Eye (2014) 28, & 2014 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved X/14 M Ho, ECF Lo, AL Young and DTL Liu
|
|
|
- Marjory Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (2014) 28, & 2014 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved X/14 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year by combined therapy of photodynamic therapy with ranibizumab and predictive factors governing the outcome M Ho, ECF Lo, AL Young and DTL Liu CLINICAL STUDY Abstract Aim To report the visual outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy receiving combined treatment with photodynamic therapy using Visudyne and intravitreal ranibizumab injections, and to analyze the predictive factors of visual outcome at 1 year post treatment. Methods Seventy-four consecutive patients with newly diagnosed polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy were treated with photodynamic therapy using Visudyne and three loading doses of intravitreal ranibizumab. The final visual outcome and polyp eradication rate at 1 year were reported. A stepwise regression model was used to estimate the baseline clinical factors predictive of better visual outcome and polyp eradication. Results Visual acuities at 12-months followup improved significantly compared with baseline from logmar to logmar (P ¼ 0.026). The mean foveal thickness decreased from 380±175 to 278±117 mm. In all 29.7% of eyes improved at least by 0.3 logmar, and 55.4% remained stable in visual acuity with less than 0.3 logmar change. Overall, 85% of eyes achieved at least stable vision, 20.2% (15/74) cases achieved polyp eradication on angiogram, and 60.8% (45/74) achieved polyp size reduction on angiogram at 1 year. Regarding predictive factors, the baseline visual acuity (P ¼ 0.003), no foveal involvement by abnormal choroidal vasculature (Po0.0001), absence of hard exudates (0.001) or subretinal fluid (o0.0001) are important clinical factors affecting the final visual outcome. Conclusions Combination therapy with photodynamic therapy using Visudyne and three loading doses of intravitreal ranibizumab injections resulted in 85% success rate on visual stabilization and 81% success rate in polypoidal lesion control. (2014) 28, ; doi: /eye ; published online 26 September 2014 Introduction Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) is a distinct macular degeneration entity characterized by a branching choroidal vascular network and polypoidal vascular dilatation. 1 Although being associated with multiple recurrent serosanguineous detachments, PCV was reported to have better prognosis than age-related macular degeneration (AMD) as PCV is usually not linked to significant fibrous proliferation typical of end-stage neovascular AMD. 2 Treatments for PCV have largely relied on photodynamic therapy (PDT) since the past decade, as PDT could eradicate abnormal choroidal polyps with up to 80% success rate. 3 6 Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong SAR, Hong Kong Correspondence: DTL Liu, Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital, Shatin, Hong Kong SAR, Hong Kong Tel: ; Fax: david_tlliu@ yahoo.com Received: 22 April 2014 Accepted in revised form: 12 August 2014 Published online: 26 September 2014
2 1470 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year Meanwhile, the role of anti-vegfs in treating PCV has been ascertained by several prospective studies with successful outcomes. 7,8 Anti-VEGF works in a mechanism different from PDT; it reduces exudation related to vasculopathy and normalizes retinal thickness. As possible synergistic effect may result by combining the two methods, we therefore conducted this study to evaluate the efficacy of combination therapy with PDT using Visudyne and ranibizumab (Lucentis; Genentech, South San Francisco, CA, USA) in PCV cases. Given the variability in clinical courses and visual outcomes in PCV cases, a risk stratification calculator based on predictive factors may help clinicians to determine the most suitable treatments and to counsel patients. Hence, a stepwise logistic regression analysis was adopted for building a risk-analysis profile for visual outcome and disease curative rate. Patients and methods This is a retrospective study of consecutive cases investigating the 1-year result of combination therapy with PDT and three loading doses of 0.5 mg ranibizumab injections followed by as-needed reinjection schedule. The recruitment period was from January 2010 to October Consecutive treatment-naive cases visiting our retinal clinic at the Prince of Wales Hospital, Chinese University of Hong Kong, were recruited. Inclusion criteria included age 445 years old, newly diagnosed PCV with presence of classic polypoidal vasculature on indocyanine green angiography (ICGA). Recruited patients were those suffering from symptomatic PCV either directly related to polyp itself or secondary to exudative symptom regardless of the site of polyp occurrence; hence both extrafoveal and macular PCV were to be considered. Diagnosis of PCV was based on both fundal findings and ICGA findings. It was based on disease characteristics of elevated orange-red lesions (not resembling a PED, choroidal hemangioma, or subretinal blood) on clinical examination or characteristic polypoidal vasculature on ICGA. 9 Exclusion criteria included previous history of AMD, history of PDT, a high myopia (of 46 D) and pre-existing macular scar. All patients underwent a comprehensive ophthalmic examination before initiation of treatment, which included comprehensive slit-lamp biomicroscopy, fundus color photography (TRC50, Image Net, Topcon, Tokyo, Japan), ICGA (TRC-50IA, Image Net, Topcon), and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) (v , Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany). The visual acuity was measured monthly. Best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was measured in a wellilluminated room with optimal refractive correction, where the standard Snellen visual acuity chart was adopted and placed at a distance of 6 feet from the patient for measurement. BCVA was converted to the log minimum angle of resolution (logmar) for analysis. OCT was performed at baseline, 3 months, 6 months and 1 year post initiation of treatment. Fluorescein angiography (FA) and ICGA were performed at baseline, 6 months and 12 months post treatment in all cases. Patients were treated with a combination therapy of one session of standard PDT and three monthly doses of intravitreal ranibizumab. Regarding PDT application, all patients received a 6 mg/m 2 infusion of verteporfin, followed by diode laser applied to the leaking choroidal polyps and abnormal vasculature guided by ICGA. A total light energy of 50 J/cm 2 and light for 83 s were used to cover the entire lesion. The entire lesion was covered by laser spot with an additional 500 mm covering the borders on each side. Intravitreal ranibizumab injection was given simultaneously following uneventful PDT on the same day. Additional doses of ranibizumab were given in a monthly manner for up to three monthly loading doses. Additional doses of intravitreal injections or repeated PDTs were administered in the event of persistent or recurrent disease. 10,11 Eligible patients for retreatments would be offered PDT as frequently as every 3 months. Repeated ranibizumab injections could be offered on a monthly basis. Fluorescein angiogram and indocyanine angiography were performed every 3 months in cases with clinical suspicion of persistent disease. Retreatment was considered when there was either angiographic or clinical evidence of persistent or recurrent disease. Angiographic evidence included persistent leakage on fluorescein angiogram or ICGA. Clinical evidence included increase in haemorrhage area on fundus photographs or increase in exudation documented on OCT. Persistent leakage directly underneath the fovea was also considered an indication for retreatment disregarding the extent of leak. Additional treatments were recommended as guided by the predominant pathology. PDT was suggested for prominent leaking polypoidal lesion, whereas ranibizumab injection was provided when significant exudations present. The number of additional ranibizumab injections was decided according to clinical response. Outcome measures were divided into two categories, functional and anatomical success. Functional success was regarded as follows: good visual outcome (X0.3 logmar gain), stabilized visual outcome (o 0.3 logmar change in visual acuity), and significant worsened visual outcome (X0.3 logmar worse). BCVA results were converted to logarithm of the minimal angle of resolution (logmar) value for statistical analysis. To assess the response on anatomic success, good response is regarded as reduced lipid exudation and reduced foveal thickness p280 mm.
3 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year 1471 As PCV carried diversity in visual outcome, baseline ophthalmic clinical factors were collected to evaluate the relationship with the clinical course and outcome. The clinical factors collected include age, gender, size of the largest polyp, distance of the largest polyp to fovea, the greatest linear dimension (GLD) of the polyp, baseline visual acuity, size of subretinal blood, number of polyps, location of abnormal choroidal vasculature, area of treatment by PDT, and presence of the following: grapelike clustering of the polyp, subretinal blood 41 disc diameter, concurrent type-2 CNV, lipid exudation, subretinal fluid, and pigment epithelial detachment. The size of the largest polypoidal lesion, the GLD, and distance between the largest polyp and foveal center were measured by examining the ICGA images. Measurements were made by an electronic caliper via the software installed in an ICGA machine (TRC50; IMAGEnet; Topcon). Patient characteristics were retrieved from corresponding medical records; information obtained included age at diagnosis, sex, and BCVA documented in decimal visual acuity charts. The baseline clinical factors retracted as predictors for analysis of long-term visual outcome were mentioned previously. The baseline clinical factors were adopted for univariable and multivariable univariate analysis against the outcome parameters. Post-treatment clinical information was not included in the regression analysis. The difference between the baseline visual acuity and post-treatment visual acuity at 1 year has been compared using the paired Student t-test; a value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Stepwise logistic regression and linear regression were used for determining predictive factors for anatomical and visual outcomes, respectively, with statistical tests of P-value o0.05 being considered significant. Statistical analysis was performed with BM SPSS 18.0 software for Windows (SPSS/IBM Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA). Results Treatment outcomes Table 1 shows the demographics of 74 eyes of 74 patients and the baseline ophthalmic clinical findings. There were 51 males (68%) and 24 females (32%). The visual acuities 1 year after the combination therapy improved significantly from the baseline (P ¼ 0.026; paired Student t-test). The mean baseline visual acuity was logmar±0.54 SD, and the mean post-treatment visual acuity was 0.728logMAR±0.54SD. The mean improvement was 0.1 logmar unit. The mean baseline foveal thickness was 380±175 mm, and the mean posttreatment foveal thickness measured at 6 months posttreatment was 278±117 mm. Table 1 Demographic data and baseline clinical characteristics of patients harboring PCV Mean±SD (range) Age, years 66.6±10.2 (45 86) Gender, male 51 (68%) Baseline visual acuity, logmar 0.828±0.54 ( ) Baseline foveal thickness 380±175 mm ( ) Choroidal vasculature with FAZ involvement 42 (57%) Baseline size of choroidal vascular networks 2749±1328 mm ( ) Size of the largest polypoidal lesion 396±192 mm ( ) Distance from the largest polyp to foveal 1224±996 mm ( ) center Presence of a cluster of grape-like polyps 22 eyes (29.7%) Presence of type-2 concurrent CNV 15 eyes (20.3%) Presence of lipid deposition 38 eyes (51.4%) Presence of subretinal fluid 38 eyes (51.4%) Presence of significant subretinal blood 40 eyes (54.1%) 41 disc diameter Baseline size of subretinal blood 2886±1974 mm ( ) Presence of pigment epithelial detachment 42 eyes (57%) Mean PDT area of treatment zone 4420±1180 mm (2 7mm) Abbreviations: CNV, choroidal neovascularization; FAZ, foveal avascular zone; logmar, log minimum angle of resolution; SD, standard deviation. Visual outcome at 1 year in our center was reported as follows. The visual acuity improved at least 0.3 logmar unit at 1 year after the combination therapy in 22 eyes (29.7%) and remained stable in 41 eyes (55.4%) with less than 0.3 logmar change in VA. In 11 eyes (14.9%), visual acuity dropped more than 0.3 logmar at 1 year after treatment. Overall, the visual acuity remained unchanged or improved in 85.1% of eyes (63/74). Regarding anatomical outcome, good outcome was observed in 56 eyes (75.7%) at 6 months post initiation of treatment. FA performed 12 months post initiation of PDT treatment showed polypoidal lesions completely resolved in 15 eyes (20.2%), and decreased in size or number in 45 eyes (60.8%). Overall, 81% of cases achieved angiographic success with evidence of polypoidal eradication or reduction at the sixth month. Evaluation of treatment-resistant cases and adverse outcomes The initial three monthly loading doses of ranibizumab were injected into 74 eyes. Nine eyes were found to suffer from clinically evident persistent leakage from polypoidal lesion with significant exudations, three eyes (4.1%) received two additional reinjections, and six eyes (8.1%) received extra three injections. Among these cases, two eyes (3%) underwent one additional PDT session 3 months apart from the first PDT. Only 1 case out of 74 cases (1.4%) suffered from subretinal hemorrhage of larger than 1 disc diameter after combination therapy throughout the 1-year follow-up period.
4 1472 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year Predictive factors for visual outcome Predictive factors for final visual outcome were estimated by regression modelling. Univariate analysis showed that baseline characteristics such as younger age, better baseline visual acuity, larger distance between the largest polyp and fovea, smaller size of the largest polyp, no foveal inovlvement by polypoidal lesion, and absence of subretinal fluid or hard exudates at the macula correlated significantly with better visual acuity at 1 year (Tables 2a and b). Backward stepwise multivariable regression analysis for linear variables showed that baseline visual acuity (regression coefficient ¼ 0.496; adjusted R 2 ¼ 0.470; P ¼ 0.003) and location of choroidal vasculature (0.467; adjusted R 2 ¼ 0.560; P ¼ 0.008) were two independent factors most significantly related to the visual outcome at 1 year. (Table 3) In summary, the important predictor factors for visual outcomes included better baseline visual acuity, farther location of polypoidal vasculature from fovea, no foveal involvement by the polypoidal lesions, and absence of hard exudates or subretinal fluid at the macula. Predictive factors in determining successful polyp eradication Univariate logistic regression showed that several factors were related to the poor response of polypoidal lesions treatment. Bigger size of the largest polyp (coefficient ¼ 0.004; P ¼ 0.007), increased number of polyps (coefficient ¼ 0.300; P ¼ 0.043), and presence of clustering grape-like polypoidal lesions (coefficient ¼ 1.656; P ¼ 0.005) were shown to correlate significantly with poor angiographic response (Table 4). In 56 eyes with good response of polyp eradication, the mean VA at 1 year post treatment was logmar Table 2a Univariate linear regression analysis for continuous variables predicting visual outcome at 1 year Predicting variables Standardized regression coefficient Adjusted R square P-value Age o a Size of the largest polyp o a Distance of the largest a polyp to fovea GLD Baseline visual acuity in o a logmar Size of subretinal blood Number of polyps Area of treatment by PDT Abbreviations: GLD, greatest linear dimension; logmar, log minimum angle of resolution; PDT, photodynamic therapy. a Statistically significant. (Snellen equivalent to 20/70)±0.13, which was significantly better than the mean VA in poor polypoidal lesion response group of logmar (Snellen equivalent to 20/200)±0.536 (P ¼ 0.028; Student s t-test). In the good angiographic response group, 19 eyes (34%) had visual improvement 40.3 logmar; compared with only three eyes (17%) in the poor angiographic response group. Table 2b Univariate logistic regression for discrete variables at baseline correlates with visual acuity at 1 year Baseline Characteristics (n, %) LogMAR (mean±sd) at 1 year Univariate analysis between baseline predictive factor and final VA outcome (P-value) Gender Male 0.762± Female 0.685±0.61 Location of abnormal choroidal vasculature FAZ involvement 1.07±0.44 o a No FAZ involvement 0.303±0.31 Grape-like clustering of polyps Present 0.883± Absent 0.678±0.561 Concurrent type-2 CNV Present 0.952± Absent 0.684±0.48 Lipids deposition Present 0.931± a Absent 0.535±0.55 Subretinal blood more than 1 disc diameter Present 0.831± Absent 0.629±0.52 Subretinal fluid Present 1.061±0.47 o a Absent 0.397±0.38 Pigment epithelial detachment Present 0.667± Absent 0.832±0.50 Abbreviations: CNV, choroidal neovascularization; FAZ, foveal avascular zone; logmar, log minimum angle of resolution; n, number; SD, standard deviation. a Statistically significant. Table 3 Multivariate analysis with backward stepwise approach showing two most important independent factors predicting final visual outcome Independent variables Regression coefficient Adjusted R square P-value Baseline visual acuity in logmar Absence of choroidal vasculature in FAZ Abbreviation: logmar, log minimum angle of resolution.
5 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year 1473 Table 4 Comparing disease characteristics of good outcome group with poor outcome group in terms of polyp clearance (angiographic evidence) at 1 year Baseline characteristics Good outcome (resolution of polyp and dry macular at 12 months) mean±sd Poor outcome (evidence of persistent disease) P-value Odds ratio Age, year 66± ± Baseline visual acuity in logmar 0.806± ± Baseline foveal thickness, mm 384± ± Choroidal vasculature involving FAZ (%) 29/56 (52%) 13/18 (72%) Distance between polyp and fovea, mm 1234± ± Size of the largest polyp, mm 357± ± a Size of choroidal vasculature, mm 2647± ± Number of polyps 2.2± ± a Grape-like clustering of polyps 12/56 (21%) 10/18 (56%) a Concurrent type-2 CNV 10/56 (18%) 5/18 (28%) Lipid deposition 28/56 (50%) 12/18 (67%) Subretinal fluid 28/56 (50%) 9/18 (50%) Size of subretinal blood more than 1 disc diameter 28/56 (50%) 9/18 (50%) Mean size of subretinal blood, mm 2745± ± Pigment epithelial detachment 27/56 (48%) 10/18(56%) Size of PDT laser treatment area, mm 4430± ± Abbreviations: CNV, choroidal neovascularization; FAZ, foveal avascular zone; PDT, photodynamic therapy; SD, standard deviation. P-values were generated via logistic regression correlating baseline characteristics with status of polyp clearance. a Statistically significant. Discussion Verteporfin PDT can achieve polyp regression in 80 95% of cases. 3 6 It is well recognized for the treatment of PCV through thrombosis of the abnormal vessels. On the other hand, anti-vegfs act through a different mechanism by restoring the normal retinal thickness. Rapid restoration of edematous retina could potentiate the final visual outcome. Our study proved the synergistic effect of the combination regime by achieving 85% rate in visual stabilization and 81% rate in polyp eradication at 1 year. Anti-VEGF was reported to have a lower efficacy in eradicating the polypoidal choroidal structure in eyes with PCV, given the persistence of polypoidal lesions or branching vascular networks in previous reports using anti-vegf as sole treatment However, the high anatomic conversion rate by verteporfin PDT is not without costs. PDT may cause putative damages to the PRE by causing choriocapillary hypoperfusion and retinal pigment epithelium atrophy. The damage by PDT was demonstrated by reduction of retinal function as documented on multifocal electroretinogaphy. 17 Recent researchers adopted enhanced depth imaging OCT in PCV examination, showing reduction of choroidal thickness after PDT application. 18 A subnormal choroidal thickness secondary to choroidal vasculature thrombosis may hinder the visual outcome. 19 Hence, PDT is seemingly not desirable for multiple recurrence cases. A direct comparison of PDT with ranibizumab treatment was carried out in a randomized, multicenter trial of 93 treatment-naive cases in the Laptop study. 20 In all 17% of eyes in the PDT arm achieved visual gain compared with 30.4% in the ranibizumab arm. The superiority of ranibizumab in PCV in terms of visual outcome was proved, but the effectiveness of combined treatment was not evaluated. 20 The EVEREST study was the only randomized study comparing the three arms for PCV, including ranibizumab, PDT, and combined therapy. 15 The study concluded that PDT was more effective than ranibizumab in causing regression of polyps, with the mean gain in visual acuity being similar among the three groups. 15 Despite being a wellconducted randomized trial, the sample size was relatively small, with only 17 cases per arm. Our study supplemented information on the efficacy of the combination regime with a relatively large series of 74 cases, which further supports the use of combination therapy by achieving good stabilization of VA. The long-term visual outcome in the eyes with PCV depends on the recurrence rate and size of atrophic changes that result from persistent lesions. Wakabayashi et al 21 showed that regression of polypoidal lesions early after PDT treatment could be up to 94%; however, 42% of cases showed evidence of recurrence with an enlarged vascular network at a mean follow-up of 19.2 months. It is still an educated assumption that polyp clearance reduces disease recurrence. Our study concluded some predictors may indicate poor polypoidal conversion and perhaps increased disease recurrences. However, we did not evaluate the direct linkage between anatomic clearances of polyp and recurrence rate.
6 1474 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year PDT combined with anti-vegf therapy is currently recommended for treatment of PCV and was reported to have good visual outcome in patients suffering from PCV However, relatively few studies have investigated the visual prognostic factors following PCV treatments, especially the predictive factors following combined therapy. Some of the clinical factors such as age, baseline best-corrected visual acuity and size of haemorrhage, and presence of PED were reported to govern the final visual outcome. 26 Recently, the baseline polyp size and the location of polyps were also proven to affect the long-term visual acuity in a retrospective cohort. 31 However, these results were rather inconsistent. Our study could help bridge the knowledge gap by a relatively large sample size and uniform follow-up schedules. 31 In our study, the most significant good predictive factors for visual outcomes included better baseline visual acuity, farther location of polypoidal vasculature from the fovea, no foveal involvement by the polypoidal lesions, and absence of hard exudates or subretinal fluid at the macula. Compared with the existing studies, presence of PED or large area of subretinal blood was not necessarily related to final visual acuity. The authors considered PED or subretinal blood as an associated feature in PCV but not a valuable predictor. 32 Instead, presence of hard exudates or subretinal fluid at macula signifies poor visual outcome. Any information regarding the polyp nature, such as the polyp size, the number of polyps, and clustering of polyps, was regarded as information related to polyp eradication ease rather than final visual outcome. The authors suggested a possible indirect pathway linking the persistence of polyps to recurrence of disease and eventually affecting long-term visual prognosis. 31 Mori et al 33 reported the good predictors for PCV patients receiving PDT as sole treatment in 181 patients. Attention was drawn to the size of the GLD for abnormal vasculature. However, the size of GLD did not correlate well with the final visual outcomes in our series. Instead, the location of lesions did matter; any active subfoveal or juxtafoveal polypoidal lesions may result in more profound damage to photoreceptors irrespective of the size of lesion. Our result on predictive factors is useful in foreseeing a patient s visual outcome at presentation solely by judging the location and extent of dilated vascular networks. In addition, the mean distance from the largest polyp to the fovea in our series was found to be 1224 mm, reflecting most cases with polypoidal lesions in close proximity to the fovea. Careful judgment is needed in such cases; the authors suggest choosing anti-vegf agents instead of PDT in treating foveal or juxtafoveal lesions to avoid direct RPE damage. This important information may serve as a compass to ophthalmic surgeons whenever they need a better comprehension of the possible treatment benefit and risk via a tactical choice of the best treatment regimen. The current study has limitations due to its retrospective nature and a lack of data regarding comparison arms. A randomized study or a control group is preferred in direct comparison of anti-vegf agents, PDT, and a combination of both. This study did not look into the relationship between polyp conversion and recurrence rate. Future studies with longer follow-up for information regarding disease recurrence are preferred. Regarding the strength, it provides an insight into the predictive factor profiles in patients receiving combined therapy. Our study further supports the efficacy of adopting the combination regime in PCV cases and is valuable for the understanding of PCV as it is one of the largest cohort study evaluating the treatment outcome of PCV. The authors also suggest risk stratification in choosing individualized treatment for PCV patients. In conclusion, combined therapy by both PDT and ranibizumab injections results in good visual outcome at 1 year. Combination therapy could achieve good disease control angiographically of up to 85% cases. The authors concluded that both anti-vegf agents (at least three loading doses) and PDT using Visudyne are essential in treating PCVs. However, it is also important to exert clinical judgment in choosing monotherapy based on individualized disease characteristics. Summary What was known before K PCV prognostication is largely lacking. K The treatment outcome in PCV patients is not sure. What this study adds K A scientific way of prognosticating PCV. K A method to predict the treatment outcomes in PCV patients. Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. Author Contributions All authors listed here are qualified for authorship. This is to certify all the authors gained credit by fulfilling substantial contributions to the conception and design, acquisition and analysis of data, drafting and revising the article, and approving the version to be published.
7 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year 1475 References 1 Yannuzzi LA, Sorenson J, Spaide RF, Lipson B. Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (IPCV) Retina 2012; 32(Suppl 1): Ciardella AP, Donsoff IM, Huang SJ, Costa DL, Yannuzzi LA. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Surv Ophthalmol 2004; 49(1): Chan WM, Lam DS, Lai TY, Liu DT, Li KK, Yao Y et al. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for symptomatic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: one-year results of a prospective case series. Ophthalmology 2004; 111(8): Gomi F, Ohji M, Sayanagi K, Sawa M, Sakaguchi H, Oshima Y et al. One-year outcomes of photodynamic therapy in age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Japanese patients. Ophthalmology 2008; 115(1): Silva RM, Figueira J, Cachulo ML, Duarte L, Faria de Abreu JR, Cunha-Vaz JG. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and photodynamic therapy with verteporfin. Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2005; 243(10): Otani A, Sasahara M, Yodoi Y, Aikawa H, Tamura H, Tsujikawa A et al. Indocyanine green angiography: guided photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2007; 144(1): Hikichi T, Higuchi M, Matsushita T, Kosaka S, Matsushita R, Takami K et al. Factors predictive of outcomes 1 year after 3 monthly ranibizumab injections and as-needed reinjections for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Japanese patients. Retina 2013; 33: Hikichi T, Higuchi M, Matsushita T, Kosaka S, Matsushita R, Takami K et al. One-year results of three monthly ranibizumab injections and as-needed reinjections for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Japanese patients. Am J Ophthalmol 2012; 154(1): e1. 9 Yuzawa M, Mori R, Kawamura A. The origins of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2005; 89(5): Fung AE, Lalwani GA, Rosenfeld PJ, Dubovy SR, Michels S, Feuer WJ et al. An optical coherence tomography-guided, variable dosing regimen with intravitreal ranibizumab (Lucentis) for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol 2007; 143(4): Lalwani GA, Rosenfeld PJ, Fung AE, Dubovy SR, Michels S, Feuer W et al. A variable-dosing regimen with intravitreal ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: year 2 of the PrONTO Study. Am J Ophthalmol 2009; 148(1): e1. 12 Cho HJ, Kim JW, Lee DW, Cho SW, Kim CG. Intravitreal bevacizumab and ranibizumab injections for patients with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. (Lond) 2012; 26(3): Lai TY, Lee GK, Luk FO, Lam DS. Intravitreal ranibizumab with or without photodynamic therapy for the treatment of symptomatic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 2011; 31(8): Gomi F, Sawa M, Sakaguchi H, Tsujikawa M, Oshima Y, Kamei M et al. Efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2008; 92(1): Koh A, Lee WK, Chen LJ, Chen SJ, Hashad Y, Kim H et al. EVEREST study: efficacy and safety of verteporfin photodynamic therapy in combination with ranibizumab or alone versus ranibizumab monotherapy in patients with symptomatic macular polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 2012; 32(8): Wakabayashi T, Gomi F, Sawa M, Tsujikawa M, Nishida K. Intravitreal bevacizumab for exudative branching vascular networks in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2012; 96(3): Lai TY, Chan WM, Lam DS. Transient reduction in retinal function revealed by multifocal electroretinogram after photodynamic therapy. Am J Ophthalmol 2004; 137(5): Maruko I, Iida T, Sugano Y, Saito M, Sekiryu T. Subfoveal retinal and choroidal thickness after verteporfin photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2011; 151(4): e1. 19 Ho M, Liu DT, Chan VC, Lam DS. Choroidal thickness measurement in myopic eyes by enhanced depth optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2013; 120(9): Oishi A, Kojima H, Mandai M, Honda S, Matsuoka T, Oh H et al. Comparison of the effect of ranibizumab and verteporfin for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: 12-month laptop study results. Am J Ophthalmol 2013; 156: Wakabayashi T, Gomi F, Sawa M, Tsujikawa M, Tano Y. Marked vascular changes of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy after photodynamic therapy. Br J Ophthalmol 2008; 92(7): Saito M, Iida T, Kano M. Combined intravitreal ranibizumab and photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 2012; 32(7): Saito M, Iida T, Kano M, Itagaki K. Two-year results of combined intravitreal ranibizumab and photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2013; 251(9): Sato T, Kishi S, Matsumoto H, Mukai R. Combined photodynamic therapy with verteporfin and intravitreal bevacizumab for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2010; 149(6): e1. 25 Tomita K, Tsujikawa A, Yamashiro K, Ooto S, Tamura H, Otani A et al. Treatment of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy with photodynamic therapy combined with intravitreal injections of ranibizumab. Am J Ophthalmol 2012; 153(1): e1. 26 Hikichi T, Ohtsuka H, Higuchi M, Matsushita T, Ariga H, Kosaka S et al. Factors predictive of visual acuity outcomes 1 year after photodynamic therapy in Japanese patients with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 2011; 31(5): Koizumi H, Yamagishi T, Yamazaki T, Kinoshita S. Predictive factors of resolved retinal fluid after intravitreal ranibizumab for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 2011; 95(11): Saito M, Iida T, Nagayama D. Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for age-related macular degeneration or polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: comparison of the presence of serous retinal pigment epithelial detachment. Br J Ophthalmol 2008; 92(12): Tsujikawa A, Ojima Y, Yamashiro K, Nakata I, Ooto S, Tamura H et al. Association of lesion size and visual prognosis to polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2011; 151(6): e1. 30 Yamashiro K, Tomita K, Tsujikawa A, Nakata I, Akagi-Kurashige Y, Miyake M et al. Factors associated with the response of age-related macular degeneration to intravitreal ranibizumab treatment. Am J Ophthalmol 2012; 154(1):
8 1476 Outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy at 1 year 31 Kang HM, Koh HJ, Lee CS, Lee SC. Combined photodynamic therapy with intravitreal bevacizumab injections for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: long-term visual outcome. Am J Ophthalmol 2014; 157(3): e1. 32 Hikichi T, Higuchi M, Matsushita T, Kosaka S, Matsushita R, Takami K et al. Factors predictive of outcomes 1 year after 3 monthly ranibizumab injections and as-needed reinjections for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Japanese patients. Retina 2013; 33(9): Mori R, Yuzawa M, Lee Z, Haruyama M, Akaza E. Factors influencing visual outcome of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy 1 year after photodynamic therapy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2010; 248(9):
Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy with Feeder Vessels: Characteristics, Fellow Eye Findings, and Long-term Treatment Outcomes
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(3):230-239 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0035 Original Article Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy with Feeder Vessels: Characteristics, Fellow
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(3):230-239 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0035 Original Article Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy with Feeder Vessels: Characteristics, Fellow
Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital of Santiago de Compostela, Ramon Baltar S/N, Santiago de Compostela, Spain 2
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 897097, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2012/897097 Case Report Verteporfin Photodynamic Therapy Combined with Intravitreal Ranibizumab for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 897097, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2012/897097 Case Report Verteporfin Photodynamic Therapy Combined with Intravitreal Ranibizumab for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and photodynamic therapy with verteporfin
 Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2005) 243: 973 979 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-005-1139-4 Rufino M. Silva João Figueira M. Luz Cachulo Liliane Duarte José R. Faria de Abreu J. G. Cunha-Vaz
Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2005) 243: 973 979 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-005-1139-4 Rufino M. Silva João Figueira M. Luz Cachulo Liliane Duarte José R. Faria de Abreu J. G. Cunha-Vaz
Stabilization of visual acuity with photodynamic therapy in eyes with chorioretinal anastomoses
 Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2004) 242:368 376 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-003-0844-0 Rufino M. Silva José R. Faria de Abreu António Travassos José G. Cunha-Vaz Stabilization of visual
Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2004) 242:368 376 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-003-0844-0 Rufino M. Silva José R. Faria de Abreu António Travassos José G. Cunha-Vaz Stabilization of visual
MONTHLY ADMINISTERED INTRAVITREOUS PHARmacotherapy
 Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Masquerading as Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Refractory to Ranibizumab ALEXANDROS N. STANGOS, JAGDEEP SINGH GANDHI, JAYASHREE NAIR-SAHNI, HEINRICH HEIMANN,
Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Masquerading as Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Refractory to Ranibizumab ALEXANDROS N. STANGOS, JAGDEEP SINGH GANDHI, JAYASHREE NAIR-SAHNI, HEINRICH HEIMANN,
CENTRAL SEROUS CHORIORETINOPATHY (CSC) IS
 Association Between the Efficacy of Half-Dose Photodynamic Therapy With Indocyanine Green Angiography and Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in the Treatment of Central Serous Chorioretinopathy MASSIMO
Association Between the Efficacy of Half-Dose Photodynamic Therapy With Indocyanine Green Angiography and Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in the Treatment of Central Serous Chorioretinopathy MASSIMO
Photodynamic therapy versus anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: A meta-analysis
 Yong et al. BMC Ophthalmology DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0064-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Photodynamic therapy versus anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy:
Yong et al. BMC Ophthalmology DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0064-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Photodynamic therapy versus anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy:
Retinal pigment epithelial atrophy over polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy lesions during ranibizumab monotherapy
 Hikichi et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2016) 16:55 DOI 10.1186/s12886-016-0237-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Retinal pigment epithelial atrophy over polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy lesions during ranibizumab monotherapy
Hikichi et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2016) 16:55 DOI 10.1186/s12886-016-0237-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Retinal pigment epithelial atrophy over polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy lesions during ranibizumab monotherapy
연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과
 연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과 40 Table. Clinical characteristics and results of patients undergoing photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation Patients No. Age/ sex Eye
연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과 40 Table. Clinical characteristics and results of patients undergoing photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation Patients No. Age/ sex Eye
Clinical Trials Related to Age Related Macular Degeneration
 Clinical Trials Related to Age Related Macular Degeneration Kirti Singh MD, DNB, FRCS Kirti Singh MD, DNB, FRCS, Pooja Jain MBBS, Nitasha Ahir MBBS, Divya Jain MD, DNB Guru Nanak Eye Centre, Maulana Azad
Clinical Trials Related to Age Related Macular Degeneration Kirti Singh MD, DNB, FRCS Kirti Singh MD, DNB, FRCS, Pooja Jain MBBS, Nitasha Ahir MBBS, Divya Jain MD, DNB Guru Nanak Eye Centre, Maulana Azad
Department of Ophthalmology, Kim s Eye Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 2
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2015;29(5):315-324 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.29.5.315 Original Article Clinical Outcomes of Eyes with Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Age-related
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2015;29(5):315-324 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.29.5.315 Original Article Clinical Outcomes of Eyes with Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Age-related
NATURAL COURSE OF PATIENTS DISCONTINUING TREATMENT FOR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH VISUAL PROGNOSIS
 NATURAL COURSE OF PATIENTS DISCONTINUING TREATMENT FOR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH VISUAL PROGNOSIS JAE HUI KIM, MD,* YOUNG SUK CHANG, MD, JONG WOO KIM, MD* Purpose: To
NATURAL COURSE OF PATIENTS DISCONTINUING TREATMENT FOR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH VISUAL PROGNOSIS JAE HUI KIM, MD,* YOUNG SUK CHANG, MD, JONG WOO KIM, MD* Purpose: To
Clinical Characteristics of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Associated with Chronic Central Serous Chorioretionopathy
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(1):15-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.1.15 Original Article Clinical Characteristics of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Associated
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(1):15-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.1.15 Original Article Clinical Characteristics of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Associated
P. Stavrakas MD PhD. Consultant Ophthalmologist and vitreoretinal surgeon 2 nd Department of Ophthalmology University of Athens
 P. Stavrakas MD PhD Consultant Ophthalmologist and vitreoretinal surgeon 2 nd Department of Ophthalmology University of Athens Primary diagnose of exudative AMD Anti-VEGF monotherapy treatment Loss of
P. Stavrakas MD PhD Consultant Ophthalmologist and vitreoretinal surgeon 2 nd Department of Ophthalmology University of Athens Primary diagnose of exudative AMD Anti-VEGF monotherapy treatment Loss of
Principal Investigator: Mårten Brelen, Assistant Professor Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences (DOVS), CUHK
 RESEARCH PROTOCOL Title: Subthreshold micropulse yellow (577 nm) laser versus half-dose photodynamic therapy for central serous chorioretinopathy : a randomized controlled pilot study Principal Investigator:
RESEARCH PROTOCOL Title: Subthreshold micropulse yellow (577 nm) laser versus half-dose photodynamic therapy for central serous chorioretinopathy : a randomized controlled pilot study Principal Investigator:
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Tears (Rips) in the ERA of Anti Vegf - When and Why?
 Original Article Retinal Pigment Epithelial Tears (Rips) in the ERA of Anti Vegf - When and Why? Dr Sreelekha S. MS, DNB, DO, FRCS, Dr Manoj Soman DNB, FICO, FRCS, Dr. Unni Nair MS, FRCS, Dr. Ruminder
Original Article Retinal Pigment Epithelial Tears (Rips) in the ERA of Anti Vegf - When and Why? Dr Sreelekha S. MS, DNB, DO, FRCS, Dr Manoj Soman DNB, FICO, FRCS, Dr. Unni Nair MS, FRCS, Dr. Ruminder
Intravitreal Injection of Ranibizumab for Recovery of Macular Function in Eyes With Subfoveal Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
 Retina Intravitreal Injection of Ranibizumab for Recovery of Macular Function in Eyes With Subfoveal Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Ken Ogino, Akitaka Tsujikawa, Kenji Yamashiro, Sotaro Ooto, Akio Oishi,
Retina Intravitreal Injection of Ranibizumab for Recovery of Macular Function in Eyes With Subfoveal Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy Ken Ogino, Akitaka Tsujikawa, Kenji Yamashiro, Sotaro Ooto, Akio Oishi,
Impact of Polyp Regression on 2-year Outcomes of Intravitreal Aflibercept Injections: A Treat-and-Extend Regimen for Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
 Original Article http ://escholarship.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/amo/ Impact of Polyp Regression on 2-year Outcomes of Intravitreal Aflibercept Injections: A Treat-and-Extend Regimen for Polypoidal Choroidal
Original Article http ://escholarship.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/amo/ Impact of Polyp Regression on 2-year Outcomes of Intravitreal Aflibercept Injections: A Treat-and-Extend Regimen for Polypoidal Choroidal
SUMMARY. Heather Casparis, MD,* and Neil M. Bressler, MD MARINA AND ANCHOR
 The following are summaries of selected presentations and posters from the American Society of Retina Specialists and European VitreoRetinal Society Annual Meeting held September 9 13, 2006, in Cannes,
The following are summaries of selected presentations and posters from the American Society of Retina Specialists and European VitreoRetinal Society Annual Meeting held September 9 13, 2006, in Cannes,
Risk factors of a reduced response to ranibizumab treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration evaluation in a clinical setting
 Korb et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2013, 13:84 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Risk factors of a reduced response to ranibizumab treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration evaluation in a clinical
Korb et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2013, 13:84 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Risk factors of a reduced response to ranibizumab treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration evaluation in a clinical
Complete regression of branching vascular network in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy by ranibizumab and photodynamic therapy, two case reports
 Iesato et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:284 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0952-6 CASE REPORT Open Access Complete regression of branching vascular network in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy by
Iesato et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:284 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0952-6 CASE REPORT Open Access Complete regression of branching vascular network in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy by
Authors. Introduction. Introduction. Materials and Methods. Objective 10/27/2015
 Idiopathic Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (IPCV) in Thai Population Presenting with Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) A multicenter study Authors Yonrawee Piyacomn 1, Chavakij Bhoomibunchoo 1, Yosanan
Idiopathic Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (IPCV) in Thai Population Presenting with Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) A multicenter study Authors Yonrawee Piyacomn 1, Chavakij Bhoomibunchoo 1, Yosanan
Despite our growing knowledge of the
 OVERVIEW OF AVAILABLE TREATMENTS FOR NEOVASCULAR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION * Carl D. Regillo, MD ABSTRACT Although potential treatments for neovascular age-related macular degeneration represent
OVERVIEW OF AVAILABLE TREATMENTS FOR NEOVASCULAR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION * Carl D. Regillo, MD ABSTRACT Although potential treatments for neovascular age-related macular degeneration represent
IQ 532 Micropulse Green Laser treatment for Refractory Chronic Central Serous Retinopathy
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Report IQ 532 Micropulse Green Laser treatment for Refractory Chronic Central Serous Retinopathy Fawwaz Al Mamoori* Medical Retina Department, Eye Specialty Hospital,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Report IQ 532 Micropulse Green Laser treatment for Refractory Chronic Central Serous Retinopathy Fawwaz Al Mamoori* Medical Retina Department, Eye Specialty Hospital,
Photodynamic Therapy for Choroidal Neovascularization
 Photodynamic Therapy for Choroidal Neovascularization Policy Number: 9.03.08 Last Review: 10/2014 Origination: 10/2000 Next Review: 10/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will
Photodynamic Therapy for Choroidal Neovascularization Policy Number: 9.03.08 Last Review: 10/2014 Origination: 10/2000 Next Review: 10/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Last Review: September 2016 Next Review: September 2017 Related Policies 9.03.20 Intraocular Radiation Therapy for Age-Related Macular Degeneration Photodynamic Therapy for Choroidal
FEP Medical Policy Manual Last Review: September 2016 Next Review: September 2017 Related Policies 9.03.20 Intraocular Radiation Therapy for Age-Related Macular Degeneration Photodynamic Therapy for Choroidal
R&M Solutions
 Mohamed Hosny El-Bradey, MD., Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, Tanta University. Wael El Haig, MD., Professor of Ophthalmology. Zagazeeg University. 1 Myopic CNV is considered the most common vision
Mohamed Hosny El-Bradey, MD., Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, Tanta University. Wael El Haig, MD., Professor of Ophthalmology. Zagazeeg University. 1 Myopic CNV is considered the most common vision
Department of Ophthalmology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea
 Department of Ophthalmology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea Purpose: To investigate the factors that affect final vision following photodynamic therapy
Department of Ophthalmology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea Purpose: To investigate the factors that affect final vision following photodynamic therapy
VERTEPORFIN IN PHOTODYNAMIC THERAPY STUDY GROUP
 Verteporfin Therapy of Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization in Age-related Macular Degeneration: Two-year Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial Including Lesions With Occult With No Classic Choroidal
Verteporfin Therapy of Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization in Age-related Macular Degeneration: Two-year Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial Including Lesions With Occult With No Classic Choroidal
Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic Syndrome
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
Bilateral Elevated Macular Lesions
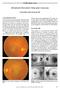 Challenging Case Bilateral Elevated Macular Lesions Section Editor: Alireza Ramezani, MD Case presentation A 65-year-old woman presented with decreased vision in both eyes of 2 months duration. She reported
Challenging Case Bilateral Elevated Macular Lesions Section Editor: Alireza Ramezani, MD Case presentation A 65-year-old woman presented with decreased vision in both eyes of 2 months duration. She reported
CENTENE PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS NEW DRUG REVIEW 2Q17 April May
 BRAND NAME Lucentis GENERIC NAME ranibizumab MANUFACTURER Genentech, Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL June 30, 2006 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE July 13, 2006 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug Review Full review of
BRAND NAME Lucentis GENERIC NAME ranibizumab MANUFACTURER Genentech, Inc. DATE OF APPROVAL June 30, 2006 PRODUCT LAUNCH DATE July 13, 2006 REVIEW TYPE Review type 1 (RT1): New Drug Review Full review of
Efficacy of Anti-VEGF Agents in the Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 Efficacy of Anti-VEGF Agents in the Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Marilita M. Moschos Abstract- Purpose: To evaluate by OCT and mf-erg the macular function in eyes with CNV due to ARMD
Efficacy of Anti-VEGF Agents in the Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Marilita M. Moschos Abstract- Purpose: To evaluate by OCT and mf-erg the macular function in eyes with CNV due to ARMD
Description. Section: Other Effective Date: July 15, Subsection: Vision Original Policy Date: December 7, 2011 Subject: Page: 1 of 23
 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Page: 1 of 23 Description Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a treatment modality designed to selectively occlude ocular choroidal neovascular tissue. The therapy is a 2-step
Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Page: 1 of 23 Description Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a treatment modality designed to selectively occlude ocular choroidal neovascular tissue. The therapy is a 2-step
Oishi A, Miyamoto K, Yoshimura N. Etiology of carotid cavernous fistula in Japanese. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2009;53:40-43.
 Kimura T, Takagi H, Miyamoto K, Kita M, Watanabe D, Yoshimura N. Macular hole with epiretinal membrane after triamcinolone-assisted vitrectomy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Retinal Cases Brief
Kimura T, Takagi H, Miyamoto K, Kita M, Watanabe D, Yoshimura N. Macular hole with epiretinal membrane after triamcinolone-assisted vitrectomy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Retinal Cases Brief
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Koh A, Lai TYY, Takahashi K, et al; the EVEREST II Study Group. Efficacy and safety of ranibizumab with or without verteporfin photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal
Supplementary Online Content Koh A, Lai TYY, Takahashi K, et al; the EVEREST II Study Group. Efficacy and safety of ranibizumab with or without verteporfin photodynamic therapy for polypoidal choroidal
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) for Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR)/ Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV)
 Photodynamic therapy (PDT) for Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR)/ Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV) About photodynamic therapy for Retinal Conditions The macula is the central part of the retina at
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) for Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR)/ Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV) About photodynamic therapy for Retinal Conditions The macula is the central part of the retina at
A Treat and Extend Regimen Using Ranibizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 A Treat and Extend Regimen Using Ranibizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Clinical and Economic Impact Omesh P. Gupta, MD, MBA, Gary Shienbaum, MD, Avni H. Patel, MD, Christopher Fecarotta,
A Treat and Extend Regimen Using Ranibizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Clinical and Economic Impact Omesh P. Gupta, MD, MBA, Gary Shienbaum, MD, Avni H. Patel, MD, Christopher Fecarotta,
Instudies of vascular endothelial growth factor
 MONITORING THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY IN THE ANTI-VEGF ERA* SriniVas R. Sadda, MD ABSTRACT One of the most important questions with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors for age-related macular
MONITORING THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY IN THE ANTI-VEGF ERA* SriniVas R. Sadda, MD ABSTRACT One of the most important questions with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors for age-related macular
Wataru Matsumiya, Shigeru Honda *, Sentaro Kusuhara, Yasutomo Tsukahara and Akira Negi
 Matsumiya et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2013, 13:10 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effectiveness of intravitreal ranibizumab in exudative age-related macular degeneration (AMD): comparison between typical neovascular
Matsumiya et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2013, 13:10 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effectiveness of intravitreal ranibizumab in exudative age-related macular degeneration (AMD): comparison between typical neovascular
Title Exudative Age-Related Macular Degen. Tsujikawa, Akitaka; Yoshimura, Naga.
 Title Prognostic Factors of Vitreous Hemo Exudative Age-Related Macular Degen Hasegawa, Tomoko; Otani, Atsushi; S Author(s) Norimoto; Ooto, Sotaro; Tamura, Hir Tsujikawa, Akitaka; Yoshimura, Naga Citation
Title Prognostic Factors of Vitreous Hemo Exudative Age-Related Macular Degen Hasegawa, Tomoko; Otani, Atsushi; S Author(s) Norimoto; Ooto, Sotaro; Tamura, Hir Tsujikawa, Akitaka; Yoshimura, Naga Citation
OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care
 OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care An Image Interpretation Primer Julie Rodman, OD, MS, FAAO and Nadia Waheed, MD, MPH Table of Contents Diabetic Retinopathy 3-6 Choroidal Neovascularization 7-9 Central
OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care An Image Interpretation Primer Julie Rodman, OD, MS, FAAO and Nadia Waheed, MD, MPH Table of Contents Diabetic Retinopathy 3-6 Choroidal Neovascularization 7-9 Central
POLYPOIDAL CHOROIDAL VASCULOPATHY, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 GENERAL REVIEW POLYPOIDAL CHOROIDAL VASCULOPATHY, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT COPPENS G., SPIELBERG L., LEYS A. ABSTRACT Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV) was first identified in 1985. Initially considered
GENERAL REVIEW POLYPOIDAL CHOROIDAL VASCULOPATHY, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT COPPENS G., SPIELBERG L., LEYS A. ABSTRACT Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV) was first identified in 1985. Initially considered
DOME SHAPED MACULOPATHY. Ιωάννης Ν. Βαγγελόπουλος Χειρ. Οφθαλμίατρος - Βόλος
 DOME SHAPED MACULOPATHY Ιωάννης Ν. Βαγγελόπουλος Χειρ. Οφθαλμίατρος - Βόλος DOME SHAPED MACULOPATHY-DEFINITIONS The entity Dome Shaped Macula ( DSM ) was first described by Gaucher and associates in 2008
DOME SHAPED MACULOPATHY Ιωάννης Ν. Βαγγελόπουλος Χειρ. Οφθαλμίατρος - Βόλος DOME SHAPED MACULOPATHY-DEFINITIONS The entity Dome Shaped Macula ( DSM ) was first described by Gaucher and associates in 2008
Macular Morphology and Visual Acuity in the Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials
 Macular Morphology and Visual Acuity in the Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials Glenn J. Jaffe, MD, 1 Daniel F. Martin, MD, 2 Cynthia A. Toth, MD, 1 Ebenezer Daniel, MPH, PhD,
Macular Morphology and Visual Acuity in the Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials Glenn J. Jaffe, MD, 1 Daniel F. Martin, MD, 2 Cynthia A. Toth, MD, 1 Ebenezer Daniel, MPH, PhD,
Current indications for photodynamic therapy in medical retina practice
 réalités Current indications for photodynamic therapy in medical retina practice No. 254 September 2018 OPHTALMOLOGIQUES SUMMARY: In medical retina practice, the use of photodynamic therapy (PDT) revolutionised
réalités Current indications for photodynamic therapy in medical retina practice No. 254 September 2018 OPHTALMOLOGIQUES SUMMARY: In medical retina practice, the use of photodynamic therapy (PDT) revolutionised
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Multivariate Analysis of Intravitreal Injection of Anti-VEGF Bevacizumab in the Treatment
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Multivariate Analysis of Intravitreal Injection of Anti-VEGF Bevacizumab in the Treatment
Although photocoagulation and photodynamic PROCEEDINGS PEGAPTANIB SODIUM FOR THE TREATMENT OF AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION *
 PEGAPTANIB SODIUM FOR THE TREATMENT OF AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION Evangelos S. Gragoudas, MD ABSTRACT In December 24, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved pegaptanib sodium. Pegaptanib
PEGAPTANIB SODIUM FOR THE TREATMENT OF AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION Evangelos S. Gragoudas, MD ABSTRACT In December 24, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved pegaptanib sodium. Pegaptanib
London Medicines Evaluation Network Review
 London Medicines Evaluation Network Review Evidence for initiating intravitreal bevacizumab for the management of wet age-related macular degeneration (wet-amd) in eyes with vision better than 6/12 November
London Medicines Evaluation Network Review Evidence for initiating intravitreal bevacizumab for the management of wet age-related macular degeneration (wet-amd) in eyes with vision better than 6/12 November
Original Article Intravitreal injections of ranibizumab in treatment of idiopathic choroidal neovascularization
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3780-3784 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017597 Original Article Intravitreal injections of ranibizumab in treatment of idiopathic choroidal neovascularization Donghua
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3780-3784 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017597 Original Article Intravitreal injections of ranibizumab in treatment of idiopathic choroidal neovascularization Donghua
Indocyanine Green Angiography Findings in Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. III (May. 2016), PP 11-21 www.iosrjournals.org Indocyanine Green Angiography Findings
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. III (May. 2016), PP 11-21 www.iosrjournals.org Indocyanine Green Angiography Findings
Ophthalmology Macular Pathways
 Ophthalmology Macular Pathways Age related Macular Degeneration Diabetic Macular Oedema Macular Oedema secondary to Central Retinal Macular Oedema secondary to Branch Retinal CNV associated with pathological
Ophthalmology Macular Pathways Age related Macular Degeneration Diabetic Macular Oedema Macular Oedema secondary to Central Retinal Macular Oedema secondary to Branch Retinal CNV associated with pathological
Retinal pigment epithelial tears after intravitreal bevacizumab injection for exudative age-related macular degeneration.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Wills Eye Institute Papers Wills Eye Institute 4-1-2008 Retinal pigment epithelial tears after intravitreal bevacizumab injection for exudative age-related
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Wills Eye Institute Papers Wills Eye Institute 4-1-2008 Retinal pigment epithelial tears after intravitreal bevacizumab injection for exudative age-related
Subgroup Analysis of the MARINA Study of Ranibizumab in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 Subgroup Analysis of the MARINA Study of in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration David S. Boyer, MD, 1 Andrew N. Antoszyk, MD, 2 Carl C. Awh, MD, 3 Robert B. Bhisitkul, MD, PhD, 4 Howard Shapiro,
Subgroup Analysis of the MARINA Study of in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration David S. Boyer, MD, 1 Andrew N. Antoszyk, MD, 2 Carl C. Awh, MD, 3 Robert B. Bhisitkul, MD, PhD, 4 Howard Shapiro,
Seokhyun Bae, Kiwon Jin, Hakyoung Kim and So Hyun Bae *
 Bae et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:180 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0170-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical parameters related to metamorphopsia outcome in patients with resolved central serous chorioretinopathy
Bae et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:180 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0170-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical parameters related to metamorphopsia outcome in patients with resolved central serous chorioretinopathy
Michael P. Blair, MD Retina Consultants, Ltd Libertyville/Des Plaines, Illinois Clinical Associate University of Chicago 17 October 2015
 Michael P. Blair, MD Retina Consultants, Ltd Libertyville/Des Plaines, Illinois Clinical Associate University of Chicago 17 October 2015 So What Parts of the Eye Retina are Affected by VHL Neural tissue
Michael P. Blair, MD Retina Consultants, Ltd Libertyville/Des Plaines, Illinois Clinical Associate University of Chicago 17 October 2015 So What Parts of the Eye Retina are Affected by VHL Neural tissue
Use of Aflibercept in cases of recurrent or refractory neovascular AMD previously treated with other antiangiogenic drug: anatomo-functional outcomes
 Use of Aflibercept in cases of recurrent or refractory neovascular AMD previously treated with other antiangiogenic drug: anatomo-functional outcomes Daniel E. Charles, MD, Martin Charles, MD, Gisela Jelusich,
Use of Aflibercept in cases of recurrent or refractory neovascular AMD previously treated with other antiangiogenic drug: anatomo-functional outcomes Daniel E. Charles, MD, Martin Charles, MD, Gisela Jelusich,
Coding Implications Revision Log. See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: Verteporfin (Visudyne) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.187 Effective Date: 03.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 Line of Business: Commercial, Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log See Important
Clinical Policy: Verteporfin (Visudyne) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.187 Effective Date: 03.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 Line of Business: Commercial, Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log See Important
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for agerelated
 Page 1 of 5 Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for agerelated eye conditions Introduction This leaflet gives you information about Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for the age--related eye conditions macular degeneration
Page 1 of 5 Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for agerelated eye conditions Introduction This leaflet gives you information about Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for the age--related eye conditions macular degeneration
Long-term Management of AMD. Motasem Al-latayfeh, MD Assistant Prof. Ophthalmology Hashemite University Jordan
 Long-term Management of AMD Motasem Al-latayfeh, MD Assistant Prof. Ophthalmology Hashemite University Jordan DEFINITION 1 Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a disorder of the macula characterized
Long-term Management of AMD Motasem Al-latayfeh, MD Assistant Prof. Ophthalmology Hashemite University Jordan DEFINITION 1 Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a disorder of the macula characterized
RETINAL PIGMENT EPITHELIUM UNDULATIONS IN ACUTE STAGE OF VOGT-KOYANAGI-HARADA DISEASE
 RETINAL PIGMENT EPITHELIUM UNDULATIONS IN ACUTE STAGE OF VOGT-KOYANAGI-HARADA DISEASE Biomarker for Functional Outcomes After High-Dose Steroid Therapy KOUHEI HASHIZUME, MD,* YUTAKA IMAMURA, MD, TAKAMITSU
RETINAL PIGMENT EPITHELIUM UNDULATIONS IN ACUTE STAGE OF VOGT-KOYANAGI-HARADA DISEASE Biomarker for Functional Outcomes After High-Dose Steroid Therapy KOUHEI HASHIZUME, MD,* YUTAKA IMAMURA, MD, TAKAMITSU
Characteristics and racial variations of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in tertiary centers in the United States and United Kingdom
 DOI 10.1186/s40942-017-0060-4 International Journal of Retina and Vitreous ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Characteristics and racial variations of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in tertiary centers in
DOI 10.1186/s40942-017-0060-4 International Journal of Retina and Vitreous ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Characteristics and racial variations of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in tertiary centers in
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PHOTODYNAMIC THERAPY FOR EFFECTIVE DATE: 07/20/00 SUBFOVEAL CHOROIDAL NEOVASCULARIZATION
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PHOTODYNAMIC THERAPY FOR PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PHOTODYNAMIC THERAPY FOR PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Clinical Study Fixed Monthly versus Less Frequent Ranibizumab Dosing and Predictors of Visual Response in Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 Ophthalmology Volume 12, Article ID 69641, 8 pages doi:1.1155/12/69641 Clinical Study Fixed Monthly versus Less Frequent Ranibizumab Dosing and Predictors of Visual Response in Exudative Age-Related Macular
Ophthalmology Volume 12, Article ID 69641, 8 pages doi:1.1155/12/69641 Clinical Study Fixed Monthly versus Less Frequent Ranibizumab Dosing and Predictors of Visual Response in Exudative Age-Related Macular
Systemic bevacizumab (Avastin) therapy for exudative neovascular age-related macular degeneration. The BEAT-AMD-Study
 1 Department of Ophthalmology, The Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Retinology and Biomicroscopic Lasersurgery, Rudolf Foundation Clinic, Vienna, Austria; 2 Department of Internal Medicine, Oncology, Rudolf
1 Department of Ophthalmology, The Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Retinology and Biomicroscopic Lasersurgery, Rudolf Foundation Clinic, Vienna, Austria; 2 Department of Internal Medicine, Oncology, Rudolf
Fluorescein Angiography
 Last revision: October 2011 by Luis Arias Fluorescein Angiography Authors: Luis Arias, MD Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge - University of Barcelona. Spain Jordi Monés, MD Institut de la Màcula i de
Last revision: October 2011 by Luis Arias Fluorescein Angiography Authors: Luis Arias, MD Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge - University of Barcelona. Spain Jordi Monés, MD Institut de la Màcula i de
Management of Neovascular AMD
 Kapusta AMD Part 1 Management of Neovascular AMD Dr. Michael A. Kapusta, MD, FRCSC Ophthalmologist in Chief Jewish General Hospital Vitreoretinal Surgeon 1 FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES Consulting honoraria Bayer,
Kapusta AMD Part 1 Management of Neovascular AMD Dr. Michael A. Kapusta, MD, FRCSC Ophthalmologist in Chief Jewish General Hospital Vitreoretinal Surgeon 1 FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES Consulting honoraria Bayer,
HIGH DOSE TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR (TPA) (100 MCG/0.1 ML) AND C3F8 GAS IN PNEUMATIC DISPLACEMENT OF SUBMACULAR
 HIGH DOSE TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR (TPA) (100 MCG/0.1 ML) AND C3F8 GAS IN PNEUMATIC DISPLACEMENT OF SUBMACULAR HAEMORRHAGE. Stephen A.M. De Souza MD, FRCSC Matthew J Welch MD, Raza M Shah MD, Alan
HIGH DOSE TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR (TPA) (100 MCG/0.1 ML) AND C3F8 GAS IN PNEUMATIC DISPLACEMENT OF SUBMACULAR HAEMORRHAGE. Stephen A.M. De Souza MD, FRCSC Matthew J Welch MD, Raza M Shah MD, Alan
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema
 Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Mitsuko Yuzawa,* Takako Isomae,* Ryuzaburo Mori,* Hiroyuki Shimada* and Izumi Utsunomiya
 Surgical Excision Versus Laser Photocoagulation for Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascular Membrane with Age-related Macular Degeneration: Comparison of Visual Outcomes Mitsuko Yuzawa,* Takako Isomae,* Ryuzaburo
Surgical Excision Versus Laser Photocoagulation for Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascular Membrane with Age-related Macular Degeneration: Comparison of Visual Outcomes Mitsuko Yuzawa,* Takako Isomae,* Ryuzaburo
NEOVASCULAR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERation
 Randomized, Double-Masked, -Controlled Trial of Ranibizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: PIER Study Year 2 PREMA ABRAHAM, HUIBIN YUE, AND LAURA WILSON PURPOSE: To evaluate efficacy
Randomized, Double-Masked, -Controlled Trial of Ranibizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: PIER Study Year 2 PREMA ABRAHAM, HUIBIN YUE, AND LAURA WILSON PURPOSE: To evaluate efficacy
Choroidal Mapping; a Novel Approach for Evaluating Choroidal Thickness and Volume
 Imaging Technique Choroidal Mapping; a Novel Approach for Evaluating Choroidal Thickness and Volume Jila Noori 1, MD; Mohammad Riazi Esfahani 1,2, MD Fedra Hajizadeh 2, MD; Mohammad-Mehdi Zaferani 1, MD
Imaging Technique Choroidal Mapping; a Novel Approach for Evaluating Choroidal Thickness and Volume Jila Noori 1, MD; Mohammad Riazi Esfahani 1,2, MD Fedra Hajizadeh 2, MD; Mohammad-Mehdi Zaferani 1, MD
Efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin TM ) for shortterm treatment of diabetic macular edema
 111 ORIGINAL Efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin TM ) for shortterm treatment of diabetic macular edema Toshihiko Nagasawa, Takeshi Naito, Shingo Matsushita, Hiroyuki Sato, Takashi Katome, and
111 ORIGINAL Efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin TM ) for shortterm treatment of diabetic macular edema Toshihiko Nagasawa, Takeshi Naito, Shingo Matsushita, Hiroyuki Sato, Takashi Katome, and
Management of Acute Submacular Hemorrhage with Intravitreal Injection of Tenecteplase, Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Gas
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2016;30(3):192-197 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.30.3.192 Original Article Management of Acute Submacular Hemorrhage with Intravitreal Injection
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2016;30(3):192-197 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.30.3.192 Original Article Management of Acute Submacular Hemorrhage with Intravitreal Injection
Original Article Ranibizumab as needed therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration combined with serous pigment epithelial detachment
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):13650-13656 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0026582 Original Article Ranibizumab as needed therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration combined with serous pigment
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):13650-13656 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0026582 Original Article Ranibizumab as needed therapy for wet age-related macular degeneration combined with serous pigment
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
ZEISS AngioPlex OCT Angiography. Clinical Case Reports
 Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Measurement of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Eyes Using 3D OCT-1000 Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
 pissn: 111-8942 eissn: 292-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 212;26(4):255-259 http://dx.doi.org/1.3341/kjo.212.26.4.255 Original Article Measurement of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Eyes Using 3D OCT-1 Spectral
pissn: 111-8942 eissn: 292-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 212;26(4):255-259 http://dx.doi.org/1.3341/kjo.212.26.4.255 Original Article Measurement of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Eyes Using 3D OCT-1 Spectral
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Verteporfin Therapy for Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization in Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Verteporfin Therapy for Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization in Age-Related Macular Degeneration Three-Year Results of an Open-Label Extension of 2 Randomized Clinical Trials TAP Report
CLINICAL SCIENCES Verteporfin Therapy for Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization in Age-Related Macular Degeneration Three-Year Results of an Open-Label Extension of 2 Randomized Clinical Trials TAP Report
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2016 January 14.
 High-Speed Ultrahigh-Resolution OCT of Bruch s Membrane in Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis Type 2 Mehreen Adhi, MD, Sarah P. Read, MD, PhD, Jonathan J. Liu, PhD, James G. Fujimoto, PhD, and Jay
High-Speed Ultrahigh-Resolution OCT of Bruch s Membrane in Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis Type 2 Mehreen Adhi, MD, Sarah P. Read, MD, PhD, Jonathan J. Liu, PhD, James G. Fujimoto, PhD, and Jay
Vitreous haemorrhage in massive hemorrhagic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: clinical characteristics and surgical outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40942-015-0025-4 International Journal of Retina and Vitreous ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Vitreous haemorrhage in massive hemorrhagic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: clinical characteristics
DOI 10.1186/s40942-015-0025-4 International Journal of Retina and Vitreous ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Vitreous haemorrhage in massive hemorrhagic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy: clinical characteristics
Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) is a variation of agerelated
 Multidisciplinary Ophthalmic Imaging Noninvasive Vascular Imaging of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy by Doppler Optical Coherence Tomography Masahiro Miura, 1,2 Daisuke Muramatsu, 1,2 Young-Joo Hong,
Multidisciplinary Ophthalmic Imaging Noninvasive Vascular Imaging of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy by Doppler Optical Coherence Tomography Masahiro Miura, 1,2 Daisuke Muramatsu, 1,2 Young-Joo Hong,
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Myopia is a major cause of visual impairment in many
 Retina Association between Choroidal Morphology and Anti- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment Outcome in Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization Seong Joon Ahn, 1 Se Joon Woo, 1 Ko Eun Kim, 2 and
Retina Association between Choroidal Morphology and Anti- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment Outcome in Myopic Choroidal Neovascularization Seong Joon Ahn, 1 Se Joon Woo, 1 Ko Eun Kim, 2 and
Intravitreal ranibizumab in the management of acute central serous Chorioretinopathy
 Open Access International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Research Article ISSN 2577-140X Intravitreal ranibizumab in the management of acute central serous Chorioretinopathy Ibrahim
Open Access International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Research Article ISSN 2577-140X Intravitreal ranibizumab in the management of acute central serous Chorioretinopathy Ibrahim
Five-year Outcomes of Ranibizumab in Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration: Real Life Clinical Experience
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(5):424-430 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0125 Original Article Five-year Outcomes of Ranibizumab in Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration:
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(5):424-430 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0125 Original Article Five-year Outcomes of Ranibizumab in Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration:
Earlier therapeutic effects associated with high dose (2.0 mg) Ranibizumab for treatment of vascularized pigment epithelial detachments in agerelated
 (2015) 29, 80 87 & 2015 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-222X/15 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY 1 Southern California Desert Retina Consultants, Palm Desert, CA, USA 2 Loma Linda
(2015) 29, 80 87 & 2015 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-222X/15 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY 1 Southern California Desert Retina Consultants, Palm Desert, CA, USA 2 Loma Linda
Evaluation of efficacy of eplerenone in the management of chronic central serous choroidoretinopathy
 Original article: Evaluation of efficacy of eplerenone in the management of chronic central serous choroidoretinopathy Dr. Sushant Madaan* Department of Ophthalmology, NIMS Medical College and Hopsital,Jaipur,
Original article: Evaluation of efficacy of eplerenone in the management of chronic central serous choroidoretinopathy Dr. Sushant Madaan* Department of Ophthalmology, NIMS Medical College and Hopsital,Jaipur,
Clinical Study Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Injection on Chinese Patients with Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration: 5-Year Follow-Up Results
 Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 6538192, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6538192 Clinical Study Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Injection on Chinese Patients with Wet Age-Related Macular
Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 6538192, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6538192 Clinical Study Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Injection on Chinese Patients with Wet Age-Related Macular
Photodynamic Therapy for Treatment of Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization in Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 Clinical Medicine Journal Vol. 4, No. 4, 2018, pp. 60-66 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/cmj ISSN: 2381-7631 (Print); ISSN: 2381-764X (Online) Photodynamic Therapy for Treatment of Subfoveal Choroidal
Clinical Medicine Journal Vol. 4, No. 4, 2018, pp. 60-66 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/cmj ISSN: 2381-7631 (Print); ISSN: 2381-764X (Online) Photodynamic Therapy for Treatment of Subfoveal Choroidal
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP
 Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Published on Points de Vue International Review of Ophthalmic Optics (http://www.pointsdevue.com)
 Published on Points de Vue International Review of Ophthalmic Optics (http://www.pointsdevue.com) Home > OCT and retinal pathologies OCT and retinal pathologies Sylvain AURIOL, Véronique PAGOT-MATHIS e-mail
Published on Points de Vue International Review of Ophthalmic Optics (http://www.pointsdevue.com) Home > OCT and retinal pathologies OCT and retinal pathologies Sylvain AURIOL, Véronique PAGOT-MATHIS e-mail
EPIRETINAL MEMBRANES IN NEOVASCULAR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION. Effect on Outcomes of Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy
 EPIRETINAL MEMBRANES IN NEOVASCULAR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION Effect on Outcomes of Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy EMINE ESRA KARACA, MD,* BURÇIN KEPEZ YILDIZ, MD, MEHMET ÖZGÜR
EPIRETINAL MEMBRANES IN NEOVASCULAR AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION Effect on Outcomes of Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy EMINE ESRA KARACA, MD,* BURÇIN KEPEZ YILDIZ, MD, MEHMET ÖZGÜR
Clinical and optic coherence tomography findings of focal choroidal excavation in Chinese patients
 Guo et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:63 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical and optic coherence tomography findings of focal choroidal excavation in Chinese patients Jie Guo 1, Lu Zhong 2, Chunhui Jiang
Guo et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:63 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical and optic coherence tomography findings of focal choroidal excavation in Chinese patients Jie Guo 1, Lu Zhong 2, Chunhui Jiang
These issues are covered in more detail below.
 26.3.07 Comments from Novartis on the Assessment Report for the Health Technology Appraisal of Pegaptinib and Ranibizumab for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration In general we feel that the
26.3.07 Comments from Novartis on the Assessment Report for the Health Technology Appraisal of Pegaptinib and Ranibizumab for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration In general we feel that the
P olypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV), first described
 602 EXTENDED REPORT The origins of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy M Yuzawa, R Mori, A Kawamura... Br J Ophthalmol 2005;89:602 607. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2004.049296 See end of article for authors affiliations...
602 EXTENDED REPORT The origins of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy M Yuzawa, R Mori, A Kawamura... Br J Ophthalmol 2005;89:602 607. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2004.049296 See end of article for authors affiliations...
Quantitative Reduction in Central Foveal Thickness After First Anti-VEGF Injection as a Predictor of Final Outcome in BRVO Patients
 Original clinical study Quantitative Reduction in Central Foveal Thickness After First Anti-VEGF Injection as a Predictor of Final Outcome in BRVO Patients Rupak Roy, MS, Kumar Saurabh, MS, Avirupa Ghose,
Original clinical study Quantitative Reduction in Central Foveal Thickness After First Anti-VEGF Injection as a Predictor of Final Outcome in BRVO Patients Rupak Roy, MS, Kumar Saurabh, MS, Avirupa Ghose,
for anti-vegf therapy
 Review Article Singapore Med J 2011, 52(4) 232 Eye and Retina Surgeons, Camden Medical Centre, 1 Orchard Boulevard, Singapore 248649 Koh A, MBBS, MMed, FAMS Ong SG, FRCSE, FRCOphth, FAMS Ophthalmic Surgeon,
Review Article Singapore Med J 2011, 52(4) 232 Eye and Retina Surgeons, Camden Medical Centre, 1 Orchard Boulevard, Singapore 248649 Koh A, MBBS, MMed, FAMS Ong SG, FRCSE, FRCOphth, FAMS Ophthalmic Surgeon,
Optical Coherence Tomography Monitoring Strategies for A-VEGF Treated Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An Evidence-Based Analysis
 Optical Coherence Tomography Monitoring Strategies for A-VEGF Treated Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An Evidence-Based Analysis G Pron August 2014 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series; Vol. 14:
Optical Coherence Tomography Monitoring Strategies for A-VEGF Treated Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An Evidence-Based Analysis G Pron August 2014 Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series; Vol. 14:
Yoshiro Minami 1*, Taiji Nagaoka 2, Akihiro Ishibazawa 1,2 and Akitoshi Yoshida 2
 Minami et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:90 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0485-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Correlation between short- and long-term effects of intravitreal ranibizumab therapy on macular edema
Minami et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:90 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0485-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Correlation between short- and long-term effects of intravitreal ranibizumab therapy on macular edema
