study in 6886 male workers
 Original artile 1 Department of Oupational and Environmental Mediine, Graduate Shool of Mediine, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan; 2 Center for Preventive Medial Siene, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan; 3
Original artile 1 Department of Oupational and Environmental Mediine, Graduate Shool of Mediine, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan; 2 Center for Preventive Medial Siene, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan; 3
RADIATION DOSIMETRY INTRODUCTION NEW MODALITIES
 RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
Chemotherapy triggers HIF-1 dependent glutathione synthesis and copper chelation that induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype
 hemotherapy triggers HIF-1 dependent glutathione synthesis and opper helation that indues the breast aner stem ell phenotype Haiquan Lu a, ebangshu Samanta a, Lisha Xiang a, Huimin Zhang a, Hongxia Hu
hemotherapy triggers HIF-1 dependent glutathione synthesis and opper helation that indues the breast aner stem ell phenotype Haiquan Lu a, ebangshu Samanta a, Lisha Xiang a, Huimin Zhang a, Hongxia Hu
Reading a Textbook Chapter
 HENR.546x.APPBpp001-013 7/21/04 9:37 AM Page 1 APPENDIX B Reading a Textbook Chapter Copyright 2005 Pearson Eduation, In. 1 2 Read the following hapter from the ollege textbook Total Fitness: Exerise,
HENR.546x.APPBpp001-013 7/21/04 9:37 AM Page 1 APPENDIX B Reading a Textbook Chapter Copyright 2005 Pearson Eduation, In. 1 2 Read the following hapter from the ollege textbook Total Fitness: Exerise,
Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an Intracellular Parasite
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1984, p. 467-471 0099-2240/84/030467-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1984, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 47, No. 3 Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1984, p. 467-471 0099-2240/84/030467-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1984, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 47, No. 3 Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as
Molecular basis for the immunosuppressive action of
 Immunology 199 7 379-384 Moleular basis for the immunosuppressive ation of steari aid on T ells P. W. TEBBEY & T. M. BUTTKE Department of Mirobiology and Immunology, East Carolina University Shool of Mediine,
Immunology 199 7 379-384 Moleular basis for the immunosuppressive ation of steari aid on T ells P. W. TEBBEY & T. M. BUTTKE Department of Mirobiology and Immunology, East Carolina University Shool of Mediine,
What causes the spacing effect? Some effects ofrepetition, duration, and spacing on memory for pictures
 Memory & Cognition 1975, Vol. 3 (3), 287 294 What auses the spaing effet? Some effets ofrepetition, duration, and spaing on memory for pitures DOUGLAS 1. HNTZMAN, JEFFERY J. SUMMERS, and RCHARD A. BLOCK
Memory & Cognition 1975, Vol. 3 (3), 287 294 What auses the spaing effet? Some effets ofrepetition, duration, and spaing on memory for pitures DOUGLAS 1. HNTZMAN, JEFFERY J. SUMMERS, and RCHARD A. BLOCK
constituent amino acids in man'
 Gut, 197, 11, 25-254 Intestinal absorption of arnosine and its onstituent amino aids in man' A. M. ASATOOR, J. K. BANDOH2, A. F. LANT, M. D. MILN, AND F. NAVAB From the Medial Unit of the Westminster Hospital,
Gut, 197, 11, 25-254 Intestinal absorption of arnosine and its onstituent amino aids in man' A. M. ASATOOR, J. K. BANDOH2, A. F. LANT, M. D. MILN, AND F. NAVAB From the Medial Unit of the Westminster Hospital,
Supplementary Table 2. Conserved regulatory elements in the promoters of CD36.
 Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
METHODS JULIO A. PANZA, MD, ARSHED A. QUYYUMI, MD, JEAN G. DIODATI, MD, TIMOTHY S. CALLAHAN, MS, STEPHEN E. EPSTEIN, MD, FACC
 JACC Vol. 17. No.3 Marh 1. 1991 :657-63 657 METHODS Predition of the Frequeny and Duration of Ambulatory Myoardial Ishemia in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease by Determination of the Ishemi
JACC Vol. 17. No.3 Marh 1. 1991 :657-63 657 METHODS Predition of the Frequeny and Duration of Ambulatory Myoardial Ishemia in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease by Determination of the Ishemi
Identification of an adipose tissue-like lipoprotein lipase in perfusates of chicken liver
 Identifiation of an adipose tissue-like lipoprotein lipase in perfusates of hiken liver Andre Bensadoun and Tung Liu Koh Division of Nutritional Sienes and Division of Biologial Sienes, Cornel1 University,
Identifiation of an adipose tissue-like lipoprotein lipase in perfusates of hiken liver Andre Bensadoun and Tung Liu Koh Division of Nutritional Sienes and Division of Biologial Sienes, Cornel1 University,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate cytokine induced lung leukocyte-epithelial adhesion and injury
 British Journal of Pharmaology (27) 152, 915 929 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmaol.org RESEARCH PAPER a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate ytokine indued lung
British Journal of Pharmaology (27) 152, 915 929 & 27 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/7 $3. www.brjpharmaol.org RESEARCH PAPER a-4/b-1 and a-l/b-2 integrins mediate ytokine indued lung
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publiation lik this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/22708
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publiation lik this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/22708
Acute transcriptional up-regulation specific to osteoblasts/osteoclasts in medaka fish
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Aute transriptional up-regulation speifi to osteoblasts/osteolasts in medaka fish immediately after exposure to mirogravity Masahiro Chatani, 1, Hiroya Morimoto,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Aute transriptional up-regulation speifi to osteoblasts/osteolasts in medaka fish immediately after exposure to mirogravity Masahiro Chatani, 1, Hiroya Morimoto,
Role of the actin cytoskeleton on epithelial Na
 Kidney International, Vol. 48 (1995), pp. 970 984 Role of the atin ytoskeleton on epithelial Na hannel regulation Hoiio F. ANTIELLO Renal Unit, Massahusetts General Hospital and Department of Mediine,
Kidney International, Vol. 48 (1995), pp. 970 984 Role of the atin ytoskeleton on epithelial Na hannel regulation Hoiio F. ANTIELLO Renal Unit, Massahusetts General Hospital and Department of Mediine,
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
EXCRETION RATE ON PLASMA NICOTINE DURING
 Br. J. lin. Pharma. (1978), 5, 293-297 EFFECT OF URINARYpH AND NICOTINE EXCRETION RATE ON PLASMA NICOTINE DURING CIGARETTE SMOKING AND CHEWING NICOTINE GUM C. FEYERABEND & 1M.A.H. RUSSELL Poisons Unit,
Br. J. lin. Pharma. (1978), 5, 293-297 EFFECT OF URINARYpH AND NICOTINE EXCRETION RATE ON PLASMA NICOTINE DURING CIGARETTE SMOKING AND CHEWING NICOTINE GUM C. FEYERABEND & 1M.A.H. RUSSELL Poisons Unit,
Hepatic Iron Overload Direct HFE (HLA-H) Mutation Analysis vs Quantitative Iron Assays for the Diagnosis of Hereditary Hemochromatosis
 IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Original Artile Hepati Iron Overload Diret HE (HLA-H) Mutation Analysis vs Quantitative Iron Assays for the Diagnosis of Hereditary Hemohromatosis RIHARD D. PRESS, MD, PhD, 1 KEN LORA,
IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Original Artile Hepati Iron Overload Diret HE (HLA-H) Mutation Analysis vs Quantitative Iron Assays for the Diagnosis of Hereditary Hemohromatosis RIHARD D. PRESS, MD, PhD, 1 KEN LORA,
Evaluation of a prototype for a reference platelet
 932 Royal Postgraduate Medial Shool, Duane Road, London W12 ONN S M Lewis Western Infirmary, Glasgow R M Rowan Toa Medial Eletronis, Kobe, Japan F Kubota Correspondene to: Dr S M Lewis Aepted for publiation
932 Royal Postgraduate Medial Shool, Duane Road, London W12 ONN S M Lewis Western Infirmary, Glasgow R M Rowan Toa Medial Eletronis, Kobe, Japan F Kubota Correspondene to: Dr S M Lewis Aepted for publiation
polymorphonuclear neutrophil release of granular
 Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mechanistic insight from a mathematical model of oscillating neuroendocrine dynamics
 Kim et al. RESEARCH Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mehanisti insight from a mathematial model of osillating neuroendorine dynamis Lae Kim, Maria D Orsogna 2 and Tom Chou 3* *
Kim et al. RESEARCH Onset, timing, and exposure therapy of stress disorders: mehanisti insight from a mathematial model of osillating neuroendorine dynamis Lae Kim, Maria D Orsogna 2 and Tom Chou 3* *
Model of α-linolenic acid metabolism
 Model of α-linoleni aid metabolism N.Kokulan, C.-H. Lai Shool of Computing and Mathematial Sienes University of Greenwih London, UK RAE2012 Competitive Grant with Shool of Siene Projet progress meeting
Model of α-linoleni aid metabolism N.Kokulan, C.-H. Lai Shool of Computing and Mathematial Sienes University of Greenwih London, UK RAE2012 Competitive Grant with Shool of Siene Projet progress meeting
Spleen VAT FMO. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Ki67 DX5 CD27. CD11b 2B4 KLRG1 CD69 NKG2D CXCR3 CD44 NKG2A/C/E CD62L CD103 CD94 CD48.
 IFN (% of ells) CD7 Marophages Medium NCR LPS PMA/Ionomyin CD IFN (% of ells) T ells Marophages B ells DX CD9 KLRG NKGD B CDL CD CD CXCR CD9 CD NKGA/C/E NCR Ly9h Ly9G Ly9d Ly9i Ly9/i/h FMO CD7 CD9a CD7
IFN (% of ells) CD7 Marophages Medium NCR LPS PMA/Ionomyin CD IFN (% of ells) T ells Marophages B ells DX CD9 KLRG NKGD B CDL CD CD CXCR CD9 CD NKGA/C/E NCR Ly9h Ly9G Ly9d Ly9i Ly9/i/h FMO CD7 CD9a CD7
DEPOSITION AND CLEARANCE OF FINE PARTICLES IN THE HUMAN RESPIRATORY TRACT
 PII: S0003^t878(96)00171-8 Ann. oup. Hyg., Vol. 41, Supplement 1, pp. 503-508, 1997 1997 British Oupational Hygiene Soiety Published by Elsevier Siene Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain
PII: S0003^t878(96)00171-8 Ann. oup. Hyg., Vol. 41, Supplement 1, pp. 503-508, 1997 1997 British Oupational Hygiene Soiety Published by Elsevier Siene Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
Retraction Retracted: Study of Effect of Salvianolic Acid B on Motor Function Recovery in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury
 Hindawi BioMed Researh International Volume 217, Artile ID 8234878, 1 page https://doi.org/1.1155/217/8234878 Retration Retrated: Study of Effet of Salvianoli Aid B on Motor Funtion Reovery in Rats with
Hindawi BioMed Researh International Volume 217, Artile ID 8234878, 1 page https://doi.org/1.1155/217/8234878 Retration Retrated: Study of Effet of Salvianoli Aid B on Motor Funtion Reovery in Rats with
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Direction of active sliding of microtubules in Tetrahymena cilia (dynein/cell motility/electron microscopy)
 Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 74, No. 5, pp.2045-2049, May 1977 Cell Biology Diretion of ative sliding of mirotubules in Tetrahymena ilia (dynein/ell motility/eletron mirosopy) WINFIELD S. SALE AND PETER
Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 74, No. 5, pp.2045-2049, May 1977 Cell Biology Diretion of ative sliding of mirotubules in Tetrahymena ilia (dynein/ell motility/eletron mirosopy) WINFIELD S. SALE AND PETER
The Development and Validation of a Finite Element Model of a Canine Rib For Use With a Bone Remodeling Algorithm.
 The Development and Validation of a Finite Element Model of a Canine Rib For Use With a Bone Remodeling Algorithm. A Thesis Presented to the Faulty of the College of Engineering California Polytehni State
The Development and Validation of a Finite Element Model of a Canine Rib For Use With a Bone Remodeling Algorithm. A Thesis Presented to the Faulty of the College of Engineering California Polytehni State
Moclobemide excretion in human breast milk
 Br. J. lin. Pharma. (199), 29, 27-31 Molobemide exretion in human breast milk G. PONS', M. P. SCHORLIN2, Y. K. TAM3, C. MORAN', J. P. PFFN2, Ch. FRANCOUAL4, A. M. PDARRIOSS5, J. CHAVINI4 & G. OLIV' Departement
Br. J. lin. Pharma. (199), 29, 27-31 Molobemide exretion in human breast milk G. PONS', M. P. SCHORLIN2, Y. K. TAM3, C. MORAN', J. P. PFFN2, Ch. FRANCOUAL4, A. M. PDARRIOSS5, J. CHAVINI4 & G. OLIV' Departement
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of TGF-β-activated Smad2
 Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of -ativated Roger S. Lo* and Joan Massagué* *Cell Biology Program, Howard Hughes Medial Institute, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Caner Center, New York, New York 10021, USA
Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of -ativated Roger S. Lo* and Joan Massagué* *Cell Biology Program, Howard Hughes Medial Institute, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Caner Center, New York, New York 10021, USA
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillance by human γδ T cell receptor binding to Endothelial Protein C Receptor
 Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
TNFa-induced GM-CSF release from human airway smooth muscle cells depends on activation of an ET-1 autoregulatory positive feedback mechanism
 Additional details of the methods and results, and an additional figure are published online only at http://thorax.bmj. om/ontent/vol64/issue12 1 Department of Pneumology, Clini III for Internal Mediine,
Additional details of the methods and results, and an additional figure are published online only at http://thorax.bmj. om/ontent/vol64/issue12 1 Department of Pneumology, Clini III for Internal Mediine,
