Limited joint mobility and other musculoskeletal problems in diabetes
|
|
|
- Betty Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Article Limited joint mobility and other musculoskeletal problems in diabetes Lesley Hordon Citation: Hordon L (2016) Limited joint mobility and other musculoskeletal problems in diabetes. Journal of Diabetes Nursing 20: Article points 1. Limited joint mobility can occur in people with diabetes. It is difficult to treat, but good glycaemic control may prevent it. 2. Other hand abnormalities that can occur in people with diabetes include Dupuytren s contracture, flexor tenosynovitis and diabetic sclerodactyly. Common shoulder problems include adhesive capsulitis and rotator cuff tendonitis. 3. There is increasing interest in the effects of metabolic syndrome on the prevalence of gout and osteoarthritis in type 2 diabetes. Key words - Diabetes - Gout - Limited joint mobility - Musculoskeletal problems - Osteoarthritis Authors Lesley Hordon is Consultant Rheumatologist, Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust and Honorary Senior Lecturer in Medicine, University of Leeds. While musculoskeletal conditions are common in the general population, people with diabetes are at greater risk than would be expected for their age. Identification and treatment of these problems are important to maintain quality of life. One specific problem of the diabetic hand, limited joint mobility, is difficult to treat, although better control of diabetes may reduce its prevalence in the future. Flexor tendon nodules, carpal tunnel syndrome and Dupuytren s contractures can also affect hand function and respond more readily to therapy. Painful shoulder problems are frequent in people with diabetes and require treatment. Obesity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, as well as for both osteoarthritis and gout, but there is increasing interest in the effects of the metabolic syndrome itself on the prevalence of gout and osteoarthritis in type 2 diabetes. It is important to recognise and treat both these common conditions in people with diabetes. The care of people with diabetes involves far more than the control of blood glucose levels. It is accepted that screening and management of retinopathy, microalbuminuria, neuropathy and cardiovascular risk factors, along with excellent foot care, are all necessary. However, joint problems, although common and often painful, are relatively neglected. This article covers some of the joint conditions commonly linked to diabetes, aiming to raise awareness of these in the diabetic clinic and the potential for treatment that can improve the individual s quality of life. Limited joint mobility Limited joint mobility was first described in children with type 1 diabetes in 1974 by Rosenbloom and colleagues (Rosenbloom et al, 1974). It is characterised by a limitation of joint movement, most marked in the small joints of the hand, and often associated with thickening and waxiness of the skin. Unlike arthritis, the condition is painless, although flexion contractures of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and metocarpophalangeal (MCP) joints can occur. Symptoms include stiffness, decreased grip strength and difficulty with fine movements of the hands. The distal interphalangeal joints (DIP) and, less commonly, the wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, neck and spine, may also be involved. Limited joint mobility in the feet may contribute to high foot pressures, which, along with other factors including neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease and trauma, can lead to foot ulceration. (Turner et al, 2007). Diagnosis is made by clinical examination. Two simple tests are the prayer sign, where the hands are flattened together as in prayer, and the table top sign, where the hand is pressed flat, palm downwards, on the table top (Figure 1). Contractures of the PIP, DIP and 166 Journal of Diabetes Nursing Volume 20 No
2 Figure 1. Table top sign MCP joints can be readily detected by these quick and easy manoeuvres. Skin texture is also examined to detect changes of thickening and waxiness. It is important to exclude other diabetic hand conditions, which are described later in the article. These conditions can co-exist with limited joint mobility and respond more readily to treatment. The cause of limited joint mobility is the deposition of abnormal collagen in the connective tissues around the joints. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic glycosylation of skin collagen and the production of advanced glycation end products, which lead to abnormal crosslinking and decreased turnover of collagen, are thought to be responsible (Brownlee et al, 1988; Kapoor et al, 1989; Rosenbloom, 2013). Estimates of the prevalence of limited joint mobility are difficult, as these depend on the populations of people with diabetes studied, ranging from those with mild, diet-controlled type 2 diabetes managed in primary care, to those with type 1 diabetes attending a specialist clinic. Furthermore, estimating prevalence is further complicated by the definition of limited joint mobility used. The condition can occur in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and is linked to both duration of diabetes and diabetic control as measured by HbA 1c values. The prevalence also increases with age and smoking (Eadington et al, 1991; Arkkila et al, 1994; Silverstein et al, 1998). The correlation of limited joint mobility with the more serious microvascular complications of diabetes, such as retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy, has been controversial, with studies giving conflicting results. Again, differences in populations studied contribute to these conflicting results, as well as whether the study is a cross-sectional or a long-term prospective study. There are too many studies to list here, but two examples are given. In one prospective study, 44 individuals with and without limited joint mobility were followed for 10 years. These study participants did not have nephropathy and retinopathy at baseline. At 10 years, similar numbers in both groups developed retinopathy and microalbuminuria (McCance et al, 1993). A larger prospective study studied 479 children for a median of 10.9 years following diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and found that 35% developed limited joint mobility at a median age of 13 years and a duration of diabetes of 5.2 years. The risk of developing limited joint mobility was related to higher HbA 1c levels, as well as puberty. Children with limited joint mobility had an increased risk of microalbuminuria (Amin et al, 2005). The association between limited joint mobility and diabetic control has been equally controversial in the past, due to differences in study populations. Perhaps more importantly, the assessment of diabetic control has been very variable in different studies. Comparing people with diabetes with and without limited joint mobility using longitudinal measurements of HbA 1c gives a better idea of long-term control in these groups, rather than a cross-sectional study of the same groups comparing HbA 1c measured at a single time point. Supportive evidence that better long-term glycaemic control reduces the frequency and severity of limited joint mobility comes from two cross-sectional studies of children at diabetes camps in the US some 20 years apart. The cohort had a prevalence of limited joint mobility of 30%, while the 1998 cohort had a prevalence of limited joint mobility of 7% (Infante et al, 2001). A similar cross-sectional British study looking at adults with type 1 diabetes (mean age 27) found the prevalence of limited joint mobility fell from 43% in to 23% in 2002 (Lindsay et al, 2005). Limited joint mobility does not respond well Page points 1. The cause of limited joint mobility is the deposition of abnormal collagen in the connective tissues around the joints. 2. Estimates of the prevalence of limited joint mobility are difficult, as these depend on the populations of people with diabetes studied, ranging from those with mild, diet-controlled type 2 diabetes managed in primary care, to those with type 1 diabetes attending a specialist clinic. Furthermore, estimating prevalence is further complicated by the definition of limited joint mobility used. 3. The association between limited joint mobility and diabetic control has been equally difficult to determine due to differences in study populations. Journal of Diabetes Nursing Volume 20 No
3 Page points 1. Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by the compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel at the wrist. It is associated with the duration of diabetes, but not metabolic control, nephropathy or retinopathy. 2. Dupuytren s contractures have been reported in % of outpatients with diabetes, the prevalence increasing with age and duration of diabetes. 3. Diabetic sclerodactyly is characterised by thickening and waxiness of the skin most marked on the dorsum of the fingers. It is associated with limited joint mobility, but can occur separately from this condition. to treatment. Ensuring good glycaemic control and stopping smoking is sensible, and may reduce progression, although this is uncertain. Both actions, however, have other health benefits to the person with diabetes and should be encouraged. Function can be improved by physiotherapy with palmar stretching and by occupational therapy. Other hand abnormalities in diabetes Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by the compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel at the wrist, and gives numbness and tingling, most commonly in the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers, which often disturbs sleep. If severe, wasting of the thenar eminence can occur. Carpal tunnel syndrome has been reported in up to 20% of people with diabetes and in up to 75% of those with limited joint mobility. Carpal tunnel syndrome is associated with the duration of diabetes, but not metabolic control, nephropathy or retinopathy (Chaudhuri et al, 1989; Gamstedt et al, 1993). Fortunately the results of carpal tunnel release are similar in people with and without diabetes (Thomsen et al, 2009). Dupuytren s contracture Dupuytren s contracture (shown in Figure 2) is the result of fibrosis in and around the palmar fascia, with nodule formation and contracture of the palmar fascia, leading to flexion contractures of the fingers, commonly the ring and little fingers. It is often painless. Dupuytren s contractures have been reported in 16 42% of outpatients with diabetes, the prevalence increasing with age and duration of diabetes (Gamstedt et al, 1984). Other associations of Dupuytren s contracture include racial and genetic factors, and chronic liver disease. Dupuytren s contracture is often asymptomatic, but severe cases may require surgery. Flexor tenosynovitis Flexor tenosynovitis, sometimes known as trigger finger, is characterised by a palpable nodule formation and thickening localised Figure 2. Dupuytren s contracture to the flexor tendon sheath. When the patient flexes the finger it may lock in a bent position and straightening the finger can be painful. The ring, middle fingers and thumb are most often affected, and the condition may be bilateral (Yosipovitch et al, 1990). The prevalence ranges from % in people with diabetes, depending on the population studied and can occur in 0.7% of people without diabetes, although those with diabetes are more likely to have multiple digit involvement (Vance et al, 2012). Collagen abnormalities induced by diabetes are thought to be responsible. Local corticosteroid injection can be successful (Kapoor et al, 1989) but some people require repeated surgery (Yosipovitch et al, 1990). Flexor tenosynovitis is more common in those with limited joint mobility (Kameyama et al, 2009) and it is important to distinguish between the two conditions as flexor tenosynovitis responds to treatment. Diabetic sclerodactyly Diabetic sclerodactyly is characterised by thickening and waxiness of the skin, most marked on the dorsum of the fingers. It is associated with limited joint mobility, but can occur separately from this condition. In most cases, the frequency of diabetic sclerodactyly increases with the duration of diabetes. It can be distinguished from scleroderma, which it resembles, by the absence of Raynaud s phenomenon, digital ulceration and calcinosis, and autoantibodies are negative. Improving 168 Journal of Diabetes Nursing Volume 20 No
4 diabetic control is the only option for treatment and has limited benefit. Shoulder problems Adhesive capsulitis Adhesive capsulitis, commonly known as frozen shoulder, is characterised by painful restriction of glenohumeral movement in all planes of motion, in the absence of joint degeneration sufficient to explain the condition. Both active and passive movements are restricted. The aetiology is unknown. While the prevalence is approximately 5% in those without diabetes, it increases to 19 29% in people with diabetes, depending on the diagnostic criteria used and the population studied. In people with diabetes, the condition is more likely to be bilateral (Pal et al, 1986; Balci et al, 1999). Adhesive capsulitis in those with diabetes is associated with increased age, longer duration of diabetes, the presence of limited joint mobility and Dupuytren s contractures. Some studies have shown associations with retinopathy and neuropathy, as well as poorer glycaemic control. For both those with and without diabetes, treatment is with analgesia, intra-articular steroids and physiotherapy. Arthroscopic release may help in resistant cases, but people with diabetes are slightly less likely to respond than those without diabetes (71% versus 90%; Mehta et al, 2014). Adhesive capsulitis commonly resolves slowly over 1 3 years, but a significant minority of patients in both groups (7 15%) are left with residual functional disability. Rotator cuff tendonitis Rotator cuff tendonitis gives an aching discomfort in the shoulder, with pain both at night and on movement. Pain is felt in the deltoid area of the upper arm and is aggravated by abduction, with a painful arc of movement between degrees. Calcific tendonitis is three times more common in those with diabetes compared to those without, although only one third have symptoms (Mavrikakis et al, 1991). Of 60 people with diabetes with shoulder pain, 58% had adhesive capsulitis and 28% tendonitis (Moren-Hybbinette et al, 1987). Treatment is by steroid injection Figure 3. Both women and men with gout have a higher risk of diabetes. and physiotherapy, although surgery may be required in persistent cases. Osteoarthritis and gout Obesity is a risk factor for gout and also for osteoarthritis, particularly of the knee, as well as for type 2 diabetes. There is increasing interest in whether diabetes itself, independent of the mechanical and metabolic effects of obesity, is a risk factor for these two conditions. Two studies, both of which adjusted for age and body mass index, have linked osteoarthritis to diabetes. A cross-sectional study of people with diabetes in Puerto Rico showed a two-fold increased risk of hand and knee osteoarthritis, with the risk lower in those who only used insulin for their diabetes (Nieves-Plaza et al 2013). A longitudinal cohort study showed that type 2 diabetes was an independent risk factor for severe osteoarthritis leading to hip and knee replacement (Schett et al, 2013). Men with gout (Figure 3) appear to have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes independent of other risk factors such as age, body mass Journal of Diabetes Nursing Volume 20 No
5 While treatment of many of the musculoskeletal problems associated with diabetes is outside the scope of the diabetic clinic, their prompt recognition can ensure the individual is referred along the correct pathway for help. index and family history of diabetes (Choi et al, 2008). In a large insurance database study, the risk of diabetes was found to be higher in people with gout, compared with that in people with osteoarthritis, even when adjusted for comorbidities, such as obesity. Women with gout appeared to be at higher risk of diabetes than men with gout in this study (Kim et al, 2015). Conclusion While treatment of many of the musculoskeletal problems associated with diabetes is outside the scope of the diabetic clinic, their prompt recognition can ensure the individual is referred along the correct pathway for help. Good blood glucose control and weight management may play a part in the reducing the prevalence of some of these musculoskeletal conditions, as well as other diabetic complications. n Amin R, Bahu TK, Widmer B et al (2005) Longitudinal relationship between limited joint mobility, height, insulin like growth factor 1 levels and risk of developing microalbuminuria: The Oxford Regional Prospective Study. Arch Dis Child 90: Arkkila PE, Kantola IM, Viikari JS (1994) Limited joint mobility in type 1 diabetic patients: Correlation to other diabetic complications. J Intern Med 236: Balci N, Balci MK, Tuzuner S (1999) Shoulder adhesive capsulitis and shoulder range of motion in type II diabetes mellitus: Association with diabetic complications. J Diabetes Complications 13: Brownlee M, Cerami A, Viassara H (1988) Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Eng J Med 318: Chaudhuri KR, Davidson AR, Morris IM (1989) Limited joint mobility and carpal tunnel syndrome in insulin dependent diabetes. Br J Rheumatol 28: Choi HK, De Vera MA, Krishnan E (2008) Gout and the risk of type 2 diabetes among men with a high cardiovascular profile. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: Eadington DW, Patrick AW, Frier BM (1991) Association between connective tissue changes and smoking habit in Type 2 diabetes and non diabetic humans. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 11: Gamstedt A, Noble J, Heathcote JG, Cohen H (1984) Diabetes mellitus in the aetiology of Dupuytren s disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 66: Gamstedt A, Holm-Glad J, Ohlson CG, Sundstrom M (1993) Hand abnormalities are strongly associated with the duration of diabetes mellitus. J Intern Med 234: Infante JR, Rosenbloom AL, Silverstein JH et al (2001) Changes in frequency and severity of limited joint mobility in children with Type 1 diabetes mellitus between and J Pediatr 138: 33 7 Kameyama M, Meguro S, Funae O et al (2009) The presence of limited joint mobility is significantly associated with multiple digit involvement by stenosing flexor tenosynovitis in diabetics. J Rheumatol 36: Kapoor A, Sibbitt WL (1989) Contractures in diabetes mellitus: the syndrome of limited joint mobility. Semin Arthritis Rheum 18: Kim SC, Liu J, Solomon DH (2015) Risk of incident diabetes in patients with gout: a cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol 67: Lindsay JR, Kennedy L, Atkinson AB et al (2005) Reduced prevalence of limited joint mobility in Type 1 diabetes in a UK clinic population over a 20 year period. Diabetes Care 28: Mavrikakis ME, Sfikakis PP, Kontoyannis SA et al (1991) Clinical and laboratory parameters in adult diabetics with and without calcific shoulder periarthritis. Calcif Tissue Int 49: McCance DR, Crowe G, Quinn MJ et al (1993) Incidence of microvascular complications in Type 1 diabetic subjects with limited joint mobility: A 10 year prospective study. Diabet Med 10: Mehta SS, Singh HP, Pandey R (2014) Comparative outcome of arthroscopic release for frozen shoulder in patients with and without diabetes. Bone Joint J 96-B: Moren-Hybbinette I, Moritz U, Scherstein B (1987) The clinical picture of the diabetic shoulder natural history, social consequences and analysis of concomitant hand syndrome. Acta Med Scand 221: Nieves-Plaza M, Castro-Santana LE, Font YM et al (2013) Association of hand or knee osteoarthritis with diabetes mellitus in a population of Hispanics from Puerto Rico. J Clin Rheumatol 19: 1 6 Pal B, Anderson J, Dick WC, Griffiths ID (1986) Limitation of joint mobility and shoulder capsulitis in insulin- and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Br J Rheumatol 25: Rosenbloom AL (2013) Limited joint mobility in Childhood diabetes: Discovery, description and decline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98: Rosenbloom AL, Grigic A, Frias JL (1974) Diabetes mellitus, short stature and joint stiffness a new syndrome. Pediatr Res 8: 441 Schett G, Kleyer A, Perricone C et al (2013) Diabetes is an independent predictor for severe osteoarthritis: Results from a longitudinal cohort study. Diabetes Care 36: Silverstein JH Gordon G, Pollock BH Rosenbloom AL (1998) Long term glycaemic control influences the onset of limited joint mobility in type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 132: Thomsen NO, Cederlund R, Rosen I et al (2009) Clinical outcomes of surgical release among diabetic patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: prospective follow up with matched controls. J Hand Surg Am 34: Turner DE, Helliwell PS, Burton AK, Woodburn J (2007) The relationship between passive range of motion and range of motion during gait and plantar pressure measurements. Diabet Med 24: Vance MC, Tucker JJ, Harness NG (2012) The association of haemoglobin A1C with the prevalence of stenosing tenosynovitis. J Hand Surg Am 37: Yosipovitch G, Yosipovitch Z, Karp M, Mukamel M (1990) Trigger finger in young patients with insulin dependent diabetes. J Rheumatol 17: Journal of Diabetes Nursing Volume 20 No
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment
 Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley.
 TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Upper limb injuries II. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Original article J Indian Rheumatol Assoc 2003 : 11 : 25-29
 Original article J Indian Rheumatol Assoc 2003 : 11 : 25-29 RHEUMATOLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF DIABETES MELLITUS R N Sarkar*, Samar Banerjee**, A K Basu*** D Bandyopadhyay**** Associate Professor,* Professor,**
Original article J Indian Rheumatol Assoc 2003 : 11 : 25-29 RHEUMATOLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF DIABETES MELLITUS R N Sarkar*, Samar Banerjee**, A K Basu*** D Bandyopadhyay**** Associate Professor,* Professor,**
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
Dr David Ruttenberg MBChB.,MSc(Med).,FAFOEM
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Dr David Ruttenberg MBChB.,MSc(Med).,FAFOEM General Practitioners Outpatient Clinics Occupational Health Clinics 5-10% Prevalence in Community Is it common? Common Usually Females,
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Dr David Ruttenberg MBChB.,MSc(Med).,FAFOEM General Practitioners Outpatient Clinics Occupational Health Clinics 5-10% Prevalence in Community Is it common? Common Usually Females,
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Soft Tissue Rheumatism. Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group
 Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist
 ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist Sarah Turner, MCSP, Clinical Specialist in Hand Therapy Grad Dip Injection Therapy Workshop! Trigger Finger! OA 1 st CMC joint! De Quervain s Tenosynovitis!
ACPOMIT Conference 2013 Workshop: Hand and Wrist Sarah Turner, MCSP, Clinical Specialist in Hand Therapy Grad Dip Injection Therapy Workshop! Trigger Finger! OA 1 st CMC joint! De Quervain s Tenosynovitis!
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
JMSCR Vol 3 Issue 10 Page October 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v3i1.6 Clinical Study of Rheumatological Manifestations in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v3i1.6 Clinical Study of Rheumatological Manifestations in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb
 Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb 2019 1 5.2. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Background Carpal tunnel syndrome present with non-traumatic tingling of the fingers due to compression of the median nerve
Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb 2019 1 5.2. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Background Carpal tunnel syndrome present with non-traumatic tingling of the fingers due to compression of the median nerve
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb
 Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 www.ijcrims.com Coden: IJCRPP(USA) Research Article http://s-o-i.org/1.15/ijcrms-2016-2-1-7 Musculoskeletal disorders of the
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 www.ijcrims.com Coden: IJCRPP(USA) Research Article http://s-o-i.org/1.15/ijcrms-2016-2-1-7 Musculoskeletal disorders of the
Rheumatology hand exercises
 Rheumatology hand exercises Irving Building Rehabilitation Services 0161 206 5319 All Rights Reserved 2014. Document for issue as handout. What are the benefits of completing hand exercises? Arthritis
Rheumatology hand exercises Irving Building Rehabilitation Services 0161 206 5319 All Rights Reserved 2014. Document for issue as handout. What are the benefits of completing hand exercises? Arthritis
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing
 King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing 1.Obtaining a health history: Ask about chief complain: History of presence of muscle pain (onset, location, Aggravating and alleviating
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing 1.Obtaining a health history: Ask about chief complain: History of presence of muscle pain (onset, location, Aggravating and alleviating
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Module Eight. Application of Health Assessment NUR 225. Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System. King Saud University. Collage of Nursing
 King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
Common Elbow Problems
 Common Elbow Problems Duncan Ferguson FRACS Knee and Shoulder Specialist Elbow Instability Common 10-25% of elbow injuries Median age 30 yrs Most simple dislocations are stable after reduction recurrence
Common Elbow Problems Duncan Ferguson FRACS Knee and Shoulder Specialist Elbow Instability Common 10-25% of elbow injuries Median age 30 yrs Most simple dislocations are stable after reduction recurrence
Duputytren's Contracture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome
 NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome What is carpal tunnel? The carpal tunnel refers to an area at the base of the wrist which contains bones, nerves,
NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome What is carpal tunnel? The carpal tunnel refers to an area at the base of the wrist which contains bones, nerves,
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture
 A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS)
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES. Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity
 UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity ANATOMY BONES Clavicle Scapula Spine of the scapula Acromion process Glenoid fossa/cavity Humerus Epicondyles ANATOMY BONES Ulna
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity ANATOMY BONES Clavicle Scapula Spine of the scapula Acromion process Glenoid fossa/cavity Humerus Epicondyles ANATOMY BONES Ulna
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery. (Minor procedure in Primary Care)
 Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery (Minor procedure in Primary Care) Information for Patients Gateshead Upper Limb Unit Page 1 of 5 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Surgery (Minor procedure in Primary Care) Information for Patients Gateshead Upper Limb Unit Page 1 of 5 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 1058/98. Fibromyalgia.
 SUMMARY DECISION NO. 1058/98 Fibromyalgia. The worker suffered a wrist injury in 1984. The worker appealed a decision of the Appeals Officer denying entitlement for fibromyalgia. Considering the evidence
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 1058/98 Fibromyalgia. The worker suffered a wrist injury in 1984. The worker appealed a decision of the Appeals Officer denying entitlement for fibromyalgia. Considering the evidence
Dupuytrens contracture
 OA Wrist Ganglion/Cysts Dupuytrens contracture Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel pathway For advice on management of CTS please follow link to Map of Medicine Trigger Finger Trigger finger pathway For
OA Wrist Ganglion/Cysts Dupuytrens contracture Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel pathway For advice on management of CTS please follow link to Map of Medicine Trigger Finger Trigger finger pathway For
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES
 ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
Rheumatology & Immunology. Regional pain syndromes to be covered today. Some definitions. Tendinitis. Bursitis. History. History. Exam.
 Rheumatology & Immunology Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating soft tissue syndromes are not! Soft tissue syndromes one of the most common reasons patients present to their doctor.
Rheumatology & Immunology Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating soft tissue syndromes are not! Soft tissue syndromes one of the most common reasons patients present to their doctor.
79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance,
79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance,
Trigger Finger Release
 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
Rotator Cuff Strain and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Rotator Cuff Strain and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: SG, Arms, and Hands Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn
Rotator Cuff Strain and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: SG, Arms, and Hands Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn
80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance,
80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance,
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
Carpal tunnel decompression advice
 Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus
 Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Frozen Shoulders FAQs. Dr Kelvin TAM
 Frozen Shoulders FAQs Dr Kelvin TAM Summary Shoulder pain is a common problem. Shoulder pain is commonly labeled frozen shoulder. But what is frozen shoulder? Is shoulder pain always frozen shoulder or
Frozen Shoulders FAQs Dr Kelvin TAM Summary Shoulder pain is a common problem. Shoulder pain is commonly labeled frozen shoulder. But what is frozen shoulder? Is shoulder pain always frozen shoulder or
Dr Ng Swee Cheng Senior Consultant Khoo Teck Puat Hospital
 Dr Ng Swee Cheng Senior Consultant Khoo Teck Puat Hospital 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism 2. Myofascial Pain 3. Neurovascular compression Syndromes 4. Complex Regional Pain Syndromes Tendinitis, tenosynovitis
Dr Ng Swee Cheng Senior Consultant Khoo Teck Puat Hospital 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism 2. Myofascial Pain 3. Neurovascular compression Syndromes 4. Complex Regional Pain Syndromes Tendinitis, tenosynovitis
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare. Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
 NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Golfers elbow. Physiotherapy of Department
 Golfers elbow Physiotherapy of Department Image copied from http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/elbow-pain/ specific-conditions.aspx This document can be provided in different
Golfers elbow Physiotherapy of Department Image copied from http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/elbow-pain/ specific-conditions.aspx This document can be provided in different
Carpal tunnel syndrome
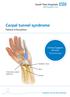 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
 INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagram of the ulnar nerve supplying the muscles of forearm and hand Cubital Tunnel is a condition that refers to the ulnar nerve being compressed around the elbow.
INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagram of the ulnar nerve supplying the muscles of forearm and hand Cubital Tunnel is a condition that refers to the ulnar nerve being compressed around the elbow.
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management. Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics
 + The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics + Why is Rheumatoid Arthritis important? + RA is a very debilitating disease median life expectancy
+ The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics + Why is Rheumatoid Arthritis important? + RA is a very debilitating disease median life expectancy
Musculoskeletal Assessment ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 Health Assessment - 1 - Lab 8: Musculoskeletal Assessment University of Kerbala / College of Nursing Adult Nursing Department Health Assessment Musculoskeletal Assessment ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY The musculoskeletal
Health Assessment - 1 - Lab 8: Musculoskeletal Assessment University of Kerbala / College of Nursing Adult Nursing Department Health Assessment Musculoskeletal Assessment ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY The musculoskeletal
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Anatomic Distribution of Sensory Symptoms in the Hand and Their Relation to Neck Pain, Psychosocial Variables, and Occupational Activities
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 157, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwf225 Anatomic Distribution
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 157, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwf225 Anatomic Distribution
Common Hand Problems and Case Examples. September 22, 2017 Carolyn Berg, MD Advanced Orthopedics of Oklahoma
 Common Hand Problems and Case Examples September 22, 2017 Carolyn Berg, MD Advanced Orthopedics of Oklahoma Sometimes the problem is obvious Sometimes the problem is everywhere Anatomy Skin Tendon Extrinsic
Common Hand Problems and Case Examples September 22, 2017 Carolyn Berg, MD Advanced Orthopedics of Oklahoma Sometimes the problem is obvious Sometimes the problem is everywhere Anatomy Skin Tendon Extrinsic
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th. Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
Lecture Notes The LocomotorSystem. W. P. Howlett 2017
 Lecture Notes The LocomotorSystem W. P. Howlett 2017 Symptoms Main Symptoms Pain Stiffness Swelling Weakness The History Joints: involved Pain: onset, precipitating& relievingfactors Stiffness: pattern
Lecture Notes The LocomotorSystem W. P. Howlett 2017 Symptoms Main Symptoms Pain Stiffness Swelling Weakness The History Joints: involved Pain: onset, precipitating& relievingfactors Stiffness: pattern
March 2015 Stiff Back: Not a Good Way to Start the Day Morning back stiffness can stem from
 Stiff Back: Not a Good Way to Start the Day Morning back stiffness can stem from a large number of conditions, from the mundane to the exotic. In an otherwise healthy individual, it can simply be the result
Stiff Back: Not a Good Way to Start the Day Morning back stiffness can stem from a large number of conditions, from the mundane to the exotic. In an otherwise healthy individual, it can simply be the result
Acute Services Division. Information for patients. Carpal Tunnel. Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary
 Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Official Definition. Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
 Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Kinesiology Tape. Table of contents:
 1 Kinesiology Tape Welcome to the Anuva application center. These application guidelines and general use instructions are intended to be used with Anuve professional quality Kinesiology tape and if followed
1 Kinesiology Tape Welcome to the Anuva application center. These application guidelines and general use instructions are intended to be used with Anuve professional quality Kinesiology tape and if followed
Aspiration, Intra-articular and Soft Tissue Injections. MR KEWAL SINGH, MS(orth), FRCS(Eng)
 Aspiration, Intra-articular and Soft Tissue Injections MR KEWAL SINGH, MS(orth), FRCS(Eng) Indications for Aspiration Haemarthrosis Septic arthritis Symptomatic relief of a large effusion Crystal-induced
Aspiration, Intra-articular and Soft Tissue Injections MR KEWAL SINGH, MS(orth), FRCS(Eng) Indications for Aspiration Haemarthrosis Septic arthritis Symptomatic relief of a large effusion Crystal-induced
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM
 TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference.
 Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Essential intervention No. 3 Oedema control KEY OBJECTIVES. Danger
 Essential intervention No. 3 Oedema control KEY OBJECTIVES To know what causes oedema. To know which kind of oedema needs to be referred for emergency surgery and why. To know the effects of oedema on
Essential intervention No. 3 Oedema control KEY OBJECTIVES To know what causes oedema. To know which kind of oedema needs to be referred for emergency surgery and why. To know the effects of oedema on
The Golfers Ten Program. 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule
 The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
GENERAL EXERCISES ELBOW BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES ELBOW BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
GENERAL EXERCISES ELBOW BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE
 GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Physiotherapy Department Rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation Information for patients This information leaflet gives you advice on rehabilitation after your
The Joints are Painful & Swollen: Do I give Steroids? Dr Tom Kennedy
 The Joints are Painful & Swollen: Do I give Steroids? Dr Tom Kennedy Learning Objectives When to use an acute rheumatology service Appropriate use of steroids by condition Injection or Oral or Intramuscular
The Joints are Painful & Swollen: Do I give Steroids? Dr Tom Kennedy Learning Objectives When to use an acute rheumatology service Appropriate use of steroids by condition Injection or Oral or Intramuscular
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome
 Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures:
 Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
SHOULDER PAIN. A Real Pain in the Neck. Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017
 SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
Range of motion and positioning
 Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination
 History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination Introduction A thorough rheumatologic assessment is performed within the context of a good general evaluation of the patient. The patient should be undressed
History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination Introduction A thorough rheumatologic assessment is performed within the context of a good general evaluation of the patient. The patient should be undressed
ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting)
 ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting) Position (A) Patient: Place arm against side of trunk. Helper: Hold elbow to stabilize. (B) - Lift hand toward shoulder, palm up. - Keep wrist straight. Do sessions
ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting) Position (A) Patient: Place arm against side of trunk. Helper: Hold elbow to stabilize. (B) - Lift hand toward shoulder, palm up. - Keep wrist straight. Do sessions
Impingement syndrome. Clinical features. Management. Rotator cuff tear diagnosed. Go to rotator cuff tear
 Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
VSRF+ Orthopaedics Referral Form. Triage Categories/ Appointment Wait Time Emergency/After Hours:
 Northern Health Orthopaedic Pre referral Management Guidelines Orthopaedic Consultants: Mr A. Bonomo Mr R. Hau Mr A. Chia Mr D. Robin Ms J. Gentle Mr A. Chehata Mr R. Unni Osteoarthritis Hip & Knee Service
Northern Health Orthopaedic Pre referral Management Guidelines Orthopaedic Consultants: Mr A. Bonomo Mr R. Hau Mr A. Chia Mr D. Robin Ms J. Gentle Mr A. Chehata Mr R. Unni Osteoarthritis Hip & Knee Service
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
Swan-Neck Deformity. Introduction. Anatomy
 Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
