NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Clin Chem. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 August 05.
|
|
|
- Leona Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Clin Chem June ; 58(6): doi: /clinchem Clinical Measurement of von Willebrand Factor by Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy Richard Torres 1,2, Jonathan R. Genzen 3, and Michael J. Levene 1,* 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yale University and Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT 2 Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yale University and Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT 3 Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY Abstract BACKGROUND Identification of von Willebrand factor (vwf) abnormalities in a variety of conditions is hampered by the limitations of currently available diagnostic tests. Although direct multimer visualization by immunoelectrophoresis is a commonly used method, it is impractical as a routine clinical test. In this study, we used a biophysical analysis tool, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS), to measure vwf distributions. The goals were to develop a method that is quicker and simpler than vwf gel electrophoresis and to evaluate the potential of FCS as a clinical diagnostic technique. METHODS We analyzed plasma from 12 patients with type 1 von Willebrand disease (vwd), 14 patients with type 2 vwd, and 10 healthy controls using a fluctuation-based immunoassay approach. RESULTS FCS enabled identification and proper classification of type 1 and type 2 vwd, producing quantitative results that correspond to qualitative gel multimer patterns. FCS required minimal sample preparation and only a 5-min analysis time. CONCLUSIONS This study represents the first implementation of FCS for clinical diagnostics directly on human plasma. The technique shows potential for further vwf studies and as a generally applicable laboratory test method. The protein von Willebrand factor (vwf) 4 functions as a recruiter, tether, and activator of platelets and as the protective carrier for factor VIII. It is normally present in plasma as a 2012 American Association for Clinical Chemistry * Address correspondence to this author at: P.O. Box , New Haven, CT michael.levene@yale.edu.. Author Contributions: All authors confirmed they have contributed to the intellectual content of this paper and have met the following 3 requirements: (a) significant contributions to the conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; (b) drafting or revising the article for intellectual content; and (c) final approval of the published article. Authors Disclosures or Potential Conflicts of Interest: Upon manuscript submission, all authors completed the author disclosure form. Disclosures and/or potential conflicts of interest: Employment or Leadership: None declared. Consultant or Advisory Role: None declared. Stock Ownership: None declared. Honoraria: None declared. Expert Testimony: None declared.
2 Torres et al. Page 2 distribution of multimers containing anywhere from 2 to 40 or more vwf monomers. Abnormalities in vwf activity, most often related to abnormal concentration or multimer distribution, are the incident cause of the group of coagulopathies known as von Willebrand disease (vwd) (1, 2). As a group, vwd is considered to be the most common inherited coagulation disorder. Abnormalities in vwf are also responsible for secondary bleeding conditions, such as in acquired vwd, and are associated with inherited and acquired thrombotic states, such as the procoagulant disease known as thrombotic thrombo-cytopenia purpura. In addition, several common conditions have been known to affect vwf distributions including coronary artery disease, pregnancy, cancer, sepsis, diabetes, autoimmune disease, and others (3-5). Despite its importance in inherited and acquired bleeding disorders, and the mounting evidence for its role in thrombotic disease, routine evaluation is hampered by the limitations of currently available laboratory tests. Limitations in vwf Testing The main clinical subclassification of vwf abnormalities is based on whether the deficiency is purely a quantitative one (type 1 vwd) or includes a functional component (type 2 vwd). Type 2 vwd is most often related to a decrease in the concentration of larger multimers, which have the highest ability to bind collagen and recruit and activate platelets. A third type (type 3 vwd) is characterized by complete or near-complete absence of vwf, which is fortunately rare. The groupings above have clinical consequences that relate to therapy and prognosis. In type 1 vwd, patients may receive the vasopressin analog 1-deamino-[8-D-arginine]-vasopressin (DDAVP), which stimulates preferentially large multimer secretion from endothelial cells (6) and often provides sufficient functional capacity for adequate hemostasis. Type 2 vwd is much more likely to require the administration of vwf concentrate. Antibody-based quantification of vwf antigen (vwf:ag) concentration does not provide information regarding the relative multimer size distribution and cannot be used independently to subclassify vwf abnormalities. Functional tests used for classification, such as ristocetin cofactor activity (vwf:rcof) and the collagen-binding assay (vwf:cb), suffer from poor reproducibility, limited reportable ranges, and lack of standardization. The gold standard for multimer visualization, gel electrophoresis, is a cumbersome, non-quantitative, and time-consuming assay primarily available only from reference laboratories. Additional diagnostic challenges associated with current vwf laboratory testing methods have been recently reviewed (7, 8). Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) measures the absolute concentration and mobility of fluorescent species as they diffuse through a well-defined observation volume. It has not been previously applied to clinical testing in human plasma. FCS is well suited for this type of testing in that it is rapid, simple to perform, and has a low cost per test. FCS can be performed without washing steps, with volume measurements that are optically defined, and with very small amounts of testing sample and reagents. In FCS, when on average only a few molecules are present in a given observation volume, fluctuations in the actual number follow predictable Poisson statistics [see references (9-11) for more detailed description]. Comparison of fluctuations in the fluorescence signal to the 4 Nonstandard abbreviations: vwf, von Willebrand factor; vwd, von Willebrand disease; DDAVP, 1-deamino-[8-D-arginine]- vasopressin; vwf:ag, vwf antigen; vwf:rcof, ristocetin cofactor activity; vwf:cb, collagen-binding assay; FCS, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy; TRITC, tetramethyl-rhodamine-isothiocyanate.
3 Torres et al. Page 3 mean fluorescence signal yields the mean number of molecules in the observation volume. The typical time scale of the fluctuations corresponds to the time it takes molecules to diffuse through the observation volume, and can therefore be related to the diffusivity of the molecules, a property that is proportional to molecule size. In practice, a laser focused to a diffraction-limited spot by a microscope objective combined with a confocal detection pinhole defines the observation volume for FCS (Fig. 1A). The basic instrument is relatively simple and inexpensive to build, consisting of a microscope objective, a high-sensitivity detector, and a specialized computer card to plot the autocorrelation of the fluorescence signal, G(τ), vs the correlation delay time τ (Fig. 1B). This curve can be fit to a function derived from the shape of the observation volume, yielding the mean number of molecules per volume, N, and the residence time (mean time of diffusion through observation volume), τ d. For the typical confocal excitation profile, one can assume a 3-dimensional gaussian observation profile such that: where τ is the correlation time, S is the structure parameter (ratio of radial to axial observation volume diameters), τ t is the triplet lifetime, and f t corresponds to the triplet state fraction. The residence time, τ d, is related to the diffusion coefficient, D, by the Stokes- Einstein equation via the diameter of the observation volume in the x,y direction. Thus, the concentration of fluorescent molecules and their diffusion coefficient can be determined directly from the fluctuations in emitted photons over time. FCS for vwf Measurement Methods The goal of this report is to examine whether FCS can address some of the limitations of current methods for vwf assessment, looking to develop a more practical tool than multimer gel analysis for measuring vwf size distributions in bleeding and clotting disorders. In this study, we used FCS for the measurement of vwf multimers in plasma from a cohort of patients with vwf test results within reference intervals and from patients with type 1 and type 2 vwd. We analyzed how the quantity and quality of vwf substrate affects measureable parameters in the FCS assay and present an approach that allows adequate subclassification of vwd with this simple-to-implement method. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN AND SAMPLE SELECTION Using institutional review board-approved protocols, we identified samples for analysis from vwf:ag, vwf:rcof, factor VIII, and multimer gel analysis data generated during routine vwd testing at Yale-New Haven Hospital and Weill Cornell Medical College. Twenty-six samples from patients who fulfilled the respective laboratory director s criteria for von Willebrand disease (12 type 1 and 14 type 2) were selected on the basis of unequivocally low values in vwf:ag (<50%), vwf:rcof (<50%), and/or antigen-toactivity ratio (<0.5). Although current recommendations for characterization as vwd vary, these concentrations correspond to the reference values used clinically at the testing site, and values below 50% are associated with progressively increased risk of excessive bleeding relative to average healthy controls regardless of cause. Samples were also collected from 1 patient who underwent a therapeutic DDAVP trial. Ten apparently healthy patients with all vwf values within reference intervals (75% < vwf:ag <150%, 75% < vwf:rcof <150%) (1)
4 Torres et al. Page 4 and confirmed normal multimer analyses were randomly selected for comparison. Antigen and activity percentage units refer to a normalized pooled standard representing 100%, equivalent to 100 U/dL, against which reference standards used for calibration are measured (Diagnostica-Stago). TRADITIONAL vwf TESTING vwf TESTING BY FCS DATA ANALYSIS Sample collection and testing were performed by standard procedures as described in the Data Supplement, which accompanies the online version of this article at Samples were thawed at 37 C and then incubated with tetramethyl-rhodamineisothiocyanate (TRITC)-labeled monoclonal anti-vwf antibody directed to the D3 domain (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) at a final concentration of 20 nmol/l for 30 min at room temperature. We diluted 40 μl plasma 1:1 with antibody-containing phosphate buffer at ph 7.1. This dilution ensures a near-normalization of the viscosity to that of saline (12). We placed 40 μl incubated sample atop a #0 coverslip (Thermo Fisher) and analyzed it in a Confocor 2 fluorescence correlation microscope (Zeiss) at room temperature with a NA coverslip-corrected water immersion objective (Zeiss) by standard FCS procedures (10, 13). Excitation was done with a helium-neon laser at 543 nm, 543 nm dichroic mirror, and nm emission filter. Pinhole diameter was 78 μm. Ten runs of 30 s were averaged for each sample. We fitted correlation curves from tagged antibody at 50 nmol/l in phosphate buffer to a 1- component FCS equation with a triplet term (Eq. 1). The structure parameter and observation volume were derived from fits of tetramethylrhodamine dye at 100 nmol/l concentration. The triplet time (τ t, approximately 10 μs) and antibody diffusion time (τ d, approximately 320 μs) were derived from fits of TRITC-labeled antibody at 50 nmol/l. The reduced χ 2 /degrees of freedom (χ 2 /DoF) was always on the order of Raw FCS curves were fitted online on Confocor or offline with Origin software (OriginLabA). Triplet fractions (f t ) ranged from 8% to 10%. Autocorrelation curves of samples without added fluorescent antibody showed background plasma counts <10% of antibody fluorescence, with a high triplet fraction and an effective mean diffusion time of approximately 120 μs, dim and of fast enough diffusion time to be neglected from the comparison of mean diffusion time and component ratios in FCS curves. The autocorrelation curves obtained from FCS analysis of patient samples incubated with fluorescently tagged anti-vwf were fitted to a 2-component FCS equation such that: where G free (τ) and G bound (τ) are the normalized autocorrelation functions for the free- and bound-antibody components, and a free and a bound are their relative contributions (corresponding fraction) to the correlation function G total (τ). The relative brightness of free and bound components affects the proportionality between a free and a bound and therefore these represent effective fractions, corresponding to the proportion if the brightness was equal between subsets (also see the online Data Supplement). Although this is not expected to be the case in these experiments, this use of effective bound fractions allowed adequate discrimination, simplified the analysis, and improved the robustness of the fits considerably. The diffusion time (τ free ) of the free component was fixed at the measured τ d of antibody alone (320 μs, appropriate for the expected molecular weight of 140 kda and an observation (2)
5 Torres et al. Page 5 Results volume diameter ω x y of 265 nm, calculated from dye diffusion times). For individual 2- component fits, the χ 2 /DoF was always < We obtained the mean nonantibody diffusion time and an effective fraction of antibody bound directly from this 2-component fit. We generated normalized curves from the G (0) calculated on the raw 2-component fits for clearer visual comparison of FCS curve shapes. These normalized curves use an alternate form of Eq. 1 that omits the leading 1. To demonstrate the effect of vwf concentration on FCS curves, we analyzed serial saline dilutions of a normal sample. The FCS curves from these dilutions show a progressive shift toward longer mean diffusion times (curves shift to the right) with higher vwf concentrations (Fig. 2A), as might be expected with increasing binding of antibody. A global two-component fit for the dilution curves, with 1 diffusion time fixed at the antibody diffusion time, describes the data well (Fig. 2A; overall fit χ 2 /DoF = , R 2 = ). We calculated proportional increases in the percentage of the curve represented by the longer diffusion time (Fig. 2B). We observed an excellent linear correlation between the antigen concentration of the dilution and the effective fraction of antibody bound to vwf as determined from the 2-component fits. These results indicate that a 2-component fit is able to extract an effective bound percentage from the FCS curves, and it is consistent with the interpretation that we are operating in the concentration range where antibody is not fully bound. The correlation (Fig. 2B) also demonstrates a leveling off at the highest vwf:ag concentrations, as would be expected when available vwf antibody binding sites approach the antibody concentration. By contrast, differences in the mean diffusion time between type 1 and type 2 vwd patient samples were not directly proportional to antigen concentration. Fig. 3A shows a representative comparison of normalized FCS curves from a patient with a type 1 vwd pattern (normal multimer distribution, reduced vwf:ag concentrations), a patient with a type 2 vwd pattern (reduced mean multimer size and higher vwf:ag concentrations higher than the type 1 sample), and a healthy control. There is an expected shift toward shorter mean diffusion times in the type 2 vwd sample, which contained only the smallest vwf multimers as seen in multimer gels (Fig. 3B). Distinction of this type 2 vwd sample from a very severe type 1 vwd sample, which would also have a fast mean diffusion time, may not be readily apparent by visual inspection of the FCS curves alone. However, the 2-component fit disentangles the effects of changes in overall vwf concentration from those of the vwf distribution, now represented by the calculated relative proportion of free and bound antibody and by the effective mean diffusion time of the bound antibody component (designated by arrows in Fig. 4). The 26 samples with vwf abnormalities also tested by FCS are described in Table 1. There is significant overlap between type 1 vwd and type 2 vwd patient samples for vwf:ag and vwf:rcof results, making individual tests insufficient for an accurate classification. The effective percentage of slowly diffusing antibody and the mean diffusion time of this bound component was calculated from 2-component fits of the FCS curve. As shown in Fig. 4, specimens from healthy controls, type 1 vwd patients, and type 2 vwd patients cluster into 3 separate groups when plotted for these 2 parameters. As physiologically expected, type 1 vwd patients show an effective bound fraction (percentage bound) that is lower than that of controls, but with a mean diffusion of the bound component (bound τ) that is in the normal range. Type 2 vwd patients show an effective bound fraction that is in the range of type 1 vwd patients (as they have largely overlapping total antigen concentrations; see Table 1), but with a reduced mean diffusion of the bound component, reflective of the lack of large multimers that defines most type 2 vwd cases. Finally, 3 samples with clinically
6 Torres et al. Page 6 Discussion established relatively mild acquired type 2 deficiency, but with vwf:ag concentrations higher than 50%, appropriately demonstrated a high bound antibody percentage but with a small mean multimer size (Fig. 4). The overall results provide a rational basis for disease classification by FCS analysis. Additional experiments were performed with samples from a type 1 vwd patient taken at baseline, 1 h, and 4 h after administration of DDAVP, a compound that stimulates endothelial cell release of ultra-large multimers, which are subsequently cleaved in the circulation to achieve the steady-state distributions observed. There are corresponding changes noted with FCS with slower diffusion at 1 h and partial return to baseline at 4 h (Fig. 5A). Two-component fits (Fig. 5B) yielded a pattern of DDAVP response consistent at 1 h with an increase in the quantity (effective percentage bound) and mean size (mean bound diffusion time) of the multimer distribution. When compared to 1 h, the 4-hour sample shows a decrease in the mean size with only a small decrease in total antigen. The antigen assays are consistent with this result (Table 1). The cofactor activity assays are also generally consistent with this result, but are difficult to interpret because activity is affected by the antigen concentration in such a way that multimer size is not easily inferred. The gel multimer analysis is also not easily quantifiable for this DDAVP response (Fig. 5C). NEED FOR ALTERNATIVE vwf METHODS Current functional tests for vwf include the ristocetin cofactor activity assay and the collagen-binding assay. The vwf:rcof assay measures the ability of patient-derived vwf to agglutinate formalin-fixed healthy donor platelets. The vwf:cb assay measures the ability of patient vwf to bind collagen affixed to reaction wells. Both tests have been designed to be sensitive to the distribution of vwf multimers, but they suffer from important limitations (14). The vwf:rcof assay has limited sensitivity and poor reproducibility. Furthermore, there is disagreement about the optimal threshold for disease classification. Repeated runs of vwf:rcof are needed for adequate precision, and a relatively high lower end of the reportable range observed with some vwf:rcof assays can render it useless in patients with moderate antigen deficiencies (<20%), as exemplified by several samples listed in Table 1. The utility of the other functional assay, vwf:cb, is limited by the lack of adequate reagent standardization and variability in the types of collagen used. The lack of a reference standard for this test makes extensive internal validations necessary. Additionally, data are lacking on the reliability of both the vwf:rcof and vwf:cb assays in detecting clinically relevant increases in large vwf multimers. The only method in current clinical use to directly visualize vwf multimers remains gel electrophoresis, which suffers from high technical complexity and a time-consuming nature (15). The use of gel electrophoresis for vwf multimers is generally restricted to reference laboratories, most often for the second-stage evaluation of vwd. A typical setup requires overnight electrophoretic runs of denatured protein in 1%-2% agarose gel. Detection is often completed through radio-immunoblotting, creating additional difficulties associated with the use of radiation-containing reagents in the clinical laboratory. Variability in results from gel to gel is another confounding factor inherent to this technique, particularly when attempting to use these results to quantify multimer distributions. Whereas minor stimuli may cause rapid, significant changes to the circulating concentrations of vwf protein (and to multimer distributions for which repeated measurements could aid in diagnosis and risk assessment), the challenges associated with vwf gel electrophoresis procedures make the technique impractical for use in this manner.
7 Torres et al. Page 7 FCS FOR vwf CLINICAL TESTING Although it has found widespread use within the biophysics community since its first implementation almost 40 years ago, FCS has not been widely used for clinically relevant diagnostics. One factor affecting the application of FCS to immunoassay-type clinical analysis is that >6-fold changes in molecular weight are typically required for shifts in mean diffusion time to be reliably detected. However, given that functional characteristics of vwf depend on the relative size of multimers present, and that the multimers achieve such large sizes, FCS is particularly well suited for vwf measurement. Additional discussion on multimeric protein analysis via FCS is presented in the online Data Supplement. In the present report, experimental FCS measurements of vwf in patients with type 1 and type 2 vwd followed in perfect agreement with the qualitative results from multimer gel analysis. Even if the measured bound fraction and bound mean diffusion times are only surrogate markers of the actual multimer size distribution, in contrast to labor-intensive gel electrophoresis, the FCS method was able to obtain clinically useful data with only 30-min antibody incubation and 5-min analysis time. The cost per test was minimal, and execution of the analysis was straightforward and quick. Also, the end points were easily comparable numerical results. As in traditional gel multimer analysis, distinction of certain type 2 vwd subtypes (such as type 2B and type 2M), would require testing in addition to multimer analysis for accurate clinical classification. The overall utility of multimer analysis, however, would still be augmented by a simpler and faster method that provides the most relevant information, i.e., the effective mean multimer size and overall amount of antigen present. The quantitative nature, short analysis time, and potential for very low cost per test in FCS would make it possible to obtain these parameters on virtually every sample for which antigen and activity are being measured, as well as potentially obviate the need for slow, laborious, nonquantitative multimer gel testing, which requires subjective interpretation. DDAVP TRIAL ANALYSIS BY FCS Conclusions The DDAVP trial demonstrates how FCS with 2-component fits can help characterize the response to therapy. Mechanisms of type 1 vwd vary and include decreased synthesis, increased clearance, and/or increased breakdown of vwf. In addition to providing therapeutic prognosis, 4-h DDAVP trials can sometimes help elucidate the underlying defect (e.g., the rapid clearance of type 1 Vincenza). Theoretically, multimer distribution changes in response to DDAVP are affected by the specific vwf abnormality, i.e., secretion, multimerization, cleavage, etc. Thus, there exists an opportunity to gain additional insight into the mechanisms responsible for vwf deficiencies during a DDAVP trial by looking at multimer distribution time-courses. The current limitations of multimer gels, such as lack of reliable quantitative data and the other afore-mentioned difficulties, make this investigation currently impractical. Whether FCS is indeed capable of yielding complementary information relevant to the mechanism responsible for vwf deficiency in individual patients should be explored further, as it could have direct implications in the therapeutic approach. Because of its ability to produce numerical results sensitive to changes in large multimers, FCS analysis may similarly be useful in assessing thrombotic risk and/or extent of abnormalities in conditions known to be associated with hypercoagulability. The findings presented in this report show that FCS can be used to measure parameters that reflect vwf distributions in patient samples and, through these measurements, can produce clinically meaningful results. To our knowledge, it represents the first medical diagnostic
8 Torres et al. Page 8 application of this biophysical technique directly on human plasma. Fluctuation-based immunoassays could find a role in the routine evaluation of vwf, in both vwd diagnosis and the assessment of therapeutic response. Implementation in clinical use will require further characterization of its analytical capabilities. We also believe that establishing FCS as a clinically relevant technique would create opportunities for expansion of this simple-toimplement approach to address a variety of shortcomings in current clinical laboratory techniques. Supplementary Material Acknowledgments References Refer to Web version on PubMed Central for supplementary material. The authors thank Dr. David Andrews from University of Miami Miller School of Medicine for helping perform multimeric gel analysis and providing the gel scans presented here. We also thank Dr. Brian R. Smith for participating in the development of the research concept. Research Funding: R. Torres, partial salary support from the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR), a component of the NIH, NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, and partial salary support from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) of the NIH; M.J. Levene, partial salary support and Clinical and Translational Science Awards grant UL1 RR from NCRR and partial salary support and grant R21 HL from NHLBI. Role of Sponsor: The funding organizations played no role in the design of study, choice of enrolled patients, review and interpretation of data, or preparation or approval of manuscript. 1. Sadler J, Budde U, Eickenboom J, Favaloro E, Hill F, Holmberg L, et al. Update on the pathophysiology and classification of von Willebrand disease: a report of the subcommittee on von Willebrand factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2006; 4: [PubMed: ] 2. Torres R, Fedoriw Y. Laboratory testing for von Willebrand disease: toward a mechanism-based classification. Clin Lab Med. 2009; 29: [PubMed: ] 3. Ono T, Mimuro J, Madoiwa S, Soejima K, Kashiwakura Y, Ishiwata A, et al. Severe secondary deficiency of von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) in patients with sepsisinduced disseminated intravascular coagulation: its correlation to development of renal failure. Blood. 2006; 107: [PubMed: ] 4. Chion CKNK, Doggen CJM, Crawley JTB, Lane DA, Rosendaal FR. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor and the risk of myocardial infarction in men. Blood. 2007; 109: [PubMed: ] 5. Nguyen TC, Carcillo JA. Understanding the role of von Willebrand factor and its cleaving protease ADAM TS13 in the pathophysiology of critical illness. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007; 8: [PubMed: ] 6. Ruggeri Z, Mannucci P, Lombardi R, Federici A, Zimmerman T. Multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor following administration of DDAVP: implications for pathophysiology and therapy of von Willebrand s disease subtypes. Blood. 1982; 59: [PubMed: ] 7. Chandler WL, Peerschke EIB, Castellone DD, Meijer P. Von Willebrand factor assay proficiency testing: the North American Specialized Coagulation Laboratory Association experience. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 135: [PubMed: ] 8. Marques MB, Fritsma GA. Von Willebrand disease laboratory diagnosis: the saga continues. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 135: [PubMed: ] 9. Magde D, Elson E, Webb WW. Thermodynamic fluctuations in a reacting system: measurement by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Phys Rev Lett. 1972; 29: Magde D, Elson EL, Webb WW. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. 2. Experimental realization. Biopolymers. 1974; 13: [PubMed: ]
9 Torres et al. Page Elson E, Magde D. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. I. Conceptual basis and theory. Biopolymers. 1974; 13: Janzen J, Elliott TG, Carter CJ, Brooks DE. Detection of red cell aggregation by low shear rate viscometry in whole blood with elevated plasma viscosity. Biorheology. 2000; 37: [PubMed: ] 13. [Accessed April 2012] Applications manual LSM Confocor 2: fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Carl Zeiss Advanced Imaging Microscopy; rdonlyres/7e60452f-336f c62-f5b713e64414/141218/confocor2manual.pdf 14. Favaloro EJ. An update on the von Willebrand factor collagen binding assay: 21 years of age and beyond adolescence but not yet a mature adult. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2007; 33: [PubMed: ] 15. Smejkal GB, Shainoff JR, Kotte-Marchant KM. Rapid high-resolution electrophoresis of multimeric von Willebrand factor with a thermopiloted gel apparatus. Electrophoresis. 2003; 24: [PubMed: ]
10 Torres et al. Page 10 Fig. 1. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: setup and FCS curve (A), Typical FCS setup. Excitation light (blue) from a laser reflects off the dichroic mirror and is focused by an objective lens. Fluorescent molecules are excited in the observation volume, and emitted light (green) is collected and directed toward the detector. Signal from the detector is autocorrelated by the correlator card. The output generated is an FCS curve. (B), Typical FCS curve. The autocorrelation variable, G(τ), is plotted as a function of the correlation time, τ. The curve can be fitted to a statistically derived model of fluctuations. G(0) is the extrapolated value of G at τ = 0, inversely proportional to the number of molecules in the observation volume and therefore concentration. The time at which G(τ) is roughly one-half of G(0) is the mean residence time in the observation volume.
11 Torres et al. Page 11 Fig. 2. vwf:ag dilution study (A), Correlation curves from dilutions of a healthy control (, black) show a progressive shift to shorter diffusion times at lower antigen concentrations (each curve is labeled with corresponding vwf:ag concentration in % units). A global fit to a 2-component standard FCS equation with the fast-diffusing component fixed at the τ d of the free antibody is shown as red lines ( ), which largely overlap the black correlation curves. (B), The resulting effective bound fraction component, plotted against the actual vwf:ag concentration (%), shows a near-perfect linear correlation for antigen concentrations from 0% to 90%, beyond which the bound fraction component approaches total antibody concentration.
12 Torres et al. Page 12 Fig. 3. Comparison of representative type 1 and type 2 samples (A), Owing to the differences in multimer distribution, the FCS curve from a sample with type 1 vwd (red) is shifted to the right compared to a sample with type 2 vwd (black), despite the lower vwf:ag concentration of the type 1 vwd sample. Both lie between a representative normal sample (green) and antibody alone (blue). (B), Multimer gels (top) show marked differences in multimer size distribution, which correspond qualitatively to activity differences. Densitometry of these samples, however, does not yield values that correspond to differences in total antigen despite being run on the same gel, a common limitation of multimer gel electrophoresis (type 1/type 2 background subtracted total intensity ratio = 2.7, differs from vwf:ag ratio = 0.6).
13 Torres et al. Page 13 Fig. 4. Identification and classification of vwd with 2-component FCS fits Type 1 vwd patients ( ) have a distribution of mean diffusion times that overlaps that of samples with vwf within reference intervals ( ), but with a significantly reduced effective bound fraction, reflecting reduced amounts of a relatively normal distribution of multimers in type 1 vwd. Type 2 vwd patients have an effective bound fraction component that overlaps that of type 1 vwd patients but with a reduced diffusion time, reflecting a lack of large multimers ( ). Three samples with high vwf:ag but abnormal multimer analysis lacking large multimers ( ) show a high effective bound fraction and short mean diffusion time. Two of these samples have been classified clinically as acquired vwd. The type 1 and type 2 vwd samples shown in Fig. 3 are denoted by arrows. The 4-h post-ddavp sample described in Fig. 5 is also shown for reference ( ).
14 Torres et al. Page 14 Fig. 5. FCS analysis of DDAVP trial in a type 1 vwd patient (A), FCS curve shows a marked shift to longer diffusion time 1 h post-ddavp (post). After 4 h, the FCS curve shows a partial return toward baseline. The FCS curves and residuals show a bump at long τ due to large particles that become more pronounced in the samples post-ddavp. (B), Two-component fit analysis at 1 h is consistent with the release of primarily large multimers, with an increase in both calculated total quantity and mean multimer size on the basis of mean bound diffusion time. At 4 h, the fit suggests the breakdown of large multimers, with a decrease in the mean bound diffusion time but less decrease in the percentage of antibody bound. (C), The corresponding multimer gel containing these 3 samples is shown for comparison. Traditional testing values for these samples were (Ag/RCof/FVIII): pre-ddavp = 48/48/69, 1 h = 115/165/151, 4 h = 83/105/109.
15 Torres et al. Page 15 Table 1 Characteristics of vwd samples subsequently tested by FCS. Sample Antigen, % RCoF, % Factor VIII, % Multimer analysis Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type <20 42 All multimers present in decreased amounts Type 1/2M 6 13 <20 13 All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type <20 48 All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type All multimers present in decreased amounts Type <20 14 No large or intermediate multimers Severe type 2A <20 39 Absence of large multimers Type 2A <20 39 Absence of large multimers Type 2A <20 41 Absence of large multimers Acquired type <20 31 Absence of large multimers Type 2A <20 31 Absence of largest multimers Type 2A < Absence of largest multimers Mild type 2A Absence of large multimers Acquired Type Absence of large multimers Type 2A Absence of large multimers Acquired type 2? <20 39 Absence of large multimers Type 2A Absence of large multimers Type Absence of large multimers Acquired type Absence of largest multimers Mild acquired type 2
Expanding your Choices: Recent additions to the VWF test menu
 Expanding your Choices: Recent additions to the VWF test menu Kenneth Friedman, M.D. Director, Hemostasis Reference Lab BloodCenter of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI Disclosures for Ken Friedman, M.D. Research
Expanding your Choices: Recent additions to the VWF test menu Kenneth Friedman, M.D. Director, Hemostasis Reference Lab BloodCenter of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI Disclosures for Ken Friedman, M.D. Research
Session II New Developments in the Classification and Diagnosis of VWD. Phenotypic classification of von Willebrand disease
 Session II New Developments in the Classification and Diagnosis of VWD Phenotypic classification of von Willebrand disease [haematologica reports] 2005;1(4):9-15 ULRICH BUDDE From the Coagulation Laboratory,
Session II New Developments in the Classification and Diagnosis of VWD Phenotypic classification of von Willebrand disease [haematologica reports] 2005;1(4):9-15 ULRICH BUDDE From the Coagulation Laboratory,
Preface to Special Issue: diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease diverse approaches to a global and common bleeding disorder
 Preface Page 1 of 7 Preface to Special Issue: diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease diverse approaches to a global and common bleeding disorder It is a pleasure to present the readership of
Preface Page 1 of 7 Preface to Special Issue: diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease diverse approaches to a global and common bleeding disorder It is a pleasure to present the readership of
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
Laboratory Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease in South Africa
 Laboratory Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease in South Africa Muriel Meiring, Ph.D., 1 Marius Coetzee, M.Med., 1 Mareli Kelderman, D.M.T., 1 and Philip Badenhorst, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT Patients
Laboratory Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease in South Africa Muriel Meiring, Ph.D., 1 Marius Coetzee, M.Med., 1 Mareli Kelderman, D.M.T., 1 and Philip Badenhorst, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT Patients
Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease Olga Olevsky, M.D. and Stephen Wong, M.D. Von Willebrand s Disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Low levels of Von
CLINICAL VIGNETTE Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease Olga Olevsky, M.D. and Stephen Wong, M.D. Von Willebrand s Disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Low levels of Von
Potential Laboratory Misdiagnosis of Hemophilia and von Willebrand Disorder Owing to Cold Activation of Blood Samples for Testing
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / MISDIAGNOSIS OF VON WILLEBRAND DISORDER AND HEMOPHILIA Potential Laboratory Misdiagnosis of Hemophilia and von Willebrand Disorder Owing to Cold Activation of Blood
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / MISDIAGNOSIS OF VON WILLEBRAND DISORDER AND HEMOPHILIA Potential Laboratory Misdiagnosis of Hemophilia and von Willebrand Disorder Owing to Cold Activation of Blood
EDUCATIONAL QUIZ WITH VOTING ON VWD TOPIC. P. Smejkal Department of Hematology, Masaryk University Hospital Brno, Czech Republic
 EDUCATIONAL QUIZ WITH VOTING ON VWD TOPIC P. Smejkal Department of Hematology, Masaryk University Hospital Brno, Czech Republic Classification of von Willebrand disease type 1 partial quantitative deficiency,
EDUCATIONAL QUIZ WITH VOTING ON VWD TOPIC P. Smejkal Department of Hematology, Masaryk University Hospital Brno, Czech Republic Classification of von Willebrand disease type 1 partial quantitative deficiency,
von Willebrand Disease
 von Willebrand Disease Jeremy Robertson Paediatric Haematologist Royal Children s s Hospital & Pathology Queensland Foglo,, April 1924: the journey begins Oskar and Augusta sail to Helsinki... ...to o
von Willebrand Disease Jeremy Robertson Paediatric Haematologist Royal Children s s Hospital & Pathology Queensland Foglo,, April 1924: the journey begins Oskar and Augusta sail to Helsinki... ...to o
Acquired Inhibitors of Coagulation
 Acquired Inhibitors of Coagulation Christine L Kempton, MD, MSc Emory University Disclosures for In compliance with COI policy, ISTH requires the following disclosures to the session audience: Research
Acquired Inhibitors of Coagulation Christine L Kempton, MD, MSc Emory University Disclosures for In compliance with COI policy, ISTH requires the following disclosures to the session audience: Research
Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. Abstract
 Progress Report No. 2-3, March 31, 1999 The Home Automation and Healthcare Consortium Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Kamal Youcef-Toumi Principal Investigator
Progress Report No. 2-3, March 31, 1999 The Home Automation and Healthcare Consortium Noninvasive Blood Glucose Analysis using Near Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy Prof. Kamal Youcef-Toumi Principal Investigator
Hemostasis. PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures
 Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE
 TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE Dr Susan Russell Director HTC Sydney Children s Hospital, Randwick HFA Meeting 2015 What is von Willebrand Factor? VWF is a large multimeric protein Two
TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE Dr Susan Russell Director HTC Sydney Children s Hospital, Randwick HFA Meeting 2015 What is von Willebrand Factor? VWF is a large multimeric protein Two
TTP, Sickle Cell Disease, and the role of von Willebrand factor
 TTP, Sickle Cell Disease, and the role of von Willebrand factor José A. López Puget Sound Blood Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Disclosures No conflicts to disclose. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic
TTP, Sickle Cell Disease, and the role of von Willebrand factor José A. López Puget Sound Blood Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Disclosures No conflicts to disclose. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic
Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD
 Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD Test Report Name Age Critical Low HEMATOLOGY Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, Plasma Critical High - 150 sec Units Fibrinogen 60 - mg/dl INR (International Normalizing
Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD Test Report Name Age Critical Low HEMATOLOGY Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, Plasma Critical High - 150 sec Units Fibrinogen 60 - mg/dl INR (International Normalizing
SensoLyte 520 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 520 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72171 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect Cathepsin K activity. Enhanced Value: Ample
SensoLyte 520 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72171 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect Cathepsin K activity. Enhanced Value: Ample
HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit
 HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3509 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use GHbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human GHbA1c. General Description vhemoglobin,
HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3509 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use GHbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human GHbA1c. General Description vhemoglobin,
Supporting Information For
 Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
Supporting Information For MicroRNA-Catalyzed Cancer Therapeutics Based on DNA-Programmed Nanoparticle Complex Xucheng Luo, 1 Zhi Li, 1 Ganglin Wang, 1 Xuewen He, 2,3 Xiaoqin Shen, 1 Quanhong Sun, 1 Li
Quantifying Lipid Contents in Enveloped Virus Particles with Plasmonic Nanoparticles
 Quantifying Lipid Contents in Enveloped Virus Particles with Plasmonic Nanoparticles Amin Feizpour Reinhard Lab Department of Chemistry and the Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston, MA May 2014
Quantifying Lipid Contents in Enveloped Virus Particles with Plasmonic Nanoparticles Amin Feizpour Reinhard Lab Department of Chemistry and the Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston, MA May 2014
Europium Labeling Kit
 Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Acquired Von Willebrand Syndrome and Heyde s Syndrome. Debra L. Smith, MD, PhD Hematology Fellows Conference April 8, 2016
 Acquired Von Willebrand Syndrome and Heyde s Syndrome Debra L. Smith, MD, PhD Hematology Fellows Conference April 8, 2016 Objectives Describe acquired von Willebrand syndrome (AVWS) clinical presentation
Acquired Von Willebrand Syndrome and Heyde s Syndrome Debra L. Smith, MD, PhD Hematology Fellows Conference April 8, 2016 Objectives Describe acquired von Willebrand syndrome (AVWS) clinical presentation
SensoLyte 520 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 520 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71147 Kit Size 100 assays (96-well) or 500 assays (384-well) Convenient Format: Complete kit including all the assay components. Optimized
SensoLyte 520 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71147 Kit Size 100 assays (96-well) or 500 assays (384-well) Convenient Format: Complete kit including all the assay components. Optimized
Near-infrared Absorbing Polymer Nano-particle as a Sensitive Contrast Agent for Photo-acoustic Imaging
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Near-infrared Absorbing Polymer Nano-particle as a Sensitive Contrast
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Near-infrared Absorbing Polymer Nano-particle as a Sensitive Contrast
Coagulation Disorders. Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU
 Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Mouse serum Insulin 200 tests
 Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_62in3pef-2µl USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax:
Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_62in3pef-2µl USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax:
Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint
 APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
SensoLyte Rh110 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Revision#1.2 Last Updated: May 2017 Catalog # Kit Size
 SensoLyte Rh110 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Revision#1.2 Last Updated: May 2017 Catalog # 72152 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit detects Cathepsin K activity.
SensoLyte Rh110 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Revision#1.2 Last Updated: May 2017 Catalog # 72152 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit detects Cathepsin K activity.
Peer Review Report #1. Desmopressin. (1) Does the application adequately address the issue of the public health need for the medicine?
 20 th Expert Committee on Selection and Use of Essential Medicines Peer Review Report #1 Desmopressin (1) Does the application adequately address the issue of the public health need for the medicine? Desmopressin
20 th Expert Committee on Selection and Use of Essential Medicines Peer Review Report #1 Desmopressin (1) Does the application adequately address the issue of the public health need for the medicine? Desmopressin
Insulin (Porcine/Canine) ELISA
 Insulin (Porcine/Canine) ELISA For the quantitative measurement of insulin in Porcine/Canine serum and plasma (EDTA) For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 80-INSPO-E01
Insulin (Porcine/Canine) ELISA For the quantitative measurement of insulin in Porcine/Canine serum and plasma (EDTA) For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 80-INSPO-E01
SensoLyte 490 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 490 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71127 Unit Size Kit Size 1 kit 500 assays (96-well) or 1250 assays (384-well) This kit is optimized to detect the activity of human immunodeficiency
SensoLyte 490 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71127 Unit Size Kit Size 1 kit 500 assays (96-well) or 1250 assays (384-well) This kit is optimized to detect the activity of human immunodeficiency
Pathologist-in-chief. Professor of Medicine and Pathology. School of Medicine
 Michael Laposata MD, PhD Pathologist-in-chief Vanderbilt University Hospital Professor of Medicine and Pathology Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Rosemary Jaromin Godmother of patient Jazmin Corinne
Michael Laposata MD, PhD Pathologist-in-chief Vanderbilt University Hospital Professor of Medicine and Pathology Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Rosemary Jaromin Godmother of patient Jazmin Corinne
Von Willebrand disease (vwd) is the most common
 Breast Augmentation in the Patient With von Willebrand Disease The authors describe breast augmentation in a patient with von Willebrand disease (vwd), providing a template for treating such patients.
Breast Augmentation in the Patient With von Willebrand Disease The authors describe breast augmentation in a patient with von Willebrand disease (vwd), providing a template for treating such patients.
ACTIFLUOR ADAMTS13 Activity *
 ACTIFLUOR ADAMTS13 Activity * A Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) assay for measuring ADAMTS13 activity in human plasma REF 812RUO 32 i 2 Cl8 C Sekisui Diagnostics, LLC 500 West Avenue, Stamford,
ACTIFLUOR ADAMTS13 Activity * A Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) assay for measuring ADAMTS13 activity in human plasma REF 812RUO 32 i 2 Cl8 C Sekisui Diagnostics, LLC 500 West Avenue, Stamford,
Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation
 Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Von Willebrand Disease. Alison Street Malaysia April 2010
 Von Willebrand Disease Alison Street Malaysia April 2010 Physiology of VWF OUTLINE Clinical presentation of VWD Classification of VWD with emphases on Type 1, 2B and 2N disease Testing for VWD Treatment
Von Willebrand Disease Alison Street Malaysia April 2010 Physiology of VWF OUTLINE Clinical presentation of VWD Classification of VWD with emphases on Type 1, 2B and 2N disease Testing for VWD Treatment
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
For Research Use Only
 LANCE Ultra camp Kit For Research Use Only 1. Intended use The LANCE Ultra camp kit is intended for the quantitative determination of 3,5 -cyclic monophosphate (camp) in cell culture and cellular membrane
LANCE Ultra camp Kit For Research Use Only 1. Intended use The LANCE Ultra camp kit is intended for the quantitative determination of 3,5 -cyclic monophosphate (camp) in cell culture and cellular membrane
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing. IgA & ttg IgA
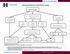 Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Multiple studies are available concerning the use of
 SPECIAL ARTICLE Evaluation of the Biosite Ò Quantitative Whole Blood D-dimer Assay and Comparison With the biomérieux VIDAS Ò D-dimer Exclusion Test Validation and Utility For Use in the Central Laboratory
SPECIAL ARTICLE Evaluation of the Biosite Ò Quantitative Whole Blood D-dimer Assay and Comparison With the biomérieux VIDAS Ò D-dimer Exclusion Test Validation and Utility For Use in the Central Laboratory
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Neurology 3-Plex A
 Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
The Clinical Features of Chinese Children with von Willebrand Disease: The Experience of a Tertiary Institute
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2011;16:95-100 The Clinical Features of Chinese Children with von Willebrand Disease: The Experience of a Tertiary Institute ZQ ZHANG, GCF CHAN, CCK LAM, JCC SO, DKL CHEUK, AKS
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2011;16:95-100 The Clinical Features of Chinese Children with von Willebrand Disease: The Experience of a Tertiary Institute ZQ ZHANG, GCF CHAN, CCK LAM, JCC SO, DKL CHEUK, AKS
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Objectives. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) and ADAMTS13 Testing. Disclosure
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) and Testing Dong Chen MD PhD Special Coagulation Laboratory Mayo Clinic-Rochester 2018 Disclosure Chair, CAP Coagulation Resource Committee Mayo Medical Laboratory
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) and Testing Dong Chen MD PhD Special Coagulation Laboratory Mayo Clinic-Rochester 2018 Disclosure Chair, CAP Coagulation Resource Committee Mayo Medical Laboratory
SERUM GLUCAGON KITS PROTOCOL
 SERUM GLUCAGON KITS PROTOCOL Part # 62SGLPEB & 62SGLPEF Test size#: 5 x 200 tests (62SGLPEB), 200 tests (62SGLPEF) - assay volume: 20 µl Revision: 02-Jan.2018 Store at: -60 C or below (62SGLPEB); -60 C
SERUM GLUCAGON KITS PROTOCOL Part # 62SGLPEB & 62SGLPEF Test size#: 5 x 200 tests (62SGLPEB), 200 tests (62SGLPEF) - assay volume: 20 µl Revision: 02-Jan.2018 Store at: -60 C or below (62SGLPEB); -60 C
Type 2B von Willebrand Disease: A Matter of Plasma Plus Platelet Abnormality
 478 Type 2B von Willebrand Disease: A Matter of Plasma Plus Platelet Abnormality Giancarlo Castaman, MD 1 Augusto B. Federici, MD 2 1 Center for Bleeding Disorders, Department of Heart and Vessels, Careggi
478 Type 2B von Willebrand Disease: A Matter of Plasma Plus Platelet Abnormality Giancarlo Castaman, MD 1 Augusto B. Federici, MD 2 1 Center for Bleeding Disorders, Department of Heart and Vessels, Careggi
Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo A1) ELISA
 Package Insert Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo A1) ELISA 1 x 96 Wells For Research Use Only (RUO). Not for use in clinical, diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 20A Northwest Blvd.,
Package Insert Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo A1) ELISA 1 x 96 Wells For Research Use Only (RUO). Not for use in clinical, diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 20A Northwest Blvd.,
Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
EXOTESTTM. ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids
 DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
Ch. 45 Blood Plasma proteins, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic components of plasma
 Chapt. 45 Ch. 45 Blood Plasma proteins, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic components of plasma Inheritance of X-linked gene for Factor VIII hemophilia A Explain the
Chapt. 45 Ch. 45 Blood Plasma proteins, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic components of plasma Inheritance of X-linked gene for Factor VIII hemophilia A Explain the
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
Move on from. based treatment
 Product class Test items Diseases Tn-l CK-MB Myoglobin Thrombosis hs-crp Cardiovascular Inflammation PSA Prostate cancer AFP Liver cancer CEA Colorectal cancer Microalbumin HbA1c Cortisol Metabolism Total
Product class Test items Diseases Tn-l CK-MB Myoglobin Thrombosis hs-crp Cardiovascular Inflammation PSA Prostate cancer AFP Liver cancer CEA Colorectal cancer Microalbumin HbA1c Cortisol Metabolism Total
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol
 Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
Product information: Human Apolipoprotein B kit 10,000 tests 1. ASSAY DESCRIPTION AND INTENDED USE 2. PROTOCOL AT GLANCE
 Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 ()4 66 79 67 5 Fax: +33 ()4 66 79 19 2 bioassays@cisbio.com USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1 781 687 15 htrfinfo@cisbio.us
Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 ()4 66 79 67 5 Fax: +33 ()4 66 79 19 2 bioassays@cisbio.com USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1 781 687 15 htrfinfo@cisbio.us
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176
 human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
RayBio Human Granzyme B ELISA Kit
 RayBio Human Granzyme B ELISA Kit Catalog #: ELH-GZMB User Manual Last revised April 15, 2016 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100 Norcross,
RayBio Human Granzyme B ELISA Kit Catalog #: ELH-GZMB User Manual Last revised April 15, 2016 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100 Norcross,
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. For. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
 SUPPRTIG IFRMATI For ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces S-1 Specific Fluorescence Probes for Lipid Droplets Based on Simple AIEgens Zhiming Wang,,,, # Chen Gui,,, Engui Zhao,, Jing Wang, # Xiaodong Li,
SUPPRTIG IFRMATI For ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces S-1 Specific Fluorescence Probes for Lipid Droplets Based on Simple AIEgens Zhiming Wang,,,, # Chen Gui,,, Engui Zhao,, Jing Wang, # Xiaodong Li,
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2*
 Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Hexagon PSA. Design Verification. Contents
 Design Verification Hexagon PSA Contents 1. Function...2 2. Sensitivity, Dynamic Range and Traceability...2 Description of Control Materials...2 Analytical Sensitivity...2 3. Clinical Evaluation...3 Evaluation
Design Verification Hexagon PSA Contents 1. Function...2 2. Sensitivity, Dynamic Range and Traceability...2 Description of Control Materials...2 Analytical Sensitivity...2 3. Clinical Evaluation...3 Evaluation
TSH ELISA Kit Medical Device Licence No.: 16419
 TSH ELISA Kit Medical Device Licence No.: 16419 Enzyme immunoassay kit for the quantitative determination of TSH concentration in serum. Catalog Number: SL100305 Catalog Number: SL100306 Catalog Number:
TSH ELISA Kit Medical Device Licence No.: 16419 Enzyme immunoassay kit for the quantitative determination of TSH concentration in serum. Catalog Number: SL100305 Catalog Number: SL100306 Catalog Number:
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit
 2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting
 Supporting Information A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting Naoko Wakabayashi 1, Yoshiaki Yano 1, Kenichi Kawano 1, and Katsumi Matsuzaki 1 1 Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Supporting Information A ph-dependent Charge Reversal Peptide for Cancer Targeting Naoko Wakabayashi 1, Yoshiaki Yano 1, Kenichi Kawano 1, and Katsumi Matsuzaki 1 1 Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit
 Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
The importance of thrombocytopenia and its causes
 SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT NO 4 2017 SEED HAEMATOLOGY The importance of thrombocytopenia and its causes Key words: Thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic, low levels of platelets What is
SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT NO 4 2017 SEED HAEMATOLOGY The importance of thrombocytopenia and its causes Key words: Thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic, low levels of platelets What is
Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes
 Electronic Supplementary Information for Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes Xi Chen and Gary A. Baker* Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia,
Electronic Supplementary Information for Cholesterol determination using protein-templated fluorescent gold nanocluster probes Xi Chen and Gary A. Baker* Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia,
Approach To A Bleeding Patient
 ABDUL MAJEED, RAHUL RAJEEV REVIEW ARTICLE INTRODUCTION Hemostasis is the process of forming clots in the walls of damaged blood vessels and preventing blood loss while maintaining blood in a fluid state
ABDUL MAJEED, RAHUL RAJEEV REVIEW ARTICLE INTRODUCTION Hemostasis is the process of forming clots in the walls of damaged blood vessels and preventing blood loss while maintaining blood in a fluid state
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of rat TNF-alpha concentrations in cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of rat TNF-alpha concentrations in cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
Reliable. results. efficiently. for CH, galactosemia, CAH and CF screening
 GSP Neonatal assays for CH, galactosemia, CAH and CF screening Reliable results efficiently GSP Neonatal kits DELFIA or enzyme-based fluorescence assays GSP is the new, automated neonatal screening system
GSP Neonatal assays for CH, galactosemia, CAH and CF screening Reliable results efficiently GSP Neonatal kits DELFIA or enzyme-based fluorescence assays GSP is the new, automated neonatal screening system
Human Creatinine Urinary Detection Kit
 Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
Development and Validation of a Polysorbate 20 Assay in a Therapeutic Antibody Formulation by RP-HPLC and Charged Aerosol Detector (CAD)
 LIFE SCIENCES AR ENOUGH? HOW DO YOU KNOW RAW MATERIALS ARE PURE? HOW DO YOU EVALUATE PRODUCT PACKAGING? HOW DO YOU DO YOU KNOW WHAT ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUE TO USE? HOW DO YOU SIMULTANEOUSLY TEST FOR TWO BYPRODUCTS?
LIFE SCIENCES AR ENOUGH? HOW DO YOU KNOW RAW MATERIALS ARE PURE? HOW DO YOU EVALUATE PRODUCT PACKAGING? HOW DO YOU DO YOU KNOW WHAT ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUE TO USE? HOW DO YOU SIMULTANEOUSLY TEST FOR TWO BYPRODUCTS?
Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation
 Laboratory Hematology 8:85-90 2002 Carden Jennings Publishing Co.. Ltd. Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation T. SCHISANO, L. VAN HOVE Abbott
Laboratory Hematology 8:85-90 2002 Carden Jennings Publishing Co.. Ltd. Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation T. SCHISANO, L. VAN HOVE Abbott
Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP
 Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP OVERVIEW Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder in humans, with an estimated prevalence ranging upward
Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP OVERVIEW Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder in humans, with an estimated prevalence ranging upward
Application Note. Agilent Application Solution Analysis of ascorbic acid, citric acid and benzoic acid in orange juice. Author. Abstract.
 Agilent Application Solution Analysis of ascorbic acid, citric acid and benzoic acid in orange juice Application Note Author Food Syed Salman Lateef Agilent Technologies, Inc. Bangalore, India 8 6 4 2
Agilent Application Solution Analysis of ascorbic acid, citric acid and benzoic acid in orange juice Application Note Author Food Syed Salman Lateef Agilent Technologies, Inc. Bangalore, India 8 6 4 2
CHAPTER 2 SIMULTANEOUS DETRMINATION OF ANASTROZOLE AND TEMOZOLOMIDE TEMOZOLOMIDE CAPSULES 20 MG AND ANASTROZOLE TABLETS 1 MG
 CHAPTER 2 SIMULTANEOUS DETRMINATION OF ANASTROZOLE AND TEMOZOLOMIDE IN TEMOZOLOMIDE CAPSULES 20 MG AND ANASTROZOLE TABLETS 1 MG ANALYTICAL METHOD VALIDATION REPORT FOR ASSAY 43 2.1 Introduction Analytical
CHAPTER 2 SIMULTANEOUS DETRMINATION OF ANASTROZOLE AND TEMOZOLOMIDE IN TEMOZOLOMIDE CAPSULES 20 MG AND ANASTROZOLE TABLETS 1 MG ANALYTICAL METHOD VALIDATION REPORT FOR ASSAY 43 2.1 Introduction Analytical
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016)
 International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
ATP-independent reversal of a membrane protein aggregate by a chloroplast SRP
 ATP-independent reversal of a membrane protein aggregate by a chloroplast SRP Peera Jaru-Ampornpan 1, Kuang Shen 1,3, Vinh Q. Lam 1,3, Mona Ali 2, Sebastian Doniach 2, Tony Z. Jia 1, Shu-ou Shan 1 Supplementary
ATP-independent reversal of a membrane protein aggregate by a chloroplast SRP Peera Jaru-Ampornpan 1, Kuang Shen 1,3, Vinh Q. Lam 1,3, Mona Ali 2, Sebastian Doniach 2, Tony Z. Jia 1, Shu-ou Shan 1 Supplementary
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Uncropped version of Fig. 2a. RM indicates that the translation was done in the absence of rough mcirosomes. (b) LepB construct containing the GGPG-L6RL6-
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Uncropped version of Fig. 2a. RM indicates that the translation was done in the absence of rough mcirosomes. (b) LepB construct containing the GGPG-L6RL6-
EliKine Free Thyroxine (ft4) ELISA Kit
 EliKine Free Thyroxine (ft4) ELISA Kit Booklet Item NO. KET0005 Product Name EliKine Free Thyroxine (ft4) ELISA Kit ATTENTION For laboratory research use only. Not for clinical or diagnostic use TABLE
EliKine Free Thyroxine (ft4) ELISA Kit Booklet Item NO. KET0005 Product Name EliKine Free Thyroxine (ft4) ELISA Kit ATTENTION For laboratory research use only. Not for clinical or diagnostic use TABLE
Exendin-4 (Exenatide) ELISA Kit
 Exendin-4 (Exenatide) ELISA Kit Catalog: DEIABL227 For the quantitative determination of Exendin-4 in serum or plasma using competitive ELISA method For Research Use Only. Protocol Provided for Informational
Exendin-4 (Exenatide) ELISA Kit Catalog: DEIABL227 For the quantitative determination of Exendin-4 in serum or plasma using competitive ELISA method For Research Use Only. Protocol Provided for Informational
Measuring Intracellular Motion in Cancer Cells using Optical Coherence Tomography
 Measuring Intracellular Motion in Cancer Cells using Optical Coherence Tomography Azhar Zam*,1,2,3 and Michael C. Kolios 1,2,3 1 Department of Physics, Ryerson University, Toronto, ON M5B 2K3, Canada 2
Measuring Intracellular Motion in Cancer Cells using Optical Coherence Tomography Azhar Zam*,1,2,3 and Michael C. Kolios 1,2,3 1 Department of Physics, Ryerson University, Toronto, ON M5B 2K3, Canada 2
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening of additives in carbonated beverages with a robust organic acid column
 APPLICATION NOTE 21673 Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening of additives in carbonated beverages with a robust organic acid column Authors Aaron Lamb and Brian King, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, UK
APPLICATION NOTE 21673 Rapid and sensitive UHPLC screening of additives in carbonated beverages with a robust organic acid column Authors Aaron Lamb and Brian King, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, UK
Mouse GLP-2 EIA. Cat. No. KT-374. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. For Research Use Only. 1 Rev.
 Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
Current issues in diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease
 Received: 18 September 2017 Accepted: 7 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12064 REVIEW ARTICLE Current issues in diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease Daniel A. Keesler 1,2,3 Veronica H. Flood
Received: 18 September 2017 Accepted: 7 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12064 REVIEW ARTICLE Current issues in diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease Daniel A. Keesler 1,2,3 Veronica H. Flood
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3631
 Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Singlet Oxygen Production Photosensitized by Fluorescein in Reversed Micellar Solutions. Norio Miyoshi and Giiti Tomita*
 Singlet Oxygen Production Photosensitized by Fluorescein in Reversed Micellar Solutions Norio Miyoshi and Giiti Tomita* Institute of Biophysics, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, Fukuoka 812,
Singlet Oxygen Production Photosensitized by Fluorescein in Reversed Micellar Solutions Norio Miyoshi and Giiti Tomita* Institute of Biophysics, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, Fukuoka 812,
Investigation of a kindred with a new autosomal
 J Clin Pathol 1985;38:665-670 Investigation of a kindred with a new autosomal dominantly inherited variant type von Willebrand's disease (possible type IID) FGH HILL, MS ENAYAT, AJ GEORGE From the Departments
J Clin Pathol 1985;38:665-670 Investigation of a kindred with a new autosomal dominantly inherited variant type von Willebrand's disease (possible type IID) FGH HILL, MS ENAYAT, AJ GEORGE From the Departments
Keywords: albuminuria; albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR); measurements. Introduction
 Clin Chem Lab Med 2015; 53(11): 1737 1743 Beryl E. Jacobson, David W. Seccombe*, Alex Katayev and Adeera Levin A study examining the bias of albumin and albumin/creatinine ratio measurements in urine DOI
Clin Chem Lab Med 2015; 53(11): 1737 1743 Beryl E. Jacobson, David W. Seccombe*, Alex Katayev and Adeera Levin A study examining the bias of albumin and albumin/creatinine ratio measurements in urine DOI
VWF other roles than hemostasis. Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis 11/4/16. Structure/function relationship & functions kDa.
 VWF other roles than hemostasis Len$ng PJ, Casari C et al JTH 2012 Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis Structure/function relationship & functions (HMWM) 20.000kDa multimerization propeptide FVIII GPIb
VWF other roles than hemostasis Len$ng PJ, Casari C et al JTH 2012 Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis Structure/function relationship & functions (HMWM) 20.000kDa multimerization propeptide FVIII GPIb
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Supplemental material Chen et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201210119/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Lack of fast reversibility of UVR8 dissociation. (A) HEK293T
Put Your Best Figure Forward: Line Graphs and Scattergrams
 56:8 1229 1233 (2010) Clinical Chemistry Put Your Best Figure Forward: Line Graphs and Scattergrams Thomas M. Annesley * There is an old saying that a picture is worth a thousand words. In truth, only
56:8 1229 1233 (2010) Clinical Chemistry Put Your Best Figure Forward: Line Graphs and Scattergrams Thomas M. Annesley * There is an old saying that a picture is worth a thousand words. In truth, only
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
