The renal glomeruli are highly specialized structures that ensure
|
|
|
- Shon Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brief Report Abatacept in B7-1 Positive Proteinuric Kidney Disease Chih-Chuan Yu, M.Sc., Alessia Fornoni, M.D., Ph.D., Astrid Weins, M.D., Ph.D., Samy Hakroush, M.D., Dony Maiguel, Ph.D., Junichiro Sageshima, M.D., Linda Chen, M.D., Gaetano Ciancio, M.D., Mohd. Hafeez Faridi, Ph.D., Daniel Behr, Kirk N. Campbell, M.D., Jer-Ming Chang, M.D., Hung-Chun Chen, M.D., Jun Oh, M.D., Christian Faul, Ph.D., M. Amin Arnaout, M.D., Paolo Fiorina, M.D., Ph.D., Vineet Gupta, Ph.D., Anna Greka, M.D., Ph.D., George W. Burke III, M.D., and Peter Mundel, M.D. Summary Abatacept (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen 4 immunoglobulin fusion protein [CTLA-4 Ig]) is a costimulatory inhibitor that targets B7-1 (CD80). The present report describes five patients who had focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) (four with recurrent FSGS after transplantation and one with primary FSGS) and proteinuria with B7-1 immunostaining of podocytes in kidney-biopsy specimens. Abatacept induced partial or complete remissions of proteinuria in these patients, suggesting that B7-1 may be a useful biomarker for the treatment of some glomerulopathies. Our data indicate that abatacept may stabilize β1-integrin activation in podocytes and reduce proteinuria in patients with B7-1 positive glomerular disease. The renal glomeruli are highly specialized structures that ensure selective ultrafiltration of plasma, by which most proteins are retained in the blood. 1 The glomerular filtration barrier consists of the glomerular capillary endothelium, the glomerular basement membrane, and specialized cells, the podocytes, that serve as a final barrier to urinary loss of plasma proteins. 1 Disrupted podocyte function damages the kidney filtration mechanism, resulting in proteinuria and, in some circumstances, the nephrotic syndrome. 1 Proteinuria is common to a heterogeneous group of kidney diseases, including minimal-change disease, FSGS, membranous nephropathy, and diabetic nephropathy, all of which affect millions of persons worldwide and often result in end-stage renal disease (ESRD). 1 In particular, primary FSGS as well as recurrent FSGS after kidney transplantation remain largely untreatable, leading to ESRD and, after transplantation, to allograft loss. 2 Abatacept (CTLA-4 Ig) is an inhibitor of the T-cell costimulatory molecule B7-1 (CD80). 3 B7-1 is induced in podocytes in various animal models of proteinuria. 4 Podocyte B7-1 expression is not evident in normal human kidney podocytes but is found in patients with certain glomerular diseases. Because we observed B7-1 immunostaining in 13 of 21 randomly selected biopsy specimens of native kidneys from patients with proteinuric kidney disease, including primary FSGS, we deduced that B7-1 had been induced during the disease. We also observed B7-1 staining in every biopsy specimen from patients with recurrent FSGS that we examined. From the Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School (C.-C.Y., A.W., S.H., D.B., M.A.A., A.G., P.M.), Department of Pathology, Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School (A.W.), and Division of Nephrology, Children s Hospital Boston (P.F.) all in Boston; the Graduate Institute of Medicine, College of Medicine (C.-C.Y.), and Department of Internal Medicine (J.-M.C., H.-C.C.), Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan; the Division of Nephrology and Hypertension (A.F., D.M., M.H.F., C.F., V.G.) and Lilian Jean Kaplan Division of Kidney Pancreas Transplantation, Miami Transplant Institute, Department of Surgery (J.S., L.C., G.C., G.W.B.), University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami; the Division of Nephrology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York (K.N.C.); and Pediatric Nephrology, Children s Hospital, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany (J.O.). Address reprint requests to Dr. Mundel at the Division of Nephrology, Massachusetts General Hospital, th St., Charlestown, MA 02129, or at mundel.peter@mgh.harvard.edu. This article was published on November 8, 2013, at NEJM.org. N Engl J Med DOI: /NEJMoa Copyright 2013 Massachusetts Medical Society n engl j med nejm.org 1
2 We treated five patients with abatacept 3 ; nephrotic-range proteinuria resolved in all four patients with rituximab-resistant recurrent FSGS and in one patient with glucocorticoid-resistant primary FSGS. Methods Cases of FSGS Clinical features of the cases of FSGS are summarized in Table 1, with details presented in the Supplementary Appendix, available with the full text of this article at NEJM.org. In Vitro Studies Cell Motility Increased podocyte migration in vitro is a surrogate marker of proteinuria in vivo. 5 To determine whether abatacept can act directly on podocytes, we performed cell-migration assays with podocytes stably expressing B7-1 or a truncated B7-1 construct that is, a construct lacking the cytoplasmic tail (B7-1Δtail) (Fig. S4D in the Supplementary Appendix). β1-integrin Activation and Cell Spreading We investigated the effect of B7-1 and its inhibitor, abatacept, on β1-integrin activation in podocytes 6,7 by means of confocal microscopy or fluorescence-activated cell sorting, as detailed in the Supplementary Appendix. We used phorbol myristate acetate induced spreading of nonadherent K562 cells 8 as an independent, functional test of the effects of B7-1 and abatacept on β1-integrin activation. 6,7 B7-1 Detection in Kidney-Biopsy Specimens B7-1 immunostaining was performed on frozen kidney-biopsy sections with the use of goat antihuman B7-1 (CD80) antibody (R&D Systems). For details, see the Supplementary Appendix. Results Patients Four patients with rituximab-resistant recurrent FSGS after transplantation (Patients 1 through 4) (Table 1, and Fig. S1 in the Supplementary Appendix) and one patient with glucocorticoid-resistant primary FSGS (Patient 5) (Table 1, and Fig. S2 in the Supplementary Appendix), with B7-1 staining of podocytes in kidney-biopsy specimens, were treated with abatacept. 3 Abatacept treatment for these five patients was consistent with institutional policies (at the University of Miami and Massachusetts General Hospital; abatacept has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis). The decision to treat patients with abatacept was based on the results of detailed mechanistic in vitro studies of podocytes. In Vitro Studies Podocyte Migration The addition of lipopolysaccharide to culture medium induced B7-1 protein expression in podocytes (Fig. 1A). Constitutive B7-1 protein expression was found in α3 integrin knockout ( ) podocytes (Fig. 1B). Abatacept blocked lipopolysaccharide-induced or B7-1 induced podocyte migration (Fig. S3A in the Supplementary Appendix). B7-1 gene silencing or expression of the truncated construct (B7-1Δtail) also suppressed podocyte migration (Fig. S3A and S3B in the Supplementary Appendix). Abatacept treatment or B7-1 gene silencing reversed podocyte motility to baseline levels (Fig. S3C in the Supplementary Appendix). Figure 1C shows the quantified effects of abatacept on podocyte migration. Biochemical Analysis of B7-1 Binding to β1 Integrin Because abatacept inhibited migration of podocytes, we hypothesized that B7-1 modulates integrin function. Endogenous coimmunoprecipitation studies showed that β1 interacted with α5 and αv integrins in normal and podocytes (Fig. S4A in the Supplementary Appendix), suggesting that α5 and αv are the α-chain partners of β1 in the absence of α3. We observed colocalization of B7-1 with vinculin in focal contacts (cell matrix adhesions that contain integrins) of podocytes (Fig. S4B in the Supplementary Appendix) and observed a specific interaction between endogenous B7-1 and β1 integrin in podocytes (Fig. S4C in the Supplementary Appendix). Domain mapping and pulldown studies with recombinant purified proteins (Fig. S4D, S4E, and S4F in the Supplementary Appendix) revealed a direct interaction between the cytoplasmic tails of B7-1 and β1, suggesting that this interaction is central to the effect of B7-1 on β1-integrin function. To test whether the observed interaction was specific for B7-1 and β1, we conducted a series of coimmunoprecipita- 2 n engl j med nejm.org
3 Brief Report Table 1. Characteristics of Five Patients with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Variable Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 Age and sex 28-yr-old woman 19-yr-old woman 14-yr-old boy 7-yr-old boy 27-yr-old woman Kidney donor Living related donor; earlier transplant from a living related donor failed owing to recurrent FSGS Cadaveric donor; earlier transplant from a living related donor failed owing to recurrent FSGS Living related donor Cadaveric donor No donor (native kidney) Induction immunosuppression Daclizumab (1 mg/kg, two doses), antithymocyte globulin (1 mg/kg, five doses), rituximab (375 mg/m 2, one dose) Daclizumab (1 mg/kg, two doses), antithymocyte globulin (1 mg/kg, five doses), rituximab (375 mg/m 2, one dose) Antithymocyte globulin (1 mg/kg, five doses), basiliximab (10 mg/kg, two doses), rituximab (375 mg/m 2, one dose) Antithymocyte globulin (1 mg/kg, five doses), basiliximab (10 mg/kg, two doses), rituximab (375 mg/m 2, one dose) Maintenance immunosuppression Tacrolimus (target serum level, 5 7 ng/ml), mycophenolate mofetil (500 mg twice daily), glucocorticoids Tacrolimus (target serum level, 5 7 ng/ml), mycophenolate mofetil (500 mg twice daily), glucocorticoids Tacrolimus (target serum level, 5 7 ng/ml), mycophenolate mofetil ( mg twice daily), glucocorticoids Tacrolimus (target serum level, 5 7 ng/ml), mycophenolate mofetil ( mg twice daily), glucocorticoids Treatment for FSGS before abatacept therapy Plasmapheresis Plasmapheresis Plasmapheresis Plasmapheresis Prednisone, cyclosporine, tacrolimus Abatacept therapy Single dose (10 mg/kg) Single dose (10 mg/kg) Two doses (10 mg/kg) Two doses (10 mg/kg) 10 mg/kg on days 1, 15, and 30 and monthly thereafter Most recent laboratory test results* 48-mo follow-up (February 3.4 g/dl; serum creatinine, 1.3 mg/dl; urinary ratio, mo follow-up (February 3.8 g/dl; serum creatinine, 0.7 mg/dl; urinary ratio, mo follow-up (February 4.0 g/dl; serum creatinine, 0.9 mg/dl; urinary ratio, mo follow-up (March 4.3 g/dl; serum creatinine, 0.3 mg/dl; urinary ratio, mo follow-up (October 3.8 g/dl; serum creatinine, 0.4 mg/dl; urinary ratio, 0.50 * To convert values for creatinine to micromoles per liter, multiply by A urinary ratio of less than 0.15 is considered normal. n engl j med nejm.org 3
4 tion studies of transfected HEK293 cells. Binding of talin, which is known to interact with β integrins, 7 to β1 or β3 integrin served as a positive control. In addition to β1, B7-1 also interacted with β3 integrin (Fig. S5A in the Supplementary Appendix) through direct binding between the two proteins (Fig. S5B in the Supplementary Appendix). In contrast, B7-2 (CD86), 9 which is not expressed in podocytes, 4 did not interact with β1 or β3 integrin (Fig. S5A in the Supplementary Appendix). Analysis of β1-integrin Activation in Podocytes The addition of lipopolysaccharide to culture medium or B7-1 overexpression caused a near-complete loss of β1-integrin activation 6,7 without affecting total β1 integrin levels (Fig. S6A in the Supplementary Appendix). Abatacept restored β1-integrin activation in B7-1 expressing podocytes, even in the presence of lipopolysaccharide (Fig. S6A in the Supplementary Appendix). Overexpression of the B7-1Δtail construct or gene silencing of B7-1 preserved β1-integrin activation in the presence of lipopolysaccharide (Fig. S6A and S6B in the Supplementary Appendix). Like abatacept treatment, B7-1 gene silencing also restored β1 activation in podocytes (Fig. S6C in the Supplementary Appendix). In independent flow-cytometric experiments, we confirmed that B7-1 blocks β1-integrin activation in podocytes (Fig. S6D in the Supplementary Appendix). Analysis of Integrin-Dependent Cell Spreading B7-1 suppressed α5β1 integrin mediated spreading of K562 cells, which was restored by abatacept (Fig. S7A, S7B, and S7C in the Supplementary Appendix). In contrast, B7-1 did not affect β3 integrin dependent cell spreading (Fig. S7D, S7E, and S7F in the Supplementary Appendix). Molecular Basis of B7-1 Effects on β1-integrin Activation We investigated the mechanism of B7-1 disruption of β1-integrin activation. The cytoplasmic protein talin is known to bind to cytoplasmic β-integrin tails, disrupting the salt bridge between the α and β subunits 10 and resulting in integrin activation. 6 Because B7-1 can also bind to β1 integrin, we hypothesized that B7-1 may block β1-integrin activation by competing with talin for β1-integrin binding. In endogenous coimmunoprecipitation studies, we confirmed an interaction between talin and β1 integrin in normal podocytes but not in podocytes. We also performed coimmunoprecipitation studies of HEK293 cells after they were cotransfected with various talin, β1-integrin, and B7-1 constructs. These experiments revealed that the cytoplasmic fragment of B7-1 (B7-1-tail) bound to the cytoplasmic tail of β1 integrin lacking the extracellular domain (β1δec) at the expense of talin (Fig. 2B). In contrast, B7-1 lacking its cytoplasmic tail (B7-1Δtail) did not disrupt β1 binding to talin (Fig. 2B). As the ultimate test of whether B7-1 competes with talin for β1 binding, we conducted in vitro reconstitution studies with purified recombinant proteins (Fig. 2C). In the absence of B7-1 (FLAG B7-1), talin (FLAG talin-hn) bound to purified β1 (GST β1δec) but not to the GST control (Fig. 2C). In contrast, the addition of B7-1 (FLAG B7-1ΔEC) led to the binding of B7-1 to purified β1 integrin (GST β1δec) at the expense of talin (FLAG talin-hn) in a concentration-dependent fashion (Fig. 2C). We confirmed that B7-1 specifically competes with talin for binding to β1 integrin but not to β3 integrin (Fig. 2D), in line with our observations in cellspreading assays (Fig. S7 in the Supplementary Appendix). Taken together, these data indicated that B7-1 mediates podocyte injury and proteinuria by disrupting the binding of talin to β1 integrin but not to β3 integrin (Fig. S8A in the Supplementary Appendix) and that this disruption can be blocked by administering abatacept (Fig. S8B in the Supplementary Appendix). B7-1 Immunostaining in Human Kidney-Biopsy Specimens To test whether podocyte B7-1 might serve as a biomarker for some proteinuric kidney diseases, we examined its expression in biopsy specimens of native kidneys from patients with various glomerular diseases and in biopsy specimens of renal allografts. Immunostaining results according to diagnosis, patient sex and age, time since transplantation (if applicable), and protein level are shown in Tables S1 and S2 in the Supplementary Appendix; representative images are shown in Figure S9 in the Supplementary Appendix. In biopsy specimens without pathologic glomerular features (Fig. S9A and Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix) and in all biopsy specimens of renal allografts from patients without recurrent proteinuria (Fig. S9B and Table S2 in the 4 n engl j med nejm.org
5 Brief Report A B pcdna B7-1 B7-1 tail B7-1 Scrambled B7-1kd Scrambled B7-1kd B7-1 GAPDH GAPDH C Average No. of Migrating Podocytes pcdna B7-1 B7-1 Abatacept B7-1 tail Scrambled B7-1kd Abatacept Scrambled B7-1kd Abatacept Figure 1. Blockade of Disease-Associated Podocyte Migration by Abatacept. Panel A shows Western blot analysis of B7-1 protein in podocytes with stable transfection of vector control (pcdna), B7-1, or B7-1Δtail before the addition of lipopolysaccharide (), which was the control condition, and after the addition of. Panel B shows B7-1 protein in normal podocytes, non-silencing short hairpin RNA (shrna) expressing podocytes (scrambled), B7-1 knockdown podocytes (B7-1kd), scrambled shrna-expressing podocytes ( /scrambled), and B7-1 knockdown podocytes ( /B7-1kd). In the analyses shown in Panels A and B, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a loading control. Panel C shows the results of quantitative analysis of podocyte migration. P values were calculated with the use of Bonferroni s multiple-comparison test; see the Supplementary Appendix for details. The T bars indicate standard deviations. Supplementary Appendix), only weak arteriolar immunostaining was observed. Three of five biopsy specimens from patients with a diagnosis of minimal-change disease showed granular staining for B7-1 along peripheral capillary walls, indicating a podocyte distribution (Fig. S9C and S9D and Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix). B7-1 was absent in specimens from four of five patients with secondary FSGS, while weak focal podocyte immunostaining was found in a specimen from one patient (Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix). In contrast, specimens from two of the three patients with primary FSGS in this series had diffuse and strong linear podocyte B7-1 staining (Fig. S9E and S9F and Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix), which was similar to the staining in the specimen from Patient 5 (Fig. S2B in the Supplementary Appendix). In keeping with previous results, 4 specimens from all three patients with lupus nephritis had moderate-to-strong granular staining in podocytes or mesangium (Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix). Specimens from patients with IgA nephropathy showed weak mesangial staining but no podocyte B7-1 staining (Fig. S9G and Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix). The strongest B7-1 staining was seen in specimens from patients with membranous nephropathy, both PLA2R-positive and PLA2R-negative 11 (Fig. S9H and Table S1 in the Supplementary Appendix). Among allograft-biopsy specimens, B7-1 staining was seen in the specimen from the one patient with recurrent FSGS in this series (Table S2 in the Supplementary Appendix), which was n engl j med nejm.org 5
6 A Input IP: Talin IP: Activated β1 Normal Normal Normal IP: Normal Blot: B GFP talin IP: FLAG Talin GFP B7-1- tail GFP B7-1 tail Talin Eluate Blot: GFP Activated β1 B7-1-tail B7-1 C Eluate Blot: FLAG GST β1 EC FLAG talin-hn GST FLAG B7-1 (µg) β1 EC B7-1 tail Talin Input Blot: GFP FLAG talin-hn B7-1-tail FLAG B7-1 FLAG β1 EC FLAG B7-1 EC D GFP-Tagged Proteins Talin-HN B7-1-tail Talin-HN+ B7-1-tail IP: FLAG Talin-HN GST β1 EC GST Eluate Blot: GFP B7-1-tail SDS-PAGE FLAG talin-hn Eluate Blot: FLAG Talin-HN FLAG B7-1 EC GST β1 EC GST Input Blot: GFP Sui Coomassie Staining B7-1-tail FLAG β3 EC 6 n engl j med nejm.org
7 Brief Report Figure 2 (facing page). Disruption of the Binding of Talin to β1 Integrin, but Not to β3 Integrin, by B7-1. As shown in Panel A, endogenous talin coprecipitated with activated β1 integrin in normal podocytes but not in podocytes. Immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti green fluorescent protein (GFP) antibody served as a negative control. Input refers to protein extracts that served as starting material from which endogenous proteins were immunoprecipitated. As shown in Panel B, FLAG B7-1 did not bind to talin (GFP talin- HN, left lane); HN denotes head N-terminal domain. GFP B7-1-tail but not GFP B7-1Δ tail blocked the interaction of talin (GFP talin-hn) with β1 integrin (FLAG β1δec) in cotransfected HEK293 cells. Instead, B7-1-tail coprecipitated with β1 integrin. As shown at the top of Panel C, immobilized β1 integrin (GST β1δec) but not the GST control bound directly to purified talin (FLAG talin-hn). In the presence of increasing amounts of FLAG B7-1ΔEC, the binding of talin-hn to GST β1δec was gradually lost, whereas the binding of B7-1 to β1 integrin could be detected. As shown at the bottom of Panel C, Coomassiestained sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis showed the purity of recombinant proteins. As shown in Panel D, coexpression of GFP B7-1-tail did not block the interaction of talin (GFP talin-hn) with β3 integrin (FLAG β3δec) in triple-transfected HEK293 cells. Instead, both GFP B7-1-tail and GFP talin-hn coprecipitated with FLAG β3δec. No binding was found with the fusion protein GFP sui (negative control). similar to the findings in the specimens from Patients 1 and 3 (Fig. S1E). Eleven allograft-biopsy specimens, all obtained from patients who did not have recurrent FSGS, were negative for B7-1 (Table S2 in the Supplementary Appendix). Discussion To date, therapy for FSGS and associated kidney disorders has been nonspecific, often ineffective, and fraught with side effects. Abatacept, a costimulatory inhibitor that targets B7-1, is currently approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and has been used to treat other autoimmune diseases. 3,12-14 Using abatacept, we successfully induced a partial or complete remission in five patients with primary or recurrent FSGS. Our clinical and in vitro data, taken together, indicate that podocyte B7-1 induction in primary and recurrent FSGS offers a rationale for using abatacept to treat a subgroup of patients with proteinuric kidney diseases. The analysis of a series of 22 randomly selected biopsy specimens of native human kidneys identified a subpopulation of patients with minimal-change disease or primary FSGS who had B7-1 immunostaining of podocytes. In contrast, immunostaining for B7-1 was negative in 4 of 5 biopsy specimens obtained from patients with secondary FSGS, despite substantial podocyte injury. Furthermore, B7-1 immunostaining of podocytes was observed in the allograft specimen from a patient with recurrent FSGS, whereas the allograft specimens from all the other patients were negative. We speculate that B7-1 immunostaining of kidney-biopsy specimens might identify a subgroup of patients with proteinuric kidney diseases who would benefit from treatment with abatacept. Mechanistically, B7-1 promotes disease-associated podocyte migration through inactivation of β1 integrin, which is reversed by abatacept. Whereas in T cells B7-1 acts by binding to CD28, CTLA-4, or PD-L1 through its extracellular domains, 9,15 in podocytes the cytoplasmic tail of B7-1 is necessary and sufficient to block β1-integrin activation, by competing with talin for β1-integrin binding. Our results thus indicate that protection of β1-integrin activation in podocytes is the putative mechanism underlying the antiproteinuric action of abatacept. Patient 5, who had relapsing nephropathy, received abatacept in conjunction with glucocorticoids alone rather than with a full post-transplantation immunosuppressive regimen. Despite modest doses of glucocorticoids, abatacept induced a remission of the nephrotic syndrome in this patient for the first time in more than 1 year. In this patient (and the others treated), for whom therapeutic options were limited, abatacept appeared to induce clinical remission. Supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (DK57683 and DK062472, to Dr. Mundel; DK093783, to Dr. Weins; DK and HL109582, to Dr. Gupta; DK , to Drs. Fornoni and Burke; and DK090316, DK083511, and DK093746, to Dr. Greka), the Boston Area Diabetes Endocrinology Research Center and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (P30DK057521, to Dr. Greka), Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (HA 6334/1-1, to Dr. Hakroush), and the NephCure Foundation and Transplant Foundation of South Florida (to Drs. Fornoni and Burke), and by an American Society of Nephrology Gottschalk Career Development Award and a NephCure Young Investigator Award (to Dr. Greka). Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text of this article at NEJM.org. We thank Terri Woo for technical assistance; Reinhard Fässler, Martinsried, Germany, for β1 integrin complementary DNA (cdna); Shimon Sakaguchi, Kyoto, Japan, for B7-2 (CD86) cdna; Anna Huttenlocher, Madison, WI, for green fluorescent protein talin cdna; and our colleagues at the University of Miami (Carolyn Abitbol, Jayanthi Chandar, Wacharee Seeherunvong, Gaston Zilleruelo, Adela Mattiazzi, Giselle Guerra, Warren Kupin, and David Roth) for help with patient care. n engl j med nejm.org 7
8 References 1. Greka A, Mundel P. Cell biology and pathology of podocytes. Annu Rev Physiol 2012;74: D Agati VD, Kaskel FJ, Falk RJ. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med 2011;365: Genovese MC, Becker JC, Schiff M, et al. Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition. N Engl J Med 2005;353: [Erratum, N Engl J Med 2005;353: 2311.] 4. Reiser J, von Gersdorff G, Loos M, et al. Induction of B7-1 in podocytes is associated with nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest 2004;113: Yanagida-Asanuma E, Asanuma K, Kim K, et al. Synaptopodin protects against proteinuria by disrupting Cdc42: IRSp53:Mena signaling complexes in kidney podocytes. Am J Pathol 2007;171: Shattil SJ, Kim C, Ginsberg MH. The final steps of integrin activation: the end game. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010;11: Calderwood DA, Zent R, Grant R, Rees DJ, Hynes RO, Ginsberg MH. The talin head domain binds to integrin beta subunit cytoplasmic tails and regulates integrin activation. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: Gupta V, Gylling A, Alonso JL, et al. The beta-tail domain (betatd) regulates physiologic ligand binding to integrin CD11b/CD18. Blood 2007;109: Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol 2005;23: Wegener KL, Partridge AW, Han J, et al. Structural basis of integrin activation by talin. Cell 2007;128: Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: Hoi AY, Littlejohn GO. Abatacept in the treatment of lupus. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2012;12: Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2010;376: Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2007;370: Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 2008;26: Copyright 2013 Massachusetts Medical Society. 8 n engl j med nejm.org
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Yu C-C, Fornoni A, Weins A, et al. Abatacept in B7-1 positive
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Yu C-C, Fornoni A, Weins A, et al. Abatacept in B7-1 positive
Abatacept in B7-1 Positive Proteinuric Kidney Disease
 correspondence practicing orthopedic surgeons, in which mechanical symptoms were not even included owing to the presumption that they would be unanimously considered a definite surgical indication. As
correspondence practicing orthopedic surgeons, in which mechanical symptoms were not even included owing to the presumption that they would be unanimously considered a definite surgical indication. As
RENAL EVENING SPECIALTY CONFERENCE
 RENAL EVENING SPECIALTY CONFERENCE Harsharan K. Singh, MD The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships No conflicts of interest to disclose. CLINICAL HISTORY
RENAL EVENING SPECIALTY CONFERENCE Harsharan K. Singh, MD The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships No conflicts of interest to disclose. CLINICAL HISTORY
Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab
 TRANSPLANTATION Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab Khadijeh Makhdoomi, 1,2 Saeed Abkhiz, 1,2 Farahnaz Noroozinia, 1,3
TRANSPLANTATION Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis After Kidney Transplantation and Successful Treatment With Rituximab Khadijeh Makhdoomi, 1,2 Saeed Abkhiz, 1,2 Farahnaz Noroozinia, 1,3
Urinary CD80 as a Replacement for Renal Biopsy for Diagnosis of Pediatric Minimal Change Disease
 KIDNEY DISEASES Urinary CD80 as a Replacement for Renal Biopsy for Diagnosis of Pediatric Minimal Change Disease Heba Mostafa Ahmed, 1 Dina Ahmed Ezzat, 1 Noha A Doudar, 2 Mai Adel 1 1 Departement of Pediatrics,
KIDNEY DISEASES Urinary CD80 as a Replacement for Renal Biopsy for Diagnosis of Pediatric Minimal Change Disease Heba Mostafa Ahmed, 1 Dina Ahmed Ezzat, 1 Noha A Doudar, 2 Mai Adel 1 1 Departement of Pediatrics,
Use of mycophenolate mofetil in steroid-dependent and -resistant nephrotic syndrome
 Pediatr Nephrol (2003) 18:833 837 DOI 10.1007/s00467-003-1175-4 BRIEF REPORT Gina-Marie Barletta William E. Smoyer Timothy E. Bunchman Joseph T. Flynn David B. Kershaw Use of mycophenolate mofetil in steroid-dependent
Pediatr Nephrol (2003) 18:833 837 DOI 10.1007/s00467-003-1175-4 BRIEF REPORT Gina-Marie Barletta William E. Smoyer Timothy E. Bunchman Joseph T. Flynn David B. Kershaw Use of mycophenolate mofetil in steroid-dependent
Case 3. ACCME/Disclosure. Laboratory results. Clinical history 4/13/2016
 Case 3 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Cornell.Lynn@mayo.edu USCAP Renal Case Conference March 13, 2016 ACCME/Disclosure Dr. Cornell has nothing to disclose Clinical history 57-year-old
Case 3 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Cornell.Lynn@mayo.edu USCAP Renal Case Conference March 13, 2016 ACCME/Disclosure Dr. Cornell has nothing to disclose Clinical history 57-year-old
Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS
 Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS Proteinuria is a major healthcare problem that affects several hundred million people worldwide. Proteinuria is a cardinal
Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS Proteinuria is a major healthcare problem that affects several hundred million people worldwide. Proteinuria is a cardinal
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
C1q nephropathy the Diverse Disease
 C1q nephropathy the Diverse Disease Danica Galešić Ljubanović School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Dubrava University Hospital Zagreb, Croatia Definition Dominant or codominant ( 2+), mesangial staining
C1q nephropathy the Diverse Disease Danica Galešić Ljubanović School of Medicine, University of Zagreb Dubrava University Hospital Zagreb, Croatia Definition Dominant or codominant ( 2+), mesangial staining
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD
 Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: use of other therapies GUIDELINES
 Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: use of other therapies Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence
Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: use of other therapies Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence
Nephrotic syndrome minimal change disease vs. IgA nephropathy. Hadar Meringer Internal medicine B Sheba
 Nephrotic syndrome minimal change disease vs. IgA nephropathy Hadar Meringer Internal medicine B Sheba The Case 29 year old man diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome 2 weeks ago and complaining now about Lt.flank
Nephrotic syndrome minimal change disease vs. IgA nephropathy Hadar Meringer Internal medicine B Sheba The Case 29 year old man diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome 2 weeks ago and complaining now about Lt.flank
Chapter 6: Idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, ; doi: /kisup.2012.
 http://www.kidney-international.org chapter 6 & 2012 KDIGO Chapter 6: Idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 181 185; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.19
http://www.kidney-international.org chapter 6 & 2012 KDIGO Chapter 6: Idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 181 185; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.19
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Membranous nephropathy role of steroids GUIDELINES
 Membranous nephropathy role of steroids Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES There is currently no data to support the use of short-term courses of
Membranous nephropathy role of steroids Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES There is currently no data to support the use of short-term courses of
Lupus Related Kidney Diseases. Jason Cobb MD Assistant Professor Renal Division Emory University School of Medicine October 14, 2017
 Lupus Related Kidney Diseases Jason Cobb MD Assistant Professor Renal Division Emory University School of Medicine October 14, 2017 Financial Disclosures MedImmune Lupus Nephritis Kidney Biopsy Biomarkers
Lupus Related Kidney Diseases Jason Cobb MD Assistant Professor Renal Division Emory University School of Medicine October 14, 2017 Financial Disclosures MedImmune Lupus Nephritis Kidney Biopsy Biomarkers
CHAPTER 2. Primary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. Sanjeev Gulati, Debashish Sengupta, Raj K. Sharma, Ajay Sharma, Ramesh K. Gupta*, Uttam Singh** and Amit Gupta
 Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Sanjeev Gulati, Debashish Sengupta, Raj K. Sharma, Ajay Sharma, Ramesh K. Gupta*, Uttam Singh** and Amit Gupta From the Departments of Nephrology, Pathology* and Biostatistics**,
Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Sanjeev Gulati, Debashish Sengupta, Raj K. Sharma, Ajay Sharma, Ramesh K. Gupta*, Uttam Singh** and Amit Gupta From the Departments of Nephrology, Pathology* and Biostatistics**,
Hasan Fattah 3/19/2013
 Hasan Fattah 3/19/2013 AASK trial Rational: HTN is a leading cause of (ESRD) in the US, with no known treatment to prevent progressive declines leading to ESRD. Objective: To compare the effects of 2 levels
Hasan Fattah 3/19/2013 AASK trial Rational: HTN is a leading cause of (ESRD) in the US, with no known treatment to prevent progressive declines leading to ESRD. Objective: To compare the effects of 2 levels
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
CHAPTER 2 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
An unusual association between focal segmental sclerosis and lupus nephritis: a distinct concept from lupus podocytopathy?
 CEN Case Rep (2015) 4:70 75 DOI 10.1007/s13730-014-0142-1 CASE REPORT An unusual association between focal segmental sclerosis and lupus nephritis: a distinct concept from lupus podocytopathy? Hironari
CEN Case Rep (2015) 4:70 75 DOI 10.1007/s13730-014-0142-1 CASE REPORT An unusual association between focal segmental sclerosis and lupus nephritis: a distinct concept from lupus podocytopathy? Hironari
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
Overview of glomerular diseases
 Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT. J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST
 RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Medicine, Pathology and Immunology Medical Director, Vanderbilt Transplant
RECURRENT AND DE NOVO RENAL DISEASES IN THE ALLOGRAFT J. H. Helderman,MD,FACP,FAST Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Medicine, Pathology and Immunology Medical Director, Vanderbilt Transplant
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
NAPRTCS Annual Transplant Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2010 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE I INTRODUCTION 1 II
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2010 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE I INTRODUCTION 1 II
ASSESSMENT OF THE PAEDIATRIC NEEDS IMMUNOLOGY DISCLAIMER
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, September 2006 Doc. Ref.: EMEA/381922/2006 ASSESSMENT OF THE PAEDIATRIC NEEDS IMMUNOLOGY DISCLAIMER The Paediatric Working Party
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, September 2006 Doc. Ref.: EMEA/381922/2006 ASSESSMENT OF THE PAEDIATRIC NEEDS IMMUNOLOGY DISCLAIMER The Paediatric Working Party
Case # 2 3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical history. Clinical history. Laboratory findings
 Case # 2 Christopher Larsen, MD Arkana Laboratories Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content
Case # 2 Christopher Larsen, MD Arkana Laboratories Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content
Chapter 4: Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, ; doi: /kisup.2012.
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 KDIGO Chapter 4: Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 172 176; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.17 INTRODUCTION This
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 KDIGO Chapter 4: Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children Kidney International Supplements (2012) 2, 172 176; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.17 INTRODUCTION This
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
NAPRTCS Annual Transplant Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2014 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE II TRANSPLANTATION Section
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2014 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE II TRANSPLANTATION Section
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Diabetes, Obesity and Heavy Proteinuria
 Diabetes, Obesity and Heavy Proteinuria Clinical Case 41 yo Black woman with heavy proteinuria History 2014: noted to have proteinuria on routine lab testing (1.1g/g). 1+ edema. Blood pressure has been
Diabetes, Obesity and Heavy Proteinuria Clinical Case 41 yo Black woman with heavy proteinuria History 2014: noted to have proteinuria on routine lab testing (1.1g/g). 1+ edema. Blood pressure has been
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
 FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Guillermo A. Herrera MD Louisiana State University, Shreveport Fibrils in bundles 10-20 nm d Diabetic fibrillosis
FIBRILLARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, PITFALLS, AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Guillermo A. Herrera MD Louisiana State University, Shreveport Fibrils in bundles 10-20 nm d Diabetic fibrillosis
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Dense deposit disease with steroid pulse therapy
 Case Report Dense deposit disease with steroid pulse therapy Jun Odaka, Takahiro Kanai, Takane Ito, Takashi Saito, Jun Aoyagi, and Mariko Y Momoi Abstract Treatment of dense deposit disease DDD has not
Case Report Dense deposit disease with steroid pulse therapy Jun Odaka, Takahiro Kanai, Takane Ito, Takashi Saito, Jun Aoyagi, and Mariko Y Momoi Abstract Treatment of dense deposit disease DDD has not
Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney. Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
 Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (MGRS) Biopsies at OSU (n=475) between 2007 and 2016 AL or AH
Monoclonal Gammopathies and the Kidney Tibor Nádasdy, MD The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (MGRS) Biopsies at OSU (n=475) between 2007 and 2016 AL or AH
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES
 How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
Approach to Glomerular Diseases: Clinical Presentation Nephrotic Syndrome Nephritis
 GLOMERULONEPHRITIDES Vivette D Agati Jai Radhakrishnan Approach to Glomerular Diseases: Clinical Presentation Nephrotic Syndrome Nephritis Heavy Proteinuria Renal failure Low serum Albumin Hypertension
GLOMERULONEPHRITIDES Vivette D Agati Jai Radhakrishnan Approach to Glomerular Diseases: Clinical Presentation Nephrotic Syndrome Nephritis Heavy Proteinuria Renal failure Low serum Albumin Hypertension
Nephrotic Syndrome NS
 Nephrotic Syndrome NS By : Dr. Iman.M. Mudawi Pediatric Nephrology Unit Gaafar Ibn Auf Hospital Definitions: In children NS is applied to any condition with a triad of: Heavy proteinuria (UACR ratio >200
Nephrotic Syndrome NS By : Dr. Iman.M. Mudawi Pediatric Nephrology Unit Gaafar Ibn Auf Hospital Definitions: In children NS is applied to any condition with a triad of: Heavy proteinuria (UACR ratio >200
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Do Anti Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibodies Predict Recurrence of Membranous Nephropathy After Transplantation?
 Do Anti Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibodies Predict Recurrence of Membranous Nephropathy After Transplantation? Rivka Ayalon MD Boston University Medical Center Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy One of
Do Anti Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibodies Predict Recurrence of Membranous Nephropathy After Transplantation? Rivka Ayalon MD Boston University Medical Center Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy One of
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report:
 Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Interesting case seminar: Native kidneys Case Report: Proximal tubulopathy and light chain deposition disease presented as severe pulmonary hypertension with right-sided cardiac dysfunction and nephrotic
Effects of pretransplant plasmapheresis and rituximab on recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adult renal transplant recipients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:482-488 Effects of pretransplant plasmapheresis and rituximab on recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adult renal transplant recipients Hoon
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:482-488 Effects of pretransplant plasmapheresis and rituximab on recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adult renal transplant recipients Hoon
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
Out of date SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions are based on level III and IV evidence)
 Membranous nephropathy role of cyclosporine therapy Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES a. The use of cyclosporine therapy alone to prevent progressive
Membranous nephropathy role of cyclosporine therapy Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES a. The use of cyclosporine therapy alone to prevent progressive
Clinicopathologic Characteristics of IgA Nephropathy with Steroid-responsive Nephrotic Syndrome
 J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24 (Suppl 1): S44-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S44 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Clinicopathologic Characteristics of IgA Nephropathy with Steroid-responsive
J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24 (Suppl 1): S44-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S44 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Clinicopathologic Characteristics of IgA Nephropathy with Steroid-responsive
Long-term prognosis of BK virus-associated nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients
 Original Article Kidney Res Clin Pract 37:167-173, 2018(2) pissn: 2211-9132 eissn: 2211-9140 https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.2.167 KIDNEY RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE Long-term prognosis of BK
Original Article Kidney Res Clin Pract 37:167-173, 2018(2) pissn: 2211-9132 eissn: 2211-9140 https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.2.167 KIDNEY RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE Long-term prognosis of BK
Minimal change nephropathy: an update (for adults) Dr. CC Szeto Department of Medicine & Therapeutics The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Minimal change nephropathy: an update (for adults) Dr. CC Szeto Department of Medicine & Therapeutics The Chinese University of Hong Kong First, it is not uncommon Cameron JS. Am J Kidney Dis 10: 157 171,
Minimal change nephropathy: an update (for adults) Dr. CC Szeto Department of Medicine & Therapeutics The Chinese University of Hong Kong First, it is not uncommon Cameron JS. Am J Kidney Dis 10: 157 171,
Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3.
 Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3. Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba, Centro de investigaciones Biológicas, Madrid Valdés Cañedo F. and Vázquez- Martul E., Complejo
Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3. Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba, Centro de investigaciones Biológicas, Madrid Valdés Cañedo F. and Vázquez- Martul E., Complejo
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
STEROID-RESISTANT NEPHROTIC SYNDROME (SRNS)
 MARIO NEGRI INSTITUTE FOR PHARMACOLOGICAL RESEARCH CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTRE FOR RARE DISEASES ALDO E CELE DACCO' Villa Camozzi - 24020 Ranica (Bergamo) Italy Telephone 39-35-4535304 fax 39-35-4535373 STEROID-RESISTANT
MARIO NEGRI INSTITUTE FOR PHARMACOLOGICAL RESEARCH CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTRE FOR RARE DISEASES ALDO E CELE DACCO' Villa Camozzi - 24020 Ranica (Bergamo) Italy Telephone 39-35-4535304 fax 39-35-4535373 STEROID-RESISTANT
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Specific management of IgA nephropathy: role of steroid therapy GUIDELINES
 Specific management of IgA nephropathy: role of steroid therapy Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES Steroid therapy may protect against progressive
Specific management of IgA nephropathy: role of steroid therapy Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES Steroid therapy may protect against progressive
Victims of success: Do we still need clinical trials? Robert S. Gaston, MD CTI Clinical Trials and Consulting University of Alabama at Birmingham
 Victims of success: Do we still need clinical trials? Robert S. Gaston, MD CTI Clinical Trials and Consulting University of Alabama at Birmingham Disclosure Employee: CTI Clinical Trials and Consulting
Victims of success: Do we still need clinical trials? Robert S. Gaston, MD CTI Clinical Trials and Consulting University of Alabama at Birmingham Disclosure Employee: CTI Clinical Trials and Consulting
Innovation In Transplantation:
 Innovation In Transplantation: Improving outcomes Thomas C. Pearson Department of Surgery Emory Transplant Center CHOA Symposium October 22, 2016 Disclosures Belatacept preclinical and clinical trial were
Innovation In Transplantation: Improving outcomes Thomas C. Pearson Department of Surgery Emory Transplant Center CHOA Symposium October 22, 2016 Disclosures Belatacept preclinical and clinical trial were
THSD7A staining of membranous glomerulopathy in clinical practice reveals cases with dual autoantibody positivity
 OPEN Official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology. 0893-3952/16 421 THSD7A staining of membranous glomerulopathy in clinical practice reveals cases with dual autoantibody positivity
OPEN Official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology. 0893-3952/16 421 THSD7A staining of membranous glomerulopathy in clinical practice reveals cases with dual autoantibody positivity
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies
 Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Immunosuppressants. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Immunosuppressants Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Immunosuppressive Agents Very useful in minimizing the occurrence of exaggerated or inappropriate
Immunosuppressants Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Immunosuppressive Agents Very useful in minimizing the occurrence of exaggerated or inappropriate
Management of Rejection
 Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach
 Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
Elevated Serum Creatinine, a simplified approach Primary Care Update Creighton University School of Medicine. April 27 th, 2018 Disclosure Slide I have no disclosures and have no conflicts with this presentation.
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
GOODPASTURE'S SYNDROME WITH CONCOMITANT IMMUNE COMPLEX MIXED MEMBRANOUS AND PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEFRITIS
 GOODPASTURE'S SYNDROME WITH CONCOMITANT IMMUNE COMPLEX MIXED MEMBRANOUS AND PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEFRITIS VESNA JURČIĆ 1, ANDREJA ALEŠ RIGLER 2, INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY, FACULTY OF MEDICINE, UNIVERSITY
GOODPASTURE'S SYNDROME WITH CONCOMITANT IMMUNE COMPLEX MIXED MEMBRANOUS AND PROLIFERATIVE GLOMERULONEFRITIS VESNA JURČIĆ 1, ANDREJA ALEŠ RIGLER 2, INSTITUTE OF PATHOLOGY, FACULTY OF MEDICINE, UNIVERSITY
Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Clinical Conference Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy: Diagnosis and Treatment Fernando C. Fervenza,* Sanjeev Sethi, and Ulrich Specks *Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Department of Pathology,
Clinical Conference Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy: Diagnosis and Treatment Fernando C. Fervenza,* Sanjeev Sethi, and Ulrich Specks *Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Department of Pathology,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
NAPRTCS Annual Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 27 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 27 Annual Report Renal Transplantation Dialysis Chronic Renal Insufficiency This is a privileged communication not for publication.
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience. Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy
 BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical Therapy for Diabetes 3-Year Outcomes
 The new england journal of medicine original article Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical for Diabetes 3-Year Outcomes Philip R. Schauer, M.D., Deepak L. Bhatt, M.D., M.P.H., John P. Kirwan, Ph.D.,
The new england journal of medicine original article Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical for Diabetes 3-Year Outcomes Philip R. Schauer, M.D., Deepak L. Bhatt, M.D., M.P.H., John P. Kirwan, Ph.D.,
Experimental and human models of membranous nephropathy : the story goes on. Pierre Ronco, Hanna Debiec Unité UMPC/IMSERM 702 HôpitalTenon
 Experimental and human models of membranous nephropathy : the story goes on Pierre Ronco, Hanna Debiec Unité UMPC/IMSERM 702 HôpitalTenon Actualités Néphrologiques 19/04/2011 Membranous Nephropathy Major
Experimental and human models of membranous nephropathy : the story goes on Pierre Ronco, Hanna Debiec Unité UMPC/IMSERM 702 HôpitalTenon Actualités Néphrologiques 19/04/2011 Membranous Nephropathy Major
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Temporal IgG Subtype Changes in Recurrent Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy
 American Journal of Transplantation 2016; 16: 2964 2972 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Copyright 2016 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 10.1111/ajt.13806
American Journal of Transplantation 2016; 16: 2964 2972 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Copyright 2016 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 10.1111/ajt.13806
Membranous nephropathy. By Mohammed Kamal Nassar, MD Lecturer of Nephrology Mansoura University
 Membranous nephropathy By Mohammed Kamal Nassar, MD Lecturer of Nephrology Mansoura University Membranous nephropathy Definition: Immune complex glomerular disease in which immune deposits of IgG and complement
Membranous nephropathy By Mohammed Kamal Nassar, MD Lecturer of Nephrology Mansoura University Membranous nephropathy Definition: Immune complex glomerular disease in which immune deposits of IgG and complement
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s. Part 1: Clinical
 Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s Part 1: Clinical Pa#ent DM 18 year old McMaster student Back pain, severe fa#gue Oct 2006 Leg swelling to ER Nov
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s Part 1: Clinical Pa#ent DM 18 year old McMaster student Back pain, severe fa#gue Oct 2006 Leg swelling to ER Nov
Better than Google- Click on Immunosuppression Renal Transplant. David Landsberg Oct
 Better than Google- Click on Immunosuppression Renal Transplant David Landsberg Oct 3 2008 OUTLINE History of Immunosuppression Trends in Immunosupression FK vs CYA Steroid Minimization CNI Avoidance Sirolimus
Better than Google- Click on Immunosuppression Renal Transplant David Landsberg Oct 3 2008 OUTLINE History of Immunosuppression Trends in Immunosupression FK vs CYA Steroid Minimization CNI Avoidance Sirolimus
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome
 Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Dra. Irma Esther del Moral Espinosa Nefrología Pediátrica Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez
 Dra. Irma Esther del Moral Espinosa Nefrología Pediátrica Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez drairma.nefroped@gmail.com Many children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome initially respond to steroid
Dra. Irma Esther del Moral Espinosa Nefrología Pediátrica Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez drairma.nefroped@gmail.com Many children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome initially respond to steroid
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Pharmacology notes Interleukin-2 receptor-blocking monoclonal antibodies: evaluation of 2 new agents
 BUMC Proceedings 1999;12:110-112 Pharmacology notes Interleukin-2 receptor-blocking monoclonal antibodies: evaluation of 2 new agents CHERYLE GURK-TURNER, RPH Department of Pharmacy Services, BUMC wo mouse/human
BUMC Proceedings 1999;12:110-112 Pharmacology notes Interleukin-2 receptor-blocking monoclonal antibodies: evaluation of 2 new agents CHERYLE GURK-TURNER, RPH Department of Pharmacy Services, BUMC wo mouse/human
47 studies found for: systemic lupus erythematosus AND mycophenolic acid
 Recherche in auf der Webseite www.clinicaltrials.gov zuletzt am 16.02.2016 47 studies found for: systemic lupus erythematosus AND mycophenolic acid Rank Status Study 1 Terminate d Myfortic Versus Azathioprine
Recherche in auf der Webseite www.clinicaltrials.gov zuletzt am 16.02.2016 47 studies found for: systemic lupus erythematosus AND mycophenolic acid Rank Status Study 1 Terminate d Myfortic Versus Azathioprine
Renal Biopsy Findings in Children Receiving Long-Term Treatment with Cyclosporine A Given as a Single Daily Dose
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., Posttreatment 2006, 209, 191-196 Renal Biopsy Following Once-daily CsA Treatment 191 Renal Biopsy Findings in Children Receiving Long-Term Treatment with Cyclosporine A Given as a
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., Posttreatment 2006, 209, 191-196 Renal Biopsy Following Once-daily CsA Treatment 191 Renal Biopsy Findings in Children Receiving Long-Term Treatment with Cyclosporine A Given as a
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment
 Specific management of IgA nephropathy: role of triple therapy and cytotoxic therapy Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES a. Triple therapy with cyclophosphamide,
Specific management of IgA nephropathy: role of triple therapy and cytotoxic therapy Date written: July 2005 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Merlin Thomas GUIDELINES a. Triple therapy with cyclophosphamide,
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
New Ideas. Better Medicines. Third Quarter Financial Results Conference Call
 New Ideas. Better Medicines. Third Quarter 2018 Financial Results Conference Call Forward-Looking Statements 2 This presentation contains forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties.
New Ideas. Better Medicines. Third Quarter 2018 Financial Results Conference Call Forward-Looking Statements 2 This presentation contains forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties.
Oral mizoribine pulse therapy for patients with steroid-resistant and frequently relapsing steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 2243 2247 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh996 Advance Access publication 19 July 2005 Brief Report Oral mizoribine pulse therapy for patients with steroid-resistant and frequently
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 2243 2247 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh996 Advance Access publication 19 July 2005 Brief Report Oral mizoribine pulse therapy for patients with steroid-resistant and frequently
* * A3027. A4623 e A3507 A3507 A3507
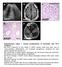 a c L A327 d e A37 A37 A37 Supplementary Figure 1. Clinical manifestations of individuals with mutations. (a) Renal ultrasound of right kidney in A327 reveals small renal cysts, loss of corticomedullary
a c L A327 d e A37 A37 A37 Supplementary Figure 1. Clinical manifestations of individuals with mutations. (a) Renal ultrasound of right kidney in A327 reveals small renal cysts, loss of corticomedullary
Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease
 Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease Mariam Priya Alexander, MD Associate Professor of Pathology GN Symposium Hong Kong Society of Nephrology July 8 th, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 The complement
Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease Mariam Priya Alexander, MD Associate Professor of Pathology GN Symposium Hong Kong Society of Nephrology July 8 th, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 The complement
C3 GLOMERULOPATHIES. Budapest Nephrology School Zoltan Laszik
 C3 GLOMERULOPATHIES Budapest Nephrology School 8.30.2018. Zoltan Laszik 1 Learning Objectives Familiarize with the pathogenetic mechanisms of glomerular diseases Learn the pathologic landscape and clinical
C3 GLOMERULOPATHIES Budapest Nephrology School 8.30.2018. Zoltan Laszik 1 Learning Objectives Familiarize with the pathogenetic mechanisms of glomerular diseases Learn the pathologic landscape and clinical
Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant
 SDC, Patients and Methods Complement-dependent lymphocytotoxic crossmatch test () Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant donor-specific CXM was
SDC, Patients and Methods Complement-dependent lymphocytotoxic crossmatch test () Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant donor-specific CXM was
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
