Wilson's Disease: Laboratory Evaluation of A Sample of Patients Attending Baghdad Teaching Hospital
|
|
|
- Charlene Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WILSON'S THE IRAQI DISEASE POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL Wilson's Disease: Laboratory Evaluation of A Sample of Patients Attending Baghdad Teaching Hospital Ahmed Kh. Mohammed*, Akram Ajeel Najeeb**, Wafaa Faeq Tawfeeq*** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: Wilson s disease (WD) is an inherited defect in copper metabolism that causes accumulation of copper in various body organs. It is a treatable; if it is diagnosed promptly and treated consistently. OBJECTIVE: Laboratory; hematological, biochemical, and diagnostic evaluation of a sample of Iraqi patients with WD, and study any association between clinical presentations and studied variables. METHODS: A case series study was conducted during 2011, from the 1 st of February till the 10 th of June. Sampling method was a convenient non-random one, through consecutive pooling of registered WD patients. A questionnaire-form paper had been developed for data collection, and required investigations were done in qualified laboratories. RESULTS: The study had enrolled 29 patients, with a male to female ratio of (1.07:1), The mean hemoglobin level was 10.64±2.53g/dl. Hemolysis was presented in 27.6% of patients, normochromicnormocytic RBCs in blood film were seen in 3.4% patient, platelet count was ±89.35ccX10 9 /L, WBC count was 5.70±2.84ccX10 9 /L. ESR was 24.98±17.16mm/hr., serum bilirubin was 6.17±5.18mg/dl, serum cholesterol was ±44.93mg/dl, serum triglycerides was 95.34±52.23mg/dl. Total serum protein was 72.86±11.15g/L, serum Albumin 39.17±7.88g/L and serum Globulin 31.07±7.89g/L. Penicillamine challenge test was positive in 96.6% patients. Serum ceruloplasmin level was ±48.48mg/L, total serum copper was 72.48±25.11µg/dl, and 24h urinary copper excretion was ±109.58µg/24hr. CONCLUSION: Most patients with WD are; anemic, with low serum levels of copper and cerulloplasmin, positive penicillamine challenge test, with abnormal liver function tests. With detected hemolysis in some of them; though no statistical difference or association was approved regarding laboratory values among patients with different presentations. KEYWORDS: Wilson Disease, copper. INTRODUCTION: Wilson's disease is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder of copper metabolism. It is a hepatolenticular degeneration that characterized by the accumulation of copper in various body organs. It is fatal unless treated, it is a potentially treatable condition with the availability of effective pharmacologic therapy, while if not treated; it can cause severe brain damage, liver failure and death (1,2,3,4). The prevalence of WD is about 1:30,000 and a frequency of heterozygotic carriers is about 1:90. * Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Iraq. **Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Medical City, Iraq. ***College of Health and Medical Technologies. WD resembles 6.9% of chronic liver diseases in Iraq (1,3,4,5,6,7,8). The gene for WD is located on chromosome 13, mutations in this gene result in a production of a defective ATPase (ATP7B), a copper transport molecule, leading to impaired incorporation of copper into ceruloplasmin and copper retention; so in WD, intestinal copper absorption is normal but biliary excretion of copper is decreased, leading to excess copper accumulation, the later exerts its toxic effect by the generation of free radicals that result in lipid peroxidation (8,9,10). The variation in the clinical presentation is tremendous. The five main categories of clinical presentation include hepatic, neurologic, psychiatric, hematologic, and ophthalmologic. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 587
2 Symptoms may be vague and nonspecific, occasionally as a self-limited illness resembling acute hepatitis or resembling chronic liver disease. In hematologic presentation; patients present with hemolysis; so the constellation of young age, liver dysfunction and hemolysis should be assumed as WD until proved otherwise (1,5,11). In WD; serum ceruloplasmin level is less than 200 mg/l in 95% of patients, the total serum copper is usually decreased (<70mg/dl" µg/L",<11µmol/L"3-10"), and the level of daily urinary copper excretion of more than 100µg/d. (1.6mmol/d.); while on chelating therapy 24-hr. urinary copper excretion should be initially range between 200 and 500μg; such a value can also suggest that the patient is adherent to the drug. Penicillamine challenge test; which is the 24hr. urinary copper excretion stimulated by penicillamine administration; is usually have levels above 1600μg copper/24-hr. (25µmol/24- hr.) in WD patients (3,4,11). The availability of effective treatment makes early diagnosis crucial. WD should be considered in any person younger than 30 years with liver disease. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis and viral hepatitis are the most frequently considered alternative diagnoses (2,11). By eliminating copper-rich foods from their diet along with an effective lifelong treatment; a normal life-expectancy and liver function improvement can be offered within 6 12 months in most patients. Liver transplantation is curative as it corrects the metabolic defect (1,3,4,5,11). So the objectives of this study is; Laboratory; hematological, biochemical, and diagnostic evaluation of a sample of Iraqi patients with WD, and study any association between clinical presentations and studied variables. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: This is a case series study with some analytic elements. The data was collected at the Department of Gastroenterology, Baghdad Teaching Hospital of Medical City, Baghdad, Iraq and its related authorized qualified teaching laboratories, in addition to toxicology center that related to study place. Arrangements for this study was approved by the local ethics committee and by the Iraqi MOH, Council of Arab Board of Medical Specialties and Baghdad Teaching Hospital/ Medical city. Data collection was extended from the 1 st of February to the 10 th of June The target population was all registered and newly diagnosed WD patients. The sampling method was a convenient nonrandom one, carried out through consecutive pooling of all WD patients. A data of 29 patients was collected by direct interviews, full clinical assessment, medical records analysis, and by doing some required laboratory investigations. Patients who accepted to participate in study, completed the required parameters and fit the inclusion criteria during the study period were included in study. The inclusion criteria were; history and clinical examination findings suggestive of WD as: hepatic manifestations, neuropsychiatric manifestations, family history of WD, serum ceruloplasmin level below 200 mg/l, presence of Kayser - Flischer ring, liver biopsy: if the liver copper concentration more than 250μg/g dry weight, serum copper level below 70 µg/dl "below 11µmol/L", 24-hr. urinary copper excretion more than 100µg/24- hr., and/or positive Penicillamine challenge test (if 24-hr. urinary Copper more than1600µg/24- hr., more than 25mmol/ L) [3,4]. The patient age should be fulfilling at least three of the above criteria and the last criterion is a definite diagnosis. These diagnostic standards had been proposed basing on Sternlieb s criteria (11,12). The exclusion criteria were; age above 60 years, evidence of coexisting liver diseases including; viral hepatitis A, B C or E, chronic liver disease with cholestatic component, Alpha one antitrypsin deficiency, Coomb's positive hemolysis, history of Alcohol intake, pregnancy, history of use of copper containing intrauterine devices (IUCD) or oral contraceptive [7], history of intake of medications that may cause extrapyramidal side effect such as antipsychotic drugs and Metoclopramide and/or history of chorea. The Statistical Package for the Social Science (SPSS) version 17.0 software had been used for all computerized statistical analysis. Numerical; normally distributed variables was expressed as mean ± standard deviation; while categorical variables were expressed as frequency, range and percentage. Continuous variables were compared by ANOVA test for the variance analysis and categorical variables were compared by using Chi-square tests. P-value equal or less than 0.05 was considered as a statistically significant. RESULTS: In the current study; laboratory evaluation was based on several domains, including; hematological tests, bleeding studies, blood film THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 588
3 findings, biochemical tests, and toxicology tests. The patients' total number was 29, males were 15 (51.7%) and females were 14 (48.3%), giving a male to female ratio of (1.07:1). Their mean age was 27.12±12.18 years(yr.). According to their main clinical presentation; patients had been classified into 4 clinical subgroups to facilitate studying them; hepatic in 8 (27.6%) of patients, neuro-psychiatric in 4 (13.8%), mixed hepatoneurologic presentation in 9 (31%), and other presentations in 8 (27.6%). Regarding the laboratory hematological tests results and blood film findings of the study group; the mean hemoglobin level was 10.64±2.53 ( ) g/dl, platelet count was ±89.35 ( ) cc X10 9 /L and WBC count was 5.70±2.84 ( ) cc X10 9 /L. ESR level was 24.98±17.16 ( ) mm/hr.. Evidence of hemolysis in blood film was found in 8 (27.6%) of patients and normochromicnormocytic RBCs in blood film were seen in only one (3.4%) patient. Regarding bleeding tests; PT was 16.76±4.66 ( ) sec., PTT was 41.00±16.03 ( ) sec. and INR was 1.39±0.28 ( ) [Table (1)]. Table (2) shows that; the mean serum ceruloplasmin level was ±48.48 ( ) mg/l, the mean total serum copper was 72.48±25.11 ( ) µg/dl, the mean basal 24h urinary copper excretion was ± ( )µg/24hr., the mean 24h urinary copper excretion while patient was on treatment was ± ( ) µg/24hr.. Regarding liver function and other biochemical tests results; the mean total serum bilirubin was 6.17±5.18 ( ) mg/dl, the mean serum AST (GOT) was 29.72±23.88 ( ) IU/L, the mean serum ALT (GPT) was 31.24±24.33 ( ) IU/L, the mean serum ALP was ±82.19 ( ) IU/L. The mean total serum cholesterol was ±44.93 ( ) mg/dl, the mean serum triglycerides level was 95.34±52.23 ( ) mg/dl. Total serum protein was 72.86±11.15 ( ) g/l, the mean serum Albumin 39.17±7.88 (20-51) g/l and the mean serum Globulin 31.07±7.89 ( ) g/l. Penicillamine challenge test was positive in almost all 28 (96.6%) patients [Table (2)]. ANA, SMA, LKMI, Viral hepatitis markers, coomb's test, α1-antitrypsin and pregnancy test (blood test for female patients) were negative in all patients. Table (3) and Table (4) show the laboratory hematological, biochemical tests results in different subtypes, though statistically there was no significant association between tests results and the main initial presentations (P value equal to or less than 0.05 is significant; while P value of more than 0.05 is not significant statistically). DISCUSSION: Comparing hematological tests results with another previous case series study (Samiullah et al) which was conducted on 24 patients at Hyderabad/Pakistan; showed similar results; hemoglobin level was 9.45±3.29g/dl, INR 1.34±.35 (13). Comparing serological and biochemical tests results in this study; which were within the diagnostic levels of WD; with other previous studies similar results of low serum ceruloplasmin, low total serum copper, and high urinary copper were reported;, like; (Samiullah et al) a descriptive series study was conducted by on 24 patients at Hyderabad/Pakistan (13), in (Merle et al) a retrospective cohort study by which was conducted in Heidelberg/Germany; low serum ceruloplasmin in 88.2% and high 24- hr. urinary copper in 87.1% of patients [14]. Another cohort study in Spain by (Rodrigo Agudo et al) was conducted on 29 patients; reported high transaminases levels in 50% of patients [15]. And other descriptive case series study (Karim et al) which was conducted on 32 WD children attending Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition departments of B. Sh. Mujib Med. University (BSMMU)/Dhaka/ Bangladesh; low serum ceruloplasmin in 50% and elevated basal urinary copper in 100% (16). In Italy (Medici et al) a prospective cohort study was conducted to follow up 35 WD patients at the Department of Gastroenterology of Padua University, a referral center for WD, it reported that ceruloplasmin levels were low in 87.5%. Urinary copper was 207±622µg/24-hr. and ALT was 126.6±100.89IU/L (17). After classifying study's participants into four groups according to their main initial clinical presentations, the mean serum ceruloplasmin level was less than 200 mg/l in all four groups. The mean serum total copper level was the lowest among those with hepato-neurologic presentation and the highest among those with other presentations. Urinary copper excetion was high and diagnostic for WD in all presentations. Penicillamine challenge test was positive in all patients except a patient with a mixed hepato- THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 589
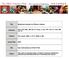
4 neurologic presentation. The mean values of liver functions tests results were abnormally high in all presentations except; neuro-psychiatric presentation. And hemolysis was the highest among those with other presentations (4 patients); a patient with pure and three with mixed hematologic presentations. Comparing these results with that of other previous studies: According to a retrospective cohort study by (Merle et al) was conducted in Germany; the mean values of serum ceruloplasmin, serum copper and urinary copper excretion levels were diagnostic for WD. However, there was no significant difference between patients with different presentations (14). A cohort study (Lowette et al) which was conducted on 24 patients at Leuven university/belgium; the mean serum ceruloplasmin (below 200mg/L) was seen in 80% of patients with neurologic symptoms and in 75% of the patients with liver disease. Urinary copper (> 100µg/24 hr.) was seen in 80% patients with neurologic symptoms and in all those with liver disease (18). This can be explained by the fact that; results were within the diagnostic levels of WD; 95% of patients with WD have serum ceruloplasmin levels less than 200 mg/l, while serum copper level may be low, normal or increased but it usually (not always) decreased (<70µg/dl) in WD, however, it can be elevated in the setting of fulminant WD if ceruloplasmin level is reduced. The daily upper normal limit of urinary copper is 40µg/24hr. and the diagnostic level of WD is more than 100µg/24hr., this level represents the increase in circulating free copper, however; in about 20% of patients urinary copper excretion is between μg/24hr.. Penicillamine challenge test was negative in a patient, and this is because of the predictive value of this test in adults which is unknown. Liver function tests results were abnormal in all presentations except; neuro-psychiatric presentation; this may be due to fact that; patients included in this study were enrolled from the Department of Gastroenterology, so most of them presented with liver disease, except those with neuropsychiatric presentation who were referred for management, so they reported normal results. In hepato-neurologic presentation hemolysis due to acute intravascular hemolysis is usually present in patients with hepatic involvement (3,4,5,11,12,19). CONCLUSION: Most of the patients with WD are; anemic, with abnormal liver function tests, low serum levels of total copper and cerulloplasmin, and positive penicillamine challenge test. With detected hemolysis in some of them; though no statistical difference or association was approved regarding laboratory values among patients with different clinical presentations.. Table 1: Laboratory hematological tests results and blood film findings of the study group (n=29). Test result Mean±SD Range Hb (g/dl) 10.64± Platelets count (cc X 10 9 /L) ± WBC (cc X 10 9 /L) 5.70± ESR (mm/hr) 24.98± PT (sec.) (normal sec.) 16.76± PTT (sec.) (normal sec.) 41.00± INR 1.39± Blood film Finding No % Hemolysis:Aniso-poikilocytosis, reticulocytes, fragmented and hypochromic-microcytic RBC Evidence of normochromic-normocytic RBC Positive Negative Positive Negative Total SD; Standard Deviation, Hb: Hemoglobin level, WBC: White blood cell count, ESR; Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, PT; Prothrombin time, PTT; Partial throboplastin time, INR; International Neutralization Ratio, sec.; second, No; number, %; percent, RBC;Red Blood Cells. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 590
5 Table 2: Laboratory biochemical tests results of the study group (n=29). Laboratory tests result Mean±SD Range Serum Ceruloplasmin ( mg/l ) ± Total serum copper (µg/dl) 72.48± Basal 24h urinary copper excretion ± (µg/24h) 24hr. urinary copper excretion during ± treatment (µg/24h) Total serum bilirubin (mg/dl) 6.17± S. AST (GOT) ( IU/L) 29.72± S. ALT (GPT) (IU/L) 31.24± S. ALP (IU/L) ± S.total cholesterol (TC) (mg/dl) ± S. Triglycerides (mg/dl) 95.34± Total serum protein level(g/l) 72.86± S. Albumin(g/L)(g/L) 39.17± S. Globulin 31.07± Pencillamine challenge test Positive 28 No % 96.6 Negative Total SD; Standard Deviation,24h ; 24 hours, S.; serum, AST; Aspartatate transferase, ALT; Alanine transferase, ALP; Alkaline phosphatase, No; Number, %; Percent. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 591
6 Table 3: Hematological, blood film and Pencillamine challenge test results among different clinical presentations (n=29). The laboratory test The main initial presentation Hepatic Other Mean±SD Mean±SD Mean±SD Mean±SD P value Hb (g/dl) 12.35± ± ± ± Plt. count (ccx10 9 /l) ± ± ± ± WBC (ccx0 9 /l) 6.08± ± ± ± ESR(mm/hr) 2.56± ± ± ± PT(sec.) 16.25± ± ± ± PTT(sec.) 41.88± ± ± ± INR 1.28± ± ± ± The test Hepatic Hepatoneurologic Neuropsychiatric Hepatoneurologic Neuropsychiatric Other No % No % No % No % Comparison of significance Chi value DF P Hemolysis in blood film Positive pencillamine challenge test Total No; number, %; percent, SD; standard deviation, Hb; Hemoglobin level, WBC; White blood cell count, ESR; Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, PT; Prothrombin time, PTT; Partial throboplastin time, INR; International Neutralization Ratio, sec.; second, RBC; Red Blood Cells, DF; degree of freedom, P; P value. Note: P value equal or less than 0.05 is considered as a statistically significant; while P value of more than 0.05 is not significant. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 592
7 Table 4: Laboratory biochemical tests results among patients with different clinical presentations (n=29). The laboratory test The main initial presentation Hepatic Hepato-neurologic Neuro-psychiatric Other Mean±SD Mean±SD Mean±SD Mean±SD S.ceruloplasmin (mg/l) ± ± ± ± S.copper (µg/dl) 70.11± ± ± ± Basal u.copper(µg/24hr) ± ± ± ± Urinary copper with treatment (µg/24hr) ± ± ± ± Total serum bilirubin (mg/dl) 7.65± ± ± ± S.AST ( IU/l) 38± ± ± ± S. ALT (IU/l) 45.88± ± ± ± S. ALP (IU/l) ± ± ± ± S.cholesterol (mg/dl) ± ± ± ± S.triglycerides (mg/dl) 91.00± ± ± ± Total serum protein 73.25± ± ± ± S. Albumin(g/l) 42.75± ± ± ± S. Globulin(g/l) 30.38± ± ± ± SD; standard deviation, P; P value, 24h; 24 hours, S.; serum, u.; urinary, AST; Aspartatate transferase, ALT; Alanine transferase, ALP; Alkaline phosphatase. Note: P value equal or less than 0.05 is considered as a statistically significant; while P value of more than 0.05 is not significant. P REFERENCES: 1. Olivarez M, Caggana M, Pass KA, Ferguson P. Estimate of the frequency of Wilson s disease in the US Caucasian population: a mutation analysis approach. Annals of Human Genetics. 2001;65: Hoffmann GF, Engelmann G: Liver Disease. In: Hoffmann G, Zschocke J, Nyhan W, eds. Inherited metabolic diseases-clinical Approach. 1st ed. New York: Springer, 2010; Niederau C: Wilson's Disease. In: Mauss S, Berg T, Rockstroh J, eds. Hepatology-A Clinical Textbook 2 nd ed. Germany: FlyingPublisher, 2010: Merle U, Stremmel W: Wilson's Disease. In: Friedman SL, eds. Henryk Dancygier Clinical Hepatology Textbook Vol (2). 1 st ed. New York: Springer, 2010: Diane W, Roberts C: Wilson Disease. In Feldman M, Friedman L, Bradnt L, eds. Sleienger & Fordtran`s gastrointestinal and liver disease. 8 th ed. California: Elsevier, 2006: Al-Rawi F, Kassir Z. [1996] Chronic liver disease in Iraq, evaluation of clinical and diagnostic parameters. Thesis. Iraqi Comission For Medical Specialization, Internal Medicine Department; Nakayama K, Kubota M, Katoh A. Early and presymptomatic detection of Wilson s disease at the mandatory 3-year-old medical health care examination in Hokkaido Prefecture with the use of a novel automated urinary ceruloplasmin assay. J Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 2008;94: Moseley RH: Approach to the patient with abnormal liver chemistries. In: Yamada T, Alpers D, Kalloo A, (eds). Principles of clinical gastroenterology. 1st ed. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2008: Ferenci P. Wilson's disease. J Clinical Gastroenterology Hepatology 2005;3: THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 593
8 10. Poterucha J: Metabolic Liver Disease. In: Hauser C, Pardi D, Poterucha, eds. Mayo clinic gastroenterology and hepatology board review 3 rd ed. 2010: Ferenci P, Czlonkowska A, Merle U. Late onset Wilson s disease: A cohort study, Austria: J Gastroenterology 2007;132: Roberts EA, Schilsky ML. American Association for Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease; an update. J Hepatology 2008;47: Samiullah S, Salma S, Faheemullah S. Wilsons Disease: Various shapes of one disease: A descriptive case series study. Pak J Med Sci 2010 ; January - March 2010;26: Medici V, Trevisan C, D Inca` R. Diagnosis and Management of Wilson s Disease: Results of a Single Center Experience: A cohort study, Italy. J Clin Gastroenterol _ 2006;40: Rodrigo A, Valds M, Vargas A, et al. Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and longterm outcome of 29 patients with Wilson's disease, Spain. J Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2008;100: Karim M, Rahman M, Islam M. Wilson's disease with hepatic presentation in childhood. Mymensingh Med J. 2007;16: Medici V, Trevisan C, D Inca` R. Diagnosis and Management of Wilson s Disease: Results of a Single Center Experience: A cohort study, Italy. J Clin Gastroenterol,2006;40: Lowette K, Desmet K, Witters P. Wilson s disease: Long-term follow-up of a cohort of 24 patients treated with D-penicillamine, Leuven, Belgium. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2010;22: Gow P, Smallwood R, Angus P Diagnosis of Wilson s disease: An experience over three decades, Australia. Gut J 2002;50:136. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 594
*Department of pediatrics, Baghdad Medical College, University of Baghdad. **Children Welfare Teaching Hospital, Medical City, Baghdad.
 WILSON S THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE DISEASE IN CHILDREN MEDICAL JOURNAL Wilson s Disease in Children (Clinical Presentations & Diagnostic Difficulties) (Three years experience in Children Welfare Teaching
WILSON S THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE DISEASE IN CHILDREN MEDICAL JOURNAL Wilson s Disease in Children (Clinical Presentations & Diagnostic Difficulties) (Three years experience in Children Welfare Teaching
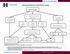
YES NO UNKNOWN PENETRANCE ACTIONABILITY SIGNIFICANCE/BURDEN OF DISEASE NEXT STEPS. YES (Proceed to Stage II) YES ( 1 of above)
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: ATP7B DISORDER: Wilson Disease HGNC ID: 870 OMIM ID: 277900 ACTIONABILITY 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic review,
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: ATP7B DISORDER: Wilson Disease HGNC ID: 870 OMIM ID: 277900 ACTIONABILITY 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as a practice guideline or systematic review,
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Mar 20; Vol 22 (No 1), Pp: 26 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings Fatemeh Mahjoub*
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Mar 20; Vol 22 (No 1), Pp: 26 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry in Wilson s Disease and Its Comparison with Other Laboratory Tests and Paraclinical Findings Fatemeh Mahjoub*
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización
 5 Congreso Argentino de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátricas Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización Eve A. Roberts, M.D., M.A., FRCPC Division of Gastroenterology,
5 Congreso Argentino de Gastroenterología, Hepatología y Nutrición Pediátricas Wilson disease an update for 2014 Enfermedad de Wilson. Actualización Eve A. Roberts, M.D., M.A., FRCPC Division of Gastroenterology,
Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker
 Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker June, 2006 WDA Medical Advisory Committee Michael L. Schilsky M.D., Chair WILSON DISEASE PATIENT LAB TRACKER TREATMENT AND MONITORING OF WILSON DISEASE The following
Wilson Disease Patient Lab Tracker June, 2006 WDA Medical Advisory Committee Michael L. Schilsky M.D., Chair WILSON DISEASE PATIENT LAB TRACKER TREATMENT AND MONITORING OF WILSON DISEASE The following
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005)
 Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005) Note: Values and units of measurement listed in these Tables are derived from several resources. Substantial variation exists in the ranges quoted as normal
Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005) Note: Values and units of measurement listed in these Tables are derived from several resources. Substantial variation exists in the ranges quoted as normal
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
A tale of two sisters with liver disease
 IM BOARD REVIEW EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider the various causes of acute liver failure MOHAMAD A. HANOUNEH, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Medicine Institute, Cleveland Clinic NIZAR
IM BOARD REVIEW EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider the various causes of acute liver failure MOHAMAD A. HANOUNEH, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Medicine Institute, Cleveland Clinic NIZAR
Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms?
 A Diagnostic Tool For Physicians Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms? Think WILSON DISEASE. ALGORITHMS FOR ASSESSMENT OF WILSON DISEASE Table 1. Clinical Features in Patients with Wilson
A Diagnostic Tool For Physicians Unexplained Hepatic, Neurologic or Psychiatric Symptoms? Think WILSON DISEASE. ALGORITHMS FOR ASSESSMENT OF WILSON DISEASE Table 1. Clinical Features in Patients with Wilson
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
 Title Mutational analysis for Wilson's disease Author(s) Seto, WK; Mak, CM; But, D; Hung, I; Lam, CW; Tam, S; Yuen, MF; Lai, CL Citation The Lancet, 2009, v. 374 n. 9690, p. 662 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/77405
Title Mutational analysis for Wilson's disease Author(s) Seto, WK; Mak, CM; But, D; Hung, I; Lam, CW; Tam, S; Yuen, MF; Lai, CL Citation The Lancet, 2009, v. 374 n. 9690, p. 662 Issued Date 2009 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/77405
RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE;
 RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE; 1998-2005 A. Fallah MD Abstract Objective Wilson disease (WD) is an inherited copper metabolism dysfunction disease characterized
RESEARCH ARTICLE NEUROLOGICAL AND OTHER MANIFESTATIONS OF WILSON DISEASE; 1998-2005 A. Fallah MD Abstract Objective Wilson disease (WD) is an inherited copper metabolism dysfunction disease characterized
Disclosure. Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes
 Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0210230718 Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study Şükrü Güngör I, Mukadder Ayşe Selimoğlu II, Fatma İlknur
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2018.0210230718 Pediatric Wilson s disease: findings in different presentations. A cross-sectional study Şükrü Güngör I, Mukadder Ayşe Selimoğlu II, Fatma İlknur
Wilson Disease. Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy
 Wilson Disease Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy What is Wilson Disease? Wilson Disease (WD)= hepatolenticular degeneration Hereditary disorder Autosomal recessive
Wilson Disease Maggie Benson Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Physical Therapy What is Wilson Disease? Wilson Disease (WD)= hepatolenticular degeneration Hereditary disorder Autosomal recessive
Interpreting Liver Function Tests
 PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
HAEMATOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF ANEMIA. Sitalakshmi S Professor and Head Department of Clinical Pathology St John s medical College, Bangalore
 HAEMATOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF ANEMIA Sitalakshmi S Professor and Head Department of Clinical Pathology St John s medical College, Bangalore Learning Objectives Laboratory tests for the evaluation of anemia
HAEMATOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF ANEMIA Sitalakshmi S Professor and Head Department of Clinical Pathology St John s medical College, Bangalore Learning Objectives Laboratory tests for the evaluation of anemia
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of the Dossier. Use only) Name of Finished Product:
 SYNOPSIS Fresenius Title of the study: A double-blind, randomized study comparing the safety and torelance of SMOFlipid 20% and Intralipid 20% in long-term treatment with parenteral nutrition Coordinating
SYNOPSIS Fresenius Title of the study: A double-blind, randomized study comparing the safety and torelance of SMOFlipid 20% and Intralipid 20% in long-term treatment with parenteral nutrition Coordinating
Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Metabolic Liver Diseases
 Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
NEW RCPCH REFERENCE RANGES-
 s vary between populations and age groups and it is important to always check the reference Haematology: Haemoglobin Male 130 175 g/l 0 6 days 145-220 g/l Female 115 165 g/l 7 days 140-186 g/l 8 days 3
s vary between populations and age groups and it is important to always check the reference Haematology: Haemoglobin Male 130 175 g/l 0 6 days 145-220 g/l Female 115 165 g/l 7 days 140-186 g/l 8 days 3
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
Wilson Disease - Our Experience
 Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE FARMACOLOGICHE MARIO NEGRI CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER ALDO E FOR CELE RARE DACCO DISEASES ALDO E CELE DACCO
 ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE FARMACOLOGICHE MARIO NEGRI CENTRO MARIO DI NEGRI RICERCHE INSTITUTE CLINICHE FOR PHARMACOLOGICAL PER LE MALATTIE RESEARCH RARE CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER ALDO E FOR CELE RARE DACCO DISEASES
ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE FARMACOLOGICHE MARIO NEGRI CENTRO MARIO DI NEGRI RICERCHE INSTITUTE CLINICHE FOR PHARMACOLOGICAL PER LE MALATTIE RESEARCH RARE CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER ALDO E FOR CELE RARE DACCO DISEASES
NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION
 E:/Biomedica Vol.4 Jan. Jun. 008/Bio-R (A) NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF AND SHAHID MEHMOOD Department of Neurology,
E:/Biomedica Vol.4 Jan. Jun. 008/Bio-R (A) NEUROLOGICAL AND NEUROPSYCHIATRIC SPECTRUM OF WILSON'S DISEASE IN LOCAL POPULATION M. ATHAR JAVED, SAMAR ZIA, SARA ASHRAF AND SHAHID MEHMOOD Department of Neurology,
Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 672985, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/672985 Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant Talal Hilal
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 672985, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/672985 Case Report Fulminant Wilson s Disease Managed with Plasmapheresis as a Bridge to Liver Transplant Talal Hilal
Inspector's Accreditation Unit Activity Menu
 01/12/20XX 15:58:57 Laboratory Accreditation Program Page 1 of 9 CHEMISTRY 1501 ALT, serum/plasma 1502 Albumin, serum/plasma 1504 Alkaline phosphatase, serum/plasma 1506 Amylase, serum/plasma 1508 Bilirubin,
01/12/20XX 15:58:57 Laboratory Accreditation Program Page 1 of 9 CHEMISTRY 1501 ALT, serum/plasma 1502 Albumin, serum/plasma 1504 Alkaline phosphatase, serum/plasma 1506 Amylase, serum/plasma 1508 Bilirubin,
Supplementary Table 1. The distribution of IFNL rs and rs and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium Genotype Observed Expected X 2 P-value* CHC
 Supplementary Table 1. The distribution of IFNL rs12979860 and rs8099917 and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium Genotype Observed Expected X 2 P-value* CHC rs12979860 (n=3129) CC 1127 1145.8 CT 1533 1495.3 TT
Supplementary Table 1. The distribution of IFNL rs12979860 and rs8099917 and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium Genotype Observed Expected X 2 P-value* CHC rs12979860 (n=3129) CC 1127 1145.8 CT 1533 1495.3 TT
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Distribution of Diseases Causing Liver Function Test Abnormality in Children and Natural Recovery Time of the Abnormal Liver Function
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pediatrics http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.11.1784 J Korean Med Sci 2016; 31: 1784-1789 Distribution of Diseases Causing Liver Function Test Abnormality in Children and Natural
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pediatrics http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.11.1784 J Korean Med Sci 2016; 31: 1784-1789 Distribution of Diseases Causing Liver Function Test Abnormality in Children and Natural
Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases
 Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FAASLD Director, Liver Care Network and Organ Care Research Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA Postgraduate Course: Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases Challenges in Management of
Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FAASLD Director, Liver Care Network and Organ Care Research Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA Postgraduate Course: Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases Challenges in Management of
Intron A Hepatitis C. Intron A (interferon alfa-2b) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.05 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis C Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Intron A Hepatitis
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.05 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis C Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Intron A Hepatitis
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist
 Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Ammonia level at admission predicts in-hospital mortality for patients with alcoholic hepatitis
 Gastroenterology Report, 5(3), 2017, 232 236 doi: 10.1093/gastro/gow010 Advance Access Publication Date: 1 May 2016 Original article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ammonia level at admission predicts in-hospital mortality
Gastroenterology Report, 5(3), 2017, 232 236 doi: 10.1093/gastro/gow010 Advance Access Publication Date: 1 May 2016 Original article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ammonia level at admission predicts in-hospital mortality
Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University
 Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Genetics of Thalassemia
 Genetics of Thalassemia Submitted by : Raya Samir Al- Hayaly Sura Zuhair Salih Saad Ghassan Al- Dulaimy Saad Farouq Kassir Sama Naal Salouha Zahraa Jasim Al- Aarajy Supervised by : Dr. Kawkab Adris Mahmod
Genetics of Thalassemia Submitted by : Raya Samir Al- Hayaly Sura Zuhair Salih Saad Ghassan Al- Dulaimy Saad Farouq Kassir Sama Naal Salouha Zahraa Jasim Al- Aarajy Supervised by : Dr. Kawkab Adris Mahmod
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
ROUTINE LAB STUDIES. Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 ROUTINE LAB STUDIES Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a tacrolimus or cyclosporine level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not
ROUTINE LAB STUDIES Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a tacrolimus or cyclosporine level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust
 ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi.
 Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. Introduction and Genetics Wilson's disease (WD; Hepatolenticular
Review Article Wilson's Disease: a review A. Hassan, F. Masood Departments of Medicine and Pediatrics*, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. Introduction and Genetics Wilson's disease (WD; Hepatolenticular
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease Zhi-Ying Wu, MD, PhD; Min-Ting Lin, MD; Shen-Xing Murong, MD; Ning Wang, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Molecular Diagnosis and Prophylactic Therapy for Presymptomatic Chinese Patients With Wilson Disease Zhi-Ying Wu, MD, PhD; Min-Ting Lin, MD; Shen-Xing Murong, MD; Ning Wang, MD, PhD
ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were measured using the α-ketoglutarate reaction (Roche,
 Supplemental Methods Analytical determinations ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were measured using the α-ketoglutarate reaction (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Glucose, triglyceride, total
Supplemental Methods Analytical determinations ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were measured using the α-ketoglutarate reaction (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Glucose, triglyceride, total
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS
 CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
REFERENCE INTERVALS. Units Canine Feline Bovine Equine Porcine Ovine
 REFERENCE INTERVALS Biochemistry Units Canine Feline Bovine Equine Porcine Ovine Sodium mmol/l 144-151 149-156 135-151 135-148 140-150 143-151 Potassium mmol/l 3.9-5.3 3.3-5.2 3.9-5.9 3.0-5.0 4.7-7.1 4.6-7.0
REFERENCE INTERVALS Biochemistry Units Canine Feline Bovine Equine Porcine Ovine Sodium mmol/l 144-151 149-156 135-151 135-148 140-150 143-151 Potassium mmol/l 3.9-5.3 3.3-5.2 3.9-5.9 3.0-5.0 4.7-7.1 4.6-7.0
Pediatrics. Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment. Definition. Epidemiology of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency.
 Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
9/28/2016. Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach. Objectives. Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
 Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
International Journal of Biology January, 2010
 International Journal of Biology January, 2010 Spectrum of ATP7B Gene Mutations in Pakistani Wilson Disease Patients: A Novel Mutation Is Associated with Severe Hepatic and Neurological Complication Abdul
International Journal of Biology January, 2010 Spectrum of ATP7B Gene Mutations in Pakistani Wilson Disease Patients: A Novel Mutation Is Associated with Severe Hepatic and Neurological Complication Abdul
Drug-induced liver injury
 Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
COPPER AND CAERULOPLASMIN: GUIDELINES FOR REQUESTING
 Version: 2.0 Ratified by: Clinical Biochemistry Senior Staff meeting Date ratified: 24 th March 2014 Name of originator/author: Director responsible for implementation: Elizabeth Hall/ Dr Joanne Carter
Version: 2.0 Ratified by: Clinical Biochemistry Senior Staff meeting Date ratified: 24 th March 2014 Name of originator/author: Director responsible for implementation: Elizabeth Hall/ Dr Joanne Carter
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski
 Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Hepatitis C: Management of Previous Non-responders with First Line Protease Inhibitors
 Hepatitis C: Management of Previous Non-responders with First Line Protease Inhibitors Fred Poordad, MD The Texas Liver Institute Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center
Hepatitis C: Management of Previous Non-responders with First Line Protease Inhibitors Fred Poordad, MD The Texas Liver Institute Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
BASIC METABOLIC PANEL
 Update 2/12/2018 BASIC METABOLIC PANEL CPT 80048 Stability: 3 days at 15-25 C; 7 days at 2-8 C; > 7 days at -70 C Colorimetric Assay, Rate reaction, ISE Components: BUN, Calcium, Chloride, CO2, Creatinine,
Update 2/12/2018 BASIC METABOLIC PANEL CPT 80048 Stability: 3 days at 15-25 C; 7 days at 2-8 C; > 7 days at -70 C Colorimetric Assay, Rate reaction, ISE Components: BUN, Calcium, Chloride, CO2, Creatinine,
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
-Liver function tests -
 -Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
-Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
The effect of aerobic exercise on serum level of liver enzymes and liver echogenicity in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of aerobic exercise on serum level of liver enzymes
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of aerobic exercise on serum level of liver enzymes
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update Eve A. Roberts 1 and Michael L. Schilsky 2 This guideline has been approved by the American Association for the Study of Liver
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson Disease: An Update Eve A. Roberts 1 and Michael L. Schilsky 2 This guideline has been approved by the American Association for the Study of Liver
Wilson disease (WD; hepatolenticular degeneration) AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease. Preamble.
 Correction The following acknowledgement was inadvertently omitted from A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease by Eve A. Roberts and Michael L. Schilsky (HEPATOLOGY 2003;37:1475-1492): This Guideline was
Correction The following acknowledgement was inadvertently omitted from A Practice Guideline on Wilson Disease by Eve A. Roberts and Michael L. Schilsky (HEPATOLOGY 2003;37:1475-1492): This Guideline was
Patients must have met all of the following inclusion criteria to be eligible for participation in this study.
 Supplementary Appendix S1: Detailed inclusion/exclusion criteria Patients must have met all of the following inclusion criteria to be eligible for participation in this study. Inclusion Criteria 1) Willing
Supplementary Appendix S1: Detailed inclusion/exclusion criteria Patients must have met all of the following inclusion criteria to be eligible for participation in this study. Inclusion Criteria 1) Willing
In 1993, the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:417 421 Validation and Modification of Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children ELIZABETH MILETI,* PHILIP ROSENTHAL,*, and MARION
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:417 421 Validation and Modification of Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children ELIZABETH MILETI,* PHILIP ROSENTHAL,*, and MARION
Susan Stegman, MD Medical Director AXA Equitable Life May 3, 2016
 Susan Stegman, MD Medical Director AXA Equitable Life May 3, 2016 Underwriting impact Anemia overview Classification of anemia Specific anemia topics Iron deficiency anemia Thalassemia Megaloblastic anemia
Susan Stegman, MD Medical Director AXA Equitable Life May 3, 2016 Underwriting impact Anemia overview Classification of anemia Specific anemia topics Iron deficiency anemia Thalassemia Megaloblastic anemia
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
Risk stratification in PBC
 Risk stratification in PBC Christophe Corpechot Reference Center for Inflammatory Biliary Diseases Saint-Antoine hospital, Paris, France What is currently known (background) PBC : chronic, progressive
Risk stratification in PBC Christophe Corpechot Reference Center for Inflammatory Biliary Diseases Saint-Antoine hospital, Paris, France What is currently known (background) PBC : chronic, progressive
Fulminant Hepatic Failure without Evidence of Cirrhosis in a Case of Wilson's Disease
 Case Report Fulminant Hepatic Failure without Evidence of Cirrhosis in a Case of Wilson's Disease Katsuaki ENOMOTO, Hiromi ISHIBASHI, Katsumi Irie, Yuzo OKUMURA, Hideyuki NOMURA, Masahiro FUKUSHIMA*, Shoichi
Case Report Fulminant Hepatic Failure without Evidence of Cirrhosis in a Case of Wilson's Disease Katsuaki ENOMOTO, Hiromi ISHIBASHI, Katsumi Irie, Yuzo OKUMURA, Hideyuki NOMURA, Masahiro FUKUSHIMA*, Shoichi
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets)
 Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets) Policy Number: 5.01.619 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2016 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets) Policy Number: 5.01.619 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2016 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests
 Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Med Chem 535P ~ Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry. General Comments
 Med Chem 535P ~ Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry General Comments Most blood chemistry and serology assays are performed automatically. Larger clinical laboratories often use sophisticated analyzers that
Med Chem 535P ~ Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry General Comments Most blood chemistry and serology assays are performed automatically. Larger clinical laboratories often use sophisticated analyzers that
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert.
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. GENERIC DRUG NAME / COMPOUND NUMBER: Tofacitinib / CP-690,550
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. GENERIC DRUG NAME / COMPOUND NUMBER: Tofacitinib / CP-690,550
Unusually low serum alkaline phosphatase activity in a patient with acute on chronic liver failure and hemolysis
 This is a Platinum Open Access Journal distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction
This is a Platinum Open Access Journal distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction
King Abdul-Aziz University Hospital (KAUH) is a tertiary
 Modelling Factors Causing Mortality in Oesophageal Varices Patients in King Abdul Aziz University Hospital Sami Bahlas Abstract Objectives: The objective of this study is to reach a model defining factors
Modelling Factors Causing Mortality in Oesophageal Varices Patients in King Abdul Aziz University Hospital Sami Bahlas Abstract Objectives: The objective of this study is to reach a model defining factors
Liver Function Tests. Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy
 Liver Function Tests Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Metabolic function Excretory function Synthetic fuction Detoxification function Storage function
Liver Function Tests Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Metabolic function Excretory function Synthetic fuction Detoxification function Storage function
Management of autoimmune hepatitis. Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France
 Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France 41 year-old woman, coming to emergency department for fatigue
Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France 41 year-old woman, coming to emergency department for fatigue
Presentation of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 3 Mimicking Wilson Disease: Molecular Genetic Diagnosis and Response to Treatment
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.3.202 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2015 September 18(3):202-208 Case Report PGHN Presentation of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2015.18.3.202 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2015 September 18(3):202-208 Case Report PGHN Presentation of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic
Wilson's disease with severe hepatic insufficiency: beneficial effects of early administration of D-penicillamine. DURAND, F, et al.
 Article Wilson's disease with severe hepatic insufficiency: beneficial effects of early administration of D-penicillamine DURAND, F, et al. Abstract Wilson's disease, heralded by severe hepatic insufficiency,
Article Wilson's disease with severe hepatic insufficiency: beneficial effects of early administration of D-penicillamine DURAND, F, et al. Abstract Wilson's disease, heralded by severe hepatic insufficiency,
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease
 Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO Selection Examination for Enrolment to the in-service Training Programme in Postgraduate Certificate in Basic Laboratory Sciences leading to the
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO Selection Examination for Enrolment to the in-service Training Programme in Postgraduate Certificate in Basic Laboratory Sciences leading to the
Suspected Isoflurane Induced Hepatitis from Cross Sensitivity in a Post Transplant for Fulminant Hepatitis from Halothane.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 25 Number 1 Suspected Isoflurane Induced Hepatitis from Cross Sensitivity in a Post Transplant for Fulminant Hepatitis from Halothane. V Sampathi,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 25 Number 1 Suspected Isoflurane Induced Hepatitis from Cross Sensitivity in a Post Transplant for Fulminant Hepatitis from Halothane. V Sampathi,
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease. Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya
 Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Cytochrome-C (rat, mouse) forward GGAGGCAAGCATAAGACTGG. mouse hexokinase 2 gene, intron 9 reverse GGGAACACAAAAGACCTCTTCTGG
 Supplementary Table 1. The sequences of oligonucleotide primers. Genes Sequence rat actin forward CGAGTACAACCTTCTTGCAG rat actin reverse GAGTCCTTCTGACCCATACC tubulin (rat, mouse) forward TAGCAGAGATCACCAATGCC
Supplementary Table 1. The sequences of oligonucleotide primers. Genes Sequence rat actin forward CGAGTACAACCTTCTTGCAG rat actin reverse GAGTCCTTCTGACCCATACC tubulin (rat, mouse) forward TAGCAGAGATCACCAATGCC
Subject ID: I N D # # U A * Consent Date: Day Month Year
 IND Study # Eligibility Checklist Pg 1 of 15 Instructions: Check the appropriate box for each Inclusion and Exclusion Criterion below. Each criterion must be marked and all protocol criteria have to be
IND Study # Eligibility Checklist Pg 1 of 15 Instructions: Check the appropriate box for each Inclusion and Exclusion Criterion below. Each criterion must be marked and all protocol criteria have to be
Burak DiK 1, Emre BAHCIVAN 1,2, Hatice ESER 1,3, Kamil UNEY 1
 Burak DiK 1, Emre BAHCIVAN 1,2, Hatice ESER 1,3, Kamil UNEY 1 1 Selcuk University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Pharmacology and Toxicology Department, Konya, TURKEY 2 Kafkas University Faculty of Veterinary
Burak DiK 1, Emre BAHCIVAN 1,2, Hatice ESER 1,3, Kamil UNEY 1 1 Selcuk University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Pharmacology and Toxicology Department, Konya, TURKEY 2 Kafkas University Faculty of Veterinary
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing. IgA & ttg IgA
 Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Provided by MedicalStudentExams.com NORMAL LABORATORY VALUES
 NORMAL LABORATORY VALUES 1. BLOOD, PLASMA, SERUM 2. CEREBROSPINAL FLUID 3. HEMATOLOGIC 4. SWEAT 5. URINE 6. SYNOVIAL FLUID 7. TOXIC LEVELS 8. Tumour Markers 9. Differential of Cerebral Spinal Fluid 10.
NORMAL LABORATORY VALUES 1. BLOOD, PLASMA, SERUM 2. CEREBROSPINAL FLUID 3. HEMATOLOGIC 4. SWEAT 5. URINE 6. SYNOVIAL FLUID 7. TOXIC LEVELS 8. Tumour Markers 9. Differential of Cerebral Spinal Fluid 10.
BC Biomedical Laboratories Adult Reference Ranges
 BC Biomedical Laboratories Adult s Name Age 25 OH VITAMIN D Blood B 0-100 nmol/l Interpretation: < 25 Deficient 25-74 Insufficient 75-199 Sufficient > 200 Toxic 5HIAA (CALC) Urine B 0-100
BC Biomedical Laboratories Adult s Name Age 25 OH VITAMIN D Blood B 0-100 nmol/l Interpretation: < 25 Deficient 25-74 Insufficient 75-199 Sufficient > 200 Toxic 5HIAA (CALC) Urine B 0-100
Intron A (interferon alfa-2b) with ribavirin, (Moderiba, Rebetol, Ribasphere, RibaTab, ribavirin tablets/capsules - all strengths)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.06 Subject: Intron A Ribavirin Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Intron A Ribavirin Description
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.06 Subject: Intron A Ribavirin Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Intron A Ribavirin Description
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Supplementary materials
 Supplementary materials Table S Adverse events identified by participants diary logs and blood hematologic and biochemical tests (n=2) group (n=) Placebo group (n=) P value for chi-squared test Asthma
Supplementary materials Table S Adverse events identified by participants diary logs and blood hematologic and biochemical tests (n=2) group (n=) Placebo group (n=) P value for chi-squared test Asthma
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD
 Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
NORMAL LABORATORY VALUES FOR CHILDREN
 Pediatric Drug Lookup Normal Laboratory Values for NORMAL LABORATORY VALUES FOR CHILDREN CHEMISTRY Normal Values Albumin 0-1 y 2.0-4.0 g/dl 1 y to adult 3.5-5.5 g/dl Ammonia Newborns 90-150 mcg/dl 40-120
Pediatric Drug Lookup Normal Laboratory Values for NORMAL LABORATORY VALUES FOR CHILDREN CHEMISTRY Normal Values Albumin 0-1 y 2.0-4.0 g/dl 1 y to adult 3.5-5.5 g/dl Ammonia Newborns 90-150 mcg/dl 40-120
PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features?
 22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
 The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
Congential scoliosis in Wilson s disease: case report and review of the literature
 Li et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:71 CASE REPORT Open Access Congential scoliosis in Wilson s disease: case report and review of the literature Zheng Li, Xin Yu, Jianxiong Shen * and Jinqian Liang Abstract
Li et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:71 CASE REPORT Open Access Congential scoliosis in Wilson s disease: case report and review of the literature Zheng Li, Xin Yu, Jianxiong Shen * and Jinqian Liang Abstract
