The Golgi Element in the Cells of the Firstand Second Convoluted Tubules of the Cat Kidney.
|
|
|
- Alison Gwenda Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Golgi Element in the Cells of the Firstand Second Convoluted Tubules of the Cat Kidney. By J. F. A. McManus, Major, R.C.A.M.C. With 5 Text-figures. CONTENTS. PREFACE 97 LITERATURE 97 MATERIALS AND METHODS RESULTS 99 DISCUSSION SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS REFERENCES APPENDIX: TECHNIQUES USED PREFACE. PREVIOUS descriptions of the Golgi element in the kidney tubules have been largely restricted to smaller animals the frog, the mouse, the rat, &c. In addition Eamon-y-Cajal has illustrated his conception of these structures as shown in the rabbit by the urano-formol technique, but the actual descriptions are rather sketchy. Since the experimental study of kidney disease has made use of larger mammals the cat, rabbit, and dog it was thought worth while to investigate the appearances of the Golgi element in the kidneys of some of these animals in their normal condition as a necessary preliminary to a cytological review of experimental nephritis which will be undertaken when circumstances permit. These studies were begun also in the hope of demonstrating some peculiar feature for the macula densa, in which respect the results have already been described briefly (McManus, 1943). LITERATURE. It is not proposed to enter into a comprehensive and detailed review of the various publications describing the Golgi element in the kidney Emmet (1938) has done this. In general, NO. 337 H
2 98 J. F. A. MCMANUS structures have been described as being of a granular or netlike nature. Their position in the tubule cell has been pointed out as being on the lumen side of the nucleus. Fischer (1938) has described a cycle of activity in which the Golgi element traverses the cell as a feature of induced diuresis in the rat. A. - { 1 f:\ ' ' _ ' /?:i A f :^> i Text-fig. 1. Ramon-y-Cajal's illustrations of the Golgi structures in the tubules of the kidney of the young rabbit. Reference in text. Eamon-y-Cajal's illustration of the Golgi element in the kidneys of the young rabbit (Text-fig. 1) shows structures comparable to those described in the lower animals. The text, accompanying the illustration, states:'... investigations prove that in the resting phase the cells of the convoluted tubes contain a diminutive apparatus of Golgi (Text-fig. 1B) which is progressively developed and elongated as the large excretory tubes are approached. Granular and rudimentary in the tubes of Henle (A), it forms in the convoluted tubules a group of anastomatic loops while in the straight excretory tubes it forms a net of longitudinal trabeculae (D).'
3 GOLGI ELEMEKT IN TUBULES OF THE CAT KIDNEY 99 MATEEIALS AND METHODS. Young kittens and older cats were killed rapidly by ether. The kidneys were immediately removed and small blocks, about 2x3x3 mm., were placed in the appropriate fixatives. Some details of technique are mentioned in the appendix to this paper. Both silver impregnation and osmification techniques were used (Da Pano, Aoyama, Weigl, and Kolatchev). Complete failure of demonstration of the Golgi element in the cat kidney followed all our osmium tetroxide techniques although the dorsal root ganglion, used as control material, showed perfect impregnation of the Golgi body. The silver techniques were more satisfactory. Da Pano's and Aoyama's methods were used interchangeably with the latter, having the advantage of being more rapid. In neither the Da Pano nor the Aoyama method did it seem as if the histological details were very well preserved, although it is possible that dehydration methods might be altered to improve this or that celloidin imbedding might be preferable to the paraffin which was employed. RESULTS. In most instances all or part of the individual block showed material in the cells which corresponded to Golgi element in size and position. These structures were usually well shown in the proximal tubules and in the loops of. Henle, but their appearance in the distal tubule was more difficult to make out because of a diffuse brown staining which was frequently a feature of the cytoplasm of the cells. Toning of the sections in gold chloride, as detailed in the appendix, helped considerably in the demonstration of the Golgi element in this area, but tended as a rule to diminish further the quality of the histological picture. In the descriptions which follow 'First Convoluted' and 'Proximal' tubule are used interchangeably, as are 'Second Convoluted' and 'Distal' tubule. In llie low magnifications the Golgi element has the appearance of a rod or bar and, in the animals killed in the manner
4 100 J. F. A. MCMANUS described, it is situated immediately on the lumen side of the nucleus. We have made no special study of the collecting tubules, the glomerulus or vessels, or of the loops of Henle; and our investigations have been restricted to the first and second convoluted tubules. S. I n IS 4 Text-fig. 2. Golgi element, first convoluted (proximal) tubule cell of cat kidney. Da Fano method. Photomicrograph ocular magnification, x 950, further enlarged. Text-fig. 3. Golgi element, second convoluted tubule cells of cat kidney. Da Fano method. Photomicrograph, x 1200 (J. R. B.). Text-fig. 4. Golgi element, macula densa of cat kidney, as Fig. 3. (J. It. B.) O, Golgi body; I, lumen of renal tubule; n, nucleus. Text-figs. 3a and 4a are simplified copies to explain the photomicrographs Figs. 3 and 4. In all the first tubules of the younger animals and in the older animals, in those portions of the proximal tubules which are not infiltrated with fat, the Golgi element has the form which is shown in Text-fig. 2. Each appears as a small, slightly crescentic structure with a width approximately equal to the
5 GOLGI ELEMENT IN TUBULES OF THE CAT KIDNEY 101 longer axis of the nucleus, and about one-third of this size in the other dimensions. It is not net-like in appearance when the impregnation has been sufficient, but appears rather as a solid, slightly irregular structure. The infiltration of a portion of the proximal tubule with fat, which occurs in the adult cat, results in a dispersion of the Golgi element as fine particles throughout the cell. '. fa//,- ;.. I. - * r. y " '/ Text-fig. 5. Juxta-glomerular (or Glomerular) complex, from McManus, Relationships at root of glomerulus. A, macula densa, in wall of distal tubule. B, afibrillar cells, in efferent arteriole. In the second (distal) tubule the appearance is very much the same as that shown in the normal proximal tubule cells with a slight decrease in all the dimensions of the Golgi element noticeable (Text-fig. 3), with perhaps some greater granularity and a concentration of its material so that it appears to be more deeply impregnated. This is a fortunate feature because of the deeper staining of the tubule cells. The position of the Golgi element in the cells of the distal tubule is the same, with exception of one area, as that in the cells of the proximal tubule; it is on the lumen or free side of the nucleus. Zimmerman (1938). described as the 'Macula Densa' an aggregation of the cells of the second convoluted tubule at the po^nt where the tubule is most closely applied to the glomerular rooi in the angle between the afferent and efferent arterioles. As we previously pointed out in a short note (McManus, 1943),
6 102 J. F. A. MCMANUS the Golgi element of the cells composing the macula densa is situated (Text-fig. 4) on the basal side of the nucleus, that is in apparent reversal to the position of the Golgi element in all of the proximal tubules and in the rest of the distal tubules. It is of interest to note that, both in the kidney of the young rabbit and in one human case of nephritis, sections from the kidneys stained by the silver techniques described showed reversal of the Golgi element in the macula densa, identical with that found in the cat. DISCUSSION. Several features appear to arise from this study. The first concerns the structure of the Golgi element in the kidney tubule cells, while the second feature indicates a unique condition obtaining in the cells of the macula densa. Where impregnation has been sufficient the Golgi element in the proximal and distal tubule appears as a solid structure, as shown in Text-figs. 2 and 3. This is hardly the result of overimpregnation since the reticulin of the kidney, which ordinarily takes up any superfluity of silver, shows no staining. Only the surface of the mass of the chemical substances appears to be stained rather than a diffuse stain of the whole body of the Golgi element. Here again the possible function of the Golgi element as an absorptive surface for the transmission of material across the cell is suggested in Text-fig. 2 in which a small globule can be seen outside the Golgi proper but attached to it. The apparent reversal of the Golgi element at the resting state in the cells of the macula densa suggests that these cells differ from the other cells of the renal tubules. The difference may be hypothesized from the customary position of the Golgi element on the side of the cell to which secretion is directed, to consist in the cells of the macula densa abstracting some material from the contents of the second convoluted tubule and transmitting this material to the cells of the arterioles at the glomerular root. It is worth while to mention that Euyter (1925) pointed out the afibrillar condition of the juxta-glomerular cells forming the
7 GOLGI ELEMENT IN TUBULES OF THE CAT KIDNEY 103 arteriolar walls in the kidneys of the mouse, and that identical cells in the corresponding position have been described in every species studied including the human (McManus, 1942). We have pointed out that the macula densa and the specialized sequents of the arterioles make up a functioning unit, for which we proposed the term of 'juxta-glomerular complex', and this reversal of the Golgi element in the cells of the macula densa gives some hint as to the manner by which the unit is integrated. Extending the hypothesis to its logical conclusions one may suppose that the conditions in the distal tubule control, by means of the macula densa transmitting some substance to the special arteriolar cells at the glomerular root, the hydrostatic adjustments in the blood supply to the nephron. This theory (resembling that which was first outlined by Goormaghtigh (1987) though without cytological evidence for its possibility) is suggested as a working basis for the investigation of the normal and diseased kidney. Added force is given to the possibility of the reversal of Golgi element in the cells of the macula densa having something to do with the working of the nephron by the fact that the maculae densae which go to make up the juxtaglomerular complexes of the glomeruli in the proliferating subcapsular zone of the kidney of the very young kitten do not show the reversal of position for the Golgi element in their cells. This reversal seems to be attained only by the more adult structures in the kitten, in the deeper portions of the cortex. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. 1. The Golgi element in the cells of the first and second convoluted tubules, of the cat kidney have been demonstrated by the Aoyama and Da Fano techniques. 2. In both sorts of tubules the Golgi element appears as a rod-like or granular, sometimes crescentic structure, solid rather than reticular. The Golgi element usually lies on the free side of the nucleus. 3. In the macula densa of the second convoluted or distal tubule the Golgi element is seen on the basal side of the nucleus, that is, in apparent reversal to the position in the other cells. This condition in the cat is similar to that which is found
8 104 J. F. A. MCMANUS in the rabbit and has been found in one autopsied case of nephritis (human). 4. The reversal of the Golgi element in the cells of the macula densa suggests (a) that some substance from the contents of the tubule here passes across the cells of the distal tubule to the specialized cells at the glomerular root, (6) this process is the method by which the haemodynamics of the nephron are integrated. This proposal, much like that made by Goormaghtigh, is here suggested as a basis upon which physiology of the normal and diseased kidney might be investigated cytologically. [REFERENCES. Emmet, 'Anat. Record', 70. Fischer, 'Ztschr. Micr. Anat. Forsch.', 43. Friedman and Kaplan, ' Journ. Exp. Med.', 76. Goormaghtigh, 'C.R. Soc. Biol., Paris', 124. McManus, 'Lancet', 'Nature', 152. Ramon-y-Cajal, ' Histology' (text). Bailliere, Tindall & Cox, London. Ruyter, 'Z. Zellforseh.', 2. Zimmerman, 'Ztschr. Mikr. Anat. Forsch.', 32. APPENDIX. Techniques used in the Study of the Golgi Element of the Kidneys. The cat kidneys were removed immediately after the animal had been asphyxiated by commercial ether. The two rabbits studied were killed each by a simple blow on the head. The human kidneys were removed at autopsy one. hour after death from a systemic infection. Small blocks were cut each about 2x3x3 mm. and several blocks placed in each of the various fixatives. In the rabbit kidneys-da Pano's technique was not used; in the human kidneys the osmium techniques were not used since their lack of value had by that time become apparent. Occasionally in the silver preparations the Golgi elements in the distal tubule could be seen but were obscured by the diffuse staining of the cytoplasm. In these cases after the sections were cut and mounted on the slides, sections were
9 GOLGI ELEMENT IN TUBULES OF THE CAT KIDNEY 105 brought through xylene and graded alcohols to water. After being rinsed in distilled water the sections were placed in 0-1 per cent, gold chloride, containing 3-4 drops of glacial acetic acid, for five to ten minutes. In the first few minutes the background loses much of its staining and the Golgi elements lose some of their clarity but longer toning appears to reinforce the impregnation of the Golgi without adding at all to the staining of the cytoplasm. This extra handling of the sections appears, unfortunately, to diminish further the preservation of histological detail. These studies would have been impossible without the advice, help, and encouragement of Dr. John E. Baker of the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford. Through Dr. Baker's kindness and that of Professor E. S. Goodrich, it was possible to confirm some of this work in their department. The technical assistance of S/Sgt. H. L. Mitchell, E.C.A.M.C., and the photographic ability of S/Sgt. M. S. Smith must be acknowledged, since the spare time of these N.C.O.s was freely given to helping in this work. Additional photomicrographs, as indicated, were taken by Dr. Baker. No. 8 Cdn. General Hospital, Cdn. Army, England. NO. 337
IN the kidneys of a wide variety of animals the second convoluted tubule
 Further Observations on the Glomerular Root of the Vertebrate Kidney BY J. F. A. McMANUS (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With five Text-figures INTRODUCTION IN the kidneys
Further Observations on the Glomerular Root of the Vertebrate Kidney BY J. F. A. McMANUS (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford) With five Text-figures INTRODUCTION IN the kidneys
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
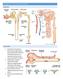
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology, University of Oxford. (From the Department of Physiology.) INTRODUCTORY.
 Note on the Comparative Effects on Tissues of Isotonic Saline and Distilled Water when used as Solvents for Mercuric Chloride and Formol in Histological Fixation. By H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology,
Note on the Comparative Effects on Tissues of Isotonic Saline and Distilled Water when used as Solvents for Mercuric Chloride and Formol in Histological Fixation. By H. M. Carleton, Lecturer in Histology,
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced
 Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Physiology Lecture 2. What controls GFR?
 Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR.CHARUSHILA RUKADIKAR ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PHYSIOLOGY GROSS ANATOMY Location *Bean-shaped *Retroperitoneal *At level of T12 L1 vertebrae. *The right kidney lies slightly inferior to left
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
Chapter 25: Urinary System
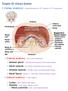 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary system. Urinary system
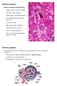 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
The entire extent of the tubule is almost continuously necrotic.
 PLATE HGIC. TERMINAL MEDULLARY PORTION OF PROXIMAL CONVOLUTION LYING IN THE ZONE OF HEMORRHAGE The entire extent of the tubule is almost continuously necrotic. 180 PLATE HID The terminal medullary segment
PLATE HGIC. TERMINAL MEDULLARY PORTION OF PROXIMAL CONVOLUTION LYING IN THE ZONE OF HEMORRHAGE The entire extent of the tubule is almost continuously necrotic. 180 PLATE HID The terminal medullary segment
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
1. The renal medulla is composed of tissue called. A. Renal pyramids B. Nephrons C. Renal sinus D.
 1. The renal medulla is composed of tissue called. A. Renal pyramids B. Nephrons C. Renal sinus D. Renal pelvis 2. Juxtaglomerular cells combine with cells to form the juxtagomerular apparatus in the kidney.
1. The renal medulla is composed of tissue called. A. Renal pyramids B. Nephrons C. Renal sinus D. Renal pelvis 2. Juxtaglomerular cells combine with cells to form the juxtagomerular apparatus in the kidney.
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences. Body fluids and.
 By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
Medical PANCE. Physician Assistant National Certifying.
 Medical PANCE Physician Assistant National Certifying http://killexams.com/exam-detail/pance QUESTION: 375 Which of the following syndromes corresponds to: chromosomal deficit of #13? A. Dubin-Johnson
Medical PANCE Physician Assistant National Certifying http://killexams.com/exam-detail/pance QUESTION: 375 Which of the following syndromes corresponds to: chromosomal deficit of #13? A. Dubin-Johnson
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
 LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
Glomerular Filtration Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Glomerular Filtration Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Formation of urine by the kidney involves
Glomerular Filtration Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Formation of urine by the kidney involves
DURING the past ten years it has been suggested that the classical form
 163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.*
 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Lecture 16: The Nephron
 Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
41B. Metabolism produces wastes that must be eliminated from the body. This. Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation
 41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - ANATOMY Glomerulus + renal tubule Each kidney has 1.3 million nephrons Cortical nephrons (85%) have shorter Loop of Henle than Juxtamedullary nephrons
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018. Rahmeh Alsukkar
 Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
(From the Harold Brunn Institute for Cardiovascular Research, Mount Zion Hospital, San Francisco)
 Published Online: 1 January, 1942 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.75.1.127 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 3, 2018 STUDIES CONCERNING THE SITE OF RENIN FORMATION IN THE KIDNEY I. Tim
Published Online: 1 January, 1942 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.75.1.127 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 3, 2018 STUDIES CONCERNING THE SITE OF RENIN FORMATION IN THE KIDNEY I. Tim
CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY
 40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
40 CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE IN RATS FOLLOWING A TEMPORARY DEFICIENCY OF POTASSIUM P. FOURMAN, R. A. McCANCE AND R. A. PARKER From the Departments of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Cambridge
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system By the end of the topic the learner should be able to: Describe the histological structure of the kidney. Illustrate the ultrastructure of the blood renal barrier. Illustrate the
Histology Urinary system By the end of the topic the learner should be able to: Describe the histological structure of the kidney. Illustrate the ultrastructure of the blood renal barrier. Illustrate the
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS
 THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 19
 Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 19 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how the anatomy of the kidney is related to its functions 2. Understand what makes up a nephron
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 19 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how the anatomy of the kidney is related to its functions 2. Understand what makes up a nephron
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
