TEST BANK FOR HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARIEB AND HOEHN
|
|
|
- Anne Shaw
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Link download full: TEST BANK FOR HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARIEB AND HOEHN Chapter 16 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not a change typically produced by a hormonal stimulus? 1) A) stimulates production of an action potential B) alters plasma membrane permeability C) induces secretory activity D) activates or deactivates enzymes Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 2) Regulating hormones from the hypothalamus. 2) A) first enter into the hypophyseal portal system B) enter the hepatic portal system, which feeds the pituitary C) enter venous circulation and travel to the heart, which pumps the hormonecontaining blood to the pituitary D) travel by arteries to the pituitary Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 3) Hormones often cause a cell to elicit multiple responses; this is because. 3) A) there are thousands of receptors on the cell membrane B) during protein kinase activation, enzymes phosphorylate many other enzymes C) the receptors bind to several hormones at the same time D) the protein kinases are rapidly metabolized into functional amino acids Answer: B Explanation: A) B) C) D) 4) Which of the following is not a type of hormone interaction? 4) A) permissiveness B) synergism C) feedback D) antagonism Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 1 5) Which of the following is not a steroid-based hormone? 5) A) aldosterone B) estrogen C) epinephrine D) cortisone Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 6) Thyroxine is a peptide hormone, but its mechanism is different from other peptide hormones.
2 Which of the following statements is true concerning this difference? 6) A) It is very specific in the cell type it targets. B) It is a stimulant of cellular metabolism and targets all cells. C) It does not require a second messenger to effect a response. D) It causes positive feedback. Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 7) Cells that respond to peptide hormones usually do so through a sequence of biochemical
3 reactions involving receptor and kinase activation. In order for cells to respond, it is necessary for first and second messengers to communicate. This is possible because. 7) A) hormones alter cellular operations through direct stimulation of a gene B) peptide hormones are converted by cell membranes enzymes into second messengers C) G protein acts as the link between first and second messengers D) the hormone receptor complex moves into the cytoplasm as a unit Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 8) The major targets of growth hormone are. 8) A) the liver B) the blood vessels C) bones and skeletal muscles D) the adrenal glands Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 2 9) How do glucocorticoids enable the body to deal appropriately with stress? 9) A) by releasing the neurotransmitters that prepare the body for the stress response B) by increasing blood glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid levels and enhancing blood pressure C) by decreasing the heart rate, thus decreasing blood pressure D) by stimulating the pancreas to release insulin Answer: B Explanation: A) B) C) D) 10) Which of the choices below is not a factor required for target cell activation by hormone receptor interaction? 10) A) strength of the bond between the receptor and hormone B) type of hormone C) blood levels of hormone D) number of receptors for that hormone Answer: B Explanation: A) B) C) D) 11) Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver due to the action of. 11) A) cortisol B) aldosterone C) secretin D) insulin Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 12) Oxytocin. 12) A) controls milk production B) is an adenohypophyseal secretion C) release is an example of a positive feedback control mechanism D) exerts its most important effects during menstruation Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 3 13) Thyroid hormone (a small iodinated amine) enters target cells in a manner similar to. 13) A) insulin, because insulin is a small peptide B) growth hormone, because the thyroid works synergistically with thyroid hormone C) steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells D) glucagon, because the structure of glucagon is similar to that of thyroid hormone Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 14) Aldosterone. 14) A) production is greatly influenced by ACTH B) is secreted by the neurohypophysis C) functions to increase sodium reabsorption D) presence increases potassium concentration in the blood Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 15)
4 A man has been told that he is not synthesizing enough follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and for this reason he may be unable to father a child. Choose the correct statement to explain this problem. 15) A) FSH stimulates sperm production in the testes. B) FSH stimulates estrogen secretion by ovarian cells; therefore it is not synthesized by males. C) The man
5 must be producing progesterone, which inhibits the synthesis of FSH. D) A hormone made in the adenohypophysis cannot influence fertility. Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 16) ADH. 16) A) is inhibited by alcohol B) increases urine production C) promotes dehydration D) is produced in the adenohypophysis Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 4 17) Several hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus and transported to the anterior pituitary gland. The mechanism of transportation from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary gland is through the. 17) A) feedback loop B) general circulatory system C) hypophyseal portal system D) hepatic portal system Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 18) In circumstances where the body requires prolonged or increased levels of a hormone, the DNA of target cells will specify the synthesis of more receptors on the surface of the cells of the target organ. This is known as. 18) A) a stressor reaction B) upregulation C) sensitivity increase D) cellular affinity Answer: B Explanation: A) B) C) D) 19) Mineralocorticoid is to aldosterone as glucocorticoid is to. 19) A) estrogen B) epinephrine C) testosterone D) cortisol Answer: D Explanation: A) B) C) D) 20) The hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract. 20) A) conducts aldosterone to the hypophysis B) is the site of prolactin synthesis C) is partly contained within the infundibulum D) connects the hypophysis to the pituitary gland Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 21) Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones exert their effects through intracellular. 21) A) nucleotides B) calcium C) second messengers D) deactivating ions Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 5 22) Cellular responses to hormones that initiate second-messenger systems include. 22) A) possible activation of several different second-messenger systems B) hormone binding to intracellular receptors C) formation of a specific protein kinase that acts on a series of extracellular intermediates D) cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase formation of an active second messenger Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 23) Which of the following is not a cardinal sign of diabetes mellitus? 23) A) polydipsia B) polycythemia C) polyuria D) polyphagia Answer: B
6 Explanation: A) B) C) D) 24) One of the least complicated of the endocrine control systems directly responds to changing blood levels of ions and nutrients. Which of the following describes this mechanism? 24) A)
7 humoral stimulation B) protein synthesis C) catabolic inhibition D) carbohydrate oxidation Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 25) Normal development of the immune response is due in part to hormones produced by the. 25) A) thymus gland B) pancreas C) adrenal medulla D) thyroid gland Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 26) When it becomes necessary to enlist the fight-or-flight response, a hormone that is released during the alarm phase of the general adaptation syndrome is. 26) A) angiotensinogen B) renin C) epinephrine D) estrogen Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 6 27) Steroid hormones exert their action by. 27) A) binding cell receptors and initiating camp activity B) activating the hypothalamic release of regulating hormones C) entering the cell and activating mitochondrial DNA D) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene Answer: D Explanation: A) B) C) D) 28) Eicosanoids do not include. 28) A) paracrines B) leukotrienes C) prostaglandins D) hydrocortisones Answer: D Explanation: A) B) C) D) 29) The neurohypophysis or posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is not a true endocrine gland because. 29) A) embryonically it was an endocrine tissue, but in the adult human it is no longer functional B) it is strictly a part of the neural system and has little or nothing to do with hormonal release C) it is only a hormone storage area that receives hormones from the hypothalamus for release D) it is unable to function as an endocrine tissue because it is actually part of the neural system due to its location Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 30) Which organ does not produce hormones? 30) A) heart B) skin C) kidney D) spleen Answer: D Explanation: A) B) C) D) 31) What ion is sometimes used as a second messenger of amino acidnbased hormones? 31) A) sodium B) calcium C) iron D) chlorine Answer: B Explanation: A) B) C) D) 7 32)
8 The most important mineralcorticoid regulator of electrolyte concentrations in extracellular fluids is. 32) A) insulin B) glucagon C) aldosterone D) cortisol Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 33) Which organ is responsible for synthesizing ANP? 33) A) the spleen B) the heart C) the kidney D) the skin Answer: B Explanation: A) B) C) D) 34) Which of the following is not a change that may be caused by hormonal stimulus? 34) A) a change in membrane potential B) an increase in enzymatic activity C) direct control of the nervous system D) the stimulation of a genetic event resulting in protein synthesis Answer: C
9 Explanation: A) B) C) D) 35) Leptin is secreted by. 35) A) adipocytes B) goblet cells C) lymphocytes D) fibroblasts Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 36) The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone is dependent on. 36) A) nothingnall hormones of the human body are able to stimulate any and all cell types because hormones are powerful and nonspecific B) the location of the tissue or organ with respect to the circulatory path C) the membrane potential of the cells of the target organ D) the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ Answer: D Explanation: A) B) C) D) 8 37) Which of the following hormones suppresses appetite and increases energy expenditure? 37) A) leptin B) secretin C) renin D) gastrin Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 38) The second-messenger mechanism of hormone action operates by. 38) A) binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and camp B) synthesizing more than one hormone at a time C) increasing the basal metabolic rate in the target organ D) altering gene expression in the nuclear DNA Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 39) Chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids and that regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body are called. 39) A) hormones B) antibodies C) enzymes D) proteins Answer: A Explanation: A) B) C) D) 40) Which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus? 40) A) hormonal B) neural C) enzyme D) humoral Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 41) ACTH. 41) A) causes the release of hormones from the adrenal medulla B) is secreted by the posterior pituitary C) is not a tropic hormone D) secretion is regulated by a hypothalamic regulatory hormone Answer: D Explanation: A) B) C) D) 9 42) Which of the following is not a parathyroid gland mechanism to maintain adequate levels of blood calcium? 42) A) increase calcium ion reabsorption by the kidneys B) increase in intestinal absorption of calcium ions C) inhibition of calcitonin synthesis D) activation of osteoclasts Answer: C Explanation: A) B) C) D) 43) The single most important regulator of calcium levels in the blood is. 43) A) calcitonin B) parathyroid hormone C) gonadotropic hormones D) thyroid hormone Answer: B
10 Explanation: A) B) C) D) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 44) The largest pure endocrine gland in the body is the. 44) Answer: thyroid Explanation: 45) Give an example of synergism in hormones. 45) Answer:
11 The liver will release glucose in the presence of glucagon or epinephrine. If both hormones are present the amount of glucose released is increased 150%. Explanation: 10 Figure 16.2 Using Figure 16.2, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone targets: 46) Thyroid stimulating hormone 46) Answer: D Explanation: 47) What is the difference between autocrines and paracrines? 47) Answer: Autocrines are self-regulating chemical messengers because their target is the cell from which they are manufactured. Paracrines are chemical messengers that act locally. They tend to affect only the cells immediately around them. Explanation: 48) How is the heart involved as an endocrine gland? 48) Answer: A few cardiac cells secrete atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), which helps regulate salt output by the kidney. ANP inhibits aldosterone and signals the kidney to remove more salt. Explanation: 11 Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match the following: 49) Produces the hormones that direct the production of the secondary male sex characteristics. 49) Answer: E Explanation: 12 Figure 16.2 Using Figure 16.2, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone targets: 50) Prolactin 50) Answer: B 51) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 51) Answer: B Explanation: 52) Hypersecretion of growth hormone after epiphyseal plate closure can result in a condition called. 52) Answer: acromegaly Explanation: 53) Compare the structure and function of endocrine and exocrine glands. 53) Answer: Endocrine glands are ductless glands that release hormones into the blood to be transported to other organs. Exocrine glands have ducts through which products are released. Explanation: 14 54) Briefly discuss target cell activation by hormone-receptor interaction. 54) Answer: The first step is hormone-receptor binding to target cells, but interaction depends on blood levels of the hormone, relative number of receptors for that hormone on or in the target cells, and the affinity of the union between the hormone and the receptor. Explanation: 55)
12 As a result of stress the adenohypophysis releases, which stimulates release of hormones from the adrenal cortex that retain sodium and water, increase blood sugar, and begin breaking down fats. 55) Answer: ACTH Explanation: 56)
13 Why should the hypothalamus instead of the adenohypophysis be called the master endocrine gland? 56) Answer: Although the adenohypophysis has many hormonal products, the hypothalamus controls anterior pituitary activity through regulatory factors. Explanation: 57) Basal metabolism declines with age. What factors contribute to that decline? 57) Answer: Thyroid follicles fill with colloid and gland fibrosis occurs, resulting in a decline in hormone synthesis and release. Increase in body fat relative to muscle also contributes because muscle tissue is more active metabolically than fat. Explanation: 15 Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match the following: 58) Produce steroid hormones and glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. 58) Answer: C Explanation: 59) A person who drinks a lot of alcoholic beverages must urinate frequently. Why? 59) Answer: Alcohol inhibits ADH secretion. Explanation: 16 Figure 16.3 Using Figure 16.3, match the following: 60) Produces androgens. 60) Answer: C Explanation: 61) Produces glucocorticoids. 61) Answer: B Explanation: 62) Acromegaly and gigantism are the result of of growth hormone. 62) Answer: hypersecretion Explanation: 17 Figure 16.2 Using Figure 16.2, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone targets: 63) Follicle stimulating hormone 63) Answer: C Explanation: 64) Which hormone stimulates production of RBCs? 64) Answer: erythropoietin Explanation: 65) Alpha islet cells produce, an extremely potent hyperglycemic hormone. 65) Answer: glucagon Explanation: 66) The gland may influence our day/night cycles and even regulate the onset of sexual maturity. 66) Answer: pineal Explanation: 18 Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match the following: 67) Produces hormones and is considered a neuroendocrine organ. 67) Answer: A Explanation: 68) Growth hormones act indirectly to make the epiphyseal plate cartilage grow. What then acts directly to make it grow? 68) Answer: Growth hormone stimulates the liver to release a growth factor called somatomedin, which in turn controls the epiphyseal plate cartilage growth. Explanation: 19 Figure 16.2
14 Using Figure 16.2, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone targets: 69) Adrenocorticotropic hormone 69) Answer: E Explanation: 70) Why would one not expect to continue increasing in height with age? 70) Answer: The amount of growth hormone secreted declines with age and the closure of the
15 epiphyseal plates prohibits further growth in length of the long bones. Explanation: 71) Which hormones are synthesized from cholesterol? 71) Answer: Steroids Explanation: 72) A woman with excessive body hair, a deep voice, and an enlarged clitoris shows the outward symptoms of which hormonal dysfunction? 72) Answer: The hormonal dysfunction is hypersecretion of androgens. Explanation: 73) Glucagon and insulin both target the cells of the liver and are both made in the pancreas, yet they have very different effects on the cells they target. What accounts for this fact? 73) Answer: Glucagon and insulin use different cell surface receptors. Explanation: 20 Figure 16.2 Using Figure 16.2, match the following hypothalamic hormones with the pituitary hormone targets: 74) Growth hormone 74) Answer: A 75) Produces aldosterone. 75) Answer: A Explanation: 76) Produces epinephrine. 76) Answer: D Explanation: 77) List the four mechanisms involved in the regulation of aldosterone secretion. 77) Answer: The four mechanisms are: (1) the renin-angiotensin mechanism, (2) plasma concentration of sodium and potassium ions, (3) control exerted by ACTH, and (4) plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic peptide. Explanation: 22 Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match the following: 78) Produces the hormones that promote the development of the female secondary sexual characteristics at puberty. 78) Answer: D Explanation: 23 Figure 16.3 Using Figure 16.3, match the following: 79) Excess hormone levels result in Cushing s syndrome. 79) Answer: B Explanation: 80) Which hormone has only one known effect: to stimulate milk production by the breasts? 80) Answer: Prolactin Explanation: 81) The gland is especially large in early childhood, then declines in size and function with age. 81) Answer: thymus Explanation: 24 Figure 16.3
16 Using Figure 16.3, match the following: 82) Hormones mimic sympathetic nervous system neurotransmitters. 82) Answer: D Explanation: TRUE/FALSE. Write T if the statement is true and F if the statement is false. 83) The endocrine gland that is probably malfunctioning if a person has a high metabolic rate is the
17 parathyroid. 83) Answer: True False Explanation: 84) Both turn on factors (hormonal, humoral, and neural stimuli) and turn off factors (feedback inhibition and others) may be modulated by the activity of the nervous system. 84) Answer: True False Explanation: 85) Oxytocin is a strong stimulant of uterine contractions. 85) Answer: True False Explanation: 86) Enteroendocrine cells of the GI tract produce some hormones that are chemically identical to neurotransmitters. 86) Answer: True False Explanation: 25 87) All peptide hormone synthesis requires gene activation that produces mrna. 87) Answer: True False Explanation: 88) LH is also referred to as a gonadotropin. 88) Answer: True False Explanation: 89) Glucocorticoids are steroid hormones that usually enhance the immune responses when an individual is suffering from severe stress. 89) Answer: True False Explanation: 90) The beta cells in the pancreatic islets produce insulin. 90) Answer: True False Explanation: 91) Most type 2 diabetics do not produce insulin. 91) Answer: True False Explanation: 92) Hypersecretion of catecholamines can result in hypertension. 92) Answer: True False Explanation: 93) The hormone that raises blood sugar levels is insulin. 93) Answer: True False Explanation: 94) All adenohypophyseal hormones except GH affect their target cells via a cyclic AMP second messenger. 94) Answer: True False Explanation: 95) Oxytocin and ADH are produced in the posterior pituitary. 95) Answer: True False Explanation: 96) Aldosterone is the most potent mineralocorticoid produced in the adrenals but the least abundant. 96) Answer: True False Explanation: 97) In aged individuals, chronic stress may increase blood levels of cortisol and possibly contribute to memory deterioration. 97) Answer: True False Explanation: 26 98) Atrial natriuretic peptide is a hormone that controls blood pressure in part by increasing the urinary excretion of sodium. 98) Answer: True False Explanation: 99) The pineal gland is used as a brain orientation landmark for brain X rays. 99) Answer: True False Explanation: 100) Type 2 diabetics may reflect declining receptor sensitivity to insulin rather than decreased insulin
18 production. 100) Answer: True False Explanation: 101) Growth hormone solely exerts its influence by targeting other endocrine glands to produce hormones. 101) Answer: True False Explanation: 102) The prime metabolic effect of cortisol is gluconeogenesis. 102) Answer: True False Explanation: 103) Many hormones synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract are chemically identical to brain
19 neurotransmitters. 103) Answer: True False Explanation: 104) Thyroid hormone production requires the presence of iodine and calcium. 104) Answer: True False Explanation: 105) Iodine is an essential element required for the synthesis of thyroxine. 105) Answer: True False Explanation: 106) Direct gene activation involves a second-messenger system. 106) Answer: True False Explanation: 107) Addison s disease is due to a insufficient output of glucocorticoids only. 107) Answer: True False Explanation: 108) ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to release corticosteroid hormones. 108) Answer: True False Explanation: ) The antagonistic hormones that regulate the blood calcium level are calcitonin-parathormone. 109) Answer: True False Explanation: MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Match the following: 110) Hyposecretion of the pancreas. Answer: A A) Diabetes mellitus 110) Match the following: 111) Hyposecretion of the thyroid in infants. Answer: A A) Cretinism 111) Match the following: 112) Hyposecretion of growth hormone. Answer: A A) Pituitary dwarfism 112) Match the following: 113) Aldosterone production Answer: A 114) Testosterone production Answer: A A) Hormonal stimulus 113) 114) Match the following: 115) Produces a hormone that controls blood levels of calcium and potassium by their removal from bone tissue. Answer: A A) Parathyroid 115) Match the following: 116) Hypersecretion of growth hormone. Answer: A A) Acromegaly 116) Match the following: 117) The gland that controls the fight-or-flight reaction. Answer: A A) Adrenal medulla 117) Match the following: 118) Hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex. Answer: A A) Addison s disease 118) Match the following: 119) Hypersecretion of the adrenal cortex. Answer: A A) Cushing s disease 119) 28 Match the following: 120) Hypersecretion of growth hormone. Answer: A A) Acromegaly 120) Match the following: 121) The size and shape of a pea; produces hormones that stimulate other
20 endocrine glands. Answer: B 122) Produces hormones that regulate glucose levels in the body. Answer: A A) Pancreas B) Hypophysis 121) 122) Match the following: 123) Hyposecretion of the thyroid in adults. Answer: A
21 A) Myxedema 123) Match the following: 124) Parathyroid hormone production Answer: A A) Humoral stimulus 124) Match the following: 125) An autoimmune problem involving the thyroid gland. Answer: A A) Graves disease 125) Match the following: 126) Produces the body s major metabolic hormones. Answer: A A) Thyroid 126) Match the following: 127) Epinephrine production Answer: A A) Neural stimulus 127) ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 128) The parents of a 17-year-old boy are concerned about his height because he is only 5 feet tall and they are both close to 6 feet tall. After tests by their doctor, a certain hormone is prescribed for the boy. What is the probable diagnosis, and what hormones were prescribed? Why might the child still expect to reach his growth potential? Answer: The diagnosis is insufficient growth hormone. The prescription is recombinant DNA-produced pituitary growth hormone. The reason the child might reach his growth potential is that the epiphyseal plates of the long bones have not yet closed, allowing additional growth of the long bones. 129) Mr. Sanchez makes an appointment to see his doctor for pain in his abdominal area. Tests and X rays reveal kidney stones as well as bones with a moth-eaten appearance. Physical exam reveals hyporeflexia and hypotonis (weakness). What is the problem and what treatment would be recommended? Answer: The problem is hyperparathyroidism resulting from a parathyroid gland tumor. The treatment is removal of the tumor ) What is the most important nursing intervention when caring for a patient with Cushing s syndrome? Answer: Because of enhanced anti-inflammatory effects, infections may become overwhelmingly severe. Therefore the nurse should warn the patient to avoid shaving nicks and other sources of infection. 131) John is a 26-year-old man who begins to notice a progressive enlargement of feet, hands, cranium, nose, and
22 lower jaw bone. His doctor recommends a pituitary gland operation. What is the most likely diagnosis? Why? Answer: The diagnosis is acromegaly. The condition results from excess secretion of growth hormone from the
23 pituitary gland postpuberty and after the epiphyseal plates of the long bones have fused. 132) Following workup for symptoms of decreased libido and erectile dysfunction, a patient is told that his pituitary is hypersecreting prolactin. Is there need for concern about this young man? Answer: Yes; there should be great concern, because hypersecretion of prolactin will lead to impotence. 133) Thomas is a diabetic. While at work, he began to tremble, was somewhat disoriented, and showed signs similar to that of a drunk. One of his colleagues gave him some hard candy, which seemed to help him return to normal functions. Why? Was this a proper action, considering that Thomas is diabetic? Answer: Thomas was suffering from hypoglycemia. The low blood sugar level affected his brain resulting in his appearance of being drunk. The candy raised his blood sugar back up to a normal level. This was a proper action because he was hypoglycemic And the brain needs constant glucose fo proper function. 134) Mrs. James appeared at the clinic complaining of extreme nervousness and sweating, saying that she could feel and hear her heart thumping when she tried to sleep at night.she was found to have a severely elevated and fluctuating blood pressure. Although laboratory testing revealed hyperglycemia and increased basal metabolic rate, tests of thyroid function were normal. What is your diagnosis? What treatment should be used? Answer: The diagnosis is hypersecretion of catecholamines, sometimes arising from a rare chromaffin cell tumor called a pheochromocytoma. Treatment is surgical removal of the tumor. 135) It was often rumored that one of our deceased presidents was suffering from Addison s disease (inadequate synthesis of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids). What symptoms may have led to the diagnosis of this condition? Answer: Low body weight, low plasma glucose and sodium levels, high potassium levels, hypotension, severe dehydration, and hypotension might all have been observed in the patient. 136) A 25-year-old male was admitted to the medical/surgical unit with a blood glucose of 600 mg/dl. On assessment, the nurse observed his breathing was deep and rapid, and his breath smelled of acetone. His face
24 was flushed and his skin was dry. His ph was low. Describe the physiological response that is occurring. Answer:
25 In severe cases of diabetes mellitus, blood levels of fatty acids and their metabolites rise dramatically. The fatty acid metabolites, collectively called ketones, are strong organic acids. When they accumulate faster than they are used or excreted, the blood ph drops, resulting in ketoacidosis, and ketones begin to spill into the urine. The nervous system responds by initiating rapid deep breathing to blow off carbon dioxide from the blood and increase ph. 137) Explain how antidiuretic hormone can help regulate an abnormal increase in solute concentration in the extracellular fluid. Answer: The release of antidiuretic hormone can regulate an increase in solute concentration by causing reabsorption of water by the kidney. With reabsorption, blood water volume increases, decreasing solute concentration. 30 Answer Key Testname: C16 1) A 2) A 3) B 4) C 5) C 6) C 7) C 8) C 9) B 10) B 11) A 12) C 13) C 14) C 15) A 16) A 17) C 18) B 19) D 20) C 21) C 22) A
26 23) B 24) A
27 25) A 26) C 27) D 28) D 29) C 30) D 31) B 32) C 33) B 34) C 35) A 36) D 37) A 38) A 39) A 40) C 41) D 42) C 43) B 44) thyroid 45) The liver will release glucose in the presence of glucagon or epinephrine. If both hormones are present the amount of glucose released is increased 150%. 46) D 47) Autocrines are self-regulating chemical messengers because their target is the cell from which they are manufactured. Paracrines are chemical messengers that act locally. They tend to affect only the cells immediately around them. 31 Answer Key Testname: C16 48) A few cardiac cells secrete atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), which helps regulate salt output by the kidney. ANP inhibits aldosterone and signals the kidney to remove more salt. 49) E 50) B 51) B 52) acromegaly 53) Endocrine glands are ductless glands that release hormones into the blood to be transported to other organs. Exocrine glands have ducts through which products are released. 54)
28 The first step is hormone-receptor binding to target cells, but interaction depends on blood levels of the hormone, relative number of receptors for that hormone on or in the target cells, and the affinity of
29 the union between the hormone and the receptor. 55) ACTH 56) Although the adenohypophysis has many hormonal products, the hypothalamus controls anterior pituitary activity through regulatory factors. 57) Thyroid follicles fill with colloid and gland fibrosis occurs, resulting in a decline in hormone synthesis and release. Increase in body fat relative to muscle also contributes because muscle tissue is more active metabolically than fat. 58) C 59) Alcohol inhibits ADH secretion. 60) C 61) B 62) hypersecretion 63) C 64) erythropoietin 65) glucagon 66) pineal 67) A 68) Growth hormone stimulates the liver to release a growth factor called somatomedin, which in turn controls the epiphyseal plate cartilage growth. 69) E 70) The amount of growth hormone secreted declines with age and the closure of the epiphyseal plates prohibits further growth in length of the long bones. 71) Steroids 72) The hormonal dysfunction is hypersecretion of androgens. 73) Glucagon and insulin use different cell surface receptors. 74) A 75) A 76) D 77) The four mechanisms are: (1) the renin-angiotensin mechanism, (2) plasma concentration of sodium and potassium ions, (3) control exerted by ACTH, and (4) plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic peptide. 78) D 79) B 80) Prolactin 81) thymus 82) D 83) FALSE 84) TRUE 85) TRUE 86) TRUE 87) TRUE 88) TRUE 32 Answer Key Testname: C16 89) FALSE 90) TRUE 91) FALSE 92) TRUE 93) FALSE 94) TRUE 95) FALSE 96) FALSE 97) TRUE 98) TRUE 99) TRUE 100) TRUE 101) FALSE 102) TRUE 103) TRUE 104) FALSE 105) TRUE 106) FALSE 107) FALSE 108) TRUE 109) TRUE 110) A 111) A
30 112) A 113) A 114) A
31 115) A 116) A 117) A 118) A 119) A 120) A 121) B 122) A 123) A 124) A 125) A 126) A 127) A 128) The diagnosis is insufficient growth hormone. The prescription is recombinant DNA-produced pituitary growth hormone. The reason the child might reach his growth potential is that the epiphyseal plates of the long bones have not yet closed, allowing additional growth of the long bones. 129) The problem is hyperparathyroidism resulting from a parathyroid gland tumor. The treatment is removal of the tumor. 130) Because of enhanced anti-inflammatory effects, infections may become overwhelmingly severe. Therefore the nurse should warn the patient to avoid shaving nicks and other sources of infection. 131) The diagnosis is acromegaly. The condition results from excess secretion of growth hormone from the pituitary gland postpuberty and after the epiphyseal plates of the long bones have fused. 132) Yes; there should be great concern, because hypersecretion of prolactin will lead to impotence. 33 Answer Key Testname: C16 133) Thomas was suffering from hypoglycemia. The low blood sugar level affected his brain resulting in his appearance of being drunk. The candy raised his blood sugar back up to a normal level. This was a proper action because he was hypoglycemic And the brain needs constant glucose fo proper function. 134) The diagnosis is hypersecretion of catecholamines, sometimes arising from a rare chromaffin cell tumor called a pheochromocytoma. Treatment is surgical removal of the tumor. 135)
32 Low body weight, low plasma glucose and sodium levels, high potassium levels, hypotension, severe dehydration, and hypotension might all have been observed in the patient. 136)
33 In severe cases of diabetes mellitus, blood levels of fatty acids and their metabolites rise dramatically. The fatty acid metabolites, collectively called ketones, are strong organic acids. When they accumulate faster than they are used or excreted, the blood ph drops, resulting in ketoacidosis, and ketones begin to spill into the urine. The nervous system responds by initiating rapid deep breathing to blow off carbon dioxide from the blood and increase ph. 137) The release of antidiuretic hormone can regulate an increase in solute concentration by causing reabsorption of water by the kidney. With reabsorption, blood water volume increases, decreasing solute concentration. 34
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
human anatomy & physiology sampler questions
 human anatomy & physiology sampler questions Please note that there are questions within this set that test material that may not have been covered in your lecture; unless otherwise specified, lecture
human anatomy & physiology sampler questions Please note that there are questions within this set that test material that may not have been covered in your lecture; unless otherwise specified, lecture
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Art labeling Activity: Figure 16.1
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
The endocrine system -- a brief overview.
 The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system
 Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Page 1. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Endocrine System (Chapter 18) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Endocrine System (Chapter 18) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Endocrine System (Chapter 18) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
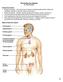 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Biology 2100 Human Physiology C. Iltis SLCC March 8, Midterm Examination #2
 Biology 2100 Human Physiology Name: KEY C. Iltis SLCC March 8, 2000 Midterm Examination #2 Multiple Choice Questions (2 POINTS EACH) 1. When glucose levels are above 100 mg/dl, which of the following is
Biology 2100 Human Physiology Name: KEY C. Iltis SLCC March 8, 2000 Midterm Examination #2 Multiple Choice Questions (2 POINTS EACH) 1. When glucose levels are above 100 mg/dl, which of the following is
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Endocrine System. Collection of glands that secrete hormones.
 Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Endocrine Control. Chapter 35
 Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
