Preeclampsia is a life-threatening pregnancy complication. Preeclampsia
|
|
|
- Garry Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preeclampsia Excess LIGHT Contributes to Placental Impairment, Increased Secretion of Vasoactive Factors, Hypertension, and Proteinuria in Preeclampsia Wei Wang, Nicholas F. Parchim, Takayuki Iriyama, Renna Luo, Cheng Zhao, Chen Liu, Roxanna A. Irani, Weiru Zhang, Chen Ning, Yujin Zhang, Sean C. Blackwell, Lieping Chen, Lijian Tao, M. John Hicks, Rodney E. Kellems, Yang Xia Abstract Preeclampsia, a prevalent hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, is believed to be secondary to uteroplacental ischemia. Accumulating evidence indicates that hypoxia-independent mediators, including inflammatory cytokines and growth factors, are associated with preeclampsia, but it is unclear whether these signals directly contribute to placental damage and disease development in vivo. We report that LIGHT, a novel tumor necrosis factor superfamily member, is significantly elevated in the circulation and placentas of preeclamptic women compared with normotensive pregnant women. Injection of LIGHT into pregnant mice induced placental apoptosis, small fetuses, and key features of preeclampsia, hypertension and proteinuria. Mechanistically, using neutralizing antibodies specific for LIGHT receptors, we found that LIGHT receptors herpes virus entry mediator and lymphotoxin β receptor are required for LIGHT-induced placental impairment, small fetuses, and preeclampsia features in pregnant mice. Accordingly, we further revealed that LIGHT functions through these 2 receptors to induce secretion of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 and endothelin-1, 2 well-accepted pathogenic factors in preeclampsia, and thereby plays an important role in hypertension and proteinuria in pregnant mice. Lastly, we extended our animal findings to human studies and demonstrated that activation of LIGHT receptors resulted in increased apoptosis and elevation of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 secretion in human placental villous explants. Overall, our human and mouse studies show that LIGHT signaling is a previously unrecognized pathway responsible for placental apoptosis, elevated secretion of vasoactive factors, and subsequent maternal features of preeclampsia, and reveal new therapeutic opportunities for the management of the disease. (Hypertension. 2014;63: ) Online Data Supplement Key Words: endothelin-1 herpes virus entry mediator lymphotoxin-beta receptor preeclampsia receptors, tumor necrosis factor, member 14 tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 14 Preeclampsia is a life-threatening pregnancy complication that affects 7% of first pregnancies and accounts for > maternal deaths worldwide each year. 1 The major features of preeclampsia are hypertension, proteinuria, and placenta and kidney damage. 1,2 It is also a leading cause of intrauterine growth restriction, a life-threatening condition that puts the fetus at risk for many long-term cardiovascular disorders. 3,4 Thus, preeclampsia is a leading cause of maternal and neonatal mortality and morbidity and has acute and long-term impact on both mothers and babies. Despite intense research efforts, the underlying molecular mechanisms of preeclampsia are poorly understood, and the clinical management of preeclampsia has been unsatisfactory, resulting from the lack of presymptomatic screening, reliable diagnostic tests, and effective therapy. Thus, the identification of specific factors and signaling pathways involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia will facilitate the development of specific presymptomatic tests and effective mechanism-based preventative and therapeutic strategies for the disease. Disease symptoms generally abate after delivery, suggesting that the placenta plays a central role in this disease. It is widely accepted that hypoxia is an initial trigger to induce placenta abnormalities, elevated secretion of vasoactive factors, and subsequent maternal features. 5 This concept is strongly supported by animal studies showing that experimentally reduced uterine perfusion pressure in pregnant rats results in abnormal placentas, increased secretion of antiangiogenic factors, and key preeclamptic features including hypertension and kidney damage. 2 However, recent studies have provided compelling evidence that various factors other than uteroplacental hypoxia also promote Received September 23, 2013; first decision October 7, 2013; revision accepted November 10, From the Departments of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (W.W., N.F.P., T.I., R.L., C.Z., C.L., R.A.I., W.Z., C.N., Y.Z., R.E.K., Y.X.) and Obstetrics and Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences (S.C.B.), University of Texas Medical School at Houston, TX; Departments of Nephrology (W.W., W.Z., L.T., Y.X.) and Urology (C.N.), First Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China; Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Texas, Houston, TX (N.F.P., R.E.K., Y.X.); Department of Biological and Biomedical Sciences, Yale University, New Haven, CT (L.C.); and Texas Children s Hospital, Houston, TX (M.J.H.). The online-only Data Supplement is available with this article at /-/DC1. Correspondence to Yang Xia, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Texas Medical School at Houston, TX yang.xia@uth.tmc.edu 2013 American Heart Association, Inc. Hypertension is available at DOI: /HYPERTENSIONAHA
2 596 Hypertension March 2014 placental abnormalities and disease progression; these include inflammatory cytokines, 6 growth factors, 7 components of the complement cascade, 8 and autoantibodies. 9 A growing body of evidence indicates that an increased inflammatory response is associated with preeclampsia and may contribute to disease. 2,6 For example, previous in vitro studies showed that tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interferon-γ induce trophoblast apoptosis 10 and that interferon-γ and interleukin-12 inhibit angiogenesis. 11 Moreover, early in vitro studies indicated that TNF-α contributes to elevated secretion of the antiangiogenic factor, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sflt-1), from cultured human villous explants. 12 Elevated sflt-1 likely leads to impaired placentation, decreased uteroplacental perfusion, and subsequent hypertension and kidney injury. Despite these accumulating data, the specific hypoxia-independent mediators and mechanisms underlying placental apoptosis, enhanced secretion of vasoactive factors, and progression of the disease have not been fully determined in vivo. Therefore, this study aimed to identify the pathological role of novel hypoxia-independent mediators in preeclampsia and the underlying mechanisms of disease pathogenesis. LIGHT, TNF superfamily member 14, is a type II transmembrane protein containing a C-terminal TNF homology domain that folds into a β-sheet sandwich and assembles into a homotrimer. 13 It is found on immature dendritic cells and activated T-cells, and, similar to many TNF superfamily ligands, LIGHT is not only anchored on the cell surface but is also secreted from cells. 14 In both humans and rodents, LIGHT is an immune signaling molecule functioning via 2 specific cellular receptors, lymphotoxin β receptor (LTβR) and herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM). 15 Additionally, decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) is a soluble form of LIGHT receptor, present in humans but not in mice. Numerous studies indicated that DcR3 functions as an immunesuppressor in cancer, 16 inflammation, 17 and transplantation. 18 Importantly, LIGHT has emerged as a key factor involved in multiple conditions, including hepatitis, 19 asthma, 20 atherosclerosis, 21 rheumatoid arthritis, 22 and Crohn disease. 23 Although LIGHT and its receptors are expressed in placentas, especially located in trophoblast cells and endothelial cells, nothing is known about the role of LIGHT in preeclampsia. In the present study, we revealed that LIGHT is substantially elevated in the circulation and placentas of preeclamptic women, and elevated LIGHT signaling via its receptors, LTβR and HVEM, directly triggers placental apoptosis, secretion of vasoactive factors including sflt-1 and endothelin-1 (ET-1), subsequent maternal symptom development, and small fetuses in vivo. Additionally, we provide evidence that LIGHT-mediated activation of its receptors directly induces apoptosis and secretion of sflt-1 from cultured human placental villous explants. These results reveal a previously unrecognized role of LIGHT signaling in pathogenesis of preeclampsia and immediately suggest novel therapeutic possibilities for the disease. Materials and Methods For additional Materials and Methods, see the online-only Data Supplement. Patients Patients admitted to Memorial Hermann Hospital were identified by the obstetrics faculty of the University of Texas Medical School at Houston. Preeclamptic patients (n=36) were diagnosed with severe disease on the basis of the definition set by the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group Report. 27 The criteria of inclusion, including no previous history of hypertension, have been reported previously and include presence of blood pressure 160/110 mm Hg and urinary protein 300 mg in a 24-hour period or a dipstick value of 1. Other criteria include presence of persistent headache, visual disturbances, epigastric pain, or hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome in women with blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg. Control pregnant women were selected on the basis of having an uncomplicated, normotensive pregnancy with a normal term delivery (n=34). The research protocol was approved by the Institutional Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects. Detailed information of human subjects is summarized in Table 1. Introduction of Recombinant Mouse LIGHT and Neutralizing Antibodies Against LTβR or HVEM Into Pregnant and Nonpregnant Mice Pregnant C57Bl/6J mice (Harlan) were anesthetized with isofluorane, and recombinant mouse LIGHT (2 ng; R&D Systems) or the same volume of saline was introduced into pregnant mice by retro-orbital sinus injection on embryonic day (E) 13.5 and E14.5 (LIGHT, n=10; saline, n=8). For neutralization experiments, either LTβR mab (100 μg; n=6) or HVEM mab (100 μg; n=6) was simultaneously coinjected with LIGHT. Some of the mice (n=5) were injected with IgG from rat as control. This dosage was adapted from Anand et al. 19 Moreover, blood pressure and proteinuria of some of the pregnant mice with saline or LIGHT injection were further monitored on postpartum day 5 and day 10 (n=5 or 6). The same amount of LIGHT and saline was also injected into nonpregnant mice (LIGHT, n=8; saline, n=6). Some mice injected with LIGHT were coinjected with LTβR mab (100 μg; n=4) or HVEM mab (100 μg; n=4) as with pregnant mice. IgG from rat was also used as control (n=4). All protocols involving animal studies were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Welfare Committee of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. Human Placental Villous Explant Collection and Culture Human placentas were obtained from normotensive patients who underwent an elective term cesarean section at Memorial Hermann Hospital in Houston. The explant culture system was conducted as described previously. 7,11 On delivery, the placentas were placed on Table 1. Clinical Characteristics Clinical Characteristic Features of Human Subjects NT Severe preeclampsia n Age, y 29.6± ±8.6 Race, % Black White Hispanic Other 1 2 Gravity 2.3± ±1.5 Body mass index 32.8± ±8.6 Weeks gestational age 37.2± ±6.4 Systolic BP, mm Hg 115.7± ±7* Diastolic BP, mm Hg 72.8± ±10.7* Proteinuria, mg/24 h ND 1809±465* The table illustrates that blood pressure (BP) and proteinuria are elevated in severe preeclamptic women as compared with normotensive (NT) pregnant women. The category mean is indicated (±SEM, where applicable). ND indicates not determined. *P<0.001 vs NT pregnant women.
3 Wang et al LIGHT Signaling and Preeclampsia 597 ice and submerged in phenol red free DMEM containing 10% BSA and 1.0% antibiotics. Five to 7 chorionic villous explant fragments were carefully dissected from the placenta and transferred to 24-well plates at 37 C and 5% CO 2. All of the initial processing occurred <30 minutes following delivery. The explants were incubated with recombinant human LIGHT (100 pg/ml; R&D Systems) and cotreated with recombinant human DcR3 (4 μg/ml; R&D Systems) or human IgG 1 -Fc (4 μg/ml; R&D Systems). 13 After 24 hours, the collection medium was siphoned and stored at 80 C, and the villous explants were lysed or fixed overnight in 10% formalin for embedding in paraffin wax for further analysis. Statistical Analysis Results are expressed as mean±sem. All data were subjected to statistical analysis using 1-way ANOVA followed by the Newman Keuls post hoc test or Student t test to determine the significance of differences among groups. Statistical programs were run by GraphPad Prism 5 statistical software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA). Statistical significance was set at P<0.05. Results Circulating LIGHT Levels and Expression Profiles of Its Receptors in Placental Tissue of Preeclamptic Patients and Normotensive Pregnant Women To determine the levels of LIGHT in the circulation of normotensive pregnant women and those with preeclampsia, we used a sensitive ELISA. We found that circulating LIGHT levels were increased 36-fold in women with preeclampsia compared with controls (Figure 1A). Additionally, we investigated the expression of LIGHT in human placental tissue using immunohistochemistry and detected LIGHT in trophoblast cells and endothelial cells, 2 major functional cell types of the placenta (Figure 1B). Quantitative RT-PCR showed that LIGHT mrna was significantly elevated in the placentas from preeclampsia patients (Figure S1 in the online-only Data Supplement), and Western blotting analysis indicated that LIGHT protein is more abundant in placentas of preeclamptic patients compared with controls (Figure 1C). Overall, we demonstrated that the placental mrna and protein of LIGHT and circulating LIGHT were elevated in preeclamptic patients. Next, we examined the localization and expression profiles of all 3 receptors for LIGHT. Similar to LIGHT, we found that all of these 3 receptors were expressed in human placenta trophoblast cells and endothelial cells (Figure 1B). The protein levels of LTβR and HVEM were significantly increased in placental tissue from preeclampsia patients compared with normotensive pregnant women (Figure 1C). In contrast, the level of DcR3, a decoy receptor for LIGHT, was decreased in placenta tissue from preeclampsia patients relative to placenta tissue from normotensive pregnant women (Figure 1C). LIGHT Induces Placental Tissue Apoptosis and Reduced Fetal Weight in Pregnant Mice Signaling Via LTβR and HVEM To evaluate the pathogenic role of elevated LIGHT in placental apoptosis, we injected recombinant mouse LIGHT into C57/BL6 pregnant mice on E13.5 and E14.5 to achieve an increase in blood concentrations of LIGHT similar to the increase seen in preeclamptic women. At the end of pregnancy, we evaluated the circulating levels of LIGHT, placental size, and analyzed the histology of the placentas in the LIGHT-injected and saline-injected pregnant mice. We used an ELISA to accurately measure circulating LIGHT levels in the pregnant mice on E18.5 after injection with LIGHT. We found that the circulating level of LIGHT was 150 pg/ml in LIGHT-injected pregnant mice versus 90 pg/ml in salineinjected pregnant mice on E18.5 (Figure S2). Next, we found that the placentas from pregnant mice injected with LIGHT were significantly smaller (0.0832± g) than placentas from control pregnant mice injected with the same volume of saline (0.1016± g; Table 2). Placenta H&E staining showed that LIGHT-injected pregnant mice had significant tissue damage, including increased calcification (Figure 2A, 2B, and 2F). To determine whether increased Figure 1. Circulating levels of LIGHT and placental expression profiles of LIGHT and its receptors in women with normotensive and preeclamptic pregnancies. A, LIGHT levels were significantly increased in the circulation of preeclamptic patients (n=36) compared with normotensive pregnant women (n=34; P<0.0001). B, Localization of LIGHT and its receptors in the placentas was determined by immunohistochemistry. LIGHT and 3 receptors lymphotoxin β receptor (LTβR), herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM), and decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) were all present in human placental tissue trophoblast cells (green arrows) and endothelial cells (inset box). Scale bar, 100 μm. C, Western blotting revealed that protein levels of LIGHT and its transmembrane receptors, LTβR and HVEM, were elevated in placental tissue from preeclamptic patients (n=4) compared with normotensive pregnant women (n=4). However, the protein level of DcR3 was decreased in the placental tissue of preeclamptic patients.
4 598 Hypertension March 2014 Table 2. Mouse Placenta and Fetal Weight Variable Placental weight, g Fetal weight, g Saline ± ±0.02 LIGHT ±0.0026* 0.85±0.02* LIGHT plus control IgG ±0.0024* 0.86±0.01* LIGHT plus anti-ltβr ± ±0.04 LIGHT plus anti-hvem ± ±0.06 The table illustrates that injection of mouse recombinant LIGHT resulted in placentas and fetuses weighing less compared with pregnant mice injected with saline. Only pups born in litters of 6 to 8 were analyzed, and those depicted in Figure 3 were selected from the center of the uterine horn (n=51 60, collected and analyzed in 4 independent experiments). HVEM indicates herpes virus entry mediator; and LTβR, lymphotoxin β receptor. *P<0.05 vs saline treatment. P<0.05 vs LIGHT treatment. placental tissue apoptosis is a potential underlying mechanism of LIGHT-induced small placental size and placental tissue damage, we performed terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferasemediated dutp nick-end labeling to detect apoptotic cells and demonstrated significantly increased apoptosis in the labyrinth zone of placentas from LIGHT-injected pregnant mice compared with placentas from control mice (Figure 2B and 2G). Additionally, increased placental apoptosis in LIGHTinjected pregnant mice was accompanied by an elevated level of Bax, a proapoptotic marker, and a decreased level of Bcl-2, an antiapoptotic marker (Figure 2I and 2J). Because DcR3 is not expressed in rodents, we investigated the importance of LTβR and HVEM for LIGHT-induced placental damage featured with apoptosis in pregnant mice by injecting neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to each receptor into LIGHT-injected pregnant mice. We found that blocking either LTβR or HVEM by specific neutralizing antibodies restored placental size to ± g and ± g, respectively (Table 2). In addition, cotreatment of LIGHTinjected mice with either anti-ltβr mab or anti-hvem mab significantly attenuated LIGHT-induced placental tissue damage, apoptosis, and elevation of Bax and reduction of Bcl-2 (Figure 2A, 2B, 2F, 2I, and 2J). Fetal development is dependent on normal placental formation; thus, we were not surprised to find that infusion of LIGHT into pregnant mice resuted in reduced fetal weight and that coinjection of neutralizing antibodies to HVEM or LTβR improved fetal weight (Table 2). Taken together, these findings provide in vivo evidence that elevated LIGHT is a previously unrecognized factor underlying placental apoptosis and reduced fetal weight in pregnant mice by activation of its membrane receptors. Injection of LIGHT Into Pregnant Mice Induces Maternal Features of Preeclampsia Via HVEM and LTβR Signaling To evaluate the pathogenic role of elevated LIGHT in maternal disease development, we injected recombinant mouse LIGHT into pregnant C57/BL6 mice on E13.5 and E14.5 as described above. Blood pressure was monitored daily, and 24-hour urine was collected for urinary protein measurement before we euthanized the mice on E18.5. We found that systolic blood pressure increased significantly in mice injected with LIGHT (161±3 mm Hg) relative to control mice injected with saline (125±2 mm Hg; P<0.001; Figure 3A). Additionally, we examined the injected mice for proteinuria, another major clinical feature of preeclampsia. The ratio of urinary albumin to creatinine was significantly increased in pregnant mice injected with LIGHT (68±9.9 μg albumin per milligram of creatinine) compared with control mice (17±2.4 μg albumin per milligram of creatinine; P<0.01; Figure 3B). Similar to women with preeclampsia, we found that on day 5 postpartum both hypertension and proteinuria were substantially reduced (Figure S3A and S3B). Furthermore, we found that the decrease in blood pressure and proteinuria postpartum is associated with reduced circulating LIGHT and sflt-1 levles (Figure S3C and S3D). Thus, these results indicate that increased circulating LIGHT contributes to hypertension and proteinuria in pregnant mice, and decreased preeclampsia features postpartum is likely because of decreased LIGHT and sflt-1 secretion from placentas. Next, we examined whether LIGHT-induced hypertension and proteinuria are dependent on activation of its receptors in pregnant mice by injecting neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to each receptor into LIGHT-injected pregnant mice. The results (Figure 3A) show that the presence of anti-ltβr mab or anti-hvem mab significantly inhibited LIGHT-induced hypertension (161±3 mm Hg in the LIGHT-injected group versus 138±4 mm Hg in the LIGHT plus anti-ltβr treated group [P<0.01] and 134±5 mm Hg in the LIGHT plus anti- HVEM treated group [P<0.01]). Additionally, we found that elevated urinary protein levels seen in LIGHT-injected pregnant mice (68±9.9 μg albumin per milligram of creatine) were significantly attenuated by infusion of anti-ltβr mab (25±5.2 μg albumin per milligram of creatinine; P<0.05) or anti-hvem mab (25±3.3 μg albumin per milligram of creatinine; P<0.05; Figure 3B). Thus, we have provided in vivo evidence that elevated LIGHT, coupled with HVEM and LTβR signaling, leads to key preeclamptic features, including hypertension and proteinuria. Additionally, to determine whether LIGHT, via LTβR and HVEM signaling, contributes to renal damage, kidneys were harvested on E18.5 from LIGHT- and saline-injected pregnant mice for histological analysis. H&E staining revealed narrowing of Bowman capsule and loss of capillary space in the majority of glomeruli of LIGHT-injected pregnant mice (Figure 2C). Periodic acid-schiff staining further demonstrated that decreased capillary lumens and narrowed Bowman capsule are caused by the extensive endothelial cell swelling but not the thickening of basement membrane (Figure 2D). The kidneys of pregnant mice injected with saline rarely showed signs of glomerular damage. Blocking LTβR or HVEM by neutralizing antibodies prevented renal abnormalities in mice that resulted from injection with LIGHT (Figure 2C and 2D). Histomorphometric analysis showed that the extent of glomerular damage was significantly greater in LIGHT-injected pregnant mice compared with saline-injected pregnant mice, and that anti-ltβr or anti-hvem treatment resulted in improved renal histology in LIGHT-injected mice (Figure 2H). Thus, LTβR and HVEM signaling both contribute to LIGHT-induced renal damage in pregnant mice.
5 Wang et al LIGHT Signaling and Preeclampsia 599 Figure 2.
6 600 Hypertension March 2014 To validate the kidney injury, we conducted electron microscopic studies. Electron microscopic studies revealed that kidney tissue from pregnant mice injected with LIGHT displayed typical endotheliosis alterations as seen in preeclampsia patients, including markedly decreased luminal space of capillary loops accompanied by enlarged and swollen endothelial cells. Thus, the narrowed capillaries tended to be engorged with erythrocytes. However, the basement membranes of the capillaries were not significantly thickened. Additionally, the overlying podocyte foot processes were partially effaced and attenuated. There was no mesangial cell or matrix hyperplasia (Figure 2E). In contrast, the kidney tissue from mice injected with LIGHT and anti-ltβr, or LIGHT and anti-hvem, showed similar ultrastructural features as the saline control group with unremarkable glomerular structure. Bland endothelial cells lined the capillary loops with basement membranes of appropriate thickness. The capillary loops were open and not engorged with erythrocytes. The podocytes showed typical foot processes without effacement and showed no evidence of hyperplasia. The mesangial cells and matrix were not increased (Figure 2E). Overall, we showed here that LIGHT signaling via both HVEM and LTβR contributes to hypertension, proteinuria, and kidney injury in pregnant mice as seen in preeclampsia patients. LIGHT Signaling Via LTβR and HVEM Induces Hypertension But Not Proteinuria in Nonpregnant Mice To determine whether pregnancy is required for LIGHTinduced features of preeclampsia, we injected LIGHT on 2 consecutive days into nonpregnant female mice. The results (Figure 3C) show that LIGHT induced high blood pressure in nonpregnant mice (153±3 mm Hg) compared with salineinjected control mice (122±8 mm Hg). Moreover, to validate blood pressure measurement by tailcuff method, we determined intracarotid mean arterial pressure 31 (Figure S4). Additionally, we coinjected anti-ltβr mab or anti-hvem mab separately into nonpregnant mice that were injected with LIGHT. As with pregnant mice, blocking LTβR (131±6 mm Hg) or HVEM (134±9 mm Hg) by neutralizing antibody significantly reduced LIGHT-induced hypertension in nonpregnant mice (Figure 3C). However, urinary protein levels in nonpregnant mice were not significantly affected by LIGHT injection (Figure 3D), with or without coinjection with neutralizing antibody to LTβR or HVEM. These findings indicate that pregnancy is required for LIGHT-induced proteinuria. However, LIGHT-induced hypertension is independent of pregnancy. Circulating sflt-1 Is a Downstream Mediator Induced by LIGHT Via HVEM and LTβR Activation in Pregnant Mice But Not Nonpregnant Mice In an effort to identify intracellular mediators functioning downstream of HVEM and LTβR that contribute to LIGHTinduced preeclampsia in pregnant mice, we measured circulating sflt-1, a well-accepted pathogenic factor thought to play an important role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 7,32 We found that circulating sflt-1 levels were significantly increased in LIGHT-injected pregnant mice (57.20±10.46 ng/ml) compared with control group (29.93±2.73 ng/ml). Moreover, we observed that elevated sflt-1 levels in the circulation of LIGHT-injected pregnant mice were significantly downregulated by cotreatment with anti-ltβr mab (43.53±3.15 ng/ ml) or anti-hvem mab (38.57±6.68 ng/ml; Figure 3E). In contrast, there were no significant differences in the low levels of circulating sflt-1 between the LIGHT-injected nonpregnant mice with or without coinjection of anti-ltβr and anti-hvem (Figure 3F). These findings indicate that LIGHTmediated sflt-1 induction is pregnancy-dependent and suggest that sflt-1 induction by LIGHT signaling via LTβR and HVEM contributes to proteinuria as seen in pregnant mice but not in nonpregnant mice. Circulating ET-1 Is a Common Downstream Mediator Induced by LIGHT Via HVEM and LTβR Activation in Pregnant and Nonpregnant Mice Several studies suggest that increased levels of ET-1 contribute to the hypertensive features of preeclampsia. 33,34 To determine whether LIGHT-induced hypertension is associated with elevated ET-1, pregnant and nonpregnant mice were injected with LIGHT in the presence or absence of neutralizing antibody to LTβR or HVEM and circulating ET-1 levels determined. The results (Figure 3G) show that LIGHT injection resulted in elevated circulating ET-1 in pregnant (2.37±0.54 pg/ml) and nonpregnant mice (1.54±0.15 pg/ml) compared with saline-injected pregnant (0.42±0.13 pg/ml) and Figure 2 (Continued). LIGHT-induced placental damage, apoptosis, and kidney injury in pregnant mice by activation of lymphotoxin β receptor (LTβR) and herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM). A, Placentas assessed by H&E staining indicated that LIGHT-injected pregnant mice had damaged placentas: calcifications (green arrows) and fibrotic areas (black arrows). Coinjection of neutralizing antibodies to LTβR or HVEM significantly attenuated placental damage. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, Placental apoptosis was assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dutp nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining ( 10 magnification; green, TUNEL-positive cells; blue, DAPI nuclear stain; scale bar, 1 mm). LIGHT-injected pregnant mice had increased apoptosis in the labyrinth zones of their placentas as compared with saline-injected animals. C to E, Kidneys assessed by H&E staining (C), periodic acid-schiff staining (D), and electron microscopic studies (E) indicated that LIGHT-injected pregnant mice had damaged kidneys with typical endotheliosis with decreased capillary lumens with swollen endothelial cells. Coinjection of neutralizing antibodies to LTβR or HVEM significantly attenuated kidney injury, Scale bar, 100 μm. F, An arbitrary histological quantification of the number of calcifications obtained per field under 10 magnification (12 placentas for each group). G, Quantification of the TUNEL assay indicated elevation of TUNEL-positive cells in the placenta of the mice injected with LIGHT. Coinjection of neutralizing antibodies for LTβR or HVEM reduced TUNEL-positive cells in the placentas as compared with LIGHT-injected animals (n=10 placentas per variable, from 5 different mice in each group). H, Kidney histological score in pregnant mice was significantly increased with LIGHT injection. Coinjection of neutralizing antibodies to LTβR or HVEM significantly reduced the kidney histological score. I and J, Western blot analysis of mouse placentas indicated that LIGHT injection led to increased proapoptotic protein Bax (I) and decreased antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 (J); n=5 for each variable collected over 4 independent experiments. Coinjection of neutralizing antibodies for LTβR or HVEM significantly reduced LIGHT-induced apoptotic features. Data are expressed as mean±sem. *P<0.05 vs saline-injected pregnant mice; **P<0.05 vs LIGHT-injected pregnant mice.
7 Wang et al LIGHT Signaling and Preeclampsia 601 Figure 3. LIGHT signaling through lymphotoxin β receptor (LTβR) and herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) induced hypertension and proteinuria in the pregnant mice by increasing both soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sflt-1) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) secretion. However, LIGHT only induced hypertension but not proteinuria in nonpregnant mice by increasing the secretion of ET-1 and not sflt-1. A and B, Pregnant mice were injected with saline or LIGHT with or without injection of neutralizing antibodies for LTβR and HVEM, respectively. LIGHT injection resulted in hypertension (A) and proteinuria (B) in pregnant mice. Neutralizing antibodies for LTβR or HVEM significantly reduced hypertension seen in these mice. *P<0.001 vs saline-injected mice; **P<0.01 vs LIGHT-injected mice. C and D, LIGHT induced hypertension (C) but not proteinuria (D) in nonpregnant mice. Neutralizing antibodies for LTβR or HVEM significantly attenuated hypertension in these mice (n=5 7). *P<0.01 vs saline-injected mice; **P<0.05 vs LIGHT-injected mice. E and F, Circulating sflt-1 level was significantly increased in LIGHT-injected pregnant mice (E) but not in nonpregnant mice (F). Neutralizing antibodies for LTβR and HVEM significantly attenuated LIGHT-induced sflt-1 production in pregnant mice (E) but had no effect on the low sflt-1 levels in nonpregnant mice (F). G, Circulating ET-1 levels were remarkably elevated in LIGHT-injected pregnant and nonpregnant mice, and LIGHT-mediated increase of circulating ET-1 in pregnant mice was significantly higher than that of nonpregnant mice ( P<0.05). Neutralizing antibodies for LTβR or HVEM significantly attenuated LIGHT-induced ET-1 production in pregnant and nonpregnant mice. *P<0.05 vs saline-injected pregnant mice; **P<0.05 vs LIGHT-injected pregnant mice; #P<0.05 vs saline-injected nonpregnant mice; ##P<0.05 vs LIGHT-injected nonpregnant mice. Control rat IgG had no effect on LIGHT-induced hypertension, proteinuria, or sflt-1 and ET-1 production. nonpregnant mice 0.54±0.23 pg/ml). Coinjection with anti- LTβR (pregnant mice, 1.11±0.13 pg/ml; nonpregnant mice, 1.04±0.19 pg/ml) or anti-hvem (pregnant mice, 0.84±0.19 pg/ml; nonpregnant mice, 1.05±0.29 pg/ml) significantly inhibited LIGHT-mediated induction of ET-1. These results indicate that LIGHT-mediated induction of ET-1 is independent of pregnancy and likely an important factor responsible for LIGHT-induced hypertension in both pregnant and nonpregnant mice. DcR3 Inhibits LIGHT-Induced sflt-1 Secretion and Placental Apoptosis in Human Villous Explants Mice and rats do not have a DcR3 gene. 35 Thus, to explore the biological function of soluble receptor DcR3 in LIGHT-induced
8 602 Hypertension March 2014 features of preeclampsia, we incubated human placental villous explants from healthy term pregnancies with recombinant human LIGHT in the presence or absence of recombinant human DcR3. We measured the supernatant sflt-1 levels by ELISA and demonstrated a significant increase in sflt-1 secretion by placenta villous explants incubated with LIGHT (0.31±0.02 ng/ml per milligram) compared with placenta villous explants incubated with saline (0.16±0.05 ng/ml per milligram). However, elevated sflt-1 secretion induced by LIGHT was significantly inhibited by cotreatment with DcR3 (0.23±0.02 ng/ml per milligram; Figure 4B). To determine whether placental tissue apoptosis is a downstream consequence of LIGHT treatment, we examined human placental tissue explants for apoptotic cells by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dutp nick-end labeling assay after incubation with LIGHT. Our results (Figure 4A and 4C) demonstrate a significant increase in the abundance of apoptotic cells in LIGHT-treated human placental tissue. Additionally, we found that LIGHT treatment increased Bax expression and reduced Bcl-2 expression in human placental explants (Figure 4D and 4E). Furthermore, increased placenta trophoblast cell apoptosis induced by LIGHT was significantly attenuated by cotreatment with DcR3 (Figure 4). Altogether, our results indicate that DcR3 can prevent LIGHT-induced sflt-1 secretion and placental trophoblast cell apoptosis in human placenta explants. Discussion As a TNF superfamily member, LIGHT was initially discovered to be expressed in mature immune cells and involved in multiple inflammatory diseases and autoimmune conditions. 36 Although LIGHT and its receptors were subsequently shown to be expressed in trophoblasts and endothelial cells of human placentas 25 and that an elevated inflammatory response is a recognized feature of preeclampsia, 6 nothing was known about the role of LIGHT signaling in preeclampsia. Here, we provide both in vivo animal studies and in vitro human evidence that elevated LIGHT is a key contributor to hypertension, proteinuria, placental apoptosis, and small fetuses in pregnant mice. Mechanistically, we determined that elevated LIGHT signaling via 2 membrane-anchored receptors, HVEM and LTβR, contributes to placental apoptosis and disease development. We further revealed that LIGHT signaling is a previously unrecognized immune cascade responsible not only for the induction of the vasoconstrictive peptide, ET-1, but also for the induction of the antiangiogenic factor, sflt- 1, and thereby plays an important role in hypertension and proteinuria in pregnant mice. Overall, both mouse and human studies reported here provide strong evidence that LIGHTmediated receptor activation is an underlying mechanism for placental damage, increased secretion of ET-1 and sflt-1, and subsequent maternal clinical manifestations and suggest that these signaling pathways are novel therapeutic targets for disease management (Figure 4F). LIGHT, as well as other TNF superfamily members, triggers both cell death and survival signaling pathways. 37,38 The functions of LIGHT are performed by the activation of 2 receptors, HVEM and LTβR, expressed on the surface of specific target cells. Biological activities of LIGHT LTβR signaling include the induction of apoptosis, 13,16,39 generation and activation of various cytokines, 40 developmental organogenesis of lymph nodes, 41 and restoration of secondary lymphoid structure and function. 42,43 LIGHT signaling through HVEM is an important costimulatory signal for activation and proliferation of T-cells. LIGHT stimulates T-cell proliferation and induces interferon-γ production, which can be inhibited by neutralizing antibodies to HVEM. 44 Although most studies indicate that HVEM works principally as a prosurvival receptor for T-cells and LTβR activation contributes to LIGHT-induced apoptosis, there is also evidence that HVEM, but not LTβR, plays a key role in LIGHTinduced tumor cell death in lymphoid malignancy. 45 Although LIGHT and its receptors are known to be expressed in the first trimester and term placental tissues, 24,25 the biological function of LIGHT in normal pregnancy and pregnancy-related diseases has not been extensively explored. Our study is the first to show that LIGHT is significantly increased (>36-fold) in the circulation of preeclamptic women compared with normotensive pregnant women. In vivo experiments using pregnant mice and in vitro experiments using cultured human villous explants demonstrated that LIGHT triggers placental damage characterized with placental apoptosis. These findings are strongly supported by early in vitro studies showing that LIGHT can induce human placental trophoblast cell apoptosis. 46 Mechanistically, we demonstrated that both LTβR and HVEM are responsible for LIGHT-induced placental cell apoptosis by increasing Bax expression and reducing Bcl-2 levels in LIGHT-injected pregnant mice. Similarly, we provide human evidence that the soluble receptor, DcR3, inhibits LIGHT-induced sflt-1 secretion and apoptosis in human placental tissue explants, indicating a potentially protective role for DcR3 in the initiation and progression of preeclampsia. Altogether, we revealed that elevated LIGHT signaling via its receptors is responsible for placental damage featured with placental apoptosis, an important mechanism in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 29 We found that both LTβR and HVEM are expressed in human placenta tissue, consistent with preliminary research reported by Gill et al. 25 To our surprise, not only was LIGHT expression but also the levels of LTβR and HVEM were increased in preeclamptic placentas. Thus, the detrimental effects of elevated LIGHT signaling through its receptors is further enhanced by the increased placental expression of LIGHT and its receptors along with increased levels of LIGHT in the circulation. Supporting this model, we used neutralizing antibodies for LIGHT receptors to demonstrate that both HVEM and LTβR function downstream of LIGHT and contribute to LIGHTinduced disease development, including small placentas and fetuses in pregnant mice. It is possible that the combination of neutralizing antibodies would have an even greater effect compared with either one individually. Taken together, these studies reveal a new function of LIGHT signaling via HVEM and LTβR in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia and highlight novel therapeutic approaches to prevent LIGHT-induced placental apoptosis and preeclampsia features. It is a widely held view that increased secretion of vasoactive factors by the placenta into the maternal circulation is responsible for systemic endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and multiorgan damage. 7,47 In this regard, numerous recent studies showed that sflt-1 is significantly elevated in
9 Wang et al LIGHT Signaling and Preeclampsia 603 Figure 4. LIGHT-mediated increase in placental tissue apoptosis and soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sflt-1) secretion from human placental villous explants are inhibited by blocking lymphotoxin β receptor (LTβR) or herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM). Human placental villous explants treated with saline or LIGHT in the presence or absence of decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) or IgG 1 -Fc. A, Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dutp nick-end labeling (TUNEL)-stained cultured human villous explants indicated that LIGHT increased apoptosis (green, TUNEL-positive cells; blue, DAPI nuclear stain; scale bars, 500 μm). B, sflt-1 secretion from cultured human villous explants was significantly increased after 24-hour incubation with LIGHT compared with saline-treated human villous explants. DcR3 significantly reduced sflt-1 secretion induced by LIGHT (n=6 for each group). C, Quantification of the increased apoptosis is reflected in an increased apoptotic index in the explants incubated with LIGHT. Coincubation of the explants with LIGHT and DcR3 partially attenuated the increase in cell death. D and E, Western blot analysis of explant proteins demonstrated increased Bax (D) and decreased Bcl-2 (E), indicating a proapoptotic state. Explants of placentas from 2 different women were cultured, and each variable was examined 6 times per placenta (n=12). IgG 1 - Fc had no effect on LIGHT-induced placental apoptosis or sflt-1 secretion from human placental villous explants. Data are expressed as mean±sem. *P<0.05 vs saline-incubated group; **P<0.05 vs LIGHT-incubated group. F, Working model: Circulating LIGHT level is increased in preeclamptic patients. Elevated LIGHT functioning via activation of 2 transmembrane receptors, LTβR and HVEM, contributes to placental damage featured with apoptosis, secretion of vasoactive factors including sflt- 1 and endothelin-1 (ET-1), and subsequent disease development including hypertension and proteinuria in pregnant mice. However, LIGHT signaling via LTβR and HVEM only induces hypertension, but not proteinuria, in nonpregnant mice. LIGHT-mediated sflt-1 production is a key mechanism underlying placenta tissue damage and preeclampsia development. Elevated ET-1 is a common factor mediating LIGHT-induced hypertension in both pregnant and nonpregnant mice. Decoy receptor 3 can attenuate sflt-1 secretion and placenta apoptosis stimulated by LIGHT. Thus, LIGHT signaling is a novel pathway contributing to pathogenesis of preeclampsia and serves as a potential therapeutic target for the disease. the circulation of women with preeclampsia compared with women with normotensive pregnancy. 32 More importantly, the introduction of viral vectors encoding sflt-1 into pregnant rats resulted in proteinuria and hypertension, the key features of preeclampsia. 7 These studies highlighted the role of sflt-1 as a placenta-derived factor contributing to preeclampsia. 48 Here, we showed that LIGHT injection into pregnant mice and LIGHT treatment of cultured human villous explants induced sflt-1 production. Moreover, we have shown that LIGHT can also induce apoptosis in mouse placentas and in cultured human villous explants. Overall, our studies provide both human and mouse evidence that elevated LIGHT can induce placental apoptosis and sflt-1 secretion. Of note, elevated sflt-1 is known to contribute to pathophysiology of preeclampsia, including abnormal placentation, hypertension, and kidney injury. 7 Thus, it is possible that circulating LIGHT induces sflt-1 secretion and placental apoptosis. Elevated sflt-1 functions as downstream mediator to further impair placental development. As such, without interference, LIGHT sflt-1 placental impairment leads to progression of the disease and symptom development. Thus, these studies support our working model that LIGHT is a detrimental factor contributing to placental damage, increased placental secretion of vasoactive factors, and disease development. Because preeclampsia is a pregnancy-specific disease, the placenta has been considered to play an indispensable role in the initiation and progression of the disease. To assess the importance of placentas in LIGHT-induced hypertension and proteinuria, we injected LIGHT into nonpregnant as well as pregnant mice. In contrast to pregnant mice, LIGHT only induced hypertension, but not proteinuria, in nonpregnant mice. Mechanistically, we further revealed that LIGHT signaling via both HVEM and LTβR led to the elevation of circulating ET-1, but not sflt-1, in nonpregnant mice. A possible explanation for these results could be our finding that LIGHT is capable of inducing ET-1 production in both pregnant and nonpregnant mice, a feature that likely accounts for the increased blood pressure in each case. However, LIGHT-induced proteinuria
10 604 Hypertension March 2014 was only observed in pregnant animals and was correlated with the induction of sflt-1 only in pregnant animals. LIGHTmediated proteinuria in pregnant mice may be attributable to renal damage caused by increased sflt-1 generation and secretion from placenta. In contrast to our findings with LIGHTinduced hypertension in nonpregnant mice, LaMarca and colleagues found that TNF-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-17 can induce high blood pressure in pregnant rats, not in nonpregnant rats However, these cytokine effects are presumably concentration-dependent, and it is possible that lower doses of LIGHT may be unable to induce hypertension in nonpregnant mice but still have effects in pregnant mice. Nevertheless, our studies provide a molecular basis underlying LIGHT-mediated differential effects between pregnant and nonpregnant mice: (1) LIGHT-mediated elevation of circulating ET-1 alone is enough to induce hypertension in nonpregnant mice; (2) the lack of renal pathology in LIGHT-injected nonpregnant mice is correlated with the lack of elevated sflt-1 in these animals; and (3) a major source of sflt-1 during pregnancy is the placenta, where LIGHT-mediated induction of sflt-1 is likely to contribute to renal pathology. In contrast to other members of the TNF receptor superfamily, the gene encoding DcR3 does not include a transmembrane domain and results in the production of an obligate secreted protein of 300 amino acids. 35 As a soluble receptor, DcR3 is capable of neutralizing the biological effects of 3 members of the TNF superfamily: Fas ligand (FasL/TNFSF6), 52 LIGHT (TNFSF14), 53 and TNF-like molecule 1A (TL1A/TNFSF15). 54 The infusion of DcR3 ameliorates the autoimmune kidney diseases, namely, crescentic glomerulonephritis 55 and IgA 56 nephropathy, in mouse models. The therapeutic potential of DcR3 has also been demonstrated for experimental rheumatoid arthritis, 38 multiple sclerosis, 57 and inflammatory bowel disease. 58 The underlying mechanisms include modulation of T-cell activation/proliferation or B-cell activation, protection against apoptosis, suppression of mononuclear leukocyte infiltration, and diminished TNF-α, interferon-γ, and interleukin-17 expression. 35 DcR3 orthologs have not been identified in the mouse or rat genomes, indicating a crucial difference between the human and rodent immune systems. 35 Thus, we took advantage of human placenta explants to investigate the biological function of DcR3 in LIGHT-induced features of preeclampsia and demonstrated that DcR3 successfully attenuated LIGHT-induced sflt-1 secretion and trophoblast cell apoptosis in human placenta explants. In contrast to the elevated expression levels of HVEM and LTβR, the expression levels of DcR3 in the placentas of preeclamptic women are significantly reduced compared with normal individuals. These results suggest that reduction of placental expression of DcR3, a soluble decoy receptor, coupled with elevated placental expression of membrane-anchored receptors, HVEM and LTβR, are additional mechanisms to amplify elevated LIGHTinduced placental damage and sflt-1 secretion. Thus, DcR3, as an endogenous soluble receptor, is likely a safe and effective therapy to prevent LIGHT-induced impaired angiogenesis and placenta tissue damage and, therefore, has potential as a treatment for human preeclampsia. Because of its strong proinflammatory properties and immunestimulatory activities, excessive LIGHT is associated with several pathological conditions. 36 In particular, LIGHT contributes to pathophysiology associated with several autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn disease, chronic arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. 37 The use of soluble DcR3 receptor or neutralizing antibodies for its membrane receptors has become important therapeutic strategies for the treatment of these autoimmune disorders in multiple animal models. 38 preeclampsia may also benefit from this therapeutic approach. Perspectives The work reported here is the first to show that elevated LIGHT, coupled with enhanced LTβR and HVEM receptor activation, promotes placental damage and triggers release of potent vasoactive factors (sflt-1 and ET-1) in both human and murine pregnancy, as well as suggest that LIGHT signaling is likely an important mediator of pathogenesis associated with preeclampsia. Therefore, the use of HVEM/LTβR neutralizing antibodies, or the soluble form of LIGHT receptor, DcR3, to blunt the effects of elevated LIGHT may represent a novel treatment for preeclampsia. The current findings significantly advanced our understanding of pathogenesis of preeclampsia by revealing the pathogenic role of LIGHT signaling in preeclampsia and also provided a strong foundation for future translational studies to determine whether circulating LIGHT is elevated before symptoms and in this way serves as a presymptomatic biomarker and therapeutic target for preeclampsia. Sources of Funding This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants RC4HD and HD34130 (to Y.X and R.E.K.), by American Heart Association grant 10GRNT (to Y.X.), and by China National Science Foundation (to Y.X.). None. Disclosures References 1. Roberts JM, Cooper DW. Pathogenesis and genetics of preeclampsia. Lancet. 2001;357: Granger JP, Alexander BT, Llinas MT, Bennett WA, Khalil RA. Pathophysiology of preeclampsia: linking placental ischemia/hypoxia with microvascular dysfunction. Microcirculation. 2002;9: Godfrey KM, Barker DJ. Fetal nutrition and adult disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71(5 suppl):1344s 1352S. 4. Barker DJ. In utero programming of chronic disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 1998;95: Saito S, Sakai M. Th1/Th2 balance in preeclampsia. J Reprod Immunol. 2003;59: Lamarca B. The role of immune activation in contributing to vascular dysfunction and the pathophysiology of hypertension during preeclampsia. Minerva Ginecol. 2010;62: Maynard SE, Min JY, Merchan J, Lim KH, Li J, Mondal S, Libermann TA, Morgan JP, Sellke FW, Stillman IE, Epstein FH, Sukhatme VP, Karumanchi SA. Excess placental soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sflt1) may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and proteinuria in preeclampsia. J Clin Invest. 2003;111: Girardi G, Yarilin D, Thurman JM, Holers VM, Salmon JE. Complement activation induces dysregulation of angiogenic factors and causes fetal rejection and growth restriction. J Exp Med. 2006;203: Zhou CC, Ahmad S, Mi T, Abbasi S, Xia L, Day MC, Ramin SM, Ahmed A, Kellems RE, Xia Y. Autoantibody from women with preeclampsia induces soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 production via angiotensin type 1 receptor and calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T-cells signaling. Hypertension. 2008;51:
Preeclampsia (PE) is a life-threatening disorder of pregnancy
 Elevated Transglutaminase Activity Triggers Angiotensin Receptor Activating Autoantibody Production and Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia Chen Liu, PhD;* Renna Luo, MD, PhD;* Serra E. Elliott, PhD; Wei Wang,
Elevated Transglutaminase Activity Triggers Angiotensin Receptor Activating Autoantibody Production and Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia Chen Liu, PhD;* Renna Luo, MD, PhD;* Serra E. Elliott, PhD; Wei Wang,
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
UNCOVERING THE ROLES OF TOLL-LIKE RECEPTOR 7 AND INTERFERON REGULATORY FACTOR 5 IN IMMUNE COMPLEX GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 Name Email Barry Horne, Jr. bkhorne@bu.edu Institutional Affiliation Campus School Medical Campus Graduate Medical Sciences Division Department Graduate Program in Genetics and Genomics, Immunology Training
Name Email Barry Horne, Jr. bkhorne@bu.edu Institutional Affiliation Campus School Medical Campus Graduate Medical Sciences Division Department Graduate Program in Genetics and Genomics, Immunology Training
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Autoantibody-Mediated Complement C3a Receptor Activation Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia
 Autoantibody-Mediated Complement C3a Receptor Activation Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia Wei Wang, Roxanna A. Irani, Yujin Zhang, Susan M. Ramin, Sean C. Blackwell, Lijian Tao, Rodney E.
Autoantibody-Mediated Complement C3a Receptor Activation Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia Wei Wang, Roxanna A. Irani, Yujin Zhang, Susan M. Ramin, Sean C. Blackwell, Lijian Tao, Rodney E.
Immunity. Acquired immunity differs from innate immunity in specificity & memory from 1 st exposure
 Immunity (1) Non specific (innate) immunity (2) Specific (acquired) immunity Characters: (1) Non specific: does not need special recognition of the foreign cell. (2) Innate: does not need previous exposure.
Immunity (1) Non specific (innate) immunity (2) Specific (acquired) immunity Characters: (1) Non specific: does not need special recognition of the foreign cell. (2) Innate: does not need previous exposure.
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interleukin 6 Underlies Angiotensin II Induced Hypertension and Chronic Renal Damage
 Interleukin 6 Underlies Angiotensin II Induced Hypertension and Chronic Renal Damage Weiru Zhang, Wei Wang, Hong Yu, Yujin Zhang, Yingbo Dai, Chen Ning, Lijian Tao, Hong Sun, Rodney E. Kellems, Michael
Interleukin 6 Underlies Angiotensin II Induced Hypertension and Chronic Renal Damage Weiru Zhang, Wei Wang, Hong Yu, Yujin Zhang, Yingbo Dai, Chen Ning, Lijian Tao, Hong Sun, Rodney E. Kellems, Michael
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome
 Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Glomerular diseases mostly presenting with Nephritic syndrome 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls escape of RBCs
Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Shokoufeh Savaj MD Associate Professor of Medicine Firoozgar hospital- IUMS
 Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy Shokoufeh Savaj MD Associate Professor of Medicine Firoozgar hospital- IUMS History Immunoglobin A nephropathy was first described by Berger and Hinglais in 1968 in Paris
Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy Shokoufeh Savaj MD Associate Professor of Medicine Firoozgar hospital- IUMS History Immunoglobin A nephropathy was first described by Berger and Hinglais in 1968 in Paris
Online Supplement. Title: Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Autoantibody as a Novel Regulator of. Aldosterone independent of Preeclampsia
 Online Supplement Title: Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Autoantibody as a Novel Regulator of Aldosterone independent of Preeclampsia Authors: Jie Yang, MS 1, Li Li, MS 2, Jian-Yu Shang, BS 1, Lin Cai,
Online Supplement Title: Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Autoantibody as a Novel Regulator of Aldosterone independent of Preeclampsia Authors: Jie Yang, MS 1, Li Li, MS 2, Jian-Yu Shang, BS 1, Lin Cai,
Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: inflammation proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls
Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: inflammation proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, psoriasis
 IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM
 MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
Agonistic Autoantibodies to Angiotensin II Type I Receptor Contributes Partly to Placental Ischemia-Induced Cerebrovascular Abnormalities
 Agonistic Autoantibodies to Angiotensin II Type I Receptor Contributes Partly to Placental Ischemia-Induced Cerebrovascular Abnormalities Junie Paula Warrington 1, Fan Fan 1, Babbette B. LaMarca 1, Ralf
Agonistic Autoantibodies to Angiotensin II Type I Receptor Contributes Partly to Placental Ischemia-Induced Cerebrovascular Abnormalities Junie Paula Warrington 1, Fan Fan 1, Babbette B. LaMarca 1, Ralf
GESTOSIS. Mourachko LE. President of Russian Gestosis Association.
 GESTOSIS Mourachko LE President of Russian Gestosis Association. Gestosis is one of the most serious pregnancy complications responsible for a significant rate of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality.
GESTOSIS Mourachko LE President of Russian Gestosis Association. Gestosis is one of the most serious pregnancy complications responsible for a significant rate of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality.
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease
 Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease Mariam Priya Alexander, MD Associate Professor of Pathology GN Symposium Hong Kong Society of Nephrology July 8 th, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 The complement
Pathology of Complement Mediated Renal Disease Mariam Priya Alexander, MD Associate Professor of Pathology GN Symposium Hong Kong Society of Nephrology July 8 th, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 The complement
Bramantyo Aji Wicaksono 1*, Siti Candra Windu Baktiyani 2, Loeki Enggar Fitri 3
 THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 5, NO. 2, pp. 60-64, May, 2015 Intraperitoneal Injection of High Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF-α) Serum Increase Soluble Fms-like
THE JOURNAL OF TROPICAL LIFE SCIENCE OPEN ACCESS Freely available online VOL. 5, NO. 2, pp. 60-64, May, 2015 Intraperitoneal Injection of High Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF-α) Serum Increase Soluble Fms-like
Quantitative PPARγ expression affects the balance between tolerance and immunity
 Quantitative PPARγ expression affects the balance between tolerance and immunity Ya-Hui Liu 1, Yau-Sheng Tsai 1,2,3, Shih-Chieh Lin 4, Nan-Shih Liao 5, Ming-Shiou Jan 6, Chung-Tiang Liang 7, Shih-Wen Hsu
Quantitative PPARγ expression affects the balance between tolerance and immunity Ya-Hui Liu 1, Yau-Sheng Tsai 1,2,3, Shih-Chieh Lin 4, Nan-Shih Liao 5, Ming-Shiou Jan 6, Chung-Tiang Liang 7, Shih-Wen Hsu
Immunological Tolerance
 Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Shiraz E Medical Journal, Vol. 10, No. 1, January In the name of God. Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 10, No. 1, January 2009
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 10, No. 1, January 2009 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol10/jan2009/87016.htm Evaluation of Insulin Resistance in Severe Preeclampsia. Teimoori B*; Sakhavar N*;
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 10, No. 1, January 2009 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol10/jan2009/87016.htm Evaluation of Insulin Resistance in Severe Preeclampsia. Teimoori B*; Sakhavar N*;
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY
 CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Clinical features. Abnormal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and releasing of antiangiogenic
 Clinical features Abnormal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and releasing of antiangiogenic factors results in Vasospasm Endothelial dysfunction Etiology of various clinical signs and symptoms So, Preeclampsia
Clinical features Abnormal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and releasing of antiangiogenic factors results in Vasospasm Endothelial dysfunction Etiology of various clinical signs and symptoms So, Preeclampsia
Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy
 Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy Johanne Kaplan, PhD VP Neuroimmunology Research Genzyme March 26, 2013 RESTRICTED USE SEE TRAINING MEMO 2011 DO Genzyme NOT 1COPY Corporation
Potential Rebalancing of the Immune System by Anti-CD52 Therapy Johanne Kaplan, PhD VP Neuroimmunology Research Genzyme March 26, 2013 RESTRICTED USE SEE TRAINING MEMO 2011 DO Genzyme NOT 1COPY Corporation
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes. Gestational diabetes;
 Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
Lecture 19 Summary Gestational Diabetes and Complications of Diabetes Gestational diabetes; - Type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy Usually diagnosed in late pregnancy Causes high blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice
 Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Supplementary Information:
 Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
The Levels of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Soluble Flt-1 in Pregnancies Complicated by Preeclampsia
 J Korean Med Sci 27; 22: 94-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Levels of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Soluble Flt-1 in Pregnancies Complicated by
J Korean Med Sci 27; 22: 94-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Levels of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Soluble Flt-1 in Pregnancies Complicated by
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Preeclampsia is estimated to affect 7% to 10% of all
 Pathophysiology of Hypertension During Preeclampsia Linking Placental Ischemia With Endothelial Dysfunction Joey P. Granger, Barbara T. Alexander, Maria T. Llinas, William A. Bennett, Raouf A. Khalil Abstract
Pathophysiology of Hypertension During Preeclampsia Linking Placental Ischemia With Endothelial Dysfunction Joey P. Granger, Barbara T. Alexander, Maria T. Llinas, William A. Bennett, Raouf A. Khalil Abstract
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy ST2 Assay for Chronic Heart Failure File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: st_assay_for_chronic_heart_failure 2/2015 4/2018 4/2019 4/2018 Description
Corporate Medical Policy ST2 Assay for Chronic Heart Failure File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: st_assay_for_chronic_heart_failure 2/2015 4/2018 4/2019 4/2018 Description
Isolated proteinuria in Chinese pregnant women with pre-eclampsia: Results of retrospective observational study
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 5162-5166 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Isolated proteinuria in Chinese pregnant women with pre-eclampsia: Results of retrospective observational study Jing Cai 1,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 5162-5166 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Isolated proteinuria in Chinese pregnant women with pre-eclampsia: Results of retrospective observational study Jing Cai 1,
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
The Immune System: The Mind Body Connection. Presented by Margaret Kemeny, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco
 The Immune System: The Mind Body Connection Presented by Margaret Kemeny, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco Psychoneuroimmunology Investigation of the bidirectional
The Immune System: The Mind Body Connection Presented by Margaret Kemeny, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry, University of California, San Francisco Psychoneuroimmunology Investigation of the bidirectional
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity. Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China
 Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
Thomas HAIDER Journal Club
 Thomas HAIDER Journal Club 20.10.2014 Background Immunology of the CNS - History Ehrlich, 1885 & 1904 dye did not stain brain -> BBB Shirai, Y. (1921) On the transplantation of the rat sarcoma in adult
Thomas HAIDER Journal Club 20.10.2014 Background Immunology of the CNS - History Ehrlich, 1885 & 1904 dye did not stain brain -> BBB Shirai, Y. (1921) On the transplantation of the rat sarcoma in adult
Overview of glomerular diseases
 Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
USTEKINUMAB and BRIAKINUMAB
 USTEKINUMAB and BRIAKINUMAB Andrew Blauvelt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Dermatology and Dept. of Molecular Microbiology & Immunology Oregon Health & Science University Chief, Dermatology Service Veteran
USTEKINUMAB and BRIAKINUMAB Andrew Blauvelt, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Dermatology and Dept. of Molecular Microbiology & Immunology Oregon Health & Science University Chief, Dermatology Service Veteran
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
HST 071. IN SUMMARY PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy HST
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy HST
Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A. Link to publication Citation for published
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Ordering Physician. Collected REVISED REPORT. Performed. IgG IF, Renal MCR. Lambda IF, Renal MCR. C1q IF, Renal. MCR Albumin IF, Renal MCR
 RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one. of the most common diseases found in the population.
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis?
 Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/381/ra59/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Analysis of single-cell cytokine secretion reveals a role for paracrine signaling in coordinating macrophage responses
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/381/ra59/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Analysis of single-cell cytokine secretion reveals a role for paracrine signaling in coordinating macrophage responses
Increased risk for the development of preeclampsia in obese pregnancies: weighing in on the mechanisms
 Review Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 39: R1326 R1343, 215. First published October 7, 215; doi:1.1152/ajpregu.178.215. Increased risk for the development of preeclampsia in obese pregnancies:
Review Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 39: R1326 R1343, 215. First published October 7, 215; doi:1.1152/ajpregu.178.215. Increased risk for the development of preeclampsia in obese pregnancies:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice
 Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice Jimmy A. Rotolo 1, Branka Stancevic 1, Jianjun Zhang 1, Guoqiang Hua 1, John Fuller 1, Xianglei Yin 1, Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman 2, Kisu
Anti-ceramide Antibody Prevents the Radiation GI Syndrome in Mice Jimmy A. Rotolo 1, Branka Stancevic 1, Jianjun Zhang 1, Guoqiang Hua 1, John Fuller 1, Xianglei Yin 1, Adriana Haimovitz-Friedman 2, Kisu
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Chapter 17B: Adaptive Immunity Part II
 Chapter 17B: Adaptive Immunity Part II 1. Cell-Mediated Immune Response 2. Humoral Immune Response 3. Antibodies 1. The Cell-Mediated Immune Response Basic Steps of Cell-Mediated IR 1 2a CD4 + MHC cl.
Chapter 17B: Adaptive Immunity Part II 1. Cell-Mediated Immune Response 2. Humoral Immune Response 3. Antibodies 1. The Cell-Mediated Immune Response Basic Steps of Cell-Mediated IR 1 2a CD4 + MHC cl.
CHAPTER 2. Primary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
Epatite B: fertilità, gravidanza ed allattamento, aspetti clinici e terapeutici. Ivana Maida
 Epatite B: fertilità, gravidanza ed allattamento, aspetti clinici e terapeutici Ivana Maida Positivity for HBsAg was found in 0.5% of tested women In the 70s and 80s, Italy was one of the European countries
Epatite B: fertilità, gravidanza ed allattamento, aspetti clinici e terapeutici Ivana Maida Positivity for HBsAg was found in 0.5% of tested women In the 70s and 80s, Italy was one of the European countries
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic
 Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic differentiation of acute myeogenouse leukemia cells that is enhanced by 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin D 3. To the Editor: Sunitinib,
Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic differentiation of acute myeogenouse leukemia cells that is enhanced by 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin D 3. To the Editor: Sunitinib,
Placental steroid receptors and sex differences in fetal growth
 Placental steroid receptors and sex differences in fetal growth Professor Vicki Clifton Mater Medical Research Institute University of Queensland Brisbane, Australia Sex differences start in utero Lying-in
Placental steroid receptors and sex differences in fetal growth Professor Vicki Clifton Mater Medical Research Institute University of Queensland Brisbane, Australia Sex differences start in utero Lying-in
The death receptors: signaling and modulation
 The death receptors: signaling and modulation 1 1 The extrinsic cell death pathway 2 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Dec;7(12):1001-12. 2 Death receptors Belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene
The death receptors: signaling and modulation 1 1 The extrinsic cell death pathway 2 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Dec;7(12):1001-12. 2 Death receptors Belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene
Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3.
 Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3. Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba, Centro de investigaciones Biológicas, Madrid Valdés Cañedo F. and Vázquez- Martul E., Complejo
Familial DDD associated with a gain-of-function mutation in complement C3. Santiago Rodríguez de Córdoba, Centro de investigaciones Biológicas, Madrid Valdés Cañedo F. and Vázquez- Martul E., Complejo
Hearing Loss as a Complication of Pre-eclampsia?
 Hearing Loss as a Complication of Pre-eclampsia? Shatha Sami Hussein* FIBMS CABOC, Manal Madany Abdulqadar* FIBMS CABOC, Feryal Shakir Taher* FIBMS ABSTRACT Background: Pre-eclampsia is a systemic disorder,
Hearing Loss as a Complication of Pre-eclampsia? Shatha Sami Hussein* FIBMS CABOC, Manal Madany Abdulqadar* FIBMS CABOC, Feryal Shakir Taher* FIBMS ABSTRACT Background: Pre-eclampsia is a systemic disorder,
Research Article Relation of Hyperuricemia with Maternal and Perinatal Complications in Severe Preeclampsia
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC GYNAECOLOGY Research Article Relation of Hyperuricemia with Maternal and Perinatal Complications in Severe Preeclampsia Armando Alberto Moreno Santillan 1, Daniela Yesenia Paz Cervantes
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC GYNAECOLOGY Research Article Relation of Hyperuricemia with Maternal and Perinatal Complications in Severe Preeclampsia Armando Alberto Moreno Santillan 1, Daniela Yesenia Paz Cervantes
Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION
 3 Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION David Shirley, Giovambattista Capasso and Robert Unwin The kidney has three homeostatic functions that can broadly be described as excretory, regulatory
3 Chapter 1 RENAL HAEMODYNAMICS AND GLOMERULAR FILTRATION David Shirley, Giovambattista Capasso and Robert Unwin The kidney has three homeostatic functions that can broadly be described as excretory, regulatory
Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
 Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN) Background Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is defined as any glomerular disease characterized by extensive crescents (usually >50%) as the principal histologic
Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN) Background Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is defined as any glomerular disease characterized by extensive crescents (usually >50%) as the principal histologic
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens
 1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
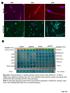 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
You admitted a previously healthy nullipara at 36 weeks gestation who presented with new-onset periorbital edema and is found to have blood pressure
 Preeclampsia Case report You admitted a previously healthy nullipara at 36 weeks gestation who presented with new-onset periorbital edema and is found to have blood pressure readings of 150/100 to 155/105
Preeclampsia Case report You admitted a previously healthy nullipara at 36 weeks gestation who presented with new-onset periorbital edema and is found to have blood pressure readings of 150/100 to 155/105
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) Western blot for the expression of RIPK1 in HK-2 cells treated with or without LPS (1 µg/ml) for indicated times.
 Supplemental Figure 1. (A) Western blot for the expression of RIPK1 in HK-2 cells treated with or without LPS (1 µg/ml) for indicated times. Western blots shown are representative results from 3 independent
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) Western blot for the expression of RIPK1 in HK-2 cells treated with or without LPS (1 µg/ml) for indicated times. Western blots shown are representative results from 3 independent
PREECLAMPSIA: THE ROLES OF ACUTE INFLAMMATION AND INTRAUTERINE STRESS
 Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 5-2016 PREECLAMPSIA: THE ROLES OF ACUTE INFLAMMATION AND INTRAUTERINE
Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 5-2016 PREECLAMPSIA: THE ROLES OF ACUTE INFLAMMATION AND INTRAUTERINE
