Medical Education. Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring Protocol. Innovating for life.
|
|
|
- Loraine Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring Protocol A Guide to Continuous Glucose Monitoring Integrated with Insulin Pump Therapy Includes Alert and Trend Management as well as Threshold Medical Education Innovating for life.
2
3 Table of Contents... Overview and Definitions. Fundamental Concepts Candidate Selection CGM Initial Alert Settings and Adjustments. 6 Low Alarm and Alert Settings. 7 High Alert Settings. 8 Threshold Feature. 9 What to Expect with Threshold 0 Identifying Threshold on the CareLink Daily Detail Report. Graphs and Displays. Using On-Screen Data to Make Therapy Adjustments. Using CareLink Pro Software to Make Therapy Adjustments. CGM Initiation Settings Form. References and Suggested Reading. Table of Contents
4 Bruce W. Bode, MD, FACE An internationally known speaker and author on insulin pump therapy and continuous glucose monitoring, Dr. Bode, a graduate of Emory University School of Medicine, is in private practice with Atlanta Diabetes Associates and is an Associate Professor of Medicine at Emory University. He is active in both Georgia Diabetes Camps and the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation. Dr. Bode is also the editor of the American Diabetes Association s Medical Management of Type Diabetes. Francine R. Kaufman, MD Francine Ratner Kaufman, MD is Chief Medical icer and VP of Global Clinical, Medical and Health affairs at Medtronic Diabetes and a Distinguished Professor Emerita of Pediatrics and Communications at the Keck School of Medicine and the Annenberg School of Communications of the University of Southern California. Dr. Kaufman was president of the American Diabetes Association (00-0), and serves on the Advisory Council of the Diabetes Branch of the National Institutes of Health. While every reasonable precaution has been taken in the preparation of this guide, the authors, sponsor and publisher assume no responsibility for errors or omissions, nor for the uses made of the materials contained herein and the decisions based on such use. This document does not contain all of the information necessary for the proper care and treatment of patients with diabetes. As such, no individual may rely on the information presented herein in forming a comprehensive treatment program or in treating any patient with diabetes. No warranties are made, expressed or implied, with regard to the contents of this work or to its applicability to specific patients or circumstances. Neither the author, sponsor, nor the publisher shall be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use the contents of this guide. Authors
5 Overview This guide is for healthcare providers and discusses the personal continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) initiation and adjustment process for patients who are also using insulin pump therapy. In the STAR protocol, patients were started on pump therapy and then began CGM therapy within 7 days using a combination of face-to-face clinic visits, follow-up telephone calls and self-study on-line modules. While timelines and visit schedules may be individualized, the sequential clinical strategy of initiation and fine-tuning glycemic control with Personal CGM is explained. Definitions Professional CGM devices are owned by the healthcare provider, clinic, or hospital. Patients typically wear the device for several days, keeping a record of food and activity, and then return it to the office for download and interpretation. During use, the data can be blinded to the patient, allowing for unbiased assessment of glucose control. Professional CGM in the masked version does not have alerts to indicate hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, and is recommended for use on an episodic basis. Professional CGM can also be used in real-time on an episodic basis described below. Personal CGM, sometimes referred to as real-time CGM, is owned by the patient. It provides glucose readings up to every five minutes and glucose alerts. CGM systems can be downloaded by the patient and the physician for interpretation. Personal CGM may be a stand-alone device, with the sole function of monitoring glucose, or a device that is integrated into an insulin pump system. * Threshold is available in the MiniMed 0G with Enlite. See the MiniMed 0G System User Guide for complete information and instructions for use. Overview
6 Fundamental Concepts During the past decade, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has evolved from being used as a research tool, to being used daily in clinical practice. Today, Personal CGM is successfully used by patients with type diabetes, including children, adolescents, and adults, as well as by patients with type diabetes. Note: MiniMed 0G with Enlite is labeled for use in ages 6 years and older. The Paradigm REAL-Time Revel System, used with Sof-sensor glucose sensor, is indicated for ages 7 years and older. A version of the product specially designed for children is indicated for patients ages 7 to 7. The following fundamental principles guide current CGM practice:. CGM devices measure interstitial glucose, which is related to, but not the same as capillary glucose CGM values will usually lag behind self-monitoring of blood glucose (SM) due to physiologic delay of glucose transfer between interstitial and blood compartments. Depending on the rate of change, CGM values are generally within % 0% of SM values, with greater differences during rapid rates of change.* Patient understanding that blood glucose () does not equal sensor glucose (SG) helps to set realistic expectations and the importance of trends versus discrete values.. CGM systems consist of four components: The glucose sensor is inserted into the subcutaneous tissue, where glucose oxidase measures the interstitial glucose. The transmitter is connected to the glucose sensor, and communicates to the receiver or insulin pump. The receiver or insulin pump displays the glucose values and trends. It also has various alert features and download capabilities. Features of the MiniMed 0G system include: Updated sensor glucose values every minutes Rate of change arrows, 6,, and -hour trend graphs Alert settings for Low and High Glucose Limits, Predictive High and Low, and Rate of Change Threshold (see pages 9 and 0) CareLink Personal and Pro software. CGM devices are indicated for use as adjunctive to SM All treatment changes are to be based on traditional SM tests, not the SG values. The CGM system is calibrated using SM with a glucose meter, usually times a day for optimal results.. The more frequently patients use CGM, the greater improvement in glucose control, Encourage patients to adopt full-time use of CGM. However, patients who use CGM intermittently also benefit. Minimizing excessive alerts upon initiation increases acceptance of the therapy. For those patients who use CGM intermittently, focus on times when glucose management is particularly difficult. Travel Illness Stress Unusual physical activity When glucose targets are not met * The MARD is.6% when calibrating times a day, and.7% when calibrating once every hours during actual use with the MiniMed 0G with the Enlite sensor. Fundamental Concepts
7 Candidate Selection Indications Patients with type diabetes and patients with type managed on insulin with the following characteristics: AC above target Excessive glycemic variability Frequent hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia unawareness Nocturnal hypoglycemia Post-prandial hyperglycemia Pregnancy/Pre-pregnancy* Trouble with glucose control during exercise or periods of stress Patient Requirements Willingness to be attached to a sensor and transmitter Willingness to perform SM to calibrate system and to validate SG values prior to making treatment decisions Willingness to work with healthcare team to analyze data and make appropriate treatment adjustments Precautionary Areas Skin and site irritation and infection Reduces available sites for insulin infusion *Enlite is not approved for pregnant women Candidate Selection
8 CGM Initial Alert Settings and Adjustments Limit Alerts at Initiation It is recommended that patients start with a limited number of alert settings at CGM initiation. This strategy eases patients into their CGM experience by minimizing alerts while they are beginning to learn about their glucose trends and patterns. It balances the benefits of seeing the rate and direction of glucose change, while avoiding information overload and the frustration of excessive alarms. As patients gain an understanding of how food, insulin, and exercise affects their glucose levels, glucose control should begin to improve. Once this occurs, additional alerts may be turned on and limits may be tightened to take full advantage of CGM capabilities. Adding and Adjusting Alerts Using CareLink Pro Software Reports After the patient has become familiar with basic functions of the CGM system and demonstrates the ability to interpret the graphs, additional alert settings can be added. It is important to balance the ability of the patient to tolerate additional alerts with the value of the information obtained from the alerts. In general, most patients want to be alerted only when it is necessary to take action. While it may seem logical for every patient to be alerted of values over 0 mg/dl, patients who have many postprandial glucoses over 0 mg/dl will find the frequency of alerts unacceptable. It is difficult to anticipate how an individual patient will respond to frequent alerts until they are actually utilizing the system. 6 Timely follow-up for alert setting evaluation and adjustment is important for success. Use CareLink software to begin adjusting the settings within the first few days, and no later than 7 days after CGM initiation. The CareLink Therapy Management Dashboard example below demonstrates how to use CareLink reports to individualize settings. For this patient, setting the Threshold at 60 mg/dl, and the Low Glucose Limit at 70 mg/dl at initialization, and later setting the High Glucose Limit at 00 mg/dl may allow the patient to use CGM without receiving excessive alarms. See pages 7 and 8 for recommended initial CGM settings and adjustment considerations. Therapy Management Dashboard Sensor Overlay 6 CGM Initial Alert Settings and Adjustments
9 Low Alarm and Alert Settings Low Alerts are intended to provide warning of actual or impending hypoglycemia so the patient can respond to prevent or reduce the low excursion. Initial settings are intended to balance safety while minimizing nuisance alerts. Settings are individualized in all cases. Alarm and Alerts Initial Settings Considerations and Adjustments Threshold Alarm (MiniMed 0G System only) Alarms with a siren and suspends all insulin delivery when the sensor glucose reaches or falls below the programmed Threshold setting Alarm will continue to siren until patient responds Patient may resume insulin delivery at any time Can be set from mg/dl Low Glucose Limit Alert Alerts when sensor glucose reaches or has fallen below the sensor glucose limit Can be set from 0 90 mg/dl May set up to 8 different time segments per day 60 mg/dl Set higher for hypoglycemia unaware Make sure there is at least 0 mg/dl difference between Low Glucose Limit and Threshold Limit For those patients who need more time to treat before Threshold is activated, consider raising the Low Glucose Limit 70 mg/dl Set higher (90 or 00 mg/dl) for hypoglycemia unaware If patient reports too many alerts, consider setting the limit lower, coupled with therapy adjustments If patient experiences hypoglycemia without alerting, set limit higher Low Predictive Alert Alerts when low glucose is predicted to occur Used to prevent or reduce the severity of the low glucose excursion Can be set at OFF, or from 0 minutes Fall Rate of Change Alert Alerts when sensor glucose has fallen at specified rate of change Fall rate is most important when sensor glucose is near the low limit Can be set from..0 mg/dl/minute OFF OFF Consider using with experienced CGM patients who want more warning before a low occurs Set at 0 minutes Set only if extreme rate of change is valuable, as this setting will increase the frequency of alerts Set at.0 mg/dl/minute If patient reports too many alerts, consider turning this alert OFF Low Repeat Used to select the length of time before the Low Alerts and Threshold alarm repeat after they are cleared, if the condition still exists Is set if one or more of the Low Alert settings or Threshold is turned on Allows time for patient to treat hypoglycemia and for glucose to rise Applies to all Low Alerts and Threshold Can be set from minutes one hour 0 minutes Default is set at 0 minutes Low Alarm and Alert Settings 7
10 High Alert Settings High alerts are intended to detect actual or potential hyperglycemia so the patient can respond and prevent or reduce the high excursion. Initial settings are intended to balance safety while minimizing nuisance alerts. Settings are individualized in all cases. Alerts Initial Settings Considerations and Adjustments High Glucose Limit Alert Alerts when the sensor glucose has reached or risen above the sensor glucose limit Can be set from 0 00 mg/dl May set up to 8 different time segments per day High Predictive Alert Alerts when high glucose is predicted to occur Used to prevent or reduce the severity of the high glucose excursion Can be set from 0 minutes Rise Rate of Change Alert Alerts when sensor glucose has risen at a specified rate of change May be used as indicator for missed boluses Set only if extreme rate of change is valuable Can be set from..0 mg/dl/minute High Repeat Used to select the length of time before the High Alerts repeat after they are cleared, when the condition still exists Can be set if one or more of the High Alert Settings is turned on Allows time for insulin to take effect and high glucose to decrease Applies to all High Alerts Can be set from minutes hours OFF OFF OFF N/A or Two hours Set at 0 mg/dl Alternatively may use CareLink data to determine initial setting If patient reports too many alerts, consider increasing the setting, coupled with therapy adjustment As glucose control improves and hyperglycemia decreases, consider decreasing the setting Set at minutes Consider leaving OFF, to decrease the burden of frequent alerts with limited perceived value If used, consider setting at.0 mg/dl/minute to alert patients only of very rapid changes in glucose levels that may occur when patient misses a bolus If patient reports too many alerts consider turning this alert OFF When patient s missed bolus behavior improves, consider turning feature OFF to prevent excessive alerts Default is set at one hour, so will need to increase setting at initiation to minimize alerts * Bode, BW, Kaufman, FR. Personal Continuous Glucose Monitoring Protocol: A Guide to Continuous Glucose Monitoring Integrated with Insulin Pump Therapy. Northridge, CA: Medtronic, Inc. Diabetes; 0. 8 High Alert Settings
11 Threshold Feature Threshold sirens and shuts off insulin delivery when the sensor glucose value reaches or drops below the programmed Threshold setting. Patient should take a fingerstick and take measures to prevent or treat hypoglycemia. The patient can resume delivery any time. All insulin delivery will be suspended for two hours if the patient is unable to respond to the Threshold alarm. After two hours, the basal rate automatically resumes for four hours. After four hours, if the sensor glucose remains below the Threshold setting, the basal rate suspends again. This cycle continues for a maximum of twelve hours (two cycles), until the calibrations run out, until the pump battery dies, etc. The patient may respond at any time, clear the alarm, and resume insulin delivery. If the patient responds, clears the alarm and chooses to continue the, the pump will stay suspended until the two hour cycle has completed Once basal insulin delivery resumes, if the patient s SG remains or falls below the programmed Threshold setting and his Low Repeat time has passed, then his pump will again suspend insulin delivery for two hours. Threshold Key Points: Makes a siren sound and suspends all insulin delivery when the sensor glucose reaches or falls below the programmed Threshold setting Sirens until the patient clears the alarm Patient can resume delivery at any time Can be set from mg/dl The Threshold Concept Glucose (mg/dl) Insulin infusion stopped Max. duration = h Insulin infusion resumed Glucose (mmol/l) AM AM Time 6 AM. Note: The Threshold feature is available in the MiniMed 0G system only. See the MiniMed 0G System User Guide for complete information and instructions for use. WARNING: The Threshold feature will cause the pump to temporarily suspend insulin delivery for two hours when the sensor glucose reaches a set threshold. Under some conditions of use the pump can suspend again resulting in very limited insulin delivery over a four hour period. Prolonged suspension can increase the risk of serious hyperglycemia, ketosis, and ketoacidosis. Before using the Threshold feature, it is important to read the Threshold information in the MiniMed 0G` System User Guide. Threshold Feature 9
12 What to Expect with Threshold Frequency of Threshold A Threshold event may occur every day or every other day, as some patients commonly experience glucose excursions of mg/dl. The initial setting for Threshold should be at mg/dl, with higher settings (80 90 mg/dl) suggested in those with a history of severe hypoglycemia, renal insufficiency, or other conditions in which avoidance of lower glucose levels is desired. Duration of Threshold The Threshold feature is designed to stop insulin delivery at a user-set threshold when the patient does not respond to a low alarm, such as during sleep. CareLink data from patients using the MiniMed Paradigm Veo system* indicate suspend events that last the full two-hours with no patient response account for 0 % of all threshold suspends, with the majority of these occurring at night. The data from these patients show glucose levels rising on average 0 0 mg/dl per hour for hours after the suspend begins, including after the automatic resumption of basal insulin delivery at the two-hour mark. 7 Threshold and Routine Treatment of Hypoglycemia Threshold should be viewed as a feature for unresponsive patients when there is no one available to help them. When the patient is awake and alert, patients should respond to a Threshold event by cancelling the alarm, checking their by fingerstick and treating their hypoglycemia with oral glucose as directed. They can resume basal insulin delivery upon treatment of the hypoglycemia. Data from CareLink show that during the daytime when Threshold occurs it is most frequently right before lunch or during exercise. 7 Reinforce with families and caregivers that a patient with hypoglycemia who is unresponsive should be treated with glucagon. Recognizing Threshold Events in CareLink Pro Software Threshold events can be easily identified in CareLink reports. A Threshold that lasts two hours and shows no patient response is bounded by an alarm symbol on both ends of the two-hour time period with the basal insulin rate going to zero. A Threshold event that has an alarm symbol only at the start indicates the patient responded and cleared the alarm. *The MiniMed Paradigm Veo insulin pump is not approved for use in the US and uses a slightly different threshold suspend algorithm from the MiniMed 0G insulin pump. 0 What to Expect with Threshold
13 Identifying Threshold on the CareLink Daily Detail Report The Daily Detail reports below each show a Threshold event. Threshold events are indicated by the basal rate drop to 0.0 units/hour as well as a color change from green to red, in the line depicting the basal rate. A patient-initiated suspend is depicted by a basal rate drop to 0.0 units/hour in green. Patient unresponsive. Basal suspended for two hours, then automatically resumed. Patient cleared the alarm, tested, and resumed insulin delivery immediately. Patient cleared Threshold alarm and kept the basal rate suspended. After approximately one hour, the patient resumed basal delivery. Identifying Threshold on the Daily Detail Report
14 Graphs and Displays There are, 6,, and -hour graphs available for display on the MiniMed 0G system. The graphs show High and Low Glucose Limit lines, the sensor glucose (SG) tracing, and the most recent SG value (or the reason why there is no value shown), as well as the time the SG value was updated. Historical data up to hours can be viewed by scrolling back through the graphs. If the SG rises or falls faster than a certain rate, trend arrows automatically appear in the graphs next to the SG measurement. Trend Arrows SG has been falling at a rate of.0 to.0 mg/dl per minute SG has been falling at a rate of.0 mg/dl or more per minute SG has been rising at a rate of.0 to.0 mg/dl per minute SG has been rising at a rate of.0 mg/dl or more per minute Below is an example of a -hour graph. Please see the MiniMed 0G System User Guide for further information about graphs and pump displays. Sensor glucose tracing Time of sensor glucose value update Time of day High alert limit Sensor glucose value Low alert limit Trend arrow Shaded area is the hours from 6 pm to 6 am Graphs and Displays
15 Using On-Screen Data to Make Therapy Adjustments The protocol for the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF) CGM study provided recommendations for insulin dose adjustments based on trend arrows. 8 The guidelines below are adapted from these recommendations. Trend Arrows After a patient has become comfortable responding to alarms and alerts and interpreting glucose trends, you may want to consider adding trend arrows to the insulin dose adjustments. Patients should use the Wizard calculator using fingerstick values to determine the bolus insulin recommendation, and then can be instructed to consider making dose adjustments to the Wizard estimate based on the on-screen trend arrows. If fingerstick is low before bed, or anytime a low alert occurs Correct the low with glucose tablets Check to see if there are trend arrows on the pump screen Consider taking more glucose if down arrows are present For example, if grams is normally used to treat a low, consider adding grams glucose for one arrow and 0 grams for arrows If fingerstick is low before food intake Do not bolus while glucose is low Treat the hypoglycemia After treating the hypoglycemia and the glucose is within target, calculate the bolus to cover the meal, check for trend arrows on the pump, and adjust based on the arrows using the guidelines below If fingerstick is at or above target before a meal or whenever a high alert occurs Check to see if there are trend arrows on the pump screen Calculate your meal bolus and/or correction dose and adjust based on the trend arrows using the guidelines below Adjustment Guidelines Using Trend Arrows Decrease dose by 0% Decrease dose by 0% No arrows No change in dose Increase dose by 0% Increase dose by 0% Adjustments can also be made for trend arrows when the is within target range. This should be initiated after the patient has experience with adjusting doses for high and low s using trend arrows. When is within target range, use the arrows to give minor correction doses and small amounts of glucose as appropriate. As always, individual patient history should be considered with all recommended dosage adjustments. Using On-Screen Data to Make Therapy Adjustments
16 Using CareLink Pro Software to Make Therapy Adjustments The data provided by CareLink should be reviewed in a systematic format. Start by looking at the Therapy Management Dashboard for a sense of overall control or areas of concern. First, look at the overnight period and make any necessary changes. Next, evaluate the pre-meal time periods and adjust basal rates as needed. Then evaluate the post-meal time periods and adjust carbohydrate ratios or timing of insulin delivery as needed. Identify any behavioral issues that might be impacting the patient s management and counsel or educate as needed. Generally, to therapy changes and to behavioral changes at a time with a follow-up evaluation is appropriate. Therapy Management Dashboard //0 - /7/0 -Hour Analysis Sensor, Insulin, & Settings Statistics Avg Readings Carbs Entered 8 ± mg/dl 6. per day 0 ± 6g per day Hypoglycemic Patterns (6)** : AM-7: AM (9) Time Period :7 PM-:9 PM (7) Insulin (U, active hr) 8:9 PM-0: PM () Basal Rate Insulin Bedtime to Wake-up Bedtime: 8:00 PM - :00 AM Wake-up: :00 AM - 9:00 AM Breakfast: 6:00 AM - 0:00 AM () Pre-meal SG Avg: 09 ± mg/dl Post-meal SG Avg: ± 0mg/dL Avg Carbs: ± 9g Avg Food : 8.9 ±.9U Lunch: :00 AM - :00 PM (6) Pre-meal SG Avg: 9 ± mg/dl Post-meal SG Avg: 0 ± mg/dl Avg Carbs: 0 ± g Avg Food : 6.7 ±.U Hyperglycemic Patterns () :00 PM-: AM Time Period 8:0 AM-0: AM :00 PM-6: PM Pump Use Per Day Insulin TDD.0 ±.U Basal/ Ratio / 8 Manual es 0.0U (0.0 boluses) Wizard.7U (.6 boluses) Food.8U (.9 boluses) Correction.U (.9 boluses) Override (+) 0.U (0. boluses) Override (-) -.U (0. boluses) Dinner: :00 PM - 0:00 PM (9) Pre-meal SG Avg: 7 ± mg/dl Post-meal SG Avg: 6 ± 9mg/dL Avg Carbs: 8 ± g Avg Food :. ±.U Duration h m per day Threshold Events. per day Time Res./Site Change h m per day Every.7 /. days Sensor Use Avg SG Wear Duration 7 ± mg/dl 6d 0h per week Low SG Alarms 0. per day High SG Alarms. per day ** Only highest priority shown. 6 Action Plan Reviewed By Date Sensor Overlay* Evaluate for a sense of overall control or areas of concern. Insulin Profile Graph Evaluate insulin profiles. How many basal rates? Are they appropriate? Is variance appropriate? Evaluate average active bolus insulin. Note active insulin in overnight time period before adjusting overnight basal rate. Sensitivity and Carb Ratio Evaluate insulin sensitivity and carb ratios. Are they appropriate? Consider checking carb ratio against 0 rule (0 divided by TDD) and insulin sensitivity against 700 or 000 rule (700 or 000 divided by TDD). Therapy Management Software Time Bedtime to Wake-up Sensor Overlay* Evaluate sensor glucose from bedtime to wake-up. Is patient within target during this time period? Meal Sensor Overlay* Evaluate glucose values around meal times when patient uses the Wizard. Is pre-meal value within target? Is post-meal rise within 0 60 mg/dl? 6 Action Plan Use this section to record notes for patient records, to provide comments and recommendations for patient therapy, and/or to record documentation for health insurance providers.
17 Example of Therapy Management Dashboard Use this report to review the big picture as well as specific behaviors. Therapy Management Dashboard //0 - /7/0 -Hour Analysis Sensor, Insulin, & Settings Statistics Avg 8 ± mg/dl 7 Statistics Avg 8 ± mg/dl Readings 6. per day Carbs Entered 0 ± 6g per day Readings 6. per day Hypoglycemic Patterns (6)** : AM-7: AM (9) Carbs Entered 0 ± 6g per day Time Period :7 PM-:9 PM (7) Basal Rate Insulin Insulin (U, active hr) 8:9 PM-0: PM () Hyperglycemic Patterns () :00 PM-: AM Time Period 8:0 AM-0: AM :00 PM-6: PM Pump Use Per Day Insulin TDD.0 ±.U 8 Hypoglycemic Patterns (6)** : AM-7: AM (9) Time Period :7 PM-:9 PM (7) 8:9 PM-0: PM () Basal/ Ratio / 8 Bedtime to Wake-up Bedtime: 8:00 PM - :00 AM Wake-up: :00 AM - 9:00 AM Breakfast: 6:00 AM - 0:00 AM () Pre-meal SG Avg: 09 ± mg/dl Post-meal SG Avg: ± 0mg/dL Avg Carbs: ± 9g Avg Food : 8.9 ±.9U Lunch: :00 AM - :00 PM (6) Pre-meal SG Avg: 9 ± mg/dl Post-meal SG Avg: 0 ± mg/dl Avg Carbs: 0 ± g Avg Food : 6.7 ±.U Dinner: :00 PM - 0:00 PM (9) Pre-meal SG Avg: 7 ± mg/dl Post-meal SG Avg: 6 ± 9mg/dL Avg Carbs: 8 ± g Avg Food :. ±.U Manual es 0.0U (0.0 boluses) Wizard.7U (.6 boluses) Food.8U (.9 boluses) Correction.U (.9 boluses) Override (+) 0.U (0. boluses) Override (-) -.U (0. boluses) Hyperglycemic Patterns () :00 PM-: AM Time Period 8:0 AM-0: AM Duration Threshold Events Time h m per day. per day h m per day :00 PM-6: PM Res./Site Change Every.7 /. days Sensor Use Avg SG 7 ± mg/dl Wear Duration 6d 0h per week 9 Pump Use Insulin TDD Per Day.0 ±.U Low SG Alarms 0. per day High SG Alarms. per day ** Only highest priority shown. Basal/ Ratio Manual es / 8 0.0U (0.0 boluses) Action Plan Wizard.7U (.6 boluses) Reviewed By Date Time Food Correction Override (+).8U (.9 boluses).u (.9 boluses) 0.U (0. boluses) Override (-) -.U (0. boluses) 0 Duration Threshold Events h m per day. per day Time h m per day Res./Site Change Every.7 /. days Sensor Use Avg SG 7 ± mg/dl Wear Duration 6d 0h per week Low SG Alarms 0. per day High SG Alarms. per day ** Only highest priority shown. 7 Statistics Table Evaluate average and standard deviation (SD). Mean glucose values between 0 60 mg/dl are generally acceptable to meet AC target. An SD of less than half the mean glucose is generally acceptable. Are there an appropriate number of readings/day? Are the carbs per day appropriate? 8 Hypo- and Hyperglycemic Patterns Tables* Evaluate hypo-and hyperglycemic patterns. Are there areas of concern? Are there extreme excursions of hypo- or hyperglycemia? 9 Pump Use Table Evaluate total daily dose of insulin. Is it appropriate based on weight and age? Evaluate basal to bolus ratio. Is it appropriate for age and type of diabetes? is generally 0%. Evaluate pump features being used, e.g. Wizard, amount of correction, number and type of overrides. Are reservoir and site changes occurring appropriately? 0 Duration*** Evaluate suspend duration. Are there lengthy periods of suspends? Are there frequent Threshold events? Sensor Use Table Evaluate average SG and SD. Evaluate amount of sensor wear. Evaluate number of alarms per day. * Targets determined by provider during report setup. To obtain the Therapy Management Dashboard, a minimum of five days (0 data points) of pump and sensor data are required in the reporting period. *** Threshold Events and Time will be displayed if device supports this feature. Therapy Management Dashboard
18 Example of Episode Summary Use this report to evaluate events that precede hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic episodes. You may also use this as a conversation map to develop questions you may want to discuss with the patient in order to make therapy changes or provide additional education. Episode Summary //0 - /7/0 Hypoglycemic Episodes, by preceding Event Type - Threshold: 70 mg/dl Hyperglycemic Episodes, by preceding Event Type - Threshold: 0 mg/dl Most Common Event Types preceding Hypoglycemia Most Common Event Types preceding Hyperglycemia Event Type Descriptions Event Types % Description Event Type Descriptions Event Types % Description Rapid Falling Sensor Rate Of Change Hyperglycemia Preceding Hypoglycemia Wizard Food 8 8 Consider counseling your patient to take action to avoid hypoglycemia. Consider assessing your patient s insulin sensitivity factors.consider counseling your patient on the management of hyperglycemia. Consider assessing the Wizard settings, counseling your patient on accurate carbohydrate counting, and/or the timing of insulin delivery with respect to carbohydrate intake. Wizard Food Overcorrection of Hypoglycemia Rising Sensor Rate of Change Without 9 Consider assessing the Wizard settings, counseling your patient on accurate carbohydrate counting, and/or the timing of insulin delivery with respect to carbohydrate intake. Consider counseling your patient on the management of hypoglycemia. Consider counseling your patient on bolus use with meals and/or correcting rapid glucose excursions. Other Observations No overall issues observed. Hypoglycemic/Hyperglycemic Episode Charts ( different algorithms)* Use this to assist in identifying and ranking events that precede hypo- and hyperglycemic episodes. There can be more than one event preceding an episode and it is possible that no events precede an episode. You may want to obtain more information from the patient about these events. Most Common Event Types Pie Charts (for top preceding events) Evaluate the hypo- and hyperglycemic episodes in relation to the total number of occurrences for each event during the reporting period. If < 0%, may not require evaluation. Event Type Descriptions Table Consider possible therapy adjustments or education related to hypo- and hyperglycemic episodes. Other Observations Table (6 algorithms) Identify possible behavior changes related to pump, CGM, and/or meter usage. *Targets determined by provider during report setup. To obtain the Episode Summary, a minimum of five days (0 data points) of pump and sensor data are required. 6 Episode Summary
19 Example of Adherence Report Use this report to analyze patient behaviors. Adherence ( of ) //0 - /7/0 Glucose Measurements Events Fill Events Readings Sensor Duration (h:mm) Manual es Wizard Events With Food With Correction Overridden Rewind Cannula Fills Cannula Amount Tubing Fills Tubing Amount Duration (h:mm) Sunday //0 : Monday //0 :00 :00 Tuesday /6/0 7 : : Wednesday /7/0 8 :00 :00 Thursday /8/0 :00 :6 Friday /9/0 Saturday /0/0 Sunday //0 Monday // :0 :00 :00 : :0 :0 : Duration (h:mm) Tuesday //0 6 :0 Wednesday //0 : :7 Thursday //0 Friday /6/0 Saturday /7/0 Summary /day :00 :00 :00 d 6h 00m 0.0/day 7 7.6/day 6 8.9% 6 8.% 7.8% 0.U /fill.u/fill :8 : 0:8 9h m :00 0: :00 Partial day Low s Note: Partial days will not be included in summary averages. Days on which a time change occurred are considered to be partial days. :6 :0 :0 Sensor Duration Evaluate the amount of time per day the sensor is worn. Duration Evaluate the total time the pump is suspended per day (includes Threshold and manual suspend events). Threshold Events Evaluate the number of Threshold events per day. The number of total Threshold events precedes the icon. No number in front of the icon signifies one event. Manual Manual suspends do not have an icon indicator. If there is no Threshold icon, all of the suspend duration is from one or more manual suspends. Adherence Report 7
20 Event Event Events Events Event Event Events Events Time Time : :AM AM Type 66 Type 6: 9:6 AM 0: AM PM 6:AM AM Delivered 9:6 AM 0: AM :06 PM Norm :06.00 Delivered Norm Type 7 6 Type 7 ++ Square Square Portion Portion (U,(U, h:mm) h:mm) 7: PM : 7: PM Statistics : PM PM 6: 6: AM AM Time: : 0: :06 7: : PM Time AM AM 6:6: AM AM 9:69:6 AM AM0: AM AM:06 PM PM 7: PM PM PM Delivered Delivered Norm Norm : Statistics Statistics Event Event Event Time Time : : AM AM 9:6 9:6 AM AM / -/ (mg/dl) Avg Avg (mg/dl) Recommended Recommended /.0.00 / -.00 /7 Example of Sensor & Meter Overview Report: Daily Snapshots Time : AM s Type rm Readings Readings - Difference -Difference ± Readings ReadingsAbove AboveTarget Target 9:6 AM 0: AM :06 7: PM 8.0 : PM Delivered Norm Delivered Norm PM Recommended Recommended Carbs Carbs (g)(g) 89 6./day - - Readings 8 Readings ReadingsBelow BelowTarget Target ++Square (U, Difference Difference Portion Square Portion (U,h:mm) h:mm) - - Setting Carb Ratio -.0 Carb Ratio Setting (g/u) (g/u) Readings Above Target 6% 8% Avg Sensor Sensor Avg(mg/dL) (mg/dl) -6.0 Recommended Recommended Carbs 6.0(g) Carbs - (g) Food Food Readings Below Target -0% Avg % >>0 AUC (mg/dl) Avg AUC 0 (mg/dl) - Ratio Difference -Carb -Difference - Carb Setting -(g/u) Ratio Setting (g/u) (mg/dl) (mg/dl) Sensor Avg (mg/dl) ± 9 7 ± Avg AvgAUC AUC<<70 70(mg/dL) (mg/dl) Carbs (g) Carbs (g) Food Food Sensor & Meter Overview ( of ) Target Target Setting Setting (mg/dl) (mg/dl) //0 - /7/0 Avg AUC > 0 (mg/dl).9 d 0h. d 6h Ratio (g/u).0.0 Carb Carb RatioSetting Setting (g/u) (mg/dl) 8 7 (mg/dl) Insulin Insulin Sensitivity Sensitivity Setting Setting Daily Carbs Daily Carbs(g) (g)6 (mg/dl per per U)U) Avg AUC <- 70.(mg/dL d d 6h -9 7Setting Food 8.0 Setting Food (mg/dl) Target (mg/dl) (mg/dl) h Target Carbs/ Insulin Carbs/ Insulin (g/u) Correction Correction (g/u) (mg/dL) (mg/dl) Insulin 98 Setting Sensitivity Setting Insulin Sensitivity 7 7 Daily Carbs (g) ± 6 (mg/dl (mg/dl per per U) U) Active Active Insulin Insulin (mg/dL).0 Setting Target Target Setting (mg/dl) Total TotalDaily DailyInsulin Insulin 0 Correction Correction Carbs/.0.0 Insulin (g/u) Sensitivity Setting 7 0 Insulin Insulin Sensitivity Setting Daily Basal 6 Daily Basal (mg/dl (mg/dlper peru) U) Active Insulin 0.00 Active Insulin Total Daily Insulin ±. Daily Daily Correction Correction Sensor Sensor trace trace reading reading Linked Linked % 8. % Active Daily Basal Interrupted ActiveInsulin Insulin Interrupted chart chart Calibration Calibration B Fills Fills 6: AM Type Type 6 (U, h:mm) +7Square Portion (U, h:mm) + Square Portion - -Avg (mg/dl) Use this report to analyze glucose levels, carbohydrate intake, and insulin delivery to assist in identifying trends. 8.0 h:mm) us ce bs (g) g (g/u).0.0 us 8.0 mg/dl) 9 08 mg/dl) etting per U) us lin Sensor trace Sensor trace reading reading Basal.0 Linked Linked Daily Basal -Interrupted Interrupted chart chart Calibration Calibration 67%.7 Temp basal Temp basal Fills 8% Pump rewind Pump 7 rewind.0u Threshold Susp Threshold Sensor Sensortrace trace reading reading Linked Linked Basal Basal Time Timechange change Exercise Exercise Interrupted Interrupted chart chart Calibration Calibration Temp Tempbasal basal Pump Pumprewind rewind Threshold Threshold Injected Injectedinsulin insulin Other Other reading Linked Basal Time change Exercise Glucose alert chart Calibration Temp basal Pump rewind Threshold Injected insulin Other Alarm Sensor trace reading Basal Interrupted chart Temp basal Time change Exercise Threshold Injected insulin Other For more details of each day, see the Daily Detail Report reading Glucose Section* chart Evaluate meter and sensor glucose. Basal Temp basal Carbs Section Evaluate carbohydrate intake. Is it appropriate for patient? Is there insulin given for all carbohydrate entries? 8 Daily Snapshots Insulin Section Threshold Evaluate insulin delivery. Are there multiple boluses? Are there frequent Threshold events? Are suspend time periods appropriate? Is the temp basal feature being used? *Targets determined by provider during report setup
21 Event l Time Time : : AM AM 6: 6: AM AM Delivered 9:6 9:6 AM AM 0: 0: AMNorm AM :06 :06 PM PM : 7: PM PM Recommended : : Statistics PM PM / /.0 -/7.0 Carbs 6.0(g) Readings Type Type 6 + Square + 7 Portion (U, (U, h:mm) h:mm) Use this report to look at more specific details (time, amount, type) of each bolus Difference Carb Ratio Setting (g/u).0 Avg given (mg/dl) as well 67as suspend 8 and.0 Readings ± temp basal events. Above Target 6% 6% 6: AM Delivered 9:6 AM 0: Norm AM :06 PM :8.0 PM8.0 Recommended : PM Carbs (g) Food Readings 8 89 Readings 6./day Below Target 0% 0% + + Square Portion (U, (U, h:mm) Difference Carb Ratio Setting (g/u) (mg/dl) Readings Above Target 6% Sensor 8% Avg Avg (mg/dl) ± 9 ± Recommended Daily.00Detail ( of ) Carbs Carbs (g) (g) Food Target 7 Setting 7 (mg/dl) Thursday //0 Readings Below Target 0% Carb Carb Ratio Ratio Setting (g/u) (g/u) (mg/dl) Avg Difference Avg Insulin Sensitivity AUC 7.0 AUC > % 0 > 0 (mg/dl).9.9 d d 0h 0h. Setting 8 7 Sensor Avg (mg/dl) ± 9 7 (mg/dl per U) Carbs (g) (g) Food Food Target 7 7 Setting (mg/dl) Avg 0.0 Avg ± AUC 00 AUC < - 70 < 0 70 (mg/dl) d 0 d 0h 0h Correction.00 C Carb Carb Ratio Ratio Setting (g/u) (g/u) (mg/dl) Insulin 7.0 Avg Sensitivity AUC > 0 Setting (mg/dl) d 7 7 0h. 0 0 d 6h 7 7 (mg/dl per U) Active Daily Insulin Daily Carbs (g) (g) Food Food Target Target 7Setting 6.0 (mg/dl) Avg 0-0 AUC < (mg/dl) d 0-0 0h d 6h Correction.00 Carbs/.0 Insulin (g/u) (g/u) (mg/dl) Insulin Sensitivity Setting (mg/dl per per U) U) Active Insulin Daily Carbs (g) ± Target Setting (mg/dl) Total Total Daily Daily Insulin Correction Carbs/.0.0 Insulin (g/u) Sensor..70 trace.70 reading Linked 08 Insulin 98 Sensitivity Setting (mg/dl per per U) U) Active Active Insulin Interrupted Daily Daily Basal % % 8. chart Calibra Events Total Daily Insulin ±. Statistics / / - /7 Correction Sensor trace reading Linked Daily Daily Basal % 67%.7 Event 6 7 Avg (mg/dl) 67 8 ± Time7: AM 7 9:6 AM 0: AM :06 7PM 7: PM : PM Active Insulin Interrupted Readings Daily Basal /day chart 6.6 % Calibration 8. % Fills Temp Fills basal Pump re 7 Type Delivered Norm + Square Portion (U, h:mm) Recommended Difference Carbs (g) reading Carb Ratio Setting (g/u).0 Food chart chart (mg/dl) 9 Target Setting (mg/dl) 0-0 Basal Insulin Sensitivity Setting (mg/dl per U) Correction : AM Sensor.70 trace Sensor trace Interrupted Linked Calibration Pump rewind Daily Basal 6.6 % 8. %.70 reading chart chart Events Time : AM Event Type Readings Above Target Readings Linked Below Linked Target Sensor Avg (mg/dl) Avg AUC > 0 (mg/dl) Avg AUC < 70 (mg/dl) Daily Carbs (g) Carbs/ Insulin (g/u) Daily.9. d 0h ± 9 6% Calibration d 0h %.7 ±. d 6h ± 6 ±. 8% Basal % Daily 0% Basal.0 d Fills Temp Temp basal basal 6h 8% 6: AM 9:6 6 7 Events Time : AM 6: AM Delivered 9:6 AM 0: Norm AM :06 PM.00 7: PM 8.0 : S Event Event Type Square 7 7 Portion (U, h:mm) No Events Time Time: : AM AM 6: 6: AM AM Delivered 9:6 9:6 AM AM0: Norm 0: AM AM:06 :06 PM.00 PM 7: 7: 8.0 PM PMRecommended : Statistics : /.00 / / Example Event of Daily Detail Report Type Type Square 7 7 Portion (U, h:mm) Difference Avg Avg (mg/dl) Sensor trace trace Interrupted Linked Calibration.60.0 Temp basal.0 Basal Temp basal basal Threshold Pump rewind Total Daily Insulin Time change Injected insulin Threshold Exercise Other 67%.7 8% Time Timc Pump Pump rewind 7 rewind.0u Threshold Injecte Time Time change Exercise Glucose Injected insulin Other Alarm Glucose alert Alarm Active Insulin Fills 7.0U Sensor trace reading Linked Basal Time change Exercise Glucose alert Interrupted chart Calibration Temp basal Pump rewind Threshold Injected insulin Other Alarm Glucose Alert Meter Reading Carbohydrate Gram Entries 6 Basal Rate Change Delivery Patient checked, calibrated, entered carbohydrates and bolused simultaneously Threshold event that was not responded to. Auto resume of basal insulin after hours of suspend shown. Threshold event that was responded to before auto resume of basal. Calibration. Exercise entered via Capture Events feature. User initiated. 6 An example of multiple repeated alerts set at narrow ranges. Daily Detail Report 9
22 Example of Device Settings Report Use this report to evaluate insulin pump and sensor settings. -Hour Total TIME 0:00 :00 :00 6:00 8:00 0:00 :00 7:00 0:00 9. U U/hr Hour Total Device Settings Snapshot Sunday /8/0 0:9 AM Basal Maximum Basal Rate.00 U/hr Temp Basal Type Percent of Basal Standard (active) Pattern A TIME 0:00 :00 :00 6:00 0:00 :00 7: U U/hr Pattern B -Hour Total TIME U/hr TIME 0:00 0:0 7:00 Maximum Dual/Square (Variable) Blood Glucose Reminder Wizard Units Active Insulin Time (h:mm) Insulin Concentration Carbohydrate Ratio (g/u) Ratio On :00.0 U On On Easy (Audio) Entry (Step) 0.0 U g, mg/dl Insulin Sensitivity (mg/dl per U) TIME 0:00 :00 Sensitivity 7 Missed Reminder Start (h:mm) Blood Glucose Target (mg/dl) TIME 0:00 :00 End (h:mm) Low 0 00 High 0 0 Sensor Sensor Transmitter ID Units Glucose Alerts TIME 0:00 Alert Repeat On mg/dl Predictive Alert Low High (mins) On Low (mg/dl) 70 0:0 High (mg/dl) 0 :00 Rate Alert: Fall Rise (mg/dl/min) Notes AUC Limit: Low High (mg/dl) Missed Data/Weak Signal (h:mm) 0: Graph Timeout (h:mm) 0:0 Auto Calibration Calibration Reminder (h:mm) Calibration (Alert) Repeat (h:mm) :00 0:0 Utilities Alert Type Threshold (mg/dl) Low Reservoir Warning Amount Beep Medium 60 Insulin Units 0 U Basal Settings Evaluate basal settings. Is the number of basal rates appropriate? Is variance between rates appropriate? Settings Evaluate bolus settings. Are they appropriate? You may want to check the carb ratio against the 0 rule and the sensitivity against the 700 rule. Are the Wizard glucose targets appropriate? Is the Active Insulin time appropriate? Overall, do the settings make sense? Sensor Settings Evaluate sensor settings. Are they appropriate? Are alerts set appropriately? Utilities Evaluate alert type, Threshold value (if pump is enabled with this feature), and low reservoir warning. Are they appropriate? Notes Use this section to record notes for patient records, to provide comments and recommendations for patient therapy. Provide a copy of this page to the patient for documentation of doses and settings. 0 Device Settings Report
23 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Initiation Settings PRESCRIBER S INSTRUCTIONS TO PATIENT Patient Name: Fax to: Date: DOB: Threshold Alarm (MiniMed 0G system only) On mg/dl (60 90 mg/dl) Low Glucose Alert Start on (date) On OR OR Low Repeat Time Units a.m. mg/dl mg/dl mg/dl mg/dl Base settings on CareLink data Low Predictive Alert On Fall Rate Alert minutes ( 0 min) On mg/dl/minute (..0) minutes ( min hour) Low Repeat is turned on to the default of 0 minutes when any Low Alert setting is programmed. High Glucose Alert Start on (date) On OR OR High Repeat Time Units a.m. mg/dl mg/dl mg/dl mg/dl Base settings on CareLink data High Predictive Alert On Rise Rate Alert minutes ( 0 min) On mg/dl/minute (..0) minutes ( min hours) Default is set at hour. May need to increase to hours to minimize alerts. Yes, patient may adjust settings as necessary after initial use. No, it is preferred that the patient not adjust settings without consulting prescriber. If patient cannot use abdomen*, I authorize use of alternate site(s) as medically necessary. Alternate site(s): Notes (optional): Prescriber Name: Prescriber Signature: Date: 90M Medtronic MiniMed, Inc. All rights reserved. *The clinical trials of sensor accuracy have been based on sensors inserted in the abdominal area. Sensor performance may differ when other insertion sites are used.
24 References and Suggested Readings References. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Consensus Panel. AACE Consensus Statement on Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Endocrine Practice. 00;(6):7-7.. Hirsch, IB, Armstrong, D, Bergenstal, RM, et al. Clinical Application of Emerging Sensor Technologies in Diabetes Management: Consensus Guidelines for Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM). Diabetes Technol Ther. 008;0()-.. The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group. Diabetes Care. 009;() Bergenstal, RM, Tamborlane, WV, Ahmann, A. Effectiveness of Sensor-Augmented Insulin-Pump Therapy in Type Diabetes. N Engl J Med 00;6()-0.. Medtronic MiniMed. MiniMed 0G System User Guide. Northridge, CA; Mastrototaro, J, Welsh, JB, Lee, S. Practical Considerations in the Use of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Alerts. J of Diabetes Sci and Technol. 00;() Data on file. Medtronic, Inc. Diabetes, 8000 Devonshire Street, Northridge, CA. 8. JDRF Study Group. JDRF Randomized Clinical Trial to Assess the Efficacy of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Management of Type Diabetes: Research Design and Methods. Diabetes Technol Ther. 008;0()0-0. Suggested Reading American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Consensus Panel. AACE Consensus Statement on Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Endocrine Practice. 00;(6):7-7. American Diabetes Association Position Statement on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 0. Diabetes Care. 0;(suppl )S-S6. Agrawal, P, Welsh, JB, Kannadr, B, Askari, S, Yang, Q, Kaufman, FR. Usage and Effectiveness of the Low Glucose Feature of the Medtronic Paradigm Veo Insulin Pump. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 0;()7-. Bode, BW, Kyllo, J, Kaufman, FR. Pumping Protocol: A Guide to Insulin Pump Therapy Initiation. Northridge, CA: Medtronic, Inc. Diabetes; 0. Buckingham, B, Wilson, DM, Lecher, T, Hanas, R, Kaiserman, K, Cameron, F. Duration of Nocturnal Hypoglycemia Before Seizures. Diabetes Care. 008;()0-. Choudhary, P, Shin, J, Yongyin, W, et al. Insulin Pump Therapy with Automated Insulin Suspension in Response to Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 0;;0-0. Danne, T, Kordonouri, O, Holder, M, et al. Prevention of Hypoglycemia by using Low Glucose Function in Sensor- Augmented Pump Therapy. Diabetes Tech Ther. 0;()9-0. Garg, S, Brazg, RL, Bailey, TS, et al. Reduction in Duration of Hypoglycemia by Automatic Suspension of Insulin Delivery: The In Clinic ASPIRE Study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 0;()0-09. Hirsch, IB. Realistic Expectations and Practical Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for the Endocrinologist. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 009;9(7)-8. The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group: Tamborlane, WV, Beck, RW, Bode, BW, et al. Continuous Glucose Monitoring and intensive Treatment of Type Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 008;9()6-76. Kaufman, FR. Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A User s Guide to Effective Diabetes Management. Alexandria, VA. American Diabetes Association. 0. Mastrototaro, J, Welsh, JB, Lee, S. Practical Considerations in the Use of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Alerts. J of Diabetes Sci Tech. 00;()7-79. Phillip, M, Danne, T, Schlomt S, et al for the Consensus Form Participants. ISPAD Consensus Statement on Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Children and Adolescents. Pediatric Diabetes. 0;:-8. References and Suggested Reading
Welcome to CareLink Pro
 Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
Reference Guide Welcome to CareLink Pro This guide was developed to serve as a reference for obtaining patient data and reviewing CareLink Pro reports. Getting Started with CareLink Pro Adding New Patients
Report Reference Guide. THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1
 Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
CareLink. software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE. Management Software for Diabetes
 CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
CareLink Management Software for Diabetes software REPORT REFERENCE GUIDE How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used
Report Reference Guide
 Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2009 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-012_a CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Adherence
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES
 THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES Report Report Interpretation Reference Guide Guide 2007 Medtronic MiniMed. All rights reserved. 6025274-0U2 120707 CareLink Pro Report Reference Guide 0 p.2 Sensor
BREAKDOWN OF THE CARELINK REPORTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE
 BREAKDOWN OF THE CARELINK REPORTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE TABLE OF CONTENTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE Introducing CareLink Personal Software Before You Start...
BREAKDOWN OF THE CARELINK REPORTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE TABLE OF CONTENTS GETTING STARTED WITH CARELINK PERSONAL SOFTWARE Introducing CareLink Personal Software Before You Start...
RELEASED. first steps. Icon Icon name What it means
 Icon Icon name What it means Connection The connection icon appears green when the Sensor feature is on and your transmitter is successfully communicating with your pump. The connection icon appears gray
Icon Icon name What it means Connection The connection icon appears green when the Sensor feature is on and your transmitter is successfully communicating with your pump. The connection icon appears gray
REPORT INTERPRETATION
 REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
REPORT INTERPRETATION: Interpreting ipro Professional Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Reports and Making Therapy Adjustments TARGET AUDIENCE The audience for this section is physicians, mid-level practitioners,
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond)
 Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM
 USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM: INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE EXPERIENCED USER Checklist for starting on your MiniMed 670G
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM: INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE EXPERIENCED USER Checklist for starting on your MiniMed 670G
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM. Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User
 USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User This is a supplemental guide. For complete instructions and safety information, please see your MiniMed 670G System
USING THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM Instructions for the Experienced MiniMed 630G System User This is a supplemental guide. For complete instructions and safety information, please see your MiniMed 670G System
What is a CGM? (Continuous Glucose Monitor) The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming
 The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
The In-Clinic Close Loop Experience in the US
 The In-Clinic Close Loop Experience in the US Keystone Symposium, Practical Ways to Achieve Targets in Diabetes Care July 14, 2012 Francine Ratner Kaufman, MD Chief Medical Officer, VP Global Medical,
The In-Clinic Close Loop Experience in the US Keystone Symposium, Practical Ways to Achieve Targets in Diabetes Care July 14, 2012 Francine Ratner Kaufman, MD Chief Medical Officer, VP Global Medical,
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
Continuous Glucose Monitoring What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring? Blood glucose meters measure glucose in your blood and glucose sensors measure glucose levels in the fluid around the cells They are
OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide
 OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide Your step-by-step guide to setting up and using the OneTouch Reveal web app OneTouch Verio meter OneTouch Verio Flex meter OneTouch Verio IQ meter OneTouch
OneTouch Reveal web app Report Reference Guide Your step-by-step guide to setting up and using the OneTouch Reveal web app OneTouch Verio meter OneTouch Verio Flex meter OneTouch Verio IQ meter OneTouch
RELEASED. Clearing your active insulin
 To clear all your settings: 1. Make sure the pump is not connected to your body. 2. Go to the Manage Settings screen. Menu > Utilities > Manage Settings 3. Simultaneously press and hold and until the Manage
To clear all your settings: 1. Make sure the pump is not connected to your body. 2. Go to the Manage Settings screen. Menu > Utilities > Manage Settings 3. Simultaneously press and hold and until the Manage
Artificial Pancreas Device Systems. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes. pump. pump
 Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
How to Transfer Your Settings
 How to Transfer Your Settings for your Replacement MiniMed 530G System Let s get started! Step 1: Before you send your original pump back, copy your current settings onto the Insulin Pump Settings Form.
How to Transfer Your Settings for your Replacement MiniMed 530G System Let s get started! Step 1: Before you send your original pump back, copy your current settings onto the Insulin Pump Settings Form.
How to Transfer Your Settings
 How to Transfer Your Settings for your Replacement Paradigm REAL-Time Revel Insulin Pump Let s get started! Step 1: Before you send your original pump back, copy your current settings onto the Insulin
How to Transfer Your Settings for your Replacement Paradigm REAL-Time Revel Insulin Pump Let s get started! Step 1: Before you send your original pump back, copy your current settings onto the Insulin
THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM SCHOOL NURSE GUIDE
 THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM SCHOOL NURSE GUIDE Indicated for type 1 patients 14 and over. Prescription required. WARNING: Medtronic performed an evaluation of the MiniMed 670G system and determined that it
THE MINIMED 670G SYSTEM SCHOOL NURSE GUIDE Indicated for type 1 patients 14 and over. Prescription required. WARNING: Medtronic performed an evaluation of the MiniMed 670G system and determined that it
Artificial Pancreas Device Systems. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With type 1 diabetes
 Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/20 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18, 05/18, 01/19 Preauthorization
Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/20 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18, 05/18, 01/19 Preauthorization
Getting Started. Learning Guide. with Insulin Pump Therapy. PUMP Foundations. for the MiniMed 530G with Enlite
 Getting Started with Insulin Pump Therapy for the MiniMed 530G with Enlite Learning Guide PUMP Foundations MiniMed 530G Insulin Pump Settings Form: We recommend that you record all settings on this form
Getting Started with Insulin Pump Therapy for the MiniMed 530G with Enlite Learning Guide PUMP Foundations MiniMed 530G Insulin Pump Settings Form: We recommend that you record all settings on this form
Understanding the CareLink TM Therapy Management Dashboard Report
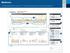 3 2 1 5 6 7 4 1 This is a great place to start recognizing trends. In this example you may see plenty of events that result in a low glucose trend. A low glucose is identified as a value less than 70mg/dL.
3 2 1 5 6 7 4 1 This is a great place to start recognizing trends. In this example you may see plenty of events that result in a low glucose trend. A low glucose is identified as a value less than 70mg/dL.
Sensor-augmented pump systems provide insulin delivery
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 18, Number 10, 2016 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2016.0216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of Automated Insulin Management Features of the MiniMed c
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 18, Number 10, 2016 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2016.0216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of Automated Insulin Management Features of the MiniMed c
CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT CARELINK REPORTS GUIDE
 CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT CARELINK REPORTS GUIDE CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT As part of your diabetes therapy you have
CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT CARELINK REPORTS GUIDE CARELINK PERSONAL ACTIONABLE INSIGHTS FOR BETTER DIABETES MANAGEMENT As part of your diabetes therapy you have
WOULD YOU LIKE MORE CONFIDENCE IN YOUR HYPOGLYCAEMIC CONTROL? SMARTGUARD. PROVIDES PREDICTIVE PROTECTION
 WOULD YOU LIKE MORE CONFIDENCE IN YOUR HYPOGLYCAEMIC CONTROL? SMARTGUARD. PROVIDES PREDICTIVE PROTECTION 1,2 MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOGLYCAEMIA HAS ON YOUR LIFE?
WOULD YOU LIKE MORE CONFIDENCE IN YOUR HYPOGLYCAEMIC CONTROL? SMARTGUARD. PROVIDES PREDICTIVE PROTECTION 1,2 MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOGLYCAEMIA HAS ON YOUR LIFE?
Paradigm/Guardian CGM Screens. CareLink Online Reports. Make Your Own Jackson Pollack. CGM by Jackson Pollack. How To Read CGM Screens/Reports
 CGM by Jackson Pollack One Pollack sold for $140 million in 1996! Make Your Own Jackson Pollack How To Read CGM Screens/Reports For only $1,000! Paradigm/Guardian CGM Screens On-Screen Reports 3 / 6 /
CGM by Jackson Pollack One Pollack sold for $140 million in 1996! Make Your Own Jackson Pollack How To Read CGM Screens/Reports For only $1,000! Paradigm/Guardian CGM Screens On-Screen Reports 3 / 6 /
Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1
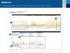 Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1 Sensor & Meter Overview (1 of 3) 4-Hour Glucose Sensor Overlay - Readings & Averages (mg/dl) 1 Glucose Sensor Overlay Bedtime to Wake-Up
Understanding the CareLinkTM Sensor Meter Overview Report: Page 1 Sensor & Meter Overview (1 of 3) 4-Hour Glucose Sensor Overlay - Readings & Averages (mg/dl) 1 Glucose Sensor Overlay Bedtime to Wake-Up
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations
 Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS)
 Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 77 Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS) Next Review: October 2019 Last Review: October 2018 Effective: November 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 77 Artificial Pancreas Device System (APDS) Next Review: October 2019 Last Review: October 2018 Effective: November 1, 2018 IMPORTANT REMINDER
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS)
 PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID CLOSED LOOP TECHNOLOGY
 PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID CLOSED LOOP TECHNOLOGY Situations Requiring Special Consideration and Resource Documents Second Edition MiniMed 67G System Medical Education TABLE OF CONTENTS A PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID
PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID CLOSED LOOP TECHNOLOGY Situations Requiring Special Consideration and Resource Documents Second Edition MiniMed 67G System Medical Education TABLE OF CONTENTS A PROTOCOL FOR HYBRID
Significant HbA1c reduction for type 2 diabetes, now clinically proven *
 Insulin Pump Significant reduction for type 2 diabetes, now clinically proven * OpT2mise: a landmark study, showing significant reduction of for T2 diabetes patients using pump * * Reznik Y. Cohen O. Aronson
Insulin Pump Significant reduction for type 2 diabetes, now clinically proven * OpT2mise: a landmark study, showing significant reduction of for T2 diabetes patients using pump * * Reznik Y. Cohen O. Aronson
Presented by Dr. Bruce Perkins, MD MPH Dr. Michael Riddell, PhD
 Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
PATIENT TRAINING CHECKLIST MINIMED 670G SYSTEM
 Technical Training Insulin Pump Infusion Set: Insulin Pump Model: BASIC FEATURES Patient has demonstrated understanding of: Button Functions Home Screen Menu review Status Screens Battery type/insertion
Technical Training Insulin Pump Infusion Set: Insulin Pump Model: BASIC FEATURES Patient has demonstrated understanding of: Button Functions Home Screen Menu review Status Screens Battery type/insertion
WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS?
 WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS? THE ONLY SYSTEM CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G SYSTEM WITH SMARTGUARD TECHNOLOGY 1 HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING
WOULD YOU LIKE TO REDUCE THE FEAR OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA FOR YOUR PATIENTS? THE ONLY SYSTEM CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G SYSTEM WITH SMARTGUARD TECHNOLOGY 1 HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING
THE ONLY SYSTEM^ CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA
 THE ONLY SYSTEM^ CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G system^ with SmartGuard technology HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING FOR GLYCAEMIC CONTROL 1 AND quality of life 2 Achieving good glucose
THE ONLY SYSTEM^ CLINICALLY PROVEN TO REDUCE HYPOGLYCAEMIA MINIMED 640G system^ with SmartGuard technology HYPOGLYCAEMIA IS CHALLENGING FOR GLYCAEMIC CONTROL 1 AND quality of life 2 Achieving good glucose
Getting you up to speed Quick Reference Guide
 Getting you up to speed Quick Reference Guide 1. Important Information This Quick Reference Guide provides a snapshot of the key features of your Animas Vibe Insulin Pump and Dexcom G4 CGM Sensor and Transmitter
Getting you up to speed Quick Reference Guide 1. Important Information This Quick Reference Guide provides a snapshot of the key features of your Animas Vibe Insulin Pump and Dexcom G4 CGM Sensor and Transmitter
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G
 DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Has your child just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Or perhaps they ve been on multiple daily injection
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Has your child just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Or perhaps they ve been on multiple daily injection
Pumps & Sensors made easy. OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University
 Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
Pumps & Sensors made easy OPADA ALZOHAILI MD FACE Endocrinology Assistant Professor Wayne State University DeFronzo RA. Diabetes. 2009;58:773-795. Ominous Octet Relationship of b-cell Dysfunction and Development
Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner & Clinical Director Integrated Diabetes Services LLC Wynnewood, PA AADE 2014 Diabetes Educator of the Year gary@integrateddiabetes.com
Making the Most of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner & Clinical Director Integrated Diabetes Services LLC Wynnewood, PA AADE 2014 Diabetes Educator of the Year gary@integrateddiabetes.com
MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD GIVES YOU CONFIDENCE TO TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR DIABETES
 MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD GIVES YOU CONFIDENCE OF YOUR DIABETES HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOS HAVE ON YOUR LIFE? AN ESTIMATED 1 HOUR EVERY DAY IS LOST TO THE MANAGEMENT OF 43% OF PEOPLE
MINIMED 640G WITH SMARTGUARD GIVES YOU CONFIDENCE OF YOUR DIABETES HAVE YOU CONSIDERED THE REAL IMPACT HYPOS HAVE ON YOUR LIFE? AN ESTIMATED 1 HOUR EVERY DAY IS LOST TO THE MANAGEMENT OF 43% OF PEOPLE
Evidence and Guidelines TECHNOLOGY 2016 Tina Kader, MD
 Evidence and Guidelines TECHNOLOGY 216 Tina Kader, MD Staff endocrinologist Jewish General Hospital Certified Diabetes Educator Montreal, Quebec AACE/ACE 215 Guidelines Glucose Monitoring: When, How, and
Evidence and Guidelines TECHNOLOGY 216 Tina Kader, MD Staff endocrinologist Jewish General Hospital Certified Diabetes Educator Montreal, Quebec AACE/ACE 215 Guidelines Glucose Monitoring: When, How, and
Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation
 Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner/Director, Integrated Diabetes Services 333 E. Lancaster Ave., Suite 24 Wynnewood, PA 1996 (877) 735-3648
Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring: From Application to Evaluation Gary Scheiner MS, CDE Owner/Director, Integrated Diabetes Services 333 E. Lancaster Ave., Suite 24 Wynnewood, PA 1996 (877) 735-3648
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology. Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education
 Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education Diabetes Management Tools in 1974 Insulin pump history
Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Sensors- Embracing Technology Susan Cavalier, BS, RN, CDE Manager, Diabetes Educator Sanford Diabetes Education Diabetes Management Tools in 1974 Insulin pump history
Report reference guide. mmol/l. One. solution EMR. No fuss
 Report reference guide mmol/l One solution No fuss 0000000000 00 0 0000 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 000000000 0 0 00 0 0 0 00 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 00 00000000000000000000 00 EMR About diasend. Plug Transmitter into your
Report reference guide mmol/l One solution No fuss 0000000000 00 0 0000 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 000000000 0 0 00 0 0 0 00 00 0 0 0 0 0 0 00 00000000000000000000 00 EMR About diasend. Plug Transmitter into your
DISCLAIMER: ECHO Nevada emphasizes patient privacy and asks participants to not share ANY Protected Health Information during ECHO clinics.
 DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN THE SCHOOL SETTING CHRISTINE HERTLER RN BSN CDE & MARY MCCARTHY RN CDE
 UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN THE SCHOOL SETTING CHRISTINE HERTLER RN BSN CDE & MARY MCCARTHY RN CDE The insulin pump Replaces injections Delivers insulin through a soft cannula
UNDERSTANDING THE BASIC FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN THE SCHOOL SETTING CHRISTINE HERTLER RN BSN CDE & MARY MCCARTHY RN CDE The insulin pump Replaces injections Delivers insulin through a soft cannula
CGM: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Making Sense of It All AW: ANCO/GEND/1016/0117
 CGM: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Making Sense of It All Objectives Review how to do a time effective interpretation of CGM and insulin pump download data Review how medications, lifestyle, and current
CGM: Continuous Glucose Monitoring Making Sense of It All Objectives Review how to do a time effective interpretation of CGM and insulin pump download data Review how medications, lifestyle, and current
Understanding the Assessment and Progress Report
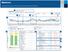 Understanding the ssessment and Progress Report ssessment and Progress 8//2-8/7/2 (7 Days) 3 7/2/2-7/27/2 (7 Days) 4 25-75% -% verage 2 4: M- 5:4 M Hyperglycemic patterns() :45 PM- :3 PM 2 3 :2 M- :5 M
Understanding the ssessment and Progress Report ssessment and Progress 8//2-8/7/2 (7 Days) 3 7/2/2-7/27/2 (7 Days) 4 25-75% -% verage 2 4: M- 5:4 M Hyperglycemic patterns() :45 PM- :3 PM 2 3 :2 M- :5 M
INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs.
 INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. Waterproof to a depth
INSPIRED BY GIVE HIM MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. Waterproof to a depth
Interpretation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Data
 Interpretation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Data Sherri Horvat, BSN, RN, CDE Blood Glucose Manager, Animas Corporation A Johnson & Johnson Diabetes Care Company Overview of CGM Continuous glucose
Interpretation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Data Sherri Horvat, BSN, RN, CDE Blood Glucose Manager, Animas Corporation A Johnson & Johnson Diabetes Care Company Overview of CGM Continuous glucose
Live life, less complicated. InPen MOBILE APP. Healthcare Provider INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE. CompanionMedical.com
 InPen MOBILE APP Healthcare Provider INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...3 InPen Mobile App...3 Intended Use...3 Indications for Use...3 Contraindications...3 Start Orders...4 General
InPen MOBILE APP Healthcare Provider INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...3 InPen Mobile App...3 Intended Use...3 Indications for Use...3 Contraindications...3 Start Orders...4 General
MiniMed 640G System Intelligent for Better Control
 Getting Started with the MiniMed 640G System Intelligent for Better Control Table Of Contents Introduction I MiniMed Care Introducing the MiniMed 640G System MiniMed Care...3 Welcome...4 The Delivery of
Getting Started with the MiniMed 640G System Intelligent for Better Control Table Of Contents Introduction I MiniMed Care Introducing the MiniMed 640G System MiniMed Care...3 Welcome...4 The Delivery of
CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION
 CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS 2016 Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION September 9-11, 2016 ~ Sonesta Resort ~ Hilton Head Island, SC This continuing
CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS 2016 Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION September 9-11, 2016 ~ Sonesta Resort ~ Hilton Head Island, SC This continuing
Interpreting the charts & graphs
 Report reference guide mg/dl The diasend solution Interpreting the charts & graphs diasend is a universal cloud-based diabetes data management system, that enables you to upload data from meters, pumps
Report reference guide mg/dl The diasend solution Interpreting the charts & graphs diasend is a universal cloud-based diabetes data management system, that enables you to upload data from meters, pumps
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G
 DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Have you just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Perhaps you ve been on multiple daily injection therapy
DISCOVER THE POWER OF CONNECTION MINIMED 640G INSULIN PUMP THERAPY CHANGING LIVES TODAY Have you just been diagnosed with insulin dependent diabetes? Perhaps you ve been on multiple daily injection therapy
Technology for Diabetes: 101 Basic Rules of the Road. Karen Hamon RN, BSN, CDE Stephen Stone MD, FAAP Neil H. White, MD, CDE
 Technology for Diabetes: 101 Basic Rules of the Road Karen Hamon RN, BSN, CDE Stephen Stone MD, FAAP Neil H. White, MD, CDE Quick Pump Facts! o Constant insulin supply o Pager-sized mini-computer worn
Technology for Diabetes: 101 Basic Rules of the Road Karen Hamon RN, BSN, CDE Stephen Stone MD, FAAP Neil H. White, MD, CDE Quick Pump Facts! o Constant insulin supply o Pager-sized mini-computer worn
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
Clinical Value and Evidence of Continuous Glucose Monitoring 9402313-012 Objective To review the clinical value and the recent clinical evidence for Professional and Personal CGM Key Points CGM reveals
Using the Bolus Wizard Calculator
 9501179-011 Using the Bolus Wizard Calculator Objective Describe the features and benefits of the Bolus Wizard Calculator Key Points The Bolus Wizard: Estimates high blood glucose corrections using the
9501179-011 Using the Bolus Wizard Calculator Objective Describe the features and benefits of the Bolus Wizard Calculator Key Points The Bolus Wizard: Estimates high blood glucose corrections using the
First steps for success.
 First steps for success. Getting to know continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. Important Safety Information The Animas Vibe Insulin Pump and
First steps for success. Getting to know continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. Important Safety Information The Animas Vibe Insulin Pump and
MiniMed 640G System Intelligent for Better Control
 Getting Started with the MiniMed 640G System Intelligent for Better Control Table Of Contents Introduction I MiniMed Care Introducing the MiniMed 640G System MiniMed Care...3 Welcome...4 The Delivery of
Getting Started with the MiniMed 640G System Intelligent for Better Control Table Of Contents Introduction I MiniMed Care Introducing the MiniMed 640G System MiniMed Care...3 Welcome...4 The Delivery of
Insulin Pump Therapy in children. Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK)
 Insulin Pump Therapy in children Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK) aagha@kau.edu.sa Highlights Evolution of insulin pump Pumps mimics Pancreas Goals of diabetes care What lowers HbA1c Criteria for selection
Insulin Pump Therapy in children Prof. Abdulmoein Al-Agha, FRCPCH(UK) aagha@kau.edu.sa Highlights Evolution of insulin pump Pumps mimics Pancreas Goals of diabetes care What lowers HbA1c Criteria for selection
INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs.
 INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. MORE TIME HERE TO USING
INSPIRED BY GIVE HER MORE. The MiniMed 670G system is the world s first insulin delivery system that automatically adapts to your child s needs. * NOW APPROVED FOR AGES 7 AND UP. MORE TIME HERE TO USING
Today s Goals 10/6/2017. New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology. Disclosures
 New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
New Frontiers in Diabetes Technology Marie E. McDonnell, MD Director, Brigham and Women's Diabetes Program Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension Brigham and Women s Hospital Today s Goals
Advances in Technology in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus 2017 How far have we come-how far are we going? Is there a final frontier?
 Advances in Technology in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus 2017 How far have we come-how far are we going? Is there a final frontier? Alan B Schorr DO FAAIM FACE www.sugardoc.com abs@sugardoc.com Disclosures
Advances in Technology in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus 2017 How far have we come-how far are we going? Is there a final frontier? Alan B Schorr DO FAAIM FACE www.sugardoc.com abs@sugardoc.com Disclosures
GETTING STARTED WITH THE MINIMED 640G SYSTEM
 GETTING STARTED WITH THE MINIMED 640G SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCING THE MINIMED 640G SYSTEM MiniMed Care...3 Welcome...4 The Delivery of Insulin...7 Menu Map...8 GETTING STARTED WITH THE MINIMED
GETTING STARTED WITH THE MINIMED 640G SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCING THE MINIMED 640G SYSTEM MiniMed Care...3 Welcome...4 The Delivery of Insulin...7 Menu Map...8 GETTING STARTED WITH THE MINIMED
Fine-tuning of The Dose of Insulin Pump
 Fine-tuning of The Dose of Insulin Pump The manual does not guarantee specific individual or specific applicability of the environment, there is no express or implied warranties. Contents of this manual
Fine-tuning of The Dose of Insulin Pump The manual does not guarantee specific individual or specific applicability of the environment, there is no express or implied warranties. Contents of this manual
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring 1. Physiology of interstitial fluid glucose 2. Comparison of CGM and self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) data 3. Insulin dosing indication in BGM vs. CGM & the FDA 4. Protection
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring 1. Physiology of interstitial fluid glucose 2. Comparison of CGM and self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) data 3. Insulin dosing indication in BGM vs. CGM & the FDA 4. Protection
Reduction in Hypoglycemia and No Increase in A1C with Threshold-Based Sensor-Augmented Pump (SAP) Insulin Suspension: ASPIRE In-Home
 Reduction in Hypoglycemia and No Increase in A1C with Threshold-Based Sensor-Augmented Pump (SAP) Insulin Suspension: ASPIRE In-Home Richard M. Bergenstal 1, David C. Klonoff 2, Bruce W. Bode 3, Satish
Reduction in Hypoglycemia and No Increase in A1C with Threshold-Based Sensor-Augmented Pump (SAP) Insulin Suspension: ASPIRE In-Home Richard M. Bergenstal 1, David C. Klonoff 2, Bruce W. Bode 3, Satish
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
Next steps for success.
 Next steps for success. More tips for using CGM* training course. The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. *Continuous Glucose Monitoring Important Safety Information The Animas
Next steps for success. More tips for using CGM* training course. The Animas Vibe System is approved for persons age 2 and older. *Continuous Glucose Monitoring Important Safety Information The Animas
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Information about fully-subsidised continuous glucose monitoring for children and young people with type 1 diabetes Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can help in managing
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Information about fully-subsidised continuous glucose monitoring for children and young people with type 1 diabetes Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can help in managing
MINIMED 640G SYSTEM^ Getting Started WITH CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING
 MINIMED 640G SYSTEM^ Getting Started WITH CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING let s get started! Table of Contents Section 1: Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Components... 2 Section 2: Sensor Glucose (SG)
MINIMED 640G SYSTEM^ Getting Started WITH CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING let s get started! Table of Contents Section 1: Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Components... 2 Section 2: Sensor Glucose (SG)
What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes?
 What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes? Dr. Fiona Wotherspoon Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Dorset County Hospital Fiona.Wotherspoon@dchft.nhs.uk
What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes? Dr. Fiona Wotherspoon Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Dorset County Hospital Fiona.Wotherspoon@dchft.nhs.uk
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management
 Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Predicts and helps prevent lows with. zero fingersticks NOW FEATURING BASAL-IQ TECHNOLOGY
 Predicts and helps prevent lows with * zero fingersticks NOW FEATURING BASAL-IQ TECHNOLOGY Basal-IQ Technology is not a substitute for active self-management of your diabetes. Please see back cover for
Predicts and helps prevent lows with * zero fingersticks NOW FEATURING BASAL-IQ TECHNOLOGY Basal-IQ Technology is not a substitute for active self-management of your diabetes. Please see back cover for
Diabetes and Technology. Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE
 Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
Diabetes and Technology Saturday, September 9, 2017 Aimee G sell, APRN, ANP-C, CDE Disclosure Speaker s Bureau: Janssan Pharmaceuticals Current Technology V-Go by Valeritas Continuous Sensors (personal
GETTING STARTED WITH MINIMED 670G CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING
 GETTING STARTED WITH MINIMED 670G CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING Contents Continuous Glucose Monitoring Getting started with continuous glucose monitoring Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: Section
GETTING STARTED WITH MINIMED 670G CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING Contents Continuous Glucose Monitoring Getting started with continuous glucose monitoring Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4: Section
State of California Health and Human Services Agency Department of Health Care Services
 State of California Health and Human Services Agency Department of Health Care Services JENNIFER KENT Director EDMOND G. BROWN JR Governor DATE: N.L.: 03-0317 Index: Benefits TO: ALL COUNTY CALIFORNIA
State of California Health and Human Services Agency Department of Health Care Services JENNIFER KENT Director EDMOND G. BROWN JR Governor DATE: N.L.: 03-0317 Index: Benefits TO: ALL COUNTY CALIFORNIA
Optimizing Therapy and Clinical Outcomes Using Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (AADE PRODUCT THEATRE) August 7, 2014 Orlando, FL
 Optimizing Therapy and Clinical Outcomes Using Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (AADE PRODUCT THEATRE) August 7, 2014 Orlando, FL Welcome and Introduction Orlando, FL August 7 th, 2014 Keri Weindel,
Optimizing Therapy and Clinical Outcomes Using Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (AADE PRODUCT THEATRE) August 7, 2014 Orlando, FL Welcome and Introduction Orlando, FL August 7 th, 2014 Keri Weindel,
Approved by: Integrated Health Quality Management Subcommittee Effective Date: Department of Origin: Integrated Healthcare Services.
 Reference #: MC/L008 Page: 1 of 8 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Community Health Plan (PCHP) PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS)
Reference #: MC/L008 Page: 1 of 8 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Community Health Plan (PCHP) PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS)
10:20 AM March 5, B 100% 235 u. 124 mg/dl 3 HRS INSULIN ON BOARD:
 DEXCOM G5 MOBILE CGM COMPATIBLE B 100% 235 u INSULIN ON BOARD: OPTIONS 10:20 AM March 5, 2017 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 1.1 u 1:09 hrs BOLUS 124 mg/dl 3 HRS The pump that gets updated, not outdated.
DEXCOM G5 MOBILE CGM COMPATIBLE B 100% 235 u INSULIN ON BOARD: OPTIONS 10:20 AM March 5, 2017 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 1.1 u 1:09 hrs BOLUS 124 mg/dl 3 HRS The pump that gets updated, not outdated.
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim
 Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bergenstal RM, Klonoff DC, Garg SK, et al. -based insulin-pump
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bergenstal RM, Klonoff DC, Garg SK, et al. -based insulin-pump
Anneli, Martina s daughter In better control with her pump since 2011 MY CHILD HAS TYPE 1 DIABETES
 Anneli, Martina s daughter In better control with her pump since 2011 MY CHILD HAS TYPE 1 DIABETES Many parents whose child is diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes wonder: Why is this happening to my child?
Anneli, Martina s daughter In better control with her pump since 2011 MY CHILD HAS TYPE 1 DIABETES Many parents whose child is diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes wonder: Why is this happening to my child?
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
MORE TIME TO BE. The MiniMed 670G system. Less time thinking about managing your diabetes. *1 More time focusing on your day. 2,3
 MORE TIME TO BE Leanne. MiniMed TM 670G Ambassador The MiniMed 670G system Less time thinking about managing your diabetes. *1 More time focusing on your day. 2,3 *Some user interaction required. THE SYSTEM
MORE TIME TO BE Leanne. MiniMed TM 670G Ambassador The MiniMed 670G system Less time thinking about managing your diabetes. *1 More time focusing on your day. 2,3 *Some user interaction required. THE SYSTEM
Preventing Hypoglycemia Using Predictive Alarm Algorithms and Insulin Pump Suspension
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 11, Number 2, 29 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 1.189/dia.28.32 Preventing Hypoglycemia Using Predictive Alarm Algorithms and Insulin Pump Suspension Bruce Buckingham,
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 11, Number 2, 29 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 1.189/dia.28.32 Preventing Hypoglycemia Using Predictive Alarm Algorithms and Insulin Pump Suspension Bruce Buckingham,
Application Highlights. Sample Reports.
 Application Highlights -- Dashboard -- Activity Summary -- Therapy Timeline -- Blood Glucose Trends -- Pump Settings -- Save and Share Sample Reports www.tandemdiabetes.com/tconnect Dashboard Helps you
Application Highlights -- Dashboard -- Activity Summary -- Therapy Timeline -- Blood Glucose Trends -- Pump Settings -- Save and Share Sample Reports www.tandemdiabetes.com/tconnect Dashboard Helps you
Continuous Glucose Monitors for Diabetes Management
 Continuous Glucose Monitors for Diabetes Management Ryan Huang, DO PGY II, Sonia Garcia-Jayne, DO PGY II Mandeep Gill, DO PGY I, Justin Leeka, DO, PGY I, Catherine Nguyen OMS IV Family Medicine Residency,
Continuous Glucose Monitors for Diabetes Management Ryan Huang, DO PGY II, Sonia Garcia-Jayne, DO PGY II Mandeep Gill, DO PGY I, Justin Leeka, DO, PGY I, Catherine Nguyen OMS IV Family Medicine Residency,
Diagnostics guidance Published: 12 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/dg21
 Integrated sensor-augmented pump therapy systems for managing blood glucose levels els in type 1 diabetes (the MiniMed Paradigm adigm Veo system and the Vibe and G4 PLATINUM CGM system) Diagnostics guidance
Integrated sensor-augmented pump therapy systems for managing blood glucose levels els in type 1 diabetes (the MiniMed Paradigm adigm Veo system and the Vibe and G4 PLATINUM CGM system) Diagnostics guidance
Diabetes Management App. Instruction Manual
 Diabetes Management App Instruction Manual Accu-Chek Connect Diabetes Management App Overview The Accu-Chek Connect diabetes management app (hereafter referred to as the app) is designed to help you: Transfer
Diabetes Management App Instruction Manual Accu-Chek Connect Diabetes Management App Overview The Accu-Chek Connect diabetes management app (hereafter referred to as the app) is designed to help you: Transfer
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy
 Line of Business: All Line of Business Effective date: August 16, 2017 Revision date: August 16, 2017 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Line of Business Effective date: August 16, 2017 Revision date: August 16, 2017 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy This policy has been developed through review
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP
 NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP No commercial support or sponsorship was received for this project I have nothing to disclose OBJECTIVES Identify at
NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR MANAGING DIABETES ANGELA THOMPSON DNP, FNP-C, BC-ADM, CDE, FAANP No commercial support or sponsorship was received for this project I have nothing to disclose OBJECTIVES Identify at
CGM Use in Pregnancy & Unique Populations ELIZABETH O. BUSCHUR, MD THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER
 CGM Use in Pregnancy & Unique Populations ELIZABETH O. BUSCHUR, MD THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER Case 1: CGM use during pregnancy 29 yo G1P0000 at 10 5/7 weeks gestation presents to set
CGM Use in Pregnancy & Unique Populations ELIZABETH O. BUSCHUR, MD THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY WEXNER MEDICAL CENTER Case 1: CGM use during pregnancy 29 yo G1P0000 at 10 5/7 weeks gestation presents to set
Calgary Diabetes Centre Insulin Pump Therapy: Preparation and Expectations
 Calgary Diabetes Centre Insulin Pump Therapy: Preparation and Expectations This is a long and important document. It lists the steps for starting insulin pump therapy at the Calgary Diabetes Centre. It
Calgary Diabetes Centre Insulin Pump Therapy: Preparation and Expectations This is a long and important document. It lists the steps for starting insulin pump therapy at the Calgary Diabetes Centre. It
